Genetic Diversity of 50 Prunus persica Germplasms Aanlyzed by SSR Markers
-
摘要: 利用16对SSR引物对不同产地的50份桃种质资源遗传多样性进行分析,结果表明:各位点的多态信息含量(polymorphism information content,PIC)在0.04~0.37,平均值为0.24。依据非加权组平均法聚类分析,50份桃种质资源可主要划分为3个类群(中晚熟种质、中早熟种质、超短低温早熟种质)。在湿热地区综合性状优异的短低温种质可单独聚类。观赏桃与鲜食普通桃亲缘关系最远。遗传分析表明:部分福建地方种质属于南方水蜜桃,从分子水平支持了先前认为这些种质源于江南(江浙沪)水蜜桃品种群的看法。Abstract: Genetic diversity of 50 Prunus persica germplasms was analyzed using 16 pairs of SSR primers. The results showed that the polymorphism information contents of the individual sites ranged from 0.04 to 0.37 with an average of 0.24. The 50 peach germplasms could be classified into 3 groups according to thecluster analysis of the unweighted pair group method witharithmetic mean. They were medium late-maturing, medium early-maturing and low-temp early-maturing peaches. In addition, the low-temp germplasms with excellent over-all properties in the hot and humid southern regions could be grouped by themselves. The ornamental varieties were genetically far remote from the common peaches. A genetic analysis indicated that some of the local germplasms found in Fujian were typical southern peaches. Thus, from the molecular level, it confirmed the previous understanding of the origin of local varieties to be south of the Yangtze River.
-
Keywords:
- peach /
- SSR /
- germplasm resource
-
果树种质资源收集、利用、评价是育种创新的基础。本研究利用已公布的SSR分子标记,对收集保存于福州闽侯地区区试的50份桃种质 (育成品种、地方种质) 进行遗传分析,从DNA水平评估遗传多样性,并进一步探究福建地方种质与引进品种间的亲缘关系,为今后的遗传育种提供可靠的遗传背景信息。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
桃种质资源共50份,包括普通桃、油桃、蟠桃、观赏桃等4大类别。50份种质中,境内育成品种由原育种单位提供,福建地方种质资源由当地采集,其他种质由产地采集。供试材料信息见表 1。
表 1 50份供试桃种质资源基本信息Table 1. Basic information on 50 peach germplasmsstudied序号 样本 分类 来源地 1 03-1 白肉普通桃 北京林果所 2 96-3-54 白肉普通桃 北京林果所 3 瑞红 白肉普通桃 北京林果所 4 FlordingKing 黄肉普通桃 北京林果所 5 2-14W 油桃 北京林果所 6 5-32W 油桃 北京林果所 7 瑞光51 油桃 北京林果所 8 穆阳水蜜 (花粉正常) 白肉普通桃 福建福安产地 9 穆阳水蜜 (花粉败育) 白肉普通桃 福建福安产地 10 大久保 白肉普通桃 福建古田产地 (原产日本) 11 新川中岛白桃 白肉普通桃 福建古田产地 (原产日本) 12 晚白凤 白肉普通桃 福建古田产地 13 美香 白肉普通桃 福建古田产地 (原产日本) 14 梦富士 白肉普通桃 福建古田产地 15 古田甜桃 白肉普通桃 福建古田产地 16 丰黄 黄肉普通桃 福建建宁产地 17 锦绣 黄肉普通桃 福建建宁产地 18 春雪 白肉普通桃 福建闽侯产地 (原产美国) 19 台湾脆桃 白肉普通桃 福建闽侯产地 (原产巴西) 20 西选1号 白肉普通桃 福建永安产地 21 南方野生桃 (砧木) 白肉普通桃 福建闽侯 22 朝晖 白肉普通桃 江苏农科院园艺所 23 霞晖6号 白肉普通桃 江苏农科院园艺所 24 霞脆 白肉普通桃 江苏农科院园艺所 25 霞晖8号 白肉普通桃 江苏农科院园艺所 26 沙红 白肉普通桃 山东农科院 27 春元 白肉普通桃 山东农科院 28 春艳 白肉普通桃 山东农科院 29 锦园 黄肉普通桃 上海农科院 30 秋月 白肉普通桃 上海农科院 31 锦香 黄肉普通桃 上海农科院 32 沪油018 油桃 上海农科院 33 沪油004 油桃 上海农科院 34 沪油002 油桃 上海农科院 35 秦王 白肉普通桃 西北农林科技大学 36 小仙桃 白肉普通桃 浙江农科院 37 99-10-7 白肉普通桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 38 99-13-9 白肉普通桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 39 理想 白肉普通桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 40 NJC83 黄肉普通桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 41 33-20 油桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 42 中油8号 油桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 43 中油10号 油桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 44 早红2号 油桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 45 曙光 油桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 46 金霞 蟠桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 47 中农蟠10号 蟠桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 48 早露 蟠桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 49 红菊花 观赏桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 50 满天红 观赏桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 1.2 SSR扩增
CTAB法提取叶片DNA。从已发表的SSR引物中筛选出能在50份样本间稳定扩增、多态性好、基因组随机分布的16对蔷薇类SSR引物 (UDP96-05、UDP98-25、UDP98-407、BPPCT006、BPPCT008、BPPCT017、BPPCT023、BPPCT025、BPPCT028、BPPCT034、BPPCT038、CPPCT022、CPPCT026、CPPCT029、CPPCT042) 用于遗传分析。反应体系20 μL,扩增程序94℃预变性3 min,94℃预变性30 s,55℃退火30 s,72℃延伸30 s,30次循环;72℃延伸5 min;12℃保存。扩增结束后,加入微量上样缓冲液 (0.005%溴酚蓝,95%甲酰胺) 混匀,2 μL扩增产物聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳分离,电泳缓冲液为1×TBE,150 V稳压电泳1h。电泳结束后将胶块置于核酸染料染色5 min,去离子水漂洗,凝胶成像系统紫外成像留影。
1.3 统计分析
选取扩增清晰的条带。在相同迁移位置, 有条带记为“1”,无条带记为“0”,缺失或不清楚记为“9”,不同引物扩增的结果构成原始的“0,1”二元数据矩阵。利用PowerMarker Ver 3.25软件计算各标记的主要等位基因频率、多态性条带、基因多态性和多态性信息含量 (PIC)。利用NTSYS-pc 2.11软件,对供试群体遗传相似系数进行UPGMA聚类分析。利用DARwin软件进行基于遗传距离的因子分析和聚类分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 遗传多样性分析
由16对SSR标记所得多样性条带,计算出每个位点的等位基因频率变化范围为0.50~1.00,平均为0.77;基因多样性 (Gene Diversity) 变化范围为0.03~0.50,平均为0.30;PIC值变化范围为0.04~0.37,平均值为0.24。
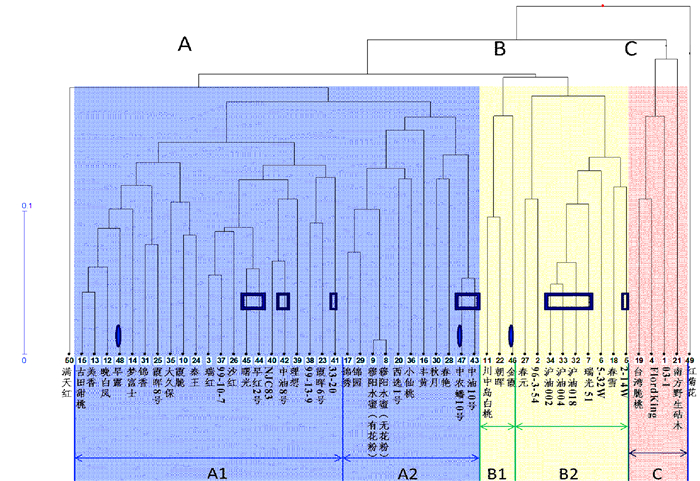
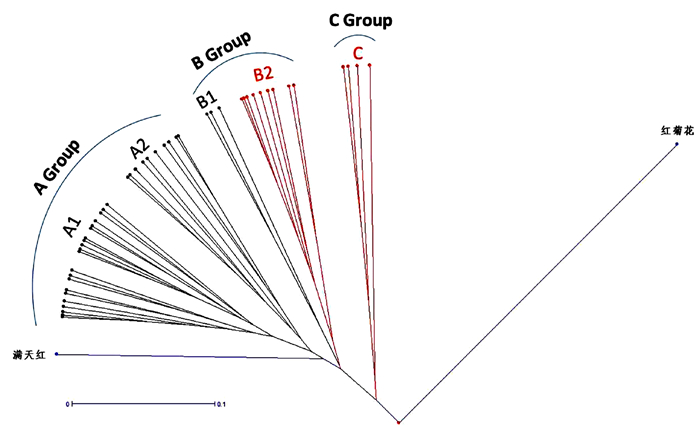
依据聚类分析, 50份桃种质可主要划分为3个类群 (图 1)。A类群基本上为中晚熟桃种质, B类群主要是中早熟种质,C类群为超短低温早熟种质。其中,在A类群种质中,可进一步细分成2个小群,涵盖了北方、中原和南方产区的主栽品种。而在B类群种质中,则包含了早熟种质B2支群,该支群种质在福建暖湿地区表现良好,成熟期皆在6月中旬之前,早于目前福建主栽品种。C类群为需冷量极少的超短低温种质,在福州平原地区即可完成冬季休眠,表现极好。不过,虽然B2与C类群均为短需冷量种质,亲缘性较其他种质近,但仍为不同遗传起源。
2.2 系统进化分析
根据果实性状可粗分桃种质为:普通桃、油桃、蟠桃、观赏桃。油桃 (果皮表面无绒毛)、蟠桃 (果形扁平) 都源自普通桃祖先,受单基因质量性状控制。从本研究选取的50份桃种质的遗传多样性和系统进化角度分析,由图 1、图 2可知,育成的油桃、蟠桃品种的遗传背景与普通桃并未有太大区别,遗传基础来自普通桃亲本,因此油桃、蟠桃并未单独聚类成簇。而观赏桃则不同,观赏桃红菊花、满天红与鲜食桃遗传差异较大,其遗传基础明显异于鲜食桃,表明其起源不同。红菊花独立分支,其亲本必然异于鲜食桃,而另一观赏鲜食兼用品种满天红则是由鲜食桃与观赏桃亲本杂交而来,与鲜食桃具有一定的亲缘关系。
2.3 福建地方特色种质起源分析
亚热带湿热地区并不是桃的最适生长区,本地野生种质资源少、分布窄。目前福建省内绝大多数的栽培品种是由省外引入,特别是江浙沪等南方水蜜桃主产区。这些栽培品种经过数十年的生产、繁育、筛选后,开始逐渐出现遗传变化,形成了目前福建本地的一些特色地方种质。较为成功的有抗流胶病的西选一号[1]、高甜浓香的穆阳水蜜[2]、古田甜桃等。遗传分析表明:西选一号、穆阳水蜜应该是源自江浙地区的南方水蜜桃品种,位于A2分支中;本试验所采集的古田甜桃与美香桃关系密切,应该具有渊源,有可能是同物异名。
3. 讨论与结论
中国是世界上最大的桃生产和消费地区,桃产量和种植面积位居第一,占世界半数以上。随着桃基因组测序的完成,桃在亚洲特别是中国地区的起源、分支、进化路线已基本清楚,大样本桃资源的遗传分析结果相继发表[3-6]。本研究重点关注了在福建地区参与品种区域试验的各地广适优异育成品种、育成待认定品种及当地特色种质,以期为今后本地化育种工作提供理论参考依据。而SSR分子标记在桃遗传多样性的研究上得到广泛应用[7-10],技术成熟、结果可靠性高、成本适宜,在本研究中取得了良好的效果,初步界定出了重要的短低温种质类群及相应品种。
桃发源于北方地区,需要一定时间的低温休眠才能成花并分化出正常的配子细胞。进入南方后,冬季低温积累时数减少,为适应自然环境,桃逐步演化出低需冷量资源。从目前来看,在福建亚热带地区表现良好的短低温桃种质归属于B2和C 2个类群,其中C类群种质与南方野生桃亲缘最近,这证实了境外短低温种质 (如C类群Flord King、台湾脆桃) 遗传背景中带有中国南方桃低需冷量基因资源的报道。B2类群与南方野生桃亲缘次之,其低需冷量表现与南方野生桃可能也有一定关系。
在鲜食桃中,油桃和蟠桃所占比例较低,其果皮无毛、果形扁平性状是单基因控制的质量性状,分别定位于第5、6连锁群[11-12]。在育种实践中,人们可以通过孟德尔遗传规律,利用特定亲本培育出符合预期性状的油桃、蟠桃。由于这2个位点属于单基因质量性状位点,不与其他数量性状连锁,在育种群体后代中可以得到不同数量性状组合 (如果实品质、果实成熟期、抗性) 的油桃、蟠桃个体,遗传多样性丰富,带有鲜食亲本的绝大多数遗传背景。这也就是在本研究中,油桃、蟠桃遗传差异不明显,在聚类分析中散落分布于鲜食普通桃群体中的主要原因。
-
表 1 50份供试桃种质资源基本信息
Table 1 Basic information on 50 peach germplasmsstudied
序号 样本 分类 来源地 1 03-1 白肉普通桃 北京林果所 2 96-3-54 白肉普通桃 北京林果所 3 瑞红 白肉普通桃 北京林果所 4 FlordingKing 黄肉普通桃 北京林果所 5 2-14W 油桃 北京林果所 6 5-32W 油桃 北京林果所 7 瑞光51 油桃 北京林果所 8 穆阳水蜜 (花粉正常) 白肉普通桃 福建福安产地 9 穆阳水蜜 (花粉败育) 白肉普通桃 福建福安产地 10 大久保 白肉普通桃 福建古田产地 (原产日本) 11 新川中岛白桃 白肉普通桃 福建古田产地 (原产日本) 12 晚白凤 白肉普通桃 福建古田产地 13 美香 白肉普通桃 福建古田产地 (原产日本) 14 梦富士 白肉普通桃 福建古田产地 15 古田甜桃 白肉普通桃 福建古田产地 16 丰黄 黄肉普通桃 福建建宁产地 17 锦绣 黄肉普通桃 福建建宁产地 18 春雪 白肉普通桃 福建闽侯产地 (原产美国) 19 台湾脆桃 白肉普通桃 福建闽侯产地 (原产巴西) 20 西选1号 白肉普通桃 福建永安产地 21 南方野生桃 (砧木) 白肉普通桃 福建闽侯 22 朝晖 白肉普通桃 江苏农科院园艺所 23 霞晖6号 白肉普通桃 江苏农科院园艺所 24 霞脆 白肉普通桃 江苏农科院园艺所 25 霞晖8号 白肉普通桃 江苏农科院园艺所 26 沙红 白肉普通桃 山东农科院 27 春元 白肉普通桃 山东农科院 28 春艳 白肉普通桃 山东农科院 29 锦园 黄肉普通桃 上海农科院 30 秋月 白肉普通桃 上海农科院 31 锦香 黄肉普通桃 上海农科院 32 沪油018 油桃 上海农科院 33 沪油004 油桃 上海农科院 34 沪油002 油桃 上海农科院 35 秦王 白肉普通桃 西北农林科技大学 36 小仙桃 白肉普通桃 浙江农科院 37 99-10-7 白肉普通桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 38 99-13-9 白肉普通桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 39 理想 白肉普通桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 40 NJC83 黄肉普通桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 41 33-20 油桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 42 中油8号 油桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 43 中油10号 油桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 44 早红2号 油桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 45 曙光 油桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 46 金霞 蟠桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 47 中农蟠10号 蟠桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 48 早露 蟠桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 49 红菊花 观赏桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 50 满天红 观赏桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 -
[1] 陈亿顺.特早熟水蜜桃新品种'西选1号'选育总结[J].中国南方果树. 2001, 30(2):35-36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FRUI200102026.htm [2] 王道平, 李以训.穆阳水蜜桃品种特性及其栽培技术[J].中国南方果树, 2010, 39(4):79-80. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FRUI201004034.htm [3] PERE A, IGNAZIO V, BRYON S, et al.The peach genome[J].Tree Genet Genomes, 2012, 8(3):531-547. DOI: 10.1007/s11295-012-0493-8
[4] THE INTERNATIONAL PEACH GENOME INITIATIVE. The high-quality draft genome of peach (Prunus persica) identifies unique patterns of genetic diversity, domestication and genome evolution[J]. Nat Genet, 2013, 45(5):487-494. DOI: 10.1038/ng.2586
[5] ABBOTT A G, VERDE I. The peach genome:Insights on genetic diversity and domestication[J]. Acta Horticulturae, 2015, 1084:63-68. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/282739350_The_peach_genome_Insights_on_genetic_diversity_and_domestication
[6] CAO K, ZHENG Z, WANG L. Comparative population genomics reveals the domestication history of the peach, Prunus persica, and human influences on perennial fruit crops[J]. Genome Biology, 2014, 15(7):1-15.
[7] DETTORI M T, MICALI S, GIOVINAZZI J, et al. Mining microsatellites in the peach genome:development of new long-core SSR markers for genetic analyses in five Prunus species[J]. Springerplus, 2015, 4(1):1-18. DOI: 10.1186/2193-1801-4-1
[8] CHEN C, BOCK C H, OKIE W R. Genome-wide characterization and selection of expressed sequence tag simple sequence repeat primers for optimized marker distribution and reliability in peach[J]. Tree Genetics & Genomes, 2014, 10(5):1271-1279. https://www.deepdyve.com/lp/springer-journals/genome-wide-characterization-and-selection-of-expressed-sequence-tag-ll06eKj39x
[9] LI X W, MENG X Q, JIA H J. Peach genetic resources:diversity, population structure and linkage disequilibrium[J]. BMC Genetics, 2013, 14(1):1-16. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2156-14-1
[10] SHEN Z J, MA R J, CAI Z X. Diversity, population structure, and evolution of local peach cultivars in China identified by simple sequence repeats[J]. Genet Mol Res, 2015, 14(1):101-117. DOI: 10.4238/2015.January.15.13
[11] MAUROUX J B, QUILOT-TURION B, PASCAL T. Building high-density peach linkage maps based on the ISPC 9K SNP chip for mapping mendelian traits and QTLs:Benefits and drawbacks[J]. Acta Horticulturae, 2015, 1084:113-118. http://www.actahort.org/books/1084/1084_13.htm
[12] XIONG-WEI L I, JIA H J, GAO Z S. Peach genomics and genome-wide association study:a review[J]. Hereditas, 2013, 35(35):1167-1178. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YCZZ201310004.htm
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 乔雨轩,申潇潇,焦雪辉,周小娟,岳长平,史喜兵. 豫中地区46份桃种质的观赏性综合评价. 果树学报. 2024(02): 216-228 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 殷纪伟,韩贝贝,马莹雪,武星廷,徐振江,姜建福,陈昌文,韩瑞玺. 基于SSR分子标记的154份桃品种遗传多样性分析. 江苏农业科学. 2023(16): 18-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 史芳芳,梁武军,张延磊. 基于SSR标记的油桃品种需冷性分析. 安徽农业科学. 2020(07): 59-61 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 袁滨,柯丽娜,陈光祥,连燕萍,张志鸿,纪鹏伟,吴振强. 应用体细胞不亲和性试验和SSR方法综合鉴定闽南地区双孢蘑菇种质资源. 福建农业学报. 2020(09): 950-956 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 焦云,柴春燕,舒巧云. 基于SSR分子标记的早熟杨梅优株遗传多样性分析. 中国南方果树. 2019(04): 42-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 唐莹莹,杨祥燕,蔡元保,李穆,曾黎明,郑文武,邱文武,李季东,叶维雁. 澳洲坚果SSR-PCR反应体系优化及其应用. 福建农业学报. 2018(02): 154-158 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: