EST-SSR-based Analyses on Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of 64 Tea Varieties
-
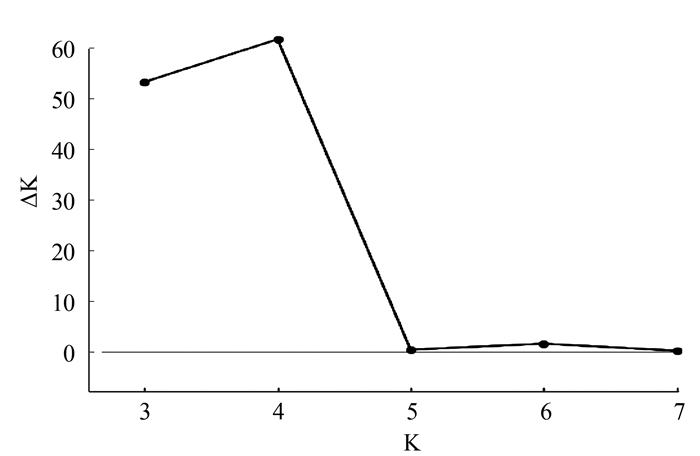
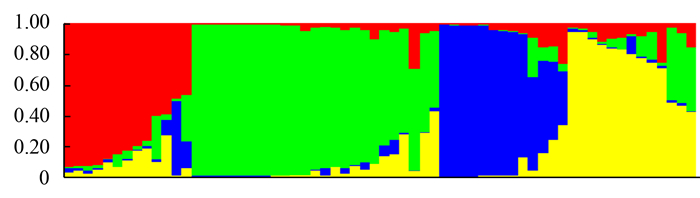
摘要: 为实现茶树亲本材料的系统分类,利用20对SSR对64个来自福建、浙江、广东的茶树品种进行遗传多样性与群体结构分析。结果表明:20对SSR引物共扩增147个多态位点,每对引物为3~15个,平均7.35个;引物多态性信息含量(PIC)在0.267-0.851,平均值为0.588。期望杂合度大小0.247~0.838,平均为0.559;观测杂合度在0.308~0.870,平均值为0.636;群体Shannon指数为1.271。群体结构分析表明,当K值等于4时,ΔK取得最大值,64份材料可以划分为4个亚群。其中60份(93.8%)供试材料的Q值大于或等于0.5,分属于4个亚群。4份材料(6.2%)划分为混合亚群。Abstract: To establish a systematic classification for the tea varieties in Fujian, Zhejiang and Guangdong, 20 pairs of SSR primers were selected in analyzing the genetic diversity and population structure of 64 tea cultivars commonly found in the regions. A total of 147 polymorphic loci were amplified with an average of 7.35 alleles per primer (ranging 3-15) and an average polymorphism information contentof 0.588 (ranged 0.267-0.851). The expected heterozygosity varied from 0.247 to 0.838 averaging 0.559; while, the observed heterozygosity, from 0.308 to 0.870 averaging 0.636. The Shannon index of the 64 teas was 1.271. The maximum ad hoc quantity, ΔK, was observed when K=4 in the population structure analysis, indicating that the entire collection could be divided into four subpopulations. Using a membership probability threshold of ≥ 0.50, 60 genotypes (accounting for 93.8% of the tested genotypes) were assigned to the four subpopulations, and 4(accounting for 6.2% of the tested breeding parents) retained in the admixed group.
-
Keywords:
- tea plant /
- EST-SSR /
- genetic diversity /
- population structure
-
近年来,我国畜牧业发展趋向规模化和集约化,生猪养殖尤为明显。据统计,2017年我国母猪存栏量4 000多万头,且规模化猪场占60%以上[1]。规模化和集约化养殖发展的同时也伴随畜禽的发病率和死淘率上升,据资料显示我国每年因各类疾病引起猪死亡率为8%~12%,大量病死猪的处理为当前棘手的问题[2]。病死猪携带病原体,若未经无害化处理、任意堆置,不仅污染环境,还可能引起重大疫情,危害畜禽生产安全甚至引发严重威胁公共卫生事件。因此,有必要探寻高效降解病死猪的处理模式。
利用微生物的好氧发酵技术无害化处理病死畜禽技术最早可追溯至20世纪80年代末期。好氧发酵技术最早被用来处理病死家禽,如鸭、鸡等,因处理方便又相对无害,逐渐被用于死猪、死牛和死马等大型动物[3-6]的处理。近些年,随着生猪养殖向规模化和集约化发展,病死猪处理成为亟待解决的问题,有关好氧发酵处理病死猪的相关研究也逐渐增多。Ahn等[7]证明大多数死猪在微生物好氧发酵处理6周后死猪的分解率可达86%。Glanville等[8]证实用自然箱式秸秆发酵模式处理4个月后才能完成病死猪的分解。Murray等[9]用堆叠发酵系统处理病死猪,整个处理周期持续了400 d,结果发现猪的基因物质和线粒体DNA均被降解。而我国对病死猪的好氧发酵也进行了一系列的研究。郭东坡等[10]在容积约1 m3的箱中对死猪进行好氧发酵试验,结果表明死猪无害化处理的合适条件是通风率小于100 L·m-3·min-1和发酵时间大于6周。可以看出,微生物好氧发酵模式可以较好地降解病死猪,但处理周期较长。
嗜热菌又名高温菌,是一类生活在高温环境中的微生物。根据温度不同可分为耐热菌、兼性嗜热菌、专性嗜热菌、极端嗜热菌和超嗜热菌。近年来,高温病死猪处理设施因处理方便和相对安全,大部分规模养殖场都有配备,政府也大力推荐这种处理模式。通过添加嗜热菌,可以加快高温处理代谢速度,减少非嗜热菌的杂菌污染,从而促进高温环境下有机物的降解,从而提高生物可利用性。但是,高温病死猪处理也存在生物降解瓶颈。在生物降解过程中,很多微生物没法在这种极热环境中生存,导致高温处理后病死猪降解不充分,有害微生物滋生,引发新的安全隐患。本研究利用前期筛选的复合极端嗜热菌对病死猪进行高温处理,研究其对病死猪高温处理中氨基酸降解效果,为提高病死猪降解效果及极端嗜热菌筛选提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
复合极端嗜热菌剂由福建省农业科学院畜牧兽医研究所动物营养研究室从有机肥发酵场分离所得,由4株嗜热菌组成;其中一株为热噬淀粉芽孢杆菌HL8103[11], 另3株经菌株形态、菌落形态和生理生化特征等初步鉴定为嗜热脂肪芽孢杆菌、速生热球菌和热红芽孢杆菌。
LB培养液(L):酵母粉10 g,蛋白胨10 g,NaCl 10 g,pH7.0,加蒸馏水定容至1 L。121℃灭菌30 min。
分离纯化固体培养基:LB培养液中时加入20 g琼脂粉,121℃灭菌30 min。液体发酵培养基:LB培养液+玉米淀粉。
酵母粉、蛋白胨、NaCl、硫酸、硼酸、硫酸铜、硫酸钾、氢氧化钠、辛醇、盐酸等均为AR级,茚三酮染色剂和缓冲液、氨基酸标准液和稀释液均购于德国menbarPure公司。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 菌株的培养
纯化培养:将HL8103菌划菌斜面置于75℃培养箱内培养18 h,置于4℃冰箱保存。
种子培养:在250 mL三角瓶中装入25 mL种子培养基,121℃灭菌30 min后,取培养好的斜面挑取1环于种子培养基中,75℃、120 r·min-1摇床培养18 h。
发酵培养:在250 mL三角瓶中装入25 mL发酵培养基,121℃灭菌30 min后,按体积分数0.1%的接种量接入种子液,75℃、120 r·min-1摇床培养18 h。
1.2.2 不同温度下HL8103菌生长曲线
研究菌株HL8103在55、60、65、70、75、80、85、90、95、100℃的生长情况,在培养9、10、11、12、14、15、16、17、18、19、20、21、22、23、24 h测定其活菌数。活菌数量测定采用平板计数法,涂布平板设置3次重复,取平均值。活菌数LG值=Log10(活菌数)。
1.2.3 复合极端嗜热菌制备
经发酵培养的HL8103菌与另3株菌按3:1:1:1(v/v/v/v)混合均匀备用。该复合极端嗜热菌含量为109CFU·mL-1。
1.2.4 复合极端嗜热菌氨基酸降解效果分析
试验在漳州市众福生物科技有限公司的漳浦县病死畜禽无害化处理中心进行。将病死猪投入自动控温的畜禽养殖场有机废弃物处理机中粉碎加热3~4 h后,添加10%锯末、稻壳、秸秆等农林副产物作为辅料。经充分混合后在处理机4个不同部位(A、B、C、D点)重复取样,3次重复,作为发酵处理前样品(Q组);此后该处理机温度达90℃,按不同添加量0.05%(a组)、0.08%(b组)、0.10%(c组)、0.12%(d组)分别加入复合极端嗜热菌,保持70~95℃进行发酵。经19 h发酵后,处理机不再加热但其搅拌系统照常工作至其罐体温度50℃时打开出料阀门,分别对处理机排出的发酵产物进行取样,3次重复。Wj组不添加复合极端嗜热菌在同上处理机高温处理后经60 d堆肥,在高100 cm堆体从上至下每20 cm采样(最底下不取样), 3次重复。采样量200 g。5组样品分别进行充分混合后分为两份,一份-18℃冷冻保存用于微生物群落测序;另一份于60℃干燥箱中干燥至恒重;用粉碎机粉碎,过60目筛,制成绝干样本,置磨口样本瓶中保存,用于测定氨基酸组分。
1.3 指标测定
1.3.1 氨基酸测定[12]
按GB/T18246-2000方法,采用德国的menbarPureA300全自动氨基酸分析仪进行测定。
1.3.2 微生物组总DNA提取及纯化
按照常规DNA提取流程提取微生物组总DNA,并对DNA进行定量。根据荧光定量结果,按照每个样本的测序量需求,对各样本按相应比例进行混合[13-16]。
1.3.3 测序文库制备及高通量测序
采用Illumina公司的TruSeq Nano DNA LT Library Prep Kit制备测序文库。上机测序前,先在Agilent Bioanalyzer上进行质检,接着采用Quant-iT PicoGreen dsDNA Assay Kit对文库进行定量,将合格的各上机测序文库按所需测序量相应比例混合,再使用MiSeq测序仪进行2×300 bp的双端测序,分析微生物多样性。
1.3.4 菌群代谢功能数据分析
运用引物和Barcode信息筛查原始下机数据;识别并踢除嵌合体等存在疑问序列;然后按照OTU归并划分序列,并根据OTU的丰度分布,评估每个样本的多样性水平,通过稀疏曲线反映测序深度;然后分析各处理(组)在不同分类水平的具体组成及组间是否具有统计学差异;通过多变量统计学分析工具,衡量不同处理(组)间的菌群结构差异及与差异相关的物种[17-18];根据物种在各样本中的组成分布,构建互作关联网络;最后再根据16S rRNA基因测序结果,预测各样本的菌群代谢功能。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 HL8103菌株生长曲线
生长曲线可反映细菌整个培养期间菌数变化规律。图 1显示,在75℃培养温度下HL8103菌的生长规律。可以看出,在培养过程中,菌体活菌数随时间呈现逐渐增长后快速下降的变化趋势,0~4 h是菌体适应新环境的偿还期;4~16 h为生长繁殖迅速、细胞活力最大的对数生长期;16~18 h为稳定生长期,活菌数(LG值)最高,为9.82;18 h后,活菌数下降,由于自溶酶作用或有毒代谢产物积累,细胞裂解。表明HL8103菌的最适培养时间为18 h。
2.2 培养温度对HL8103菌株生长的影响
培养温度是影响微生物生长和代谢的最重要的环境因素之一。适当提高培养温度有助于促进微生物的生长和酶促反应。从图 2可以看出,在培养温度为55℃时,活菌数(LG值)5.24,随着培养温度的升高,活菌数逐渐提高,当培养温度为75℃时,活菌数(LG值)最高(9.36);之后随着培养温度升高,菌活数下降。当培养温度为100℃时,活菌数(LG值)仍有6.41。可知该菌的最佳培养温度为70~95℃。
2.3 复合极端嗜热菌处理病死猪的氨基酸降解效果
从表 1可以看出,除了色氨酸无法测,其他17种氨基酸均能测出。氨基酸总量由高到低为Q组>a组>b组>d组>c组>Wj组。试验组a、b、c、d间无显著差异,比Q组分别下降4.36%、13.22%、14.58%、13.31%,差异显著(P<0.05),显著高于Q组;b、c、d组与a组相比,下降7.04%、8.49%、7.13%(P>0.05)。
表 1 氨基酸含量(干物质基础,n=13,%)Table 1. Amino acid composition (% ondry matter base, n=13)项目 Q组 a组 b组 c组 d组 Wj组 天冬氨酸 2.53±0.11a 2.47±0.08a 2.27±0.10b 2.28±0.09b 2.24±0.12b 1.95±0.07c 苏氨酸 1.01±0.02a 0.97±0.04a 0.82±0.01b 0.80±0.05b 0.81±0.02b 0.75±0.03c 丝氨酸 0.94±0.06a 0.89±0.07a 0.85±0.02a 0.84±0.05a 0.87±0.03a 0.70±0.04b 谷氨酸 4.03±0.09a 3.96±0.11a 3.27±0.13b 3.21±0.08b 3.25±0.10b 3.23±0.08b 甘氨酸 1.87±0.05a 1.84±0.07a 1.71±0.01b 1.68±0.04b 1.72±0.03b 1.51±0.05c 丙氨酸 1.71±0.06a 1.67±0.03a 1.47±0.05b 1.48±0.01b 1.45±0.05b 1.32±0.02c 胱氨酸 0.16±0.01a 0.12±0.02b 0.13±0.01a 0.14±0.03a 0.11±0.04b 0.14±0.02a 缬氨酸 1.45±0.07a 1.44±0.05a 1.20±0.03b 1.18±0.07b 1.16±0.04b 1.16±0.09b 蛋氨酸 0.25±0.01a 0.19±0.04b 0.21±0.05b 0.20±0.04b 0.18±0.02b 0.24±0.06a 异亮氨酸 0.95±0.02a 0.91±0.05a 0.82±0.03b 0.81±0.06b 0.85±0.03b 0.80±0.05b 亮氨酸 1.92±0.03a 1.90±0.02a 1.67±0.02b 1.65±0.04b 1.70±0.03b 1.52±0.05c 酪氨酸 0.44±0.01a 0.38±0.02a 0.35±0.04b 0.36±0.02b 0.33±0.01b 0.35±0.04b 苯丙氨酸 1.18±0.06a 1.17±0.08a 1.05±0.04b 1.01±0.06b 1.06±0.08b 0.980.07c 组氨酸 0.71±0.02a 0.67±0.01a 0.70±0.05a 0.68±0.03a 0.73±0.03a 0.59±0.01b 赖氨酸 1.64±0.03a 1.59±0.05a 1.34±0.02b 1.31±0.09b 1.35±0.07b 1.19±0.03c 精氨酸 1.23±0.08a 1.19±0.06a 0.97±0.07b 0.93±0.09b 0.99±0.08b 0.90±0.05b 脯氨酸 1.61±0.11a 1.58±0.09a 1.64±0.07a 1.60±0.08a 1.68±0.09a 1.08±0.07b 总量 23.60±0.21a 22.03±0.37b 20.48±0.51b 20.16±0.13b 20.46±0.46b 18.41±0.25c 注:同行数据后不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 从氨基酸组分来看,所测的17种氨基酸中,胱氨酸a、d组含量显著低于Q、b、c、Wj组,蛋氨酸a、b、c、d组显著低于Q、j组。两种氨基酸的变化没有明显规律,可能是酸水解法造成含硫氨基酸的破坏;天冬氨酸、苏氨酸、甘氨酸、丙氨酸、亮氨酸、苯丙氨酸、赖氨酸等7种氨基酸变化的趋势相近,均为Q、a组>b、c、d组>Wj组,差异显著。谷氨酸、缬氨酸、异亮氨酸、酪氨酸、精氨酸等5种氨基酸变化的趋势相近,Q组和a组间没有显著差异,但显著高于b、c、d、Wj组。丝氨酸、组氨酸、脯氨酸等3种氨基酸的变化趋势相近,Q、a、b、c、d组之间无显著差异,均显著高于Wj组。说明添加0.08%~0.12%的复合极端嗜热菌对大部分氨基酸组分有更充分降解的效果。
2.4 菌群代谢功能差异
如图 3所示,病死猪处理前样品A1~A3(A), B1~B3(B), C1~C3(C), D1~D3(D)(4个样点3次重复取样,共计12份样品)的菌群结构非常接近,只有D1、C1和其他采样点的菌群有一定差异。加入不同浓度的极端嗜热菌处理后(F组,a、b、c、d处理)菌群的结构差异非常明显,完全不在一个区,同时极端嗜热菌处理后的菌群结构(a、b、c、d)和无添加菌高温处理后发酵60 d的Wj处理在同一区,菌群结构相似,说明复合极端嗜热菌处理病死猪的氨基酸降解菌群与发酵堆肥处理接近。
从图 4可看出,极端嗜热菌处理后(F组,a、b、c、d处理)的菌群氨基酸的代谢功能类群的丰度远高于处理前的样品Q组(A、B、C、D),说明F组中的氨基酸代谢更为旺盛,进一步证实大量的氨基酸代谢菌的存在,推动病死猪处理中的氨基酸代谢,促进了病死猪的氨基酸的降解,提升了降解率。
![]() 图 4 各组微生物群代谢功能类群相对丰度注:图中横坐标为KEGG第二等级功能类群,横坐标下各类代谢通路A~L分别表示。A:异物生物降解与代谢; B:核酸代谢;C:萜类和聚酮代谢;D:其他氨基酸代谢;E:辅酶因子及维生素代谢;F:脂肪代谢;G:多糖生物合成及代谢;H:酶家族;I:能量代谢;J:碳水化合物代谢;K:其他次代谢物合成;L:氨基酸代谢。纵坐标为各功能类群在各样本(组)内的相对丰度。横线代表中位值,上下触须分别代表上下四分位以外的1.5倍IQR范围,符号“-”表示超过范围的极端值。Figure 4. Relative abundance of metabolic functional groups of microbial communities in each group
图 4 各组微生物群代谢功能类群相对丰度注:图中横坐标为KEGG第二等级功能类群,横坐标下各类代谢通路A~L分别表示。A:异物生物降解与代谢; B:核酸代谢;C:萜类和聚酮代谢;D:其他氨基酸代谢;E:辅酶因子及维生素代谢;F:脂肪代谢;G:多糖生物合成及代谢;H:酶家族;I:能量代谢;J:碳水化合物代谢;K:其他次代谢物合成;L:氨基酸代谢。纵坐标为各功能类群在各样本(组)内的相对丰度。横线代表中位值,上下触须分别代表上下四分位以外的1.5倍IQR范围,符号“-”表示超过范围的极端值。Figure 4. Relative abundance of metabolic functional groups of microbial communities in each group3. 讨论与结论
从病死猪混合物发酵前后氨基酸的总量可知,在同等条件下添加复合极端嗜热菌可使病死猪组织的氨基酸分解、吸收及代谢加快,与张浩等[19]、Maricou H等[20]的研究结果一致。
本研究病死猪在畜禽养殖场有机废弃物处理机中经95℃、19 h发酵,从处理后的氨基酸组分的降解可以看出,添加0.08%~0.12%复合极端嗜热菌处理可明显提高病死猪的氨基酸降解效果,与处理前样品相比,0.08%~0.12%添加量可显著降低氨基酸总量及大部分氨基酸组分(除丝氨酸、组氨酸、脯氨酸)含量,与低剂量0.05%添加量相比,添加0.08%~0.12%复合极端嗜热菌可显著降低谷氨酸、缬氨酸、异亮氨酸、酪氨酸、精氨酸等5种氨基酸的量,其降解效果与堆肥60 d处理Wj组没有显著差异。说明添加0.08%~0.12%极端嗜热菌就能有效降解病死猪组织。病死畜禽好氧发酵(堆肥)是利用微生物在一定温度、湿度和pH条件下,使有机物氧化分解成简单无机物,并释放能量产生高温,高温可使病原菌灭活。有机物发生各种理化性质和生物学性质的变化,然后逐渐趋于稳定,最终达到腐殖化,形成有机复合肥[21]。和堆肥发酵相比,接种极端嗜热菌处理,降解效果相似,但可明显减少处理时间,高效安全,促进病死猪组织蛋白质彻底分解。
为了更深入分析复合极端嗜热菌影响病死猪氨基酸代谢的机制,本研究比较各处理样品的菌群代谢功能丰度差异。结果表明,添加复合极端嗜热菌处理的氨基酸代谢功能菌群丰度增加明显,这一方面是因为添加复合极端嗜热菌的代谢功能,另一方面可能是复合极端嗜热菌激活了其他氨基酸代谢功能菌的代谢作用,这在菌群组成上可以看到菌群丰度大大增加,氨基酸代谢加快,病死猪降解速度提高, 以减少二次污染和次生人畜共患疾病的风险。
病死猪降解主要是碳水化合物、脂肪、蛋白质及矿物质微量元素的代谢,本试验研究结果表明添加复合极端嗜热菌的脂肪代谢菌的丰度也高于其他处理组,说明添加复合极端嗜热菌处理的脂肪代谢也更为旺盛。具体有待进一步验证[22-25]。
本研究采取的高温生物降解病死猪处理模式,为高温灭菌和生物降解有机结合,既提高了效率,又保证了无害化处理,是一种无害化处理病死猪的较好模式。
-
表 1 64份供试茶树品种(系)
Table 1 64 tea varieties (strains) used for study
品(系)种名称 来源 萌芽期 主要适制茶类 白芽奇兰 福建 晚生种 乌龙茶 春闺 福建 晚生种 乌龙茶 大红袍 福建 晚生种 乌龙茶 凤圆春 福建 晚生种 乌龙茶 福建水仙 福建 晚生种 乌龙茶 铁观音 福建 晚生种 乌龙茶 杏仁茶 福建 晚生种 乌龙茶 八仙茶 福建 特早生种 乌龙茶 朝阳 福建 早生种 乌龙茶 春兰 福建 早生种 乌龙茶 黄观音 福建 早生种 乌龙茶 黄玫瑰 福建 早生种 乌龙茶 黄奇 福建 早生种 乌龙茶 黄棪 福建 早生种 乌龙茶 金观音 福建 早生种 乌龙茶 金牡丹 福建 早生种 乌龙茶 矮脚乌龙 福建 中生种 乌龙茶 大叶乌龙 福建 中生种 乌龙茶 红芽佛手 福建 中生种 乌龙茶 九龙袍 福建 晚生种 乌龙茶 绿芽佛手 福建 中生种 乌龙茶 毛蟹 福建 中生种 乌龙茶 梅占 福建 中生种 乌龙茶 瑞香 福建 晚生种 乌龙茶 悦茗香 福建 中生种 乌龙茶 紫玫瑰 福建 中生种 乌龙茶 紫牡丹 福建 中生种 乌龙茶 丹桂 福建 早生种 乌龙茶 肉桂 福建 晚生种 乌龙茶 白鸡冠 福建 晚生种 乌龙茶 福鼎大白茶 福建 早生种 绿茶 福鼎大毫茶 福建 早生种 绿茶 福云10号 福建 早生种 绿茶 福云20号 福建 中生种 绿茶 福云595 福建 早生种 绿茶 福云6号 福建 特早生种 绿茶 福云7号 福建 早生种 绿茶 歌乐茶 福建 早生种 绿茶 九龙大白茶 福建 早生种 绿茶 榕春早 福建 早生种 绿茶 霞浦春波绿 福建 特早生种 绿茶 霞浦元宵茶 福建 特早生种 绿茶 早春毫 福建 特早生种 绿茶 政和大白茶 福建 晚生种 绿茶 白毛2号 广东 早生种 乌龙茶 凤凰单枞 广东 早生至晚生种 乌龙茶 金萱 台湾 中生种偏早 乌龙茶 四季春 台湾 早生种 乌龙茶 安吉白茶 浙江 中生种 绿茶 丽早香 浙江 早生种 绿茶 龙井43 浙江 特早生种 绿茶 平阳特早茶 浙江 特早生种 绿茶 千年雪 浙江 中生种 绿茶 乌牛早 浙江 特早生种 绿茶 中茶108 浙江 特早生种 绿茶 迎霜 浙江 早生种 绿茶 湘妃翠 湖南 早生种 绿茶 FJ-1 福建 中生种 乌龙茶 FJ-2 福建 早生种 乌龙茶 FJ-3 福建 早生种 乌龙茶 FJ-4 福建 中生种 乌龙茶 FJ-5 福建 早生种 绿茶 FJ-6 福建 早生种 绿茶 FJ-7 福建 早生种 绿茶 注:表中FJ-1~FJ-4为铁观音后代,FJ-5、FJ-6为福云6号后代,FJ-7为福云7号后代。 表 2 20对SSR引物及其序列
Table 2 Nucleotide sequences of 20 primer pairs
名称 重复位点 引物序列 退火温度/℃ 目的片段大小/bp TM241 (GAGAA)3 ATCGGCGACGGTGGAAGT 58 130 GCCAGCGGAGAGGAGAAG TM262 (CT)21 CGACCAGACGGTGAAAT 56 164 AGGCTTGTGAGCAAAATC TM341 (TA)10 CATGCTCCCATCCCACCT 58 111 ATGCTGCTCATTCAAACCAACT TM369 (GAA)8 CGGAGCTGGAATCTGAAGAG 52 196 GGAAGGGTTGCAAATTCTGA TM407 (CAAGAT)3 AACAACAGCAGCGAAGATGA 52 251 CCACCACTGATGACCCTTTT TM422 (TTC)7 GGACTTCGTTGCTTCCTTTG 52 167 CCATTCTCGACGAATCCAGT TM426 (AGA)11 TGAGAGTGCTTGTCTGGGTG 52 245 CAACTACCCCTTTTCCCCAT TM428 (CAC)7 TCTCCTCCTCGATCCTCAGA 52 195 CCCTCTTCTTCGGATCCTTC TM440 (TTTGC)3 TTGACCCGAATAAAATGGGA 52 159 CCTCAAAACATGCTTTTCTTAATC TM442 (ATACAC)3 CAAGCCAAACCTTGCTGAAT 52 275 CTGTCCTGTGTCTGGTGGTG TM447 (AAAAG)5 TGTTGTTAACGGTGTTCGGA 54 156 GCATTTGTTTTCTCTCTCTGCC TM453 (TTC)6 AAGTCACAACACCACCACCA 52 268 GAGGCAGCGATAGTACCAGG TM461 (ATTTTT)6 GGCTAGGGTTTCTCCCACTT 52 211 GAAGGTCGAAGCGATGTTGT TM480 (GTA)5 CGAAGAGTCGTTTCGAGGAG 52 208 CATCCCTTGTCTTCTCCCCT TM499 (AGA)5 AACTGTGACACCGATTGCAG 54 255 AAGTTTCACTTGCCAGCACC TM513 (AG)10 CAAGCGATCAACAACAATGG 54 265 TTGAGAAATCAACCCCTTGG TM514 (TCA)5 ATGTCTGGCCGTGGATTAAG 52 257 ATGGCAGGCTGTTCTGATTT TM569 (GTGA)5 GCAAATTCGTAAGGCGAGAG 52 274 CTGACGTTTACCCTCGTTCC TM589 (CTCCT)3 CACCACTGCCCAACAAACT 52 211 GAGGATGATGATTCGGGAGA TM601 (GGA)5 TTGCACTGGAGTGCGATAAG 52 276 CATCGCCACCAAACTCTTCT 表 3 20对引物的扩增结果
Table 3 Amplified 20 primers
引物名称 等位变异数 多态信息含量PIC 期望杂合度 观察杂合度 TM241 5 0.651 0.708 0.581 TM262 15 0.83 0.854 0.459 TM341 10 0.750 0.784 0.611 TM369 10 0.684 0.727 0.649 TM407 10 0.494 0.511 0.521 TM422 15 0.851 0.870 0.838 TM426 7 0.752 0.791 0.534 TM428 7 0.718 0.757 0.736 TM440 7 0.618 0.681 0.838 TM442 5 0.546 0.612 0.419 TM447 6 0.520 0.588 0.274 TM453 9 0.543 0.595 0.507 TM461 5 0.682 0.737 0.822 TM480 5 0.473 0.519 0.441 TM499 3 0.347 0.398 0.457 TM513 11 0.569 0.619 0.671 TM514 4 0.267 0.308 0.247 TM569 6 0.591 0.664 0.634 TM589 3 0.558 0.639 0.568 TM601 4 0.319 0.358 0.375 平均值 7.35 0.588 0.636 0.559 表 4 64个茶树品种的群体结构结果
Table 4 Population structures of 64 tea varieties
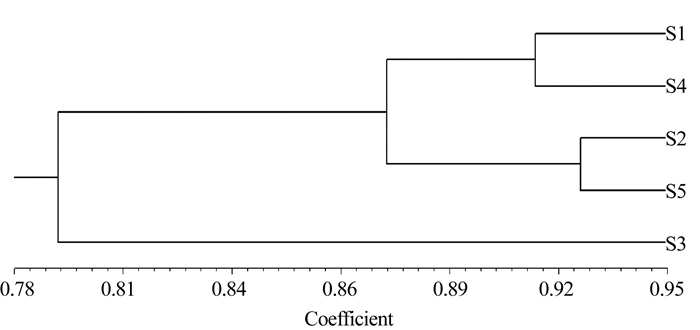
类群名称 样本大小 所占比例/% 参试材料 S1类群 11 17.2 龙井43、霞浦春波绿、福建水仙、八仙茶、凤凰单枞、白毛2号、金萱、安吉白茶、大红袍、政和大白茶、朝阳 S2类群 25 39.1 九龙袍、铁观音、凤圆春、悦茗香、黄观音、绿芽佛手、红芽佛手、梅占、瑞香、春兰、大叶乌龙、黄玫瑰、白芽奇兰、春闺、黄奇、四季春、黄棪、金牡丹、矮脚乌龙、紫玫瑰、金观音、杏仁茶、FJ-1、FJ-2、FJ-3 S3类群 13 20.3 福云6号、福云10号、福云7号、福云20号、福鼎大白茶、福云595、迎霜、福鼎大毫茶、九龙大白茶、早春毫、FJ-5、FJ-6、FJ-7 S4类群 11 17.2 榕春早、丽早香、霞浦元宵茶、乌牛早、平阳特早、千年雪、中茶108、湘妃翠、丹桂、白鸡冠、肉桂 S5混合类群 4 6.2 毛蟹、歌乐茶、紫牡丹、FJ-4 表 5 5个群体遗传多样性
Table 5 Genetic diversity among 5 groups
组号 样本数 观测杂合度 期望杂合度 Shannon信息指数 基因多样性指数 S1类群 11 0.545 0.642 1.214a 0.613 S2类群 25 0.517 0.559 0.989b 0.547 S3类群 13 0.563 0.588 1.049ab 0.565 S4类群 11 0.506 0.597 1.069ab 0.567 S5混合类群 4 0.570 0.606 0.972b 0.545 所有材料 64 0.538 0.633 1.270 0.628 注:表中小写字母不同表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 6 群体间相似系数(对角线上方)与基因流(对角线下方)
Table 6 Genetic identity(above diagonal line) and gene flow(below diagonal line) between groups
群体 S1 S2 S3 S4 S1 0.855 0.823 0.915 S2 4.157 0.740 0.831 S3 3.521 2.32 0.766 S4 6.098 3.350 2.559 -
[1] 段云裳, 成浩, 姜燕华, 等.乌龙茶品种(系)遗传多样性与亲缘关系的SSR分析[J].茶叶科学, 2010, 30(2):141-148. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cykx201002011 [2] 李付鹏, 秦晓威, 郝朝运, 等.可可核心种质遗传多样性及果实性状与SSR标记关联分析[J].热带作物学报, 2016, 37(2):226-233. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95551X/201602/668196932.html [3] 孙晓棠, 卢冬冬, 欧阳林娟, 等.水稻纹枯病抗性关联分析及抗性等位变异发掘[J].作物学报, 2014, 40(5):779-787. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zuowxb201405003 [4] 刘金, 关建平, 徐东旭, 等.小扁豆种质资源SSR标记遗传多样性及群体结构分析[J].作物学报, 2008, 34(11):1901-1909. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/a4bf446c25c52cc58bd6becd.html [5] 陈斐, 魏臻武, 李伟民, 等.基于SSR标记的苜蓿种质资源遗传多样性与群体结构分析[J].草地学报, 2013, 21(4):759-768. DOI: 10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2013.04.020 [6] 孟亚雄, 孟林祎, 汪军成, 等.青稞遗传多样性及其农艺性状与SSR标记的关联分析[J].作物学报, 2016, 42(2):180-189. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90181X/201602/667999178.html [7] 刘志斋, 吴迅, 刘海利, 等.基于40个核心SSR标记揭示的820份中国玉米重要自交系的遗传多样性与群体结构[J].中国农业科学, 2012, 45(11):2107-2138. DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2012.11.001 [8] 刘文, 萧凤回, 武剑, 等.大白菜和白菜群体的遗传结构分析[J].云南农业大学学报:自然科学版, 2011, 26(2):156-163. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/YYXB201206009.htm [9] 强新涛, 赵春芳, 赵凌, 等.籼稻栽培品种中淀粉合成相关基因的遗传变异和群体结构分析[J].江苏农业学报, 2016, 32(2):241-249. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JSNB201602001.htm [10] 王晋, 王世红, 赖勇, 等.大麦SSR标记遗传多样性及群体遗传结构分析[J].核农学报, 2014, 28(2):177-185. DOI: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2014.02.0177 [11] 杜凤凤, 刘晓静, 常雅军, 等.基于SSR标记的荷花品种遗传多样性及群体结构分析[J].植物资源与环境学报, 2016, 25(1):9-16. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZWZY201601002.htm [12] 乔婷婷, 马春雷, 陈亮, 等.浙江省茶树地方品种与选育品种遗传多样性和群体结构的EST-SSR分析[J].作物学报, 2010, 36(5):744-753. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/XBZW201005007.htm [13] 姚明哲, 刘振, 梁月荣, 等.利用EST-SSR分析江北茶区茶树资源的遗传多样性和遗传结构[J].茶叶科学, 2009, 29(3):243-250. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/CYKK200903014.htm [14] 姚明哲, 马春雷, 金基强.川、渝地方茶树品种的遗传多样性和群体结构[J].茶叶科学, 2012, 32(5):419-425. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/CYKK201205007.htm [15] 吴晓梅, 姚明哲, 陈亮, 等.利用EST-SSR标记研究适制绿茶与乌龙茶品种的遗传多样性与遗传结构[J].茶叶科学, 2010, 30(3):195-202. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/CYKK201003010.htm [16] 白堃元, 虞富莲, 杨亚军, 等.福建省茶树品种图志[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社, 2001. [17] 金基强, 崔海瑞, 龚晓春, 等.用EST-SSR标记对茶树种质资源的研究[J].遗传, 2007, 29(1):103-108. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Ji_Qiang_Jin/publication/6521159_Studies_on_tea_Plants_Camellia_sinensis_germplasms_using_EST-_SSR_marker/links/584cd35a08aed95c24fc5a7b/Studies-on-tea-Plants-Camellia-sinensis-germplasms-using-EST-SSR-marker.pdf [18] MA J Q, YAO M Z, MA C L, et al.Construction of a SSR-based genetic map and identification of QTLs for catechins content in tea plant(Camellia sinensis)[J].PloS ONE, 2014, 9(3):1-11. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Xinchao_Wang2/publication/261187217_Construction_of_a_SSR-Based_Genetic_Map_and_Identification_of_QTLs_for_Catechins_Content_in_Tea_Plant_Camellia_sinensis/links/0deec53bd4605d23c3000000.pdf
[19] 杨军, 王让剑, 孔祥瑞, 等.4个茶树品种自交后代群体遗传结构分析[J].茶叶学报, 2016, 57(2):59-63. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10434-1012487695.htm [20] PRICHARD J K, STEPPHEN M, DONNELLY P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data[J]. Genetics, 2000, 155:945-959. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10011887457
[21] YEH F C, YANG R C, BOYLE T B J, et al.POPGENE, the user friendly shareware for population genetic analysis[M].Canada:Molecular Biology and Biotechnology Centre, University of Alberta, 1997.
[22] 黄晓霞, 唐探, 姜永雷, 等.千家寨不同海拔野生茶树的EST-SSR遗传多样性研究[J].茶叶科学, 2015, 35(4):347-353. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CYKK201504009.htm [23] 周萌, 李友勇, 孙雪梅, 等.基于EST-SSR标记的云南野生茶树遗传多样性分析[J].江苏农业科学, 2013, 41(12):22-27. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1302.2013.12.007 [24] 杨阳, 刘振, 赵洋, 等.利用EST-SSR标记研究黄金茶群体遗传多样性及遗传分化[J].茶叶科学, 2009, 29(3):236-242. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/CYKK200903014.htm [25] 周炎花, 乔小燕, 马春雷, 等.广西茶树地方品种遗传多样性和遗传结构的EST-SSR分析[J].林业科学, 2011, 47(3):59-67. DOI: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20110310 [26] 李丹, 李端生, 杨春, 等.江华苦茶种质资源遗传多样性和亲缘关系的ISSR分析[J].茶叶科学, 2012, 32(2):135-141. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cykx201202007 [27] 何智宏, 司二静, 赖勇, 等.大麦亲本材料SSR标记遗传多样性及群体结构分析[J].麦类作物学报, 2013, 33(5):894-900. DOI: 10.7606/j.issn.1009-1041.2013.05.008 [28] 郭吉春, 叶乃兴, 何孝延, 等. 乌龙茶品种资源研究进展[C]//海峡两岸茶叶科技学术研讨会论文集, 2000: 35-38. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=conference&id=6402974 [29] 马淑梅, 张宏纪, 孙岩, 等.俄罗斯远东及黑龙江省大豆种质资源遗传多样性和群体结构分析[J].中国油料作物学报, 2017, 39(1):23-29. DOI: 10.7505/j.issn.1007-9084.2017.01.004 -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 阳茜,饶得花,刘洪,杨哲,苏镇柱,江院,殷纪伟,徐振江. 卡特兰DUS测试性状与SSR标记的关联分析. 园艺学报. 2024(04): 787-803 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张磊,赵翊暄,陈强,俞滢,杨如兴. 福建省茶树种质资源DNA分子标记研究综述. 茶叶学报. 2024(06): 1-9 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 黄厚宸,蒋维昕,梁彩霞,姚茜,聂海泉,白天道. 广西六堡茶古茶树及其子代遗传多样性的EST-SSR标记分析. 分子植物育种. 2021(07): 2410-2418 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 罗亦纾,张霞,毛君林,李华钧,刘勤晋,童华荣,梁国鲁,魏旭. 35份重庆大茶树种质资源遗传多样性的SSR分析. 分子植物育种. 2019(19): 6549-6557 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)





 下载:
下载: