Combining Ability on Main Agronomic Traits and Genetic Clustering of Nine New Breeds of Sweet Corns
-
摘要:目的 利用遗传聚类和配合力分析来了解新育成9个甜玉米自交系的遗传背景和配合力,为组配新品种提供科学依据。方法 以TS01-1、BS02-1、GS132、AS67、SS1等5个白粒自交系为母本,闽甜系688、闽甜系G73、闽甜系197、X90-34等4个高配合力黄粒自交系为父本,按5×4不完全双列杂交设计组配20个杂交组合,并对其株高、穗位高、穗长、穗粗、穗行数、行粒数、百粒重、出籽率、带苞叶穗重和去苞叶穗重等10个性状的配合力进行研究。结果 从去苞叶穗重的一般配合力值得出,供试甜玉米自交系的配合力大小顺序,白粒自交系为AS67 > GS132 > TS01-1 > BS02-1 > SS1,黄粒自交系为闽甜系688 > X90-34 >闽甜系G73 >闽甜系197。从特殊配合力值得出,杂交组合AS67×闽甜系688的特殊配合力值最大,实际测产产量也最高。从分子水平对9个亲本的亲缘关系进行聚类分析,将9个亲本分成黄粒和白粒两个群。结论 黄、白粒自交系间杂交具有一定的杂种优势;聚类分析结果与试验设计的父母本划分一致。Abstract:Objective Genetic backgrounds and combining abilities of 9 newly bred sweet corn inbred lines were studied.Method The inbred lines included 5 white sweet corn female parents P1 (i.e., TS01-1, BS02-1, GS132, AS67 and SS1) and 4 sweet corn male parents P2 (i.e., Mintianxi 688, Mintianxi G73, Mintianxi 197 and X90-34). They were cross-bred into 20 two-tone crosses by a 5×4 incomplete diallel design. The combining ability on 10 traits including plant height, ear location, panicle length, ear girth, ear row count, grains per row, hundred-grain weight, kernel ratio, panicle weight with and without husk, of each hybrid was determined.Result Based on the de-husk panicle weight, the general combining abilities of the white sweet corn inbred lines were in the order of AS67 > GS132 > TS01-1 > BS02-1 > SS1, and those of the yellow sweet corns Mintianxi 688 > X90-34 > Mintianxi G73 > Mintianxi 197. AS67×Mintianxi 688 exhibited the highest specific combining ability with the greatest actual yield among all. The genetic cluster analysis classified the 9 parents into yellow-and white-kernel groups.Conclusion The yellow-kernel and white-kernel sweet corn inbred lines crossed between the 9 parents showed superior heterosis, and the classifications were consistent between the parents and the experimental design.
-
Keywords:
- sweet corn /
- inbred lines /
- combining ability /
- genetic clustering
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】目前,黄白双色水果玉米广受消费者喜爱,俗称“金银粟”,市场潜力巨大,以市场需求为导向进行新品种选育,已成为我国甜玉米育种的发展动向。在玉米育种实践中发现,通过对自交系遗传背景和配合力的综合认识,可以更加科学准确地利用自交系组配出更优秀的品种,比如有些自交系虽然自身性状表现较好,但组配的杂交种表现一般;有些自交系则自身性状表现一般,却能组配出杂种优势明显的杂交种,因此需要对自交系进行综合的了解。【前人研究进展】杂交种的杂种优势表现主要取决于亲本自交系各性状的配合力,配合力是杂种优势利用的基础,玉米自交系配合力的测定,已成为玉米田间育种工作中必不可少的环节[1-4]。结合采用现代分子生物技术SSR分子标记聚类分析方法,可进一步提高对玉米自交系的认识水平和利用效率。前人的研究结果表明,现代生物学分子标记技术为认识玉米种质资源的亲缘关系提供了准确的方法,包括RAPD技术、RFLP技术、SSR技术、AFLP技术等多种分子标记技术在玉米自交系遗传多样性研究上都有应用,但是SSR标记技术提供的遗传多态性信息含量丰富,更适合在分子水平上分析玉米自交系间的亲缘关系[5-7]。前人利用SSR分子标记对我国玉米骨干自交系进行聚类分析,结果与系谱关系基本一致,说明SSR分子标记结果可靠,可以应用于玉米自交系种群划分及遗传多样性分析[8-10]。【本研究切入点】利用从国外引进的多个白色甜玉米杂交种进行二环系选育,选育出5个性状较优良的白粒型玉米自交系,与本课题组先前育成的4个配合力好、性状优良的黄色甜玉米骨干自交系进行测配,分析新选育的5个优良白粒型玉米自交系的配合力,同时利用SSR分子标记技术和聚类分析方法对这9个自交系进行遗传聚类分析。【拟解决的关键问题】通过对9个甜玉米自交系的主要农艺性状配合力和遗传聚类分析,更深入了解它们的亲缘关系,以期为新自交系和新品种的选育提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 供试材料
2017年春季,在福建省农业科学院作物研究所青口试验基地种植9个新育成的甜玉米自交系,其中:5个白粒自交系(TS01-1、BS02-1、GS132、AS67、SS1)作母本,设为P1组,对应文中编号分别为T1、T2、T3、T4、T5;4个黄粒自交系(闽甜系688、闽甜系G73、闽甜系197、X90-34)作父本,设为P2组,对应文中编号分别为M1、M2、M3、M4,按照不完全双列杂交设计组配20个黄白双色杂交组合。
1.2 试验方法
2017年秋季,在福建省农业科学院作物研究所青口试验基地种植上述20个黄白双色组合。
1.2.1 田间试验方案与考察性状
试验采用随机区组设计,3次重复,栽培管理同大田。双行区种植,行长4 m,行距60 cm,株距24 cm,种植密度52 500株·hm-2。从授粉日算起,第22d采摘考种,选取小区中间有代表性的10株测定其株高和穗位高。收获小区中间连续、有代表性的8株,考察产量和穗部性状,包括:穗长、穗粗、穗行数、行粒数、百粒重、出籽率、带苞叶穗重(以下简称穗重)、去苞叶穗净重(以下简称穗净重)等。
1.2.2 分子标记与分析软件
利用玉米DUS测试所用的40对SSR核心引物(表 1),对9个玉米自交系进行扩增,最终选取带型清晰,且有多态性的引物进行统计[11]。试验数据的分析处理采用DPS软件,聚类分析采用PowerMarker V3.25和MEGA5.1软件。
表 1 40对核心引物Table 1. 40 pairs of core primers编号
Number标记
Marker1 bnlg439w1 2 umc1335y5 3 umc2007y4 4 bnlg1940k7 5 umc2105k3 6 phi053k2 7 phi072k4 8 bnlg2291k4 9 umc1705w1 10 bnlg2305k4 11 bnlg161k8 12 bnlg1702k1 13 umc1545y2 14 umc1125y3 15 bnlg240k1 16 phi080k15 17 phi065k9 18 umc1492y13 19 umc1432y6 20 umc1506k12 21 umc1147y4 22 bnlg1671y17 23 phi96100y1 24 umc1536k9 25 bnlg1520k1 26 umc1489y3 27 bnlg490y4 28 umc1999y3 29 umc2115k3 30 umc1429y7 31 bnlg249k2 32 phi299852y2 33 umc2160k3 34 umc1936k4 35 bnlg2235y5 36 phi233376y1 37 umc2084w2 38 umc1231k4 39 phi041y6 40 umc2163w3 2. 结果与分析
2.1 性状配合力方差分析
性状配合力方差分析结果(表 2)表明,参试组合的性状配合力除百粒重、出籽率和穗重外的其余性状均在组合间存在极显著差异。进一步进行一般配合力(GCA)和特殊配合力(SCA)方差分析,结果发现:亲本P1组中,穗粗和百粒重的一般配合力差异分别达到显著和极显著水平,表明P1组自交系穗粗和百粒重两个性状的一般配合力存在真实差异;亲本P2组中,穗粗、穗行数、行粒数、百粒重的一般配合力无显著差异,表明P2组自交系这些性状的一般配合力无真实性差异。特殊配合力方差分析结果表明,10个性状差异均达显著或极显著水平,表明这些性状在组合间均存在真实差异。本结果与黎裕等[12]的研究结果类似。
表 2 9个自交系10个主要性状配合力方差分析结果(F值)Table 2. Analysis of variance on combining ability on yield traits of inbred corns (F-value)变异来源
Variation source自由度
Translation freedom株高
Plant height穗位高
Ear high穗长
Panicle length穗粗
Ear thick穗行数
Ear rows行粒数
Grains per row百粒重
Hundred-grain weight,出籽率
Kernel ratio穗重(带苞叶)
Panicle weight(with husk)穗净重
Panicle weight区组Block 2 3.791 42.569* 0.674 0.036 2.467 3.791 5.958** 0.007** 0.001 0.021 杂交种Hybrids 19 22.697** 238.348** 15.079** 0.171** 6.018** 22.697** 0.267 0.003 0.035** 0.039 P1 4 4.368 151.977 31.028 0.373* 4.167 4.367 1.917** 0.003 0.026 0.028 P2 3 0.999 156.923 3.206 0.076 4.867 0.999 0.037 0.003 0.008 0.013 P1×P2 12 34.232** 287.495* 12.731** 0.128** 6.922** 34.232** 0.141* 0.003* 0.045** 0.049* 误差Error 38 5.558 12.004 0.349 0.041 1.344 5.557 0.250 0.001 0.004 0.028 注:*、**分别表示差异达5%和1%显著水平。
Note: *, ** respectively indicate differences significant levels of 5% and 1%.2.2 一般配合力效应分析
一般配合力效应是由亲本加性基因所决定的,是可遗传的部分,其效应值大小与性状的遗传可能性呈正比。一般配合力高的性状,其遗传力也高,受环境影响较小。从表 3可以看出,同一自交系的不同性状和不同自交系的同一性状的GCA相对效应值有一些差别;从株高来看,自交系T2、T3、T5和M4的效应值为正,说明它们有增加后代株高的作用;从穗位高来看,自交系T1、T2、M1和M4的效应值为正,说明它们有提高后代穗位高的作用,在组配过程中宜选择穗位较低的亲本进行组配;从穗长来看,自交系T3、T4、T5、M2、M3的效应值为正,其中T4的效应值高达10.53,说明它们有增加后代穗长的作用,利于增加行粒数;从穗粗来看,自交系T1、T2、T3、M2、M4的效应值为正,说明它们有增加后代穗粗的作用;从穗行数来看,自交系T2、T5、M2、M4的效应值为正,说明它们有提高后代穗行数的作用,有利于增加穗粒数;从行粒数来看,自交系T4、T5、M2、M3、M4的效应值为正,说明它们有增加后代行粒数的作用;从百粒重来看,自交系T3、M1、M4的效应值为正,说明它们有增加后代粒重的作用;从出籽率来看,自交系T2、T5、M1、M4的效应值为正,说明它们有提高后代出籽率的作用;从穗重来看,自交系T3、T4、M2、M4的效应值为正,说明它们有提高后代穗重的作用;从穗净重来看,自交系T1、T3、T4、M1、M4的效应值为正,说明它们有增加后代穗净重的作用。
表 3 9个自交系主要性状一般配合力(GCA)相对效应值Table 3. Relative effect of general combining ability(GCA)on yield traits of 9 inbred lines亲本
Parent株高
Plant height穗位高
Ear high穗长
Panicle length穗粗
Ear thick穗行数
Ear rows行粒数
Grains per row百粒重
Hundred-grain weight出籽率
Kernel ratio穗重(带苞叶)
Panicle weight(with husk)穗净重
Panicle weightT1 -5.47 2.71 -7.98 1.21 -0.92 -0.23 -1.89 -0.56 -4.81 1.05 T2 2.44 6.18 -7.61 4.12 4.59 -1.41 -1.48 3.50 -0.58 -5.60 T3 1.74 -1.92 4.69 0.44 -1.83 -1.25 9.20 -0.32 3.25 5.90 T4 -2.34 -5.96 10.53 -5.40 -3.67 2.81 -0.66 -2.99 4.27 4.97 T5 3.63 -1.01 0.37 -0.36 1.83 0.08 -5.17 0.37 -2.13 -6.32 M1 -0.32 1.41 -1.94 -1.06 -3.85 -1.06 0.16 2.34 -0.36 2.04 M2 -0.95 -5.69 0.17 1.14 3.49 0.44 -1.81 -2.20 2.10 -2.22 M3 -0.73 -0.05 3.17 -1.34 -0.92 0.50 -0.49 -0.63 -2.31 -3.67 M4 2.00 4.33 -1.40 1.26 1.28 0.13 2.13 0.49 0.57 3.85 自交系T2、T5、M3的穗重与穗净重效应值均为负值,说明它们会降低后代果穗净重量。自交系T1和M1穗重为负、穗净重为正,自交系M2穗重为正、穗净重为负,说明自交系T1和M1的苞叶较薄,而自交系M2的苞叶较厚。
2.3 特殊配合力效应分析
特殊配合力是指特定组合内,杂交一代的性状值与亲本一般配合力平均数的偏差,是指两亲本自交系各自贡献给杂交种的基因通过互作而表现的非加性基因效应,受环境影响较大,不能稳定遗传,但可指导杂种优势利用和杂交种选育[13]。从表 4可以看出,同一性状不同组合特殊配合力效应值存在显著差异,本试验组配的20个双色组合中,株高特殊配合力效应表现为负值的有8个组合,负效应值较大的组合为T4×M1、T3×M4、T3×M3和T1×M3。穗位高特殊配合力效应表现为负值的有11个组合,负效应值较大的组合为T3×M4、T3×M3、T2×M2和T5×M1。由此可见,T3×M4和T3×M3两组合的株高和穗位高都较低。
表 4 20个组合主要性状特殊配合力(SCA)相对效应值Table 4. Estimates on specific combining ability (SCA) on yield traits of 20 hybrids组合
Hybridized combination株高
Plant height穗位高
Ear high穗长
Panicle length穗粗
Ear thick穗行数
Ear rows行粒数
Grains per row百粒重
Hundred-grain weight出籽率
Kernel ratio穗重(带苞叶)
Panicle weight(with husk)穗净重
Panicle weightT1×M1 3.03 -3.48 2.34 1.45 -3.49 5.98 1.89 -1.76 4.30 0.51 T1×M2 1.96 -7.34 -1.92 -3.17 0.18 -4.27 10.43 -2.32 -3.85 -0.85 T1×M3 -6.30 0.52 -2.17 0.62 -2.75 5.36 -10.59 3.06 -5.18 1.75 T1×M4 1.31 10.30 1.74 1.10 6.06 -7.08 -1.72 1.02 4.73 -1.41 T2×M1 -2.66 -4.66 -8.61 -3.68 -8.99 -12.53 -8.37 -5.35 -15.06 -13.48 T2×M2 0.22 -11.87 3.00 -0.91 -5.32 6.28 5.09 2.43 3.92 -17.55 T2×M3 3.76 5.81 2.87 5.95 6.42 5.28 8.70 -0.53 11.65 28.73 T2×M4 -1.32 10.72 2.74 -1.36 7.89 0.97 -5.42 3.45 -0.50 2.30 T3×M1 8.56 21.00 -5.42 -0.27 8.44 -6.13 -5.91 3.10 -8.24 -10.55 T3×M2 7.12 13.75 -16.53 6.69 4.77 -7.31 -0.66 3.94 -1.59 -1.76 T3×M3 -6.80 -16.40 8.00 -3.84 -1.83 6.69 1.31 0.97 5.71 6.38 T3×M4 -8.88 -18.36 13.94 -2.58 -11.38 6.75 5.25 -8.01 4.13 5.94 T4×M1 -9.54 -2.10 8.92 1.06 6.61 7.94 2.30 4.38 13.36 11.78 T4×M2 -5.73 -1.59 9.68 0.36 -0.73 -1.69 -0.66 -4.51 3.71 8.69 T4×M3 9.24 5.11 -12.58 -5.39 -11.01 -15.19 2.96 -1.00 -16.88 -21.55 T4×M4 6.03 -1.43 -6.02 3.97 5.14 8.94 -4.60 1.13 -0.19 1.09 T5×M1 0.61 -10.77 2.76 1.45 -2.57 4.73 10.10 -0.37 5.65 11.74 T5×M2 -3.57 7.04 5.76 -2.97 1.10 6.98 -14.20 0.46 -2.19 11.48 T5×M3 0.11 4.95 3.87 2.65 9.17 -2.14 -2.38 -2.50 4.71 -15.30 T5×M4 2.85 -1.23 -12.40 -1.13 -7.71 -9.58 6.49 2.41 -8.17 -7.92 穗长特殊配合力相对效应表现为正值的有12个组合,正效应值较大的组合为T3×M4、T4×M2和T4×M1;穗粗特殊配合力相对效应表现为正值的有10个组合,正效应值较大的组合为T3×M2和T2×M3;穗行数特殊配合力相对效应表现为正值的有10个组合,正效应值较大的组合为T5×M3和T3×M1;行粒数特殊配合力相对效应表现为正值的有11个组合,正效应值较大的组合为T4×M4和T4×M1;百粒重特殊配合力相对效应表现为正值的有10个组合,正效应值较大的组合为T1×M2、T5×M1和T2×M3;出籽率特殊配合力相对效应表现为正值的有11个组合,正效应值较大的组合为T4×M1和T3×M2。
穗重特殊配合力效应表现为正值的有10个组合,正效应值前3名的组合为T4×M1、T2×M3、T3×M3,而穗重实际表现前3名的组合为T4×M1、T4×M2、T2×M3;穗净重特殊配合力效应表现为正值的有11个组合,正效应值前3名的组合为T2×M3、T4×M1、T5×M1,而穗净重实际表现前3名的组合为T4×M1、T2×M3、T3×M4。可以看出,穗重与穗净重特殊配合力效应值前两名的组合均与其实际产量表现基本一致。表明组合产量特殊配合力基本能反映组合的实际表现。本结果与张世煌的研究结果类似[14]。
2.4 遗传聚类分析
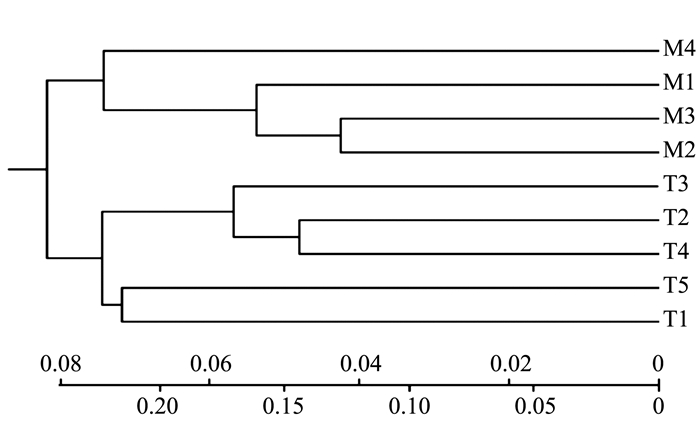
从40对SSR引物中筛选出多态性好的分布于10条染色体上的引物17对,在9个玉米自交系间共检测出53个等位基因变异,每对引物检测出等位基因2~6个,平均3.1个。SSR扩增产物以0、1、9统计建立数据库,在相同迁移位置上,有条带记为1,无条带记为0,缺失记为9,进行遗传聚类分析,用邻近法对9个自交系进行聚类,结果将母本P1群体和父本P2群体分成两个群,与母本群主要为温带血缘,父本群主要为热带血缘的结果吻合(图 1)。
3. 讨论与结论
经配合力分析发现, AS67(T4)、GS132(T3)、TS01-1(T1)、闽甜系688(M1)和X90-34(M4)的穗净重一般配合力效应值为正,对提高杂交后代产量有利,有望选育出高产型品种。其中:GS132(T3)的穗位高一般配合力效应值为负值,百粒重和穗净重均为正值(一般配合力效应值均居参试自交系首位),组配出的杂交种GS132×闽甜系197穗位最低;AS67(T4)的穗长和行粒数均为正值,均居参试自交系首位,组配出的大穗型杂交种AS67×X90-34穗重最大;闽甜系G73(M2)的株高和穗位高一般配合力效应值为负值,穗长和行粒数均为正值,组配出了穗重较大的杂交种AS67×闽甜系G73,说明一般配合力效应值能够较好地反映亲本的育种价值。在品种选育过程中,可以根据预先制定的育种目标,有针对性地选择目标性状表现突出的亲本加以利用。自交系闽甜系197(M3)和BS02-1(T2)单株产量的一般配合力并不高,而配制组合BS02-1×闽甜系197的特殊配合力值在穗重和穗净重方面都排名前3名,说明一般配合力低的自交系, 其组合特殊配合力也可能较高;AS67×闽甜系688、BS02-1×闽甜系197、SS1×闽甜系688、AS67×闽甜系G73、GS132×闽甜系197这5个组合的穗重和穗净重的特殊配合力值均较高,具有较强的产量杂种优势。本团队利用闽甜系688为父本选育的闽甜6855[15]和闽甜683[16]均具有较高产量,均已通过福建省品种审定委员会审定,以后可进一步结合糖度、果皮厚薄、抗性等性状加以研究利用,为选育高产、优质甜玉米新品种奠定基础。
本研究进行的遗传聚类分析初步从分子水平上认识9个亲本间的亲缘关系,遗传聚类树状图显示,按照Dice遗传相似系数(GS)以0.08为阀值,可将9个亲本分为两个群体,遗传聚类分析结果与试验中的P1组和P2组分组相一致。说明本试验中组配的20个杂交组合均具有一定的杂种优势。亲缘关系较近的P1组(母本),根据其株叶形态和生育期判断属于温带材料;而P2组(父本),根据其株叶形态和生育期判断属于热带或者亚热带材料,后续研究将通过进一步验证P1群内和P2群内自交系间的杂种优势,为种质资源高效利用和组合测配提供参考。
-
表 1 40对核心引物
Table 1 40 pairs of core primers
编号
Number标记
Marker1 bnlg439w1 2 umc1335y5 3 umc2007y4 4 bnlg1940k7 5 umc2105k3 6 phi053k2 7 phi072k4 8 bnlg2291k4 9 umc1705w1 10 bnlg2305k4 11 bnlg161k8 12 bnlg1702k1 13 umc1545y2 14 umc1125y3 15 bnlg240k1 16 phi080k15 17 phi065k9 18 umc1492y13 19 umc1432y6 20 umc1506k12 21 umc1147y4 22 bnlg1671y17 23 phi96100y1 24 umc1536k9 25 bnlg1520k1 26 umc1489y3 27 bnlg490y4 28 umc1999y3 29 umc2115k3 30 umc1429y7 31 bnlg249k2 32 phi299852y2 33 umc2160k3 34 umc1936k4 35 bnlg2235y5 36 phi233376y1 37 umc2084w2 38 umc1231k4 39 phi041y6 40 umc2163w3 表 2 9个自交系10个主要性状配合力方差分析结果(F值)
Table 2 Analysis of variance on combining ability on yield traits of inbred corns (F-value)
变异来源
Variation source自由度
Translation freedom株高
Plant height穗位高
Ear high穗长
Panicle length穗粗
Ear thick穗行数
Ear rows行粒数
Grains per row百粒重
Hundred-grain weight,出籽率
Kernel ratio穗重(带苞叶)
Panicle weight(with husk)穗净重
Panicle weight区组Block 2 3.791 42.569* 0.674 0.036 2.467 3.791 5.958** 0.007** 0.001 0.021 杂交种Hybrids 19 22.697** 238.348** 15.079** 0.171** 6.018** 22.697** 0.267 0.003 0.035** 0.039 P1 4 4.368 151.977 31.028 0.373* 4.167 4.367 1.917** 0.003 0.026 0.028 P2 3 0.999 156.923 3.206 0.076 4.867 0.999 0.037 0.003 0.008 0.013 P1×P2 12 34.232** 287.495* 12.731** 0.128** 6.922** 34.232** 0.141* 0.003* 0.045** 0.049* 误差Error 38 5.558 12.004 0.349 0.041 1.344 5.557 0.250 0.001 0.004 0.028 注:*、**分别表示差异达5%和1%显著水平。
Note: *, ** respectively indicate differences significant levels of 5% and 1%.表 3 9个自交系主要性状一般配合力(GCA)相对效应值
Table 3 Relative effect of general combining ability(GCA)on yield traits of 9 inbred lines
亲本
Parent株高
Plant height穗位高
Ear high穗长
Panicle length穗粗
Ear thick穗行数
Ear rows行粒数
Grains per row百粒重
Hundred-grain weight出籽率
Kernel ratio穗重(带苞叶)
Panicle weight(with husk)穗净重
Panicle weightT1 -5.47 2.71 -7.98 1.21 -0.92 -0.23 -1.89 -0.56 -4.81 1.05 T2 2.44 6.18 -7.61 4.12 4.59 -1.41 -1.48 3.50 -0.58 -5.60 T3 1.74 -1.92 4.69 0.44 -1.83 -1.25 9.20 -0.32 3.25 5.90 T4 -2.34 -5.96 10.53 -5.40 -3.67 2.81 -0.66 -2.99 4.27 4.97 T5 3.63 -1.01 0.37 -0.36 1.83 0.08 -5.17 0.37 -2.13 -6.32 M1 -0.32 1.41 -1.94 -1.06 -3.85 -1.06 0.16 2.34 -0.36 2.04 M2 -0.95 -5.69 0.17 1.14 3.49 0.44 -1.81 -2.20 2.10 -2.22 M3 -0.73 -0.05 3.17 -1.34 -0.92 0.50 -0.49 -0.63 -2.31 -3.67 M4 2.00 4.33 -1.40 1.26 1.28 0.13 2.13 0.49 0.57 3.85 表 4 20个组合主要性状特殊配合力(SCA)相对效应值
Table 4 Estimates on specific combining ability (SCA) on yield traits of 20 hybrids
组合
Hybridized combination株高
Plant height穗位高
Ear high穗长
Panicle length穗粗
Ear thick穗行数
Ear rows行粒数
Grains per row百粒重
Hundred-grain weight出籽率
Kernel ratio穗重(带苞叶)
Panicle weight(with husk)穗净重
Panicle weightT1×M1 3.03 -3.48 2.34 1.45 -3.49 5.98 1.89 -1.76 4.30 0.51 T1×M2 1.96 -7.34 -1.92 -3.17 0.18 -4.27 10.43 -2.32 -3.85 -0.85 T1×M3 -6.30 0.52 -2.17 0.62 -2.75 5.36 -10.59 3.06 -5.18 1.75 T1×M4 1.31 10.30 1.74 1.10 6.06 -7.08 -1.72 1.02 4.73 -1.41 T2×M1 -2.66 -4.66 -8.61 -3.68 -8.99 -12.53 -8.37 -5.35 -15.06 -13.48 T2×M2 0.22 -11.87 3.00 -0.91 -5.32 6.28 5.09 2.43 3.92 -17.55 T2×M3 3.76 5.81 2.87 5.95 6.42 5.28 8.70 -0.53 11.65 28.73 T2×M4 -1.32 10.72 2.74 -1.36 7.89 0.97 -5.42 3.45 -0.50 2.30 T3×M1 8.56 21.00 -5.42 -0.27 8.44 -6.13 -5.91 3.10 -8.24 -10.55 T3×M2 7.12 13.75 -16.53 6.69 4.77 -7.31 -0.66 3.94 -1.59 -1.76 T3×M3 -6.80 -16.40 8.00 -3.84 -1.83 6.69 1.31 0.97 5.71 6.38 T3×M4 -8.88 -18.36 13.94 -2.58 -11.38 6.75 5.25 -8.01 4.13 5.94 T4×M1 -9.54 -2.10 8.92 1.06 6.61 7.94 2.30 4.38 13.36 11.78 T4×M2 -5.73 -1.59 9.68 0.36 -0.73 -1.69 -0.66 -4.51 3.71 8.69 T4×M3 9.24 5.11 -12.58 -5.39 -11.01 -15.19 2.96 -1.00 -16.88 -21.55 T4×M4 6.03 -1.43 -6.02 3.97 5.14 8.94 -4.60 1.13 -0.19 1.09 T5×M1 0.61 -10.77 2.76 1.45 -2.57 4.73 10.10 -0.37 5.65 11.74 T5×M2 -3.57 7.04 5.76 -2.97 1.10 6.98 -14.20 0.46 -2.19 11.48 T5×M3 0.11 4.95 3.87 2.65 9.17 -2.14 -2.38 -2.50 4.71 -15.30 T5×M4 2.85 -1.23 -12.40 -1.13 -7.71 -9.58 6.49 2.41 -8.17 -7.92 -
[1] 赵猛, 刘志雄, 陈强.玉米自交系主要数量性状的配合力分析与利用[J].北方农业学报, 2016, 44(5):21-24. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-1197.2016.05.04 ZHAO M, LIU Z X, CHEN Q.Analysis of combining ability and use of maize inbred lines[J]. Inner Mongolia Agricultural Science, 2016, 44(5):21-24.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-1197.2016.05.04
[2] 李潮海, 赵亚丽, 王小星, 等.玉米昌7-2近缘系遗传多样性及其配合力分析[J].河南农业大学学报, 2008, 42(2):150-154. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hennannydxxb200802006 LI C H, ZHAO Y L, WANG X X, et al.Genetic Diversity of Chang7-2 Related Inbred Lines of Maize and Analysis of Their Combining Ability[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 2008, 42(2):150-154.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hennannydxxb200802006
[3] 王瑞莲, 王永行, 韩凤英, 等.几个玉米自交系材料的配合力分析[J].内蒙古农业科技, 2015, 43(5):88-91. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-0907.2015.05.032 WANG R L, WANG Y H, HAN F Y, et al.Analysis on the Combining Ability of Several Maize Inbred Lines[J]. Inner Mongolia Agricultural Science And Technology, 2015, 43(5):88-91.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-0907.2015.05.032
[4] 袁克录, 李继强, 谢新学, 等.6个新育玉米自交系配合力测定[J].分子植物育种, 2016, 14(1)216-222. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fzzwyz201601029 YUAN K L, LI J Q, XIE X X, et al.Determination of Combining Ability of 6 newly maize inbred lines[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2016, 14(1)216-222.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fzzwyz201601029
[5] YANG Y, XU Y, SHAH T, et al.Comparison of SSRs and SNPs in Assessment of Genetic Relatedness in Maize[J]. Genetic, 2011, 139(8)1045-1054. DOI: 10.1007/s10709-011-9606-9
[6] 刘东军, 张宏纪, 张举梅.91份俄罗斯玉米自交系的遗传多样性分析[J].核农学报, 2016, 30(11):2112-2118. DOI: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2016.11.2112 LIU D J, ZHANG H J, ZHANG, J M.Genetic Diversity Analysis of 91 Russian Maize Inbred Lines[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 30(11):2112-2118.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2016.11.2112
[7] 杨文鹏, 关琦, 杨留启, 等.贵州70份玉米自交系的SSR标记遗传多样性及其杂种优势群分析[J].植物遗传资源学报, 2011, 12(2):241-248. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwyczyxb201102012 YANG W P, GUAN Q, YANG L Q, et al.Genetic Diversity and Heterotic Group of 70Maize Inbred Lines in Guizhou SSR Markers[J]. Plant of Journal Genetic Resources, 2011, 12(2):241-248.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwyczyxb201102012
[8] 李新海, 袁力行, 李晓辉, 等.利用SSR标记划分70份我国玉米自交系的杂种优势[J].中国农业科学, 2003, 36(6):622-627. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2003.06.004 LI X H, YUAN L X, LI X H, et al.Heterotic Grouping of 70 Maize Inbred Lines by SSR Markers[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2003, 36(6):622-627.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2003.06.004
[9] 赵旭, 方永丰, 王汉宁, 等.玉米SSR标记杂优类群划分及群体遗传结构分析[J].核农学报, 2013, 27(12):1828-1838. DOI: 10.11869/hnxb.2013.12.1828 ZHAO X, FANG Y F, WANG H N.Genetic diversity analysis and Heterosis grouping of Maize Inbred Lines[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 27(12):1828-1838.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11869/hnxb.2013.12.1828
[10] 韩晴, 沈雪芳, 陆卫平.20个鲜食玉米杂交种DNA指纹库的构建[J].上海农业学报, 2014, 30(1):36-39. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3924.2014.01.009 HAN Q, SHEN X F, LU W P.Construction of DNA Fingerprint Database of 20 Table Corn Hybrids[J]. Acta Agricalture Shanghai, 2014, 30(1):36-39.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3924.2014.01.009
[11] 王兵伟, 覃嘉明, 黄安霞, 等.SSR分子标记分析60份玉米自交系的遗传多样性[J].西南农业学报, 2014, 27(4):1358-1362. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4829.2014.04.003 WANG B W, TANG J M, HUANG A X, et al.Analysis of Genetic Diversity by SSR Markers for 60 Maize Inbred Lines[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 27(4):1358-1362.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4829.2014.04.003
[12] 黎裕, 王天宇.我国玉米育种种质基础与骨干亲本的形成[J].玉米科学, 2010, 18(5):1-8. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ymkx201005001 LI Y, WANG T Y.Germplasm Base of Maize Breeding in China and Formation of Foundation Parents[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2010, 18(5):1-8.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ymkx201005001
[13] 王玉民, 尹大鹏, 张春宵, 等.利用SSR标记分析35份糯玉米种质的遗传多样性[J].玉米科学, 2014, 22(6):27-31, 35. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YMKX201406006.htm WANG Y M, YI D P, ZHANG C X, et al.Genetic Diversity of 35 Waxy Maize Germplasms Based on SSR Markers[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2014, 22(6):27-31, 35.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YMKX201406006.htm
[14] 张世煌.商业育种只需要两个杂种优势群[J].种子科技, 2014(7):7-8. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zzkj201407007 ZHANG S H.Commercial breeding requires only two heterotic groups[J]. Seed Science and Technology, 2014(7):7-8.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zzkj201407007
[15] 林建新, 陈山虎, 廖长见, 等.甜玉米新品种闽甜6855的选育[J].福建农业学报, 2016, 31(11):1171-1174. DOI: 10.19303/j.issn.1008-0384.2016.11.006 LIN J X, CHEN S H, LIAO C J, et al.Breeding a New Sweet Corn variety, Mintian 6855[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 31(11):1171-1174.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.19303/j.issn.1008-0384.2016.11.006
[16] 廖长见, 张扬, 林建新, 等.甜玉米新品种'闽甜683'的选育[J].福建农业学报, 2018, 33(6):591-596. DOI: 10.19303/j.issn.1008-0384.2018.06.009 LIAO C J, ZHANG Y, LIN J X, et al.Breeding of a New Sweet Corn Variety 'Min Tian 683'[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 33(6):591-596.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.19303/j.issn.1008-0384.2018.06.009
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 付连双,和阳升,王欣晨,王晓楠,单大鹏,严洪冬,李祥羽,唐贵. 179份高粱种质资源表型鉴定与遗传多样性分析. 东北农业大学学报. 2024(02): 1-9 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王辉,王天友,曹新川,刘春艳,张凤娇,何良荣. 南疆陆地棉种质资源遗传多样性及群体结构分析. 分子植物育种. 2022(10): 3434-3447 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 廖长见,张扬,陈伟,林建新,滕振勇,陈山虎,林静,卢和顶. 优质超甜玉米新品种闽双色4号的选育. 福建农业学报. 2021(04): 386-393 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 陈志坚. 87份糯玉米自交系的遗传多样性分析. 种子. 2021(06): 70-75+2 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)




 下载:
下载: