Full-length Transcriptome of She Herbal Medicine Plant Clematis florida
-
摘要:
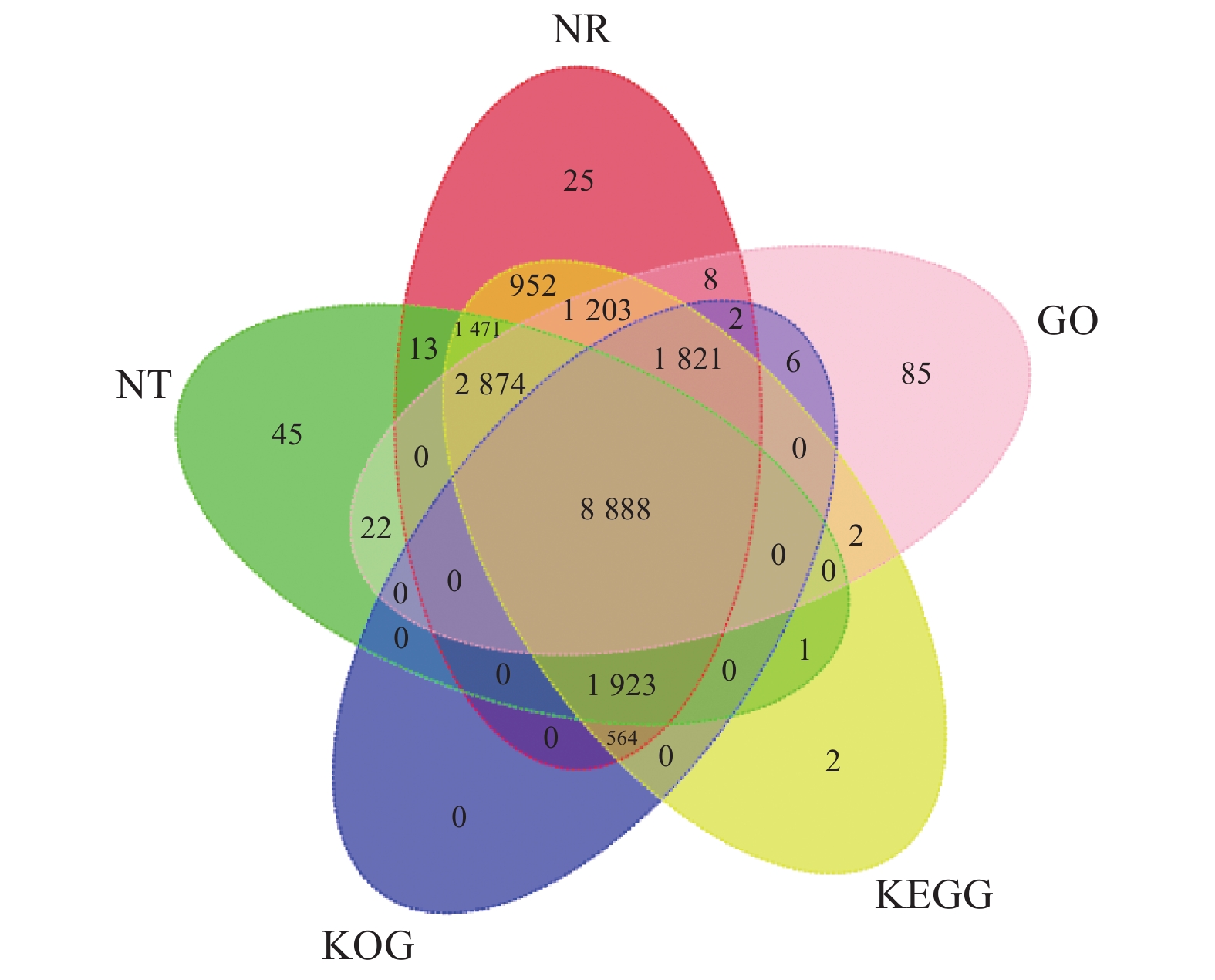
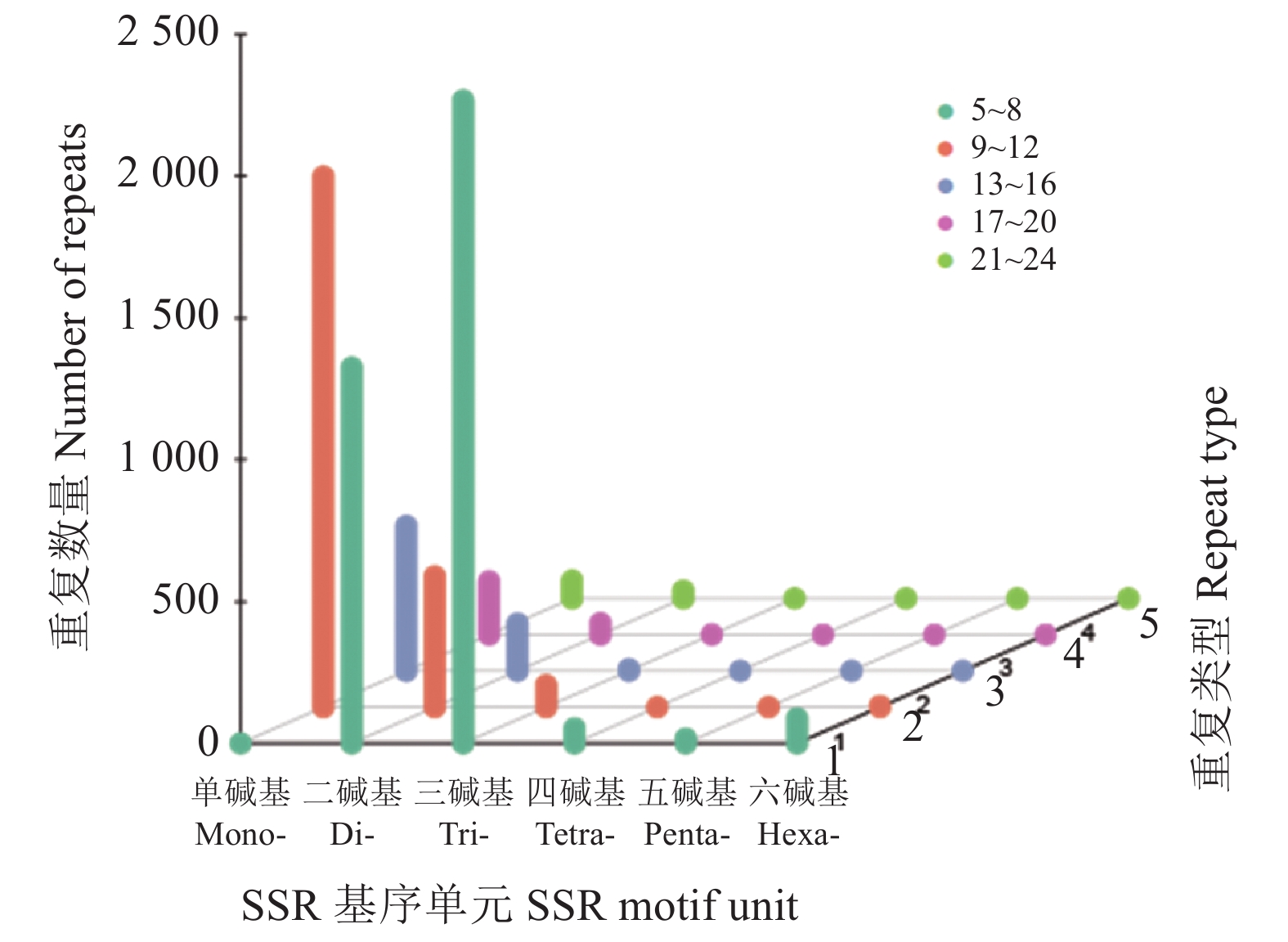
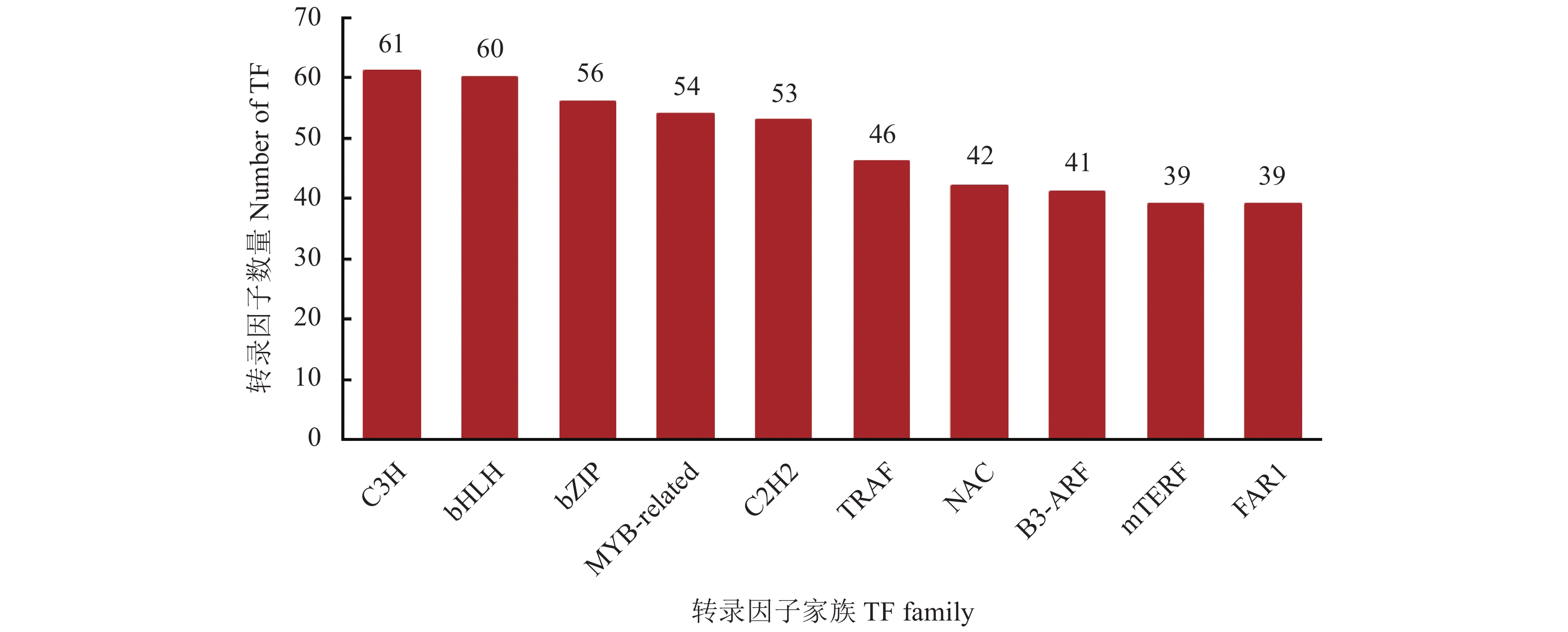
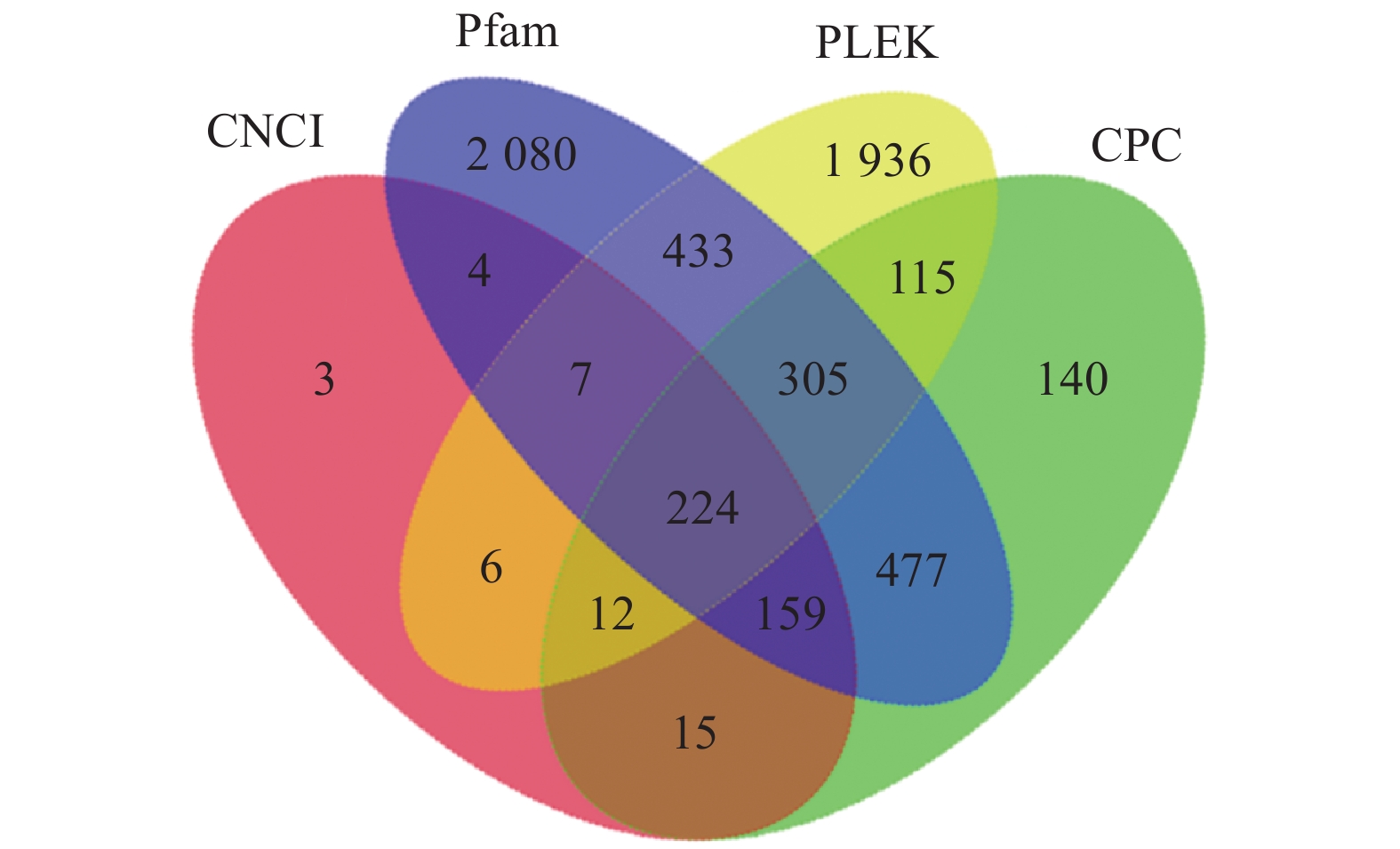
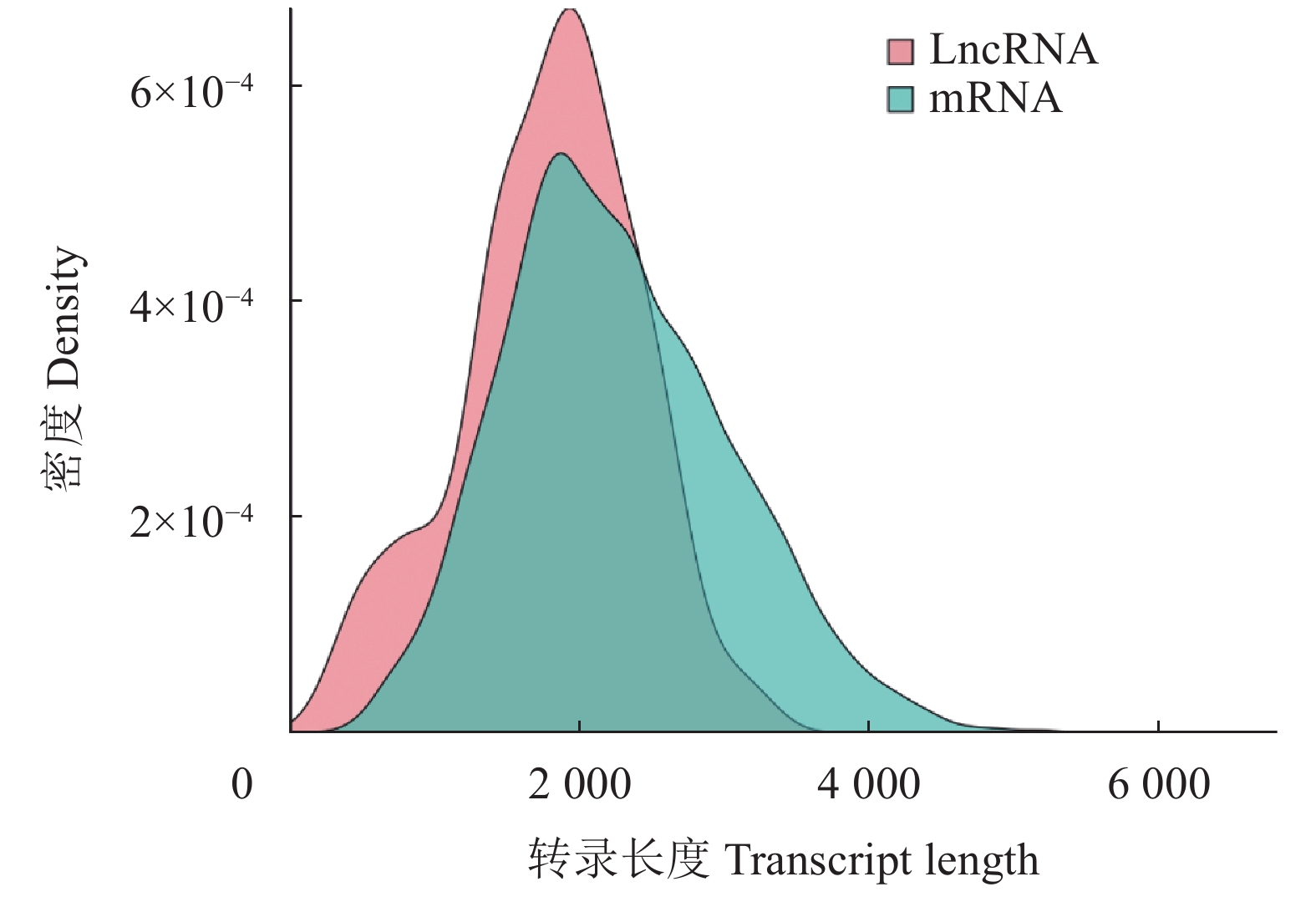
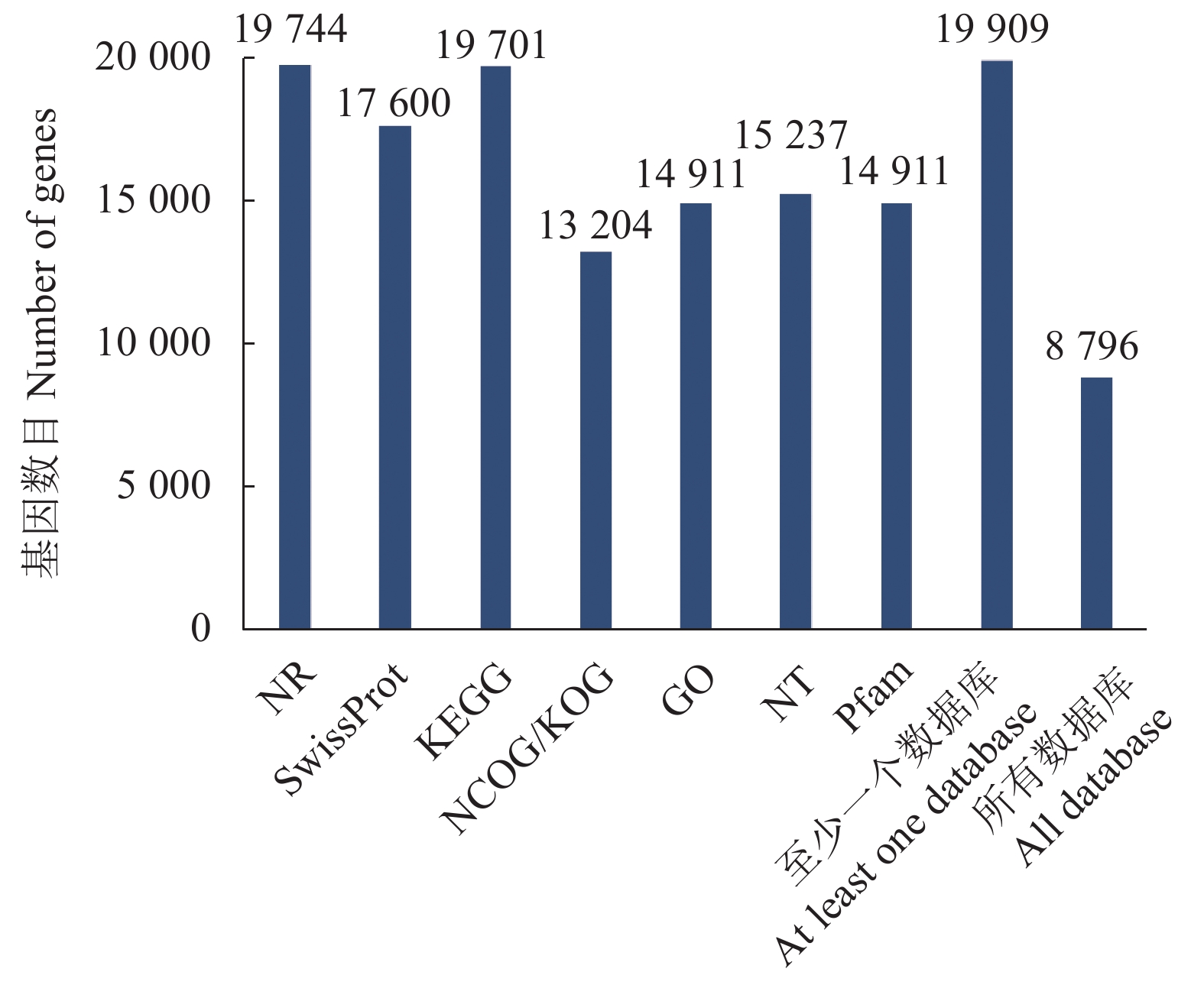
目的 重瓣铁线莲是畲药十二时辰基源植物,以根入药,含有丰富的活性成分,本研究旨在了解重瓣铁线莲基因注释信息,次级代谢产物代谢通路及基因功能,丰富其转录组信息,为进一步筛选和鉴定其药用成分代谢通路相关基因奠定基础。 方法 利用-SMRT测序技术,对重瓣铁线莲根进行全长转录组测序,并借助生物信息学工具进行功能注释、结构分析以及萜类合成途径基因的挖掘。 结果 测序共获得高质量测序subreads数据量为62.21 Gb,通过数据处理分析,获到 20540 条高质量去冗余转录本。利用NR, GO, NT, Pfam, COG/KOG, SwissProt, KEGG等7个数据库对高质量去冗余序列进行基因功能注释,共有19909 条转录本至少在1个数据库得到注释,有8888 条转录本在NR、NT、COG/KOG、KEGG、GO等5个公共数据库中均有注释。GO注释结果显示,14911 条转录本共富集在包含生物学过程、细胞组成和分子功能三大类的53个条目中。KEGG分析显示,19701 条转录本序列被富集到6条主通路和44条子通路。COG/KOG注释发现,13204 条转录本被注释,其中注释最多的功能类别为一般功能预测。对转录本结构分析发现,共预测到978个转录因子、224条LncRNA、7167 个SSR。对萜类化合物生物合成途径进行挖掘,共鉴定到48个转录本(16个关键酶候选基因)参与萜类骨架生物合成。结论 本研究成功对畲药十二时辰基源植物重瓣铁线莲的根进行了全长转录组测序,获得该物种的全长转录组相关基因功能信息,填补了重瓣铁线莲的基因信息的空白,为深入研究重瓣铁线莲的调控网络、生物学特征、相关代谢途径、信号通路及分子机制等提供参考。 Abstract:Objective Transcription of herbal plant Clematis florida Thunb. var. plena D. Don was used to identify the key genes involved in the metabolic pathways of the active compounds in the famed “Shiershichen” of She medicine. Method PacBio single-molecule real-time (SMRT) was employed to sequence the full-length transcriptome of the roots of the herbal plant that contains the active compounds of the She medicine. Functional annotation, gene structure, and mining of the terpenoid biosynthetic pathway were conducted using bioinformatics tools to secure the transcript data. Result From the 62.21 G polymerase read bases generated, 20,540 non-redundant high-quality transcript sequences were identified after data treatment. At least one of the 7 major databases including NR, NT, Pfam, COG/KOG, SwissProt, GO, and KEGG applied annotated the gene functions of 19,909 transcripts, and 8,888 were in NR, NT, COG/KOG, KEGG, and GO. The GO annotation showed 14,911 transcripts enriched in 53 terms that included biological processes, cellular components, and molecular functions. The KEGG database annotated 19,701 transcripts and classified them into 6 major pathways and 44 sub-pathways with the largest number of transcripts enriched in metabolic pathways. The COG/KOG annotation identified 13,204 transcripts with the general function prediction being the most predominant. There were 978 transcription factors, 224 lncRNAs, and 7,167 SSRs predicted, and 48 transcripts with 16 key candidate genes involved in the terpenoid backbone biosynthesis identified. Conclusion The full-length transcriptome sequencing on the roots of C. florida was successfully obtained with the comprehensive gene function information. It provided a basis for further studies on the regulatory network, biological characteristics, related metabolic pathways, signaling pathways, and molecular mechanisms associated with the well-known She herbal medicine. -
Key words:
- Clematis florida /
- full-length transcriptome /
- transcription /
- LncRNA
-
表 1 单分子实时测序数据统计
Table 1. Statistics of sequencing data by SMRT
类别
Type总数
Total number最小长度
Min length/bp最大长度
Max length/bp平均长度
Mean length/bpN50长度
N50 length/bp原始序列中的单个子序列
Subreads27863322 — — 2233 2469 环形一致性序列
Circular consensus sequence (CCS)595827 54 14994 2488 2659 全长非嵌序列
Full-Length non-chimericRead (FLNC)494732 57 14860 2333 2531 优化一致性序列
Polished consensus sequence41768 87 6251 2272 2468 去冗余高质量序列
Isoform20540 87 6251 2248 2457 表 2 转录本KEGG注释结果
Table 2. KEGG annotated transcripts
KEGG主通路
Main pathwayKEGG子通路
Sub-pathway of KEGG转录本数量
Number of
transcriptsKEGG主通路
Main pathwayKEGG子通路
Sub-pathway of KEGG转录本数量
Number of
transcripts细胞过程
Cellular Process运输与催化
Transport and catabolism595 代谢
Metabolism异种生物降解和代谢
Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism85 细胞群落-原核生物
Cellular community-prokaryotes93 核酸代谢
Nucleotide metabolism198 细胞群落-真核生物
Cellular community-eukaryotes124 萜类和聚酮类代谢
Metabolism of terpenoids and polyketides203 细胞运动
Cell motility39 其他氨基酸代谢
Metabolism of other amino acids333 细胞生和与死亡
Cell growth and death276 辅助因子和维生素代谢
Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins345 环境信息处理
Environmental
information Processing信号转导
Signal transduction984 脂类代谢
Lipid metabolism437 膜运输
Membrane transport51 聚糖生物合成和代谢
Glycan biosynthesis and metabolism171 遗传信息处理
Genetic information Processing翻译
Translation806 全局和总览图
Global and overview maps718 转录
Trancription480 能量代谢
Eenergy metabolism540 复制与修复
replication and repair176 碳水化合物代谢
Carbohydrate metabolism1010 折叠,分类和降解
Folding, sorting and degradation657 其他生长代谢物合成
Biosynthesis of other secondary metabolites243 人类疾病
Human Diseases药物依赖
Substance dependence44 氨基酸代谢
Amino acid metabolism561 神经退行性疾病
Neurodegenerative diseases165 组织系统
Organismal Systems感官系统
Sensory system15 感染疾病-病毒
Infectious diseases:Viral496 神经系统
Nervours system294 感染疾病-寄生生物
Infectious diseases:Parasitic217 免疫系统
Immune system359 感染疾病-细菌
Infectious diseases:Bacterial309 分泌系统
Excretory system51 免疫疾病
Immune diseases35 环境适应
Environmental adaptation362 内分泌与代谢疾病
Endocrine and metabolic diseases141 内分泌系统
Endocrine system404 耐药性:抗肿瘤药
Drug resistance:Antineoplastic94 消化系统
Digestive system77 心血管疾病
Cardiovascular diseases88 发育
Development17 癌症:特殊类型
Cancers:Specific types86 循环系统
Circulatory system57 癌症:总览
Cancers:Overview384 老龄化
Aging148 表 3 重瓣铁线莲转录组中与萜类化合物合成相关的转录本
Table 3. Isoforms encoding key enzymes involved in terpenoid biosynthesis in C. florida
合成途径
Pathway关键酶名称
Key enzyme name酶的系统编号
Enzyme No转录本数
No. of IsoformMVA途径
MVA Pathway羟甲基戊二酰辅酶A合酶
hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase (HMGS)EC:2.3.3.10 1 羟甲基戊二酰辅酶A还原酶
hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase(HMGR)EC:1.1.1.34 2 甲羟戊酸激酶
mevalonate kinase(MK)EC:2.7.1.36 1 磷酸甲羟戊酸激酶
phosphomevalonate kinase(PMK)EC:2.7.4.2 1 二磷酸甲羟戊酸脱羧酶
diphosphomevalonate decarboxylase (MVD)EC:4.1.1.33 2 MEP途径
MEP Pathway1-脱氧-D-木酮糖5-磷酸合酶
1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase(DXS)EC:2.2.1.7 11 1-脱氧-D-木酮糖5-磷酸还原异构酶
1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase(DXR)EC:1.1.1.267 5 2-C-甲基-D-赤藓醇-4-磷酸胱氨酰转移酶
2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase(MCT)EC:2.7.7.60 1 4-二磷酸二胺-2-C-甲基-D-赤藓糖醇激酶
4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase(CMK)EC:2.7.1.148 1 4-羟基-3-甲丁-2-烯基二磷酸合酶
4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl-diphosphate synthase(HDS)EC:1.17.7.1 9 4-羟基-3-甲丁-2-烯基二磷酸还原酶
4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate reductase(HDR)EC:1.17.7.4 2 分支点
Branch points异戊烯二磷酸Delta-异构酶
Isopentenyl-diphosphate delta-isomerase(IPPI)EC:5.3.3.2 2 牻牛儿基牻牛儿基焦磷酸合酶
geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase(GGPS)EC: 2.5.1.29 6 法呢基焦磷酸合酶
farnesyl diphosphate synthase(FPPS)EC:2.5.1.10 1 蛋白香叶烯基转移酶 protein farnesyltransferase subunit (FNTB) EC:2.5.1.58 1 内肽酶endopeptidase(STE24) EC:3.4.24.84 2 -
[1] 黄泽豪, 张月玲. 畲药十二时辰的本草考证 [J]. 中国民族民间医药, 2014, 23(1):2−3,5.HUANG Z H, ZHANG Y L. Textual research on she medicine’s twelve o’clock materia Medica [J]. Chinese Journal of Ethnomedicine and Ethnopharmacy, 2014, 23(1): 2−3,5. (in Chinese) [2] 何舒澜, 杨谨, 黄娴, 等. 重瓣铁线莲鲨烯合酶SQS基因的克隆及表达分析 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2022, 37(11):1430−1437.HE S L, YANG J, HUANG X, et al. Cloning and expression of squalene synthase gene from Clematis florida Thunb. var. plena D. don [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 37(11): 1430−1437. (in Chinese) [3] 沈廷明, 黄春情, 吴军军, 等. GC-MS法分析畲药十二时辰花中挥发油成分 [J]. 中草药, 2020, 51(24):6362−6366.SHEN T M, HUANG C Q, WU J J, et al. GC-MS analysis of volatile oil from traditional She medicine Clematis florida var. plena flower [J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2020, 51(24): 6362−6366. (in Chinese) [4] YANG N N, ZHANG Y F, ZHANG H T, et al. The in vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory activities of triterpene saponins from Clematis florida [J]. Natural Product Research, 2021, 35(24): 6180−6183. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2020.1833203 [5] SUN K H, MA X H, ZENG X M, et al. A new indole-type alkaloid from the roots of Clematis florida var. plena [J]. Natural Product Research, 2019, 33(20): 2925−2931. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2018.1510396 [6] WU Y, ZHANG Y F, ZHANG H T, et al. A new cyclopeptide alkaloid from Clematis Florida [J]. Natural Product Research, 2022, 36(7): 1693−1699. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2020.1809399 [7] 黄丽容, 郭晓云, 胡营, 等. 香附子全长转录组测序及生物信息学分析 [J]. 中国现代中药, 2023, 25(7):1428−1440.HUANG L R, GUO X Y, HU Y, et al. Full-length transcriptome sequencing and bioinformatics analysis of Cyperus rotundus L [J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 2023, 25(7): 1428−1440. (in Chinese) [8] 米琪, 赵艳丽, 徐萍, 等. 滇黄精全长转录组测序及生物信息学分析 [J]. 药学学报, 2024, 59(6):1864−1872.MI Q, ZHAO Y L, XU P, et al. Full-length transcriptome sequencing and bioinformatics analysis of Polygonatum kingianum [J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica, 2024, 59(6): 1864−1872. (in Chinese) [9] HE B, SHAN T Y, XU J Y, et al. Full-length transcriptome profiling of Acanthopanax gracilistylus provides new insight into the kaurenoic acid biosynthesis pathway [J]. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 2024, 30(3): 383−399. doi: 10.1007/s12298-024-01436-7 [10] BUCHFINK B, XIE C, HUSON D H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND [J]. Nature Methods, 2015, 12(1): 59−60. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3176 [11] ZHENG Y, JIAO C, SUN H H, et al. iTAK: A program for genome-wide prediction and classification of plant transcription factors, transcriptional regulators, and protein kinases [J]. Molecular Plant, 2016, 9(12): 1667−1670. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2016.09.014 [12] THIEL T, MICHALEK W, VARSHNEY R K, et al. Exploiting EST databases for the development and characterization of gene-derived SSR-markers in barley (Hordeum vulgare L. ) [J]. TAG Theoretical and Applied Genetics Theoretische und Angewandte Genetik, 2003, 106(3): 411−422. doi: 10.1007/s00122-002-1031-0 [13] SUN L, LUO H T, BU D C, et al. Utilizing sequence intrinsic composition to classify protein-coding and long non-coding transcripts [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2013, 41(17): e166. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt646 [14] KANG Y J, YANG D C, KONG L, et al. CPC2: A fast and accurate coding potential calculator based on sequence intrinsic features [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, 45(W1): W12−W16. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx428 [15] FINN R D, COGGILL P, EBERHARDT R Y, et al. The pfam protein families database: Towards a more sustainable future [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2016, 44(D1): D279−D285. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1344 [16] LI A M, ZHANG J Y, ZHOU Z Y. PLEK: A tool for predicting long non-coding RNAs and messenger RNAs based on an improved k-mer scheme [J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2014, 15(1): 311. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-15-311 [17] 沈廷明, 陈懿冲, 黄春情, 等. 畲药十二时辰的质量标准研究 [J]. 海峡药学, 2023, 35(8):36−41.SHEN T M, CHEN Y C, HUANG C Q, et al. Quality standard of she medicine Clematis florida var. plena [J]. Strait Pharmaceutical Journal, 2023, 35(8): 36−41. (in Chinese) [18] 陈懿冲, 沈廷明, 陈艳柠, 等. 基于网络药理学探讨畲药十二时辰镇痛作用机制 [J]. 海峡药学, 2024, 36(1):1−6.CHEN Y C, SHEN T M, CHEN Y N, et al. Based on the network pharmacology to explore the mechanism of analgesic action of she medicine Clematis florida var. flore-pleno [J]. Strait Pharmaceutical Journal, 2024, 36(1): 1−6. (in Chinese) [19] JIANG C H, BI Y K, MO J B, et al. Proteome and transcriptome reveal the involvement of heat shock proteins and antioxidant system in thermotolerance of Clematis florida [J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 8883. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65699-2 -






 下载:
下载: