Nutrients in Soil Layers at Vineyards in Regions of Hu'nan
-
摘要: 研究分析湖南省不同地区的葡萄种植土壤不同土层的养分特征,以期为湖南省葡萄种植的土壤养分管理以及合理施肥提供参考。本研究选择湘北、湘中、湘南、湘西4个有代表性的葡萄种植区取样,测定分析了各地区0~20、20~40、40~60 cm 3个土层的养分差异。结果表明:(1)4个地区的土壤pH值在5.0~6.1,均随着土层深入而逐渐增加;(2)不同地区土壤有机质含量差异显著,0~20 cm土层湘西地区的土壤有机质含量最高(27.4 g·kg-1),湘北地区最低(16.7 g·kg-1),4个地区的土壤有机质含量均随土层深入而降低;(3)随着土层的深入,4个地区土壤全氮和碱解氮含量均呈降低趋势,0~20 cm土层,湘西地区的土壤全氮和碱解氮含量均最高,分别为1.68 g·kg-1和149.2 mg·kg-1;(4)随着土层的深入,4个地区的土壤全磷和有效磷含量均呈下降趋势,0~20 cm土层,4个地区的土壤全磷差异不显著,土壤有效磷含量湘南地区最高(32.0 mg·kg-1),湘中地区最低(8.8 mg·kg-1);(5)0~20 cm土层,湘西地区的土壤全钾含量最高(19.2 g·kg-1),湘北地区土壤速效钾含量最高(639.9 mg·kg-1),4个地区土壤全钾和速效钾含量均随土层加深而降低。通过施用碱性肥料中和偏酸性土壤,对于养分含量低的地区合理的增加肥料的投入,再加上规范化的管理措施,有助于葡萄提高产量,提升品质。Abstract: Contents of nutrients in soil layers at vineyards in 4 regions of Hunan province were determined for efficient management and fertilization. The sampling of the 0-20 cm, 20-40 cm and 40-60 cm soil layers took place at 4 typical areas in Xiangbei, Xiangzhong, Xiangnan and Xiangxi. The results showed that (1) the soil pHs ranged from 5.0 to 6.1 with a gradual increase along with the depth of the soil at a same location; (2) significant variations in content of organic matters existed among the regions that decreased with the depth, and the greatest was found in 0-20 cm layer sample from Xiangxi (i.e., 27.4 g·kg-1), while the lowest, from Xiangbei (i.e., 16.7 g·kg-1); (3) the deeper the soil beneath the ground level, the lower the contents of total and alkaline nitrogen, as Xiangxi had the highest total nitrogen at 1.68 g·kg-1 and available nitrogen at 149.2 mg·kg-1 in the 0-20 cm layer; (4) the contents of total and available phosphorus declined with the depth, but no significant difference on total phosphorus among the regions in 0-20 cm layer, however, the available phosphorus was the highest in Xiangnan (i.e., 32 mg·kg-1) and the lowest in Xiangzhong (i.e., 8.8 mg·kg-1); (5) the potassium was found less in the deeper layers in 0-20 cm layer, the highest total potassium content was 19.2 g·kg-1 in Xiangxi, and the available potassium at 639.9 mg·kg-1 in Xiangbei. It appeared that the acidity of the soil could be neutralized by using alkaline fertilizers, and a balanced fertility be achieved by appropriate applications coupled with proper management for the vineyards in the regions.
-
Keywords:
- Hu'nan province /
- vineyard /
- soil /
- nutrient
-
土壤的质量优劣直接影响葡萄种植的情况,土壤的类型和结构、土壤深度等都会影响土壤养分的分布,从而影响葡萄植株根系对养分的吸收[1]。关于湖南葡萄种植前人有很多研究成果,而对土壤中养分的含量的关注较少,因此,针对湖南省葡萄产业区的葡萄生产现状,开展地区葡萄种植土壤养分的调查研究,对湖南葡萄产业的施肥和管理具有重要意义。为了种植高产高质的葡萄,在葡萄种植管理施肥中需要注意很多问题,因为各地区葡萄种植的肥料施用和管理都不一样,土壤各耕层养分含量也不同[2]。在不同省市,有学者研究了本土葡萄产业区的土壤养分相关状况,尹兴等[3]研究显示,河北省很多葡萄园有机质含量较低,微量元素缺乏。葡萄种植周期需要施肥的次数很多,其生长好坏是由土壤养分含量决定的,所以在什么时期施用何种肥料需要掌握好时机和管理措施[4-6]。肥料施用不合理,土壤性质也会改变,唐美玲等[7]在烟台的研究显示,土壤酸化严重,施肥不合理,有机肥施用较少,土壤酸碱度很大程度上影响葡萄植株的生长,该地区应该合理施用肥料改善这一情况。毋永龙等[8]研究结果显示,辽西的葡萄园土壤养分含量很高,容易导致土壤营养过剩,土壤盐渍化等现象,该地区需考虑合理施用肥料,否则易造成养分过度累积。很多葡萄产业园为了获得更高的效益,加大肥料施用,但是土壤的承受力有限,过量施肥会使得土壤中的平衡被打破,造成一系列问题,长此以往,易导致土壤产生退化,保肥能力变弱,不利于葡萄的生长。为了使葡萄获得更高的效益,葡萄种植户加大土壤中肥料的投入,土壤的养分供应呈超饱和状态,使得土质变化且葡萄植株生长出现问题。本研究分析了湖南省4个葡萄主产业区土壤养分含量的分布情况,通过对比分析合理控制肥料的管理和施用。以探索葡萄土壤合理改进方式,改善土壤不同土层养分含量的分布情况,进而改良葡萄土壤,使得葡萄种植获得更大的收益。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验设计与样品采集
试验于2017年6月份葡萄果实膨大期进行,土样采集地点为湖南省内的葡萄产业区,具体采样点在湘北(29°31′44″~29°31′58″N, 111°37′37″~111°45′34″E)、湘中(28°8′9″~28°43′42″N, 112°55′9″~113°14′35″E)、湘南(26°24′1″~26°29′49″N, 112°38′19″~112°54′35″E)、湘西(27°25′44″~27°33′5″N, 109°26′27″~109°37′13″E) 4个有代表性葡萄种植区域,葡萄种植区的肥料施用量均为当地常规施肥用量,在每个葡萄种植区选择6个有代表性的种植区采集土样,每个区选取有代表性的3个土样采集点,每个土样采集点以葡萄藤主干为中心,在离葡萄藤主干水平距离50~60 cm的行内用土壤采样器采集0~20、20~40、40~60 cm层次的土壤分析样品,湖南省4个葡萄种植园区一共采集土样216个带回实验室,经过自然风干,研磨过筛后供测试。
1.2 测定项目与方法
土壤的养分指标包括土壤pH,土壤有机质,土壤全氮、全磷、全钾,土壤碱解氮,土壤有效磷,土壤速效钾,测定方法[9]如下。
pH:酸度法(水:土=5:1);有机质:重铬酸钾氧化-硫酸亚铁滴定法;全氮:凯氏定氮法;碱解氮:碱解扩散法;全磷:氢氧化钠熔融-钼锑抗锑抗比色;有效磷:碳酸氢钠浸提-钼锑抗比色法;全钾:氢氧化钠熔融-火焰光度法;速效钾:醋酸铵浸提-火焰光度法。
1.3 数据处理
用Excel 2003软件进行数据整理和作图,用SPSS数据分析软件进行统计分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同地区不同耕层的土壤pH值
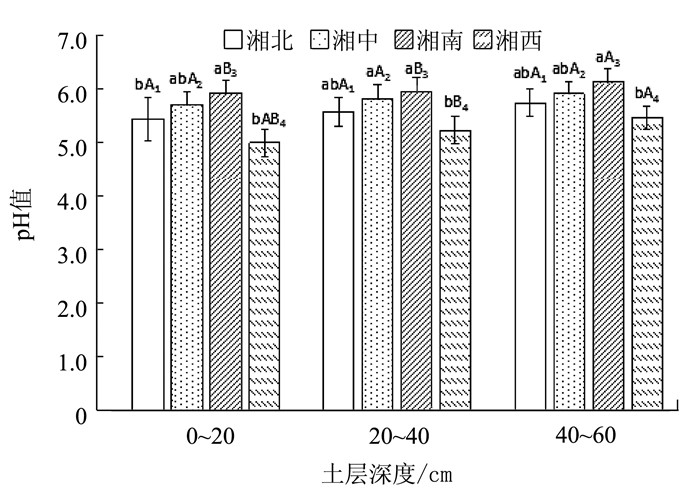
不同地区随着土壤类型、气候条件、施肥措施和种植方式等的差异导致土壤的pH值发生相应的变化。从横向来分析(图 1),在0~20 cm土层,湘南地区的土壤pH值达5.9,与湘中地区差异不显著(P>0.05);在20~40 cm土层,湘南地区的土壤pH值高达6.0,湘西地区土壤pH值最低(P < 0.05);4个地区之间的40~60 cm土层和20~40 cm土层的规律类似。从纵向来分析,同一地区不同土层的pH值随着土层深度的增加而增加(图 1)。在湘北和湘中地区,pH值均随着土层深度的增加而缓慢增加(P>0.05),在湘南和湘西地区0~20 cm和20~40 cm 2个土层的土壤pH值差异不显著(P>0.05), 40~60 cm土层的土壤pH值显著高于前2个土层(P < 0.05)。湘西地区0~20 cm土层则与20~40 cm土层和40~60 cm土层之间差异不显著(P>0.05)。
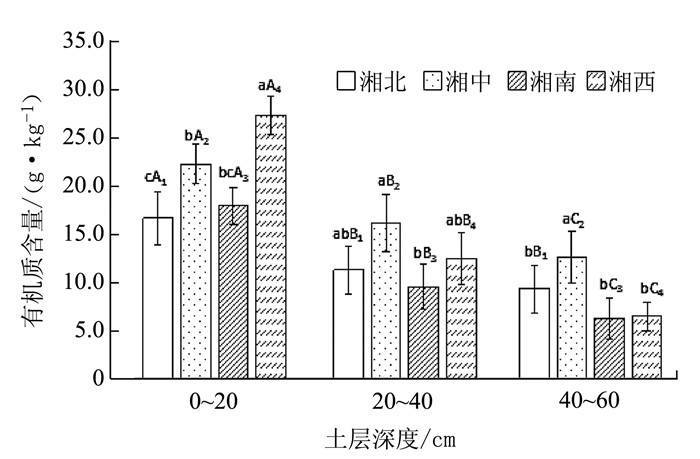
表 1 湖南省不同地区葡萄园不同土层土壤全氮含量情况Table 1. Total nitrogen in soil layers at vineyards in regions of Hu′nan[单位/(g·kg-1)] 地区 土层深度/cm 0~20 20~40 40~60 湘北 1.01 bA1 0.64 aB1 0.54 aB1 湘中 1.17 bA2 0.71 aB2 0.60 aB2 湘南 0.93 bA3 0.61 aB3 0.55 aB3 湘西 1.68 aA4 0.84 aB4 0.54 aC4 表 2 湖南省不同地区葡萄园不同土层土壤碱解氮含量Table 2. Alkali hydrolysable nitrogen in soil layers at vineyards in regions of Hu′nan[单位/(mg·kg-1)] 地区 土层深度/cm 0~20 20~40 40~60 湘北 81.3 bA1 51.5 abB1 42.1 bB1 湘中 119.0 aA2 76.9 aB2 62.3 aB2 湘南 82.3 bA3 43.3 bB3 34.7 bB3 湘西 149.2 aA4 58.1 abB4 37.2 bB4 表 3 湖南省不同地区葡萄园不同土层土壤全磷含量Table 3. Total phosphorus in soil layers at vineyards in regions of Hu′nan[单位/(g·kg-1)] 地区 土层深度/cm 0~20 20~40 40~60 湘北 0.71 aA1 0.56 aA1 0.52 aA1 湘中 0.84 aA2 0.56 aAB2 0.46 abB2 湘南 0.77 aA3 0.43 aB3 0.38 abB3 湘西 0.67 aA4 0.37 aB4 0.29 bB4 表 4 湖南省不同地区葡萄园不同土层土壤有效磷含量Table 4. Available phosphorus in soil layers at vineyards in regions of Hu′nan[单位/(mg·kg-1)] 地区 土层深度/cm 0~20 20~40 40~60 湘北 20.5 bA1 4.6 bB1 2.3 cB1 湘中 8.8 cA2 4.7 bB2 3.9 bcB2 湘南 32.0 aA3 16.9 aB3 10.2 aB3 湘西 25.5 abA4 14.9 aAB4 7.3 abB4 表 5 湖南省不同地区葡萄园不同土层土壤全钾含量Table 5. Total potassium in soil layers at vineyards in regions of Hu′nan[单位/(g·kg-1)] 地区 土层深度/cm 0~20 20~40 40~60 湘北 12.3 bA1 8.9 bB1 7.3 bB1 湘中 14.3 abA2 13.2 abB2 12.4 aB2 湘南 16.6 abA3 14.7 aA3 13.6 aA3 湘西 19.2 aA4 16.6 aAB4 14.3 aB4 表 6 湖南省不同地区葡萄园不同土层土壤速效钾含量Table 6. Available potassium in soil layers at vineyards in regions of Hu′nan[单位/(mg·kg-1)] 地区 土层深度/cm 0~20 20~40 40~60 湘北 639.9 aA1 405.9 aB1 239.6 aB1 湘中 326.9 bA2 288.1 aA2 216.7 abA2 湘南 97.1 cA3 59.6 bB3 31.2 bC3 湘西 98.4 cA4 53.4 bB4 44.4 bB4 2.2 不同地区不同耕层的土壤有机质含量
图 2中显示,在0~20 cm土层,湘西地区的土壤有机质含量最高,较湘北地区高64.1%(P < 0.05),较湘中地区高22.9%(P < 0.05),较湘南地区高52.2%(P < 0.05);湘中地区的土壤有机质含量比湘北地区高33.5%(P < 0.05),湘北和湘南地区的有机质含量比较接近(P>0.05)。在20~40 cm土层下,湘中地区的土壤有机质含量最高,达16.1 g·kg-1,比湘南地区显著高出67.7%(P < 0.05),湘西地区比湘北、湘南地区都高一些(P>0.05)。在40~60 cm土层,湘中地区的土壤有机质含量最高,达12.6 g·kg-1,较湘北地区高35.5%(P < 0.05),比湘南地区高1倍(P < 0.05);湘北、湘南和湘西地区之间差异不显著(P>0.05)。同一地区,随着土层的深入,土壤有机质的含量均呈现降低趋势,湘北地区土壤有机质含量0~20 cm土层比20~40 cm和40~60 cm土层分别显著高出47.8%和79.6%,20~40 cm土层比40~60 cm土层高21.5%(P>0.05)。湘中、湘南和湘西地区均随着土层深入,有机质含量显著降低(P < 0.05)。
2.3 不同地区不同耕层的土壤全氮含量
表 1中数据显示,在0~20 cm的土层,湘西地区的土壤全氮含量最高,达到1.68 g·kg-1,较湘北地区高66.3%(P < 0.05),较湘中地区高43.6%(P < 0.05),较湘南地区高80.6%(P < 0.05)。在20~40 cm土层,4个地区的土壤全氮含量没有显著差异(P>0.05)。在40~60 cm的土层和20~40 cm土层规律类似,4个地区的土壤全氮含量在0.54~0.60 g·kg-1。同一地区,土壤全氮含量随着土层深度的增加而减少,湘北、湘中、湘南地区均表现出0~20 cm土层的土壤全氮含量显著高于20~40 cm和40~60 cm土层(P < 0.05)。湘西地区0~20 cm土层含量比20~40 cm土层高出1倍(P < 0.05),比40~60 cm土层显著高出2.1倍(P < 0.05),而20~40 cm土层也比40~60 cm土层要高55.6%(P < 0.05)。
2.4 不同地区不同耕层的土壤碱解氮含量
表 2显示,在0~20 cm的土层,湘西的土壤碱解氮含量较湘北地区高83.5%(P < 0.05),较湘中地区高25.4%(P>0.05),较湘南地区高81.3%(P < 0.05),湘北和湘南之间差异不显著(P>0.05);在20~40 cm土层,4个地区的土壤碱解氮含量在43.3~76.9 mg·kg-1,湘北地区的土壤碱解氮含量与其他3个地区均没有显著差异(P>0.05);湘中地区的土壤碱解氮含量比湘南地区高77.6%(P < 0.05),与湘西地区差异不显著(P>0.05)。在40~60 cm的土层,湘中地区较湘北高48%(P < 0.05),较湘南高79.5%(P < 0.05),较湘西高67.5%(P < 0.05)。同一地区,0~20 cm土层的碱解氮含量显著高于20~40 cm和40~60 cm土层(P < 0.05)。
2.5 不同地区不同耕层的土壤全磷含量
表 3显示,在0~20 cm和40~60 cm的土层,4个地区的土壤全磷含量相互之间差异不显著(P>0.05);在40~60 cm的土层,湘北地区的土壤全磷含量比湘西地区的高79.3%(P < 0.05),与湘中和湘南2个地区之间差异不显著(P>0.05)。同一地区,4个地区均表现出随着土层深度加深,全磷含量降低,在湘北地区3个土层的土壤全磷含量之间差异不显著(P>0.05)。湘中地区的土壤全磷含量20~40 cm土层与0~20 cm土层、40~60 cm土层之间差异不显著(P>0.05),湘西地区均表现出0~20 cm土层与20~40 cm土层差异显著(P < 0.05),20~40 cm土层与40~60 cm土层之间差异不显著(P>0.05)。
2.6 不同地区不同耕层的土壤有效磷含量
从表 4可以看出,在0~20 cm的土层,土壤有效磷含量属湘南地区的最高,比湘北地区高56.1%(P < 0.05),比湘中地区高出2.6倍(P < 0.05),和湘西地区差异不显著(P>0.05)。湘西地区有效磷含量比湘中地区高出1.9倍(P < 0.05),和湘北、湘南地区差异不显著(P>0.05)。在20~40 cm的土层,湘北和湘中之间差异不显著(P>0.05),且均比湘南和湘西地区含量低(P < 0.05),湘南和湘西之间差异也不显著(P>0.05),湘南地区土壤有效磷含量比最低的湘北地区高出2.7倍(P < 0.05)。在40~60 cm的土层,湘南地区的土壤有效磷含量比湘北地区高出3.4倍(P < 0.05),比湘中地区高出1.6倍(P < 0.05),较湘西地区高39.7%(P>0.05)。对于同一地区来说,随着土层的加深,土壤有效磷养分含量降低,湘北、湘中和湘南地区均表现出0~20 cm土层与20~40 cm土层差异显著(P < 0.05),20~40 cm土层与40~60 cm土层差异不显著(P>0.05);湘西地区的土壤有效磷含量20~40 cm土与0~20、40~60 cm土层差异均不显著(P>0.05)。
2.7 不同地区不同耕层的土壤全钾含量
表 5显示,在0~20 cm的土层中,湘西地区的土壤全钾含量最高,比湘北地区高56.1%(P < 0.05),比湘中地区高34.3%(P>0.05),比湘南地区高15.7%(P>0.05)。在20~40 cm土层,湘中、湘南和湘西地区的土壤全钾含量之间差异不显著(P>0.05),湘西地区比湘北地区高86.5%(P < 0.05)。在40~60 cm的土层,湘中、湘南和湘西地区的土壤全钾含量之间差异不显著(P>0.05),湘北含量最低。同一地区,4个地区均表现出随着土层加深,土壤全钾含量呈降低趋势,湘南地区3个土层之间土壤全钾含量差异不显著(P>0.05);湘北和湘中地区均在0~20 cm土层土壤全钾含量显著高于20~40 cm土层(P < 0.05),而20~40 cm土与40~60 cm土层差异不显著(P>0.05),在湘西地区,20~40 cm土层的土壤全钾含量与0~20 cm土层、40~60 cm土层均不显著(P>0.05)。
2.8 不同地区不同耕层的土壤速效钾含量
从表 6可以看出,在0~20 cm的土层,湘北地区的土壤速效钾含量最高,比湘中地区高95.7%(P < 0.05),比湘南地区高出5.6倍(P < 0.05),比湘西地区高出5.5倍(P < 0.05),湘中地区比湘南地区高出2.4倍(P < 0.05),比湘西地区高出2.3倍(P < 0.05),湘南和湘西地区差异不显著(P>0.05)。在20~40 cm的土层,湘北地区比湘中地区高40.9%(P>0.05),比湘南地区高出5.8倍(P < 0.05),比湘西地区高出6.4倍(P < 0.05),湘南和湘西地区差异不显著(P>0.05)。同样的规律在40~60 cm土层也表现出来,在40~60 cm的土层,湘北的土壤速效钾含量比湘中地区高10.6%(P>0.05),比湘南地区高出6.7倍(P < 0.05),比湘西地区高出4.4倍(P < 0.05),湘南和湘西地区差异不显著(P>0.05)。同一地区,随着土层的加深,土壤速效钾的含量逐渐降低,湘中地区3个土层之间差异不显著(P>0.05);湘北和湘西地区均表现出0~20 cm土层与20~40 cm土层差异显著(P < 0.05),而20~40 cm土层与40~60 cm土层差异不显著(P>0.05),而湘南地区的土壤速效钾含量3个土层差异均显著(P < 0.05)。
3. 讨论
测定结果显示,随土层深入,土壤养分含量下降,这可能与施肥方式有关。孙权等[10]研究得出,传统施肥均是将不同肥料施于15~20 cm的土层,根系无法延伸、养分吸收受阻,葡萄的产量和品质也受到影响。葡萄种植户一般采用表土施肥,通过施水淋洗表土达到肥料下渗目的,尽管此种施肥方式相对简单,人工操作相比于其他方法轻松,但是会降低肥料利用率。结果表现在养分多聚集在表层,且葡萄根系不能深扎并裸露在外,根系浅,长此以往土壤不能均匀地吸收养分,保肥能力也变差,土壤容纳的养分不足,葡萄根系吸收营养元素也会减少,葡萄植株生长受阻,产量和品质下降。单一的施用化肥对土壤的影响也很大,需要合理配施有机肥等改善土壤养分,增强葡萄根系对土壤养分的吸收[10-12]。
土壤pH值可以通过改变土壤的性状,微生物活性,刺激葡萄根系的能力等影响葡萄植株对于养分的吸收。多数葡萄种植所需pH值在4.0~8.5,在6.5~7.0更有利[13]。本研究结果显示,4个地区的土壤pH值变化区间很小,为5.0~6.1,而对于稳产、优质葡萄的pH指标来说,应施用碱性肥料以调节pH值。土壤有机质所含养分可以有效改善土壤性质,为土壤微生物提供碳源,高产、优质葡萄对于土壤有机质的需求较高。在葡萄种植方面,主要施用有机肥料来增加土壤中的有机质含量,通过微生物的分解等作用转化为养分为葡萄根系所吸收,从而将养分运输至葡萄植株各组织器官。本试验数据显示,湘北、湘中和湘南地区土壤有机质含量都比湘西地区低,可以考虑增施有机肥,湘西地区随着土层深入,有机质的含量降低幅度显著大于其他3个地区,可能是施肥方式的差异导致,建议采用有机肥料开沟施肥、覆土埋施等施肥方式,以利于有机肥料的营养元素充分利用。
缺乏某些营养元素会限制葡萄植株的生长,进而影响葡萄产量和品质,了解土壤中不同的土层全量及速效养分含量很有必要[14]。晁无疾等[15]研究表明,葡萄植株每生产100 kg葡萄果实,需要从土壤中吸收0.3~0.6 kg的氮素、0.1~0.3 kg的五氧化二磷,0.30~0.65 kg的钾素。葡萄种植户在施用肥料过程中增施尿素,葡萄果实成熟期氨基酸等营养物质的积累需要大量的氮素,在葡萄生长期合理施用氮肥会显著地增加葡萄产量。本试验结果显示,湘西地区的全氮和碱解氮的含量在表层土高于其他3个地区,湘北、湘中和湘南地区需要考虑合理增施氮肥来增加葡萄的产量。随着土层加深,氮素的含量虽有减少,但是幅度不大,葡萄种植施肥过程中可以考虑施用控释肥料,延长土壤中养分供应,以利于葡萄生长。葡萄植株生长过程中磷素的作用不可或缺,葡萄产业园改变以往的单一施肥模式,改用施用复混肥料和有机肥料,在增加土壤中的营养元素同时还能合理的配比施肥,有利于葡萄植株的生长。土壤有效磷可以促进葡萄花芽分化和果实发育,不同的地区磷肥的施用配比不一样,最终的结果差异很大。湘中地区的土壤有效磷含量低于其他3个地区,需要及时补充磷肥。钾素对葡萄植株的生长和养分运输很重要,钾素能使葡萄的茎秆硬实,不易倒伏,增强根系对土壤中水分和养分的吸收,缺钾会使得葡萄植株的抵抗力变差,易感病害,果实品质也会受到影响。湘南和湘西地区土壤速效钾相对较低,为了葡萄植株的良好生长,可以考虑施用钾肥的同时加施有机肥,增加土壤的养分保持能力,肥料施用可以采用有机无机肥配合施用提高土壤养分。
4. 结论
不同区域葡萄种植土壤养分含量均有所变化,除了土壤pH值变化差异不大之外,其他均表现出0~20 cm土层的养分含量为最高,而随着土层深入,土壤养分含量逐渐下降。湘北、湘中、湘南和湘西4个葡萄种植区域均适合葡萄种植,湘中地区土壤的养分含量更适合葡萄种植。
-
表 1 湖南省不同地区葡萄园不同土层土壤全氮含量情况
Table 1 Total nitrogen in soil layers at vineyards in regions of Hu′nan
[单位/(g·kg-1)] 地区 土层深度/cm 0~20 20~40 40~60 湘北 1.01 bA1 0.64 aB1 0.54 aB1 湘中 1.17 bA2 0.71 aB2 0.60 aB2 湘南 0.93 bA3 0.61 aB3 0.55 aB3 湘西 1.68 aA4 0.84 aB4 0.54 aC4 表 2 湖南省不同地区葡萄园不同土层土壤碱解氮含量
Table 2 Alkali hydrolysable nitrogen in soil layers at vineyards in regions of Hu′nan
[单位/(mg·kg-1)] 地区 土层深度/cm 0~20 20~40 40~60 湘北 81.3 bA1 51.5 abB1 42.1 bB1 湘中 119.0 aA2 76.9 aB2 62.3 aB2 湘南 82.3 bA3 43.3 bB3 34.7 bB3 湘西 149.2 aA4 58.1 abB4 37.2 bB4 表 3 湖南省不同地区葡萄园不同土层土壤全磷含量
Table 3 Total phosphorus in soil layers at vineyards in regions of Hu′nan
[单位/(g·kg-1)] 地区 土层深度/cm 0~20 20~40 40~60 湘北 0.71 aA1 0.56 aA1 0.52 aA1 湘中 0.84 aA2 0.56 aAB2 0.46 abB2 湘南 0.77 aA3 0.43 aB3 0.38 abB3 湘西 0.67 aA4 0.37 aB4 0.29 bB4 表 4 湖南省不同地区葡萄园不同土层土壤有效磷含量
Table 4 Available phosphorus in soil layers at vineyards in regions of Hu′nan
[单位/(mg·kg-1)] 地区 土层深度/cm 0~20 20~40 40~60 湘北 20.5 bA1 4.6 bB1 2.3 cB1 湘中 8.8 cA2 4.7 bB2 3.9 bcB2 湘南 32.0 aA3 16.9 aB3 10.2 aB3 湘西 25.5 abA4 14.9 aAB4 7.3 abB4 表 5 湖南省不同地区葡萄园不同土层土壤全钾含量
Table 5 Total potassium in soil layers at vineyards in regions of Hu′nan
[单位/(g·kg-1)] 地区 土层深度/cm 0~20 20~40 40~60 湘北 12.3 bA1 8.9 bB1 7.3 bB1 湘中 14.3 abA2 13.2 abB2 12.4 aB2 湘南 16.6 abA3 14.7 aA3 13.6 aA3 湘西 19.2 aA4 16.6 aAB4 14.3 aB4 表 6 湖南省不同地区葡萄园不同土层土壤速效钾含量
Table 6 Available potassium in soil layers at vineyards in regions of Hu′nan
[单位/(mg·kg-1)] 地区 土层深度/cm 0~20 20~40 40~60 湘北 639.9 aA1 405.9 aB1 239.6 aB1 湘中 326.9 bA2 288.1 aA2 216.7 abA2 湘南 97.1 cA3 59.6 bB3 31.2 bC3 湘西 98.4 cA4 53.4 bB4 44.4 bB4 -
[1] 杜章留, 高伟达, 陈素英, 等.保护性耕作对太行山前平原土壤质量的影响[J].中国生态农业学报, 2011, 19(5):1134-1142. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4407595 [2] SCHMIDT H, KAMMANN C, NIGGLI C, et al.Biochar and biocharcompost as soil amendments to a vineyard soil:Influences on plant growth, nutrient uptake, plant health and grape quality[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2014, 191: 117-123. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=8504763567d833599bd943895c2d2d88&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[3] 尹兴, 吉艳芝, 倪玉雪, 等.河北省葡萄主产区土壤养分丰缺状况[J].中国农业科学, 2013, 46(10): 2067-2075. DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2013.10.012 [4] GUO X W, LI K, GUO Y S, et al. Root zone soil nutrient change of vineyard with different planting years and related effect on replanted grape growth[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2010, 18(3): 477-481. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2010.00477
[5] GAO Y M, TONG Y A, MA W J. Study on grapery soil nutrients condition and balanced fertilization in Shaanxi Guanzhong area[J]. Journal of Northwest Sci-Tech University of Agriculture and Forestry(Natural Science Edition), 2006, 34(9): 41-44. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5b08915fa66082c040152e2c0c5da01a&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[6] LI M Y, ZHU J H, LIAN X J, et al. Soil nutrients management and balanced fertilization based on GIS in grape region[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2010, 26(3): 202-205.
[7] 唐美玲, 郑秋玲, 张超杰, 等.烟台地区葡萄园的土壤营养状况分析[J].北方园艺, 2013(24): 164-166. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/BFYY201324050.htm [8] 毋永龙, 聂继云, 李海飞, 等.辽西主产区葡萄的根区土壤养分研究[J].土壤通报, 2013, 44(1): 138-143. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-TRTB201301026.htm [9] 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析:第3版[M].北京:中国农业出版社, 2000. [10] 孙权, 王静芳, 王素芳, 等.不同施肥深度对酿酒葡萄叶片养分和产量及品质的影响[J].果树学报, 2007, 24(4):455-459. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gskx200704009 [11] MENG H Q, LIU J, XU M G, et al. Evolution of pH in topsoils of typical Chinese croplands under long-term fertilization[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2013, 50(6): 1109-1116.
[12] MA Y C, YAO Y X, DU Y P, et al. Changes of soil physical and chemical properties in greenhouse of different grapevine planting years[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2015, 32(2): 225-231. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=0b76a27feffb28f888a9856d3d446eda&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[13] 唐琨, 朱伟文, 周文新, 等.土壤pH对植物生长发育影响的研究进展[J].作物研究, 2013, 27(2): 207-212. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_zuowuyj201302025.aspx [14] DUPLAY J, SEMHI K, ERRAIS E, et al. Copper, zinc, lead and cadmium bioavailability and retention in vineyard soils(Rouffach, France): The impact of cultural practices[J]. Geoderma, 2014(7):318-328. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ee4b94d62ebee43a5092f25b8167e790&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[15] 晁无疾.葡萄优质高效栽培指南[M].北京:中国农业出版社, 2002:36-42. -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 刘谊锋,田耀武. 不同种植年限葡萄园土壤及微生物量碳、氮、磷生态化学计量特征. 河南农业科学. 2021(08): 57-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 杨阳,谭玉超,汤小宁. 济南市葡萄园土壤肥力水平分析及施肥建议. 中国果菜. 2020(04): 61-67 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: