Effect of Extremely Thermophilic Bacteria on Amino Acid Degradation of High-temperature Treated Dead Pigs
-
摘要: 为探明复合极端嗜热菌对高温病死猪处理中氨基酸降解效果,采集发酵处理前样品(Q组)及无菌处理组样品Wj组(无添加菌处理后再堆肥发酵60 d)为对照,设置4个不同添加量的嗜热菌混合菌样品处理(0.05%、0.08%、0.10%、0.12%),分析样品的氨基酸种类和含量变化情况,运用Illumina MiSeq对样品微生物群落进行测序,将所得的16S基因测序数据与代谢功能已知的微生物参考基因组数据库相对比,预测细菌代谢功能。结果表明添加0.08%~0.12%复合嗜热菌组处理可明显促进高温处理中病死猪的氨基酸降解,显著降低病死猪样品的氨基酸总量和各氨基酸组分含量;和0.05%添加量处理组相比,氨基酸总量下降了7.04%~8.49%(P < 0.05),天冬氨酸、苏氨酸、甘氨酸、丙氨酸、亮氨酸、苯丙氨酸、赖氨酸等7种氨基酸的量显著降低;谷氨酸、缬氨酸、异亮氨酸、酪氨酸、精氨酸等5种氨基酸的降解效果与堆肥60 d处理Wj组没有显著差异。处理前和处理后病死猪菌群氨基酸代谢功能差异明显,添加嗜热菌混合菌组与无菌处理后堆肥Wj组的菌群氨基酸代谢功能接近,两者差异不明显。说明添加0.08%~0.12%复合极端嗜热菌促进了高温病死猪处理过程中氨基酸的代谢和降解,与长时间堆肥发酵处理的病死猪降解效果相似。Abstract: Effect of addition of mixed extremely thermophilic bacteria on the degradation of amino acids in the high-temperature-treated pig carcass was studied.Samples applied in this study included materials of dead, diseased pigs prior to fermentation (Group Q) and after aseptic treatment (thermophile-free Group Wj that had been composted for 60 days) as controls, as well as those with additions of various ultra-thermophiles at 0.05%, 0.08%, 0.10% or 0.12%.Changes on the composition and content of amino acids of the samples after treatments were determined. The Illumina MiSeq method was used to analyze the microbial community on the samples. The 16S gene sequencing data obtained were compared to a reference genome database of known metabolic functions to predict those of the bacteria collected. The results showed that the addition of 0.08%-0.12% thermophiles significantly promoted the amino acid degradation that significantly reduced the total and individual amino acid contents. The reductions on total amino acid content were 7.04%-8.49% with an addition of the thermophiles more than 0.05% (P < 0.05)as the asparagine, threonine, glycine, alanine, leucine, phenylalanine, lysine contents decreased significantly. On the other hand, the degradations on glutamic acid, valine, isoleucine, tyrosine and arginine did not differ significantly in Group Wj. The amino acid metabolic functions of the dead pigs before and after treatment were significantly different. Those of Group Q and the treatment groups were significantly different indicating the addition of 0.08%-0.12% the extremely thermophilic bacteria enhanced the metabolism and amino acid degradation in the high-temperature-treated pig carcass, and that the effect was similar to a 60 day compost fermentation.
-
Keywords:
- composite extreme thermophilic bacteria /
- dead pig /
- amino acid /
- 16S sequencing /
- degradation
-
近年来,我国畜牧业发展趋向规模化和集约化,生猪养殖尤为明显。据统计,2017年我国母猪存栏量4 000多万头,且规模化猪场占60%以上[1]。规模化和集约化养殖发展的同时也伴随畜禽的发病率和死淘率上升,据资料显示我国每年因各类疾病引起猪死亡率为8%~12%,大量病死猪的处理为当前棘手的问题[2]。病死猪携带病原体,若未经无害化处理、任意堆置,不仅污染环境,还可能引起重大疫情,危害畜禽生产安全甚至引发严重威胁公共卫生事件。因此,有必要探寻高效降解病死猪的处理模式。
利用微生物的好氧发酵技术无害化处理病死畜禽技术最早可追溯至20世纪80年代末期。好氧发酵技术最早被用来处理病死家禽,如鸭、鸡等,因处理方便又相对无害,逐渐被用于死猪、死牛和死马等大型动物[3-6]的处理。近些年,随着生猪养殖向规模化和集约化发展,病死猪处理成为亟待解决的问题,有关好氧发酵处理病死猪的相关研究也逐渐增多。Ahn等[7]证明大多数死猪在微生物好氧发酵处理6周后死猪的分解率可达86%。Glanville等[8]证实用自然箱式秸秆发酵模式处理4个月后才能完成病死猪的分解。Murray等[9]用堆叠发酵系统处理病死猪,整个处理周期持续了400 d,结果发现猪的基因物质和线粒体DNA均被降解。而我国对病死猪的好氧发酵也进行了一系列的研究。郭东坡等[10]在容积约1 m3的箱中对死猪进行好氧发酵试验,结果表明死猪无害化处理的合适条件是通风率小于100 L·m-3·min-1和发酵时间大于6周。可以看出,微生物好氧发酵模式可以较好地降解病死猪,但处理周期较长。
嗜热菌又名高温菌,是一类生活在高温环境中的微生物。根据温度不同可分为耐热菌、兼性嗜热菌、专性嗜热菌、极端嗜热菌和超嗜热菌。近年来,高温病死猪处理设施因处理方便和相对安全,大部分规模养殖场都有配备,政府也大力推荐这种处理模式。通过添加嗜热菌,可以加快高温处理代谢速度,减少非嗜热菌的杂菌污染,从而促进高温环境下有机物的降解,从而提高生物可利用性。但是,高温病死猪处理也存在生物降解瓶颈。在生物降解过程中,很多微生物没法在这种极热环境中生存,导致高温处理后病死猪降解不充分,有害微生物滋生,引发新的安全隐患。本研究利用前期筛选的复合极端嗜热菌对病死猪进行高温处理,研究其对病死猪高温处理中氨基酸降解效果,为提高病死猪降解效果及极端嗜热菌筛选提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
复合极端嗜热菌剂由福建省农业科学院畜牧兽医研究所动物营养研究室从有机肥发酵场分离所得,由4株嗜热菌组成;其中一株为热噬淀粉芽孢杆菌HL8103[11], 另3株经菌株形态、菌落形态和生理生化特征等初步鉴定为嗜热脂肪芽孢杆菌、速生热球菌和热红芽孢杆菌。
LB培养液(L):酵母粉10 g,蛋白胨10 g,NaCl 10 g,pH7.0,加蒸馏水定容至1 L。121℃灭菌30 min。
分离纯化固体培养基:LB培养液中时加入20 g琼脂粉,121℃灭菌30 min。液体发酵培养基:LB培养液+玉米淀粉。
酵母粉、蛋白胨、NaCl、硫酸、硼酸、硫酸铜、硫酸钾、氢氧化钠、辛醇、盐酸等均为AR级,茚三酮染色剂和缓冲液、氨基酸标准液和稀释液均购于德国menbarPure公司。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 菌株的培养
纯化培养:将HL8103菌划菌斜面置于75℃培养箱内培养18 h,置于4℃冰箱保存。
种子培养:在250 mL三角瓶中装入25 mL种子培养基,121℃灭菌30 min后,取培养好的斜面挑取1环于种子培养基中,75℃、120 r·min-1摇床培养18 h。
发酵培养:在250 mL三角瓶中装入25 mL发酵培养基,121℃灭菌30 min后,按体积分数0.1%的接种量接入种子液,75℃、120 r·min-1摇床培养18 h。
1.2.2 不同温度下HL8103菌生长曲线
研究菌株HL8103在55、60、65、70、75、80、85、90、95、100℃的生长情况,在培养9、10、11、12、14、15、16、17、18、19、20、21、22、23、24 h测定其活菌数。活菌数量测定采用平板计数法,涂布平板设置3次重复,取平均值。活菌数LG值=Log10(活菌数)。
1.2.3 复合极端嗜热菌制备
经发酵培养的HL8103菌与另3株菌按3:1:1:1(v/v/v/v)混合均匀备用。该复合极端嗜热菌含量为109CFU·mL-1。
1.2.4 复合极端嗜热菌氨基酸降解效果分析
试验在漳州市众福生物科技有限公司的漳浦县病死畜禽无害化处理中心进行。将病死猪投入自动控温的畜禽养殖场有机废弃物处理机中粉碎加热3~4 h后,添加10%锯末、稻壳、秸秆等农林副产物作为辅料。经充分混合后在处理机4个不同部位(A、B、C、D点)重复取样,3次重复,作为发酵处理前样品(Q组);此后该处理机温度达90℃,按不同添加量0.05%(a组)、0.08%(b组)、0.10%(c组)、0.12%(d组)分别加入复合极端嗜热菌,保持70~95℃进行发酵。经19 h发酵后,处理机不再加热但其搅拌系统照常工作至其罐体温度50℃时打开出料阀门,分别对处理机排出的发酵产物进行取样,3次重复。Wj组不添加复合极端嗜热菌在同上处理机高温处理后经60 d堆肥,在高100 cm堆体从上至下每20 cm采样(最底下不取样), 3次重复。采样量200 g。5组样品分别进行充分混合后分为两份,一份-18℃冷冻保存用于微生物群落测序;另一份于60℃干燥箱中干燥至恒重;用粉碎机粉碎,过60目筛,制成绝干样本,置磨口样本瓶中保存,用于测定氨基酸组分。
1.3 指标测定
1.3.1 氨基酸测定[12]
按GB/T18246-2000方法,采用德国的menbarPureA300全自动氨基酸分析仪进行测定。
1.3.2 微生物组总DNA提取及纯化
按照常规DNA提取流程提取微生物组总DNA,并对DNA进行定量。根据荧光定量结果,按照每个样本的测序量需求,对各样本按相应比例进行混合[13-16]。
1.3.3 测序文库制备及高通量测序
采用Illumina公司的TruSeq Nano DNA LT Library Prep Kit制备测序文库。上机测序前,先在Agilent Bioanalyzer上进行质检,接着采用Quant-iT PicoGreen dsDNA Assay Kit对文库进行定量,将合格的各上机测序文库按所需测序量相应比例混合,再使用MiSeq测序仪进行2×300 bp的双端测序,分析微生物多样性。
1.3.4 菌群代谢功能数据分析
运用引物和Barcode信息筛查原始下机数据;识别并踢除嵌合体等存在疑问序列;然后按照OTU归并划分序列,并根据OTU的丰度分布,评估每个样本的多样性水平,通过稀疏曲线反映测序深度;然后分析各处理(组)在不同分类水平的具体组成及组间是否具有统计学差异;通过多变量统计学分析工具,衡量不同处理(组)间的菌群结构差异及与差异相关的物种[17-18];根据物种在各样本中的组成分布,构建互作关联网络;最后再根据16S rRNA基因测序结果,预测各样本的菌群代谢功能。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 HL8103菌株生长曲线
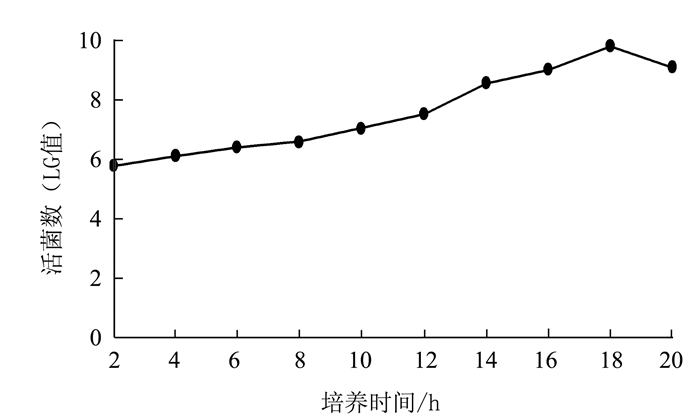
生长曲线可反映细菌整个培养期间菌数变化规律。图 1显示,在75℃培养温度下HL8103菌的生长规律。可以看出,在培养过程中,菌体活菌数随时间呈现逐渐增长后快速下降的变化趋势,0~4 h是菌体适应新环境的偿还期;4~16 h为生长繁殖迅速、细胞活力最大的对数生长期;16~18 h为稳定生长期,活菌数(LG值)最高,为9.82;18 h后,活菌数下降,由于自溶酶作用或有毒代谢产物积累,细胞裂解。表明HL8103菌的最适培养时间为18 h。
2.2 培养温度对HL8103菌株生长的影响
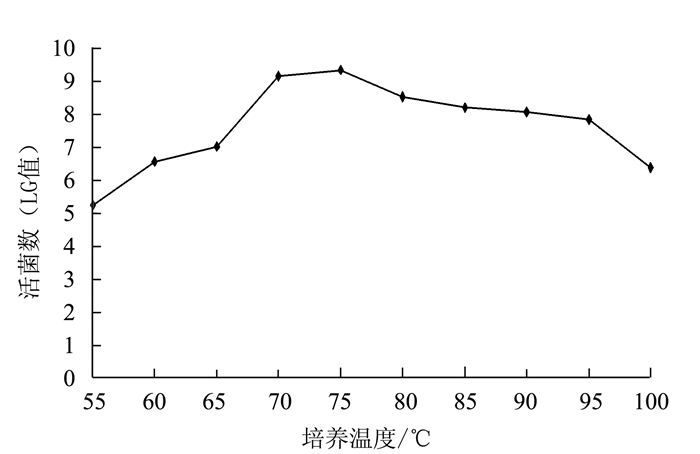
培养温度是影响微生物生长和代谢的最重要的环境因素之一。适当提高培养温度有助于促进微生物的生长和酶促反应。从图 2可以看出,在培养温度为55℃时,活菌数(LG值)5.24,随着培养温度的升高,活菌数逐渐提高,当培养温度为75℃时,活菌数(LG值)最高(9.36);之后随着培养温度升高,菌活数下降。当培养温度为100℃时,活菌数(LG值)仍有6.41。可知该菌的最佳培养温度为70~95℃。
2.3 复合极端嗜热菌处理病死猪的氨基酸降解效果
从表 1可以看出,除了色氨酸无法测,其他17种氨基酸均能测出。氨基酸总量由高到低为Q组>a组>b组>d组>c组>Wj组。试验组a、b、c、d间无显著差异,比Q组分别下降4.36%、13.22%、14.58%、13.31%,差异显著(P<0.05),显著高于Q组;b、c、d组与a组相比,下降7.04%、8.49%、7.13%(P>0.05)。
表 1 氨基酸含量(干物质基础,n=13,%)Table 1. Amino acid composition (% ondry matter base, n=13)项目 Q组 a组 b组 c组 d组 Wj组 天冬氨酸 2.53±0.11a 2.47±0.08a 2.27±0.10b 2.28±0.09b 2.24±0.12b 1.95±0.07c 苏氨酸 1.01±0.02a 0.97±0.04a 0.82±0.01b 0.80±0.05b 0.81±0.02b 0.75±0.03c 丝氨酸 0.94±0.06a 0.89±0.07a 0.85±0.02a 0.84±0.05a 0.87±0.03a 0.70±0.04b 谷氨酸 4.03±0.09a 3.96±0.11a 3.27±0.13b 3.21±0.08b 3.25±0.10b 3.23±0.08b 甘氨酸 1.87±0.05a 1.84±0.07a 1.71±0.01b 1.68±0.04b 1.72±0.03b 1.51±0.05c 丙氨酸 1.71±0.06a 1.67±0.03a 1.47±0.05b 1.48±0.01b 1.45±0.05b 1.32±0.02c 胱氨酸 0.16±0.01a 0.12±0.02b 0.13±0.01a 0.14±0.03a 0.11±0.04b 0.14±0.02a 缬氨酸 1.45±0.07a 1.44±0.05a 1.20±0.03b 1.18±0.07b 1.16±0.04b 1.16±0.09b 蛋氨酸 0.25±0.01a 0.19±0.04b 0.21±0.05b 0.20±0.04b 0.18±0.02b 0.24±0.06a 异亮氨酸 0.95±0.02a 0.91±0.05a 0.82±0.03b 0.81±0.06b 0.85±0.03b 0.80±0.05b 亮氨酸 1.92±0.03a 1.90±0.02a 1.67±0.02b 1.65±0.04b 1.70±0.03b 1.52±0.05c 酪氨酸 0.44±0.01a 0.38±0.02a 0.35±0.04b 0.36±0.02b 0.33±0.01b 0.35±0.04b 苯丙氨酸 1.18±0.06a 1.17±0.08a 1.05±0.04b 1.01±0.06b 1.06±0.08b 0.980.07c 组氨酸 0.71±0.02a 0.67±0.01a 0.70±0.05a 0.68±0.03a 0.73±0.03a 0.59±0.01b 赖氨酸 1.64±0.03a 1.59±0.05a 1.34±0.02b 1.31±0.09b 1.35±0.07b 1.19±0.03c 精氨酸 1.23±0.08a 1.19±0.06a 0.97±0.07b 0.93±0.09b 0.99±0.08b 0.90±0.05b 脯氨酸 1.61±0.11a 1.58±0.09a 1.64±0.07a 1.60±0.08a 1.68±0.09a 1.08±0.07b 总量 23.60±0.21a 22.03±0.37b 20.48±0.51b 20.16±0.13b 20.46±0.46b 18.41±0.25c 注:同行数据后不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 从氨基酸组分来看,所测的17种氨基酸中,胱氨酸a、d组含量显著低于Q、b、c、Wj组,蛋氨酸a、b、c、d组显著低于Q、j组。两种氨基酸的变化没有明显规律,可能是酸水解法造成含硫氨基酸的破坏;天冬氨酸、苏氨酸、甘氨酸、丙氨酸、亮氨酸、苯丙氨酸、赖氨酸等7种氨基酸变化的趋势相近,均为Q、a组>b、c、d组>Wj组,差异显著。谷氨酸、缬氨酸、异亮氨酸、酪氨酸、精氨酸等5种氨基酸变化的趋势相近,Q组和a组间没有显著差异,但显著高于b、c、d、Wj组。丝氨酸、组氨酸、脯氨酸等3种氨基酸的变化趋势相近,Q、a、b、c、d组之间无显著差异,均显著高于Wj组。说明添加0.08%~0.12%的复合极端嗜热菌对大部分氨基酸组分有更充分降解的效果。
2.4 菌群代谢功能差异
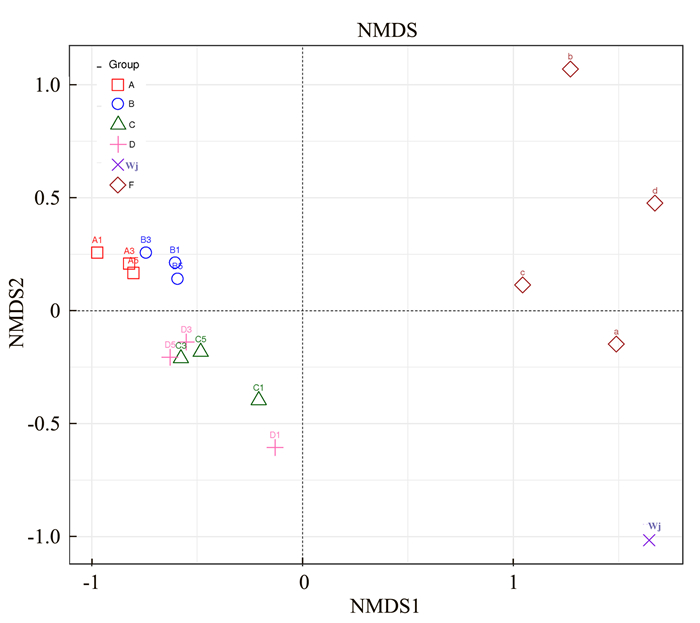
如图 3所示,病死猪处理前样品A1~A3(A), B1~B3(B), C1~C3(C), D1~D3(D)(4个样点3次重复取样,共计12份样品)的菌群结构非常接近,只有D1、C1和其他采样点的菌群有一定差异。加入不同浓度的极端嗜热菌处理后(F组,a、b、c、d处理)菌群的结构差异非常明显,完全不在一个区,同时极端嗜热菌处理后的菌群结构(a、b、c、d)和无添加菌高温处理后发酵60 d的Wj处理在同一区,菌群结构相似,说明复合极端嗜热菌处理病死猪的氨基酸降解菌群与发酵堆肥处理接近。
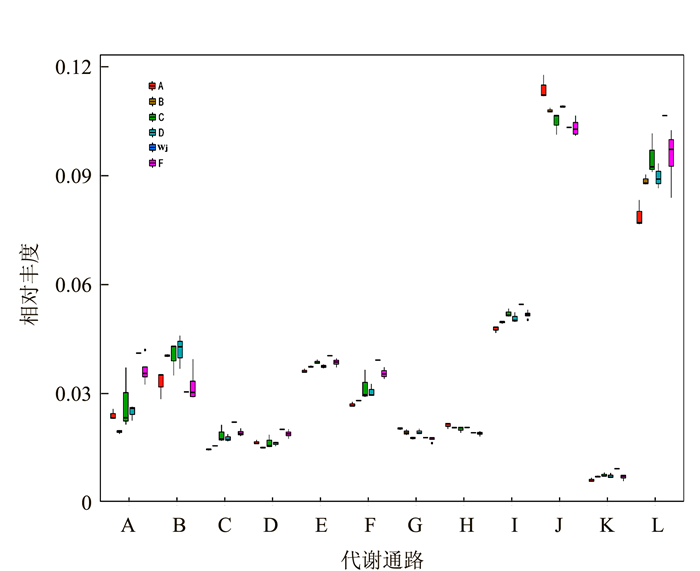
从图 4可看出,极端嗜热菌处理后(F组,a、b、c、d处理)的菌群氨基酸的代谢功能类群的丰度远高于处理前的样品Q组(A、B、C、D),说明F组中的氨基酸代谢更为旺盛,进一步证实大量的氨基酸代谢菌的存在,推动病死猪处理中的氨基酸代谢,促进了病死猪的氨基酸的降解,提升了降解率。
![]() 图 4 各组微生物群代谢功能类群相对丰度注:图中横坐标为KEGG第二等级功能类群,横坐标下各类代谢通路A~L分别表示。A:异物生物降解与代谢; B:核酸代谢;C:萜类和聚酮代谢;D:其他氨基酸代谢;E:辅酶因子及维生素代谢;F:脂肪代谢;G:多糖生物合成及代谢;H:酶家族;I:能量代谢;J:碳水化合物代谢;K:其他次代谢物合成;L:氨基酸代谢。纵坐标为各功能类群在各样本(组)内的相对丰度。横线代表中位值,上下触须分别代表上下四分位以外的1.5倍IQR范围,符号“-”表示超过范围的极端值。Figure 4. Relative abundance of metabolic functional groups of microbial communities in each group
图 4 各组微生物群代谢功能类群相对丰度注:图中横坐标为KEGG第二等级功能类群,横坐标下各类代谢通路A~L分别表示。A:异物生物降解与代谢; B:核酸代谢;C:萜类和聚酮代谢;D:其他氨基酸代谢;E:辅酶因子及维生素代谢;F:脂肪代谢;G:多糖生物合成及代谢;H:酶家族;I:能量代谢;J:碳水化合物代谢;K:其他次代谢物合成;L:氨基酸代谢。纵坐标为各功能类群在各样本(组)内的相对丰度。横线代表中位值,上下触须分别代表上下四分位以外的1.5倍IQR范围,符号“-”表示超过范围的极端值。Figure 4. Relative abundance of metabolic functional groups of microbial communities in each group3. 讨论与结论
从病死猪混合物发酵前后氨基酸的总量可知,在同等条件下添加复合极端嗜热菌可使病死猪组织的氨基酸分解、吸收及代谢加快,与张浩等[19]、Maricou H等[20]的研究结果一致。
本研究病死猪在畜禽养殖场有机废弃物处理机中经95℃、19 h发酵,从处理后的氨基酸组分的降解可以看出,添加0.08%~0.12%复合极端嗜热菌处理可明显提高病死猪的氨基酸降解效果,与处理前样品相比,0.08%~0.12%添加量可显著降低氨基酸总量及大部分氨基酸组分(除丝氨酸、组氨酸、脯氨酸)含量,与低剂量0.05%添加量相比,添加0.08%~0.12%复合极端嗜热菌可显著降低谷氨酸、缬氨酸、异亮氨酸、酪氨酸、精氨酸等5种氨基酸的量,其降解效果与堆肥60 d处理Wj组没有显著差异。说明添加0.08%~0.12%极端嗜热菌就能有效降解病死猪组织。病死畜禽好氧发酵(堆肥)是利用微生物在一定温度、湿度和pH条件下,使有机物氧化分解成简单无机物,并释放能量产生高温,高温可使病原菌灭活。有机物发生各种理化性质和生物学性质的变化,然后逐渐趋于稳定,最终达到腐殖化,形成有机复合肥[21]。和堆肥发酵相比,接种极端嗜热菌处理,降解效果相似,但可明显减少处理时间,高效安全,促进病死猪组织蛋白质彻底分解。
为了更深入分析复合极端嗜热菌影响病死猪氨基酸代谢的机制,本研究比较各处理样品的菌群代谢功能丰度差异。结果表明,添加复合极端嗜热菌处理的氨基酸代谢功能菌群丰度增加明显,这一方面是因为添加复合极端嗜热菌的代谢功能,另一方面可能是复合极端嗜热菌激活了其他氨基酸代谢功能菌的代谢作用,这在菌群组成上可以看到菌群丰度大大增加,氨基酸代谢加快,病死猪降解速度提高, 以减少二次污染和次生人畜共患疾病的风险。
病死猪降解主要是碳水化合物、脂肪、蛋白质及矿物质微量元素的代谢,本试验研究结果表明添加复合极端嗜热菌的脂肪代谢菌的丰度也高于其他处理组,说明添加复合极端嗜热菌处理的脂肪代谢也更为旺盛。具体有待进一步验证[22-25]。
本研究采取的高温生物降解病死猪处理模式,为高温灭菌和生物降解有机结合,既提高了效率,又保证了无害化处理,是一种无害化处理病死猪的较好模式。
-
图 4 各组微生物群代谢功能类群相对丰度
注:图中横坐标为KEGG第二等级功能类群,横坐标下各类代谢通路A~L分别表示。A:异物生物降解与代谢; B:核酸代谢;C:萜类和聚酮代谢;D:其他氨基酸代谢;E:辅酶因子及维生素代谢;F:脂肪代谢;G:多糖生物合成及代谢;H:酶家族;I:能量代谢;J:碳水化合物代谢;K:其他次代谢物合成;L:氨基酸代谢。纵坐标为各功能类群在各样本(组)内的相对丰度。横线代表中位值,上下触须分别代表上下四分位以外的1.5倍IQR范围,符号“-”表示超过范围的极端值。
Figure 4. Relative abundance of metabolic functional groups of microbial communities in each group
表 1 氨基酸含量(干物质基础,n=13,%)
Table 1 Amino acid composition (% ondry matter base, n=13)
项目 Q组 a组 b组 c组 d组 Wj组 天冬氨酸 2.53±0.11a 2.47±0.08a 2.27±0.10b 2.28±0.09b 2.24±0.12b 1.95±0.07c 苏氨酸 1.01±0.02a 0.97±0.04a 0.82±0.01b 0.80±0.05b 0.81±0.02b 0.75±0.03c 丝氨酸 0.94±0.06a 0.89±0.07a 0.85±0.02a 0.84±0.05a 0.87±0.03a 0.70±0.04b 谷氨酸 4.03±0.09a 3.96±0.11a 3.27±0.13b 3.21±0.08b 3.25±0.10b 3.23±0.08b 甘氨酸 1.87±0.05a 1.84±0.07a 1.71±0.01b 1.68±0.04b 1.72±0.03b 1.51±0.05c 丙氨酸 1.71±0.06a 1.67±0.03a 1.47±0.05b 1.48±0.01b 1.45±0.05b 1.32±0.02c 胱氨酸 0.16±0.01a 0.12±0.02b 0.13±0.01a 0.14±0.03a 0.11±0.04b 0.14±0.02a 缬氨酸 1.45±0.07a 1.44±0.05a 1.20±0.03b 1.18±0.07b 1.16±0.04b 1.16±0.09b 蛋氨酸 0.25±0.01a 0.19±0.04b 0.21±0.05b 0.20±0.04b 0.18±0.02b 0.24±0.06a 异亮氨酸 0.95±0.02a 0.91±0.05a 0.82±0.03b 0.81±0.06b 0.85±0.03b 0.80±0.05b 亮氨酸 1.92±0.03a 1.90±0.02a 1.67±0.02b 1.65±0.04b 1.70±0.03b 1.52±0.05c 酪氨酸 0.44±0.01a 0.38±0.02a 0.35±0.04b 0.36±0.02b 0.33±0.01b 0.35±0.04b 苯丙氨酸 1.18±0.06a 1.17±0.08a 1.05±0.04b 1.01±0.06b 1.06±0.08b 0.980.07c 组氨酸 0.71±0.02a 0.67±0.01a 0.70±0.05a 0.68±0.03a 0.73±0.03a 0.59±0.01b 赖氨酸 1.64±0.03a 1.59±0.05a 1.34±0.02b 1.31±0.09b 1.35±0.07b 1.19±0.03c 精氨酸 1.23±0.08a 1.19±0.06a 0.97±0.07b 0.93±0.09b 0.99±0.08b 0.90±0.05b 脯氨酸 1.61±0.11a 1.58±0.09a 1.64±0.07a 1.60±0.08a 1.68±0.09a 1.08±0.07b 总量 23.60±0.21a 22.03±0.37b 20.48±0.51b 20.16±0.13b 20.46±0.46b 18.41±0.25c 注:同行数据后不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 -
[1] 高计会, 王明磊.病死畜禽处理体系建设现状及经验探讨[J], 中国畜禽种业, 2017(11):8-9. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4556.2017.11.004 [2] 朱秀君, 常见, 刘文科, 等.台湾地区病死动物无害化处理及再利用[J].北方牧业, 2014(13):16. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bfmy201413014 [3] MURPHY D W, HANDWERKER T S. Preliminare investigations of composting as a method of dead bird disposal[C]//In: Proceeding of the 1988 National Poulty waste Management Symposium, Coulumbus Ohio, 1988: 65-72.
[4] FULHAGE C, ELLIS C E. Composting Dead Swine[EB/OL].http://wed.extension.illinois.edu/clmt/workbook/WK-FILES/COMPOST,PDF,1994.
[5] GLANVILLE T D, TRAMPEL D W. Composting alternative for animalcarcass disposal[J].J Am Veter Med Assoc, 1997, 210(8):1116-1120. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9108911
[6] ELWELL D, KEENER H, MOELLERS. Preferred disposal option:composting animal mortalities[J].Biocycle, 2001, 42(5):67-68. http://agris.fao.org/openagris/search.do?recordID=US201300087810
[7] Ahn H K, Glanville T D, Crawford B P, et al. Evaluation of the biodegradability of animal carcasses in passively aerated biosecure composting system[C]//In: Proceeding of ASABE Annual Intematonal Meeting, Minnesota Minneapolis, ASABE Annual International Meeting, 2007.
[8] GLANVILLE T D, AHN H K, KOZIEL J A, et al. Pathongen inactivation poten tial and carcass degradation in a biosecure emergency livestock mortality composting system[C]//In: Proceedings of ASABE AnnualInternational Meeting, Rhode island Providence, ASABE Annual International Meeting, 2008.
[9] MURRAY D, MEININGER R G, GOLOVAN S P, et al. Transgene and mitochondrial DNA are indicators of efficient composting of transgenic pig carcasses[J].Biores Technol, 2007, 98(9):1795-1804. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2006.06.029
[10] 郭东坡, 陶秀萍, 尚斌, 等.死猪堆肥处理的通风率选择探讨[J].农业工程学报, 2013, 29(5):187-193. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nygcxb201305027 [11] 缪伏荣, 董志岩, 陈鑫珠, 等, 一株热噬淀粉芽孢杆菌的分离和鉴定[J], 福建农业学报, 2018, 33(4):413-417. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fjnyxb201804015 [12] 于泓, 牟世芬.氨基酸分析方法的研究进展[J].分析化学, 2005, 33(3):398-404. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2005.03.028 [13] ANDERSON M J, WILLIS T J. Canonical analysis of principal coordinates:a useful method of constrained ordination for ecology[J]. Ecology, 2003, 84:511-525. DOI: 10.1890/0012-9658(2003)084[0511:CAOPCA]2.0.CO;2
[14] ASNICAR F, WEINGART G, TICKLE T L, et al. Compact graphical representation of phylogenetic data and metadata with Gra[J].Phl An, 2015, 3(11):e1029. http://mbe.oxfordjournals.org/external-ref?access_num=10.7717/peerj.1029&link_type=DOI
[15] BLAXTER M, MANN J, CHAPMAN T, et al. Defining operational taxonomic units using DNA barcode data[J]. Philos Trans R Soc B-Biol Sci, 2005, 360:1935-1943. DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2005.1725
[16] BOKULICH N A, SUBRAMANIAN S, FAITH J J, et al. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing[J]. Nat Methods, 2013, 10:57-59. DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.2276
[17] BREIMAN L. Random forests[J]. Mach Learn, 2001, 45:5-32. DOI: 10.1023/A:1010933404324
[18] CAPORASO J G, KUCZYNSKI J, STOMBAUGH J, et al. QⅡME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data[J]. Nat Methods, 2010, 7:335-336. DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.f.303
[19] 张浩, 覃燕灵, 于俊勇, 等.发酵堆肥法无害化处理病死猪技术研究[J].今日养猪业, 2017(2):78-81. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8977.2017.02.021 [20] MARICOU H, VERSTRAETE W, MESUERE K. Hygienic aspects of biowaste composting[J]. Waste Management and Research, 1998, 16(4):304-311. DOI: 10.1177/0734242X9801600402
[21] 李国学, 李玉春, 李彦富.固体废物堆肥化及堆肥添加剂研究进展[J].农业环境科学学报, 2003, 22(2):252-256. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2003.02.034 [22] CHAO A, SHEN T J. Nonparametric prediction in species sampling[J]. J Agric Biol Environ Stat, 2004, 9:253-269. DOI: 10.1198/108571104X3262
[23] CHAO A, YANG M C K. Stopping rules and estimation for recapture debugging with unequal failure rates[J]. Biometrika, 1993, 80:193-201. DOI: 10.1093/biomet/80.1.193
[24] CLARKE K R. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure[J]. Australian Journal of Ecology, 1993, 18:117-143. DOI: 10.1111/aec.1993.18.issue-1
[25] COLE J R, WANG Q, CARDENAS E, et al. The Ribosomal Database Project:improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2009, 37:141-145. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_pubmedcentral.nih.gov_2686447




 下载:
下载: