A Preliminary Report on Genomics of Vitis davidii Foëx from Fuan District UsingHigh-throughput Genome Sequencing Method
-
摘要: 为进一步了解福建福安刺葡萄的遗传背景,寻找刺葡萄与欧亚种葡萄之间的遗传差异,本研究基于高通量测序技术展开对福安刺葡萄基因组的分析,共得到测序数据8.4 Gb,鉴定出3 192 484处非冗余遗传差异。差异位点分布位置结果显示,30.34%的差异位于基因间区,3.67%的差异位于基因外显子区。通过对比葡萄参考基因组序列,共鉴定出刺葡萄基因组上存在1 863 237个同源SNP、1 244 590个异源SNP位点,表明本次测序所用的福安刺葡萄有可能是异源二倍体。Abstract: Genetic variants in Vitis davidii from Fuan District in Fujian were studied using the high-throughput genome sequencing method. The 8.4 Gb of raw data were analyzed to result in the identification of 3 192 484 non-redundant genetic variants. Distribution of the variants showed 30.34% in the intergenic regionand 3.67% in the exon region. By comparing the genome sequences of the V. davidii under study with those of the entire grape references, 1 863 237 homo-type SNP and 1 244 590 hetero-type SNP were found. It appeared that the V. davidii from Fuan were most likely to be allodiploidy. The study also indicated that using genetic sequencing to determine the genome-wide variants of V. davidii was a viable tool for better understanding of the genetic background of the plant in question.
-
Keywords:
- high-throughput sequencing /
- Vitis davidii /
- genome
-
刺葡萄Vitis davidi是葡萄属Vitis L.东亚种群中珍贵的野生种质资源,广泛分布于我国南方海拔400~1 800 m的山坡、沟谷疏林或灌丛中,在野生葡萄中其浆果最大[1],品质优良,产量高,鲜食与加工兼用。福安刺葡萄为野生刺葡萄经人工驯化而来,栽培历史较久[2],对黑痘病、炭疽病、白腐病等有较强的抗性,且耐高温高湿,适应性强,是抗病、抗逆育种方面极其珍贵的种质材料,但目前对福安刺葡萄基因组的研究尚为空白,抗病抗逆特性尚未得到充分利用。
为了解刺葡萄遗传特点,本研究开展基于高通量测序的福安刺葡萄基因组初步研究,比对分析刺葡萄与欧亚种葡萄黑比诺[3-4]的遗传差异,有利于了解刺葡萄的遗传背景及遗传演化过程,以期挖掘刺葡萄优良抗性基因,推动对刺葡萄种质资源的开发和利用。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
福安刺葡萄叶片,采自福安刺葡萄种植园。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 测序文库构建、检测与高通量测序
超声片段化刺葡萄基因组DNA,以便获得400~500 bp的DNA片段;将所述DNA片段进行末端修复,补平断口;再将所述DNA片段加A后与特定接头相连,获得连接产物,筛选特定大小片段;最终利用特异序列将所述目的片段进行PCR扩增,获得的扩增产物构成高通量测序文库。
Qubit@2.0测定DNA浓度,Agilent 2000 DNA chip检测文库插入片段大小,Q-PCR定量文库浓度。最终稀释文库至合适浓度,cBOT自动成簇,illuminar 2000 PE250模式双端测序。
1.2.2 高通量测序数据的处理
trim_galore检测并去除测序数据中的index和adapter污染,保留Q20测序数据,获得clean reads。将clean reads利用bowtie2程序 (http://bowtie-bio.sourceforge.net/bowtie2/index.shtml) 比对至黑比诺葡萄参考基因组 (vinifera_145_genoscope.12x, https://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/pz/portal.html)。以生成的比对bam文件为输入文件,freebayes程序 (https://github.com/ekg/freebayes) 计算分析可能存在的遗传多态性位点 (small polymorphisms),生成标准vcf文件用于SNPEFF (http://snpeff.sourceforge.net/SnpEff.html) 进一步解析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 检测文库与高通量测序数据的质量检测
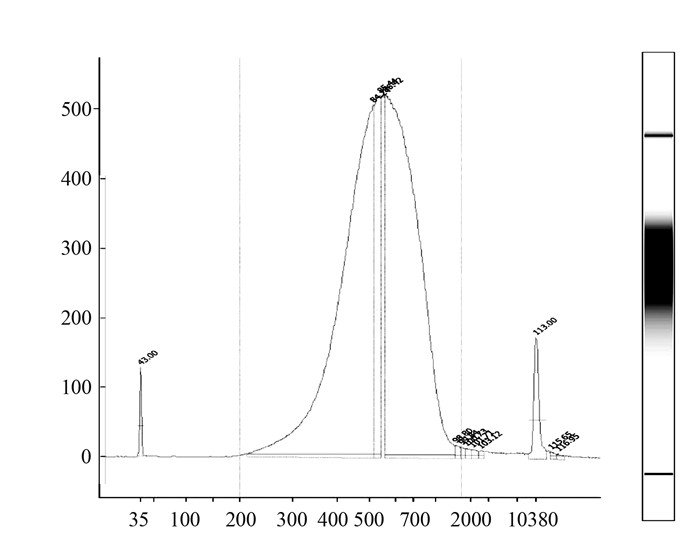
超声片段化基因组DNA,吸附获得DNA片段,经检测使用片段化后DNA构建的测序文库大小符合预期,峰值位于550 bp左右,呈现正态分布,片段集中 (图 1),达到illuminar 2000测序要求。
所构建刺葡萄基因组测序文库上机后,共获得33 501 200条raw reads,8.4 G数据量,Q30质量指标0.938 1,表明此次测序效果良好,数据可信度高。若以葡萄基因组471 M大小为参考,则本次刺葡萄基因组测序深度约为17.8 X。使用trim_galore后获得clean reads约占raw reads的96.2%。
2.2 刺葡萄高通量测序reads比对情况分析
使用bowtie2比对刺葡萄clean reads至黑比诺葡萄基因组,共有34.75%的reads有且只有1个位点精确配对,23.71%的reads有多个位点的匹配,41.54%的reads没有匹配。
2.3 刺葡萄基因组与葡萄基因组的遗传差异
以葡萄基因组序列为参考,刺葡萄基因组片段化读长 (reads) 与之相比,存在SNP (single nucleotide polymorphisms,单核苷酸多态性)、indel (insert/, 插入/缺失)、MNP (multi-nucleotide polymorphisms,多核苷酸多态性) 差异共计3 192 484处,平均每152 bp存在1个差异位点 (1 variant every 152 bases),见表 1。
表 1 刺葡萄与葡萄基因组遗传差异Table 1. Genetic variants of V.davidiidetermined by comparing genomes of grape varieties染色体 染色体长度/bp 遗传差异数/个 遗传差异率/(bp·差异-1) 1 23037639 172435 133 2 18779844 110172 170 3 19341862 112461 171 4 23867706 179247 133 5 25021643 183681 136 6 21508407 170936 125 7 21026613 161855 129 8 22385789 202686 110 9 23006712 137911 166 10 18140952 117766 154 11 19818926 153580 129 12 22702307 159011 142 13 24396255 164821 148 14 30274277 210515 143 15 20304914 120874 167 16 22053297 126617 174 17 17126926 134454 127 18 29360087 216932 135 19 24021853 145933 164 1_random 568933 2995 189 3_random 1220746 7883 154 4_random 76237 543 140 5_random 421237 3224 130 7_random 1447032 6758 214 9_random 487831 737 661 10_random 789605 3497 225 11_random 282498 1756 160 12_random 1566225 9315 168 13_random 3268264 15616 209 16_random 740079 365 2027 17_random 829735 4596 180 18_random 5170003 27137 190 Un 43154196 126175 342 Total 486198630 3192484 152 其中位于基因间区的多态性位点约占总数的30.34%,数目最大;其次是基因上游、下游区域,分别为18.763%和20.854%;基因外显子、内含子区比例为3.67%、24.071%(表 2)。
表 2 不同基因区遗传差异所占比例Table 2. Percentage of variants in different genetic regions基因间区 SNP位点 所占比例/% 基因下游区 1104311 20.854 外显子区 194335 3.670 内含子区 1274699 24.071 基因上游区 993575 18.763 基因间区 1606641 30.34 以SNP数据为参考,检测到刺葡萄基因组中转换 (transitions,嘌呤之间替换或嘧啶之间替换) 数2 616 895,颠换 (transversions,嘌呤和嘧啶之间的替换) 数1 410 733,Ts/Tv比率 (transitions /transversions) 为1.855。同源SNP位点 (homo-type SNP)1 863 237个,异源SNP位点 (hetero-type SNP)1 244 590个,SNP分析基因型结果表明试验用福安刺葡萄在多数等位位点上存在不同的核苷酸类型,相同位置等位基因数最大为2,故初步认为福安刺葡萄有可能为异源二倍体的杂合体,但仍有待通过进一步试验进行验证。
3. 讨论与结论
葡萄属包含圆叶葡萄亚属Muscadinia Planch和真葡萄亚属Euvitis Planch。其中真葡萄亚属内物种通常按原产地划分为欧亚、东亚和北美3个种群,共70余种,且属内种间可以自由杂交,不存在遗传障碍[5]。目前,生产栽培的优良品种多属于欧亚种、北美种及其杂交后代或栽培变种,优良经济性状的有利基因在现有栽培种中已充分利用。作为葡萄属中最大种群的东亚种群,在抗病、抗逆育种资源方面蕴藏着不少珍贵的种质,刺葡萄就是其中重要的种质资源之一。
刺葡萄植株强健,枝梢上密布直立或稍弯皮刺,果皮厚,多籽,品质较好,产量高,与生产栽培种相比,刺葡萄具有抗湿热、抗病性强[6]的优良特性,因而越来越受到人们的重视与利用。自张浦亭等[7]首次在江西玉山县发现由野生刺葡萄经驯化栽培而成的‘塘尾’刺葡萄,研究者陆续利用本地特色刺葡萄野生资源进行人工驯化栽培与优系选育,得到了‘雪峰’[8]、‘紫秋’[9]、‘水晶’[10]、‘惠良’[11]、‘福安’等刺葡萄品种,其在器官形态、果实理化性状等方面存在差异[12-15]。其中,福安刺葡萄为两性花类型,可自花结实[2],本研究采用高通量测序方法获得福安刺葡萄基因组,并与欧亚种葡萄进行序列比对,结果显示福安刺葡萄异源SNP位点1 244 590个,且在多数等位位点上存在不同的核苷酸类型,相同位置等位基因数最大为2,表明福安刺葡萄有可能是异源二倍体,但仍需进一步研究验证。由于闭花自交植物,随着繁殖代数的增加,其纯合度高,这与本试验福安刺葡萄为异源杂合体的结果不符,因此推测刺葡萄花器在原始状态时为单性花,经异花授粉产生后代,遗传上表现异源杂合特点,此后在人类选择栽培过程中,野生葡萄由清一色的雌雄异株出现了雌雄同株[5],产生了两性花类型。焦健等[16]在对刺葡萄两性花类型的研究中,发现刺葡萄种内的两性花类型含有仅存在于欧亚种葡萄的VvmyBA1a基因,因此,刺葡萄两性花类型的出现是驯化过程的自然变异还是混入欧亚种的遗传基因,也有待进一步研究。
刺葡萄属于葡萄属东亚种群,资源分布区域较广,生态环境复杂多样,其种内变异多样性值得重视。有学者对东亚种群主要野生种的初步研究表明,其抗病性差异存在于类型间、株系间,表现为复杂的种内多样性[5]。目前,有关刺葡萄的遗传研究多集中于分子标记与聚类分析考量亲缘关系[17-19],种内与表型相关的特异基因差异尚不完全明确。而本研究尝试利用高通量测序手段对刺葡萄进行分析,有利于全面揭示刺葡萄遗传背景,深入发掘和利用刺葡萄种质资源中的特异基因。
-
表 1 刺葡萄与葡萄基因组遗传差异
Table 1 Genetic variants of V.davidiidetermined by comparing genomes of grape varieties
染色体 染色体长度/bp 遗传差异数/个 遗传差异率/(bp·差异-1) 1 23037639 172435 133 2 18779844 110172 170 3 19341862 112461 171 4 23867706 179247 133 5 25021643 183681 136 6 21508407 170936 125 7 21026613 161855 129 8 22385789 202686 110 9 23006712 137911 166 10 18140952 117766 154 11 19818926 153580 129 12 22702307 159011 142 13 24396255 164821 148 14 30274277 210515 143 15 20304914 120874 167 16 22053297 126617 174 17 17126926 134454 127 18 29360087 216932 135 19 24021853 145933 164 1_random 568933 2995 189 3_random 1220746 7883 154 4_random 76237 543 140 5_random 421237 3224 130 7_random 1447032 6758 214 9_random 487831 737 661 10_random 789605 3497 225 11_random 282498 1756 160 12_random 1566225 9315 168 13_random 3268264 15616 209 16_random 740079 365 2027 17_random 829735 4596 180 18_random 5170003 27137 190 Un 43154196 126175 342 Total 486198630 3192484 152 表 2 不同基因区遗传差异所占比例
Table 2 Percentage of variants in different genetic regions
基因间区 SNP位点 所占比例/% 基因下游区 1104311 20.854 外显子区 194335 3.670 内含子区 1274699 24.071 基因上游区 993575 18.763 基因间区 1606641 30.34 -
[1] 孔庆山.中国葡萄志[M].北京:中国农业科学技术出版社, 2004:28. [2] 李以训, 袁韬, 薛晓虹.福建福安市刺葡萄的开发利用及栽培技术[J].中国南方果树, 2008, 37(4):68-69. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FRUI200804033.htm [3] THE FRENCH-ITALIAN PUBLIC CONSORTIUM FOR GRAPEVINE GENOME CHARACTERIZATION. The grapevine genome sequence suggests ancestral hexaploidization in major angiosperm phyla[J]. Nature, 2007, 449:463-468. DOI: 10.1038/nature06148
[4] ADAM-BLONDON A, WEISSENBACH J, PE E, et al. A major advance in plant biology: the grapevine genome is completely sequenced[J]. Press Release, Paris, . http://www2.cnrs.fr/en/977.htm
[5] 贺普超.葡萄学[M].北京:中国农业出版社, 2001. [6] 贺普超, 晁无疾.我国葡萄野生种的抗病性研究[J].中国果树, 1982, (4):17-20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGS198204007.htm [7] 张浦亭, 范邦文, 余烈, 等.刺葡萄品种'塘尾葡萄'[J].中国果树, 1985, (1):32-34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGS198501011.htm [8] 张浦亭, 罗家信, 贺开业.雪峰刺葡萄的发现与研究[J].湖南农业科学, 1989, (6):27-28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNNK198906009.htm [9] 熊兴耀, 王仁才, 孙武积, 等.葡萄新品种'紫秋'[J].园艺学报, 2006, 33(5):1165. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FRUI200701033.htm [10] 石雪晖, 杨国顺, 倪建军, 等.刺葡萄新类型——水晶刺葡萄的生物学性状研究[J].中外葡萄与葡萄酒, 2008, (5):60-62. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-PTZP200805007.htm [11] 王道平, 雷龑, 施金全, 等.惠良刺葡萄性状表现及其分子鉴定[J].东南园艺, 2013, (3):40-42. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJGS201303013.htm [12] 黄乐, 王美军, 蒋建雄, 等.刺葡萄花器官形态特征研究[J].湖南农业科学, 2013, (15):31-33. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-060X.2013.15.010 [13] 程大伟, 姜建福, 樊秀彩, 等.中国葡萄属植物野生种多样性分析[J].植物遗传资源学报, 2013, 14(6):996-1012. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWYC201306004.htm [14] 罗彬彬, 石雪晖, 杨国顺, 等.湖南省部分地区刺葡萄调查及植物学性状观测[J].中外葡萄与葡萄酒, 2010, (3):17-23. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-PTZP201009005.htm [15] 万怡震, 乔飞, 贺普超.中国野生葡萄种子及果皮单宁的研究[J].西北农林科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2001, 29(6):43-45. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBNY200106009.htm [16] 焦健, 刘崇怀, 樊秀彩, 等.中国野生种葡萄mybA转录因子SNP特征分析[J].植物遗传资源学报, 2013, 14(5):885-891. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWYC201305034.htm [17] 张萌. 基于SSR分子标记的葡萄种质资源遗传多样性分析及品种鉴定[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2012. [18] 刘昆玉, 徐丰, 石雪晖, 等.基于SRAP标记的刺葡萄亲缘关系分析[J].湖南农业大学学报:自然科学版, 2012, 38(6):607-611. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNND201206009.htm [19] 张旭彤. 中国野生葡萄种质资源的亲缘关系研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2012. -
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载:
