Effect of Microbial Agents on Composting of Sludge Collected in Fuqing
-
摘要: 以福清生活污泥为原料,草木灰及鸡粪为辅料,添加枯草芽孢杆菌(T1处理)和BFA腐殖酸(T2处理)进行堆肥,研究微生物菌剂对堆肥过程中堆体(表层和中间)温度、水分、腐殖酸、有机质、全氮、全磷、全钾和GI(种子发芽率指数)的影响。结果表明:T1和T2处理较对照升温迅速,且高温期的温度高,维持时间长;堆肥期内各处理的水分均逐渐减少,而T2处理水分减少最多,减少了22.9%,其次是T1处理减少了19.6%,而对照仅减少了16.9%;堆肥40 d后,T1、T2处理的堆体腐殖酸、有机质、全氮和全钾含量均高于对照;堆肥40 d后,各处理的GI值均大于50%,其中T2处理的GI值大于80%,堆肥腐熟度达到最佳。Abstract: Addition of microbial agents to the sludge collected in the city of Fuqing for composting was investigated. Changes on the surface and center temperatures, contents of moisture, humus acid, organic matters, total nitrogen, total phosphorus and total potassium, as well as the seed germination rate index (GI) of the compost during the fermentation process were monitored as the sewage sludge was mixed with plant ash, chicken manure, Bacillus subtilis (Agent A, Treatment T1) and/or BFA humus acid (Agents B, Treatment T2). The results showed that (a) T1 and T2 rendered the compost to reach a higher maximin temperature faster and maintain it longer than CK did; (b) the moisture content in compost decreased as the fermentation progressed, with the greatest reduction by T2 at 22.9%, followed by T1 at 19.6% and CK at 16.9%; (c) after 40 d composting, the humus acids, organic matters, total nitrogen and total potassium contents in the composts were higher with T1 or T2 than CK; and (d) the 40 d fermentation resulted in GIs by all treatments greater than 50%, and that of T2 beyond 80% achievinga maximal degree of composting effect.
-
Keywords:
- sludge /
- composting /
- microbial agents /
- humus acid
-
随着我国城市污水排放量和污泥产生量的不断增加[1],城市环境问题日益突出,合理的处理处置城市污泥更为棘手[2-4]。城市生活污泥是指处理生活污水所产生的固态废物,生活污泥中既含有多种重金属、病原微生物、寄生虫卵和有机污染物等有毒有害物质[5],也含有植物生长发育所需的营养元素、微量元素以及能改良土壤结构的有机物质[6]。目前城市污泥处理方式中应用较为广泛、有效的方式是污泥堆肥化处理[7-9]。污泥经过堆肥化处理不仅可以降解有机污染物、杀死寄生虫卵和病原菌、钝化重金属,还可以将部分有机物转化为腐殖质,实现污泥的无害化和资源化[10-12]。
堆肥可以分为好氧堆肥和厌氧堆肥2种,好氧堆肥是城市污泥资源化处理常用的技术。好氧堆肥是一种生物学工艺过程, 具有发酵周期短、高温发酵快、无害化程度高、卫生条件好、易于实现产业化操作等特点[13-15]。故国内外对污泥、垃圾、人畜粪便等有机废物处理多采用好氧堆肥。堆肥是一个微生物参与的过程,微生物的数量和种类及其活性影响着堆体中物质的分解及堆肥的进程[16-17],研究表明人工加入高效微生物菌剂可以调节菌群结构、提高微生物的活性,从而提高堆肥的效率、缩短发酵时间、提高堆肥制品质量[15]。王卫平等[18]和冯明谦等[19]研究发现人工接种微生物菌剂可以促进堆肥腐熟速度、堆肥产品质量及环境影响控制作用。本研究拟通过接种不同微生物菌剂,进行条垛式好氧发酵试验,探讨不同菌剂对福清市生活污泥堆肥的影响,以期为优选微生物菌剂以及提高污泥堆肥化工艺提供科学依据。
1. 试验与方法
1.1 主要材料
以城市生活污泥为主要基质,草木灰和鸡粪为辅料。城市生活污泥来自福清市融元污水处理厂,草木灰来自福清市某碾米厂,鸡粪来自南平市某大型养鸡场,为烘干后的鸡粪。微生物菌剂A为含有枯草芽孢杆菌的微生物肥,有效活菌数≥3×108cfu·g-1;微生物菌剂B为BFA生物腐植酸,是经发酵后的黄腐酸 (FA) 与复合微生物及其他有机活性物质的混合物,其有益微生物≥2×108cfu·g-1。各材料的主要理化性状见表 1。
表 1 不同原料主要理化性状Table 1. Main physical and chemical properties of raw materials材料 水分/% 总氮/(g·kg-1) 总磷/(g·kg-1) 总钾/(g·kg-1) 有机质/(g·kg-1) 鸡粪 13.4 21.7 29.2 27.9 872 污泥 83.2 20.1 27.4 15.1 587 草木灰 15.1 0.30 21.0 10.3 - 微生物菌剂A 26.7 18.7 20.2 16.5 788 微生物菌剂B 6.25 20.7 14.3 12.4 997 注:以干基计。 1.2 试验处理
试验设3个处理,各处理配方见表 2。
表 2 试验处理配方Table 2. Formulation fortreatments(单位/kg) 处理 污泥 鸡粪 草木灰 微生物菌剂A 微生物菌剂B CK 5000 1500 500 0 0 T1 5000 1500 500 300 0 T2 5000 1500 500 0 300 注:表中的比例为质量比。 1.3 试验方法
污泥计重后倒入场地,将鸡粪、草木灰和微生物菌剂等辅料按比例称重后利用铲车进行混合均匀,搅拌均匀后取样待测;再将搅拌均匀的物料堆放在事先准备好的场地,堆成高90 cm、宽200 cm的堆体。
堆肥期内,根据堆肥升温情况每5~8 d翻堆1次,翻堆安排在下午15:00~17:00,并在翻堆后取样。取样时均匀布点,每堆取5个点,每次取堆肥样品1.0 kg,混合均匀后装入密封袋放入冰箱待测。将采集的样品分成2份,一份用于测定含水率,另一份经风干、粉碎后用于测定有机质、全氮、全磷和全钾含量。
1.4 测定指标与方法
(1) 温度:堆肥期内,每天9:00用温度计测量堆体温度,随机取6个堆体部位分别测定距离表层15 cm和45 cm位置的温度,取平均值;(2) 水分:105℃烘干法测定;(3) 有机质:重铬酸钾容量法-外加热法测定;(4) 全氮、磷、钾含量:样品用H2SO4-H2O2消煮,全氮用开氏定氮法,全磷 (P2O5) 用钒钼黄比色法测定,全钾 (K2O) 用火焰光度法测定;(5) 游离腐植酸含量:1%NaOH浸提-重铬酸钾氧化法测定;(6) 种子发芽指数 (GI):新鲜样品与水按照1:10(W/V) 比例混合振荡2 h,上清液经滤纸过滤后待用。把一张大小合适的滤纸放入干净无菌的9 cm培养皿中滤纸上整齐摆放10粒黄瓜种子。准确吸取5 mL滤液于培养皿中,在25℃黑暗条件下的培养箱中培养48 h,测定种子的发芽率和根长,同时用去离子水做空白对照。
GI/%=(浸提液发芽数×根长)/(对照液发芽数×根长)×100%。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 温度变化
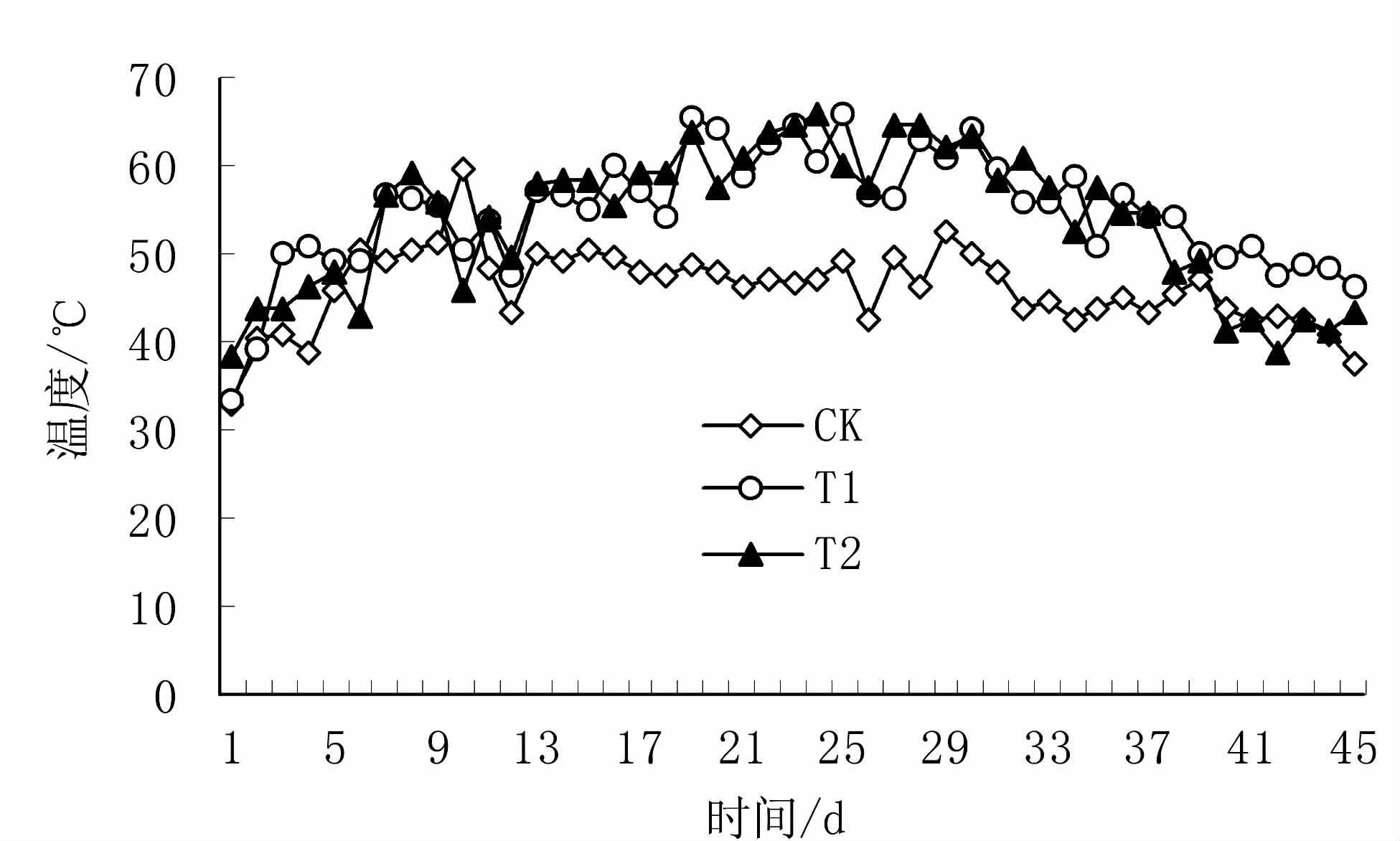
堆肥温度的变化是整个堆肥过程最直观的表现,可以直接表征堆肥的腐熟程度,也是影响堆肥中微生物活动和决定堆肥能否顺利进行并完成的重要指标[20]。堆肥一般包括升温期、高温期和降温期3个阶段[21-22]。图 1、2分别是堆体表层 (堆体15 cm处) 和中间温度 (堆体45 cm处) 变化曲线图。从图 1可以看出,建堆后3个处理的堆体表层温度就开始迅速上升,其中T1、T2处理在建堆后升温更快,在第2 d的时候均达到了50℃以上,而对照则在第3 d达到50℃以上;但是与表层温度相比,3个处理的堆体中间部位的温度在建堆后升温速度相对较慢,T1处理第3 d时温度达到50℃,T2处理的温度在第7 d才达到50℃,而对照则在第6 d达到50℃。这说明添加微生物菌剂加快堆肥进入高温期,这可能是因为一方面添加微生物菌剂降低了物料的含水率,加快了物料升温,另一方面物料中增加了有益微生物,微生物新陈代谢活动频繁,促进了发酵过程,提高堆体高温期温度。
污泥堆肥处理过程,堆体经过高温阶段,可抑制甚至杀死对热敏感的病原体,进而提高污泥堆肥的卫生安全性,达到无害化处理[23]。根据GB7959-87《粪便无害化卫生标准》规定,堆肥温度在50~55℃以上并维持5~7 d,就能够达到粪便无害化卫生标准。从图 1可以看出T1、T2处理堆体表层在堆肥期间最高温度达到了67.3℃、67.8℃,且维持在高温期的天数分别达到了38 d和37 d,而对照最高温度仅为58.8℃,且维持在高温期的天数仅为27 d;而从图 2可以看出T1、T2处理堆体中间温度在堆肥中期达到了最高值分别为65.7℃和66℃,且维持在高温期的天数分别达到了35 d和29 d,而对照最高温度为59.8℃,且维持在高温期的天数仅为8 d。这说明添加微生物菌剂有利于提高堆体中间的温度,并增加堆体维持在高温期的时间。这是因为添加微生物菌剂之后堆肥中大量微生物的活动释放大量的能量,使得堆体能够维持较高的温度,促进堆体快速升温,提高堆体的腐熟程度,更利于污泥无害化处理。这与吕子文等[24]的研究结果相同。
2.2 水分变化
堆体中水分的主要作用有3点:一是溶解污泥中的有机物;二是作为微生物新陈代谢的原料;三是通过蒸发作用带走热量,调节堆肥温度,进而影响堆肥发酵质量。由此看出水分含量也是堆肥完成程度的重要指标[25-26],高温堆肥时含水率以50%~60%为佳[5]。图 3是堆体水分变化曲线图。从图 3可以看出,建堆后各处理的水分均逐渐减少,而T2处理水分减少最多,减少了22.9%,其次是T1处理减少了19.6%,最后是对照减少了16.9%。堆肥过程水分变化主要是受温度、通风以及堆体孔隙度等因素影响。T1和T2处理水分含量都低于对照,这是因为添加微生物菌剂提高了堆体温度和增加了堆体高温维持时间,使得堆体水分损失加剧,从而促进有机肥形成,这与李承强等研究结果相似[27]。
2.3 游离腐殖酸含量变化
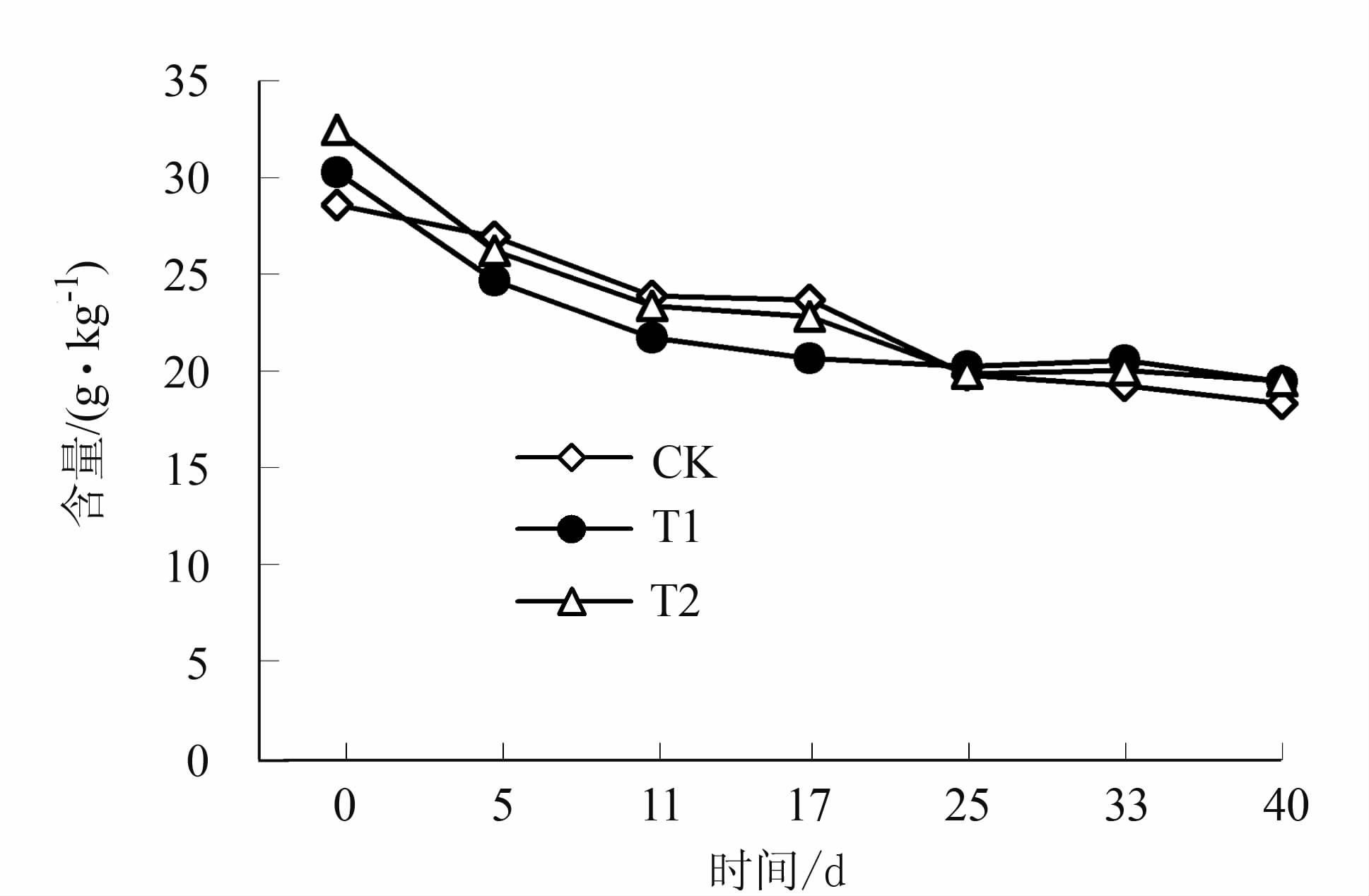
堆肥是有机物质腐殖化与稳定化的过程,因此腐殖酸在堆肥过程中的变化可以有效评价堆肥腐熟程度。游离腐殖酸是能够溶于碱液的腐殖酸部分,通常以1%氢氧化钠浸提,是总腐殖酸的主要组成部分,其含量变化直接影响总腐殖酸含量。图 4是堆肥游离腐殖酸含量变化图。从图 4可以看出,各处理游离腐殖酸含量逐渐下降,到第25 d时,各处理的游离腐殖酸含量基本一致,之后变化不明显,这与马怀良[28]的研究一致。目前,许多学者研究了堆肥过程中腐殖酸含量的变化,但得出的结论有所不同,其原因可能与堆肥时的原料、C/N比、堆肥条件等不同有较大关系[29-31]。
2.4 有机质变化
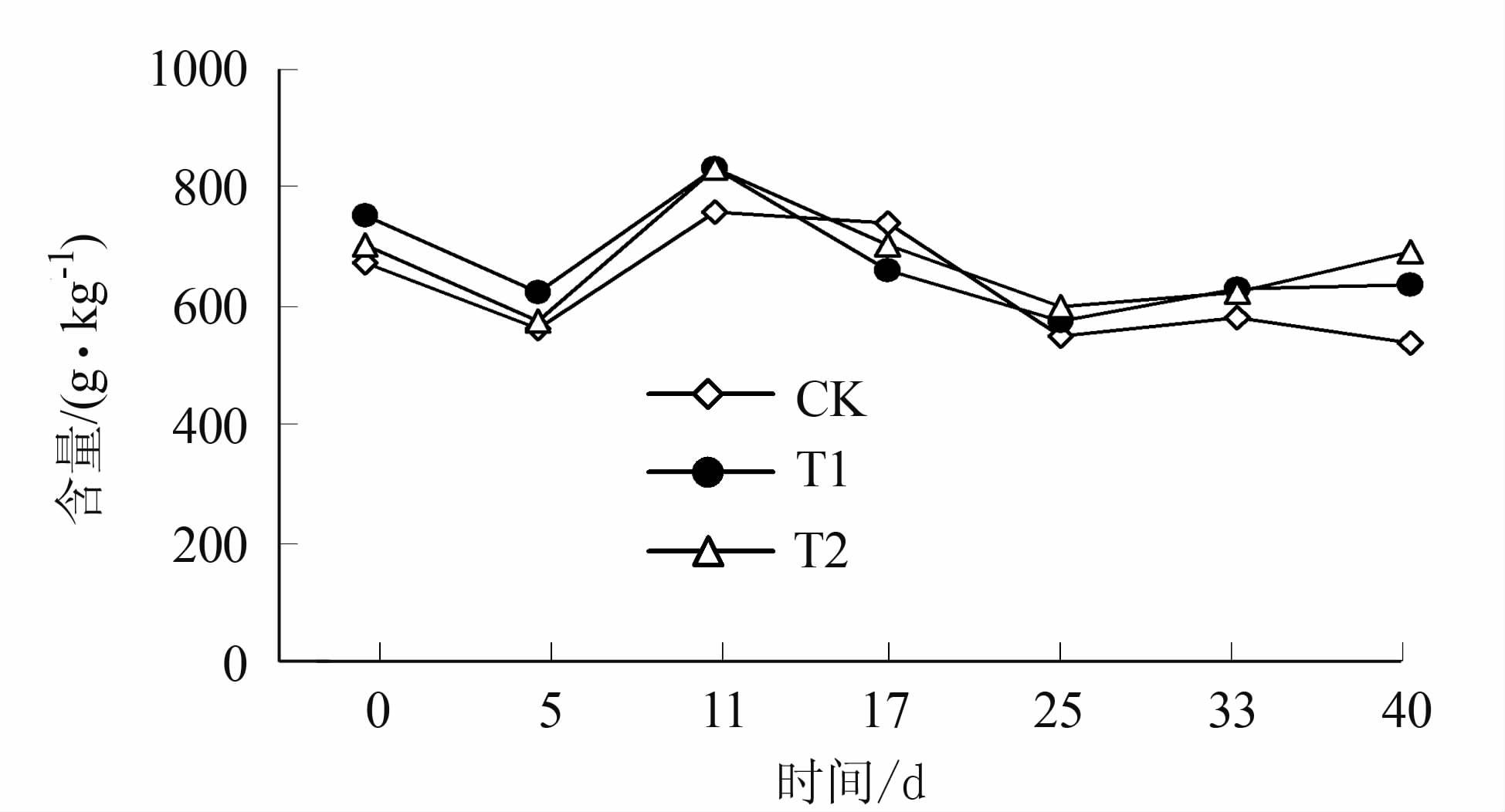
堆肥过程中有机物在微生物活动作用下分解为二氧化碳、水等小分子物质,伴随能量的释放,堆体的温度上升,同时又促进新的物质-腐殖酸的合成。所以,在整个堆肥的过程中,堆体有机质含量会呈现逐渐减少的趋势[32]。图 5是堆肥有机质含量变化曲线图,从中可看出对照及处理的有机质变化趋势均是先下降后上升,接着再下降,最后趋于稳定,其中T1、T2处理的有机质含量分别由初始时的752、703 g·kg-1降至638、694 g·kg-1,而CK处理则由初始时672 g·kg-1降至534 g·kg-1。这可能是因为在堆肥升温阶段,微生物迅速分解易降解有机物,有机质迅速减少,随后微生物迅速繁殖造成有机质含量的上升,随着堆肥的进行,有机物质消耗不断减少,产生大量二氧化氮和挥发性有机酸,并最终趋于稳定。
2.5 养分变化
堆肥发酵过程中,堆肥物料随着有机质被微生物分解,物料的水分的损失,物质总量不断减少,养分往往表现为“浓缩效应”,但是氮素除了“浓缩效应”以外还有氮素挥发损失[33]。表 3是各处理堆肥养分含量变化情况表。氮是堆肥的重要营养元素,全氮含量的变化可以反应堆肥过程氮素变化趋势,也是评价堆肥养分的重要指标之一。从表 3中可以看出各处理堆肥全氮含量是先下降后再逐渐小幅回升,且最终各处理的全氮含量比较接近,均在17.0 g·kg-1左右。造成堆肥初期全氮含量下降的主要原因是有机氮被分解为NH3和NH4+,而在堆垛的条件下有利于NH3的挥发,造成氮素损失比较严重。堆肥后期,物料的全氮含量又有所升高,这是随着堆肥的进行,物料中有机质被分解,造成全氮绝对含量下降,而相对含量有所上升。
表 3 各处理堆肥养分含量变化情况Table 3. Nutrient content in compost under different treatments发酵天数/d 全氮/(g·kg-1) 全磷/(g·kg-1) 全钾/(g·kg-1) CK T1 T2 CK T1 T2 CK T1 T2 0 19.0 20.8 18.4 24.9 21.2 20.1 18.0 18.2 15.1 5 16.0 16.1 15.3 22.2 20.8 19.1 19.2 19.3 16.3 11 15.0 17.3 16.6 25.8 22.2 23.5 18.8 19.2 16.9 17 14.3 14.4 14.7 25.6 23.5 21.4 17.2 18.4 15.1 25 14.1 14.1 14.1 27.4 25.7 25.1 19.7 21.2 18.7 33 16.8 17.3 17.8 29.2 26.7 26.4 18.5 20.5 17.8 40 17.6 17.8 16.8 28.1 27.0 24.6 18.7 22.3 19.2 从表 3中可以看出各处理堆肥全磷含量呈逐渐升高的趋势。全磷含量的增加主要是由于随着堆肥的进行,有机物质不断分解,堆体体积减小、重量减轻,磷的“浓缩效应”较为明显。另外,堆肥结束后T1、T2处理的堆肥全磷含量比开始时增加5.8、4.5 g·kg-1,而对照则只增加了3.2 g·kg-1,这说明了污泥堆肥加入微生物菌剂,促进了堆体有机物质的分解,“浓缩效应”要高于对照。
从表 3中可以看出T1和T2处理全钾含量的变化也是呈逐渐增加的趋势,而对照处理则增加较少,堆肥结束后T1、T2处理的全钾含量分别比开始时增加4.1、4.1 g·kg-1,而对照则只增加了0.7 g·kg-1。这也进一步说明了添加微生物菌剂促进了堆体有机物质的有效分解。
2.6 种子发芽率指数
相对于其他的理化指标,种子发芽率指数 (GI) 是更能够直接反应堆肥浸提液对植物毒性的指标,可较为准确地评价污泥堆肥的腐熟度,因为未腐熟的堆肥浸提液含有高浓度的NH4+、小分子有机酸、重金属等有毒物质对植物种子的生长有很强的抑制作用。一般认为,当GI大于50%时,可以判定堆肥腐熟;当GI大于80%时,堆肥对植物完全没有毒性。表 4是不同处理堆肥前后GI变化情况表,从表 4可以看出堆肥前,各处理的GI均小于50%;而堆肥40 d后,各处理的GI值均大于50%,其中T2处理的GI大于80%。这说明,发酵40 d后各处理堆肥均可达到腐熟标准,其中T2处理堆肥腐熟度最佳。
表 4 不同处理堆肥前后GI变化情况Table 4. GI of compost before and after composting treatments发酵天数/d CK/% T1/% T2/% 0 34 38 41 40 67 72 84 3. 讨论与结论
(1) 从温度、水分、腐殖酸等各项指标数据可以看出,添加微生物菌剂的T1和T2处理较对照升温迅速,且高温期的温度高,维持时间长,发酵效果较好。表明添加微生物菌剂,可以促进堆肥的腐熟,缩短发酵周期,提高污泥堆肥处理处置的卫生安全性。
(2) T1和T2处理堆肥结束后腐植酸含量略高于对照。各处理的全氮含量均经过先下降后上升的阶段,各处理的全磷、全钾含量均呈逐渐增加的趋势,且全磷、全钾的增加幅度均高于对照,说明添加微生物菌剂的处理有机碳损耗多,而不易损失的磷钾相对就提高了。表明添加微生物菌剂可以提高污泥堆肥产品的稳定性,保证肥效和品质。
(3) 经过各处理间的比较,可以看出加入微生物菌剂A的T1处理在污泥堆肥40 d后,温度、腐殖酸、有机质、全氮、全磷和全钾含量都高于加入微生物菌剂B的T2处理,T1处理的含水量也低于T2处理,但T2处理的种子发芽指数 (GI) 值大于T1处理,为84%,堆肥腐熟度效果最好。这可能与试验时添加的微生物菌剂A (枯草芽孢杆菌) 的微生物数量多于微生物菌剂B (BFA生物腐殖酸) 有关。2种微生物菌剂都有利于城市生活污泥堆肥化处理,但引起两者对堆肥作用效果不同的原理,还有待后期进一步的研究分析。
-
表 1 不同原料主要理化性状
Table 1 Main physical and chemical properties of raw materials
材料 水分/% 总氮/(g·kg-1) 总磷/(g·kg-1) 总钾/(g·kg-1) 有机质/(g·kg-1) 鸡粪 13.4 21.7 29.2 27.9 872 污泥 83.2 20.1 27.4 15.1 587 草木灰 15.1 0.30 21.0 10.3 - 微生物菌剂A 26.7 18.7 20.2 16.5 788 微生物菌剂B 6.25 20.7 14.3 12.4 997 注:以干基计。 表 2 试验处理配方
Table 2 Formulation fortreatments
(单位/kg) 处理 污泥 鸡粪 草木灰 微生物菌剂A 微生物菌剂B CK 5000 1500 500 0 0 T1 5000 1500 500 300 0 T2 5000 1500 500 0 300 注:表中的比例为质量比。 表 3 各处理堆肥养分含量变化情况
Table 3 Nutrient content in compost under different treatments
发酵天数/d 全氮/(g·kg-1) 全磷/(g·kg-1) 全钾/(g·kg-1) CK T1 T2 CK T1 T2 CK T1 T2 0 19.0 20.8 18.4 24.9 21.2 20.1 18.0 18.2 15.1 5 16.0 16.1 15.3 22.2 20.8 19.1 19.2 19.3 16.3 11 15.0 17.3 16.6 25.8 22.2 23.5 18.8 19.2 16.9 17 14.3 14.4 14.7 25.6 23.5 21.4 17.2 18.4 15.1 25 14.1 14.1 14.1 27.4 25.7 25.1 19.7 21.2 18.7 33 16.8 17.3 17.8 29.2 26.7 26.4 18.5 20.5 17.8 40 17.6 17.8 16.8 28.1 27.0 24.6 18.7 22.3 19.2 表 4 不同处理堆肥前后GI变化情况
Table 4 GI of compost before and after composting treatments
发酵天数/d CK/% T1/% T2/% 0 34 38 41 40 67 72 84 -
[1] 杭世珺, 刘旭东, 梁鹏.污泥处理处置的认识误区与控制对策[J].中国给水排水, 2004, 20(12):89-92. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4602.2004.12.027 [2] 梁鹏, 黄霞, 钱易, 等.污泥减量化技术的研究进展[J].环境污染治理技术与设备, 2003, (1):44-52. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBLG200902034.htm [3] 王守仁, 王增长, 宋秀兰, 等.污泥处理技术发展[J].水资源保护, 2010, 26(1):80-83. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJHG201509054.htm [4] 陈菊香.剩余污泥减量化一资源化的研究[J].环境科技, 2011, 24(2):7-9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKT201403013.htm [5] 王绍文, 秦华.城市污泥资源利用与污水土地处理技术[M].北京:中周建筑工业出版社, 2007. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY201603027.htm [6] 许晓英, 李季.复合微生物菌剂在污泥高温好氧堆肥中的应用[J].中同生态农业学报, 2006, 14(3):64-66. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTN200603018.htm [7] 张颖.固体废物的资源化和综合利用技术[J].环境科学研究, 1998, 11(3):49-52. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXDB201613041.htm [8] 马娜, 陈玲, 何培松, 等.城市污泥资源化利用研究[J].生态学杂志, 2004, 23(1):86-89. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNCX201201016.htm [9] STYLIANOU M A, INGLEZAKIS V J, MOUSTAKAS K G, et al.Improvement of the Quality of Sewage Sludge Compost by Adding Natural Clinoptilolite[J].Desalination, 2008, 224:240-249. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2007.06.009
[10] 姚岚, 王成, 徐灵.秸秆与污泥混合好氧堆肥研究[J].西南科技大学学报, 2008, 23(3):53-56. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10635-2010095938.htm [11] 李艳霞, 陈同斌, 罗维, 等.中国城市污泥有机质及养分含量与土地利用[J].生态学报, 2003, 23(11):2464-2474. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2003.11.031 [12] 刘洪涛, 陈同斌, 郑国砥, 等.有机肥与化肥的生产能耗、投入成本和环境效益比较分析[J].生态环境学报, 2010, 19(4):1000-1003. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201004046.htm [13] 冯宏, 李华兴.菌剂对堆肥的作用及其应用[J].生态环境, 2004, 13(3):439-441. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ200403050.htm [14] 李艳霞, 王敏健, 王菊思, 等.城市固体废弃物堆肥化处理的影响因素[J].土壤与环境, 1999, 8(1):61-65. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ199901014.htm [15] HAUG R T.The Practical Handbook of Compost Engineering[M].Boca Raton, FI :Lewis Publishex, 1993.
[16] 陈华癸.微生物学[M].北京:农业出版社, 1997:72-73. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY201603027.htm [17] 罗安程, 史彩芬, 孙晓华, 等.猪粪堆肥发酵过程中磷组分的转化[J].浙江农业学报, 2005, 17(5):298-299. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJNB200505012.htm [18] 王卫平, 汪开英, 薛智勇, 等.不同微生物菌剂处理对猪粪堆肥中氨挥发的影响[J].应用生态学报, 2005, 16(4):693-697. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB200504021.htm [19] 冯明谦, 汪立飞, 刘德明.高温好氧垃圾堆肥中人工接种初步研究[J].四川环境, 2000, 19(3):27-30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCHJ200003010.htm [20] 徐凤花, 孙冬梅, 宋金柱.微生物制品技术及应用[M].北京:化学工业出版社; 2007. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY201603027.htm [21] HUANG DEYANG, LU WENJING, WANG HONGTAO, et al. Application of high-efficient cellulose utilization microorganisms in composting of vegetable wastes and flower stalk[J]. Environmental Science, 2004, 25(2):145-149.
[22] LI J. Compost Project Manual[M]. Beijing:Chemical Industry Press, 2005:35-36.
[23] 丁文川, 李宏, 郝一琼, 等.污泥好氧堆肥主要微生物类群及其生态规律[J].重庆大学学报, 2002, 25(6):113-116. DOI: 10.11835/j.issn.1000-582X.2002.06.032 [24] 吕子文, 顾兵, 方海兰, 等.绿化植物废弃物和污泥的堆肥特性研究[J].中国土壤与肥料, 2010, 12(1):57-64. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRFL201001015.htm [25] 李秀艳, 吴星五, 高廷耀, 等.接种高温菌剂的生活垃圾好氧堆肥处理[J].同济大学学报, 2004, 32 (3):367-371. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJDZ200403017.htm [26] 王伟东, 刘建斌, 牛俊玲, 等.堆肥化过程中微生物群落的动态及接菌剂的应用效果[J].农业工程学报, 2006, 22 (4):148-152. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NYGU200604031.htm [27] 李承强, 魏源送, 樊耀波, 等.不同填充料污泥好氧堆肥的性质变化及腐熟度[J].环境科学, 2001, 22(3):60-65. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ200103013.htm [28] 马怀良, 许修宏.不同C/N对堆肥腐殖酸的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料, 2009, (6):64-66, 73. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRFL200906015.htm [29] 张盛华, 郑凯琪, 薛红波, 等.城市污泥堆肥过程中腐殖酸及重金属形态的变化[J].江苏农业学报, 2014, 30(6):1350-1354. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSNB201406027.htm [30] 许修宏, 马怀良.接种菌剂对鸡粪堆肥腐殖酸的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料, 2010, (1):54-56. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRFL201001014.htm [31] 陈迪, 赵洪颜, 葛长明, 等.中药渣堆肥化过程中腐殖酸的动态变化研究[J].延边大学农学学报, 2015, 37(4):292-295. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YDNX201504005.htm [32] 孙干, 裴宗平, 凃永成等.复合微生物菌剂在有机堆肥中的应用研究[J].土壤与肥料, 2015, (15):166-170. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BFYY201515045.htm [33] 王卫平, 朱凤香, 钱红, 等.接种发酵菌剂和添加不同调理剂对猪粪发酵堆肥氮素变化的影响[J].浙江农业学报, 2005, 17(5):276-279. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJNB200505007.htm -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 刘子奇,田志为,王楚濛. 污泥快速堆肥发酵技术在北京河西再生水厂中的试验. 净水技术. 2024(11): 164-169 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 范嘉妍,王帅,姜岩,董振宇,严婷,王楠. 稻秸与猪粪静态好氧共堆肥的最佳配比. 中国土壤与肥料. 2020(03): 82-87 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 黄金枝,胡桂萍,俞燕芳,杜贤明,石旭平,王军文. 微生物在农业废弃物堆肥应用中的研究进展. 广东农业科学. 2019(01): 64-70 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: