Migration and Dispersion of Empoasca vitis in Tea Plantations Analyzed by HYSPLIT
-
摘要:
目的 明确假眼小绿叶蝉[Empoasca vitis (Gothe)]迁飞扩散行为特征,初步揭示影响其种群迁飞扩散的关键因素。 方法 利用系留气球悬挂诱虫黄板诱捕不同朝向、不同高度假眼小绿叶蝉,通过HYSPLIT-4气流动力模型和气象数据,分析模拟假眼小绿叶蝉迁飞扩散行为。通过田间虫口调查,结合种群密度与扩散系数分析,明确推动假眼小绿叶蝉种群分布转化的驱动因素。 结果 假眼小绿叶蝉最高飞行高度为8 m,2~8 m高度内,随高度增加,假眼小绿叶蝉数量逐步下降。HYSPLIT-4气流动力模型分析结果表明,假眼小绿叶蝉迁飞轨迹只与迁飞时间有关,高度对其迁飞轨迹与直线扩散距离没有影响。此外,HYSPLIT-4气流动力模型分析结果还表明,假眼小绿叶蝉24 h直线迁飞距离为35.70~178.10 km。种群密度与扩散系数分析表明,假眼小绿叶蝉有聚集分布和随机分布两种分布型,迁飞和扩散是导致两种分布型转化的重要因素。 结论 借助气流,假眼小绿叶蝉可以实现区域性的迁飞。在种群密度驱动下,假眼小绿叶蝉种群分布存在聚集分布和随机分布的转化,也促使假眼小绿叶蝉种群发生田间扩散和区域性迁飞。因此,假眼小绿叶蝉的防控应以主要防治区为中心,向外扩展200 km 的范围内开展统防统治。 Abstract:Objective Migratory and dispersal behaviors of Empoasca vitis (Göthe) at tea plantations were analyzed. Method Yellow insect-trapping boards attached to ballons were strategically placed at varying heights and orientations in a tea plantation to catch E. vitis. The HYSPLIT-4 airflow dynamics model and meteorological data were used to analyze and simulate the insect migration and dispersion patterns. Based upon the field survey and the data on the population density and dispersion, factors driving the E. vitis movement were postulated. Result The maximum flying altitude of E. vitis was 8 m. The insect population steadily declined from 2 m up to 8 m. The HYSPLIT-4 generated insect movement trajectory indicated that the migration time was the only determinant, not the flying altitude nor dispersal distance. The 24h-migration of the insects ranged 35.70-178.10km and transformed between aggregated and random distribution patterns that typified the dispersion. Conclusion E. vitis migrated from region to region affected by prevailing air currents. The movement transitioned between aggregated and random dispersion in the field and regions. Consequently, effective pest control should be executed in the target area and extended no more than 200 km from the border. -
Key words:
- Empoasca vitis /
- migration /
- HYSPLIT model /
- dispersion patterns /
- tea plants
-
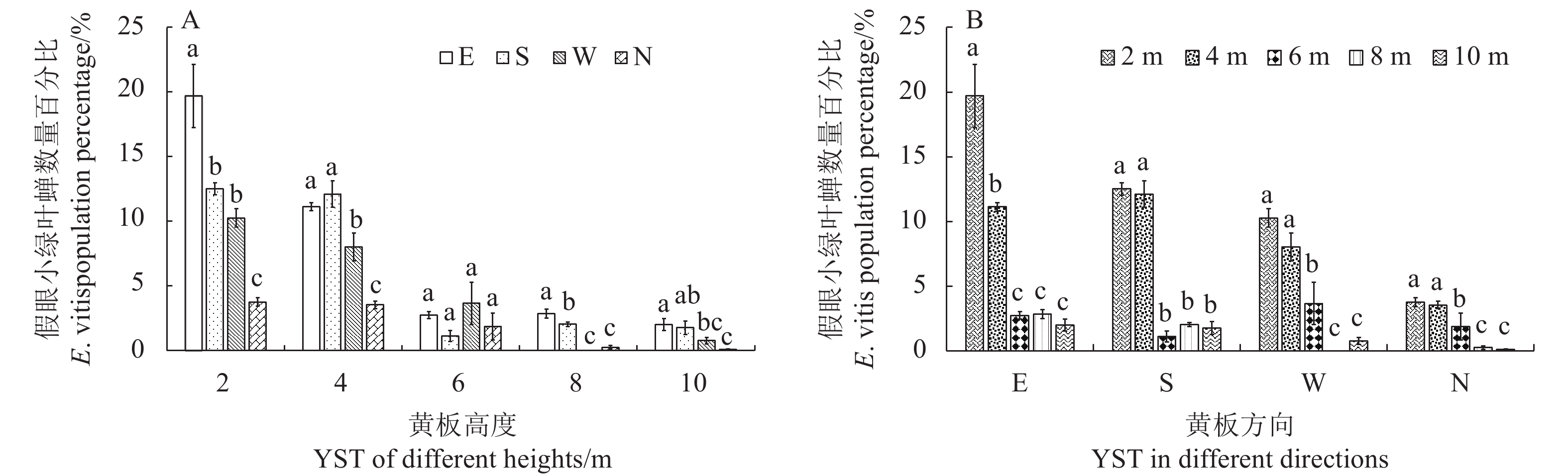
图 1 不同高度黄板诱集的叶蝉数量
A:相同高度不同方向上黄板所粘假眼小绿叶蝉数量百分比比较;B:同一方向,不同高度黄板所粘假眼小绿叶蝉数量百分比比较;图中数据为平均值±标准误,经Duncan’s新复极差检验(One-way ANOVA,P>0.05),A图中同一高度数据具有相同字母者表示差异不显著;B图中同一朝向数据具有相同字母者表示差异不显著。
Figure 1. Number of E. vitis trapped at different heights
A: Comparison by percentage of E. vitis caught on traps at same height and different orientations; B: Comparison by percentage of E. vitis caught on traps at same orientation and different heights; data are mean±standard error, as tested by Duncan's new replicated extreme variance test (one-way ANOVA, P>0.05); data with same letter on columns of same height in A indicate insignificant differences; data with same letter on columns of same orientation in B indicate insignificant differences.
表 1 试验地气象数据
Table 1. Meteorological data at test site
日期
Date最高气温
Mmaximum
temperature /℃最低气温
Minimum
temperature /℃日平均气温
Average daily
temperature /℃天气
Weather风级与风向
Beaufort scale
and direction日平均风速
Average daily wind
speed/ (m·s−1)06-10 27.0 18.0 24.2 阴 西南风2级 2.5 06-11 25.0 19.0 22.1 阴 东北风2级 1.9 06-12 25.0 19.0 22.3 阴 东风2级 2.8 06-13 25.0 20.0 22.6 雾 东南风4级 6.2 06-14 29.0 23.0 24.5 小雨 东北风2级 3.2 使用当日2:00、8:00、14:00、20:00的温度值、风速值计算日平均气温和日平均风速。日最低气温和日最高气温由仪器自动记录。风向以当日持续时间最长的风向为当日风向。
Daily average air temperature and wind speed are calculated using measurements at hours of 2:00, 8:00, 14:00, and 20:00. Daily minimum and maximum temperatures are recorded automatically by instrument. Wind direction is the prevailing one of a day.表 2 不同起飞时间假眼小绿叶蝉模拟迁飞着落点及直线距离
Table 2. Simulated landing sites and migration distances of E. vitis at different take-off times
日期
Date迁飞起算时间
Take-off time历时
Flight time/h高度
Height/m着落经度
Longitude of the landing site着落纬度
Latitude of the landing site着落点位置
Landing site直线迁飞距离
Straight-line migration distance/km06-11 5:00 24 2 106.5467o E 29.2040 o N 重庆市巴南区 35.27 4 106.5467o E 29.2040 o N 重庆市巴南区 35.27 6 106.5467o E 29.2040 o N 重庆市巴南区 35.27 8 106.5467o E 29.2040 o N 重庆市巴南区 35.27 06-12 5:00 24 2 106.2560o E 29.5961 o N 重庆市璧山区 48.78 4 106.2419 o E 29.6080 o N 重庆市璧山区 50.47 6 106.2289 o E 29.6200 o N 重庆市璧山区 52.07 8 106.2150 o E 29.6340 o N 重庆市璧山区 53.84 06-13 5:00 24 2 105.2911 o E 28.7945 o N 四川省泸州市 159.57 4 105.2909 o E 28.7947 o N 四川省泸州市 159.58 6 105.2212 o E 28.7953 o N 四川省泸州市 165.54 8 105.0697 o E 28.8094 o N 四川省泸州市 178.10 06-14 5:00 24 2 105.7789 o E 29.3321 o N 重庆市永川区 94.36 4 105.7789 o E 29.3321 o N 重庆市永川区 94.36 6 105.7789 o E 29.3321 o N 重庆市永川区 94.36 8 105.7789 o E 29.3321 o N 重庆市永川区 94.36 根据HYSPLIT模拟轨迹,利用Google earth 6.0 (Google Inc.,NASDAQ:GOOG)测得着落点经纬度及直线迁飞距离。
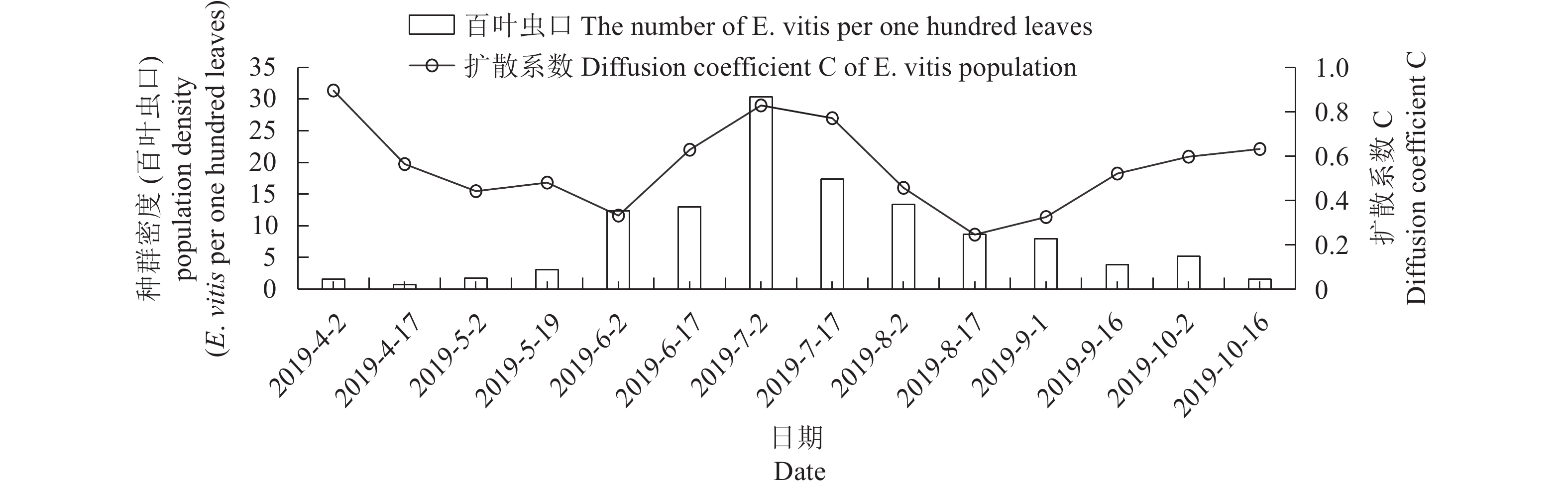
Latitude, longitude, and distance of a landing site were measured from HYSPLIT simulated trajectory using Google Earth 6.0 (Google Inc., NASDAQ: GOOG).表 3 假眼小绿叶蝉种群扩散系数
Table 3. Dispersion coefficient on E. vitis population
日期
Date扩散系数C
Coefficient扩散系数95%置信区间
Diffusion coefficient 95%
confidence interval2019/4/2 0.8962* 1±0.6089 2019/4/17 0.5643* 1±0.9462 2019/5/2 0.4421* 1±0.5839 2019/5/19 0.4807 1±0.4281 2019/6/2 0.3318 1±0.2087 2019/6/17 0.6290 1±0.2036 2019/7/2 0.8289 1±0.1328 2019/7/17 0.7715 1±0.1758 2019/8/2 0.4571 1±0.2010 2019/8/17 0.2460 1±0.2502 2019/9/1 0.3253 1±0.2808 2019/9/16 0.5267 1±0.3652 2019/10/2 0.5976 1±0.3243 2019/10/16 0.6324* 1±0.6077 *代表扩散系数C值在95%置信区间内。
*: Dispersion coefficient C within 95% confidence intervals. -
[1] 熊兴平. 假眼小绿叶蝉防治研究进展 [J]. 茶叶科学技术, 2003, 44(4):1−5.XIONG X P. Research progress on control of Empoasca vitis [J]. Technology of Tea Science, 2003, 44(4): 1−5. (in Chinese) [2] 王庆森, 王定锋, 吴光远. 我国茶树假眼小绿叶蝉研究进展 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2013, 28(6):615−623. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2013.06.022WANG Q S, WANG D F, WU G Y. Research advances on Empoasca vitis(Göthe)in tea trees in China [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 28(6): 615−623. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2013.06.022 [3] 朱俊庆. 茶树害虫[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 1999. [4] HELDEN V M, DECANT D. The possibilities for conservation biocontrol as a management strategy against Empoasca vitis [J]. IOBC/WPRS Bull., 2001, 24(7): 291−299. [5] DECANT D, HELDEN V M. Intra-plot distribution of the green leafhopper Empoasca vitis in a Bordeaux vineyard [J]. IOBC/WPRS Bull., 2003, 26(8): 181−188. [6] DECANT, D, HELDEN, V M. Green leafhopper (Empoasca vitis Göthe) migrations and dispersions [J]. IOBC/WPRS Bull., 2003, 26(8): 189−196. [7] 边磊, 孙晓玲, 陈宗懋. 假眼小绿叶蝉的日飞行活动性及成虫飞行能力的研究 [J]. 茶叶科学, 2014, 34(3):248−252. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2014.03.008BIAN L, SUN X L, CHEN Z M. Studies on daily flight activity and adult flight capacity of Empoasca vitis Göthe [J]. Journal of Tea Science, 2014, 34(3): 248−252. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2014.03.008 [8] 芦芳, 翟保平, 胡高. 昆虫迁飞研究中的轨迹分析方法 [J]. 应用昆虫学报, 2013, 50(3):853−862. doi: 10.7679/j.issn.2095-1353.2013.119LU F, ZHAI B P, HU G. Trajectory analysis methods for insect migration research [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 2013, 50(3): 853−862. (in Chinese) doi: 10.7679/j.issn.2095-1353.2013.119 [9] STEIN A F, DRAXLER R R, ROLPH G D, et al. NOAA’s HYSPLIT atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system [J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2015, 96(12): 2059−2077. doi: 10.1175/BAMS-D-14-00110.1 [10] OTUKA A, WATANABE T, SUZUKI Y, et al. Real-time prediction system for migration of rice planthoppers Sogatella furcifera (Horváth) And Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Homoptera: Delphacidae) [J]. Applied Entomology and Zoology, 2005, 40(2): 221−229. doi: 10.1303/aez.2005.221 [11] 王凤英, 胡高, 陈晓, 等. 近年来广西南宁稻纵卷叶螟大发生原因分析 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2009, 23(5):537−545. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7216.2009.05.14WANG F Y, HU G, CHEN X, et al. Analysis on the causes of recent outbreaks of Cnaphalocrocis medinalis in Nanning, China [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2009, 23(5): 537−545. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7216.2009.05.14 [12] HU G, LU F, LU M H, et al. The influence of Typhoon Khanun on the return migration of Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) in Eastern China [J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(2): e57277. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057277 [13] 郁振兴, 武予清, 蒋月丽, 等. 利用HYSPLIT模型分析麦蚜远距离迁飞前向轨迹 [J]. 生态学报, 2011, 31(3):889−896.YU Z X, WU Y Q, JIANG Y L, et al. Forward trajectory analysis of wheat aphids during long-distance migration using HYSPLIT model [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(3): 889−896. (in Chinese) [14] TAYLOR L. Assessing and interpreting the spatial distributions of insect populations [J]. Annual Review of Entomology, 1984, 29: 321−357. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.29.010184.001541 [15] 高宇, 孙晓玲, 边磊, 等. 假眼小绿叶蝉成虫在茶园中的活动规律研究 [J]. 北方园艺, 2013, (16):134−136.GAO Y, SUN X L, BIAN L, et al. Study on activity rhythms of adult Empoasca vitis Göthe in tea plantations [J]. Northern Horticulture, 2013(16): 134−136. (in Chinese) [16] 李金玉, 王庆森, 李良德, 等. 茶小绿叶蝉种名变更及其种群发生与生物生态环境关系的研究进展 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2022, 37(1):123−130.LI J Y, WANG Q S, LI L D, et al. Research progress on the dominant species identification of tea green leafhopper and the relationship between its population and the biological and ecological environment [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 37(1): 123−130. (in Chinese) [17] 翟保平, 张孝羲. 迁飞过程中昆虫的行为: 对风温场的适应与选择 [J]. 生态学报, 1993, 13(4):356−363. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.1993.04.002ZHAI B P, ZHANG X X. Behaviour of migrating insects: Adaptation and selection to atmospheric environment [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 1993, 13(4): 356−363. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.1993.04.002 [18] FENG H L, GUO X, SUN H Y, et al. Flight muscles degenerate by programmed cell death after migration in the wheat aphid, Sitobion avenae [J]. BMC Research Notes, 2019, 12(1): 672. doi: 10.1186/s13104-019-4708-z [19] 周宁宁, 王梦馨, 崔林, 等. 基于COI基因全长序列的假眼小绿叶蝉地理种群遗传分化研究 [J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(23):6879−6889.ZHOU N N, WANG M X, CUI L, et al. Genetic variation of Empoasca vitis(Göthe)(Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) among different geographical populations based on mtDNA COI complete sequence [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(23): 6879−6889. (in Chinese) [20] 贝文勇. 茶树小绿叶蝉空间分布型及抽样技术探讨 [J]. 广西植保, 2010, 23(2):5−8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8779.2010.02.002BEI W Y. Discussion on spatial distribution pattern and sampling technology of tea leafhopper [J]. Guangxi Plant Protection, 2010, 23(2): 5−8. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8779.2010.02.002 [21] 包云轩, 孙梦秋, 严明良, 等. 基于两种轨迹模型的褐飞虱迁飞轨迹比较研究 [J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(19):6122−6138.BAO Y X, SUN M Q, YAN M L, et al. Comparative study of migration trajectories of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens(Stål), in China based on two trajectory models [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(19): 6122−6138. (in Chinese) -






 下载:
下载: