Contents and Transport of Heavy Metals in Grain Parts of Rice Grown on Cd-Contaminated Soil
-
摘要: 为了解镉污染土壤中稻谷各部位重金属的含量及其迁移特征,以闽西矿区周边种植的水稻为研究对象,测定稻谷各部位的Cd、Pb、Cu、Zn含量,分析这4种重金属在稻谷各部位的分布及迁移规律,结果表明:在无镉污染、轻度镉污染、中度镉污染、重度镉污染环境中种植的水稻,其Cd、Cu、Zn在稻谷中不同部位的含量基本呈糠粉>糙米>精米>稻壳的趋势,即镉污染及其程度不会影响Cd、Cu、Zn在稻谷中不同部位的分布,而Pb在稻谷各部位的含量呈稻壳>糠粉>糙米>精米或糠粉>稻壳>精米>糙米的趋势;稻壳中的Cd较易被迁移到糙米中,糙米中的Pb、Cu、Zn极易积累到糠粉中,而糠粉中积累的Cd、Pb、Cu、Zn较难被迁移到精米中;糙米从去掉糠粉加工成精米的过程中,Cd、Pb、Cu、Zn含量最大程度可分别减少70.2%、95.0%、97.1%和81.4%;重金属在稻谷各部位间的迁移能力与各部位重金属含量有一定的相关性。说明糠粉对这4种重金属有较强的吸收力,稻谷加工过程尽可能去除糠粉部位可以减少食用部分的重金属含量。Abstract: Contents and transport of heavy metals in various parts of a grain from the rice grown on Cd-contaminated soil were determined. The contents of Cd, Pb, Cu and Zn in specimens collected from the mining regions in western Fujian were analyzed to study the distribution and transport characteristics of these heavy metals in the parts of the grain. The results showed that although the metal distribution was not affected by the severity of soil pollution, the Cd, Cu or Zn contained in a grain increased in the order of:bran > brown rice > milled rice > hull, and, the Pb in the order of:hull > bran > brown rice > milled rice or bran > hull > milled rice > brown rice. There seemed a significant correlation between the contents and transport of heavy metals in the grains. And, the bran appeared to absorb the heavy metals more readily than other tissues, as it was easier for Cd in the hull to transport to the brown rice grains, or Pb, Cu and Zn in brown rice to the bran; but more difficult for Cd, Pb, Cu and Zn in the bran to move to the milled grains. As a result, the contents of Cd, Pb, Cu and Zn in the grains could be maximally reduced by 70.2%, 95.0%, 97.1% and 81.4%, respectively, through the milling process with the removal of bran, thereby, an improvement for the safety of rice consumption.
-
Keywords:
- rice grains /
- heavy metals /
- distribution /
- transfer characteristics /
- Cd-pollution
-
由于污水灌溉、污泥使用、工业活动、机动车尾气和固体废弃物排放等原因,使农田土壤重金属污染日益严重[1-3]。水稻是我国乃至世界上的主要粮食作物,稻米的食品安全问题已经成为专家学者关注的焦点[4]。水稻种植在重金属污染的土壤中,土壤中的重金属会通过食物链在稻谷中积累,进入人们的餐桌,从而威胁人体健康[5]。因此,分析稻谷中重金属含量的分布及其迁移特征,并采取有效措施阻控重金属向食物链迁移,对提高稻米的食用安全性具有重要的现实意义。
目前,关于有效降低稻谷中重金属含量的途径已有很多报道,如选育低积累重金属的水稻品种[6-8]、降低土壤中重金属的生物有效性[9]、稻米深层加工技术[10]等。水稻植株的器官大致分为根、茎、叶和稻谷,稻谷又可分为稻壳、糠粉、糙米、精米不同的部位。仲维功等[11]研究了水稻不同部位对重金属的富集系数,表明水稻不同部位中重金属元素的富集能力呈根>茎叶>稻谷>精米的趋势,根系的富集系数最高。也有研究表明,随着碾米精度的提高,稻谷中的Cd含量[12]和Pb含量[13]呈降低趋势。然而,土壤不同程度的镉污染对稻谷各部位重金属累积量的影响及重金属在稻谷中各部位间迁移特征方面的相关研究少见报道。鉴此,本研究测定、分析了不同程度土壤镉污染(无污染、轻度污染、中度污染、重度污染)环境下水稻样品的6种重金属(Cd、Pb、Cu、Zn、Hg、As)在稻谷不同部位的含量及其迁移特征,本文报道其中前4种(Hg和As另文报道)。旨在通过分析土壤镉污染环境下稻谷各部位重金属分布情况,采用迁移系数揭示稻谷中各部位重金属的迁移转化规律,并探讨稻谷不同部位重金属含量与重金属在各部位间迁移能力的相关性,为在稻谷加工环节尽可能去除重金属累积量高的部位提供理论依据,以期达到降低稻谷食用部位重金属残留量的目的。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
根据前期研究结果,闽西矿区周边农田土壤受到不同程度的镉污染[14],本研究的试验材料取自在该地区不同镉污染程度农田上种植的水稻样品,品种均为中浙优1号。参照《土壤环境质量标准》(GB l5618-1995)[15]中的分级标准(表 1),分别在无镉污染、轻度镉污染、中度镉污染和重度镉污染的农田上采集水稻样品,并标记为Cd0(无污染)、Cd1(轻度污染)、Cd2(中度污染)和Cd3(重度污染)。采用梅花形取样法,将每块稻田分割成5小块,然后在分割后的小田块中取5个点,每点取代表性水稻植株2株、共50株混合为1份稻谷样品。供试土壤的基本理化性质见表 2。在水稻生长的全生育期中,除在分蘖末期进行晒田外,其他时期均保持2~3 cm的浅水层。插秧后7~10 d施尿素150 kg·hm-2,插秧后15~20 d施复合肥225 kg·hm-2,抽穗后施氯化钾150 kg·hm-2。
表 1 土壤环境质量分级标准Table 1. Criteria for classification of soil quality等级 污染指数
(P)污染程度 Ⅰ P≤0.7 清洁(安全) Ⅱ 0.7<P≤1.0 尚清洁(警戒线) Ⅲ 1.0<P≤2.0 轻度污染 Ⅳ 2.0<P≤3.0 中度污染 Ⅴ P>3.0 重度污染 注:表中资料来源于文献[15]。 表 2 供试土壤样品基本理化性质Table 2. Physiochemical properties of soil sample collected from paddy field理化指标 Cd0 Cd1 Cd2 Cd3 pH 5.20±0.014 5.05±0.007 6.18±0.014 4.85±0.014 有机质/(g·hg-1) 3.10±0.126 3.48±0.037 2.23±0.026 5.07±0.061 全氮/(g·hg-1) 0.152±0.002 0.161±0.001 0.125±0.001 0.166±0.002 全磷/(g·hg-1) 0.029±0.004 0.071±0.003 0.101±0.007 0.131±0.001 全钾/(g·hg-1) 1.90±0.018 3.81±0.017 4.45±0.060 4.16±0.038 Cd/ (mg·kg-1) 0.089±0.002 1.32±0.001 2.77±0.005 3.14±0.058 1.2 样品的前处理
采集的稻谷经脱壳机(JLG-Ⅱ,成都粮食仪器厂)脱壳、精米机(SDJ-100,杭州汇尔仪器公司)脱糠,收集稻壳、糙米、糠粉和精米4种样品,分别用粉碎机(JSFM-Ⅰ,成都粮食仪器厂)研磨成粉末后贮存于干净塑封袋中备用。
1.3 稻谷不同部位重金属含量测定
稻谷各部位样品采用HNO3-HCLO4消解法消解。据样品消解液的Cd、Pb、Cu、Zn含量和仪器的最低检测限,用原子吸收光谱仪(石墨炉法,PE-900Z)测定Cd、Pb含量,用原子吸收光谱仪(火焰法,岛津AA-6880)测定Cu、Zn含量,元素提取进行全程同步试剂空白控制,分析过程中每个样品均设平行双样,采用《生物成分分析标准物质》(GBW10044,中国地质科学院地球物理地球化学勘查研究所认定、国家质量监督检验检疫总局批准)作为质控样进行分析质量控制,且回收率在90%~111%。
1.4 重金属在稻谷不同部位间的迁移能力分析
用迁移系数反映稻谷各部位间Cd、Pb、Cu、Zn的迁移特征,可以较好地反映这些重金属元素迁移的难易程度[16-17]。具体计算方法:
TF=(Cc/Ce)×100% (1) 式中:TF为迁移系数;Ce为稻壳、糙米和糠粉部位某个重金属元素含量(mg·kg-1);Cc为迁入部位某个重金属含量(mg·kg-1),稻壳、糙米和糠粉的迁入部位分别对应糙米、糠粉和精米。
1.5 数据处理
采用Excel 2007、Origin 9.0和SPSS 18.0软件进行数据分析与统计。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 重金属在稻谷不同部位的分布情况
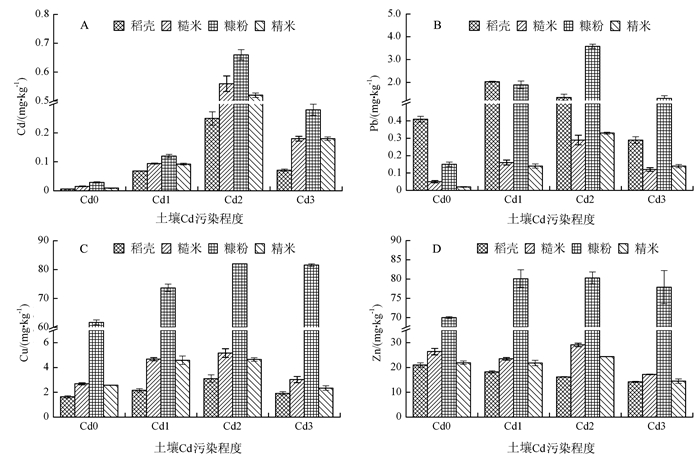
不同镉污染程度稻谷不同部位的Cd、Pb、Cu、Zn含量分布情况如图 1所示。
![]() 图 1 稻谷不同部位重金属含量注:Cd0为无污染,Cd1为轻度污染,Cd2为中度污染,Cd3为重度污染。图 2同。Figure 1. Heavy metals in parts of rice grain
图 1 稻谷不同部位重金属含量注:Cd0为无污染,Cd1为轻度污染,Cd2为中度污染,Cd3为重度污染。图 2同。Figure 1. Heavy metals in parts of rice grain从图 1-A看出,随着土壤镉污染程度的增加,稻谷各部位的Cd含量呈先升后降的趋势,表明土壤镉污染程度会影响稻谷对Cd的吸收;当土壤达中度镉污染时,稻谷可食部位糙米与精米中的Cd含量分别为0.56 mg·kg-1和0.52 mg·kg-1,超出国家《食品中污染物限量标准》(GB 2762-2017)规定的0.2 mg·kg-1标准值[18];不同程度的镉污染,稻谷不同部位Cd含量基本呈糠粉>糙米>精米>稻壳的趋势,表明土壤的镉污染及其程度不会影响Cd在稻谷各部位的分布;稻谷中稻壳Cd含量最低,说明稻壳部位对Cd的吸收力较弱;糠粉Cd含量明显高于其他部位,说明通过进一步的去糠可以明显降低精米部位Cd的含量。
从图 1-B看出,随着土壤镉污染程度的增加,稻谷各部位的Pb含量呈先升后降的趋势,表明土壤镉污染程度会影响稻谷对Pb的吸收;当土壤为中度镉污染时,稻谷可食部位糙米与精米中的Pb含量分别是0.29和0.33 mg·kg-1,均超出国家《食品中污染物限量标准》(GB 2762-2017)规定的0.2 mg·kg-1标准值[18];在无镉污染和轻度镉污染环境下,稻谷不同部位Pb含量呈稻壳>糠粉>糙米>精米的趋势;在中度镉污染和重度镉污染环境下,稻谷不同部位Pb含量呈糠粉>稻壳>精米>糙米的趋势。上述结果表明,土壤镉污染程度会影响Pb在稻谷各部位的分布;不同程度的镉污染,稻壳和糠粉中的Pb含量均高于在糙米和精米的含量,稻谷加工成糙米或精米可以在不同程度上减轻人体通过膳食摄入Pb的风险。
从图 1-C看出,随着土壤镉污染程度的增加,稻谷各部位的Cu含量基本呈先升后降的趋势,表明土壤镉污染会影响稻谷对Cu的吸收;Cd0、Cd1、Cd2和Cd3的稻谷糠粉中Cu含量分别达到61.7、73.7、82.0和81.5 mg·kg-1,均大大超出粮食卫生标准NY 861-2004规定的10 mg·kg-1标准值[19];不同程度的镉污染,稻谷不同部位Cu含量均呈糠粉>糙米>精米>稻壳的趋势,表明土壤镉污染程度不会影响Cu在稻谷各部位的分布;糠粉中的Cu含量显著高于其他部位,说明糠粉部位对Cu具有很强的吸收力。
从图 1-D看出,随着土壤镉污染程度的增加,稻壳部位Zn含量逐渐降低,糠粉部位Zn含量呈先增加后略降的趋势,糙米和精米的Zn含量在重度镉污染环境下有下降的趋势,表明土壤镉污染会影响稻谷对Zn的吸收;在不同程度镉污染环境下,糠粉中的Zn含量分别达到70.0、80.1、80.3和77.9 mg·kg-1,均超出粮食卫生标准NY 861-2004规定的50 mg·kg-1标准值[19];在不同程度镉污染环境下,稻谷不同部位中Zn含量均呈糠粉>糙米>精米>稻壳的趋势,表明土壤镉污染不会影响Zn在稻谷各部位的分布;糠粉中的Zn含量显著高于其他部位,说明糠粉部位对Zn具有很强的吸收力。
2.2 重金属在稻谷不同部位间的迁移能力
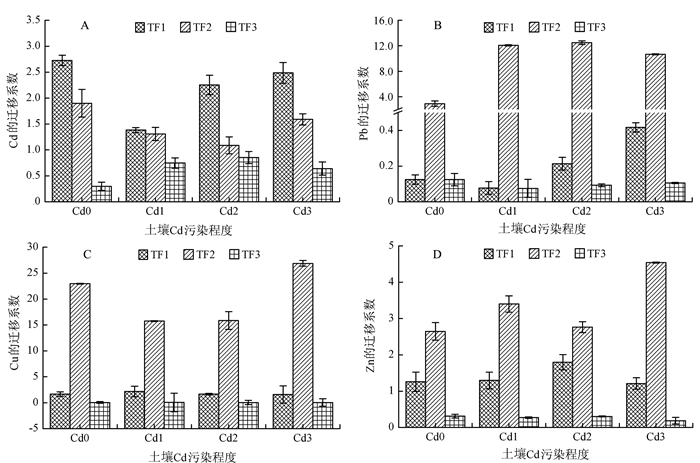
采用迁移系数(TF)对重金属元素在稻谷各部位间的迁移转化规律进行分析,结果如图 2所示。
从图 2-A看出,在不同程度的镉污染环境下,Cd元素在稻壳→糙米(TF1)的迁移系数均值都为最大,分别为2.73、1.38、2.25和2.49;在糠粉→精米(TF3)的迁移系数均值都为最小,分别为0.298、0.748、0.854和0.642。说明稻壳中的Cd较易被转移到糙米中,而糠粉积累的Cd较难被转移到精米中。
从图 2-B看出,在不同程度镉污染环境下,Pb元素在糙米→糠粉(TF2)的迁移系数均值都为最大,分别为2.91、12.1、12.5和10.6;在糠粉→精米(TF3)的迁移系数均值都为最小,分别为0.125、0.075、0.093和0.106。说明糙米中的Pb极易被积累到糠粉中,而糠粉积累的Pb较难被转移到精米中。
从图 2-C看出,在不同程度镉污染环境下,Cu元素在糙米→糠粉(TF2)的迁移系数均值都为最大,分别为22.9、15.7、15.9和26.9;在糠粉→精米(TF3)的迁移系数均值都为最小,分别为0.041、0.062、0.057和0.029。说明糙米中的Cu极易被积累到糠粉中,而糠粉积累的Cu较难被转移到精米中。
从图 2-D看出,在不同程度镉污染环境下,Zn元素在糙米→糠粉(TF2)的迁移系数均值都为最大,分别为2.65、3.41、2.77和4.54;在糠粉→精米(TF3)的迁移系数均值都为最小,分别为0.313、0.272、0.304和0.186。说明糙米中的Zn极易被累积到糠粉中,而糠粉累积的Zn较难被转移到精米中。
2.3 重金属含量与重金属迁移系数的相关性
为进一步探讨重金属在稻谷各部位间迁移能力的变化对各部位重金属累积量的影响,采用统计学软件对稻谷各部位重金属含量与重金属在各部位间迁移系数的相关性进行了分析,结果如表 3~6所示。
表 4 稻谷各部位Pb含量与Pb迁移系数的相关性Table 4. Correlation between Pb contents and Pb transport coefficients of parts of rice grainPb的迁移 稻谷各部位Pb含量 稻壳 糙米 糠粉 精米 稻壳→糙米(TF1) -0.626 0.033 0.048 0.191 糙米→糠粉(TF2) 0.608 0.788 0.825 -0.987* 糠粉→精米(TF3) -0.906* -0.618 -0.659 -0.539 表 5 稻谷各部位Cu含量与Cu迁移系数的相关性Table 5. Correlation between Cu contents and Cu transport coefficients of parts of rice grainCu的迁移 稻谷各部位Cu含量 稻壳 糙米 糠粉 精米 稻壳→糙米(TF1) 0.020 0.492 -0.120 0.633 糙米→糠粉(TF2) -0.683 -0.902* -0.110 -0.975* 糠粉→精米(TF3) 0.562 0.841 -0.002 0.945 表 6 稻谷各部位Zn含量与Zn迁移系数的相关性Table 6. Correlation between Zn contents and Zn transport coefficients of parts of rice grainZn的迁移 稻谷各部位Zn含量 稻壳 糙米 糠粉 精米 稻壳→糙米(TF1) -0.195 0.723 0.456 0.673 糙米→糠粉(TF2) -0.741 -0.963* 0.336 -0.930* 糠粉→精米(TF3) 0.764 0.954* -0.309 0.942 从表 3看出,稻壳Cd含量与Cd在糠粉→精米迁移系数呈显著正相关(r=0.898,P<0.05),其余的相关性均不显著。说明稻壳Cd含量的提高,会显著促进Cd从糠粉向精米的迁移。
从表 4看出,稻壳Pb含量与Pb在糠粉→精米迁移系数呈显著负相关(r=-0.906,P<0.05),说明稻壳Pb含量的提高,会显著抑制Pb在糠粉→精米的迁移,从而显著减少精米中的Pb含量;精米Pb含量与Pb在糙米→糠粉迁移系数也呈显著负相关(r=-0.987,P<0.05),说明Pb在糙米中向糠粉累积能力的提高,会显著减少精米中的Pb含量。
从表 5看出,糙米和精米Cu含量与Cu在糙米→糠粉迁移系数均呈显著负相关(r=-0.902和r=-0.975,P<0.05),说明Cu从糙米向糠粉累积能力的提高,会显著减少糙米和精米中的Cu含量。
从表 6看出,糙米Zn含量与Zn在糙米→糠粉和糠粉→精米间的迁移系数相关性显著,其中与糙米→糠粉间的迁移系数呈显著负相关(r=-0.963,P<0.05),与糠粉→精米间的迁移系数呈显著正相关(r=0.954,P<0.05),说明糙米Zn含量的提高,会显著抑制糙米中的Zn向糠粉的累积,同时会显著促进Zn在糠粉→精米间的迁移;精米Zn含量与Zn在糙米→糠粉间的迁移系数呈显著负相关(r=-0.930,P<0.05),说明在糙米中Zn在糠粉中累积能力的提高,会显著降低精米中的Zn含量。
3. 讨论
试验结果表明,Cd、Cu、Zn和Pb等4种重金属在稻谷各部位含量高低顺序如下:Cd、Cu、Zn表现为糠粉>糙米>精米>稻壳,Pb则表现为稻壳>糠粉>糙米>精米或糠粉>稻壳>精米>糙米。由此可见,糠粉对重金属具有很强的吸收能力,稻谷加工成精米能有效减少食用部位中重金属的含量,这与前人的研究结果一致[20-21]。在糠粉中积累的Cd、Cu、Zn、Pb量明显多于其他部位,也较难被转移到精米中,因此对糠粉中的重金属进行去除是十分必要的。从稻谷加工成精米,Cd含量最大程度可减少70.2%,Pb含量最大程度可减少95.0%,Cu含量最大程度可减少97.1%,Zn含量最大程度可减少81.4%。这可能是由于稻谷加工精度越高,富含蛋白质的米胚和皮层去得越多,而重金属易于集中在蛋白质含量较高的部位,另外谷物中的重金属含量除了与蛋白质含量有关外,还与纤维素含量密切相关[22]。值得一提的是,本试验材料是在野外大田环境中采集的水稻样品,虽然研究结果更贴近生产实际,但会受到天气等不可控因素的影响,因此在今后研究中应考虑采取盆栽试验的方法进行补充验证。
4. 结论
4.1 重金属在稻谷中的分布存在差异性
不同程度的镉污染均不会影响Cd、Cu、Zn在稻谷各部位的分布,三者在稻谷中的含量基本呈糠粉>糙米>精米>稻壳的趋势;Pb在稻谷各部位的含量受土壤镉污染程度影响较明显,呈稻壳>糠粉>糙米>精米或糠粉>稻壳>精米>糙米的趋势;糠粉对重金属具有很强的吸收能力,稻谷加工成精米能有效减少食用部位的重金属含量。
4.2 重金属在不同部位间的迁移能力存在差异性
稻壳中的Cd比较容易被转移到糙米中,Cd在稻壳→糙米间的迁移系数明显较糙米→糠粉、糠粉→精米间的迁移系数大;糙米中的Pb、Cu、Zn极易被转移到糠粉中,Pb、Cu、Zn在糙米→糠粉间的迁移系数明显较其他部位大;糠粉中的Cd、Pb、Cu、Zn较难被转移到精米中。因此,稻谷加工过程尽可能去除糠粉部位可以减少食用部分的重金属含量。
4.3 重金属在各部位间的迁移能力与各部位重金属含量有一定的相关性
稻壳Cd含量的提高,会显著促进Cd从糠粉向精米的迁移;稻壳Pb含量的提高,会显著抑制Pb在糠粉→精米的迁移,从而显著减少精米中的Pb含量;Pb在糙米中向糠粉累积能力的提高,会显著减少精米中的Pb含量;Cu从糙米向糠粉累积能力的提高,会显著减少糙米和精米中的Cu含量;糙米Zn含量的提高,会显著抑制糙米中的Zn向糠粉的累积,同时会显著促进Zn在糠粉→精米间的迁移;糙米中Zn在糠粉中累积能力的提高,会显著降低精米中的Zn含量。
-
图 1 稻谷不同部位重金属含量
注:Cd0为无污染,Cd1为轻度污染,Cd2为中度污染,Cd3为重度污染。图 2同。
Figure 1. Heavy metals in parts of rice grain
表 1 土壤环境质量分级标准
Table 1 Criteria for classification of soil quality
等级 污染指数
(P)污染程度 Ⅰ P≤0.7 清洁(安全) Ⅱ 0.7<P≤1.0 尚清洁(警戒线) Ⅲ 1.0<P≤2.0 轻度污染 Ⅳ 2.0<P≤3.0 中度污染 Ⅴ P>3.0 重度污染 注:表中资料来源于文献[15]。 表 2 供试土壤样品基本理化性质
Table 2 Physiochemical properties of soil sample collected from paddy field
理化指标 Cd0 Cd1 Cd2 Cd3 pH 5.20±0.014 5.05±0.007 6.18±0.014 4.85±0.014 有机质/(g·hg-1) 3.10±0.126 3.48±0.037 2.23±0.026 5.07±0.061 全氮/(g·hg-1) 0.152±0.002 0.161±0.001 0.125±0.001 0.166±0.002 全磷/(g·hg-1) 0.029±0.004 0.071±0.003 0.101±0.007 0.131±0.001 全钾/(g·hg-1) 1.90±0.018 3.81±0.017 4.45±0.060 4.16±0.038 Cd/ (mg·kg-1) 0.089±0.002 1.32±0.001 2.77±0.005 3.14±0.058 表 3 稻谷各部位Cd含量与Cd迁移系数的相关性
Table 3 Correlation between Cd contents and Cd transport coefficients of parts of rice grain
表 4 稻谷各部位Pb含量与Pb迁移系数的相关性
Table 4 Correlation between Pb contents and Pb transport coefficients of parts of rice grain
Pb的迁移 稻谷各部位Pb含量 稻壳 糙米 糠粉 精米 稻壳→糙米(TF1) -0.626 0.033 0.048 0.191 糙米→糠粉(TF2) 0.608 0.788 0.825 -0.987* 糠粉→精米(TF3) -0.906* -0.618 -0.659 -0.539 表 5 稻谷各部位Cu含量与Cu迁移系数的相关性
Table 5 Correlation between Cu contents and Cu transport coefficients of parts of rice grain
Cu的迁移 稻谷各部位Cu含量 稻壳 糙米 糠粉 精米 稻壳→糙米(TF1) 0.020 0.492 -0.120 0.633 糙米→糠粉(TF2) -0.683 -0.902* -0.110 -0.975* 糠粉→精米(TF3) 0.562 0.841 -0.002 0.945 表 6 稻谷各部位Zn含量与Zn迁移系数的相关性
Table 6 Correlation between Zn contents and Zn transport coefficients of parts of rice grain
Zn的迁移 稻谷各部位Zn含量 稻壳 糙米 糠粉 精米 稻壳→糙米(TF1) -0.195 0.723 0.456 0.673 糙米→糠粉(TF2) -0.741 -0.963* 0.336 -0.930* 糠粉→精米(TF3) 0.764 0.954* -0.309 0.942 -
[1] SINGH R P, AGRAWAL M. Variations in heavy metal accumulation, growth and yield of rice plants grown at different sewage sludge amendment rates[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2010, 73(4):632-641. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.01.020
[2] SINGH A, SHARMA R K, AGRAWAL M, et al. Risk assessment of heavy metal toxicity through contaminated vegetables from waste water irrigated area of Varanasi, India[J]. Tropical Ecology, 2010, 51(2):375-387. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ0217042035
[3] MARKOVI M, CUPA S, DUROVI R, et al. Assessment of heavy metal and pesticide levels in soil and plant products from agricultural area of Belgrade, Serbia[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2010, 58(2):341-351. DOI: 10.1007/s00244-009-9359-y
[4] 路子显.粮食重金属污染对粮食安全, 人体健康的影响[J].粮食科技与经济, 2011, 36(4):14-17. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1458.2011.04.004 [5] 崔玉静, 赵中秋, 刘文菊, 等.镉在土壤-植物-人体系统中迁移积累及其影响因子[J].生态学报, 2003, 1(10):2133-2143. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2003.10.022 [6] ZENG F, MAO Y, CHENG W, et al. Genotypic and environmental variation in chromium, cadmium and lead concentrations in rice[J]. Environmental pollution, 2008, 153(2):309-314. DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2007.08.022
[7] 杨祥田, 周翠, 何贤彪, 等.田间试验条件下不同基因型水稻对Cd和Pb的吸收分配特征[J].农业环境科学学报, 2013, 32(3):438-444. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QKC20132013042300010557 [8] 刘侯俊, 梁吉哲, 韩晓日, 等.东北地区不同水稻品种对Cd的累积特性研究[J].农业环境科学学报, 2011, 30(2):220-227. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nyhjbh201102003 [9] 周航, 周歆, 曾敏, 等. 2种组配改良剂对稻田土壤重金属有效性的效果[J].中国环境科学, 2014, 34(2):437-444. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zghjkx201402025 [10] 鞠兴荣, 丁哲慧, 高瑀珑, 等.重金属在水稻中的分布及加工过程对其影响的探讨[J].粮食与食品工业, 2016, 23(3):1-6. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5026.2016.03.001 [11] 仲维功, 杨杰, 陈志德, 等.水稻品种及其器官对土壤重金属元素Pb、Cd、Hg、As积累的差异[J].江苏农业学报, 2006, 22(4):331-338. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2006.04.004 [12] 田阳. 稻米加工技术对产品镉含量的影响[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2013. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-82101-1013357531.htm [13] 李琛, 章月莹.不同加工程度对稻米中铅含量的影响[J].粮油仓储科技通讯, 2013, 29(6):46-48. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lycckjtx201306015 [14] 刘兰英, 涂杰峰, 黄薇, 等.福建闽西矿区周边土壤Cd、Pb、Cr含量及风险评价[J].福建农业学报, 2017, 32(1):68-74. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fjnyxb201701015 [15] 刘凤枝, 马锦秋.土壤监测分析实用手册[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2010:338-339. [16] GUPTA S, NAYEK S, SAHHAR N, et al. Assessment of heavy metal accumulation in macrophyte, agricultural soil, and crop plants adjacent to discharge zone of sponge iron factory[J]. Environmental geology, 2008, 55(4):731-739. DOI: 10.1007/s00254-007-1025-y
[17] SATPATHY D, REDDY M V, DHAL S P. Risk assessment of heavy metals contamination in paddy soil, plants, and grains (Oryza sativa L.) at the East Coast of India[J]. BioMed research international, 2014, 2014:545473. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ0233906114
[18] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准食品污染物限量: GB 2762-2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. [19] 中华人民共和国农业部. 粮食(含谷物, 豆类, 薯类)及制品中铅、铬、镉、汞、硒、砷、铜、锌等八种元素限量: NY 861-2004[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2004. [20] 莫文莲, 陈祎清, 孙禧华.石墨炉原子吸收光谱法测定稻米各加工阶段铅含量研究[J].粮食与油脂, 2010(8):34-35. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2010.08.011 [21] 倪小英, 许艳霞, 梅广, 等.主要重金属在污染稻谷籽粒中的分布规律研究[J].中国粮油学报, 2017, 32(1):7-11. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2017.01.002 [22] 查燕, 杨居荣.污染谷物中重金属的分布及加工过程的影响[J].环境科学, 2000, 21(3):52-55. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkx200003012 -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 黄鹏, 陈汉鑫, 姚锦爱, 黄建成, 余德亿. 金龟子绿僵菌对石蒜绵粉蚧的室内毒力与防治效果. 中国生物防治学报. 2019(06): 884-890 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 黄鹏, 姚锦爱, 余德亿. 金龟子绿僵菌FM-03生物学特性及其对柑橘粉蚧的侵染. 中国生物防治学报. 2018(06): 858-865 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: