Rapid Detection of Monoclonal Antibody against Vibrio anguillarum by Using Conjugated Colloidal Gold
-
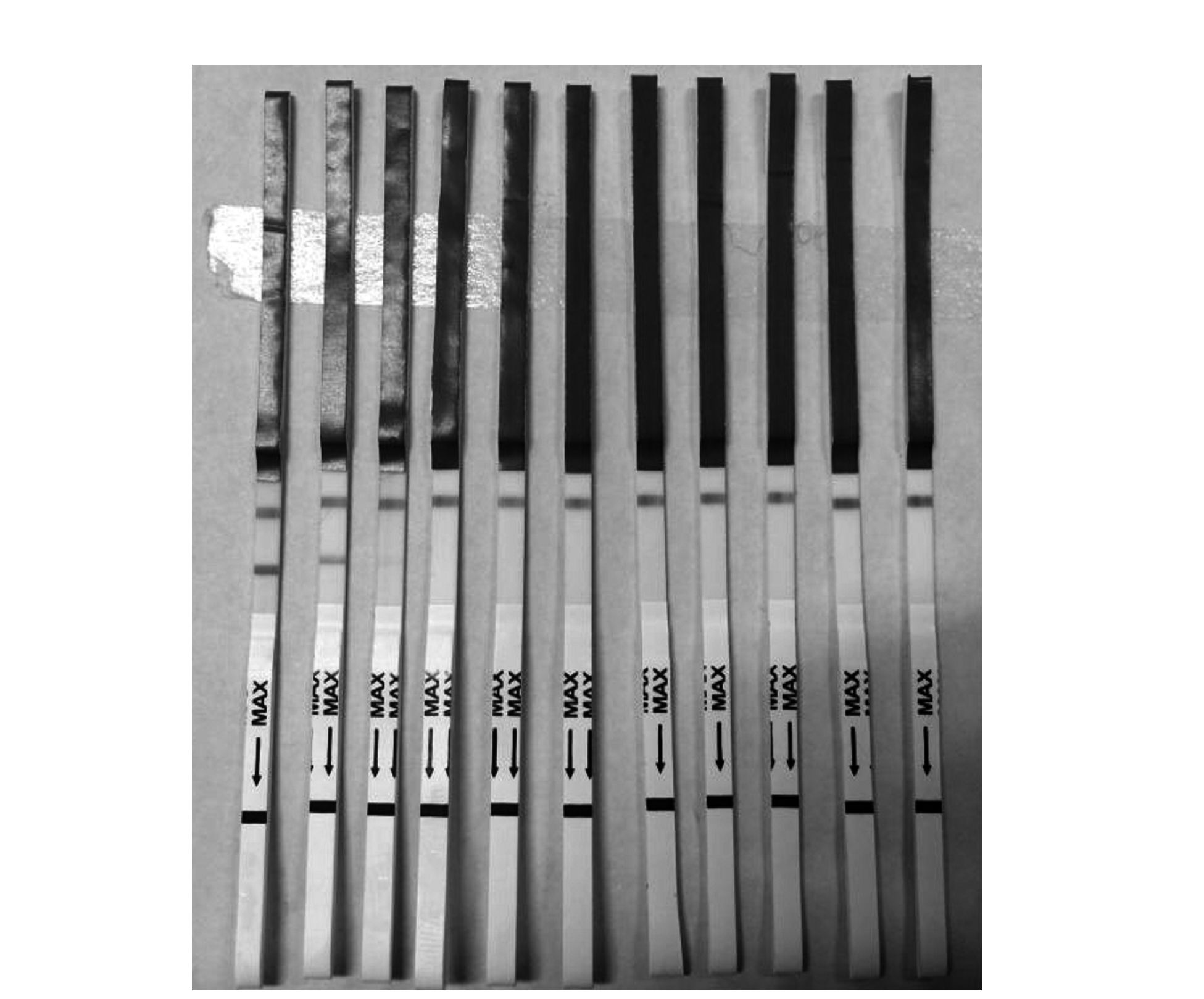
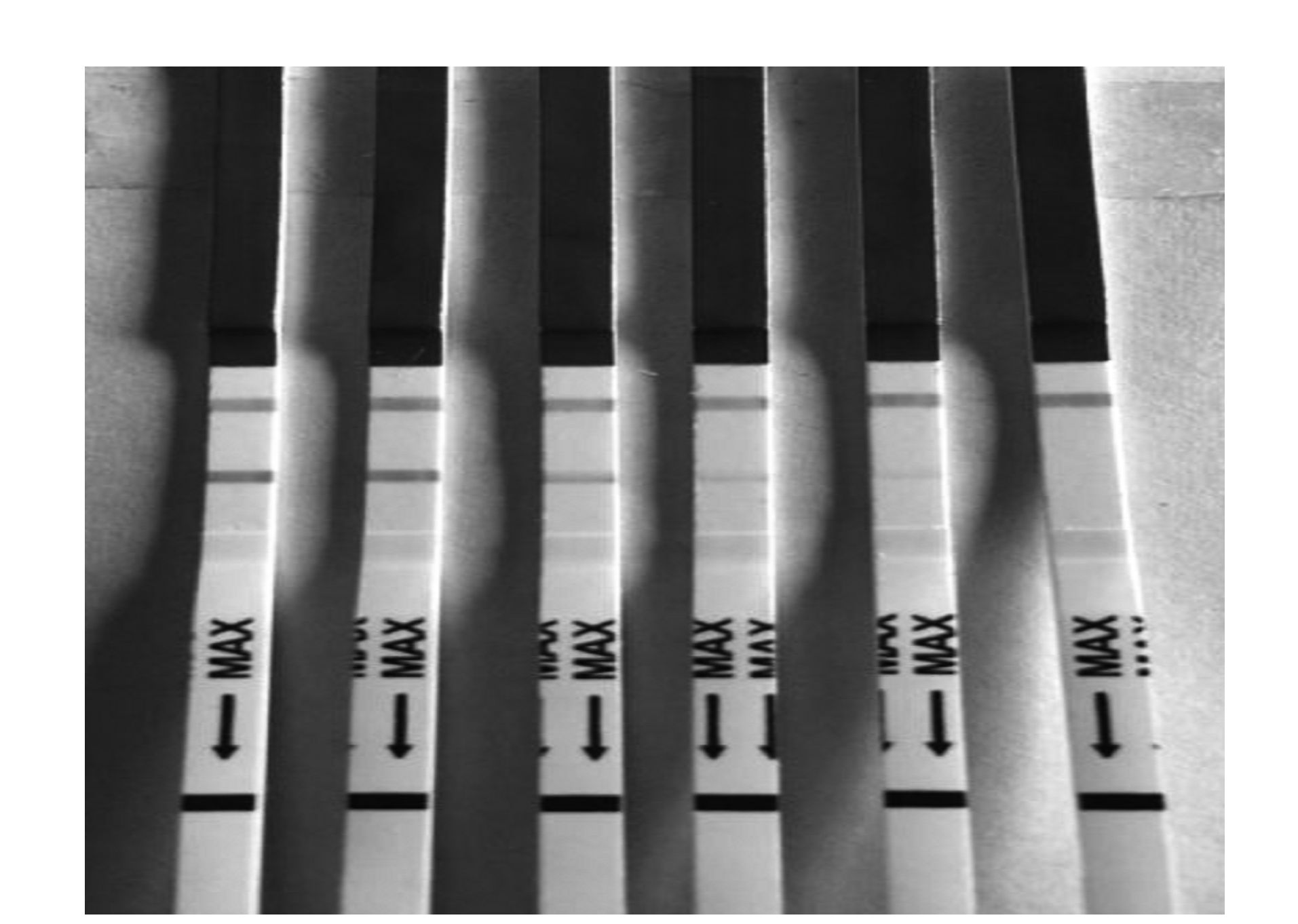
摘要: 以灭活鳗弧菌(SMW5)全菌为抗原,应用杂交瘤技术,制备了鳗弧菌单克隆抗体3株,分别命名为1H9、1C12、6F8,细胞亚类分别为IgG2a、IgM、IgG2b,其中1H9腹水效价为1:6.4×105。制备鳗弧菌(SMW5)兔多克隆抗体,效价为1:3.2×105。应用纳米胶体金颗粒标记单克隆抗体1H9并制备金标垫,抗鳗弧菌(SMW5)兔多克隆抗体与羊抗鼠抗体作为捕获抗体包被硝酸纤维素膜,分别作为检测线T和质控线C,建立鳗弧菌的胶体金免疫层析快速检测方法。经过对试纸条的特异性和灵敏度测定,结果表明:试纸条与嗜水气单胞菌、温和气单胞菌、豚鼠气单胞菌、创伤弧菌、副溶血弧菌、副溶藻弧菌、迟缓爱德华氏菌,7种水产常见病原菌没有交叉反应,与鳗弧菌特异性反应,检测灵敏度为6.3×104cfu·mL-1,检测所需时间低于10 min。所制备的鳗弧菌胶体金免疫层析检测试纸条具有快速、简便、特异性高和适应基层生产推广应用等优点。Abstract: Vibrio anguillarum, strain SMW5, were inactivated by formaldehyde to be used as the antigen for immunizing Balb/c mice. Three hybridomas strains secreting monoclonal antibodies (McAb) against V. anguillarum were obtained and named as 1H9, 1C12, and 6F8 with the isotypes of IgG2a, IgM, and IgG2b, respectively. The titers of 1H9 in ascites of Balb/c mice were 1:6.4×105. The polyclonal antibody was prepared against V. anguillarum, with a titer of 1:3.2×105. A rapid, accurate and easy gold immunochromatographic lateral flow assay methodology (GICA) was developed for detecting V. anguillarum. The monoclonal antibody, 1H9, was conjugated with colloidal gold as a signal generator on the conjugate pad. The polyclonal antibody was used as a capture antibody for the test line (T), and the goat anti-mouse IgG antibody as the capture antibody for the control line (C) on nitrocellose membrane. A GICA test strip was assembled with an absorbing pad, a conjugate pad, and a nitrocellose membrane sprayed with the capture antibody. The sensitivity of the GICA test strip towards V. anguillarum was high with a detection limit of 6.3×104cfu·mL-1. The specificity of the assay showed no cross-reaction with 7 other aquaculture pathogens, including Aeromonas hydrophila, A. cavia, A. sobria, Edwardsiella tarda, and Streptococcus agalactiae. An accurate confirmation could be completed in 10 min for the assay. It appeared that the newly developed method using the GICA test strip was adequate for V. anguillarum detection.
-
丝瓜Luffacylindrica原产东印度,主要分布于热带、亚热带的亚洲各地,有普通丝瓜Luffa cylindrica Roem和有棱丝瓜Luffa acutangula Roxb 2个栽培种,在我国南北均有栽培,是我国主要的瓜类蔬菜[1]。丝瓜营养丰富,且具有很好的医疗保健功能,随着人们对饮食营养保健的日益重视,丝瓜作为一种药食兼用的高温季节市场供应的蔬菜和保健蔬菜,其需求量不断增大,栽培面积日益扩大,蕴含着巨大的市场前景,但丝瓜果肉及汤汁出现褐变,大大降低了果蔬的贮藏加工性能,严重影响丝瓜产品的商品价值,造成巨大经济损失,因此成为丝瓜育种和采后的研究热点。
酚类物质是植物体内重要的次生代谢产物,主要存在于细胞液泡内[2-3],是苹果[4]、梨[5]、荔枝[6]、莲藕[7]等果蔬酶促褐变的底物,导致品质下降,降低园艺产品经济效益[8-9]。本试验采用超声波辅助提取和福林-酚比色法研究丝瓜总酚的提取和测定方法,为今后丝瓜酶促褐变机理研究及丝瓜新品种选育奠定理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
1.1.1 试验丝瓜品种
本试验供试丝瓜品种(系)‘黑12'由福建省农业科学院作物研究所蔬菜中心提供。用双蒸水进行清洗,晾干,快速削皮后分装于保鲜袋中,液氮速冻后置于-80℃冰箱中储存备用。
1.1.2 试验试剂
福林-酚购自美国Signa公司;甲醇(CH3OH)、丙酮(CH3COCH3)、乙醇(C2H6O)、碳酸钠(Na2CO3)、没食子酸(C7H605)等为国产分析纯(广通贸易化学试剂有限公司)。
没食子酸溶液配制:称取 0.11 g没食子酸,用双蒸水溶解定容至1 000.0 mL,得到浓度为 100 μg·mL-1的没食子酸标准溶液。
1.1.3 试验仪器
DK-8D电热恒温水槽(上海-恒科学仪器有限公司)、BILON-96超声波细胞粉碎机(成都比郎实验设备有限公司)、UV1000紫外可见分光光度计(天美科学仪器有限公司)、AR224CN电子分析天平(上海奥豪斯仪器有限公司)、CR22N冷冻高速离心机(北京顺心万昌科技发展有限公司)。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 超声辅助提取丝瓜总酚工艺优化
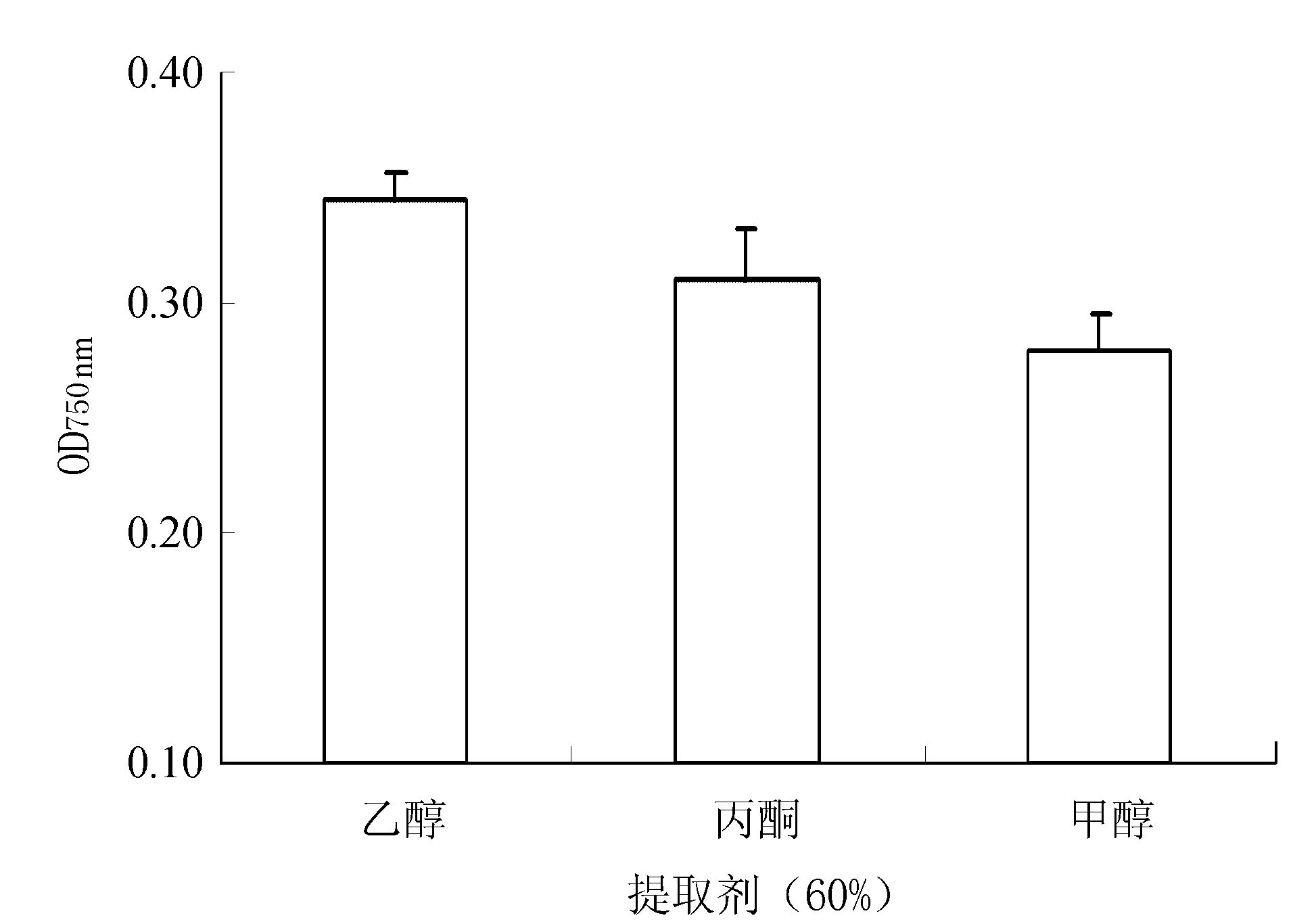
(1) 不同提取剂的选择:精确称取丝瓜果肉样品3.000 g,分别加入60%的乙醇、甲醇、丙酮,料液比1∶8,冰浴下研磨至匀浆,于40℃、300 W下超声辅助提取20 min,提取1次,提取液于4℃ 10 000 r·min-1离心10 min,收集上清液定容至25 mL待测。
(2) 不同乙醇浓度的选择:精确称取丝瓜果肉样品3.000 g,分别加入50%、60%、70%、80%、90%的乙醇,料液比1∶8,冰浴下研磨至匀浆,于40℃、300 W下超声辅助提取20 min,提取1次,提取液于4℃ 10 000 r·min-1 离心10 min,收集上清液定容至25 mL待测。
(3) 不同液料比的选择
精确称取丝瓜果肉样品3.000 g,加入80%乙醇,料液比分别为1∶4、1∶6、1∶8、1∶10、1∶12,冰浴下研磨至匀浆,于40℃、300 W下超声辅助提取20 min,提取1次,提取液于4℃ 10 000 r·min-1 离心10 min,收集上清液定容至25 mL待测。
(4) 不同超声时间的选择
精确称取丝瓜果肉样品3.000 g,加入80%乙醇,料液比1∶10,冰浴下研磨至匀浆,超声时间分别为10、20、30、40、50、60 min,40℃、300 W下超声辅助提取,提取1次,提取液于4℃ 10 000 r·min-1 离心10 min,收集上清液定容至25 mL待测。
(5) 不同超声温度的选择:精确称取丝瓜果肉样品3.000 g,加入80%乙醇,料液比1∶10,冰浴下研磨至匀浆,超声温度分别为25、40、60℃,300 W下超声辅助提取30 min,提取1次,提取液于4℃ 10 000 r·min-1离心10 min,收集上清液定容至25 mL待测。
1.2.2 福林-酚比色法测定丝瓜总酚含量的优化
(1) 测量波长的选择:移取没食子酸溶液(100 μg·mL-1)1 mL于25 mL试管中,加入5 mL的蒸馏水,再加入1 mL的福林-酚比色剂,混匀后静置4~5 min,再加入0.5 mol·L-1的Na2CO3溶液2 mL,用双蒸水定容至25 mL,于室温下避光反应1 h后,在500~900 nm的波长范围内扫描。
(2) 试剂体积的选择:①Na2CO3体积的确定:移取没食子酸溶液7份各1 mL,加5 mL蒸馏水,加入1 mL的福林-酚比色剂,混匀静置4~5 min,再加入0.5 mol·L-1的Na2CO3溶液各1.0、1.5、2.0、2.5、3.0、3.5、4.0 mL,用双蒸水定容至25 mL,在室温下避光反应1 h后,待反应液显色后于750 nm波长处测定OD值,确定最大OD值所对应的Na2CO3体积; ②福林-酚体积的确定:取没食子酸溶液5份各1 mL,加5 mL蒸馏水,再分别加入0.25、0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0 mL福林-酚试剂,混匀后静置4~5 min,再加入0.5 mol·L-1的Na2CO3溶液3 mL,加蒸馏水定容至25 mL,于室温下避光反应1 h后,待反应液显色后于750 nm波长处测定OD值,以确定福林-酚的体积。
(3) 测定时间的选择:取没食子酸溶液5份各1 mL,加5 mL蒸馏水,加入1.5 mL福林-酚试剂,混匀后静置4~5 min,再加入0.5 mol·L-1 Na2CO3溶液的3 mL,用双蒸馏水定容至25 mL,在室温下分别避光反应10、20、30、40、50、60、90、120 min后,于750 nm波长处测定OD值,确定最佳测定时间。
(4) 测定温度的选择:取没食子酸溶液5份各1 mL,加5 mL蒸馏水,加入1.5 mL福林-酚试剂,混匀后静置4~5 min,再加入0.5 mol·L-1 Na2CO3溶液的3 mL,用双蒸馏水定容至25 mL,分别在10、20、30、40、50、60℃下避光反应1 h后,显色后于波长750 nm处测定吸光度值,确定适宜的反应温度。
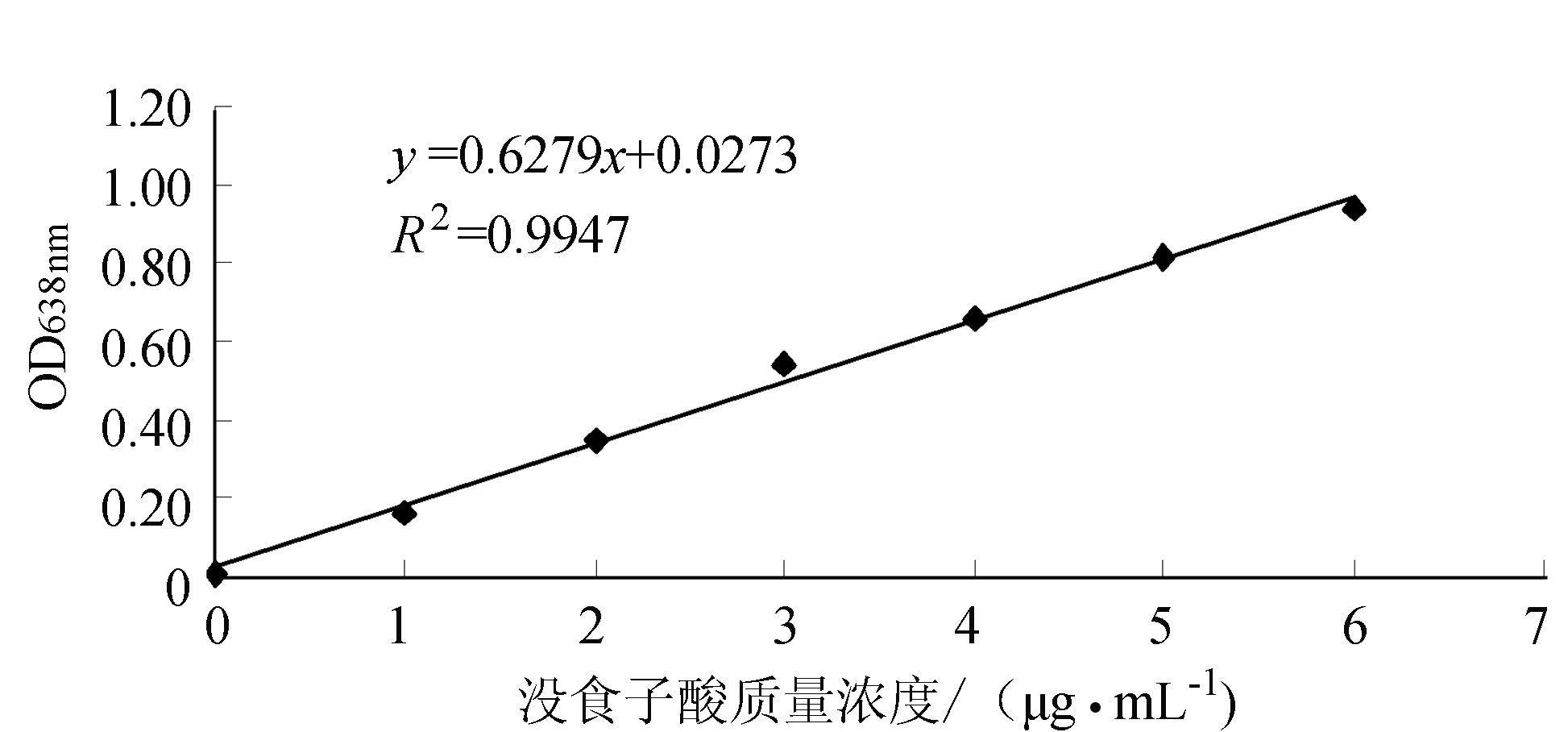
(5) 标准曲线的绘制:移取0、0.25、0.5、0.75、1、1.25、1.5 mL的没食子酸标准液于25 mL试管中,加入5 mL的蒸馏水,再加入1.5 mL的福林-酚比色剂,混匀后静置4~5 min,再加入0.5 mol·L-1的Na2CO3溶液3 mL,加蒸馏水定容至25 mL,在室温下避光反应1 h后。显色后在750 nm波长处测定OD值,以吸光值为纵坐标,标准溶液浓度为横坐标,绘制标准曲线。
以上试验方法均重复3次。
1.3 数据处理与分析
运用Excel 2003进行数据整理和作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 超声辅助提取丝瓜总酚工艺优化
2.1.1 不同提取剂对丝瓜总酚提取效果的影响
由图 1可知,提取剂不同,总酚的提取效果也不同。其中,乙醇的吸光值最高,丙酮次之,甲醇最小。提取液对总酚物质的显色反应较大,其吸光值也越大,说明丝瓜总酚提取效果越好;同时,考虑到甲醇和丙醇的毒性及价格均高于乙醇,因此,选择乙醇作为丝瓜果肉总酚的提取剂。
2.1.2 不同提取剂浓度对丝瓜总酚提取效果的影响
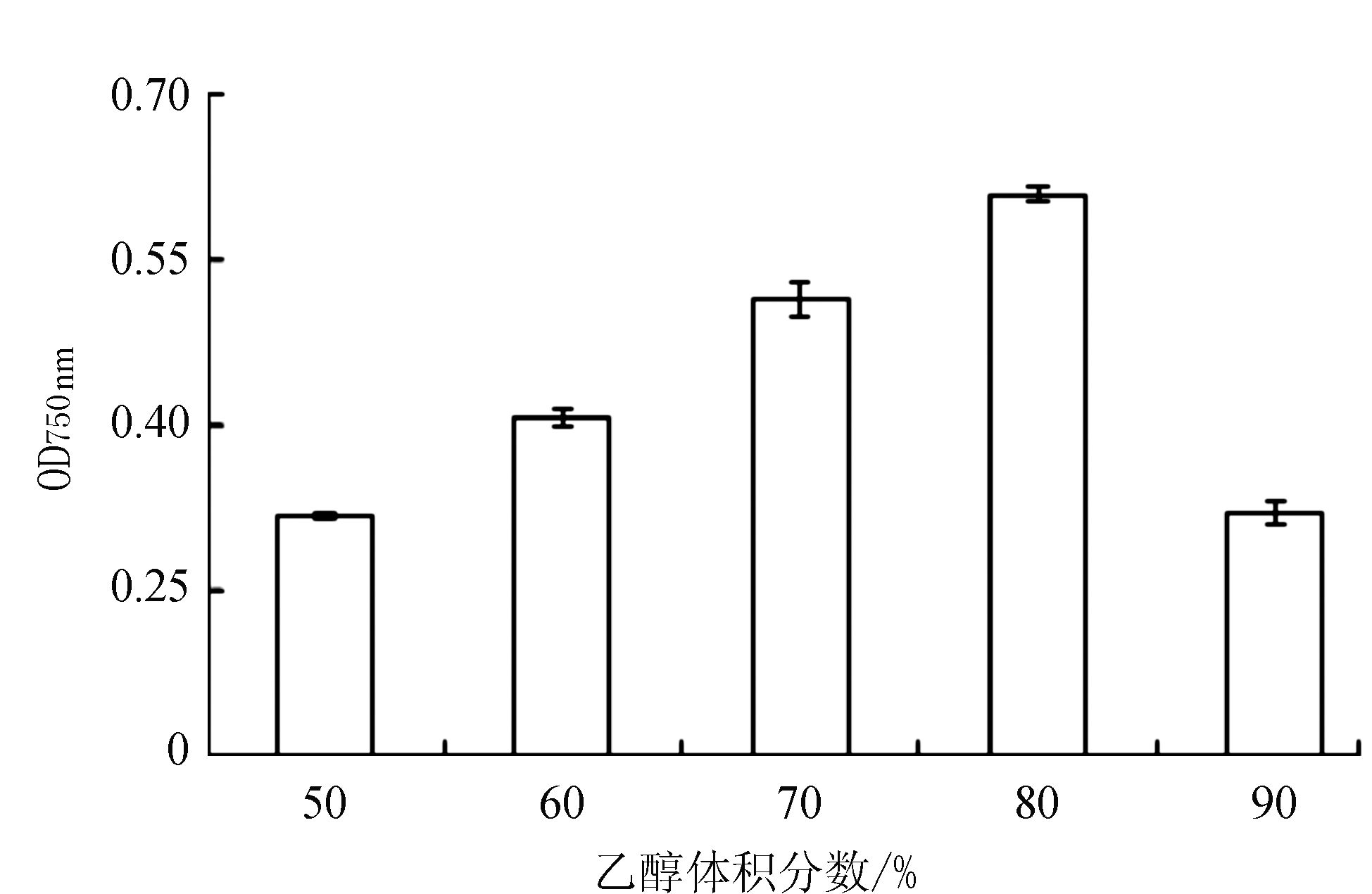
由图 2可知,随着乙醇浓度的增大,丝瓜提取液的吸光度在50%~80%的浓度范围内呈上升趋势,在80%时其吸光值最高;而后随着乙醇浓度升高,其吸光值呈现下降趋势,下降幅度明显。提取剂浓度为80%时吸光值最高,说明丝瓜总酚的提取效果较好,因此,选择80%的乙醇为丝瓜果肉总酚提取剂浓度。
2.1.3 不同液料比对丝瓜总酚提取效果的影响
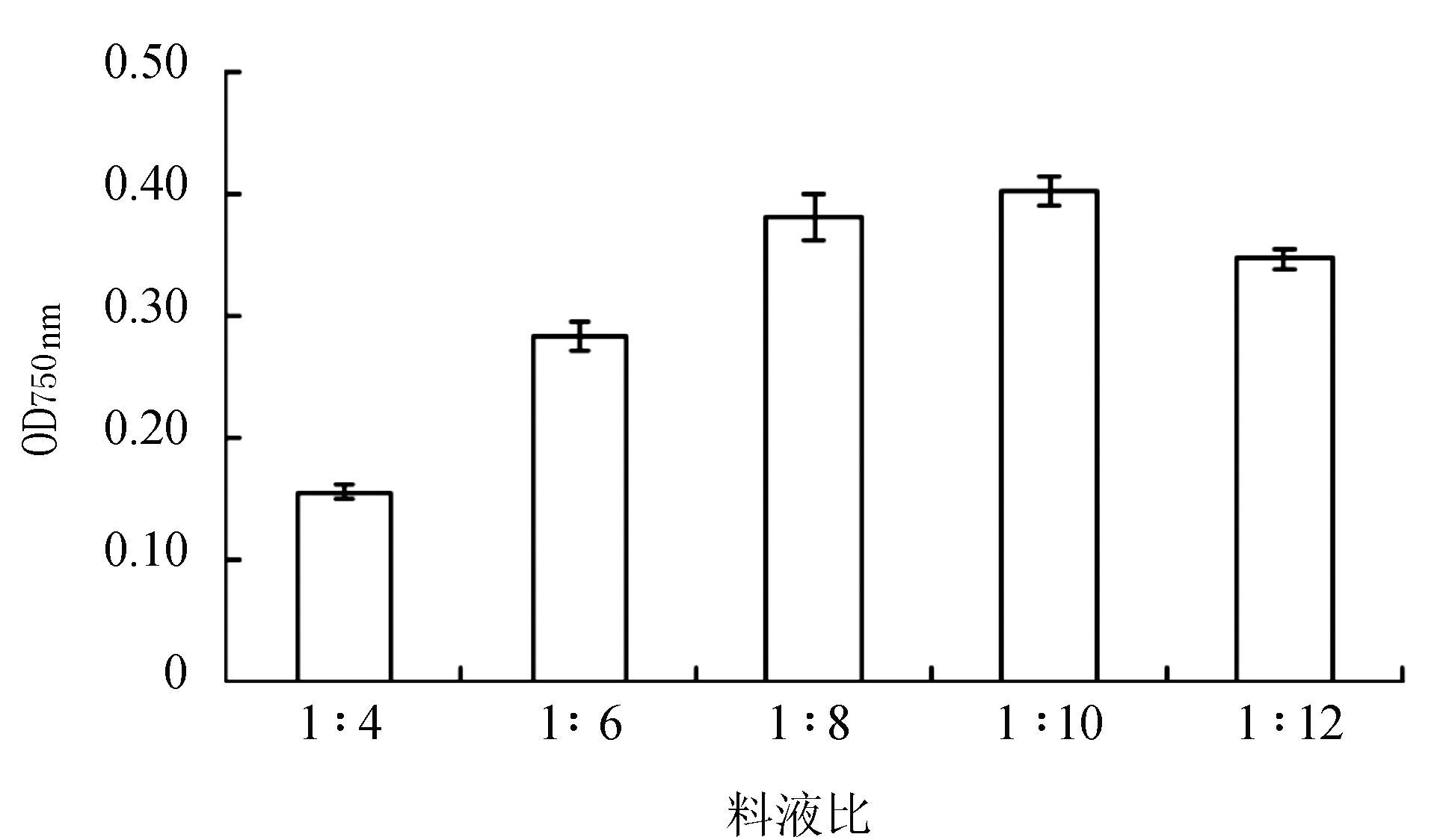
由图 3 可知,总酚提取液随着液料比的变化而变化。当料液比为1∶10时,丝瓜的总酚提取液基本上达到饱和,而后随着料液比的升高而下降。当吸光值越高,说明总酚提取越完全。当液料比为1∶12总酚提取量呈现下降趋势,表明液料比为1∶10时,丝瓜总酚提取效果较为充分。
2.1.4 超声时间对丝瓜总酚提取效果的影响
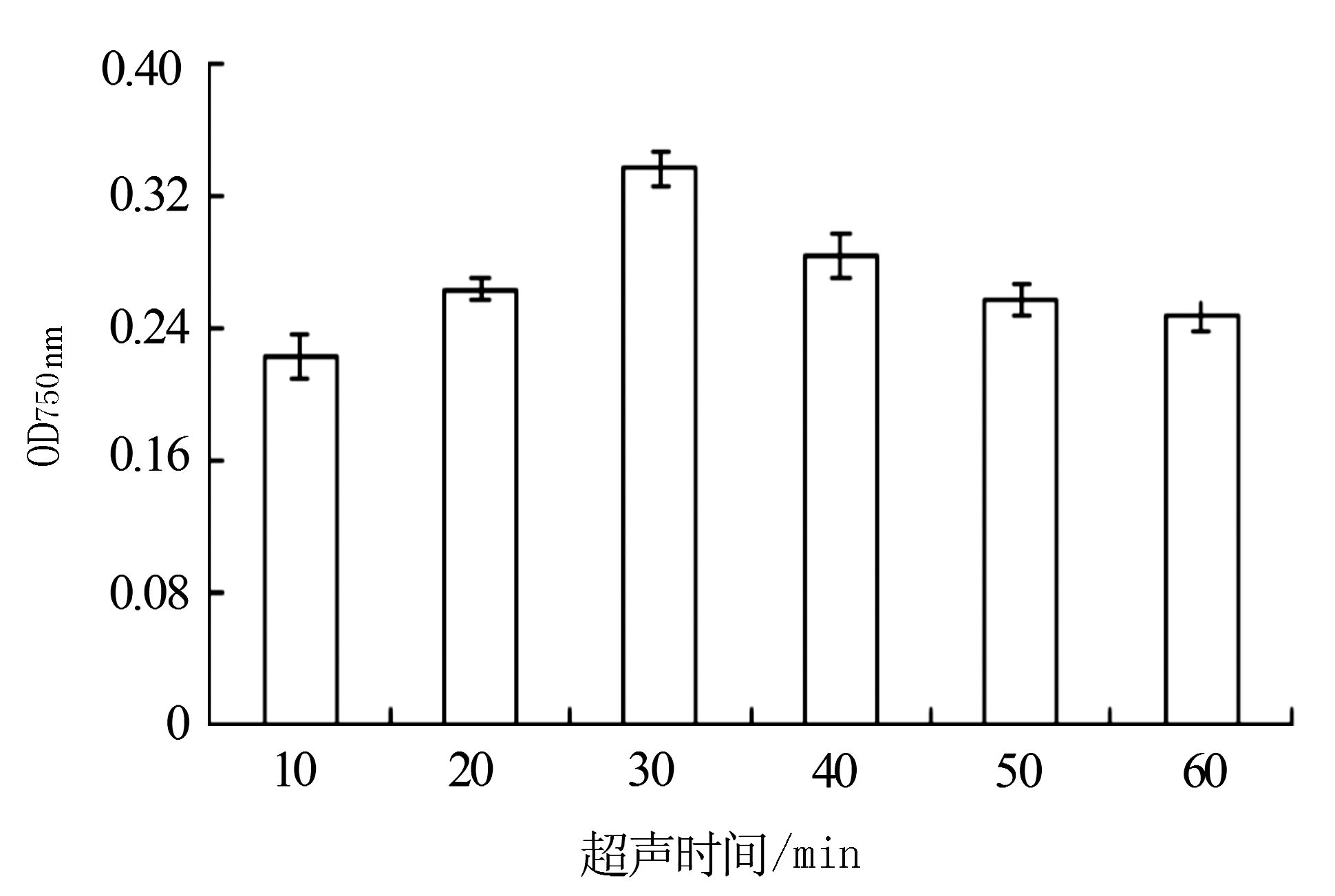
由图 4所示,随着超声波时间的增加,总酚的吸光值呈现先上升后下降的趋势,在30 min中达到峰值,之后逐渐呈下降趋势。表明超声时间在30 min时,丝瓜总酚提取效果较好。
2.1.5 超声温度对丝瓜总酚提取效果的影响
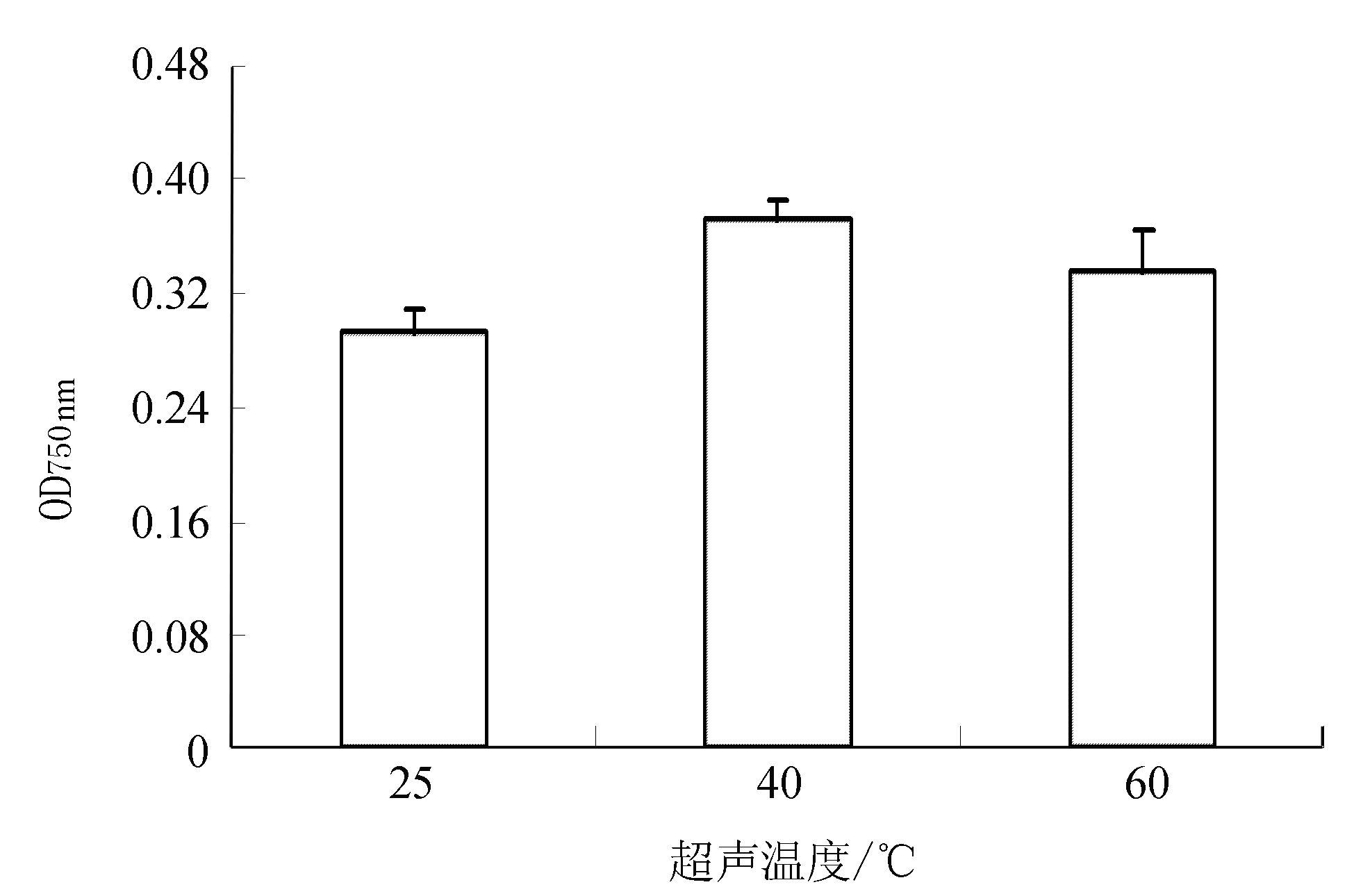
由图 5所示,随着超声波温度的增加,总酚的吸光值升高,其吸光值在40℃时达到峰值,在60℃时吸光值下降。表明超声温度在40℃时,丝瓜总酚提取效果较好。
2.2 福林-酚比色法测定丝瓜总酚含量的优化
2.2.1 最佳波长的确定
将没食子酸标准溶液置于波长500~900 nm范围内进行扫描,没食子酸标准溶液在波长750 nm达到最大值。吸光值越大,没食子酸溶液反应越完全,因此,选用750 nm作为本次丝瓜总酚含量测定的最适吸收波长。
2.2.2 最佳试剂体积的确定
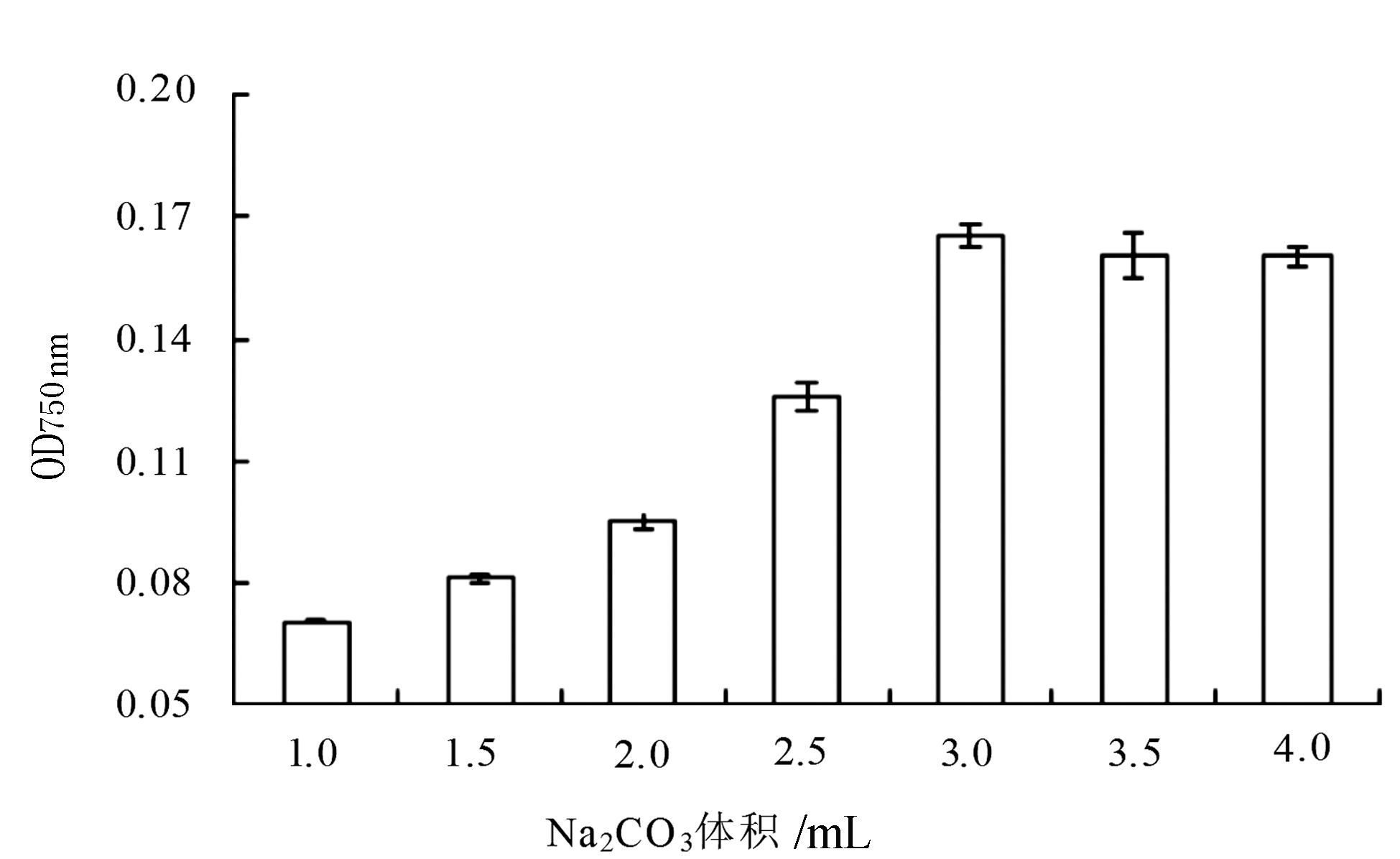
由图 6可知,总酚物质的显色效果随着Na2CO3体积的增加越来越明显,Na2CO3体积为1~3 mL时,吸光度呈现上升趋势,其对总酚物质显色效果越来越好;当Na2CO3体积达到3 mL时,吸光度达到最大值,对总酚物质的显色效果最好;但 Na2CO3体积超过3 mL时,其OD值不再明显增加,基本保持稳定;说明Na2CO3体积不足会导致总酚物质显色不完全。当Na2CO3的最佳体积为3 mL时吸光度值最大,反应也最明显,因此,表明Na2CO3的最佳体积为3 mL。
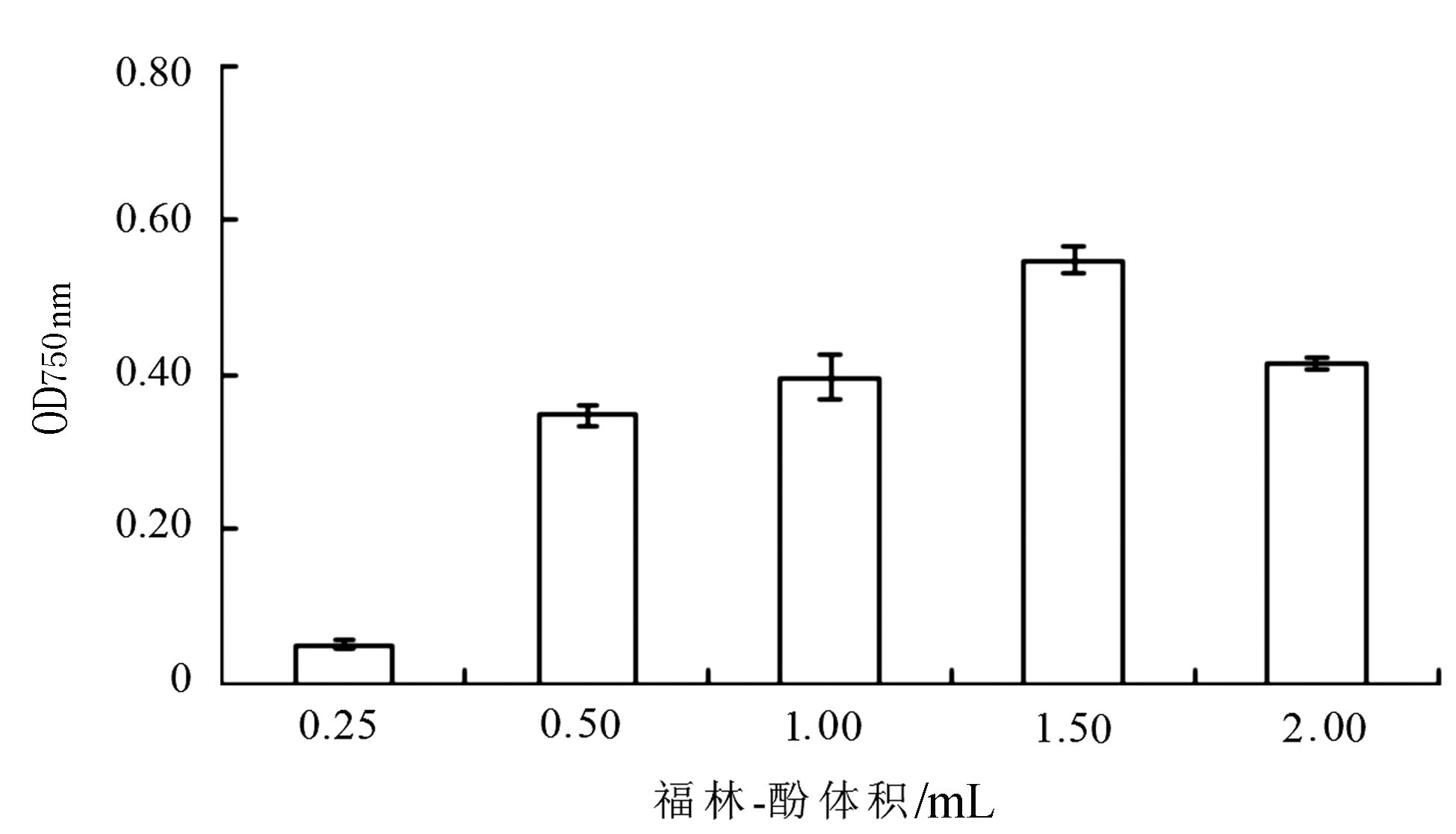
由图 7所示,随着福林-酚体积的增加,吸光值也相应增加,总酚物质的显色效果也越好。当福林-酚体积为1.5 mL时,吸光值达最大,反应最完全。当福林-酚体积过低(0.25 mL)或过高(2 mL)时,对显色反应均产生抑制作用,降低其吸光值。因此,确定最佳福林-酚体积为1.5 mL。
2.2.3 最佳反应时间的确定
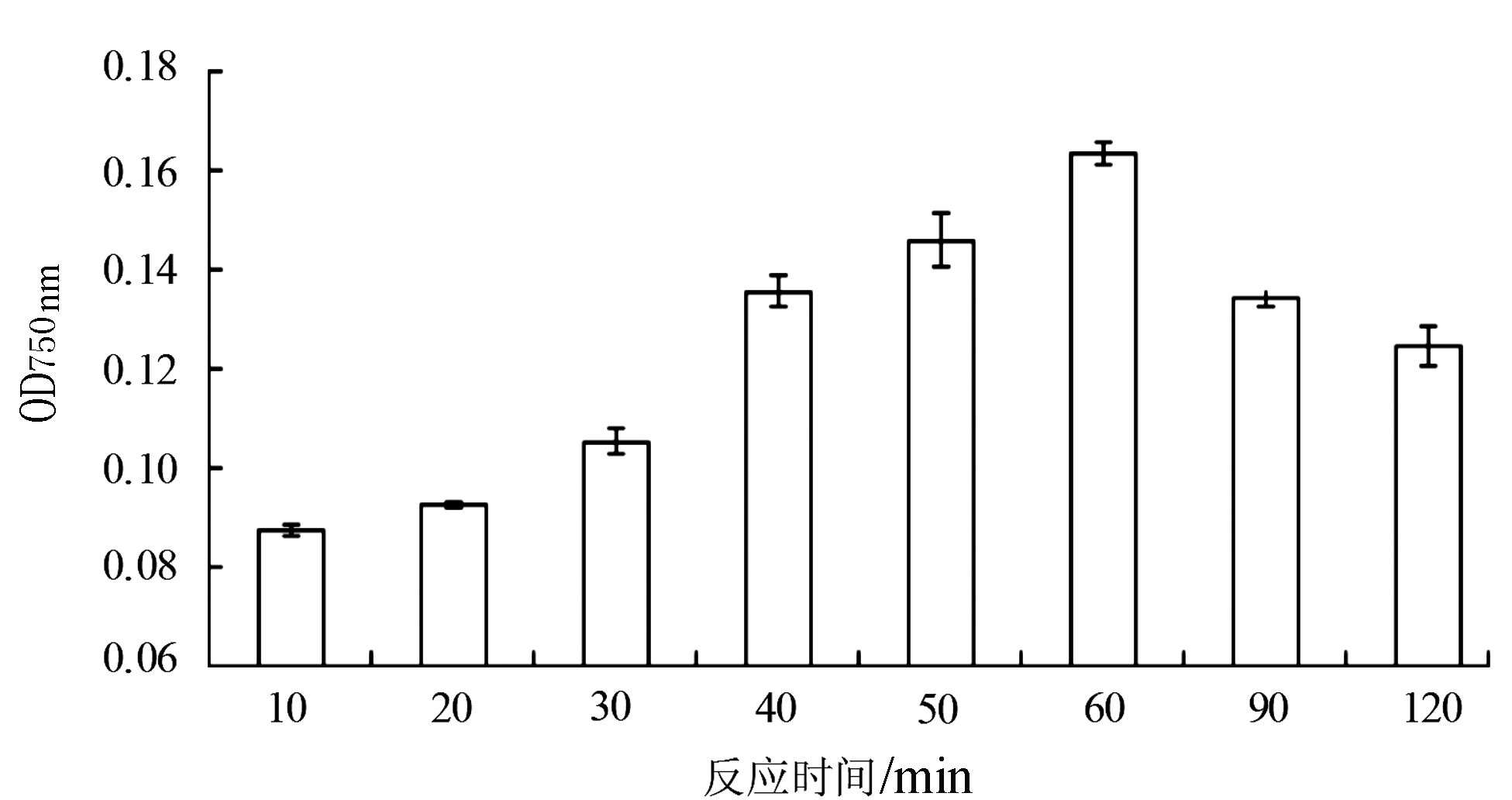
由图 8可知,随着反应时间的增加,总酚物质的吸光值也相应增加,在前10 min吸光度值最小,反应效果不显著;在60 min时吸光值达到最大,反应最完全,显色反应明显;在60 min之后吸光值呈现下降趋势,变化幅度较小,显色反应不明显。因此,最佳反应时间为60 min。
2.2.4 最佳反应温度的确定
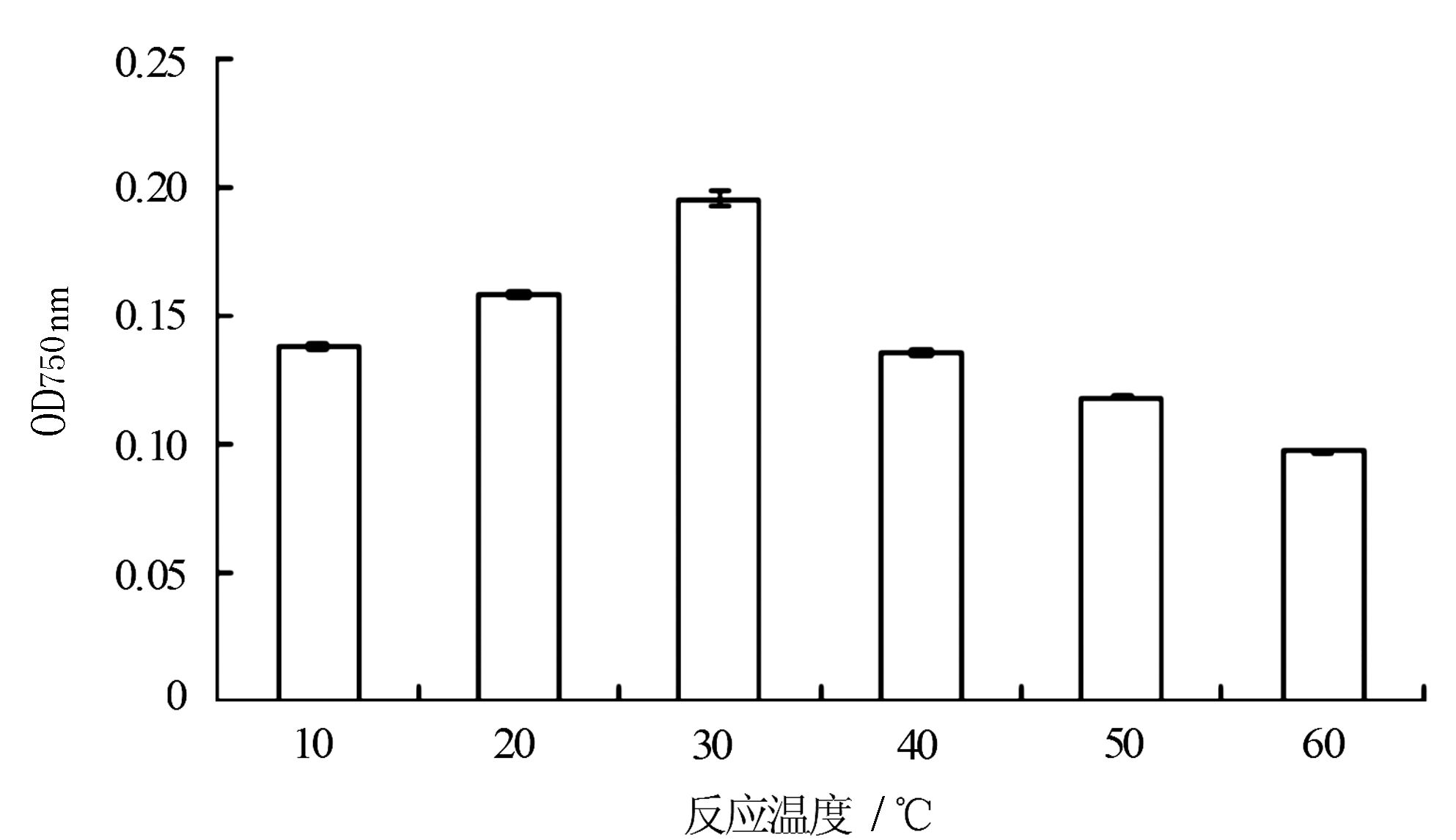
由图 9可知,总酚的显色反应受温度的影响。随着反应温度(10~60℃)的增加,其反应产物的吸光值呈增长趋势,其中在30℃时吸光值达到最大值,之后随着反应时间的延长,其吸光值呈下降的趋势。说明当超过一定温度时,总酚的稳定性较差,反应产物在高温下易被分解。因此,选择30℃作为本次丝瓜总酚测定的最佳温度。
2.2.5 标准曲线的建立
由图 10所示,将测定结果进行线性回归,结果得出吸光度与没食子酸标准溶液之间的关系方程式为Y=0.6279X+0.0273,R2=0.994 7,相关系数为0.994 7,说明在1~6 μg·mL-1有较好的线性关系。
3. 讨论与结论
本试验以‘黑12'丝瓜品种(系)为试材,利用超声波提取方法[10-11],对丝瓜总酚提取的提取剂、乙醇浓度、液料比、超声时间、超声温度等影响因子进行优化,利用福林酚比色法[12-13],对丝瓜总酚测定的测量波长、试剂体积、测定时间、 测定温度等影响因子进行优化,获得了总酚提取和测定的反应体系:(1)提取优化结果:乙醇浓度为80%,液料比1∶10,超声波温度40℃,超声时间30 min;(2)测定优化结果:测定波长750 nm,反应时间60 min,反应温度30℃,0.5 mol·L-1 Na2CO3体积3 mL,0.5 mol·L-1福林-酚体积1.5 mL。总酚含量与吸光度呈良好的线性关系: Y=0.6279 X+ 0.0273(R2= 0.994 7)。本研究建立的丝瓜总酚提取和测定方法具有稳定性好、精密度高、操作简便、省时、不受蛋白质的干扰等优点,为丝瓜中总酚含量的研究提供技术支持,为后期抗褐变丝瓜品种选育研究提供了理论依据。
超声波辅助提取总酚效果好,具有回收率高、损耗小等优势,已在果蔬总酚中广泛应用[14-20]。本试验以‘黑12'丝瓜果肉鲜果为试材,利用超声波辅助提取丝瓜总酚提取液,提取效果较好。由于总酚含有某些羟基类物质,可与蛋白质和多糖等物质结合,形成稳定的化合物,因此选择丙酮、甲醇、乙醇作为丝瓜总酚提取剂[21]。通过上述有机溶剂提取总酚效果来看,乙醇效果最佳,所以选用乙醇作为总酚提取剂。何志勇[22]通过对橄榄总酚的提取比较,因丙酮具有剧毒,故选择乙醇;同时乙醇提取工艺简单,成本低且提取率高,故选择乙醇作为提取溶剂。超声时间与温度是提取果蔬总酚过程中重要的影响因素,本试验得出丝瓜总酚最佳超声波时间与温度分别为30 min和40℃。若超声波时间过短或者温度过低,丝瓜总酚提取效果也低,时间过长或者温度过高,则会破坏丝瓜总酚物质。因此,超声提取丝瓜总酚温度和时间不宜过长。
目前,总酚含量的测定方法有多种,如纸层析、薄层层析、气液色谱、高效液相色谱、福林-酚法等多种方法。其中纸层析、薄层层析在分离效果、速度和准确定量方面存在缺陷; 气液色谱用于植物酚类物质的分离测定速度快、灵敏度高,但该法需要衍生化处理,前处理比较麻烦; 而高效液相色谱法比较昂贵,不适于大量的定量分析[23]。福林-酚比色法反应原理为酚类化合物在碱性条件下可将钨钼酸还原,生成蓝色的化合物,颜色的深浅与酚含量呈正相关,结果精确稳定,且具有操作方便、所用试剂价格低廉、适用于批量检测等优点,在植物总酚含量测定中应用广泛。本试验利用福林-酚法进行丝瓜总酚含量的测定,探索出基层实验室简单、快速、准确测定丝瓜总酚的有效方法。在不同的研究文献[24-25]中,比色条件选择差异较大,且不同的提取和测定条件下其测定结果也有所不同;测定最佳波长在650~760 nm,反应温度为20~60℃,反应时间在30~120 min等比色条件范围。本试验的结果与相关果蔬的总酚研究结果相同或者相近,但其反应体系的变化均在总酚反应的合适范围内。如黄树苹等[26]通过福林-酚法测定丝瓜总酚的波长为770 nm,而本试验的最佳波长为750 nm。严娟等[27]利用福林-酚法对桃总酚进行测定,测定波长为765 nm。张立新等[28]研究认为,测定总酚的反应体系存在一定的差异,其原因可能与品种和产地有关,因为同一果蔬,若品种不同,或种植在不同地区,其化学成分也会存在较大的差异。
-
表 1 单克隆抗体上清液效价及亚类鉴定
Table 1 Titers and subclasses of McAb supernatant
单抗株 效价 IgG亚类 1H9 1∶6400 IgG2a 1C12 1∶3200 IgM 6F8 1∶800 IgG2b 表 2 单克隆抗体特异性试验
Table 2 Specificity test on McAbs
菌株 交叉反应结果 1H9 1C12 6F8 鳗弧菌(SMW5) + + + 鳗弧菌(参考株) + + + 溶藻弧菌(Js60517NA1) - + - 创伤弧菌(FJ04-L1) - + - 副溶血弧菌(ATCC17802) - - + 哈维氏弧菌(03152) - - + 河流弧菌(参考株) - - - 嗜水气单胞菌(ML316) - - - 嗜水气单胞菌(JS01-1) - + - 温和气单胞菌(Fp60325NA) - - - 非0-1群霍乱弧菌(96-2) - - + 类志贺邻单胞(LCCi190625) - - - 无乳链球菌(070717LL) - - - 注:“-”表示阴性结果,“+”表示阳性结果。 表 3 单克隆抗体灵敏度
Table 3 Sensitivity test on McAbs
细胞株 McAb 灵敏度 /
(cfu·mL-1)1H9 4×103 1C12 2×103 6F8 8×103 表 4 鳗弧菌胶体金试纸条交叉反应测试结果
Table 4 Cross reactivity of colloidal gold test strip on 10 bacteria strains
序号 菌株 结果判定 1 鳗弧菌(SMW5) + 2 鳗弧菌(标准株) + 3 鳗弧菌(1H00003) ± 4 副溶血弧菌(ATCC17802) - 5 溶藻弧菌(Js60517NA1) - 6 创伤弧菌(FJ04-L1) - 7 嗜水气单胞菌(ML316) - 8 温和气单胞菌(Fp60325NA) - 9 豚鼠气单胞菌(AB40511NA1) - 10 迟缓爱德华氏菌(AL60306NA1) - 11 阴性对照(BSA) - 注:“-”表示阴性结果;“+”表示阳性结果;“±”表示弱阳性结果。 表 5 试纸条检测鳗弧菌(SMW5)灵敏度试验结果
Table 5 Sensitivity of gold test strip on V. anguillarum (SMW5)
序号 菌体浓度/
(cfu·mL-1)检测结果 1 6.3×103 - 2 6.3×104 ± 3 6.3×105 + 4 6.3×106 + 5 6.3×107 + 6 6.3×108 + 注:“-”表示阴性结果;“+”表示阳性结果;“±”表示弱阳性结果。 -
[1] BIOSEA E G, AMARO C, ESTEVE C,et al.First record of Vibrio vulnificus biotype 2 from diseased European eel,Anguilla anguilla[J].Fish Dis,1991,14:103-109. DOI: 10.1111/jfd.1991.14.issue-1
[2] 吴后波,潘金培.弧菌属细菌及其所致海水养殖动物疾病[J].中国水产科学,2001,(3):90. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSCK200101020.htm [3] 刘杰.欧鳗弧菌病的诊断与防治技术[J].渔业致富指南,2001,(13):42. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYZF200113043.htm [4] 莫照兰,茅云翔,陈师勇,等.一株牙鲆皮肤溃烂症病原菌的鉴定[J].微生物学报,2002,42(3):263-269. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSXB200203000.htm [5] 郭杨柳,吴楠,房海,等.大菱鲆病原鳗弧菌的检验与分析[J].生物技术通报,2015,31(11):222-227. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWJT201511029.htm [6] 肖慧,唐学玺,陈吉祥,等.鳗弧菌W-1对花鲈鱼苗致病性的初步研究[J].海洋科学,2008,32(3)36-39. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYKX200803007.htm [7] 肖慧,李军,徐怀恕,等.鲈鱼苗烂鳃、烂尾病病原的研究[J].青岛海洋大学学报,1999,(1):89. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QDHY901.013.htm [8] 李清禄,陈强.海水网箱养殖大黄鱼细菌性病原鉴定与感染治疗研究[J].应用与环境生物学报,2001,7(5):489. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYHS200105017.htm [9] 向赟,王刚,陈兆明,等.不同温度条件下鳗弧菌和白斑综合症病毒对凡纳滨对虾的致病性[J].热带生物学报,2015,6(1):11-17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNNX201501003.htm [10] EGIDIUS E.Vibriosis:pathogenicity and pathology[J].Aquaculture,1987,67:15. DOI: 10.1016/0044-8486(87)90004-4
[11] 夏永娟.抗鳗弧菌独特型单克隆抗体的研制[D].西安:第四军医大学,2001. [12] 余俊红,姚婓,王宝坤,等.应用间接ELISA技术快速检测花鲈病原菌--鳗弧菌[J].高技术通讯,2001,11(7):23-27. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJSX200107004.htm [13] 余俊红,姚斐,俞勇.应用间接荧光抗体技术快速检测花鲈病原菌--鳗弧菌[J].海洋水产研究,2002,23(2):38-44. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYSC200202006.htm [14] 邹玉霞,莫照兰,高光,等. 间接ELISA技术在病原性鳗弧菌SMP1快速检测中的应用[J].海洋科学,2007,31(6):75-78. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYKX200706014.htm [15] 边慧慧,蒋继志,黄倢,等.双抗原夹ELISA检测抗鳗弧菌抗体效价的研究[J].科技信息,2009,(7):41-42. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJXX200907338.htm [16] 吴斌.豚鼠气单胞菌快速检测间接ELISA法的建立[J].福建水产,2006,(4):48-51. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJSC200604013.htm [17] 徐志凯.实用单克隆抗体技术[M].西安:陕西科学技术出版社,l992:27-102. [18] 辛志明.迟缓爱德华氏菌胶体金快速检测试纸的研制[J].中国海洋大学学报,2011,41(10):40-44. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QDHY201110008.htm [19] 吴圆圆.鳗弧菌快速检测试纸条的研制[D].上海:华东理工大学,2014. [20] 黄艺丹,汪开毓,郑建,等.鱼类致病性豚鼠气单胞菌单克隆抗体一胶体金检测方法的建立[J].水生生物学报,2010,34(3):509-516. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10626-2010244619.htm [21] 辛志明,樊海平,吴斌,等. 嗜水气单胞菌胶体金快速检测试纸条的研制[J].中国兽医科学,2012,42(7):708-712. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSY201207011.htm [22] 辛志明,樊海平,吴斌,等.豚鼠气单胞菌胶体金免疫层析试纸条的研制[J].水产学报,2009,33(4):679-684. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCKX200904020.htm [23] 王蓓,梁军,简纪常,等.溶藻弧菌免疫胶体金快速检测试纸条的制备[J].广东海洋大学学报,2013,33(4):49-55. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHDX201304010.htm [24] 刘亦娟,徐晓丽,孙金生,等.哈维氏弧菌胶体金免疫层析试纸条的制备[J].水产学杂志,2015,28(2):6-11. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCXZ201502002.htm [25] 秦璞,胡晓,张在阳,等.鱼类致病性迟钝爱德华氏菌胶体金快速检测试纸的研制[J].华东理工大学学报:自然科学版,2011,37(3):330-334. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLDX201103015.htm [26] LYEDY D M,PHELPS C J AND WILKINS T D.Monoclonal and specific polyclonal antibodies for immunoassay of Clostridium dificile ToxinA[J].Journal of clinical microbiology,1985,21(1):12-14. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=394574602d051c86d09daf70dc51c08b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 王雅慧,刘晓宏,雍明丽,熊爱生,苏小俊. 基于代谢组学分析丝瓜果肉褐变过程酚酸类物质变化. 中国农业科学. 2021(22): 4869-4879 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 高志远,胡亚亚,韩美坤,张静,于翠红,赵俊梅,刘兰服,焦伟静,马志民. 甘薯块根多酚高效测定技术优化与应用. 中国粮油学报. 2021(11): 49-56 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 蔡章棣,薛珠政. 设施大棚丝瓜春早熟“摘心换头”高效栽培技术. 东南园艺. 2021(05): 67-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 康玉妹,薛珠政,刘建汀. 18个丝瓜新组合主要农艺性状聚类分析及褐变度鉴定. 福建农业科技. 2020(05): 20-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张强,尹丽,周旖璇,于琛琛,张纯刚,程岚. 丝瓜多酚组成、提取分离、含量测定及生物活性的研究进展. 中国药房. 2020(23): 2928-2932 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 朱海生,康娟,刘建汀,陈敏氡,李永平,王彬,林碧英,温庆放. 丝瓜多酚氧化酶PPO基因家族的克隆与表达分析. 核农学报. 2018(08): 1502-1512 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 朱海生,刘建汀,王彬,陈敏氡,张前荣,叶新如,林珲,李永平,温庆放. 丝瓜过氧化物酶基因的克隆及其在果实褐变中的表达分析. 农业生物技术学报. 2018(01): 43-52 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 朱海生,温文旭,刘建汀,叶新如,陈敏氡,王彬,张前荣,李永平,温庆放. 丝瓜苯丙氨酸解氨酶基因PAL克隆及表达分析. 植物遗传资源学报. 2018(02): 305-313 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 刘建汀,朱海生,温庆放,王彬,张前荣,陈敏氡,林珲,薛珠政. 丝瓜WRKY转录因子基因的分离与褐变分析. 农业生物技术学报. 2017(12): 1950-1960 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 刘建汀,朱海生,庄尹宏,温庆放,叶新如,王彬,陈敏氡,张前荣,薛珠政. 普通丝瓜褐变度概率分级与总酚的回归分析. 中国农学通报. 2017(24): 124-128 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 朱海生,刘建汀,陈敏氡,李永平,王彬,张前荣,叶新如,林珲,温庆放. 丝瓜铜锌超氧化物歧化酶Cu/Zn-SOD基因家族的克隆与表达分析. 中国农业科学. 2017(17): 3386-3399 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: