Optimized Fermentation for Production of Xanthan Gum Using Xanthomonas axonopodis
-
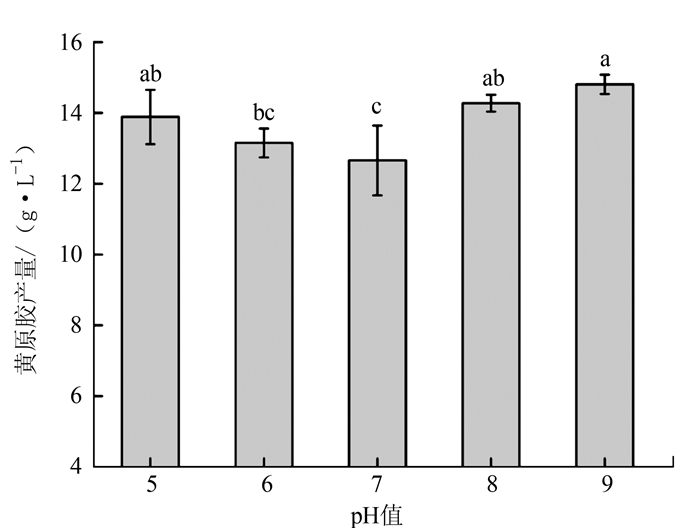
摘要: 为了获得更高品质的黄原胶,优化黄原胶高产菌株地毯草黄单胞菌FJAT-10151的发酵工艺,通过单因素及正交设计对培养基(碳源、氮源和无机盐离子)和发酵条件(发酵时间、pH、装液量和接种量)进行优化,试验获得最佳发酵培养基为葡萄糖30 g·L-1、豆饼粉30 g·L-1、KH2PO42 g·L-1、pH值9.0。在装液量50 mL/250 mL、接种量8%培养条件下发酵72 h,黄原胶产量达到21.0 g·L-1,是初始培养条件产量8.65 g·L-1的2.43倍。优化发酵工艺后,黄原胶品质提高,丙酮酸含量从8.9%升高到16.3%,而蛋白质含量从15.27%降低到4.8%。Abstract: Conditions of fermentation to produce extracellular xanthan gum by using Xanthomonas axonopodis FJAT-10151 were optimized to maximize quality of the gum. Single factor and orthogonal experiments on medium composition (including sources of carbon, nitrogen and inorganic ions) and fermentation conditions (including pH, time duration, fill volume and inoculum ratio) were conducted. It was found that using a medium consisting of glucose 30 g·L-1, soybean cake powder 30 g·L-1, and KH2PO4 2 g·L-1 at pH 9.0 with a filled culture of 50 mL containing 8% of inoculum per 250 mL flask, a yield of 21.0 g·L-1 of xanthan gum could be obtained after fermentation for 72 h. The production capacity was 243% higher than that prior to the optimization. More importantly, a higher quality of xanthan gum with the content of pyruvic acid increased from 8.9% to 16.3% and the content of protein decreased from 15.27% to 4.8% was realized.
-
Keywords:
- Xanthomonas axonopodis /
- xanthan gum /
- orthogonal design
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】植物种质资源的收集与保存是植物研究重要内容,其中超低温保存作为植物组织和细胞长期保存的理想方法,尤其适合营养繁殖作物的茎尖或分生组织的保存,具有直接再生完整小植株、减少遗传变异等优点[1]。海棠是蔷薇科(Rosaceae)苹果属(Malus)中果径较小(≤5 cm)的落叶乔木或小乔木,其中观赏海棠(Malus sp.)观赏价值高,是重要的优质绿化树种,研究海棠茎尖超低温保存在生产上具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】超低温保存后较高的存活率和再生率是主要的技术目标,已有研究显示,玻璃化超低温保存中活性氧(Reactive oxygen species, ROS)诱导的氧化应激是引起植物材料冻存后存活率下降的原因之一,因此,可以采用外源抗氧化剂来保护机体在超低温保存中免受伤害,如过氧化氢酶(Catalase, CAT)[2]、超氧化物歧化酶(Superoxide dismutase, SOD)[3]等酶类抗氧化剂以及抗坏血酸(Ascorbic acid, AsA)[4]和谷胱甘肽(Glutathione, GSH)[5]等非酶类抗氧化剂,均可以有效降低ROS生成量,减少氧化应激的发生,显著改善超低温保存效果。此外,细胞程序性死亡(Programmed cell death, PCD)作为一种基因编码主动性的死亡方式,在植物超低温保存中也扮演了重要的角色,添加细胞凋亡抑制剂D-CHO[6]、NO供体(Sodium Nitroprusside, SNP)[7]和乙烯(乙烯利Ethephon, Eth)[8] 等抑制PCD发生的物质可以提高存活率。【本研究切入点】目前除了对苹果属一些种类有少量超低温保存[9-12],特别是涉及观赏海棠的超低温保存研究极少,而极具观赏价值的北美海棠品种之一——红丽海棠(Malus Red Splendor)超低温保存鲜见报道。【拟解决的关键问题】本文以红丽海棠茎尖为试材,研究其超低温保存技术程序,探讨添加不同含量的抗氧化剂及PCD抑制剂对茎尖超低温保存冻后存活率的影响,建立红丽海棠玻璃化超低温保存技术程序,为观赏海棠种质资源保存提供一种技术思路,并为抗氧化剂和PCD抑制剂在超低温保存中的应用提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
供试材料为观赏海棠品种红丽,以健康且带有饱满腋芽的当年生枝条为外植体(采自国家植物园海棠栒子园),在1/2MS+1.5 mg·L−1 6BA+0.1 mg·L−1 IAA的培养基中诱导无菌苗,并于1/2MS+1.0 mg·L−1 6-BA+0.5 mg·L−1 IAA的培养基中进行继代培养,诱导和继代培养条件:(23±3)℃,光照强度40 μmol·m−2·s−1,光照时间14 h·d−1,取生长旺盛的组培苗用于超低温保存试验。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 茎尖玻璃化法超低温保存
根据初步预试验设置玻璃化超低温保存的基本程序,再采用“逐步单因子法”对关键环节进行优化。(1)预培养:将红丽组培苗切成5 mm左右的带顶芽茎段,分别接种在不同蔗糖浓度(0.1、0.3、0.5、0.7、0.9 mol·L−1)的MS培养基中4 ℃下培养2 d,然后继续下述程序:(2)装载(Loading):在双目解剖镜下,用镊子和手术刀切下带3~4片叶原基、大小为1.5~2.0 mm的茎尖;将切下的茎尖放入1.5 mL 装有1 mL MS溶液的离心管中,吸出离心管中的MS溶液,加入1 mL Loading溶液(2 mol·L−1丙三醇+0.4 mol·L−1蔗糖,蒸馏水配置,pH 5.8),在室温下静置处理30 min;(3)PVS2处理:吸出离心管中的Loading溶液,加入1mL PVS2溶液[30%(m/V)丙三醇+15 %(m/V)乙二醇+15%(m/V)二甲基亚砜+0.4 mol·L−1蔗糖,1/2MS盐溶液配置,pH 5.8],在0 ℃于冰浴中处理90 min;(4)液氮冻存:更换新的1 mL PVS2溶液后,封紧离心管口,立即投入液氮,冻存1 h;(5)化冻:将装有PVS2和茎尖的离心管从液氮中取出,迅速放入38 ℃水浴中化冻1 min;(6)去装载(Unloading):将离心管中的PVS2溶液吸出,加入Unloading溶液(用1/2MS盐溶液配置的1.2 mol·L−1蔗糖,pH 5.8)后在室温下震荡洗涤2次,每次10 min。然后用于存活率或恢复生长率测定。相关步骤示意图见图1。
![]() 图 1 茎尖玻璃化超低温保存及存活率检测A.红丽海棠组培苗;B.预培养;C.切取1.5~2.5 mm茎尖;D.茎尖在离心管中;E.经TTC染色变红(左)与未染色(右)的茎尖;F.冻后茎尖接种到恢复培养基中。Figure 1. Survival rate of post-cryopreservation shoot tipsA: Crabapple tissue culture; B: pre-culture; C: 1.5-2.5 mm cut of shoot tip; D: shoot tip segment in centrifugal tube; E: TTC stained red (left) and original (right) shoot tips; F: post-frozen shoot tips inoculated on recovery medium.
图 1 茎尖玻璃化超低温保存及存活率检测A.红丽海棠组培苗;B.预培养;C.切取1.5~2.5 mm茎尖;D.茎尖在离心管中;E.经TTC染色变红(左)与未染色(右)的茎尖;F.冻后茎尖接种到恢复培养基中。Figure 1. Survival rate of post-cryopreservation shoot tipsA: Crabapple tissue culture; B: pre-culture; C: 1.5-2.5 mm cut of shoot tip; D: shoot tip segment in centrifugal tube; E: TTC stained red (left) and original (right) shoot tips; F: post-frozen shoot tips inoculated on recovery medium.关键环节的优化:在获得适宜预培养蔗糖浓度基础上,分别设置不同预处理时间(1、2、3 d),不同Loading溶液处理时间(0、10、20、30、40 min)和不同PVS2溶液处理时间(0、30、60、90、120 min),每个优化环节之前的步骤采用上一步已优化的处理方法,之后的步骤采用上述基本程序,直至完成所有关键环节的优化。每处理10~15个茎尖,重复3次。
1.2.2 存活率测定
采用氯化三苯基四氮唾(TTC)法检测冻存后茎尖的存活率。将经过Unloading溶液处理的茎尖置于含0.4%(m/V)的TTC溶液的离心管中,再放入37 ℃的水浴中黑暗处理30 min,将茎尖取出后,置于体视显微镜下,观察其染色情况。顶端分生组织被染红的茎尖记为存活的茎尖,而未被染红的茎尖记为死亡的茎尖。存活率/%=(被染红的茎尖/所有经过TTC处理的茎尖)×100%。每处理10~15个茎尖,重复3次。
1.2.3 恢复生长率测定
将经过液氮保存后的茎尖接种于MS培养基中暗培养2周后,然后转入正常光照条件(与组织培养的条件相同)下培养,茎尖长叶记为恢复生长。每处理10~15个茎尖,重复3次。
1.2.4 外源抗氧化剂和PCD抑制剂的添加
在建立的玻璃化超低温保存程序的基础上,根据课题组前人研究结果[4, 7-8, 13],分别在预培养基中添加Eth(100、200、400、800 mg·L−1);在Loading溶液中添加CAT,使其终浓度分别为50、100、200、400 U·mL−1和硝普钠(SNP),使其终浓度分别为50、100、200、1000 μmol·L−1;在PVS2溶液中添加GSH,使其终浓度分别为0.04、0.08、0.16、0.32 μmol·L−1;在Unloading溶液中添加AsA,使其终浓度分别为100、200、400、600 μmol·L−1,各处理均以原溶液为对照。
1.2.5 数据处理及分析
采用SPSS 26.0和Excel软件分别对试验数据进行单因素方差分析和数据整理、图表绘制。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 红丽海棠茎尖玻璃化超低温保存程序的建立
2.1.1 预培养基蔗糖浓度对液氮冻存后茎尖存活率的影响
将红丽海棠带顶芽茎段分别在含0.1、0.3、0.5、0.7、0.9 mol·L−1蔗糖的预培养基上进行2 d的培养,之后采用后续的基本程序,测定液氮冻存后茎尖存活率。如图2所示,茎尖冻后存活率随蔗糖浓度的升高先上升再下降,0.3 、0.5 、0.7 mol·L−1蔗糖浓度培养的茎尖存活率没有显著差异,但0.7 mol·L−1蔗糖浓度的预培养基上茎尖冻后存活率最高,为76.54%,显著高于0.1 、0.9 mol·L−1蔗糖浓度。因此红丽海棠超低温保存程序中预培养基的最适蔗糖浓度为0.7 mol·L−1,浓度过低过高则会降低茎尖的存活率。
2.1.2 预处理时间对液氮冻存后茎尖存活率的影响
将带顶芽的红丽海棠茎段接种于含0.7 mol·L−1蔗糖的预培养基上,在4 ℃条件下分别培养1 、2 和3 d,继续超低温保存基本程序的后续环节,液氮冻存后红丽茎尖存活率见图3。随预处理时间的增加,茎尖存活率逐渐升高,在2 d时存活率最高达到79.24%,后又下降。表明液氮冻后茎尖存活率受预培养环节冷锻炼时间的影响,适宜时长可以提高茎尖的抗冻能力。
2.1.3 Loading溶液处理时间对液氮冻存后茎尖存活率的影响
红丽海棠茎段在含0.7 mol·L−1蔗糖浓度的预培养2 d后,将茎尖分别在Loading溶液中处理不同时间,继续超低温保存基本程序的后续环节,从液氮取出化冻后茎尖存活率的结果如图4所示。Loading处理20 min时茎尖存活率最高,为60.61%,而随着处理时间的继续延长逐渐下降,处理40 min时的茎尖存活率为0。因此,Loading溶液处理时间不宜过长,否则可能会造成茎尖过度脱水而降低存活率。红丽海棠茎尖超低温保存的适宜Loading处理时间为20 min。
2.1.4 PVS2溶液处理时间对液氮冻存后茎尖存活率的影响
红丽海棠茎段在4 ℃下,含0.7 mol·L−1蔗糖浓度的预培养基上培养2 d后,Loading溶液处理20 min,分别采用PVS2溶液处理不同时间,继续超低温保存基本程序的后续环节,结果如图5。未经PVS2溶液处理的茎尖全部死亡,说明PVS2处理对玻璃化超低温保存过程起着至关重要的作用,随处理时间的增加,茎尖冻后存活率逐渐升高,处理90 min时茎尖存活率最高,为62.88%,后随时间的延长而显著下降。红丽海棠茎尖超低温保存PVS2处理适宜时间为90 min。
2.2 外源添加剂对茎尖超低温保存效果的影响
2.2.1 预培养环节添加外源Eth对液氮冻存后茎尖存活率的影响
在红丽海棠茎尖超低温保存中预培养环节添加4个质量浓度的外源Eth,继续超低温保存优化后的后续环节,茎尖冻后存活率见图6。添加100~400 mg·L−1与对照没有显著差异,200 mg·L−1时存活率稍高,而100 、400 mg·L−1时存活率稍低,而质量浓度过高时(800 mg·L−1)存活率显著下降。说明在预培养环节导入200 mg·L−1Eth时可能起到一定保护作用,小幅度提高冻后存活率,高浓度反而会导致其存活率降低。
2.2.2 Loading环节添加外源CAT或SNP对液氮冻存后茎尖存活率的影响
采用预培养优化方案后,在Loading环节添加不同浓度的外源CAT,之后继续超低温保存优化后的后续环节,茎尖液氮冻存后存活率见图7。添加200 U·mL−1时,茎尖的存活率最高,为86.67%,显著高于其他处理;含量为50 U·mL−1稍有提高,但差异不显著,其余含量显著下降。由此可知,Loading环节添加适宜浓度的外源CAT浓度可以发挥抗氧化保护作用,显著提高茎尖冻后存活率。
采用预培养优化方案后,在Loading环节添加不同浓度的外源SNP,之后继续超低温保存优化后的后续环节,茎尖超低温保存后存活率如图8所示。各浓度处理后冻后存活率均下降,但添加100和1000 μmol·L−1SNP时与对照无明显差异,而添加50和200 μmol·L−1SNP时存活率显著下降,相比对照分别降低了23.25%和13.25%。表明对PCD有拮抗作用的SNP在这里没有显示其作用。
2.2.3 PVS2环节添加外源GSH对液氮冻存后茎尖存活率的影响
采用优化的预培养和Loading方案后,在PVS2环节添加不同浓度的外源GSH,之后继续超低温保存后优化的后续环节,茎尖液氮冻存后存活率见图9。添加各种浓度的GSH,较对照均显著提高了茎尖冻后的存活率,其中导入浓度为0.04 μmol·L−1时存活率最高,为94.19%。由此表明,在PVS2环节导入外源GSH可有效发挥抗氧化保护作用,提高存活率。
2.2.4 Unloading环节添加外源AsA对液氮冻存后茎尖存活率的影响
采用优化的保存程序后,在Unloading环节导入不同浓度的外源AsA,茎尖超低温保存后存活率如图10所示,除200 μmol·L−1存活率下降外,其余浓度均可提高冻后存活率,效果最好的浓度为400 μmol·L−1,说明外源AsA起到了一定的抗氧化保护作用,小幅度提高了存活率。
2.3 红丽海棠茎尖超低温保存后恢复培养
采用优化后的超低温保存程序,在PVS2环节添加0.04 μmol·L−1的外源GSH,之后继续超低温保存后优化的后续环节,并进行恢复培养。没有添加GSH的对照组恢复生长率为16.67%,添加0.04 μmol·L−1外源GSH的恢复生长率为41.39%,提高了24.73%。
3. 讨论
冷锻炼能够提高植物茎尖的抗冻能力[14],通过在含有一定浓度的高糖、山梨醇或DMSO的培养基中培养植物茎尖,可以显著提高冻存后茎尖的存活率[15]。在大部分苹果属玻璃化超低温保存中,都至少需要3~4周的4 ℃或5 ℃的冷锻炼[16-19]。本试验通过4 ℃预培养,起到冷锻炼作用,预培养2 d,超低温保存后的茎尖存活率可到79.24%。在苹果属其他茎尖超低温保存的研究中,有不使用Loading处理直接脱水处理[20-22],本试验不经Loading溶液处理也可达到36.11%的存活率,但经Loading溶液处理20 min的茎尖冻后存活率更高,因为装载阶段是实现玻璃化而脱水处理的过渡阶段,能够避免高浓度玻璃化溶液引起的剧烈渗透变化导致的材料损伤。另外在本试验中0 ℃条件下PVS2处理90 min后茎尖冻后存活率最高,也有研究在室温下进行脱水处理,如将苹果品种嘎啦、望山红在室温下用PVS2处理30 min[10]或40 min[11]后再生率分别为55.6%和17.9%,但Uragami等[23]认为低温能降低玻璃化溶液的高渗作用导致的植物损伤,因此在大多数植物的超低温研究中,玻璃化步骤均在0 ℃下进行[24, 25]。
ROS是需氧生物中细胞有氧代谢的副产物,在正常状态下,机体可以在ROS的产生和清除之间保持动态平衡,但当ROS在逆境胁迫下产生过量时,自身的抗氧化系统,包括CAT、SOD和POD等酶类,以及AsA和GSH等非酶类系统会协同作用清除抵抗ROS可能带来的伤害,但当抗氧化能力不足以清除过量的ROS时,机体就会出现氧化应激。这启发研究人员们通过导入外源抗氧化剂来抵御氧化损伤,研究证明外源CAT[4, 13, 26]、AsA[4, 27]和GSH[6]均有抑制氧化应激的作用。本研究结果也显示,外源抗氧化剂CAT、AsA和GSH可以提高红丽海棠茎尖冻后存活率,说明外源抗氧化剂可能抑制了ROS造成的氧化损伤。3种外源抗氧化剂在不同环节中使用,分别提高了红丽海棠茎尖冻后存活率20.28%、6.75%、27.61%。
PCD作为一种自发性、有序的细胞死亡方式,受基因调控,是生物生活的基本过程。多项研究表明植物PCD存在于植物的各个生长发育过程及植物对非生物胁迫的响应中[28]。有研究显示超低温保存中预培养是PCD的一个信号起始环节,PCD相关调控基因显著上调[7],由于细胞凋亡存在一定的延迟性,预培养后的Loading环节也成为超低温保存中PCD研究的另一重要环节。本试验在预培养和Loading环节添加了PCD抑制剂,结果显示预培养环节添加外源Eth只是小幅度提高了红丽海棠茎尖冻后存活率,而在Loading环节添加外源SNP冻后存活率反而下降了,SNP通过抑制PCD信号分子NO而其作用,而NO调控PCD具有双重作用,可以促进PCD的发生[29, 30],也可以抑制PCD的发生[31, 32],而添加环节对NO在PCD发生的作用也十分关键,如在春石斛类原球茎中预培养环节导入NO供体(SNP)促进了PCD的发生,降低了存活率,而在Loading环节添加则抑制了PCD的发生[7],故推测外源SNP对不同的植物和不同添加环节可能有不同的影响效果。
4. 结论
红丽海棠茎尖采用以下程序可以实现超低温保存:取组培苗4~5 mm带顶芽茎段,接种在含0.7 mol·L−1蔗糖的预培养基,4 ℃冰箱培养2 d;切取1.5~2.0 mm的茎尖,Loading溶液室温下处理20 min;PVS2溶液0 ℃下处理90 min,可存入液氮保存;需用时将其取出放入38 ℃水浴快速化冻1 min;在室温下Unloading溶液震荡洗涤2次,每次10 min;进行恢复培养,存活率为66.58%,恢复生长率为16.67%。在Loading、PVS2和Unloading环节导入适宜浓度的抗氧化物质CAT、GSH、AsA可明显提高冻后存活率,最佳添加量分别为200 U·ml−1、0.04 μmol·L−1和400 μmol·L−1,较对照存活率分别提高了20.28%、27.61%和6.75%,而添加PCD抑制剂没有显示明显作用
-
表 1 L9(34)正交试验分析因素与水平
Table 1 Factors and levels of orthogonal experiment
因素 因素/(g·L-1) 葡萄糖 豆饼粉 KH2PO4 -1 20 10 1 0 30 20 2 1 40 30 4 表 2 正交优化结果极差分析
Table 2 Range analysis on orthogonal test results
水平 因素/(g·L-1) 黄原胶产量
/(g·L-1)葡萄糖 豆饼粉 KH2PO4 1 40 30 1 15.29±1.83 2 20 20 4 13.61±1.22 3 40 10 4 11.14±0.55 4 20 30 2 14.39±0.48 5 30 30 4 17.71±1.02 6 40 20 2 16.34±0.19 7 30 20 1 13.83±0.43 8 30 10 2 12.07±0.37 9 20 10 1 9.51±0.09 低 20 10 1 - 中 30 20 2 - 高 40 30 4 - Ⅰ 0.625 0.545 0.644 - Ⅱ 0.713 0.730 0.713 - Ⅲ 0.727 0.790 0.708 - R 0.102 0.245 0.070 - 表 3 黄原胶中中性糖、丙酮酸和蛋白质的含量
Table 3 Neutral sugar, pyruvic acid and protein contents in xanthan gum produced from fermentation
项目 中性糖
/%丙酮酸
/%蛋白质
/%标准曲线 葡萄糖 葡萄糖醛酸 牛血清白蛋白 相关系数(R2) 0.9980 0.9982 0.9980 黄原胶1 36.81 8.9 15.27 黄原胶2 25.3 16.3 4.8 注:黄原胶1:基础培养基提取的黄原胶[10];黄原胶2:优化培养基后提取的黄原胶。中性糖线性方程为OD490nm=0.0331CGlu +0.1151;丙酮酸线性方程为OD530nm=15.256CGlcA+0.0782;蛋白质线性方程为OD580nm=0.0293CBSA +0.4233。 -
[1] 吉武科, 李振平.黄原胶的应用与发展前景[J].中国食品添加剂, 1994, (4):27-30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPKJ605.023.htm [2] GARCIÍA-OCHOA F, SANTOS V E, CASAS J A, et al. Xanthan gum:production, recovery, and properties[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2000, 18(7):549-579. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-9750(00)00050-1
[3] ESQUENET C, BUHLER E. Aggregation Behavior in Semidilute Rigid and Semirigid Polysaccharide Solutions[J]. Macromolecules, 2002, 35(9):3708-3716. DOI: 10.1021/ma012047q
[4] SPICLIN P, HOMAR M, ZUPANCIC-VALANT A, et al. Sodium ascorbyl phosphate in topical microemulsions[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2003, 256(1-2):65-73. DOI: 10.1016/S0378-5173(03)00063-2
[5] 马天玲, 于娟, 朱海霞, 等.黄原胶的生产应用及发展趋势[J].新疆石油科技, 2007, (2):27-30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXJ200702012.htm [6] 颜震, 吴尽, 朱希强, 等.黄原胶发酵工艺条件的优化研究[J].食品与药品, 2006, 8(11):39-42. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-979X.2006.11.011 [7] KALOGIANNIS S, IAKOVIDOU G, LIAKOPOULOU-KYRIAKIDES M, et al. Optimization of xanthan gum production by Xanthomonas campestris grown in molasses[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2003, 39(2):249-256. DOI: 10.1016/S0032-9592(03)00067-0
[8] PALANIRAJ A, JAYARAMAN V. Production, recovery and applications of xanthan gum by Xanthomonas campestris[J]. Journal of Food Engineering, 2011, 106(1):1-12. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2011.03.035
[9] 张超凤, 范丽君, 李情敏, 等.突变型黄单胞杆菌产黄原胶条件的优化[J].中国酿造, 2016, 35(5):92-96. DOI: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2016.05.019 [10] 郑梅霞, 朱育菁, 刘波, 等.微生物多糖胶质高产菌株的筛选与鉴定[J].食品科学, 2016, 37(15):171-178. DOI: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201615029 [11] 程蓉, 张永奎, 张春红, 等.高丙酮酸黄原胶的发酵研究[J].食品工业科技, 2008, 29(3):234-236. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPKJ200803087.htm [12] 莫晓燕, 吉丽娜, 詹谷宇.黄原胶发酵培养基优化研究[J].工业微生物, 2003, 33(2):15-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYWS200302004.htm [13] SOMAS S K, LIAKOPOULOU-KYRIAKIDES M, KYRIAKIDIS D A. Optimization study of xanthan gum production using response surface methodology[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2007, 35(3):273-280. DOI: 10.1016/j.bej.2007.01.036
[14] DUBOIS M, GILLES K A, HAMILTON J K, et al. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1956, 28(3):350-356. DOI: 10.1021/ac60111a017
[15] 梁涛. 微生物胞外多糖-结冷胶提取工艺研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2011. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10335-1011244784.htm [16] 王孝平, 邢树礼.考马斯亮蓝法测定蛋白含量的研究[J].天津化工, 2009, 23(3):40-42. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJHG200903020.htm [17] 刁虎欣, 梁兴杰, 梁凤来, 等.野油菜黄单胞菌原生质体分泌黄原胶的电镜观察[J].微生物学通报, 2001, 28(5):18-20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSWT200105004.htm [18] 秦志刚, 詹晓北, 贾薇, 等, 高丙酮酸黄原胶发酵与流变特性研究[J], 食品与发酵工业, 2007, 33(1):32-35. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPFX200701008.htm [19] 田益玲, 沈磊, 祝彦忠, 等.丙酮酸荧光分光光度法在黄原胶质量控制上的应用[J].中国食品学报, 2006, 6(1):79-82. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSP200601021.htm [20] 张禹, 张国佩, 张茶, 等.提高黄原胶丙酮酸含量的发酵实践[J].食品工业科技, 2002, 22(9):30-31. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPKJ200209018.htm -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 朱建行,何亚文,欧杰. 白原胶基因工程菌株Xanthomonas campestris ΔrpfBΔxanK发酵工艺优化. 微生物学杂志. 2024(04): 14-22 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 冯玉红,李菊生,吴伟都,陈晓霞,徐玲玲,王雅琼,王静,赵志红,李言郡. 氯化钾对黄原胶溶液质量特性的影响研究. 饮料工业. 2022(05): 8-12 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李玉平,李惟雄. 微量元素对大花金挖耳悬浮细胞生长与黄酮含量的影响及其化感作用. 福建农业学报. 2019(01): 1-8 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 郑梅霞,朱育菁,刘波,陈峥,黄素芳. 黄原胶FJAT-10151-DTJZ提高酸奶冰淇淋的抗融性. 福建农业学报. 2018(10): 1113-1118 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载: