Endophytic and Rhizosphere Microbes in Pinellia ternata and Habitat Soils in Guizhou Affected by Environmental Conditions
-
摘要:
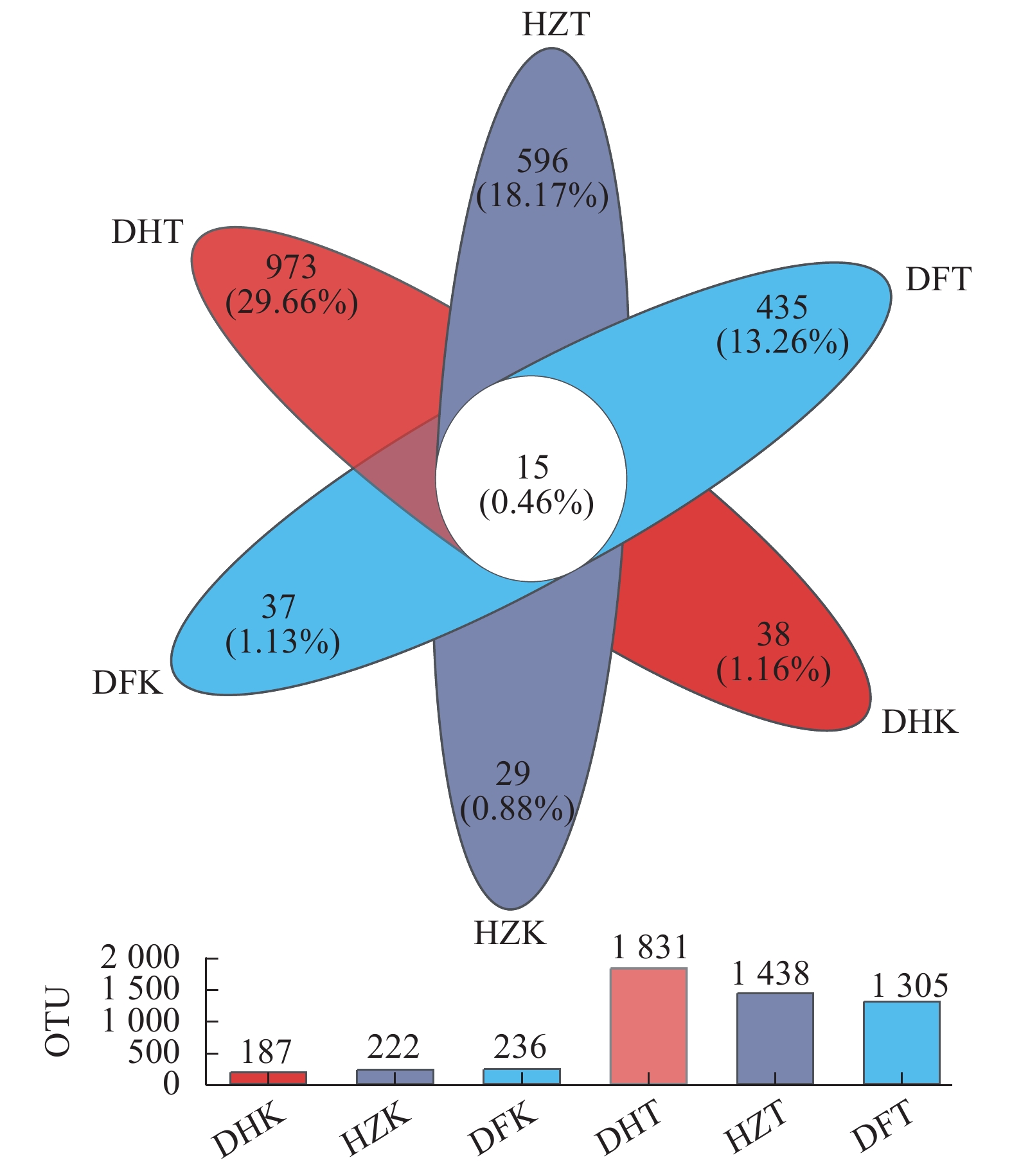
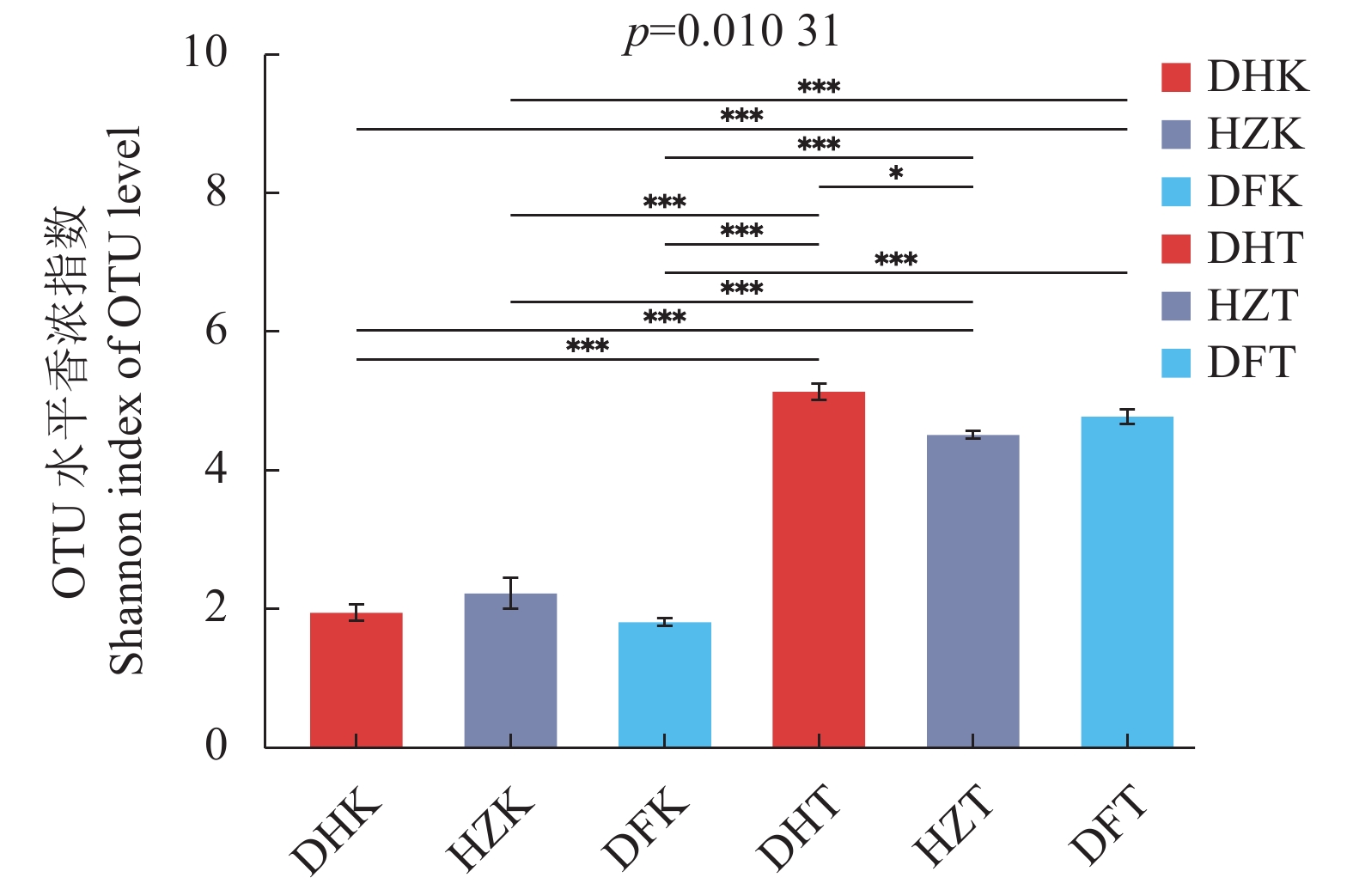
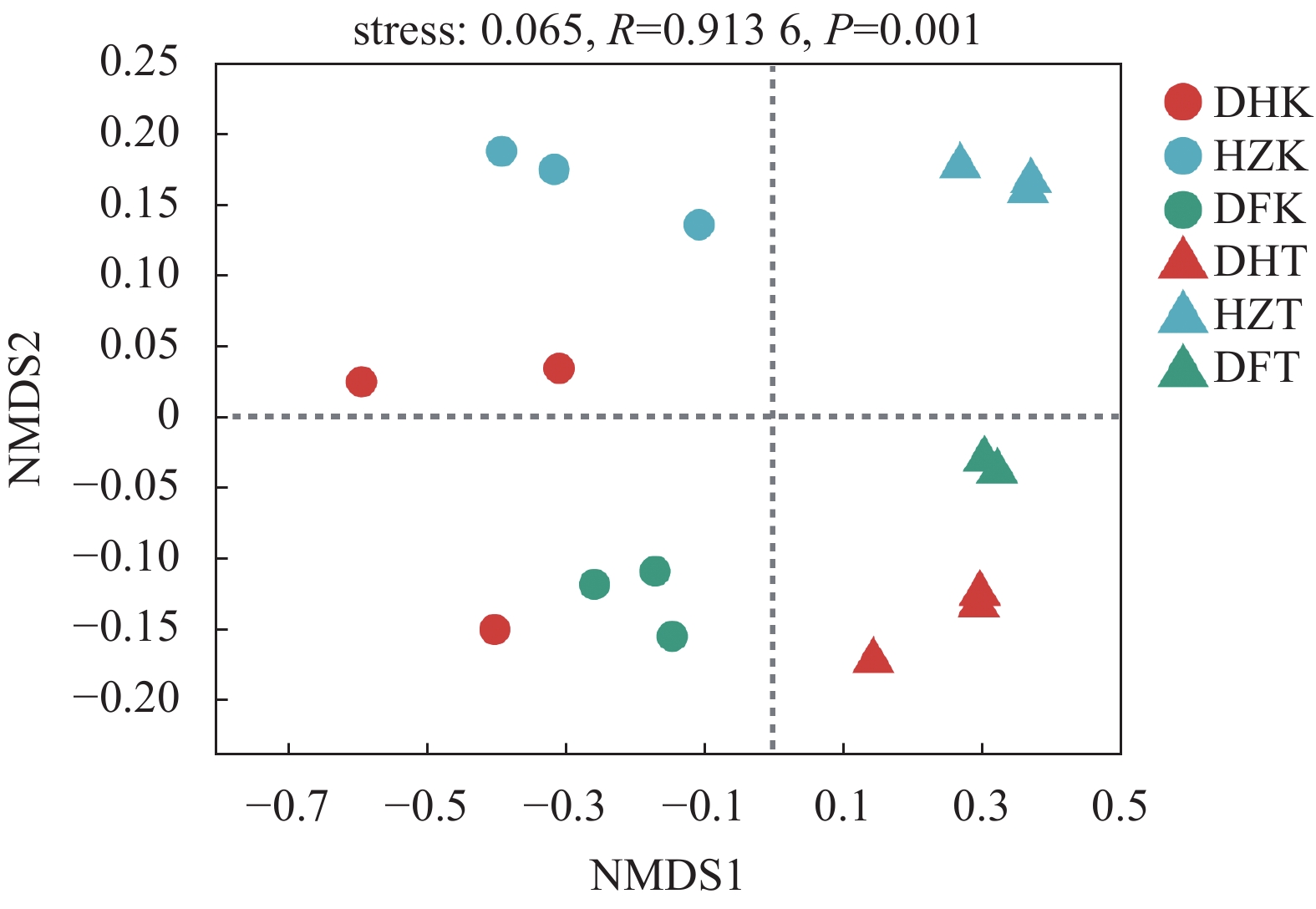
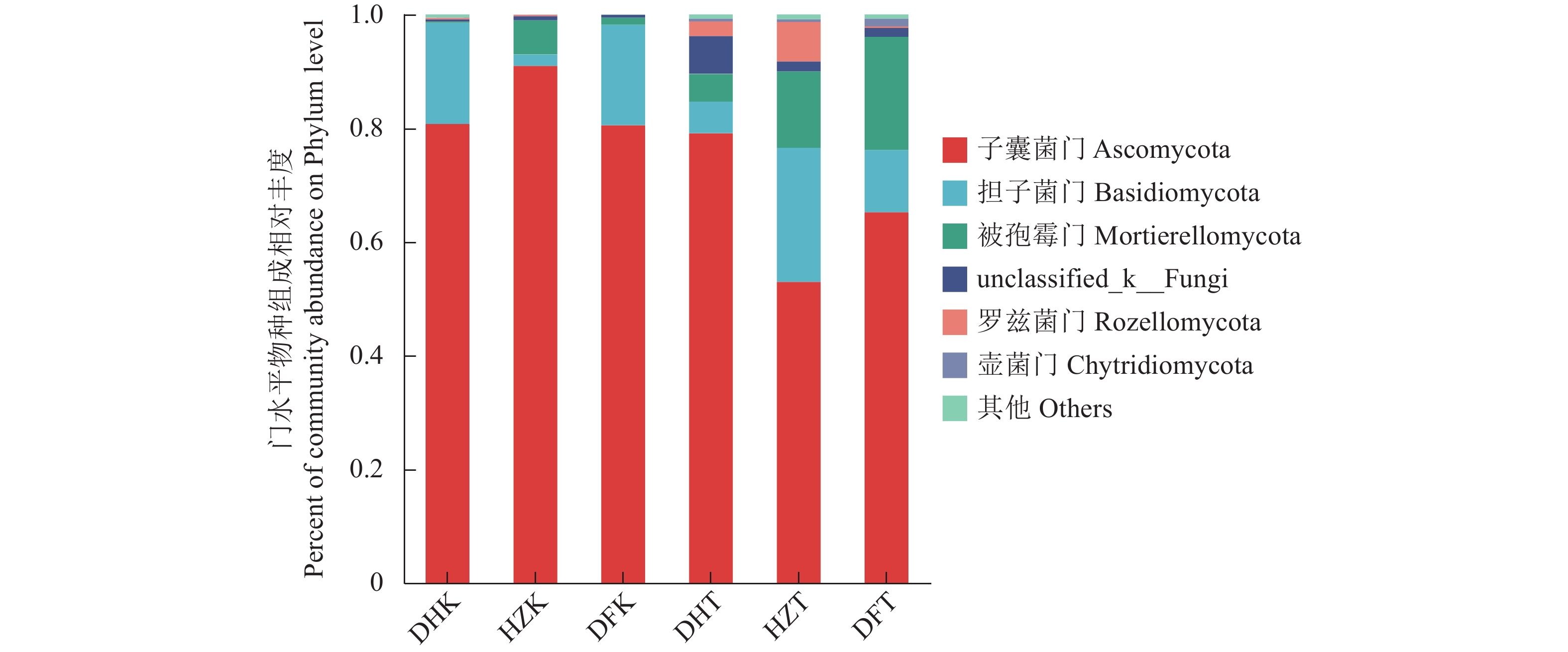
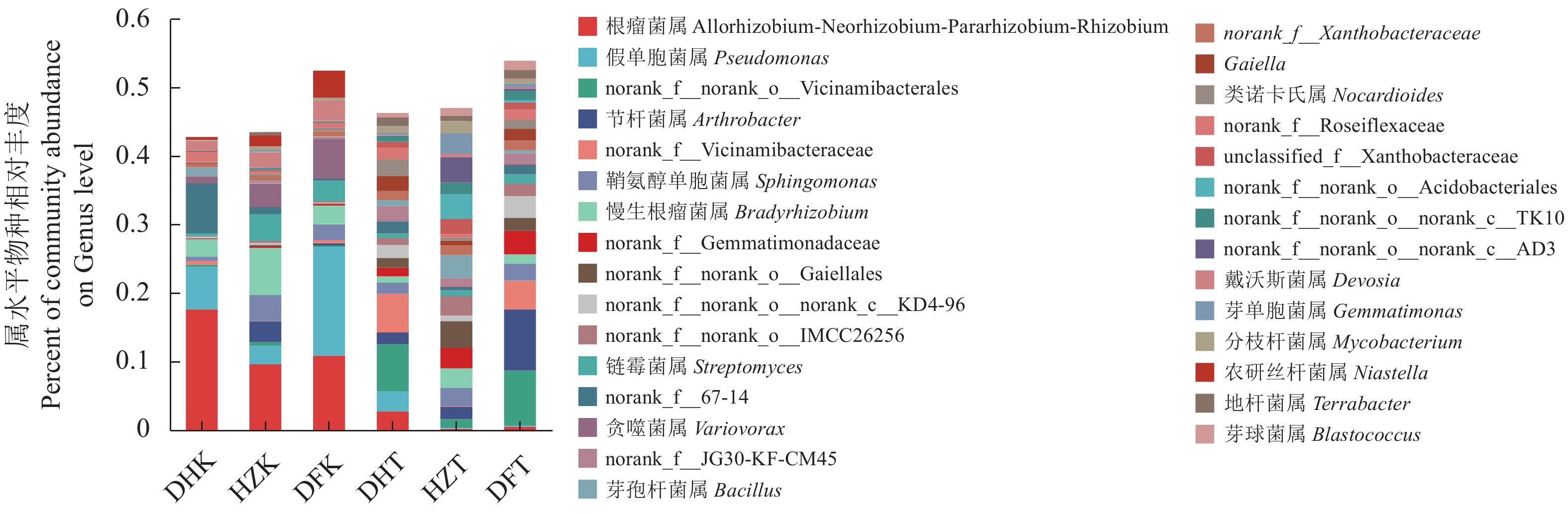
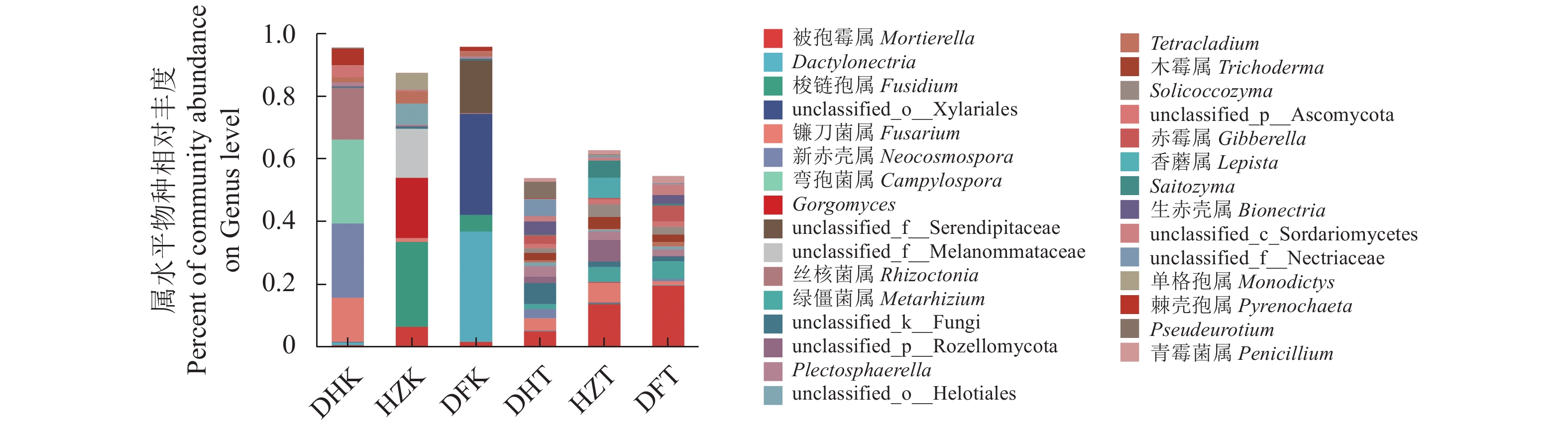
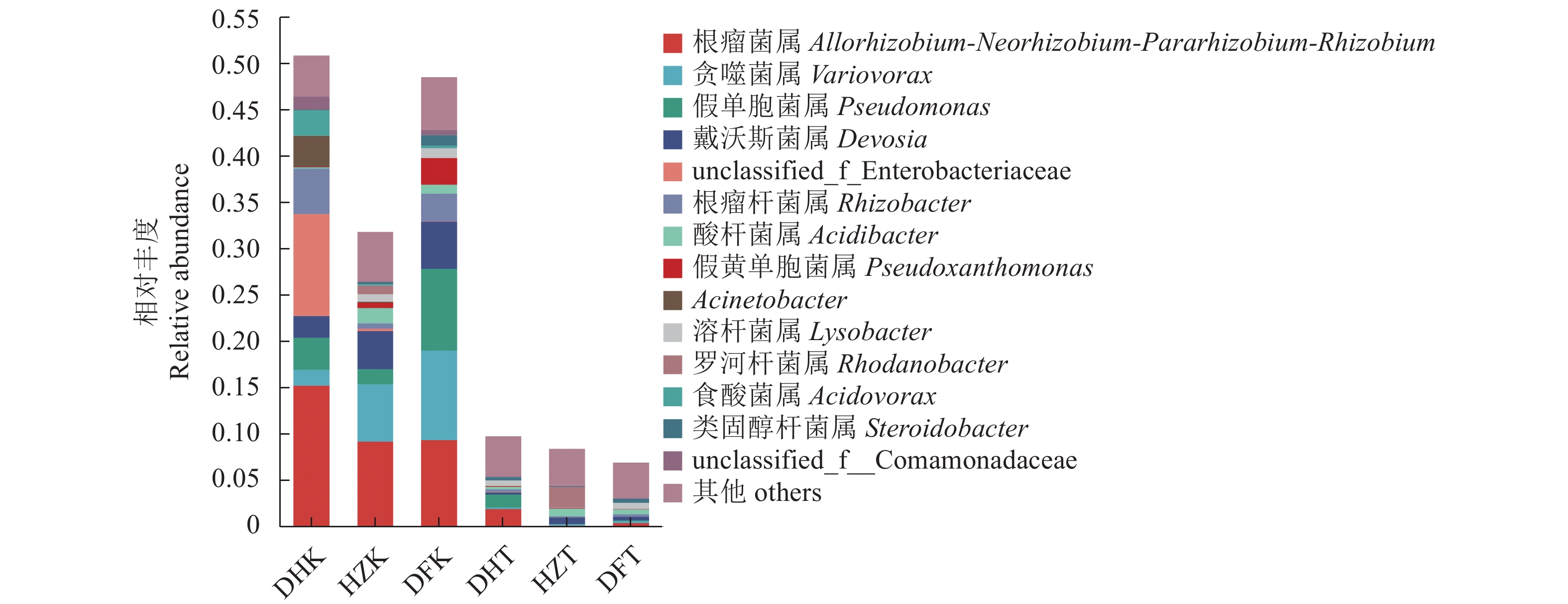
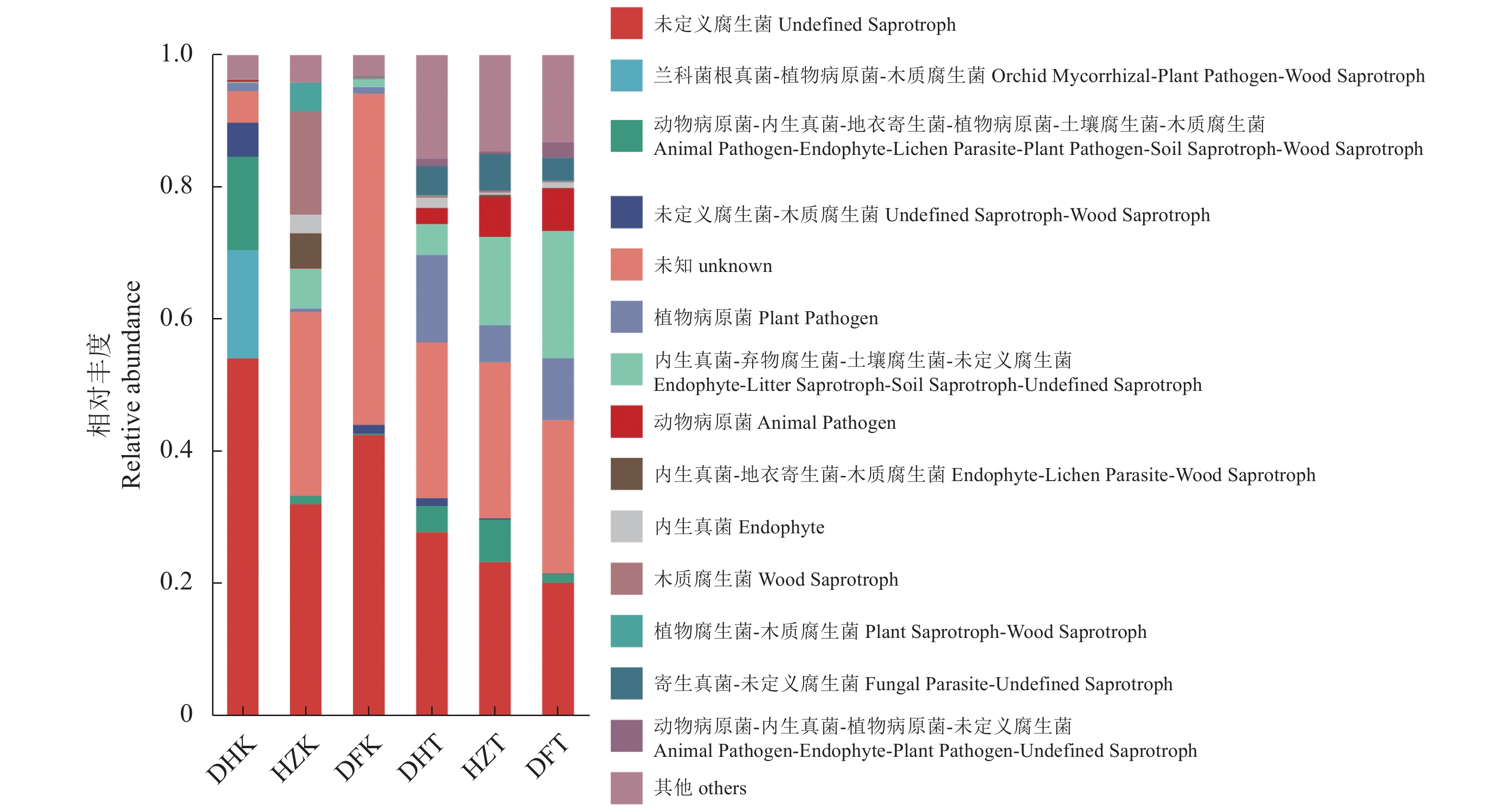
目的 探究贵州不同生境半夏内生和根际土壤微生物群落多样性、物种组成、物种网络关系和功能菌群预测,并分析与环境因子的相关性,为半夏菌群资源开发利用提供理论依据。 方法 对贵州野生半夏、规模化种植半夏和套种半夏的内生菌群、根际土壤菌群进行高通量测序,检测土壤理化因子和酶活性,并通过生信学进行数据分析。 结果 人工种植和野生半夏土壤环境因子差异性明显,且栽培方式对土壤理化性质与酶活有显著影响,人工种植样地的有机质含量高且土壤酸性高,野生样地酶活性偏高;半夏内生细菌优势菌属包括根瘤菌属、假单胞菌属、芽孢杆菌属、慢生根瘤菌属等,半夏内生真菌优势菌属包括弯孢菌属、新赤壳属、丝核菌属、镰刀菌属、Dactylonectria、炭角菌目未分类属等,半夏根际优势菌属种类更丰富,各优势菌属在不同样本以不同丰度聚集且具有规律性,受生长环境和种植方式影响;细菌优势菌群中有10属、真菌优势菌群中有13属与土壤理化性质或酶活性呈显著相关性,内生菌群对环境因子更为敏感,半夏内生菌群既互利又拮抗,根际土壤菌群网络关系相对稳定;半夏内生菌群优势菌属中除了未明确分类、未知菌属外,有益菌属丰度占比高。 结论 可通过人为调节土壤PH、施入菌肥等方式改良土壤微生态环境;半夏内生菌群包括根瘤菌、假单胞菌、芽孢杆菌、农研丝杆菌、木霉菌和绿僵菌等可开发利用,助力半夏栽培,促进半夏产业发展。 Abstract:Objective Endophytic microbes of Pinellia ternata and rhizosphere microbial communities in the habitat soils in Guizhou as affected by the environmental conditions were analyzed. Methods High throughput sequencing to identify the endophytic and rhizosphere microbiota in P. ternata and soils of the wild, large-scale cultivated, and intercropped P. ternata plants grew in Guizhou was conducted. Microbial diversity, species, relationships, and enzyme activities as well as functional microflora were analyzed. Bioinformatics was employed to decipher the ecological relationship between the plant and its habitat. Results The environmental, physiochemical, and enzymatic conditions on the land where P. ternata plants were grown in the wild or under cultivation varied significantly. For instance, the organic matter content and acidity were high in the cultivated plots, but the enzyme activity high in the soil of virgin forest. In the plants, Rhizobium, Pseudomonas, Bacillus, and Bradyrhizobium were the dominant endophytic bacteria genera, whereas Campylospora, Neocosmospora,Rhizoctonia, Fusarium, Dactylonectria, unclassified genera of Xylariales order, etc. were found to be the dominant fungi genera. In the rhizosphere soil, abundant dominant microbial species regularly aggregated and were affected by the environmental factors and planting method. For example, 10 dominant bacteria genera and 13 fungi genera significantly correlated with the physicochemical properties and/or enzyme activity of the soil they inhabited. In general, the endophytic microbes in the plants were more sensitive to the environmental factors than those in the rhizosphere soil. And they could be synergistic as well as antagonistic to one another, but the rhizosphere community tended to be stable. Aside from the unclassified and unknown genera, the dominant endophytic bacteria were mostly considered beneficial for the plant. Conclusion The microbial community in the soil could be improved by adjusting pH and applying microbial fertilizers. The endophytic microbes of P. ternate including Rhizobia,Pseudomonas, Bacillus, Agrobacterium, Trichoderma, and Metarhizium anisopliae could be used to enhance the plant growth ushering in the development of a pharmaceutical industry based on the medicinal material. -
Key words:
- Pinellia ternata /
- endophyte /
- soil microbes /
- Environmental factor
-
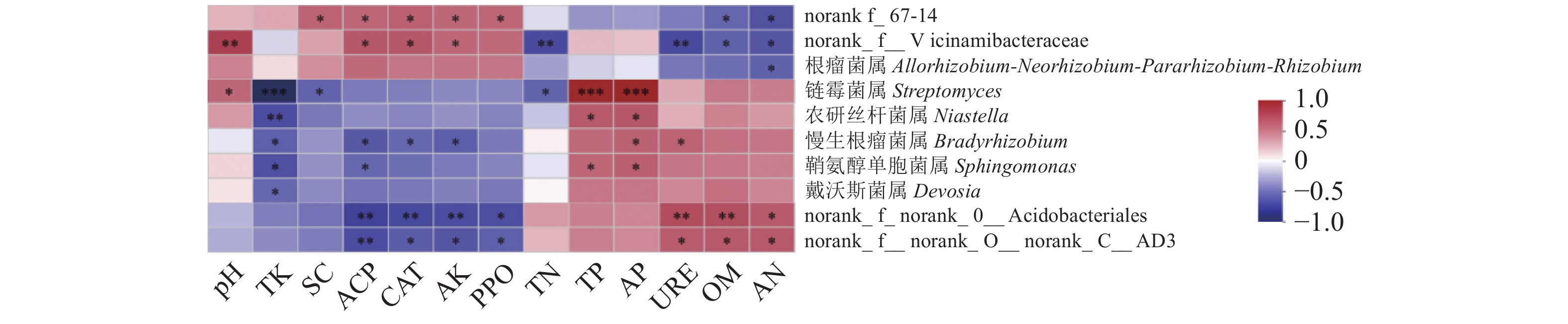
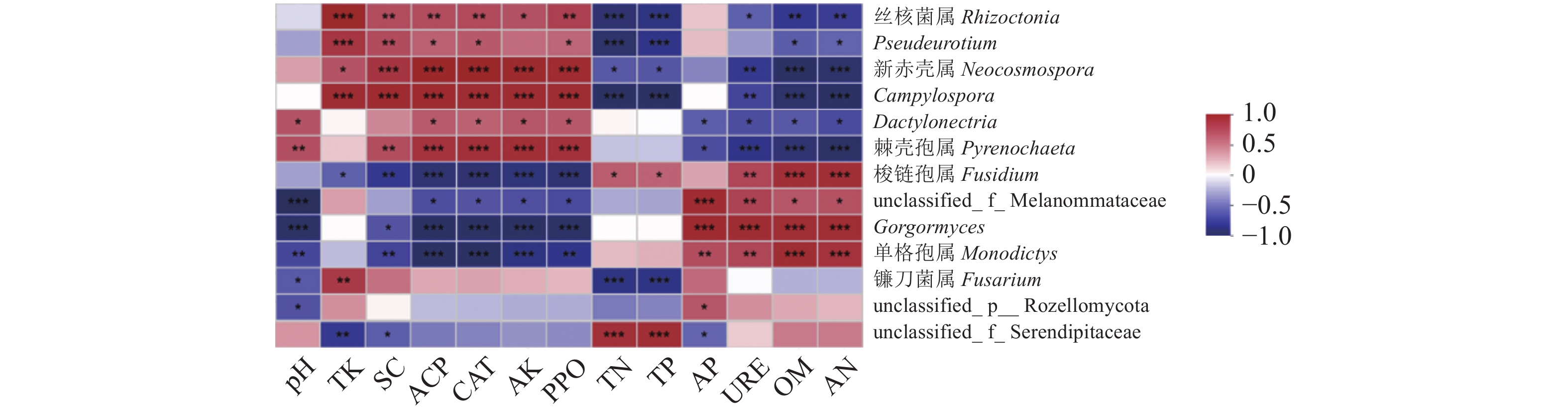
图 11 细菌属水平物种间相关性分析
圆点的大小表示物种之间相关性大小,圆点的颜色以图下方柱状图为基准,0点处左侧颜色代表负相关,右侧颜色代表正相关。即圆点越大,相关性越强;颜色越红,负相关越强,颜色越蓝,正相关性越强。下同。
Figure 11. Correlations among bacteria species at genus level
Size of dot indicates correlation between species; color corresponds to bar chart below; colored dot placed left to point 0 represents negative correlation; that on the right, positive correlation; the larger the dot, the stronger the correlation; the redder the color, the stronger the negative correlation; and the bluer the color, the stronger the positive correlation. Same for below.
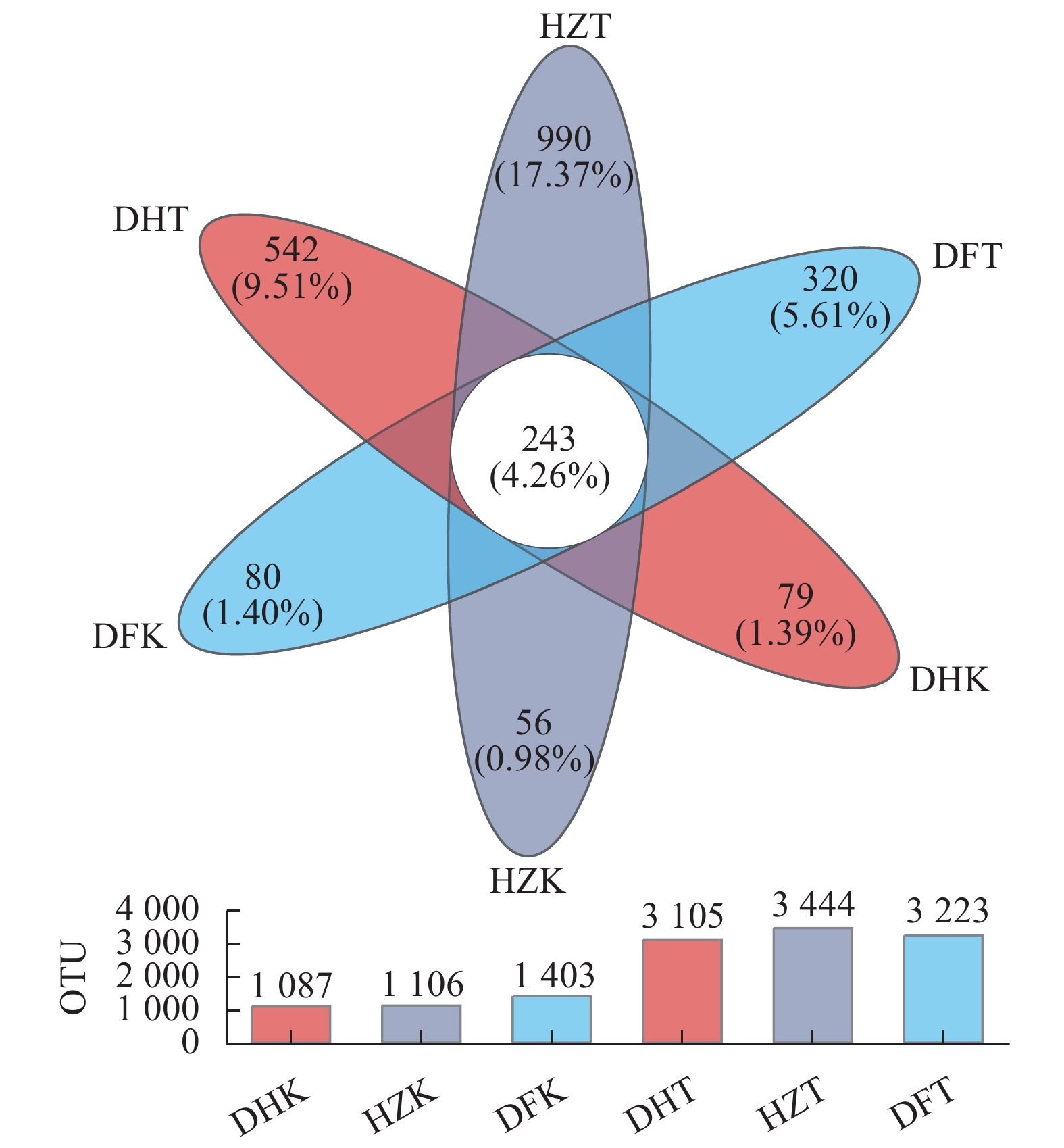
表 1 半夏采样信息表
Table 1. Sampling of P. ternata
编号
Code采集地点
Locality采集部位和对应编号
Collection location and coding生长环境
Growth environment经度
Longitude ( N)纬度
latitude( E)海拔
Altitude/mDH 毕节市大河乡 块茎和根须(DHK)、根际土(DHT) 林下野生 27.319420 104.920517 1638.5 HZ 毕节市赫章县半夏种植基地 块茎和根须(HZK)、根际土(HZT) 大田人工起垄栽培 27.074467 104.420799 2216.4 DF 毕节市百里杜鹃管委会鹏程管理区 块茎和根须(DFK)、根际土(DFT) 滇重楼套种,人工起垄栽培,
种植基地周边为针阔混交林27.232323 105.785965 1633.7 表 2 不同生境半夏土壤理化性质及酶活性
Table 2. Physiochemical properties and enzyme activities of P. ternata habitat soils
指标
IndexDH HZ DF TN/(g·kg−1) 1.45±0.01b 1.63±0.03a 1.42±0.02b TP/(g·hg−1) 0.08±0.01c 0.10±0.00b 0.21±0.00a TK/(g·hg−1) 1.45±0.03a 1.11±0.00b 1.01±0.02c AN/(mg·kg−1) 207.73±4.68c 301.13±2.85a 234.86±0.43b AK/(mg·kg−1) 462.84±1.08a 368.87±1.69c 398.78±1.35b AP/(mg·kg−1) 44.23±0.44c 47.71±0.62b 76.82±0.42a OM/(g·kg−1) 44.64±0.78c 73.14±0.60a 55.33±0.23b pH 6.69±0.03b 5.45±0.02c 6.84±0.02a URE/(U·g−1) 0.58±0.03b 0.83±0.08a 0.64±0.07b SC/(U·g−1) 20.99±1.64a 10.47±0.43b 11.05±0.89b ACP/(U·g−1) 2.35±0.06a 0.82±0.07c 1.52±0.10b PPO/(U·g−1) 3.80±0.13a 0.88±0.07c 1.79±0.03b 同行中数值后面的不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Data with different lowercase letters on same row indicate significant differences at P<0.05. -
[1] 陈晓芳, 张翔宇, 柳敏, 等. 贵州半夏叶褐斑病病原菌鉴定及其防治药剂室内毒力测定 [J]. 中药材, 2023, 46(5):1094−1099.CHEN X F, ZHANG X Y, LIU M, et al. Identification of pathogen causing leaf brown spot of Pinellia ternata in Guizhou and indoor toxicity test of its control chemicals [J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2023, 46(5): 1094−1099. (in Chinese) [2] 许佳伟, 罗鸣, 徐荣, 等. 中国半夏主产地软腐病致病菌分离、鉴定及比较研究 [J]. 西南农业学报, 2023, 36(9):1950−1961.XU J W, LUO M, XU R, et al. Isolation, identification and comparative study of soft rot pathogens of Pinellia ternata in China [J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 36(9): 1950−1961. (in Chinese) [3] 赵玳琳, 何海永, 谭清群, 等. 贵州省赫章县半夏软腐病病原鉴定 [J]. 中药材, 2022, 45(2):278−283.ZHAO D L, HE H Y, TAN Q Q, et al. Identification of pathogens of Pinellia ternatea soft rot in Hezhang County of Guizhou Province [J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2022, 45(2): 278−283. (in Chinese) [4] HE Z G, MAO R J, DONG J E, et al. Remediation of deterioration in microbial structure in continuous Pinellia ternata cropping soil by crop rotation [J]. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 2019, 65(4): 282−295. doi: 10.1139/cjm-2018-0409 [5] 何冬梅, 赖长江生, 严铸云, 等. 中药微生态研究与展望 [J]. 中国中药杂志, 2018, 43(17):3417−3430.HE D M, LAI C J S, YAN Z Y, et al. Research and prospect of Traditional Chinese Medical Microecology [J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2018, 43(17): 3417−3430. (in Chinese) [6] 王红阳, 康传志, 王月枫, 等. 药用植物微生物组的研究现状及展望 [J]. 中国中药杂志, 2022, 47(20):5397−5405.WANG H Y, KANG C Z, WANG Y F, et al. Medicinal plant microbiome: Advances and prospects [J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2022, 47(20): 5397−5405. (in Chinese) [7] 吕佩, 王新绘, 刘晓颖, 等. 药用植物刺山柑不同部位细菌群落结构及其多样性 [J]. 微生物学报, 2023, 63(10):3939−3954.LÜ P, WANG X H, LIU X Y, et al. Bacterial diversity and communities in different parts of the medicinal plant Capparis spinosa L [J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2023, 63(10): 3939−3954. (in Chinese) [8] 王礼科, 罗夫来, 王华磊, 等. 半夏不同连作年限土壤酶活性、微生物及化感物质的分析 [J]. 中药材, 2021, 44(4):798−801.WANG L K, LUO F L, WANG H L, et al. Analysis of soil enzyme activities, microorganisms and allelochemicals in different continuous cropping years of Pinellia ternata [J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2021, 44(4): 798−801. (in Chinese) [9] 刘诗蓉, 王红兰, 孙辉, 等. 半夏连作对根际土壤微生物群落的影响研究 [J]. 中草药, 2022, 53(4):1148−1155.LIU S R, WANG H L, SUN H, et al. Effects of continuous cropping of Pinellia ternata on rhizospheric microbial community [J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2022, 53(4): 1148−1155. (in Chinese) [10] 陈晓芳, 张翔宇, 柳敏, 等. 根腐病半夏内生菌群及其土壤微生物群落分析 [J]. 中药材, 2023, 46(10):2399−2407.CHEN X F, ZHANG X Y, LIU M, et al. Analysis of endophytic flora and soil microbial community of Pinellia ternata with root rot [J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2023, 46(10): 2399−2407. (in Chinese) [11] MISHRA S, GOYAL D, PHURAILATPAM L. Targeted 16S rRNA gene and ITS2 amplicon sequencing of leaf and spike tissues of Piper longum identifies new candidates for bioprospecting of bioactive compounds [J]. Archives of Microbiology, 2021, 203(7): 3851−3867. doi: 10.1007/s00203-021-02356-w [12] 张翔宇, 陈晓芳, 柳敏, 等. 不同栽培模式重楼内生真菌、根际真菌多样性与环境因子关联性研究[J/OL]. 中药材, 2023(6): 1353-1360.ZAHNG X Y, CHEN X F, LIU M, et al. Study on the Diversity of Endophytic Fungi and Rhizosphere Fungi in Different Cultivation Models and their Correlation with Environmental Factors of Paris polyphylla[J/OL]. ProvinceJournal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2023(6): 1353-1360. (in Chinese) [13] 秦杰, 高振峰, 岳爱琴, 等. 一株晋大53号大豆中慢生根瘤菌的分离鉴定及抗逆分析 [J]. 大豆科学, 2020, 39(6):898−905. doi: 10.11861/j.issn.1000-9841.2020.06.0898QIN J, GAO Z F, YUE A Q, et al. Isolation, identification and stress resistance analysis of A Mesorhizobium isolated from soybean variety jinda 53 [J]. Soybean Science, 2020, 39(6): 898−905. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11861/j.issn.1000-9841.2020.06.0898 [14] 马福林, 仁增卓玛, 王昌玲, 等. 西藏沙棘根瘤内生假单胞菌的分离鉴定及促生性研究 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2023, 38(5):624−631.MA F L, RENZENG Z M, WANG C L, et al. Identification and Growth-promoting Effects of Endophytic Pseudomonas sp. From Hippophae thibetana Root Nodules [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 38(5): 624−631. (in Chinese) [15] 刘艳丽, 赵娜娜, 范贝贝, 等. 浓缩沼液中添加芽孢杆菌对促生和抑菌功能的强化效应 [J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2023, 28(7):68−78. doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2023.07.06LIU Y L, ZHAO N N, FAN B B, et al. Enhancement effect of Bacillus spp. added to concentrated biagas slurry on the functions of growth promotion and bacterial inhibition [J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2023, 28(7): 68−78. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2023.07.06 [16] 施河丽, 向必坤, 彭五星, 等. 有机无机肥料配施对植烟土壤养分及细菌群落结构的影响 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2019, (4):58−66. doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.18352SHI H L, XIANG B K, PENG W X, et al. Effects of combined application of organic and inorganic fertilizers on flue-cured tobacco soil nutrients and bacterial community structure [J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2019(4): 58−66. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.18352 [17] 石义妃, 耿佩冰, 吴皓, 等. 金黄垂直链霉菌DF06的分类鉴定及防病促生作用 [J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2023, 39(2):407−417.SHI Y F, GENG P B, WU H, et al. Classification and identification of Streptomyces aureoverticillatus DF06 and its effect on disease control and growth promotion [J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2023, 39(2): 407−417. (in Chinese) [18] 刘辉, 韦璐璐, 朱龙发, 等. 鞘氨醇单胞菌的研究进展 [J]. 微生物学通报, 2023, 50(6):2738−2752.LIU H, WEI L L, ZHU L F, et al. Research progress of Sphingomonas [J]. Microbiology China, 2023, 50(6): 2738−2752. (in Chinese) [19] KHAN A A R. 木霉属次生代谢提取物对植物病原真菌、细菌和线虫的活性筛选研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2021.KHAN A A R . Screening and Antimicrobial Efficacy of Secondary Metabolites from Trichoderma species Against Plant Pathogenic Fungus, Bacteria and Nematode[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2021. (in Chinese) [20] 农向群, 王广君, 蔡霓, 等. 绿僵菌与植物的多重关系及其在植物保护中的应用潜力 [J]. 植物保护, 2022, 48(3):22−30,54.NONG X Q, WANG G J, CAI N, et al. Multiple association of Metarhizium with plants and the application potential in plant protection [J]. Plant Protection, 2022, 48(3): 22−30,54. (in Chinese) -






 下载:
下载: