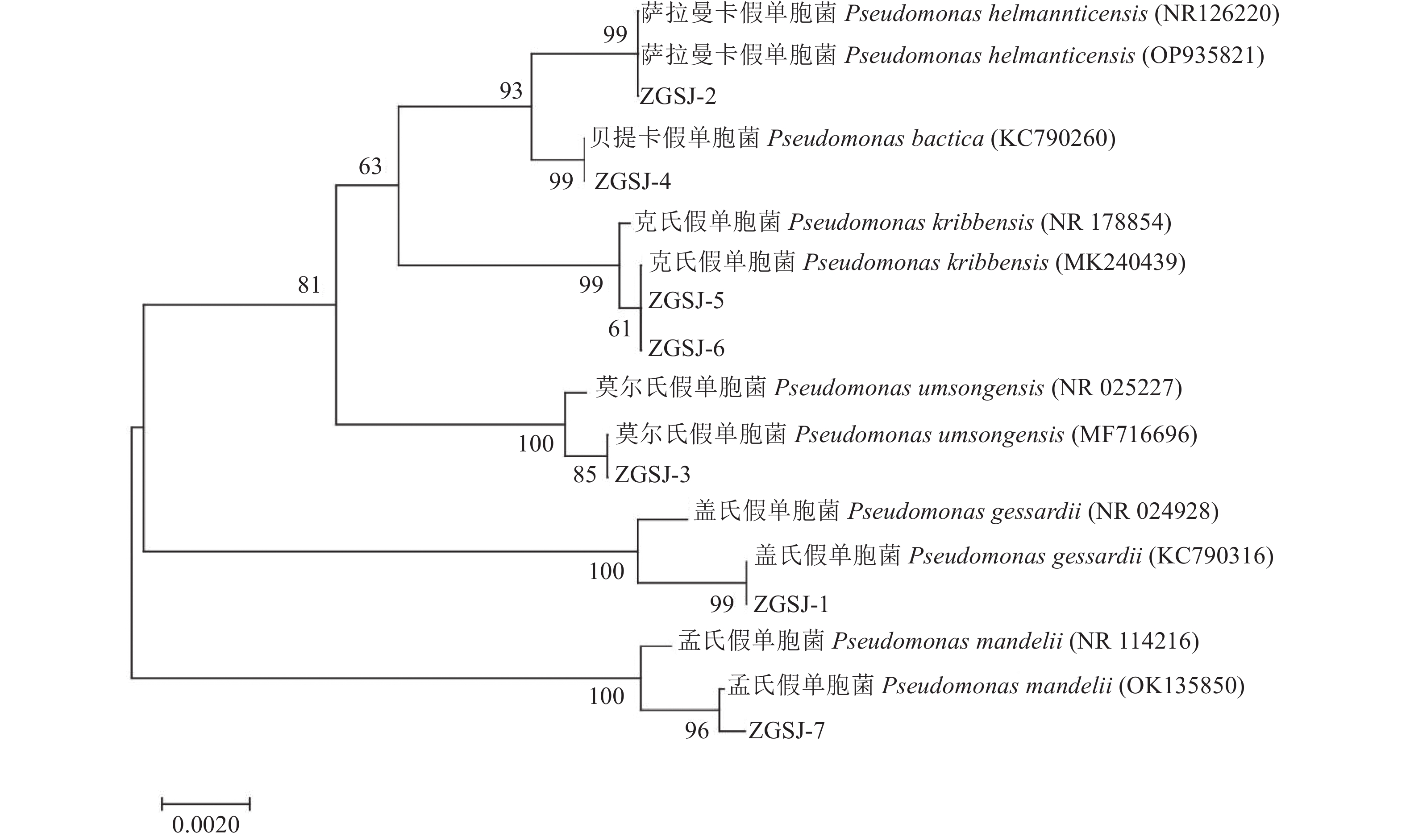
Pseudomonas in Hippophae rhamnoides Rhizosphere Affecting Growth of Ipomoea aquatica
-
摘要:
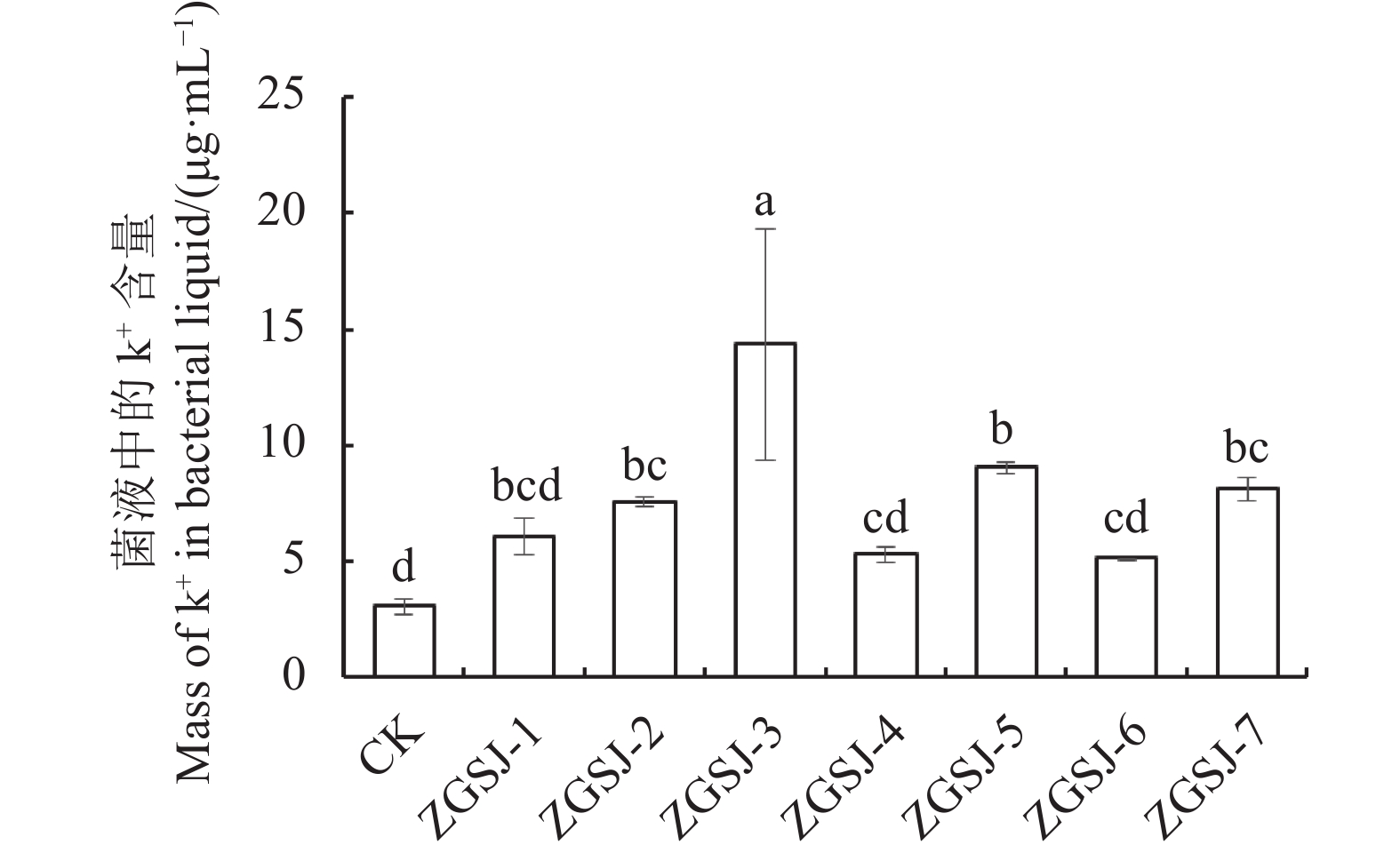
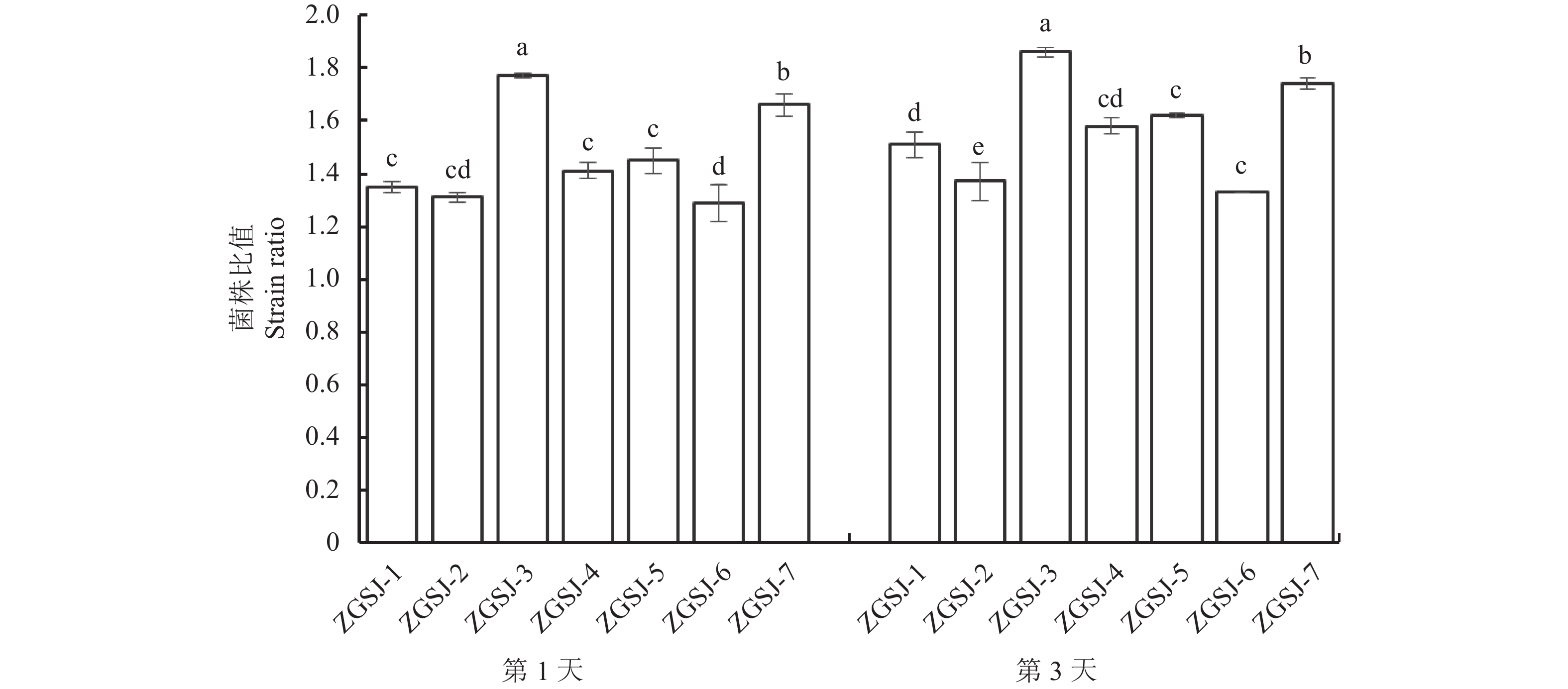
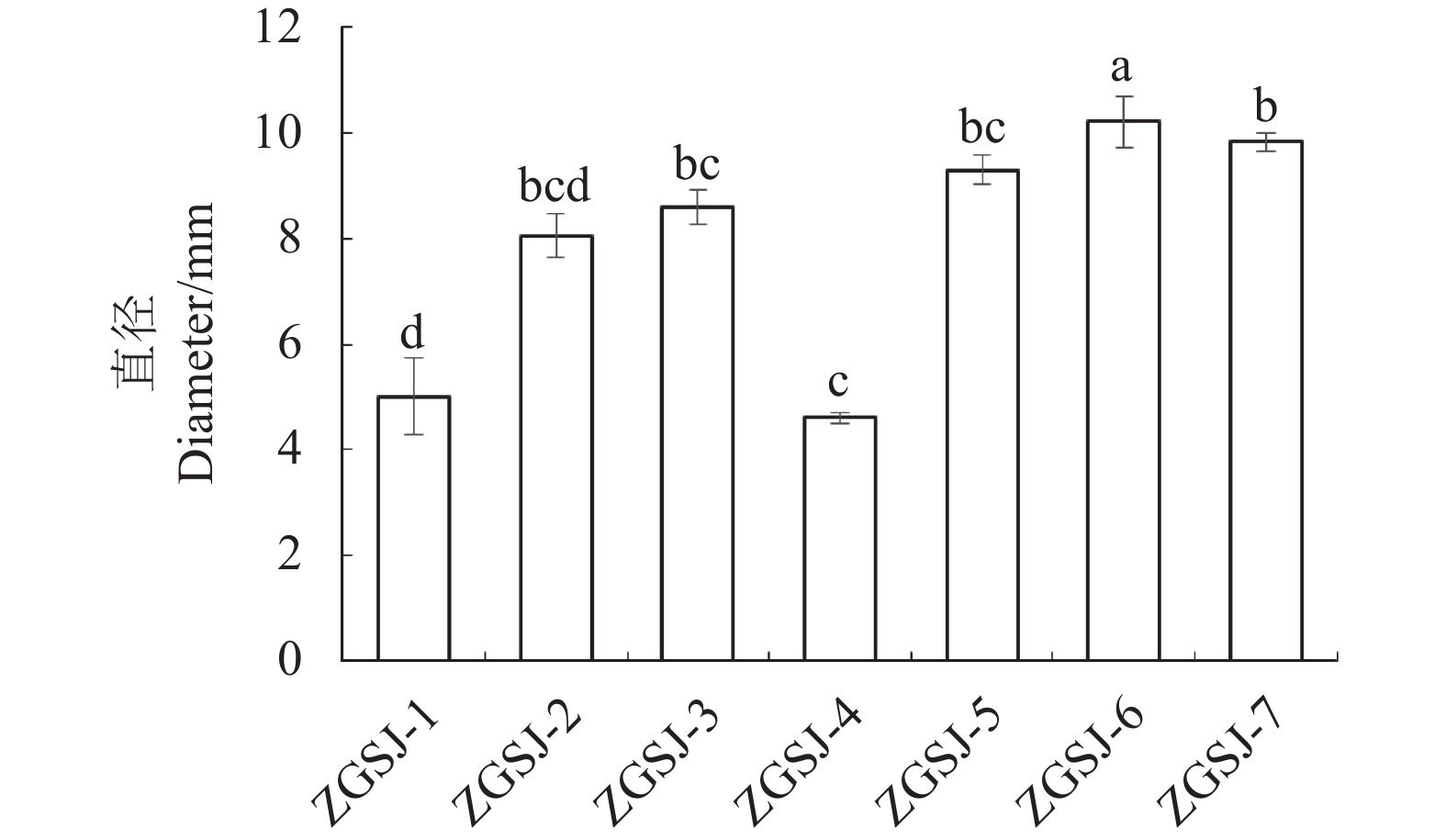
目的 从青海野生中国沙棘根际土中筛选出具有多重功能的假单胞属菌株,为生物菌肥的研发创造条件。 方法 利用筛选培养基对沙棘根际土中的微生物进行分离,利用平板划线法对菌株进行纯化。通过形态、生理生化及16S rDNA序列比对鉴定菌株,并测定菌株解有机磷、解无机磷、解钾、固氮和降解纤维素能力。以空心菜为试验材料,检测各假单胞菌属菌株促进空心菜种子萌发以及空心菜幼苗生长能力。 结果 从中国沙棘根际土壤中分离出7株假单胞菌,培养3 d,7株假单胞菌溶解有机磷浑浊圈直径为4.28~13.71 mm,溶解无机磷透明圈直径为3.51~7.62 mm,解有机磷菌液中磷的质量浓度为5.15~25.41 μg·mL−1,解无磷菌液中磷的质量浓度为2.15~22.26 μg·mL−1,解钾黄色光圈直径为11.12~21.85 mm,解钾菌液中K+质量浓度为5.07~14.33 μg·mL−1,固氮透明圈直径(D)和菌落生长直径(d)的比值(D/d)为1.33~1.86,降解纤维素透明圈直径为4.61~10.22 mm。平板促生试验结果表明,假单胞菌可提高空心菜种子发芽率,并且可显著提高空心菜幼苗生长。其中菌株ZGSJ-3促生效果最好,其叶宽和茎长分别为3.69 mm和50.25 mm,较CK显著增加了35.2%和41.2%。 结论 经综合评价后得出,不同假单胞菌菌液处理下空心菜的生长状况均得到一定程度改善,发芽率得到显著提高,其中ZGSJ-3和ZGSJ-7效果较好。 Abstract:Objective Pseudomonas sp. in the rhizosphere of Hippophae rhamnoides were isolated and studied for potential application as a biofertilizer. Method Microorganisms in the rhizosphere soil of Hippophae rhamnoides sinensis subsp. in the wild in Qinghai Province were isolated by using selected media and purified by plate streaking. Candidate Pseudomonas strains were morphologically, physiologically, and biochemically identified as well as 16S rDNA sequenced. Abilities of the isolates to degrade organic and inorganic phosphorus, potassium, cellulose and/or to fix nitrogen were examined. Effects of spraying the bacterial culture broth of the individual isolates on the seed germination and seedling growth of Ipomoea aquatica Forssk were observed. Result On different media of specific formulations, the diameters of the turbid circles born by the 7 isolated Pseudomonas strains cultured for 3d ranged 4.28-13.71mm with 5.15-25.41 μg·mL-1 of dissolved organic phosphorus, those of clear circles 3.51-7.62mm with 2.15-22.26 μg·mL−1 of dissolved inorganic phosphorus, those of halos 11.12-21.85mm with 5.07-14.33 μg·mL-1 of dissolved potassium, those of transparent circles 4.61-10.22 mm of cellulose-degradation, and the ratios of the nitrogen-fixing clear circle diameter (D) to the colony growth circle diameter (d) 1.33-1.86. The isolated Pseudomonas strains significantly improved the I. aquatica seed germination rate and seedling growth. Among them, ZGSJ-3 showed the largest increases of 35.2% on the 3.69 mm leaf width and of 41.2% on the 50.25 mm stem length over control. Conclusion Presence of the Pseudomonas sp., especially ZGSJ-3 and ZGSJ-7, isolated in this study significantly improved the seed germination and seedling growth of I. aquatica. -
表 1 菌株生理生化特征鉴定结果
Table 1. Physio-biochemical characteristics of isolates
试验
项目
Pilot
project菌株
Strain试验
项目
Pilot
project菌株
StrainZGSJ-1 ZGSJ-2 ZGSJ-3 ZGSJ-4 ZGSJ-5 ZGSJ-6 ZGSJ-7 ZGSJ-1 ZGSJ-2 ZGSJ-3 ZGSJ-4 ZGSJ-5 ZGSJ-6 ZGSJ-7 接触酶
Catalase+ + + + + + + 7%氯化钠
7%sodium
chloride+ − − + + + + 氧化酶
Oxidase− + − − + − − 木糖
Xylose+ − − + − − + 甲基红
Methyl
redMethyl
red− − − − − − − pH5.7 + + + + + + + 明胶液化
Gelatin liquefaction+ − − − − − + 水杨苷
Salicin− − − − − − − 淀粉水解
Starch
hydrolysis− − − − − − − 吲哚
Indole− − − − − − − 硝酸盐
还原
Nitrate
reduction+ − − − − − + L-精氨酸
双水解
L-arginine dihydrolyze− − − + − + − 葡萄糖
Glucose− + + − + + − 葡萄糖
OFGlucose
OF产碱
Alkali production产碱
Alkali production氧化
Oxidation发酵
Fermentation发酵
Fermentation氧化
Oxidation氧化
Oxidation表 2 菌株解磷能力的定性测定结果
Table 2. Phosphate-degrading ability of isolates
菌株
Strain1 d后的浑浊圈直径
Diameter of turbid circle
after 1 d/mm3 d后的浑浊圈直径
Diameter of turbid circle
after 3 d/mm1 d后的透明圈直径
Diameter of transparent ring
after 1 d/mm3 d后的透明圈直径
Diameter of transparent ring
after 3 d/mmZGSI-1 7.79±1.10b 13.71±0.49a 1.66±0.16c 4.27±1.06b ZGSI-2 2.91±2.91d 4.28±0.70c 0.82±0.51d 5.13±0.78b ZGSI-3 3.75±0.74cd 8.05±0.49b 0.63±0.35d 5.45±0.8ab ZGSI-4 7.56±0.98b 11.65±2.48a 3.62±0.96ab 7.62±0.78a ZGSI-5 4.92±0.52c 9.07±0.36b 4.30±0.11a 4.31±0.85b ZGSI-6 9.75±0.80a 12.05±0.67a 1.93±0.07c 4.82±2.75b ZGSI-7 4.12±0.00cd 7.95±0.29b 2.94±0.24b 3.51±0.01b 同列不同小写字母表示差异表达显著水平(P<0.05)。下同。
Data with different lowercase letters on same column indicate significant differences at p<0.05. Same for below.表 3 菌株的解磷量
Table 3. Phosphorus-degrading capacity of isolates
菌株
Strain解有机磷量
Organophosphorus
hydrolysis
/(μg·mL−1)解无机磷量
Hydrolysis of
inorganic phosphorus
/(μg·mL−1)ZGSJ-1 8.08±0.41e 2.15±0.13f ZGSJ-2 7.41±0.39e 2.49±0.43f ZGSJ-3 18.77±0.14b 16.62±0.36b ZGSJ-4 17.79±0.47c 9.46±0.41d ZGSJ-5 25.41±0.77a 22.26±0.68a ZGSJ-6 5.15±0.14f 13.01±0.07c ZGSJ-7 9.76±0.19d 3.06±0.51e 表 4 菌株解钾能力的定性测定结果
Table 4. Potassium-degrading ability of isolates
菌株
Strain1 d后的黄色光圈直径
Diameter of yellow
aperture after
1 d /mm3 d后的黄色光圈直径
Diameter of yellow
aperture after
3 d /mmZGSI-1 9.18±1.39c 13.70±1.94bc ZGSI-2 3.01±0.42e 11.12±1.85c ZGSI-3 21.66±0.40a 21.85±0.60a ZGSI-4 12.17±2.29b 16.98±0.19b ZGSI-5 5.99±1.73d 14.00±3.10bc ZGSI-6 8.25±1.34cd 17.61±3.58b ZGSI-7 3.48±0.67e 11.49±1.39c 表 5 菌株对空心菜发芽率的影响
Table 5. Effect of isolates on I. aquatica seed germination rate
菌株 Strain 第3 天/% 第5 天/% CK 53.3±5.77d 63.3±5.77d ZGSI-1 63.3±23.09c 66.7±11.55d ZGSI-2 80.0±20.00a 80.0±20.00ab ZGSI-3 80.0±10.37a 80.0±10.00b ZGSI-4 70.0±10.00b 90.0±0.00ab ZGSI-5 76.7±20.81ab 96.7±5.80a ZGSI-6 66.7±5.77bc 76.7±15.3bc ZGSI-7 73.3±11.54b 86.7±11.5a 表 6 菌液处理对空心菜生长的影响
Table 6. Effect of bacterial broth treatment on I. aquatica growth and development
处理
Treatment茎长
Stem length /mm鲜重
Fresh weight /g叶长
Leaf length /mm叶宽
Blade width /mm主根长
Taproot length /mm须根数
Number of hairsCK 35.60±4.34c 0.21±0.04a 15.57±3.05bc 2.73±0.43c 13.47±3.03de 15.00±8.58d ZGSI-1 38.48±9.44bc 0.18±0.04b 15.79±2.94bc 2.48±0.47e 14.88±3.81d 24.83±7.08b ZGSI-2 48.39±5.52ab 0.20±0.03a 17.01±2.00b 3.08±0.63b 15.92±3.73c 25.00±7.32b ZGSI-3 50.25±7.15a 0.22±0.04a 19.88±3.05a 3.69±0.62a 18.23±3.15a 25.33±4.41ab ZGSI-4 39.23±6.49bc 0.21±0.04a 17.86±3.65ab 3.11±0.63b 14.30±2.76d 31.50±7.61a ZGSI-5 42.87±6.36b 0.17±0.04b 18.99±2.34a 3.67±0.79a 14.32±3.11d 23.17±10.19b ZGSI-6 44.92±3.07b 0.22±0.03a 14.60±3.51c 2.44±0.51de 17.05±4.90b 21.67±7.76c ZGSI-7 46.54±10.76ab 0.22±0.03a 20.23±2.25a 3.25±0.44b 18.36±7.48a 17.50±6.47d -
[1] 王亚菲, 张鑫宇, 刘佳慧, 等. 沙棘功能研究进展及其发展前景[J]. 中国果菜, 2021, 41(12): 49-53.WANG Y F, ZHANG X Y, LIU J H , et al. The research progress of the function of the sea buckthorn function [J]. Chinese fruit and vegetables, 2021, 41 (12): 49-53. (in Chinese) [2] 刘青青, 李雄杰, 马亚琼, 等. 青海野生中国沙棘资源表型性状多样性分析[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2023, 24 (4): 1057-1064.LIU Q Q, LI X J, MA Y Q, et al. Phenotypic diversity of wild sea buckthorn in qinghai [J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2019, 24(4): 1057-1064. (in Chinese) [3] 张爱梅, 殷一然, 孔维宝, 等. 西藏沙棘5种不同组织内生细菌多样性 [J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9):1236−1244. doi: 10.17520/biods.2021034ZHANG A M, YIN Y R, KONG W B, et al. Diversity of endophytic bacteria in five types of tissues of Hippophae tibetana [J]. Biodiversity Science, 2021, 29(9): 1236−1244. (in Chinese) doi: 10.17520/biods.2021034 [4] 李晴晴, 徐松, 赵维, 等. 根际微生物组介导的解淀粉芽孢杆菌FH-1对水稻的促生机制 [J]. 微生物学报, 2019, 59(12):2410−2426.LI Q Q, XU S, ZHAO W, et al. Rhizosphere microbiome mediated growth-promoting mechanisms of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FH-1 on rice [J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2019, 59(12): 2410−2426. (in Chinese) [5] 褚屿, 骆洪义, 林举梅, 等. 番茄对氮磷钾及中微量元素的吸收规律研究 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2021, (1):247−255. doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.19595CHU Y, LUO H Y, LIN J M, et al. Study on the absorption law of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and trace elements of tomatoes [J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2021(1): 247−255. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.19595 [6] SHIN R, BERG R H, SCHACHTMAN D P. Reactive oxygen species and root hairs in Arabidopsis root response to nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium deficiency [J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2005, 46(8): 1350−1357. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pci145 [7] 温佳旭, 陈雪丽, 肖洋, 等. 土壤中主要溶磷菌种类及其作用机制 [J]. 北方园艺, 2023, (14):139−145.WEN J X, CHEN X L, XIAO Y, et al. Major phosphorus-dissolving bacteria species in soils and mechanisms of action [J]. Northern Horticulture, 2023(14): 139−145. (in Chinese) [8] REZAKHANI L, MOTESHAREZADEH B, TEHRANI M M, et al. Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and silicon synergistically augment phosphorus (P) uptake by wheat (Triticum aestivum L. ) plant fertilized with soluble or insoluble P source [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 173: 504−513. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.02.060 [9] REIS V M, DOS SANTOS TEIXEIRA K R. Nitrogen fixing bacteria in the family Acetobacteraceae and their role in agriculture [J]. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 2015, 55(8): 931−949. doi: 10.1002/jobm.201400898 [10] 马福林, 仁增卓玛, 王昌玲, 等. 西藏沙棘根瘤内生假单胞菌的分离鉴定及促生性研究 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2023, 38(5):624−631.MA F L, RENZENG Z M, WANG C L, et al. Isolation, identification and growth promotion of endophytic Pseudomonas from Seabuckthorn nodules in Xizang [J]. Journal of Fujian Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 38(5): 624−631. (in Chinese) [11] HAMEEDA B, HARINI G, RUPELA O P, et al. Growth promotion of maize by phosphate-solubilizing bacteria isolated from composts and macrofauna [J]. Microbiological Research, 2008, 163(2): 234−242. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2006.05.009 [12] 杨晓帆, 梁家慧, 于文英, 等. 促生荧光假单胞菌对桃树根区土壤环境和植株生长的影响 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(8):1494−1508. doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2021625YANG X F, LIANG J H, YU W Y, et al. Effect of Pseudomonas fluorescens on rhizospheric soil quality and growth of peach(Prunus persica L. Batsch) [J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(8): 1494−1508. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2021625 [13] 胡蒙爱, 张雪艳. 芽孢杆菌与壳寡糖混施对基质环境和黄瓜幼苗生长的影响[J]. 西北农业报, 2023, 32(11): 1789-1798.HU M A, ZHANG X Y. Effects of mixed application of Bacillus and chitosan oligosaccharides on substrate environment and growth of cucumber seedlings [J]. Journal of Northwest Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 32(11): 1789-1798. (in Chinese) [14] DI BENEDETTO N A, CAMPANIELLO D, BEVILACQUA A, et al. Isolation, screening, and characterization of plant-growth-promoting bacteria from durum wheat rhizosphere to improve N and P nutrient use efficiency [J]. Microorganisms, 2019, 7(11): 541. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7110541 [15] JI S H, GURURANI M A, CHUN S C. Isolation and characterization of plant growth promoting endophytic diazotrophic bacteria from Korean rice cultivars [J]. Microbiological Research, 2014, 169(1): 83−98. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2013.06.003 [16] MUJAHID T Y, SIDDIQUI K, AHMED R, et al. Isolation and partial characterization of phosphate solubilizing bacteria isolated from soil and marine samples[J]. Pakistan Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2014, 27(5 ): 1483-1490. [17] 东秀珠, 蔡妙英. 常见细菌系统鉴定手册[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001: 23-28. [18] 张祥胜. 钼锑抗比色法测定磷细菌发酵液中有效磷含量测定值的影响因素分析 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2008, 36(12):4822−4823. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2008.12.009ZHANG X S. Analysis of the factors affecting the available P content in the fermentation liquid of P bacteria determined by Mo-Sb colorimetry [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2008, 36(12): 4822−4823. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2008.12.009 [19] 高佩, 王彬贤, 郭思雨, 等. 青海野生中国沙棘根际解钾菌的分离、鉴定及其促生能力比较 [J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 53(3):401−409.GAO P, WANG B X, GUO S Y, et al. Isolation and identification of potassium-solubilizing bacteria in the rhizosphere of wild China Hippophae rhamnoides in Qinghai and comparison of their growth-promoting ability [J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2024, 53(3): 401−409. (in Chinese) [20] 曹巍, 高惠嫣, 王鑫鑫, 等. 不同配施肥措施对滨海盐碱地大豆生长和产量的影响 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2023, 51(22):53−60.CAO W, GAO H Y, WANG X X, et al. Effects of different fertilization measures on soybean growth and yield in coastal saline-alkali land [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 51(22): 53−60. (in Chinese) [21] 邱睿, 李小杰, 白静科, 等. 烟草镰刀菌根腐病生防假单胞菌的筛选与鉴定 [J]. 中国烟草学报, 2023, 29(3):84−93.QIU R, LI X J, BAI J K, et al. Screening and identification of Pseudomonas against Fusarium root rot of tobacco [J]. Acta Tabacaria Sinica, 2023, 29(3): 84−93. (in Chinese) [22] 杨杉杉, 李国光, 张胜男, 等. 假单胞菌BP16的分离鉴定及其植物促生性状和效应 [J]. 微生物学通报, 2018, 45(10):2121−2130.YANG S S, LI G G, ZHANG S N, et al. Isolation and identification of Pseudomonas sp. BP16 and its plant growth-promoting traits and effects [J]. Microbiology China, 2018, 45(10): 2121−2130. (in Chinese) [23] TOMÁS M S J, BRU E, NADER-MACÍAS M E F. Estimation of combined effects of carbon and nitrogen sources on the growth and bacteriocin production of Lactobacillus salivarius from human source [J]. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 2010, 50(2): 190−199. doi: 10.1002/jobm.200900122 [24] 初旭, 胡霞, 刘静, 等. 杉木根际溶磷菌的筛选鉴定及溶磷能力分析 [J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 2021, 41(2):85−92.CHU X, HU X, LIU J, et al. Screening and identification of rhizosphere phosphorus soluble bacteria of chinese fir [J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University (Natural Science), 2021, 41(2): 85−92. (in Chinese) [25] 彭帅, 韩晓日, 马晓颖, 等. 产葡萄糖酸荧光假单胞菌的分离鉴定及解磷作用 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2011, (5):137−141.PENG S, HAN X R, MA X Y, et al. Isolation and identification of gluconic-acid producing Pseudomonas fluorescens and phosphate dissolution [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2011(5): 137−141. (in Chinese) [26] 张成省, 陈雪, 张玉芹, 等. 烟草根际土壤中解钾细菌的分离与多样性分析 [J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2013, 21(6):737−743. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2013.00737ZHANG C S, CHEN X, ZHANG Y Q, et al. Diversity and isolation of potassium solubilizing bacteria in tobacco rhizosphere soils [J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2013, 21(6): 737−743. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2013.00737 [27] SUGUMARAN P, JANARTHANAM B. Solubilization of potassium containing minerals by bacteria and their effect on plant growth [J]. World Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2007, 3(3): 350−355. [28] BERENDSEN R L, PIETERSE C M J, BAKKER P A H M. The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health [J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2012, 17(8): 478−486. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2012.04.001 [29] 闫雅楠, 叶小齐, 吴明, 等. 入侵植物加拿大一枝黄花根际解钾菌多样性及解钾活性 [J]. 植物生态学报, 2019, 43(6):543−556. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2019.0045YAN Y N, YE X Q, WU M, et al. Diversity and potassium-solubilizing activity of rhizosphere potassium-solubilizing bacteria of invasive Solidago canadensis [J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2019, 43(6): 543−556. (in Chinese) doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2019.0045 [30] 伊国云, 程亮. 纤维素降解菌株的筛选、鉴定及其酶活力的测定 [J]. 青海农林科技, 2022, 13(4):13−18.YI G Y, CHENG L. Screening, identification and determination of enzyme activity of cellulose degrading strains [J]. Qinghai Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology, 2022, 13(4): 13−18. (in Chinese) [31] 王奎萍, 郑颖, 褚光耀, 等. 解磷、固氮、产吲哚乙酸微生物菌株的筛选及其对植物的促生效果 [J]. 江苏农业学报, 2013, 29(6):1352−1359. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2013.06.026WANG K P, ZHENG Y, CHU G Y, et al. Screening of bacterial strains for phosphate solubilization, nitrogen fixation and IAA production and their promotive effects on plant growth [J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 29(6): 1352−1359. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2013.06.026 [32] 李利坤. 沙棘根瘤菌的分离鉴定及根瘤菌对植株生长发育的影响[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2018.LI L K. Isolation and identification of rhizobia from Hippophae rhamnoides and their effects on plant growth and development[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2018. (in Chinese) [33] 吴菊艳. 沙棘根瘤内生细菌中促生菌的筛选及促生性能研究[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学, 2019.WU J Y. Screening of growth-promoting bacteria from endophytic bacteria in seabuckthorn nodules and study on their growth-promoting properties[D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University, 2019. (in Chinese) -







 下载:
下载: