Diversity and Characteristics of Endophytic Bacteria Isolated from Peperomia dindygulensis Miq
-
摘要: 采用菌落表征性状统计和16S rRNA基因序列分析法,对石蝉草根、茎、叶内生细菌的数量分布、群落组成和遗传多样性进行初步研究。从各组织器官中分离出内生细菌383株,通过菌落表征性状,以类平均连锁聚类法进行聚类分析,在欧氏距离为0的水平上可聚为19个亚群。多样性分析结果表明,19个亚群隶属于8属13种;其数量表现为叶>根>茎,多样性表现为茎>叶>根,其中鞘氨醇单胞菌属Sphingomonas和寡养单胞菌属Stenotrophomonas为石蝉草内生细菌的优势属。Abstract: Statistical classification of colony characteristics and 16S rRNA gene sequencing were performed to obtain the information on the quantitative distribution, community composition, and diversity of endophytic bacteria in the roots, stems and leaves of Peperomia dindygulensis Miq. A total of 383 endophytic bacteria were isolated and clustered according to their colony characteristics. After the average linkage clustering, the groups were divided into 19 subgroups at the Euclidean distance of 0 level. The subgroups were phylogenetically classified into 8 genera and 13 species based on their partial 16S rDNA sequences. The quantities of endophytic bacteria in the tissues were in order of leaves > roots > stems; and, the diversity of the bacteria, stems > leaves > roots. The predominant endophytic bacteria in P. dindygulensis Miq were found to belong to the genera of Sphingomonas and Stenotrophomonas.
-
Keywords:
- Peperomia dindygulensis Miq /
- endophytic bacteria /
- diversity /
- 16S rRNA
-
植物内生菌是指定殖于健康植物组织内部,而又不引发宿主植物表现出明显感染症状的一类微生物[1]。在与宿主植物协同共生的过程中,部分植物内生菌具有固氮、解磷、分泌生长素等能力,可促进植物生长[2];部分植物内生菌能有效抑制植物病原菌活性,具有生防作用[3];植物内生菌可产生与宿主植物相同或相似的代谢产物,包括萜类、芳香类等化合物,这些物质具有多种生物学活性,如抗菌、降糖等[4]。
在农业和医药领域,药用植物内生菌资源的开发利用具有很大的应用潜力。1993年Stierle等首次从红豆杉韧皮部分离得到的内生真菌紫杉霉Taxomyces anreanae可以产生紫杉醇或其他紫杉烷类化合物,该类物质对多种恶性肿瘤具有突出疗效,从此掀起了开发内生菌及活性物质的热潮[1]。周佳宇等[2]从茅苍术叶片分离的内生细菌,34株具有溶解磷的作用,43株能够将色氨酸转化为生长素。王娜[5]研究发现,乌头内生细菌群落结构与宿主主要有效成分生物碱有密切相关性。梁子宁等[6]从药用植物鸦胆子中分离得到1株抑菌谱广、活性较高的内生细菌,为新型生物杀菌剂的开发利用提供了理论依据。总之,药用植物内生菌的研究将会在人类健康、环境保护和农业生产等多个领域发挥巨大潜力和价值。
石蝉草Peperomia dindygulensis Miq.系胡椒科草胡椒属植物,在我国南方各省区有较多分布。《中华本草》、《云南中草药选》等对其均有记载,其味辛、性凉,具有清热解毒、化瘀散结、利水消肿的功效,对肺癌、肝癌、胃癌等有治疗作用[7]。目前,石蝉草的研究多集中于化学成分、药理作用等方面,而忽视了植物内生菌在中药材形成中所发挥的作用。朱文君等[8]对石蝉草乙醇提取物进行了分离和鉴定,得到聚酮类化合物11个,其中2个为新的化合物;陈立[7]研究发现石蝉草的乙醇提取物中氯仿部位对肿瘤细胞株抑制作用最强,分离得到的3个断联木脂素对肿瘤细胞株有较强的抑制作用。尚未见石蝉草内生细菌的相关研究和报道。本研究采用稀释涂布平板法,对石蝉草根、茎、叶内生细菌进行分离和鉴定,旨在了解石蝉草内生细菌的数量分布、群落组成和遗传多样性。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料的采集
石蝉草于2015年10月上旬采自云南省文山州马关县,根、茎、叶分别取自5株生长健壮的石蝉草植株。不同部位样品从植株分离后立即装入无菌采样袋中,低温保鲜,于48 h内进行内生细菌的分离。
1.2 培养基
参照方中达[9]方法配制培养基,其中内生细菌分离和培养采用NA培养基,液体培养采用LB培养基。
1.3 内生细菌的分离
将材料用自来水洗净,移入超净工作台内,无菌滤纸吸干样品表面水分,分别称取石蝉草根、茎、叶各1 g,用75%酒精浸没1 min,转入2%次氯酸钠5 min,无菌水漂洗5次,并不断摇动。取最后1次漂洗无菌水涂布于NA平板作为对照,以此检验表面消毒是否彻底。将已消毒材料置于无菌研钵中加2 mL无菌水研磨至匀浆,梯度稀释10~103倍,各取100 μL涂布于NA平板,重复3次,在28℃黑暗环境中培养2~3 d。
1.4 内生细菌的菌落调查、纯化和保存
选择菌落密度(30~300个·皿-1)适宜的NA平板统计菌落总数,计算各部位样品每克鲜重所含活菌数,用cfu·g-1FW表示。参照陈泽斌等[10]方法对菌落形态进行初步归类,得出表型特征数值分类聚类图。根据聚类图挑选各亚群单菌落划线纯化,纯菌落转接入NA试管斜面保存。
1.5 内生细菌的16S rDNA序列分析
将纯化菌株接入LB液体培养基中,恒温28℃、100 r·min-1振荡培养2 d,8 000 r·min-1离心取沉淀物,用细菌基因组DNA提取试剂盒(TAKARA)提取菌株总DNA。采用通用引物F27/R1492[11]进行16S rRNA基因序列扩增。扩增产物送上海桑尼生物科技有限公司进行序列测定,将测得的16S rDNA全序列在GenBank中进行BLAST同源性搜索,获得已知分类地位同源性相近的菌株序列,参照Felsenstein J[12]方法,对各菌株的系统发育地位进行分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 内生细菌的分离
石蝉草各部位表面消毒后最后1次漂洗无菌水涂布于NA平板,在28℃环境中培养3 d未见菌落生长,说明此方法消毒彻底。菌落计数结果表明,各组织分离出的内生细菌数量差异明显,其中叶部的内生细菌数量最多,为(2.16±0.11)×104cfu·g-1FW,其次为根部,平均内生细菌数量为(6.36±1.29)×103cfu·g-1FW,茎部内生细菌数量最少,仅为(3.93±0.24)×103cfu·g-1FW。
2.2 内生细菌表征性状的多样性分析
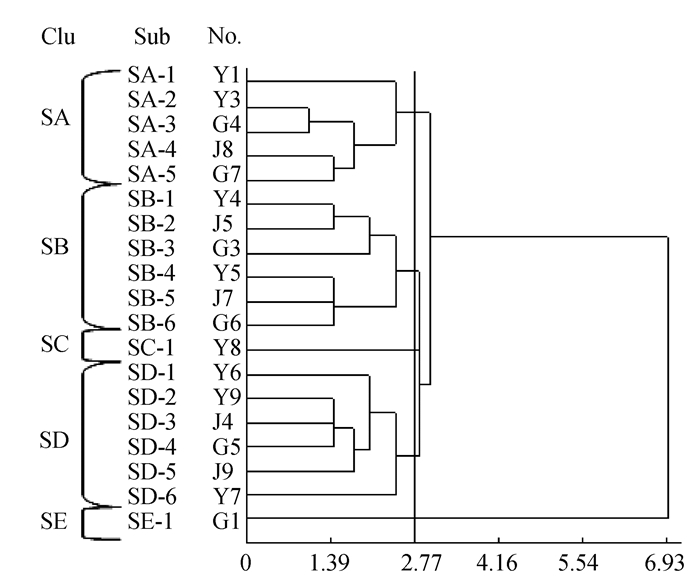
由图 1可以看出,从石蝉草各组织分离出的383株内生细菌具有丰富的多样性。在欧氏距离为2.77时,可聚分为5个表观群:SA、SB、SC、SD、SE,分别在分离总数中所占比例依次为87.21%、6.01%、0.26%、3.92%、2.61%(表 1),其中表观群SA菌株最多;在欧氏距离为0时,可聚分为19个亚群(图 1、表 1)。
表 1 亚群菌落形态特征Table 1. Colonial morphology of sub-clusters亚群 菌株 菌落形态 分离株数 所占比
例/%根 茎 叶 SA-1 Y1 点状、湿、黄色、有光泽、表面凸起、边缘整齐、不透明 2 20 244 69.45 SA-2 Y3 圆形、直径2~3 mm、湿、乳白、有光泽、表面凸起、边缘整齐、半透明 0 6 4 2.61 SA-3 G4 圆形、直径2~3 mm、湿、乳白、有光泽、表面凸起、边缘整齐、不透明 3 0 0 0.78 SA-4 J8 圆形、直径1~2 mm、湿、白色、有光泽、表面凸起、边缘整齐、不透明 0 4 0 1.04 SA-5 G7 圆形、直径1~2 mm、湿、乳黄、有光泽、表面凸起、边缘整齐、透明 51 0 0 13.32 SB-1 Y4 形状不规则、长7~8 mm、黏稠、乳白、无光泽、中间凸起、边缘不整齐、不透明 0 0 3 0.78 SB-2 J5 形状不规则、长6~8 mm、湿、乳白、无光泽、中间凸起、边缘不整齐、不透明 0 7 0 1.83 SB-3 G3 形状不规则、长7~8 mm、黏稠、白色、无光泽、中间凸起、边缘不整齐、不透明 10 0 0 2.61 SB-4 Y5 形状不规则、长6~7 mm、干、白色、无光泽、表面凸起褶皱、边缘不整齐、不透明 0 0 1 0.26 SB-5 J7 形状不规则、长5~7 mm、干、乳白、无光泽、表面凸起褶皱、边缘不整齐、不透明 0 1 0 0.26 SB-6 G6 形状不规则、长5~6 mm、干、乳白、无光泽、中间凸起、边缘不整齐、不透明 1 0 0 0.26 SC-1 Y8 形状不规则、长3~4 mm、湿、乳白、有光泽、表面凸起褶皱、边缘不整齐、半透明 0 0 1 0.26 SD-1 Y6 圆形、直径4~5 mm、黏稠、乳白、无光泽、表面内凹、边缘整齐、不透明 0 0 1 0.26 SD-2 Y9 圆形、直径4~5 mm、湿、乳白、有光泽、中间凸起、边缘整齐、半透明 0 0 4 1.04 SD-3 J4 圆形、直径5~6 mm、黏稠、乳白、有光泽、中间凸起、边缘整齐、半透明 0 6 0 1.57 SD-4 G5 圆形、直径4~5 mm、湿、白色、有光泽、中间凸起、边缘整齐、不透明 1 0 0 0.26 SD-5 J9 圆形、直径3~4 mm、湿、乳白、有光泽、表面内凹、边缘整齐、半透明 0 1 0 0.26 SD-6 Y7 圆形、直径5~6 mm、干、乳白、无光泽、表面扁皱、边缘整齐、半透明 0 1 1 0.52 SE-1 G1 水渍状、长25 mm、湿、乳白、无光泽、表面凹凸不平、边缘不整齐、半透明 8 1 1 2.61 2.3 内生细菌16S rDNA序列分析结果
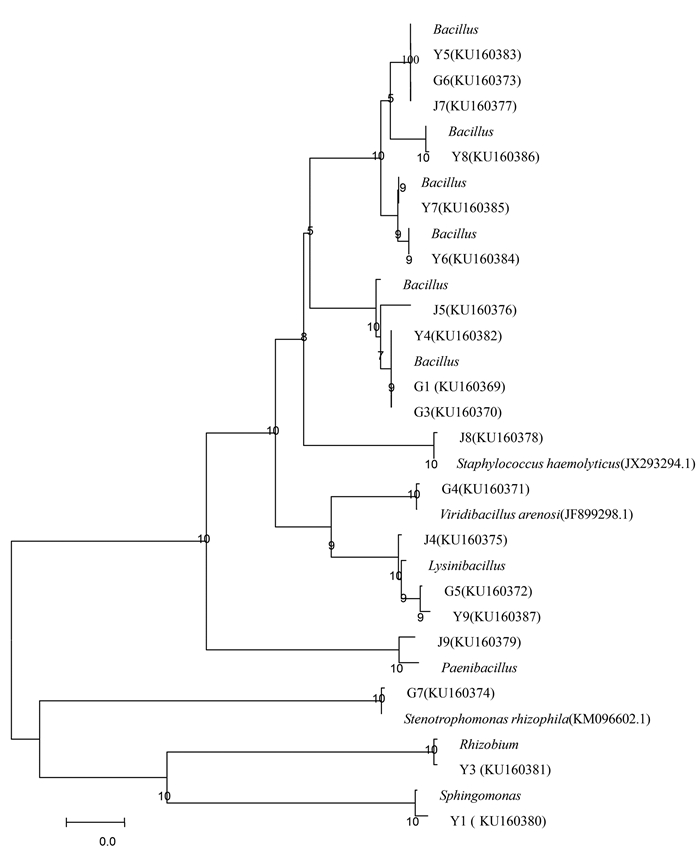
根据表征性状数值分类聚类图结果,选择19株代表菌株的16S rDNA进行测序,获得基因序列提交GenBank数据库,收录号分别为KU160369-KU160387。通过BLAST程序进行相似性比对,与已知分类地位菌株16S rDNA序列相似性均大于97%,大部分相似性达99%以上,19株代表菌株分属于8属13种,并构建了系统发育树(图 2)。其中石蝉草根、茎、叶内生细菌种类分别为6种、9种、8种(表 2)。寡养单胞菌属Stenotrophomonas、绿芽孢杆菌属Viridibacillus为根部特有;类芽孢杆菌属Paenibacillus、葡萄球菌属Staphylococcus为茎部特有;根瘤菌属Rhizobium为茎、叶部共有;芽孢杆菌属Bacillus、赖氨酸芽孢杆菌属Lysinibacillus、鞘氨醇单胞菌Sphingomonas为根、茎、叶部共有。
表 2 石蝉草内生细菌的种类组成Table 2. Species of endophytic bacteria isolated from P. dindygulensis Miq菌株 相近的属、种 登录号 序列相
似性/%G6 J7 Y5 Bacillus subtilis KT957306.1 100 Y8 Bacillus licheniformis KM289130.1 100 Y7 Bacillus altitudinis KT758448.1 100 Y6 Bacillus pumilus KT003271.1 100 J5 Bacillus anthracis AB190217.1 98 G1 G3 Y4 Bacillus cereus KC692201.1 99~100 J8 Staphylococcus haemolyticus JX293294.1 97 G4 Viridibacillus arenosi JF899298.1 100 G5 J4 Y9 Lysinibacillus fusiformis KP334988.1 99 J9 Paenibacillus sp KF011612.1 99 G7 Stenotrophomonas rhizophila KM096602.1 100 Y3 Rhizobium sp KR067598.1 100 Y1 Sphingomonas aeria KJ572399.1 99 各类群在石蝉草所分离内生细菌中所占比例最高且大于10%的2种类群为:Sphingomonas aeria所占比例69.45%,Stenotrophomonas rhizophila所占比例13.32%(表 2)。由此推断,石蝉草内生细菌的优势菌群为Sphingomonas aeria和Stenotrophomonas rhizophila。
3. 讨论与结论
从石蝉草根、茎、叶中共分离出内生细菌383株,通过表型特征数值分类,在欧氏距离为0时,聚类为19个亚群。运用16S rRNA基因序列分析法对19个亚群代表菌株多样性进行分析,结果表明19株内生细菌分属于8个属13个种,内生细菌多样性较丰富,3个部位材料中内生细菌的种类和数量均有差异。从两种方法的分析结果看,聚类情况存在一定差异,表明某些菌株具有不同表型特征,或特征甄别受主观因素影响较大。
石蝉草内生细菌的优势菌群为鞘氨醇单胞菌Sphingomonas aeria和嗜根寡养单胞菌Stenotro-phomonas rhizophila,其中Sphingomonas aeria菌在所分离菌株中所占比例最高,达到69.45%。据报道,鞘氨醇单胞菌具有固氮酶活性,解磷能力较强,可分泌IAA,能促进植物生长[13-14];有很强的逆境生长潜能,对有机磷、氨基甲酸酯和除虫菊酯等3类农药具有不同的降解效能[15-16],下一步可人工栽培石蝉草,探索喷施该菌株发酵液对其生长的影响。
已有研究证实,内生菌的分布特征和群落结构不仅受宿主植物基因型的影响,还受外界环境因子的影响。即使是同一种植物,不同组织中内生细菌的种类和数量也不尽相同,存在复杂的多样性[17-18]。目前对于内生细菌的分布有两种观点,一种认为内生菌多从土壤进入植物体,随蒸腾作用逐渐扩散至地上部分,在植株体内的分布通常上部组织少于下部组织,越往植株顶部,内生菌越少[19];一种则认为,环境中的微生物一般会沿着植物的气孔、水孔及伤口等破损处进入植物选择合适的营养和生态位定殖,造成地下部位内生菌的种类少于地上部位[20]。本研究发现石蝉草可培养内生细菌数量表现为叶部最多,茎部最少;多样性表现为茎部最多,根部最少。综合两种观点,作者认为石蝉草内生细菌主要从根部和叶部进入植物体,因叶两面被短柔毛,叶面孔隙增多,表面积增大,微生物更易在此聚集进入植物体,从而导致内生细菌数量叶部高于根部,茎部多样性最为丰富可能与内生菌在植物体内的扩散有关。
本研究采用传统的微生物研究方法,且选用的培养基较为单一,具有一定的局限性。目前得到纯培养并鉴定的微生物种类只占环境中微生物的0.1%~10.0%,90%以上的微生物迄今仍处于存活但不可人工培养的状态,称未培养(Uncultured)微生物[21]。下一步可采用非培养的方法,对石蝉草内生细菌进行更加深入的研究。
-
表 1 亚群菌落形态特征
Table 1 Colonial morphology of sub-clusters
亚群 菌株 菌落形态 分离株数 所占比
例/%根 茎 叶 SA-1 Y1 点状、湿、黄色、有光泽、表面凸起、边缘整齐、不透明 2 20 244 69.45 SA-2 Y3 圆形、直径2~3 mm、湿、乳白、有光泽、表面凸起、边缘整齐、半透明 0 6 4 2.61 SA-3 G4 圆形、直径2~3 mm、湿、乳白、有光泽、表面凸起、边缘整齐、不透明 3 0 0 0.78 SA-4 J8 圆形、直径1~2 mm、湿、白色、有光泽、表面凸起、边缘整齐、不透明 0 4 0 1.04 SA-5 G7 圆形、直径1~2 mm、湿、乳黄、有光泽、表面凸起、边缘整齐、透明 51 0 0 13.32 SB-1 Y4 形状不规则、长7~8 mm、黏稠、乳白、无光泽、中间凸起、边缘不整齐、不透明 0 0 3 0.78 SB-2 J5 形状不规则、长6~8 mm、湿、乳白、无光泽、中间凸起、边缘不整齐、不透明 0 7 0 1.83 SB-3 G3 形状不规则、长7~8 mm、黏稠、白色、无光泽、中间凸起、边缘不整齐、不透明 10 0 0 2.61 SB-4 Y5 形状不规则、长6~7 mm、干、白色、无光泽、表面凸起褶皱、边缘不整齐、不透明 0 0 1 0.26 SB-5 J7 形状不规则、长5~7 mm、干、乳白、无光泽、表面凸起褶皱、边缘不整齐、不透明 0 1 0 0.26 SB-6 G6 形状不规则、长5~6 mm、干、乳白、无光泽、中间凸起、边缘不整齐、不透明 1 0 0 0.26 SC-1 Y8 形状不规则、长3~4 mm、湿、乳白、有光泽、表面凸起褶皱、边缘不整齐、半透明 0 0 1 0.26 SD-1 Y6 圆形、直径4~5 mm、黏稠、乳白、无光泽、表面内凹、边缘整齐、不透明 0 0 1 0.26 SD-2 Y9 圆形、直径4~5 mm、湿、乳白、有光泽、中间凸起、边缘整齐、半透明 0 0 4 1.04 SD-3 J4 圆形、直径5~6 mm、黏稠、乳白、有光泽、中间凸起、边缘整齐、半透明 0 6 0 1.57 SD-4 G5 圆形、直径4~5 mm、湿、白色、有光泽、中间凸起、边缘整齐、不透明 1 0 0 0.26 SD-5 J9 圆形、直径3~4 mm、湿、乳白、有光泽、表面内凹、边缘整齐、半透明 0 1 0 0.26 SD-6 Y7 圆形、直径5~6 mm、干、乳白、无光泽、表面扁皱、边缘整齐、半透明 0 1 1 0.52 SE-1 G1 水渍状、长25 mm、湿、乳白、无光泽、表面凹凸不平、边缘不整齐、半透明 8 1 1 2.61 表 2 石蝉草内生细菌的种类组成
Table 2 Species of endophytic bacteria isolated from P. dindygulensis Miq
菌株 相近的属、种 登录号 序列相
似性/%G6 J7 Y5 Bacillus subtilis KT957306.1 100 Y8 Bacillus licheniformis KM289130.1 100 Y7 Bacillus altitudinis KT758448.1 100 Y6 Bacillus pumilus KT003271.1 100 J5 Bacillus anthracis AB190217.1 98 G1 G3 Y4 Bacillus cereus KC692201.1 99~100 J8 Staphylococcus haemolyticus JX293294.1 97 G4 Viridibacillus arenosi JF899298.1 100 G5 J4 Y9 Lysinibacillus fusiformis KP334988.1 99 J9 Paenibacillus sp KF011612.1 99 G7 Stenotrophomonas rhizophila KM096602.1 100 Y3 Rhizobium sp KR067598.1 100 Y1 Sphingomonas aeria KJ572399.1 99 -
[1] 刘学周, 赵智灵, 李绍宾, 等.西洋参内生菌群落结构与多样性[J].微生物学报, 2015, 55(3):330-340. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSXB201503013.htm [2] 周佳宇, 贾永, 王宏伟, 等.茅苍术叶片可培养内生细菌多样性及其促生潜力[J].生态学报, 2013, 33(4):1106-1117. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201304011.htm [3] 杜晓宁, 徐惠娟, 黄盼盼, 等.宁夏枸杞内生细菌的多样性及其抑菌活性研究[J].微生物学通报, 2015, 42(9):1779-1787. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSWT201509021.htm [4] 朱妍妍, 艾嫦, 张嘉, 等.具有生物活性的植物内生真菌次生代谢产物[J].化学进展, 2011, 23(4):704-730. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXJZ201104012.htm [5] 王娜.乌头内生细菌群落结构及其与宿主生物碱合成关系研究[D].杨凌:陕西师范大学, 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10718-1014398431.htm [6] 梁子宁, 赖开平, 朱华, 等.药用植物鸦胆子内生细菌分离及其抑菌活性研究[J].南方农业学报, 2014, 45(3):389-394. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXNY201403008.htm [7] 陈立.石蝉草化学成分及抗肿瘤活性的研究[D].北京:中国人民解放军军事医学科学院, 2007. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-90106-2007121376.htm [8] 朱文君, 林梦感, 杨国红, 等.石蝉草中两个新的聚酮类化合物[J].中草药, 2011, 42(3):420-423. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZCYO201103003.htm [9] 方中达.植病研究方法[M].北京:中国农业出版社, 1998:47. [10] 陈泽斌, 夏振远, 雷丽萍, 等.烟草可培养内生细菌的分离及多样性分析[J].微生物学通报, 2011, 38(9):1347-1354. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSWT201109006.htm [11] DEVEREUX R, HINES M E, STAHL D A. S cycling:characterization of natural communities of sulfate-reducing bacteria by 16S rRNA sequence comparisons[J]. Microb Ecol, 1996, 32(3):283-292. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8849423
[12] FELSENSTEIN J. Confidence limits on phylogenies:An approach using the bootstrap[J]. Evolution, 1985, 39:783-791. DOI: 10.2307/2408678
[13] 王志刚, 胡云龙, 徐伟慧, 等.鞘氨醇单胞菌菌株CL01的分离鉴定及其对连作西瓜的促生效应[J].农业生物技术学报, 2015, 23(10):1360-1367. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NYSB201510012.htm [14] 傅晓方, 韩红江, 郝勇锋, 等.玉米内生固氮菌的分离鉴定及对小麦幼苗的促生效应[J].西北农业学报, 2012, 21(1):66-71. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBNX201201017.htm [15] 台喜生, 冯佳丽, 李梅, 等.鞘氨醇单胞菌在生物降解方面的研究进展[J].湖南农业科学, 2011, (7):21-25. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNNK201107008.htm [16] 欧阳主才, 王奕恒, 李小妮, 等.鞘氨醇单胞菌株XJ对农药的降解效能[J].华南农业大学学报, 2008, 29(2):47-49. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNNB200802012.htm [17] ANDREOTE F D, ROCHA U N, ARAVJO W L. Effect of bacterial inoculation plant genotype and develop mental stage on root-associated and endophytic bacterial communities in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.)[J]. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 2010, 97(4):389-399. DOI: 10.1007/s10482-010-9421-9
[18] LEO V O, JAN D E. Effects of plant genotype and growth stage on the structure of bacterial communities associated with potato (Solanum tuberosum L.)[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2008, 64(2):183-296. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/5497803_Effects_of_plant_genotype_and_growth_stage_on_the_structure_of_bacterial_communities_associated_with_potato_Solanum_tuberosum_L
[19] ROSENBLUETH M, MARTÍNEZ R E. Bacterial endophytes and their interactions with hosts[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbel Interactions, 2006, 19(8):827-837. DOI: 10.1094/MPMI-19-0827
[20] HOLLIS J P. Bacteria in the healthy potato tissue[J]. Phytopathology, 1951, (41):197-209. http://digitalcommons.unl.edu/dissertations/AAIDP13795/
[21] AMMANN R R, LUDWIG W, SCHLEIFER K H.Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation[J]. Microbiol Rev. 1995, 59(1):143-169. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7535888
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 刘勉,肖玉辉,勾朝金,古旭,芦俊佳. 大花海棠炭疽病病原菌鉴定、生物学特性测定及防治药剂室内毒力测定. 南方农业学报. 2025(02): 508-519 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: