Effects of Alternanthera philoxeroides Grown in Different CO2 Environment on the Reproductive Ability of Agasicles hygyophila
-
摘要: 为探究CO2含量升高对莲草直胸跳甲种群生长发育和种群繁殖能力的间接影响,建立了取食不同CO2含量(420、750 μL·L-1)条件下生长的空心莲子草的莲草直胸跳甲F5代种群两性生命表。结果表明,随着CO2含量的增加,取食相应环境中生长的空心莲子草的莲草直胸跳甲的发育历期缩短、产卵期延长、产卵量增加,说明CO2含量增加间接有利于莲草直胸跳甲的繁殖力。而同CO2含量(420 μL·L-1)条件下,F5代的产卵期和产卵量均少于F1代,发育历期延长,说明实验室条件下随着世代积累,莲草直胸跳甲种群繁殖力下降。420 μL·L-1 CO2含量下,莲草直胸跳甲F5代种群的净增值率(R0)和内禀增长率(r)低于F1代;而750 μL·L-1 F5代莲草直胸跳甲种群的净增值率和内禀增长率低于420 μL·L-1 CO2含量的F1代,但高于420 μL·L-1 CO2含量的F5代;周限增长率(λ)、平均世代周期(T)均无显著差异;高含量可育雌雄比率高于低含量且差异显著。上述结果表明,取食高CO2含量环境下生长的空心莲子草增加了莲草直胸跳甲F5代种群的繁殖能力,间接对莲草直胸跳甲的生长发育产生了积极影响。Abstract: To understand the indirect effects of elevated CO2 concentrations on the growth, development and population reproduction of A. hygrophila, Age-stage two-sex life table of A. hygrophila feeding on A. philoxeroides grown in different CO2 concentrations were constructed. The results showed that, as the CO2 concentration increasing, the development duration was shortened, the oviposition period was lengthened, and the fecundity increased of A. hygrophila feeding on A. philoxeroides grown in correspond CO2 environment. So it's indirectly beneficial for the fecundity of A. hygrophila. In the same CO2 concentration (420 μL·L-1) condition, the oviposition period and the fecundity of F5 were less than those of F1, but the development duration was lengthened. This indicated that the fecundity of A. hygrophila was declined with generation development under laboratory conditions. In the 420 μL·L-1 CO2 concentration condition, the net reproductive rate (R0), intrinsic rate of increase (r) of F5 were less than F1, and the R0 and r of F5 in 750 μL·L-1 CO2 concentration condition were also less than F1, but higher than that of F5 in 420 μL·L-1 CO2 concentration. The finite rate of increase (λ) and mean generation time (T) had no significant differences. The fertile female ratio at higher concentration was significantly higher than those at lower concentration. These results indicated that the reproductive of A. hygrophila feeding on A. philoxeroides grown in elevated CO2 concentrations may be enhanced and the elevated CO2 concentrations plays a positive effect on the growth and the development of A. hygrophila population.
-
Keywords:
- A. hygrophila /
- CO2 /
- Growth, Development /
- Two-sex life table
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】鲫(Carassius auratus)是我国主要的淡水养殖鱼类,因具有营养价值高、适应性强和生长快等特点而深受消费者青睐,在我国绝大部分地区都有大规模养殖,目前鲫鱼已成为鲜活淡水鱼市场中仅次于草鱼的第二大消费品种。高密度池塘养殖在淡水鱼养殖中占据重要地位[1],该模式主要以人工投料为主,在养殖过程中会产生大量残饵和粪便,导致水质污染问题,从而引起养殖动物疾病暴发,其中氨氮是养殖水体中最主要的污染物之一。因此研究慢性氨氮胁迫对鲫幼鱼肝、肾组织及非特异性免疫指标的影响对鲫鱼养殖意义重大。【前人研究进展】氨氮是制约水生动物生长、存活和繁殖的重要环境化学因子,主要是由池塘或海洋黏土沉积物的咸水渗透[2]、田地施肥、大气沉降、农田固氮[3]、粪便残饵等产生,因此养殖期间水体管理不当会造成氨氮的快速产生和积累。当水生环境中的氨氮浓度过高时,会导致鱼类氨氮生物蓄积,引起酶代谢紊乱,从而过于兴奋,降低免疫力,损害鱼类的中枢神经系统等[4],并对鱼类的存活、生长代谢、组织结构、生理和免疫功能等产生毒性效应[5]。近年来,国内外学者在氨氮对鱼类养殖的影响方面做了大量研究,结果表明,急性氨氮胁迫会引起大口黑鲈(Micropterus salmoides)肝脏氧化应激[6],洞庭青鲫(Carassius auratus indigentiaus)幼鱼抗氧化防御系统功能紊乱[7],进入鱼体血液循环快速引发毒性效应[8],导致斑石鲷(Oplegnathus punctatus)幼鱼行为异常[9]等。慢性氨氮胁迫会抑制幼年钝吻鲷(Megalobrama amblycephala)的生长[10],诱发黄颡鱼(Pelteobagrus fulvidraco)鳃出现严重的增生和炎症[11],导致尼罗罗非鱼(Oreochromis niloticus)[12]和团头鲂(Megalobrama Amblycephala)[13]发生氧化应激和免疫抑制效应,肝脏出现不同程度的损伤。【本研究切入点】目前,虽然关于氨氮胁迫对鱼类影响的研究有很多,但都集中在急性胁迫方面,有关慢性氨氮胁迫的研究较少,且影响指标大部分集中在生长方面,对鱼类肝、肾组织及非特异性免疫指标的影响鲜少报道。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究通过研究慢性氨氮胁迫对鲫幼鱼肝、肾组织及非特异性免疫指标的影响,以期为解析氨氮对鲫鱼的危害及鲫鱼集约化养殖过程中水体氨氮的调控、水质管理提供科学的理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验动物及管理
试验动物为从太原鱼种场购买的健康幼鲫,体长(3.5±0.2) cm,体重(3.10±0.15) g,共计500尾。试验用水为充分曝气后的自来水,水温控制在(25±1) ℃,pH为(7.5±0.3),溶解氧不低于5 mg·L−1,每天13:00换全水1次,并重新加入配制好的氨氮溶液,换水1 h后投喂饲料,正式试验前停食1 d。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 急性毒理试验
暂养结束后开始进行急性毒性试验,以NH4Cl配制质量浓度为10 g·L−1的NH4Cl母液,根据需要稀释成不同质量浓度的使用液,选取300尾幼鲫,将试验鱼饲养于NH4Cl质量浓度分别为240、320、400、480、560 mg·L−1的5个处理组中,同时以未添加氨氮的正常饲养用水作为对照组,每组设置5个重复,每个重复10尾鱼。试验期间不投饵,分别记录24、48、72、96 h的个体死亡数,并及时清除死亡个体,以停止呼吸、针刺无反应作为死亡标准。每天换水后对氨氮浓度进行校正,使用奥克丹多参数水质分析仪进行氨氮浓度检测,以确保试验水体中氨氮浓度与设计浓度吻合。
以Bliss法求取不同攻毒时间的96 h半致死质量浓度(LC50),同时获得不同胁迫时间的回归方程、可决系数和95%置信区间,并估算出氨氮对鲫鱼幼鱼的和安全质量浓度(safe concentration, SC)。安全质量浓度的计算公式为:
SC/(mg·L−1) =0.1×96 h LC50
1.2.2 慢性毒理试验
通过预试验确定体重为3.10 g左右的幼鲫96 h半致死浓度LC50为289.29 mg·L−1,安全浓度(SC)按照LC50的10%估算为28.9 mg·L−1。试验于60 cm×40 cm×40 cm的养殖箱中进行,将试验鱼随机分为4组,设0 mg·L−1(对照,CK)、6 mg·L−1(低质量浓度,L组)、15 mg·L−1(中质量浓度,M组)和24 mg·L−1(高质量浓度,H组)4个氨氮浓度梯度处理,每组设置5个重复,每个重复10尾鱼。试验期间维持试验水体的溶氧量和温度,每天13: 00全换水1次。所换水均经过24 h的曝气,换水后再重新加入配置好的氨氮溶液,使用奥克丹多参数水质分析仪进行氨氮浓度检测,确保试验水体中氨氮浓度与设计浓度吻合。每组浓度实测值分别为(0.40±0.02)、(6.05±0.21)、(15.06±0.10)、(24.05±0.14)mg·L−1。参考《地面水环境质量标准非离子氨换算方法》[14]将其转换成非离子氨浓度,分别为0.00、0.04、0.10、0.16 mg·L−1。
1.2.3 样品采集
分别于第15、30、45、60天从各组随机取10尾试验鱼进行解剖取样,采集其肝脏、肾脏组织,置于有波恩氏液(Bouin’s liquid)的1.5 mL离心管中固定,用于制作石蜡切片。每组另取5尾鱼的肝、肾组织样品置于−80 ℃冰箱保存,用于非特异性免疫指标的测定。
1.2.4 幼鲫肝、肾组织结构分析
用自来水冲洗已经固定好的组织12 h,采用常规石蜡切片制作方法,经酒精(50%、75%、85%、95%、100%、100%)脱水后,用1/2二甲苯(V二甲苯∶V酒精=1∶1)、二甲苯Ⅰ、二甲苯Ⅱ透明,之后用1/2石蜡(V石蜡∶V二甲苯=1∶1)、经石蜡Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ依次浸蜡,再进行包埋、切片、展片、脱蜡、H.E.染色,最后中性树脂封片,自然风干后置于光学显微镜下观察并拍照。
1.2.5 酶活性测定
使用预冷过的PBS将分离的肝脏、肾脏组织充分匀浆,
3000 r·min−1冷冻离心20 min后取上清液,用于测定肝、肾组织的谷丙转氨酶(Alanine aminotransferase, ALT)、谷草转氨酶(Aspartate aminotransferase, AST)、过氧化氢酶(Catalase, CAT)和超氧化物歧化酶(Superoxide dismutase, SOD)活性。参照《水产动物机能学实验》采用比色法测定肝、肾组织中ALT、AST活性。以37 ℃与底物作用30 min、产生2.5 μg的丙酮酸为一个ALT活力单位(U·mL−1)。在37 ℃下每mL组织匀浆样本每分钟催化产生1 nmol丙酮酸定义为一个AST活力单位(U·mL−1)。用南京建成生物公司研究所研制的试剂盒测定CAT,按说明书操作。CAT活力定义为每毫克组织蛋白每秒钟分解1 µmol的H2O2为一个活力单位(U·mg−1)。使用南京建成生物公司研究所研制的试剂盒测定SOD,按说明书操作。SOD活力定义为每毫克组织蛋白在1 mL反应液中SOD抑制率达50%时所对应的SOD量为一个SOD活力单位(U·mg−1)。1.3 数据处理
试验数据用SPSS 21.0的单因素(ANOVA)方法进行分析,数据结果以平均值±标准差(Mean ± SD)表示,采用Duncan法进行多重比较,显著水平为P<0.05,极显著水平为P<0.01。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 氨氮对幼鲫的半致死浓度(LC50)及安全浓度
氨氮对幼鲫的急性毒性测定结果见表1。由表1可知,幼鲫对氨氮敏感,随着处理时间的延长,半致死质量浓度值呈减小趋势,96 h LC50为289.29 mg·L−1,转换成非离子氨为1.98 mg·L−1,SC按照LC50的10%估算为28.9 mg·L−1,转换成非离子氨为0.20 mg·L−1。
表 1 氨氮对鲫幼鱼急性毒性试验结果Table 1. Acute toxicity test of ammonia nitrogen on mortality of juvenile C. auratus胁迫时间
Stress time/h回归方程
Regressive equation相关系数R2 半致死浓度
LC50/(mg·L−1)95%置信区间
95% confidence interval/(mg·L−1)安全浓度SC/
(mg·L−1)24 P= 5.7327 X-15.0845 0.9939 427.86 393.45~465.28 42.8 48 P= 7.7711 X-19.9359 0.9985 367.62 356.67~378.91 36.8 72 P= 8.6415 X-21.7653 0.9879 330.14 271.14~401.98 33.0 96 P= 5.5711 X-13.7124 0.9980 289.29 264.08~316.90 28.9 LC50采用概率单位法计算;P为死亡率;X为NH4+质量浓度对数。
LC50 was calculated by probabilistic unit method; P is mortality probability unit; X is log of NH4+ concentration.2.2 慢性氨氮胁迫对幼鲫肝组织的影响
慢性氨氮胁迫对幼鲫肝组织结构的影响见图1。对照组肝脏组织结构完整,肝细胞排列整齐,轮廓清晰,核仁明显,肝血窦大小正常,清晰可见(图1A、E、I、M)。
L组(6 mg·L−1)前两个周期内,肝细胞无明显变化,细胞排列整齐,细胞轮廓清晰、大小正常,细胞核明显(图1B、F)。胁迫45 d,肝组织部分细胞开始出现空泡化,部分细胞核核仁溶解(图1J);胁迫60 d,肝细胞空泡化严重,胞浆开始变得透明,各个细胞间细胞膜界限不明显(图1N)。
M组(15 mg·L−1)胁迫15 d时,肝细胞无明显变化(图1C)。胁迫30 d,肝细胞肿大,核仁出现溶解现象(图1G)。胁迫45 d,肝细胞轮廓模糊、排列混乱、水肿变性严重,部分细胞核核仁溶解,肝血窦扩张(图1K)。胁迫60 d,肝细胞空泡变性,核仁溶解(图1O)。
H组(24 mg·L−1)胁迫15 d,观察到肝细胞肿胀,细胞核发生偏移,核仁溶解,细胞轮廓模糊,排列混乱(图1D)。胁迫45 d,肝细胞水肿变性、空泡化严重,多数细胞核核仁溶解(图1L)。胁迫60 d,肝细胞水肿变性严重,大量细胞核溶解,轮廓严重模糊,肝组织结构严重损伤(图1P)。
2.3 慢性氨氮胁迫对幼鲫肾组织的影响
慢性氨氮胁迫对幼鲫肾组织的影响见图2。对照组肾组织结构整齐(图2A、E、I、M),肾小管上皮细胞结构完整,肾小球饱满。L组(6 mg·L−1)前两个周期内,肾组织细胞无明显变化(图2B、F),胁迫45 、60 d时后肾上皮细胞水肿变性,肾小球萎缩(图2J、N)。M组(15 mg·L−1)胁迫第15天时无明显变化(图2C),第30 d、45 d和60 d观察到肾小管上皮细胞肿胀变性,肾小管胞浆疏松透明(图2G、K、O)。H组(24 mg·L−1)各时间段均出现肾上皮细胞水样变性,肾小管管腔缩小(图2D、H、L、P)。
2.4 慢性氨氮胁迫对幼鲫肝、肾脏非特异性免疫指标的影响
2.4.1 慢性氨氮对幼鲫肝、肾脏ALT的影响
如图3A所示,幼鲫经氨氮胁迫后,肝脏中ALT活力随着氨氮浓度的升高以及氨氮暴露时间的增加而增强。15 d时,H组(24 mg·L−1)ALT活力显著高于对照组,30 ~ 60 d,各胁迫组在肝组织中ALT活力均显著高于对照组。30 d时,L组(6 mg·L−1)和M组(15 mg·L−1)与H组(24 mg·L−1)差异显著,45 ~ 60 d,各胁迫组之间差异显著。如图3B所示,随着氨氮浓度的升高和暴露时间的延长,肾脏ALT的活性一直保持升高的趋势。15 ~ 60 d各胁迫组肾脏ALT的活力均与对照组差异显著。15~45 d各胁迫组之间差异显著,60 d时L组、M组与H组差异显著。
2.4.2 慢性氨氮对幼鲫肝、肾脏AST的影响
由图4可知,在整个氨氮胁迫期间,随着氨氮浓度的升高和暴露时间的延长,3个试验组中肝、肾组织AST活性升高且与对照组差异显著;肝组织在15 ~ 30 d时,L组与M组AST活性无显著差异,第15 d时二者与H组差异显著,肾组织在60 d时,L组与H组之间AST活性差异显著。
2.4.3 慢性氨氮对幼鲫肝、肾脏CAT的影响
由图5A可知,幼鲫经氨氮胁迫后,其肝组织中CAT的活性随着氨氮浓度的升高以及氨氮暴露时间的增加逐渐升高,于45 d时达到峰值,L组、M组、H组分别为372.89 、379.30、381.26 U·mg−1,且3组均与对照组差异显著;60 d时各试验组CAT活性开始降低,但仍与对照组差异显著。
由图5B可知,随着氨氮浓度的升高,各试验组在15 d时肾组织CAT与对照组相比有升高趋势,且差异显著。L组和M组在60 d时肾组织CAT比活力达到峰值,分别为230.65、279.78 U·mg−1。H组肾组织CAT比活力在45 d时达到峰值,60 d时较之前比活力有下降趋势。
2.4.4 慢性氨氮对幼鲫肝、肾脏SOD的影响
由图6A可知,幼鲫经氨氮胁迫后,其肝脏中SOD的活性随着氨氮浓度的升高以及氨氮暴露时间的增加而增加,各氨氮浓度胁迫15 d时肝组织中SOD比活力就已经显著高于对照组,在胁迫45 d时达到峰值,L组、M组、H组分别为6.31、6.76、6.93 U·mg−1。60 d时各胁迫组肝脏SOD的活性有降低的趋势,但仍与对照组存在显著差异。
由图6B可知,随着氨氮浓度的升高,各试验组肾组织SOD活性升高。各胁迫组在各时间段SOD酶的比活力均显著高于对照组。15 、60 d时,L组与H组之间差异显著,30 、45 d时,L组与M和H两组之间差异显著。
3. 讨论
3.1 氨氮胁迫对幼鲫的急性毒性效应
养殖水体中氨氮对鱼类的致毒作用主要是由于水体中非离子氨浓度过高,表现为不同程度的组织损伤[15]。非离子氨对水生生物危害较大的主要原因是非离子氨是带有较强脂溶性的中性分子,它可以透过细胞膜进入水生生物体,影响水生生物体内的酶水解反应进程,对细胞膜稳定性也会产生影响,导致水生生物的某些生理生化指标与生长指标发生改变,引起水生生物发病,严重时致死[16]。
本研究以幼鲫为试验对象进行96 h的急性氨氮攻毒,通过Bliss法得出其LC50为289.29 mg·L−1,SC按照LC50的10%估算,为28.9 mg·L−1。由于不同种类水生生物对氨氮胁迫的耐受力不同,因此受氨氮胁迫后的致死率也不相同。唐忠林等[17]在对大口黑鲈(M. salmoides)北方亚种引进种F1代幼鱼的急性氨氮胁迫研究中得到96 h半致死浓度和安全浓度分别为25.08 、2.51 mg·L−1;杨西伟等[18]在研究刀鲚(Coilia nasus)幼鱼的急性毒性时得到其96 h半致死浓度和安全浓度分别为46.83 mg·L−1和4.68 mg·L−1。幼鲫对于氨氮的毒性耐受力要高于大多数硬骨鱼的幼鱼[14, 15],也远高于经济虾蟹类[19 - 21],但低于海湾豹蟾鱼(Opsanus beta)、毒棘豹蟾鱼(Opsanus tau)和斑光蟾鱼(Porichthys notatus),因其具有通过尿素合成进行氨解毒的替代或附加机制[22]。
3.2 慢性氨氮胁迫对幼鲫肝、肾组织的影响
肝脏是鱼体内最大的消化腺,其基本组织结构能很大程度上揭示鱼类的营养需求及生态习性的内部本质,在新陈代谢、解毒和免疫中都起着重要作用[23]。研究表明,鱼体暴露在高浓度氨氮的水体中,会造成肝组织的损伤,导致其肝脏出现水肿、空泡化严重和局部坏死等病变[24 - 26]。本研究中,肝脏出现肿大、空泡化、细胞核溶解、细胞轮廓不清晰等现象,且随着氨氮浓度的升高及胁迫时间的延长,肝组织损伤逐渐严重,这与其他鱼类中的研究结果一致。
肾脏是鱼类的排泄器官,鱼类的代谢产物主要通过肾脏排出体外[27]。研究表明,外界水环境中的污染物如农药[28]、重金属[29]等均会引起鱼类肾脏的病变。本研究中,肾组织在氨氮的胁迫下,出现肾小管管腔缩小、肾小管上皮细胞水肿变性、肾小球萎缩等现象,且随着氨氮浓度的升高及胁迫时间的延长,肾组织损伤逐渐严重。在急性氨胁迫对团头鲂(Megalobrama amblycephala)肾组织结构影响的研究中,肾脏出现同样的变化[30]。因此,高浓度的氨氮或长时间的氨氮胁迫都会导致鱼类肾脏出现损伤。
3.3 慢性氨氮胁迫对幼鲫肝、肾非特异性免疫指标的影响
氨氮暴露会导致水产养殖动物免疫功能受到抑制[10, 31, 32]。鱼类的非特异性免疫在应对环境应激中起主导作用,其中免疫酶主要包括ALT、AST、CAT、SOD等[33, 34]。本研究发现,氨氮胁迫对幼鲫肝、肾组织的非特异性免疫指标影响显著,随着胁迫时间的延长,不同氨氮浓度下幼鲫ALT、AST、CAT和SOD活性均发生了明显变化。
AST与ALT是一种重要的氨基转移酶,广泛存在于生物机体内,对生物机体内的氨基酸合成以及分解代谢具有重要作用,是评价肝肾损伤的重要指标[35, 36]。当组织中氨浓度升高时,会导致膜转运能力降低从而减少氧的摄入,使得机体能量消耗增加,诱发机体生理紊乱,损害水生动物的健康[37]。据Chandra等[38]研究发现,AST由肝细胞合成,通常见于肝脏,而ALT常见于肝脏和肾脏中,因此AST和ALT是肝功能检查中的标志物。Rahimnejad等[39]试验表明,当肝细胞受损时,ALT和AST比活力增强。EL Euony等[40]研究显示,革胡子鲶(Clarias garipenus)噻虫嗪中毒后,其肝脏和头肾出现退行性改变和坏死,AST、ALT活性水平显著升高。本试验中各浓度组肝、肾组织中AST和ALT的比活力随着氨氮暴露时间的延长而明显升高,且一直保持较高水平,说明高浓度的氨氮或者氨氮长期暴露会导致鱼类肝、肾受到损伤。
CAT和SOD是机体抗氧化系统中最重要的两种抗氧化酶,主要作用是清除机体产生的氧自由基(ROS),防止由于ROS过多造成机体损伤[41]。本研究发现,幼鲫肝组织中CAT和SOD的活性呈现先升后降的趋势,且均与对照组有极显著差异,这与姜会民[42]氨氮胁迫鲤(Cyprinus carpio)幼鱼的结果相似。其主要原因是在受到氨氮胁迫时,鱼体产生了毒物兴奋效应,机体产生大量的ROS,导致机体损伤,之后机体启动抗氧化防御系统抑制ROS的生产,使得CAT、SOD活性呈现升高趋势,但经过高浓度且长时间的氨氮暴露会造成肝组织损伤,导致组织中2种抗氧化酶的活性降低。氨氮胁迫后肾组织中的SOD和CAT活性也明显高于对照组,这是为了清除过多的ROS,以减轻过氧化损伤。而高浓度组(H组)CAT活性在60 d时降低,这可能是因为长时间高浓度胁迫所产生的有害物质超过了鱼体的耐受上限。
4. 结论
氨氮对幼鲫的96 h LC50为289.29 mg·L−1,安全浓度为28.9 mg·L−1,随着氨氮浓度的升高和胁迫时间的延长,幼鲫肝和肾组织受到的损害增加。慢性氨氮的毒性会对幼鲫的肝、肾组织产生伤害,并严重影响其非特异性免疫指标,进而影响鱼体健康。因此在进行鲫鱼养殖时,应关注水体的氨氮浓度,防止氨氮对鲫鱼的毒性效应。
-
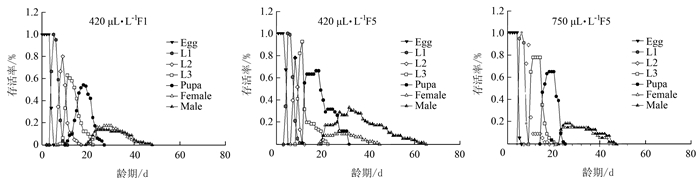
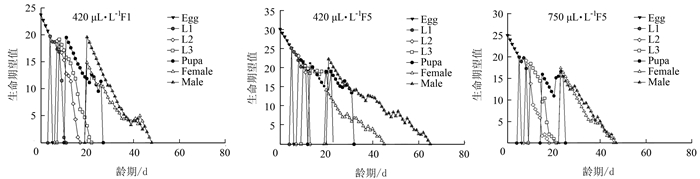
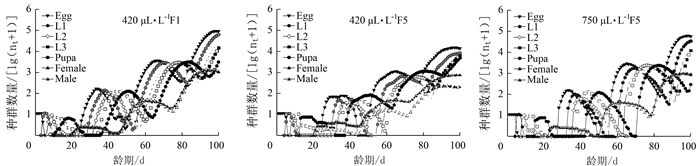
表 1 不同CO2含量对莲草直胸跳甲生长发育及繁殖力的间接影响
Table 1 Indirect impaction of different CO2 concentrations on growth development and fecundity of A. hygrophila
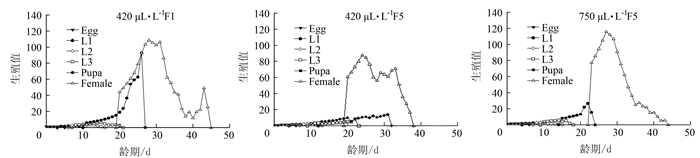
参数 CO2含量 420 μL·L-1 F1 420 μL·L-1 F5 750 μL·L-1 F5 n Mean ± SE n Mean ± SE n Mean ± SE 卵/d 81 4.33±0.05 c 77 5.66±0.05 a 54 5.06±0.03 b 1龄/d 72 3.53±0.08 a 74 3.20±0.08 b 48 3.19±0.06 b 2龄/d 66 3.09±0.14 a 72 1.86±0.07 c 44 2.23±0.15 b 3龄/d 47 4.38±0.21 b 59 3.93±0.36 b 35 5.40±0.15 a 蛹/d 28 8.39±0.19 b 41 10.83±0.48 a 18 7.78±0.19 c 卵~蛹/d 28 23.14±0.36 b 41 25.63±0.69 a 18 23.33±0.14 b 雌成虫寿命/d 17 11.47±1.39 b 12 10.33±0.51 b 8 17.25±1.31 a 雄成虫寿命/d 11 17.73±1.74 a 29 17.97±1.97 a 10 15.90±2.25 a 总虫/d 81 37.07±1.12 b 77 41.37±1.56 a 54 39.83±1.32 b 雌虫/d 17 35.41±1.50 b 12 35.17±1.63 b 8 40.38±1.35 a 雄虫/d 11 39.64±1.45 a 29 43.93±1.93 a 10 39.4±2.19 a 成虫产卵前期/d 13 4.77±0.28 a 10 3.4±0.43 b 8 4.38±0.26 b 总产卵前期/d 13 28.77±0.74 a 10 27.9±1.09 a 8 27.5±0.27 a 产卵期/d 13 6.31±0.79 b 10 4.4±0.54 b 8 8.00±0.73 a 产卵量/(粒·雌-1) 17 149.82±32.29 b 12 109.17±22.40 b 8 177.00±18.13 a 注:同行数据后不同小写字母表示经Bootstrap test差异达显著水平(P < 0.05),表 2同。 表 2 不同CO2含量对莲草直胸跳甲种群参数的间接影响
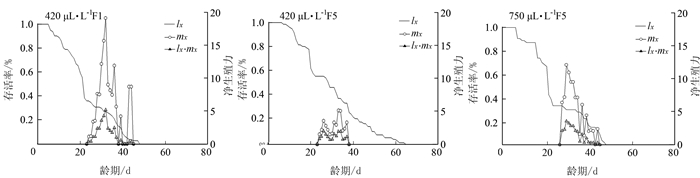
Table 2 Indirect impactions of different CO2 concentrations on population parameters of A.hygrophila
种群参数 CO2含量 420 μL·L-1 F1 420 μL·L-1 F5 750 μL·L-1 F5 净增值率(R0, offspring) 3144 ± 9.491 a 17.01 ±5.642 a 26.22±8.887 a 内禀增长率(r,d-1) 0.11 ± 0.011 a 0.09±0.012 a 0.10±0.012 a 周限增长率(λ,d-1) 111 ± 0.012 a 110±0.013 a 111 ± 0.013 a 平均世代周期(T,d-1) 32.14±0.622 a 30.72± 1 260 a 32.14±0.559 a 成虫前期存活率/% 0.35 ± 0.053 b 0.53±0.057 a 0.33 ± 0.064 b 雄雌比率(雄:雌) 0.65 ± 0.291 a 2.42± 1 095 a 1.25 ±0.946 a 可育雌虫比率(产雌:总雌) 0.76 ± 0.106 b 0.83±0.112 b 100±0?000 a -
[1] 马瑞燕. 空心莲子草天敌——莲草直胸跳甲引进中国后的生态适应性研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2001. [2] 沈国军, 徐正浩, 俞谷松.空心莲子草的分布、危害与防除对策[J].植物保护, 2005, 31(3):14-18. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zwbh200503003 [3] JULIEN M H, SKARRATT B, MAYWALD G F. Potential geographical distribution of alligator weed and its biological control by Agasicles hygrophila[J]. Journal of Aquatic Plant Management, 1995, 33: 55-60. http://www.oalib.com/references/17075834
[4] 马瑞燕, 王韧.喜旱莲子草在中国的入侵机理及其生物防治[J].应用与环境生物学报, 2005, 11(2): 246-250. http://www.oalib.com/paper/5178713 [5] 潘晓云, 耿宇鹏, ALEJANDRO SOSA, 等.入侵植物喜旱莲子草——生物学、生态学及管理[J].植物分类学报, 2007, 45(6):884-900. http://www.doc88.com/p-9923452063157.html [6] 中国国家环境保护总局. 中国科学院关于发布中国第一批外来入侵物种名单的通知[EB]. 环发·第11号, 2003. [7] 王韧, 王远, 张格成, 等.空心莲子草叶(虫甲)的寄主专一性测验[J].生物防治通报, 1988, 4(1):14-17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSWF200803013.htm [8] 吴浪明, 田世尧, 王晓容, 等.广东莲草直胸跳甲生物学的观察[J].中国生物防治, 2000, 16(3): 144-145. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgswfz200003013 [9] 马瑞燕, 王韧, 丁建清.利用传统生物防治控制外来杂草的入侵[J].生态学报, 2003, 23(12): 2677-2688. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2003.12.023 [10] 王慧, 来小龙, 马瑞燕, 等.入侵种喜旱莲子草天敌——莲草直胸跳甲的生物学特性[J].昆虫知识, 2008, 45(3):480-482. DOI: 10.7679/j.issn.2095-1353.2008.104 [11] 史梦竹, 郭建英, 傅建炜, 等.利用光谱特征评价莲草直胸跳甲对喜旱莲子草的控制效果[J].中国生物防治学报, 2012, 28(2):220-225. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgswfz201202012 [12] 解海翠, 彩万志, 王振营, 等.大气CO2浓度升高对植物、植食性昆虫及其天敌的影响研究进展[J].应用生态学报, 2013, 24(12):3595-3602. http://www.cjae.net/CN/abstract/abstract19363.shtml [13] YOLANDE L, SERRA, KERRIE GEIL. Historical and Projected Eastern Pacific and Intra-Americas Sea TD-Wave Activity in a Selection of IPCC AR5 Models[J]. Journal of Climate, 2017, 30(7): 2269-2294. DOI: 10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0453.1
[14] 中国气象局. 中国气候公报(总第13期)[Z]. 中国气象局科技与气候变化司, 2017. [15] INTERGROVERNMENTAL PANEL ON CLIMATE CHANGE. Climate change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Summary for Policy Makers. Working group Ⅰ to the Fifth Assessment[C]//Report of Intergovernmental Panel on Cliamte Change. IPCC Secretariat, WMO. Geneva, Switzerland, 2013: 3.
[16] 傅桦.全球气候变暖的成因与影响[J].首都师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 28(6): 11-15, 21. http://www.docin.com/p-1285273042.html [17] 单国雷, 朱世东, 朱秀蕾, 等. CO2浓度对西瓜枯萎病菌丝生长和孢子萌发的影响[J].中国瓜菜, 2007, 20(1): 1-3. http://lprapp14.fao.org/XML_Output/2010/CN/CN0912.xml [18] 戈峰.应对全球气候变化的昆虫学研究[J].应用昆虫学报, 2011, 48(5): 1117-1122. DOI: 10.7679/j.issn.2095-1353.2011.185 [19] 刘俊雅, 葛亚明, PUGLISES MASSIMO, 等. CO2和温度升高情况下白粉菌侵染对西葫芦生长特性的影响[J].生态学报, 2011, 31(2): 491-497. [20] LINCOLN D E, FAJER E D, JOUNSON R I. Plant-insect herbivore interactions in elevated CO2 environments[J]. Trends Ecol Evol, 1993(8): 64-68.
[21] BENZEMER T M, KNIGHT K J, NEWINGTON J G, et al. How general are aphid Responses to elevated atmospheric CO2[J].Ann Ent Soc Am, 1999, 92(5): 724-730. DOI: 10.1093/aesa/92.5.724
[22] WHITTAKER J B. Impacts and reponses at population level of herbivorous insects to elevated CO2[J]. Eur J Ent, 1999, 96:149-156. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ea14a8d84b14911f80b4ffd15c64c11a&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[23] 陈法军, 吴刚, 戈峰.大气CO2浓度升高对棉蚜生长发育和繁殖的影响及其作用方式[J].生态学报, 2005, 25(10):2601-2607. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2005.10.021 [24] 孟玲, 李保平.大气二氧化碳浓度升高对植物昆虫相互关系的影响[J].生态学杂志, 2005, 24(2): 200-205. http://med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail?id=PeriodicalPaper_stxzz200502017 [25] 王晓伟, 姬兰柱, 王桂清, 等.大气CO2浓度升高对森林食叶昆虫的潜在影响[J].应用生态学报, 2006, 17(4):4720-4726. http://www.cjae.net/CN/Y2006/V17/I04/720 [26] 孙玉诚, 郭慧娟, 刘志源, 等.大气CO2浓度升高对植物-植食性昆虫的作用机制[J].应用昆虫学报, 2011, 48(5):1123-1129. DOI: 10.7679/j.issn.2095-1353.2011.186 [27] 解海翠, 彩万志, 王振营, 等.大气CO2浓度升高对植物、植食性昆虫及其天敌的影响研究进展[J].应用生态学报, 2013, 24(12):3595-3602. http://www.cjae.net/CN/abstract/abstract19363.shtml [28] FU J W, SHI M Z, W T, et al. Demography and Population Projection of Flea Beetle, Agasicles hygrophila(Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae) Fed on Alligator Weed under Elevated CO2[J]. Journal of Economic Entomology, 2016, 109(3): 1116-1124. DOI: 10.1093/jee/tow037
[29] 丁波, 史梦竹, 李建宇, 等.空心莲子草及其天敌莲草直胸跳甲对高含量CO2的响应[J].福建农业学报, 2017, (2): 195-200. http://www.doc88.com/p-9923452063157.html [30] CHI H. TWOSEX-MSChart: A computer program for the life tables and population growth of insect[OL]. National Chung Hsing University, Taichung, Taiwan. 2015.
[31] CHI H. TIMING-MSChart: A computer program for the population projection based on age-stage, two-sex life table[OL]. National Chung Hsing University, Taichung, Taiwan. 2015.
[32] HSIN CHI. Life-Table Analysis Incorporating Both Sexes and Variable Development Rates Among Individuals[J]. Environmental Entomology, 1988, 17(1): 26-34. DOI: 10.1093/ee/17.1.26
[33] YU J Z, HSIN CHI, BING-HUEI CHEN. Life table and predation of Lemnia biplagiata(Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) fed on Aphis gossypii(Homoptera: Aphididae) with a proof on relationship among gross reproduction rate, net reproduction rate, and pre-adult survivorship[J]. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 2005, 98(4):475-482. DOI: 10.1603/0013-8746(2005)098[0475:LTAPOL]2.0.CO;2
[34] CHI HSIN, SU HAWYUAN. Age-stage, two-sex life tables of Aphidius gifuensis(Ashmead)(Hymenoptera: Braconidae) and its host Myzus persicae(Sulzer)(Homoptera: Aphididae) with mathematical proof of the relationship between female fecundity and the net reproductive rate[J]. Environmental Entomology, 2006, 35(1): 10-21. DOI: 10.1603/0046-225X-35.1.10
[35] HUANG Y B, H CHI. Life tables of Bactrocera cucurbitae(Diptera: Tephritidae): with an invalidation of the jackknife technique[J]. Journal of Applied Entomology, 2013, 137(5): 327-339. DOI: 10.1111/jen.2013.137.issue-5
[36] 冯利. 大气CO2浓度升高对"棉花-棉蚜-棉蚜茧蜂"系统的影响[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2008. [37] 钱蕾, 和淑琪, 刘建业, 等.在CO2浓度升高条件下西花蓟马和花蓟马的生长发育及繁殖力比较[J].环境昆虫学报, 2015, 37(4):701-709. [38] 丁波. 空心莲子草及其天敌莲草直胸跳甲对CO2浓度升高的响应[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2017. -
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(4)




 下载:
下载: