Active Components in Wild and Cultivated Ganoderma Fruiting Bodies
-
摘要: 研究采集的野生灵芝子实体与其进行组织分离后同菌株人工代料的栽培子实体,比较二者主要活性成分的差异,分析判断何者利用价值更高,以挖掘到更好、利用价值更高的灵芝子实体。ITS(Internal Transcribed Spacer)鉴定结果表明采集的野生菌株YX、ZJ均属于Ganoderma sp.组群且两个G.sp.菌株之间的相似度较高。主要活性成分检测结果显示:野生灵芝子实体YX多糖含量为7.93 mg·g-1,是其栽培子实体多糖含量(10.25 mg·g-1)的77%;三萜含量7.16 mg·g-1,是其栽培子实体三萜含量(9.30 mg·g-1)的77%;野生灵芝子实体ZJ的多糖含量(5.34 mg·g-1)是其栽培子实体(6.72 mg·g-1)的87%,三萜含量(9.30 mg·g-1)是其栽培子实体(10.66 mg·g-1)的75%。利用高效液相色谱分析三萜中各灵芝酸含量发现,两栽培子实体灵芝酸F含量均显著高于其对应野生灵芝子实体。野生与栽培灵芝子实体活性成分差异分析结果表明:同一菌株的栽培子实体多糖、三萜含量明显高于其野生子实体。该研究结果为市场上灵芝产品的选择提供参考,为野生灵芝驯化必要性提供理论依据。Abstract: Major active components in wild and cultivated Ganoderma fruiting bodies were determined for comparison. Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) identified the selected wild strains, YX and ZJ, to be Ganoderma sp. with a high homology. The chemical analysis showed the polysaccharide content in the fruiting bodies of YX to be 7.93 mg·g-1, which was 77% of that of the cultivated counterparts (10.25 mg·g-1); the triterpenes of YX to be 7.16 mg·g-1, which was also 77% of that of the cultivated fruiting bodies (9.30 mg·g-1); the polysaccharides in ZJ fruiting bodies to be 5.34 mg·g-1, which was 87% of the cultivated counterparts (6.72 mg·g-1); and, the triterpenes of ZJ to be 9.30 mg·g-1, which was 75% of the cultivated fruiting bodies (10.66 mg·g-1). HPLC showed the ganoderic acid F in the fruiting bodies of the cultured Ganoderma to be significantly higher than that in the wild of a same strain as well. The results demonstrated a distinctive difference on the active ingredients between the G.lucidum grown in the wild and that cultivated artificially which could be of interest for marketing and breeding of the fungal material used as a dietary supplement.
-
Keywords:
- wild Ganoderma /
- cultivated Ganoderma /
- ITS sequencing /
- main active components
-
灵芝Ganoderma属真菌界Kingdom Fungi,担子菌门Basidiomycota,担子菌纲Basidiomycetes,多孔菌目Polyporales,多孔菌科Polyporaceae灵芝属Ganoderma[1],是中国传统药用真菌。
灵芝含有丰富的生物活性物质,如多糖、三萜、不饱和脂肪酸、生物碱、甾醇类物质等[2]。其中多糖和三萜两大类活性物质被认为是其主要药效成分,其含量可作为衡量栽培和野生灵芝质量的标准[3]。灵芝多糖具有降“三高”、抗癌、提高免疫调节作用等活性[4];灵芝三萜具有保肝排毒、抑制肿瘤细胞、抗HIV病毒、降低胆固醇、调血脂和抗炎等活性[5-6]。灵芝多糖和三萜类物质的提取纯化是对其分子结构、药理活性等进行深入研究的基础。
灵芝的药用价值被广泛发掘,人们对灵芝的需求日益增长。为满足市场需求,人工栽培灵芝逐渐成为灵芝生产的重要来源。目前对灵芝的研究趋于完善,适合人工栽培的品种被广泛推广,但灵芝基础研究一直难以取得突破性进展。目前市场上主要是以赤芝与紫芝作为栽培种,其他品种较少。野生灵芝可能有栽培灵芝所没有的优良性状,存在人们意想不到的优良品种。
野生灵芝和人工栽培灵芝的有效成分及药理作用是否有很大的差异,学术界意见不统一,分歧较大,可以说是众说纷纭,各执一词。曹恒生等[7]对大别山野生灵芝和栽培灵芝子实体主要生化成分的含量进行比较研究,结果表明:野生灵芝的多糖含量比栽培灵芝的高。陈康林[8]也认为在栽培灵芝中多糖含量只有野生的1/3左右,药理活性很强的灵芝酸含量已很低,各种有效成分的活性极低。吉清妹等[9]分析认为,通过改进栽培技术可提高栽培灵芝的某些成分和功效,并优于野生灵芝。目前大多研究认为野生灵芝主要活性成分高于栽培灵芝,其大都是对不同菌株亦或不同种的野生灵芝与栽培灵芝主要活性成分的研究,实际意义低且不具备说服性,利用同一菌株野生子实体和栽培子实体进行比较,更具有说服性。
本研究以采集的野生灵芝作为试验对象,对组织分离后的野生菌株子实体进行ITS测序并构建系统进化树以确定野生菌株的种类,利用所采集的野生菌株进行组织分离人工代料培养得到栽培子实体,对其提取多糖和三萜,分析比较野生子实体与其栽培子实体的多糖和三萜含量,以期比较野生和栽培子实体利用价值,更好地挖掘利用野生灵芝的潜在价值,充分发挥栽培灵芝的功效。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 供试菌株
供试菌株为采集自漳州市云霄县的野生灵芝YX,采集自湛江市的野生灵芝ZJ,将野生灵芝进行组织分离人工代料培养得到的栽培灵芝YX(z)、ZJ(z)。
1.2 培养基
PDA固体培养基:马铃薯200 g、葡萄糖20 g、琼脂20 g、蒸馏水1 000 mL、pH自然。
LB液体培养基:胰蛋白胨10 g·L-1、氯化钠10 g·L-1、酵母粉5 g·L-1、pH 7.0。
LB固体培养基:胰蛋白胨10 g·L-1、氯化钠10 g·L-1、酵母粉5 g·L-1、琼脂15 g·L-1、pH 7.0。
木屑培养基:木屑76%,麸皮20%,玉米粉3%,石膏1%。
1.3 子实体的组织分离
在超净工作台,用已灭菌的解剖刀在新鲜无病虫害的灵芝子实体边缘截取子实体内部的一小块菌管转到PDA斜面上,置于27℃生化培养箱中培养。待长出菌丝后,挑取边缘新鲜的菌丝块活化到新的PDA试管斜面,27℃培养。
1.4 ITS测序及比对
1.4.1 DNA的提取
制备PDA平板,挑取两个野生菌株的菌块接种到贴有玻璃纸的PDA平板中,封口倒置,27℃培养。待菌丝长满平板收集灵芝菌丝,于预冷研钵中加入液氮研磨成细粉。参照傅俊生改良的CTAB法[10]提取供试菌株的总DNA。
1.4.2 ITS序列扩增及测序
参照White等[11]ITS通用引物序列设计引物:ITS1:5′-TCC GTA GGT GAA CCT GCG G- 3′;ITS4:5′-TCC TCC GCT TAT TGA TAT GC- 3′。其ITS- PCR 30 μL扩增体系:10×Buffer 3 μL,DNTP 2 μL,ITS1 1 μL,ITS4 1 μL,Taq DNA聚合酶0.3 μL,模版1 μL,ddH2O 21.7 μL。反应程序:94℃ 5 min;94℃ 45 s,55℃ 45 s,72℃ 1 min,35个循环;72℃ 10 min;4℃保存。
ITS- PCR产物用1.0%琼脂糖凝胶电泳,在凝胶成像系统下成像保存。
选择YX、ZJ菌株,按照说明书的要求做产物的克隆试验。按照ITS体系和程序经PCR验证后,阳性克隆子委托福州博尚公司测序。
1.4.3 构建系统进化树
将测定的序列结果在NCBI数据库中进行比对,选择在线BLAST分析,再选取nucleotide blast得到与测定序列相近的序列结果。在CLUSTXAL1.83软件中将ITS序列对位排列并去掉两端差异的部分,用MEGA 6.0软件采用最大可能性法(Maximum Likelihood,ML)构建系统进化树,运行1 000次bootstrap检验评价系统发育树拓扑结构的可靠性[12],根据Kimura-2法计算各序列间的进化距离[13]。
1.5 灵芝主要活性成分的比较
1.5.1 子实体多糖的提取及检测
子实体多糖的提取:用粉碎机将干燥的灵芝子实体粉碎,并过孔径1 mm的筛子,精确称取2 g粉末,加蒸馏水到料液比为1:50,在90℃回流提取3 h,过滤,用旋转蒸发仪将提取液浓缩,定容至25 mL。吸取10 mL多糖提取液,加入80 mL无水乙醇,醇沉约12 h,5 000 r·min-1离心10 min,将沉淀物定容至25 mL。采用改良后的苯酚-硫酸法[14]检测子实体粗多糖。每组3个重复。
1.5.2 子实体三萜的提取及检测
结合黄书铭等[15]与张志军等[16]的灵芝中三萜化合物的提取方法:精确称取细粉末1 g,加85%乙醇25 mL(料液比1:25),常温浸提2h,再超声30 min,过滤;滤液用旋转蒸发仪于60℃减压抽滤除去乙醇。色谱级甲醇溶解蒸干析出物,用容量瓶定容至25 mL。采用香草醛-冰醋酸法[17]检测,每组3个重复。
1.5.3 子实体三萜的高效液相色谱法(HPLC)分析
提取液用0.45 μm的有机微孔过滤膜过滤备用,三萜的HPLC分析程序采用叶丽云等[18]的方法。采用Inertsustain C18色谱柱,以0.1%乙酸水(A)和浓度梯度的乙腈(B)洗脱系统,洗脱比例B浓度为:0~20 min:30%~40%;20~25 min:40%~55%;25~30 min:55%~65%;30~40 min:65%~65%;柱温40℃,流速0.8 mL·min-1,进样量10 μL,检测波长254 nm。
灵芝酸A标准样品图谱,精确称取4.0 mg的灵芝酸A晶体,用色谱级甲醇定容至50 mL,得到浓度为0.08 mg·mL-1的灵芝酸A标准液。按照以上方法对其进行HPLC分析。其他标准样品的分析同理。
1.6 数据统计与分析
应用Excel 2010和SPSS 22.0数据分析软件对多糖、三萜提取结果进行统计分析,应用中药色谱指纹图谱相似度评价系统2004A版对各三萜酸含量及指纹图谱相似度进行统计分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 ITS克隆测序及系统进化树构建
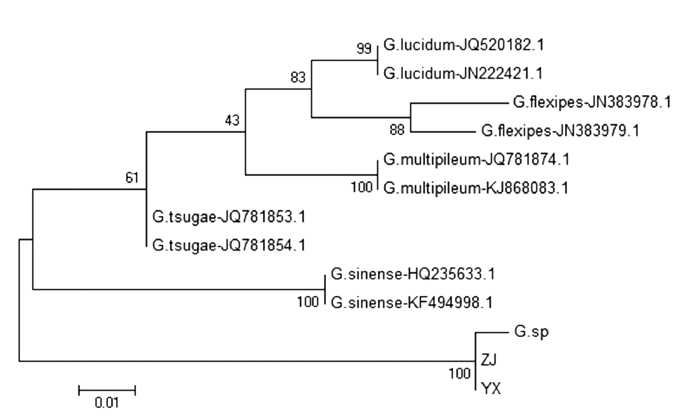
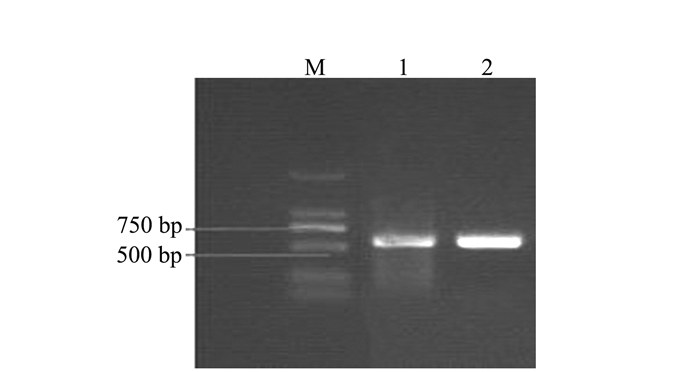
克隆测序的菌株ITS序列已上传至NCBI,登录号为:MH023509。ITS琼脂凝胶电泳结果(图 1),可以看出菌株YX、ZJ的ITS序列片段大小在500~750 bp,符合灵芝菌株的ITS序列片段在650 bp左右的现象。将克隆测序的菌株ITS序列置于NCBI数据库进行BLAST分析比对,结果表明菌株YX、ZJ为Ganoderma sp.。下载各组群比对结果相应的灵芝菌株ITS序列:G.lucidum-JQ520182.1和G.lucidum-JN222421.1,G.multipileum-JQ781874.1和G.multipileum-KJ868083.1,G.flexipes-JN383978.1和G.flexipes-JN383979.1;G.tsugae-JQ781853.1和G.tsugae-JQ781854.1,Ganoderma sp.,G.sinense-HQ235633.1和G.sinense-KF494998.1构建系统进化树。系统进化树(图 2)显示,采集的两个野生菌株YX、ZJ均属于Ganoderma sp.。
2.2 野生和栽培灵芝主要活性成分的比较
2.2.1 野生和栽培子实体多糖含量比较
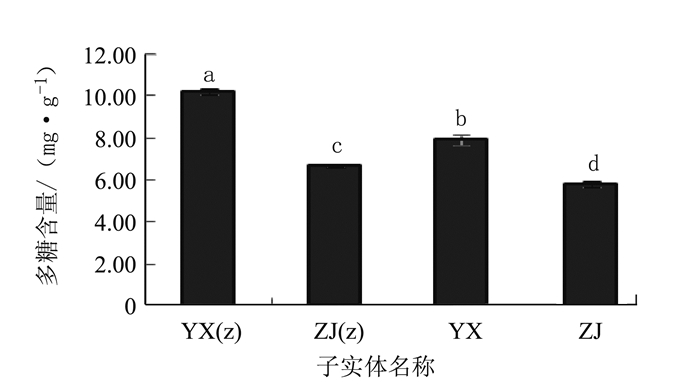
两个G.sp.的野生和栽培子实体多糖含量如图 3所示。比较栽培子实体和野生子实体的多糖,可知野生子实体YX的多糖含量为7.93 mg·g-1,约为相应菌株栽培子实体YX(Z)含量的77%;野生子实体ZJ的多糖含量为5.84 mg·g-1,约为相应菌株栽培子实体ZJ(z)含量的87%。可以发现同一菌株其栽培子实体多糖含量明显高于野生子实体多糖含量。但是G.sp.-YX的野生子实体多糖含量高于G.sp.-ZJ的栽培子实体ZJ(z),因此不同菌株的栽培子实体和野生子实体的多糖含量没有可比性。
2.2.2 野生和栽培子实体三萜含量比较
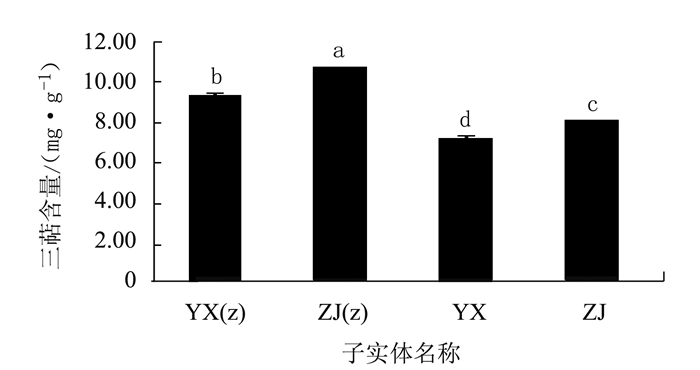
两个G.sp.菌株的野生和栽培子实体三萜含量如图 4所示,比较栽培子实体和野生子实体的多糖,可知野生子实体YX的三萜含量为7.16 mg·g-1,约为相应菌株栽培子实体YX(z)含量的77%;野生子实体ZJ的多糖含量为7.97 mg·g-1,约为相应菌株栽培子实体ZJ(z)含量的75%,可以发现两个菌株的栽培子实体三萜含量均高于野生子实体的三萜含量。
2.2.3 灵芝子实体三萜的HPLC图谱比较
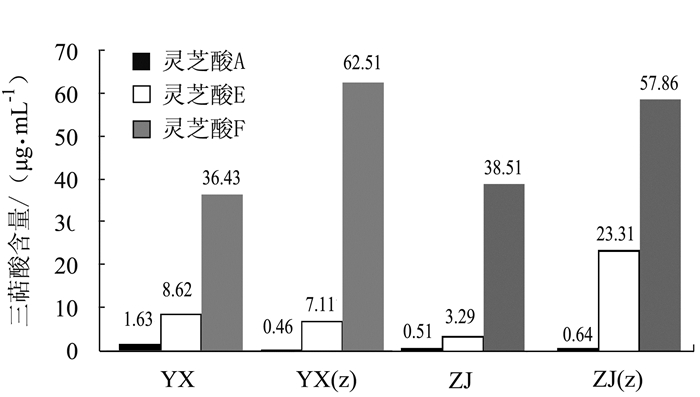
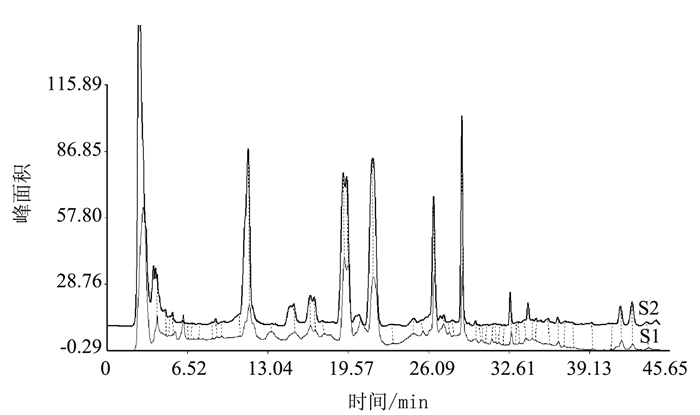
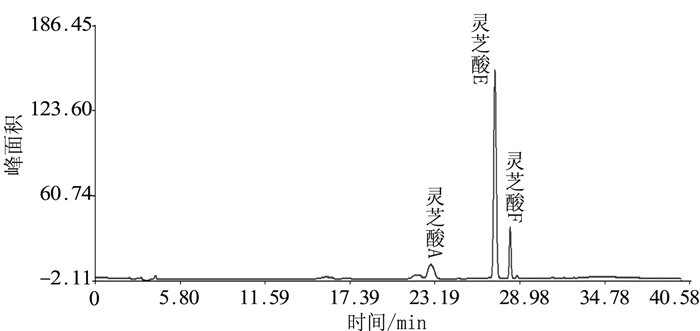
灵芝的3个三萜酸的标准样品HPLC指纹图谱如图 5所示,保留时间逐渐递增对应的标准样品为灵芝酸A、灵芝酸E、灵芝酸F,其保留时间分别为23.6、27.9、28.7 min。将G.sp子实体根据标准样品计算公式计算三萜酸含量,分别得出子实体的灵芝酸A、E、F含量(图 6),分析三萜中各灵芝酸含量发现:G.sp子实体主要含灵芝酸F,且其栽培子实体灵芝酸含量为野生子实体的1.5倍左右。G.sp.-YX的野生和栽培子实体三萜HPLC图谱如图 8所示,虽然相似度计算结果很低(表 1),野生子实体和栽培子实体的图谱相似度仅0.439,但是图 7显示两者的主要峰型一致,说明野生和栽培子实体的主要三萜酸成分相似。峰面积结果表明,G.sp.-YX的栽培子实体三萜酸含量总体高于野生子实体,因此从三萜酸成分和含量分析,说明野生的灵芝子实体并没有比栽培的好。结合其多糖和总三萜检测结果,栽培灵芝的子实体两大主要有效成分明显高于相应的野生子实体,说明栽培灵芝子实体的主要活性成分较高。
表 1 指纹图谱相似度比较Table 1. Similarity on fingerprints项目 S1 S2 对照指纹图谱 S1 10.439 0.753 S2 0.439 10.922 对照指纹图谱 0.753 0.9221 3. 讨论与结论
分子生物学技术手段是对灵芝菌株进行分类鉴定的有效方法,ITS序列能够有效分析近缘种对其进行分类鉴定[19]。通过野生灵芝ITS序列的凝胶电泳图谱得知ITS片段大小500~750 bp,符合灵芝菌株的片段大小。克隆测序菌株,在NCBI数据库进行BLAST比对,确定两野生灵芝是G.sp.种类。利用下载的相应灵芝菌株ITS序列与试验菌株的ITS序列构建系统进化树,确定了两个野生灵芝属于G.sp.种群。
通过提取两个G.sp.菌株的野生和栽培子实体多糖、三萜含量,得出两个G.sp.菌株的栽培子实体三萜含量均高于野生子实体的三萜含量,野生子实体三萜含量约为相应菌株栽培子实体三萜含量的75%,对其多糖含量的比较分析略有不同,同一菌株的栽培子实体多糖含量明显高于其野生子实体多糖含量,然而G.sp.-YX的野生子实体多糖含量高于G.sp.-ZJ的栽培子实体多糖含量。因此不同菌株的栽培和野生子实体没有可比性,只能说明同一菌株的栽培子实体的多糖比野生子实体的要高。
高效液相色谱法检测三萜类化合物,快速、简便、灵敏、分离度好,适用于灵芝子实体、孢子粉、发酵菌丝体及相关制剂的三萜类物质检查和含量测定。通过HPLC对野生和栽培的同菌株子实体的三萜酸成分分析得知:G.sp三萜酸种类丰富,且含量高,其主要峰面积显示有5种含量较高的三萜酸,因此认为G.sp的三萜酸成分方面开发价值较高。将G.sp子实体和标准样品进行匹配得出其主要含有灵芝酸F。从野生和栽培子实体三萜HPLC图谱三萜酸成分和含量分析可知野生的灵芝子实体并没有比栽培好。
结合其多糖和总三萜检测结果可知,同一菌株栽培的子实体两大主要有效成分明显高于相应的野生子实体,可以得出本研究中同一灵芝菌株的栽培子实体优于野生子实体。数据处理分析结果表明,对于同一菌株来说野生灵芝并不一定比栽培的有效成分要高,相反栽培子实体的主要活性成分高于野生子实体,因为是对同一菌株的野生子实体和栽培子实体的主要活性成分分析,较之前人所研究的不同种抑或是不同菌株野生和栽培子实体主要活性成分而言更具有比较性和说服性。且通过数据比较证明不同菌株栽培和野生子实体没有可比性,无法得出一致的结论,从侧面说明关于野生灵芝要优于人工栽培灵芝的说法有待商榷,人工栽培灵芝主要活性成分不比野生灵芝差。本研究对人工栽培灵芝提出更正确客观的认识,为市场上灵芝产品的选择提供参考,同时充分挖掘利用野生灵芝菌株的潜在价值,为野生灵芝驯化必要性提供理论依据。
-
表 1 指纹图谱相似度比较
Table 1 Similarity on fingerprints
项目 S1 S2 对照指纹图谱 S1 10.439 0.753 S2 0.439 10.922 对照指纹图谱 0.753 0.9221 -
[1] 赵继鼎, 张小青.中国真菌·灵芝科[M].北京:科学出版社, 2000:185-192. [2] ZHOU X W, SU K Q, ZHANG Y M. Applied modern biotechnology for cultivation of Ganoderma and development of their products[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2012, 93(3):941-963. DOI: 10.1007/s00253-011-3780-7
[3] 林志彬.灵芝的现代研究[M].北京:北京医科大学、中国协和医科大学联合出版社, 1996.145-146. [4] 李平作, 章克昌.灵芝胞外多糖的分离纯化及生物活性[J].微生物学报, 2000, 40(2):217-220. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/97426A/200304/8342882.html [5] 李晔, 朱忠敏, 姚渭溪, 等.灵芝三萜类化合物的研究进展[J].中国中药学杂志, 2012, 37(2):165-171. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95973X/201202/1002016400.html [6] 李国华, 李晔, 梅锡玲, 等.灵芝三萜类化合物研究进展[J].中草药, 2015, 46(12):1858-1862. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2015.12.028 [7] 曹恒生, 赵立新.野生和栽培灵芝主要生化成分的比较[J].安徽农业科学, 1996(S2):54-56. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90168X/1996S2/4001091408.html [8] 陈康林.野生灵芝和人工栽培灵芝的不同[J].医药世界, 2008(7):70-71. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93998X/201404/663531077.html [9] 吉清妹, 潘孝忠, 符传良, 等.野生灵芝与栽培灵芝主要成分和功效的比较分析[J].热带农业科学, 2015, 35(12):80-83. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2196.2015.12.015 [10] 傅俊生. 草菇杂交育种研究及其分子遗传标记的建立[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2007: 18. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10389-2007136027.htm [11] WHITE T J, BRUNS T, LEE S, et al. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics[J]. PCR-Protocols:A guide to methods and applications, 1994, 38:315-322. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4a2cef2a8fc47e1fbe684b4b2f80e023&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[12] FELSENSTEIN J. Confidence limits on phylogenies:all approach using the bootstrap[J]. Evolution, 1985, 39(4):783-791. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/317316010_CONFIDENCE_LIMITS_ON_PHYLOGENIES_AN_APPROACH_USING_THE_BOOTSTRAP
[13] KIMURA M. Estimation of evolutionary distances between homologo us nucleotide sequences[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1981, 78(1):454-458. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=29648c0f1abdf62b6861e70bc1d65ac6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[14] 马敏, 刘嘉宝, 陈兰兰.苯酚-硫酸法测定多糖含量显色条件的优化与改进[J].江苏农业科学, 2015, 43(12):323-324. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JSNY201512102.htm [15] 黄书铭, 杨新林, 张自强, 等.超声循环提取灵芝中三萜类化合物的研究[J].中草药, 2004, 35(5):508-510. http://med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail/PeriodicalPaper_zcy200405013 [16] 张志军, 朱越, 罗莹, 等.灵芝中三萜化合物提取工艺[J].食品研究与开发, 2009, 30(9):81-83. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hbnydxxb200804014 [17] 金珊珊, 柯斌榕, 吴小平, 等.适于菌草代料栽培的杂交灵芝菌株选育[J].亚热带资源与环境学报, 2014, 9(4):56-62. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/83207A/201404/663721190.html [18] 叶丽云, 林强, 刘梅, 等.钙离子和水杨酸诱导灵芝多糖和三萜的合成[J].菌物学报, 2017, 36(2):220-228. http://manu40.magtech.com.cn/Jwxb/CN/abstract/abstract3570.shtml [19] 苏春丽, 唐传红, 张劲松, 等.基于rDNA ITS序列探讨中国栽培灵芝菌株的亲缘关系[J].微生物学报, 2007, 47(1):11-16. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDZX201305012.htm -
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 赖腾强,谢娜,吴伯文. 野生灵芝农芝1号驯化栽培. 热带农业科学. 2022(08): 18-24 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张彬彬,王慧真,刘晓雪,郭金英,王春霞,郑素月. 野生灵芝驯化前后子实体活性成分比较. 食品研究与开发. 2022(20): 164-171 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 韩晓静,于大庆,单婷玉,徐睿,查良平,杨健. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS技术的霍山野生及栽培赤芝的代谢组学分析. 中国现代中药. 2021(02): 280-285 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 牛君,王傲,史钏,卓丽君,谢意珍,李文治,胡惠萍. 中国食用菌降血糖研究进展. 中国食用菌. 2020(01): 1-7+15 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 孟国良,程冰,郝金斌,李诗艺,叶丽云,吴小平. 灵芝线粒体及其对菌丝生长、主要活性成分影响的分析. 菌物学报. 2020(01): 42-56 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 刘绍雄,刘春丽,李建英,张俊波,尚陆娥,罗孝坤,孙达锋. 白肉灵芝人工栽培及活性成分研究进展. 中国食用菌. 2020(04): 1-4+16 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: