ISSR Fingerprints and Genetic Variations of Sun-Cured Tobacco Germplasms
-
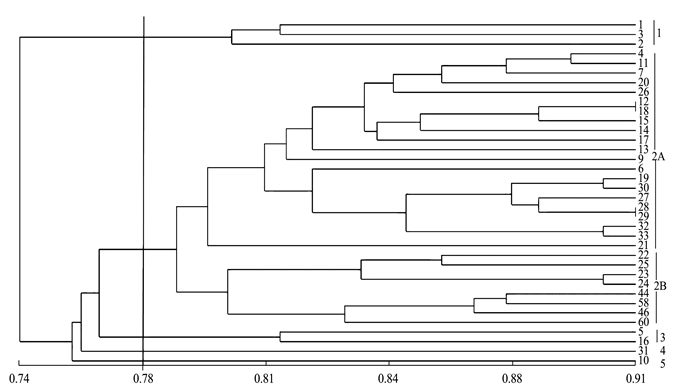
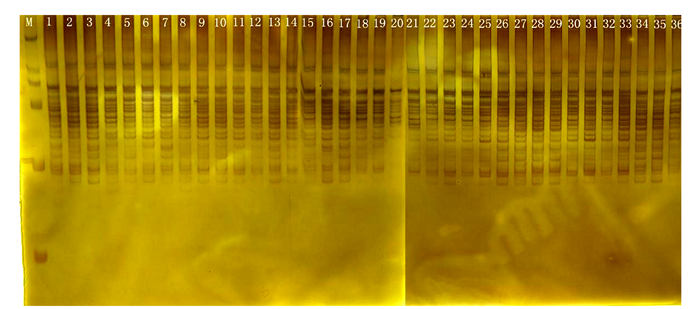
摘要:目的 较为准确地揭示晾晒烟种质间的遗传关系,提高晾晒烟种质资源的利用率和育种效率。方法 利用ISSR分子标记技术对36份晾晒烟种质资源进行遗传多样性分析。结果 从100个ISSR引物中筛选出7条多态性好的引物,扩增出113个条带,其中91条多态性条带,多态性条带比例有80.5%;ISSR标记有效等位基因数(Ne)的平均值为1.64,Nei's基因多样性指数(H)的平均值为0.37,Shannon's信息指数(I)值的平均值为0.55,表明ISSR标记具有较高的多态性检测效率;聚类分析结果表明36份晾晒烟种质间的遗传相似性系数(GS)为0.74~0.91,品种间遗传多样性水平较低,以0.78处作为截值可以划分为5个组;数字指纹图谱可以较为有效地将供试材料进行区分。结论 ISSR标记适合用于构建晾晒烟的DNA指纹图谱,可以为晾晒烟的品种鉴定提供科学依据。Abstract:Objective This study was aimed to accurately reveal the genetic relationship among sun-cured tobacco germplasms, and improve the utilization and breeding efficiency of sun-cured tobacco resources.Method Genetic diversity of 36 sun-cured tobacco germplasms was analyzed using ISSR.Result From the samples, 113 DNA bands were amplified with 7 polymorphic primers selected from 100 ISSR primers. Among them, 91 bands (80.5%) were polymorphic. The average effective number of alleles (Ne), Nei's gene diversity index (H), and Shannon's information index (I) of the ISSR markers were 1.64, 0.37, and 0.55, respectively, indicating a high detection efficacy. The UPGMA analysis showed a low diversity among the germplasms with the genetic similarity coefficients (GS) ranging from 0.74 to 0.91. With the new method, the germplasms were clustered into 5 groups at the level of 0.78.The digital fingerprints effectively distinguish the germplasms.Conclusion The ISSR markers chosen for the DNA fingerprints of 36 sun-cured tobacco germplasms were appropriate for the otherwise difficult task of differentiating and identifying those genetically closely related varieties.
-
Keywords:
- sun-cured tobacco /
- ISSR /
- fingerprint maps /
- genetic diversity
-
-
表 1 供试晾晒烟材料
Table 1 Selected sun-cured tobacco germplasms
编号Code 名称Name 来源Collectionsite 类型Type 1 贵港土烟1号Guigang No. 1 广西贵港Guigang Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 2 贵港土烟2号Guigang No. 2 广西贵港Guigang Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 3 贵港土烟3号Guigang No.3 广西贵港Guigang Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 4 横县土烟1号Hengxian No.1 广西横县Hengxian Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 5 柳城土烟1号Liucheng No. 1 广西柳城Liucheng Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 6 凌云土烟1号Lingyun No.1 广西凌云Lingyun Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 7 全州土烟1号Quanzhou No. 1 广西全州Quanzhou Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 8 三里烟Shanglin 广西上林Shanglin Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 9 资源土烟1号Ziyuan No. 1 广西资源Ziyuan Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 10 阳朔土烟1号Yangshuo No. 1 广西阳朔Yangshuo Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 11 临桂土烟1号Lingui No. 1 广西临桂Lingui Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 12 临桂土烟2号Lingui No. 2 广西临桂Lingui Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 13 凌云土烟2号Lingyun No 2 广西凌云Lingyun Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 14 凌云土烟3号Lingyun No 3 广西凌云Lingyun Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 15 环江土烟3号Huanjiang No. 3 广西环江Huanjiang Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 16 环江土烟1号Huanjiang No. 1 广西环江Huanjiang Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 17 环江土烟2号Huanjiang No. 2 广西环江Huanjiang Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 18 马山土烟1号Mashan No 1 广西马山Mashan Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 19 横县土烟2号Hengxian No.2 广西横县Hengxian Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 20 平果土烟2号Pingguo No.2 广西平果Pingguo Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 21 平果土烟1号Pingguo No.1 广西平果Pingguo Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 22 横县土烟3号Hengxian No.3 广西横县Hengxian Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 23 凌云土烟4号Lingyun No.4 广西凌云Lingyun Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 24 安太土烟1号Antai No.1 广西融水Rongshui Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 25 安太土烟2号Antai No.2 广西融水RongshuiGuangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 26 凌云土烟5号Lingyun No.5 广西凌云Lingyun Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 27 环江土烟4号Huanjiang No.4 广西环江Huanjiang Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 28 马山土烟2号Mashan No.2 广西马山Mashan Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 29 平乐土烟1号Pingle No.1 广西平乐Pingle Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 30 平乐土烟2号Pingle No.2 广西平乐Pingle Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 31 河池土烟1号Hechi No.1 广西河池Hechi Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 32 都安土烟1号Du′an No.1 广西都安Du′an Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 33 都安土烟2号Du′an No.2 广西都安Du′an Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 34 靖西土烟1号Jingxi No.1 广西靖西Jingxi Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 35 德保土烟1号Debao No.1 广西德保Debao Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 36 靖西土烟2号Jingxi No.2 广西靖西Jingxi Guangxi 晒烟Sun-cured Tobacco 表 2 ISSR引物序列和扩增结果
Table 2 ISSR primer sequences and amplifications
引物编号No.Pri-mer 序列Primer sequences 多态性条带数Polymorphi-c bands 总条带数Total bands 多态性条带百分比The proportion of polymorphic bands/% 808 AGA GAG AGA GAG AGA GC 13 15 86.7 809 AGA GAG AGA GAG AGA GG 7 14 50.0 825 ACA CAC ACA CAC ACA CT 10 10 100 855 ACA CAC ACA CAC ACA CYT 23 24 95.8 856 ACA CAC ACA CAC ACA CYA 14 18 77.8 886 VDV CTC TCT CTC TCT CT 8 15 53.3 899 CAT GGT GTT GGT CAT TGT TCC A 16 17 94.1 平均数Mean - 13 16.1 80.5 总数Total - 91 113 - 表 3 晾晒烟ISSR标记的多态性分析
Table 3 ISSR genetated banding patterns on sun-cured tobacco germplasms
引物编号No.Primer 有效等位基因数Effective number of alleles(Ne) Nei′s基因多样性指数Nei′s gene divesity(H) Shannon′s信息指数Shannon′s informaion index (I) 808 1.64 0.39 0.58 809 1.88 0.47 0.66 825 1.69 0.39 0.57 855 1.50 0.33 0.50 856 1.66 0.39 0.58 886 1.95 0.49 0.68 899 1.17 0.14 0.25 平均数Mean 1.64 0.37 0.55 表 4 7条引物区分开的晾晒烟种质
Table 4 Sun-cured tobacco germplasms differentiated by using 7 primers
引物Primer 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 808 + + + + 809 + + 825 + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + 855 + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + 856 + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + 886 + + + + + + + + 899 + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + 注:1~36号材料编号同表 1,“+”表示该种质可被鉴定出来。
Note:1-36 are the same as Table 1, “+”said the germplasm could be identified.表 5 36份晾晒烟种质的ISSR数字指纹图谱
Table 5 ISSR fingerprints of 36 sun-cured tobacco germplasms
材料编号Code 808 809 825 855 856 886 899 1 000001100111010 11101101111111 1001111010 101010000100010101011101 101000101011101000 101011111111010 00000000000010100 2 000000011101010 11101101111111 1001111101 010101000100000000010101 101000101010101000 101010111101110 00000000000010000 3 100011100101100 11101101111111 1001111111 000001000100010100010101 101000011010001000 111110111111010 00010000000010100 4 100011100101100 11101011111111 0011011000 110000111100110000010101 101000101111101000 111110111111010 00000000000011000 5 100011100101100 11101011111111 1101011011 000000100011001100110101 101000101010101000 111010111111010 01000000000010010 6 000011100101100 11101011111111 1001010001 010000101100010000000101 101000100110101000 111111111101010 00000000001011000 7 100011100101100 11101011111111 1000011100 010000111100110100010101 111101011011001000 111110111111000 00000000000010000 8 100011100101100 11101011111111 0000011000 110000111100000000000011 101010001011101000 111010111111000 10001000000010000 9 111110000111111 11101011111111 0100011001 010000111101110100010101 101010001010101000 001110111101010 00000000000010000 10 100011100101100 11101011111111 0000011000 110000111100110100010001 101000111011001000 001010111101010 00000000000010000 11 100011000101100 11101011111111 1100000001 110000011100110100010101 101000111010101000 101110111101010 00000000000010000 12 100011100101100 11101111111111 0001000000 110000101101001100110001 101000111011001000 101110111111010 00100010000010000 13 100011100101100 11101011111111 1100011000 110000000000110100010101 101000111011011100 101110111101010 10100000000011010 14 100011100101100 11101011111111 1100001101 110000000100000100010101 101010001010001000 101110111101010 00100000100010000 15 100011100101100 11101011111111 1100001011 110000000001001010101101 101010001010001111 101110111101010 00001000000010010 16 000011100101100 11101011111111 0000001010 110000000110110100010101 101010001111111100 101110111111011 00000000000010000 17 100011100101100 11101011111111 1100001011 110000101100100100010001 101010111010101000 101110111111010 00000000001010000 18 100011100101100 11101011111111 0000001100 000000000000000000000101 101000111110101000 001111111101010 00000000000010000 19 100011100101100 11101011111111 0010001110 110001111100110100010101 101000111010001000 101111111101010 10000100100010000 20 100011100101100 00110011111110 0010001100 000000011101110100010001 101010111010001000 101111111101010 00000000000010000 21 100011100101100 11110011111111 1111101010 000000011100000100000001 101010111011001000 101110111101010 10001001100010000 22 100011100101100 11110011111111 1111101011 000001010001010101010101 101000111011001000 101110111101010 01100100000110000 23 100011100101100 11110011111111 1111111011 110001011001110101010101 101000111011001000 101110111101010 00010101011110000 24 100011100101100 11110011111111 1111001011 110001010111010000000001 101000111011001000 101110111101010 00000010000010000 25 100011100101100 11101011111111 1111111010 110001011110110100010001 101000001110001000 001010111101010 00000000000010000 26 100011100101100 11101011111111 0001111101 110001011000000000000001 101000000111101000 001111111101010 00000000000010000 27 100011100101100 11101011111111 1101001101 010001011101000000000001 101010111011001000 001111111111010 00000000000010000 28 100011100101100 11101011111111 1101101101 110000111000010000000001 101010111111111000 001111111111010 00000000000010000 29 100011100101100 11101011111111 0001101100 000000111010000000000001 101010111110001000 001111111111010 00000000000010000 30 100011100101100 11101011111111 1101111011 000000111010010100010001 101110000110001000 001111111101010 00000111011110000 31 100011100101100 11101011111111 1101111011 100000111010001001100101 101010111111001000 101111111101010 00000000000010000 32 100011100101100 11101011111111 1101111011 110000111000010101010101 101000111110111000 101111111101010 00000000000010000 33 100011100101100 11101011111111 0001101010 110000111000010101010111 101000111111111000 001010111101010 00000110000010000 34 100011100101100 11110011111111 0111111010 110000101010010011001111 101000111111111000 101010111101010 00010000000010000 35 100011100101100 11110011111111 0011111010 000000111000000101010111 101000111111111000 101010111111010 00000001001110000 36 100011100101100 11110011111111 1111111101 000000101000000101010101 101000111111001000 101010111101010 00000000000011101 -
[1] 杨友才, 周清明, 尹晗琪.烟草RAPD反应体系的建立与优化研究[J].中国农学通报, 2005, 21(5):97-100. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2005.05.029 YANG Y C, ZHOU Q M, YIN H Q.Establishment and Optimization of RAPD Reaction System in Tobacco[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2005, 21(5):97-100.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2005.05.029
[2] 杨友才, 周清明, 尹晗琪.利用RAPD和AFLP标记分析烟草种质资源的遗传多样性[J].农业生物技术学报, 2006, 14(4):585-593. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7968.2006.04.029 YANG Y C, ZHOU Q M, YIN H Q. Analysis of Genetic Diversity in Tobacco Germplasm by RAPDs and AFLPs[J].Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2006, 14(4):585-593.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7968.2006.04.029
[3] 肖炳光.利用RAPD和ISSR标记分析烤烟品种间遗传关系[J].武汉植物学研究, 2006, 24(5):392-396. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0837.2006.05.002 XIAO B G.Assessment of Genetic Relationships between the F lue-cured TobaccoVarieties by RAPD and ISSR Markers[J].Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research, 2006, 24(5):392-396.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0837.2006.05.002
[4] 杨友才, 余硕辉, 尹晗琪.48个烟草品种遗传多样性的RAPD分析[J].亚热带植物科学, 2008, 37(3):10-14. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7791.2008.03.003 YANG Y C, YU S H, YIN H Q.Studies on Genetic Diversity of 48 Tobacco Varieties by RAPD Analysis[J].Subtropical Plant Science2008, 37(3):10-14.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7791.2008.03.003
[5] 郭金平, 朱惠丽, 周以飞, 等.部分烤烟种质遗传多样性与亲缘关系的RAPD分析[J].中国烟草科学, 2009, 30:15-18, 24. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgyckx2009z1003 GUO J P, ZHU H L, ZHOU Y F, et al. Genetic Diversity and Genetic Relationship Analysis of Some Flue-curedTobacco Germplasms Based on RAPD[J].Chinese Tobacco Science, 2009, 30:15-18, 24.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgyckx2009z1003
[6] 王慧颖, 王曼, 朴世领, 等.晒烟种质资源形态学标记及SSR标记的多样性分析[J].湖北农业科学, 2015, 54(23):5943-5948. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hbnykx201523038 WANG H Y, WANG M, PIAO S L, et al. The Genetic Diversity Analyses on Sun-cured Tobacco Germplasm by Morphological Markers and SSR Markers[J].Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 54(23):5943-5948.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hbnykx201523038
[7] 张雪廷, 童治军, 焦芳婵, 等.38份晾晒烟种质资源遗传关系的SSR分析[J].植物遗传资源学报, 2013, 14(4):653-658. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwyczyxb201304012 ZHANG X T, TONG Z J, JIAO F C, et al.Genetic Relationship Analysis of Thirty-eight Sun/Air-Cured TobaccoGermplasms Based on Simple Sequence Repeat (SSR) Markers[J].Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2013, 14(4):653-658.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwyczyxb201304012
[8] 陈杰, 杨静, 龙胜贤, 等.SSR分子标记在烟草研究中的应用进展[J].生物技术通报, 2015, 31(3):43-48. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/swjstb201503006 CHEN J, YANG J, LONG S X, et al.Advance of the Application of SSR Molecular Markers in Tobacco Research[J].Biotechnology Bulletin, 2015, 31(3):43-48.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/swjstb201503006
[9] 刘林, 罗文学, 官思成, 等.用SSR标记揭示部分烤烟种质资源的遗传差异[J].四川农业大学学报, 2018, 36(2):153-160. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/scnydxxb201802005 LIU L, LUO W X, GUAN S C, et al.Accessment of Genetic Difference among Some Flue-cured Tobacco Germplasms Using SSR Markers[J].Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2018, 36(2):153-160.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/scnydxxb201802005
[10] 龙腾, 刘雷, 黄玉碧.四川部分晾晒烟种质遗传关系的SRAP分析[J].作物学报, 2009, 35(1):173-178. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zuowxb200901023 LONG T, LIU L, HUANG Y B.Genetic Analysis of Sichuan Sun-Cured Tobacco Germplasm by SRAP[J].Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2009, 35(1):173-178.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zuowxb200901023
[11] 王日新, 任民, 贾兴华, 等.烟草主要栽培类型的SRAP标记研究[J].生物技术通报, 2009(6):100-104. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/swjstb200906023 WANG R X, REN M, JIA X H, et al.Study of SRAP Markers in Major Cultivated Forms of Nicotiana tabacum L.[J].Biotechnology Bulletin, 2009(6):100-104.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/swjstb200906023
[12] 祁建民, 梁景霞, 陈美霞, 等.应用ISSR与SRAP分析烟草种质资源遗传多样性及遗传演化关系[J].作物学报, 2012, 38(8):1425-1434. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zuowxb201208010 QI J M, LIANG J X, CHEN M X, et al.Genetic Diversity and Evolutionary Analysis of Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.)Germplasm Resources Based on ISSR and SRAP Markers[J].Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2012, 38(8):1425-1434.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zuowxb201208010
[13] 张吉顺, 张孝廉, 杨春元, 等.地方晒烟种质资源SRAP标记的遗传多样性分析[J].分子植物育种, 2016, 14(7):1906-1913. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fzzwyz201607038 ZHANG J S, ZHANG X L, YANG C Y, ,et al.The Genetic Diversity Analysis of Sun-cured Tobacco Landraces Germplasms by SRAP Markers[J].Molecular Plant Breeding, 2016, 14(7):1906-1913.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fzzwyz201607038
[14] 刘超, 党江波, 魏烨昕, 等.SCoT分子标记技术初步应用于烟草属部分材料的遗传分析及种间杂种的鉴定[J].中国烟草学报, 2013, 19(5):107-111. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5708.2013.05.019 LIU C, DANG J B, WEI Y X, et al.The application of SCoT molecular marker technology ingenetic analysis and interspecifc hybrid identifcation in genus Nicotiana[J].Acta Tabacaria Sinica, 2013, 19(5):107-111.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5708.2013.05.019
[15] 王建波.ISSR分子标记及其在植物遗传学研究中的应用[J].遗传学报, 2002, 24(5):613-616. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yc200205022 WANG J B.ISSR Markers and Their Application in Plant Genetic[J].Hereditas(Beijing), 2002, 24(5):613-616.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yc200205022
[16] 覃剑峰, 何江, 王新钧, 等.烟草ISSR-PCR反应体系优化的初实验[J].农业研究与应用, 2018, 31(3):19-22. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0764.2018.03.004 QIN J F, HE J, WANG X J, et al Preliminary experiment on Optimization of ISSR-PCR Reaction System for Tobacco[J].Agricultural Research and Application.2018, 3:19-22.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0764.2018.03.004
[17] 杨祥燕, 蔡元保, 黄秋伟, 等.番木瓜主栽品种SCoT指纹图谱构建及遗传变异分析[J].西北植物学报, 2013, 33(9):1756-1761. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbzwxb201309007 YANG X Y, CAI Y B, HUANG Q W, et al.SCoT Fingerprints and Genetic Variations of the Papaya(Carica papaya L.)Major Cultivars[J].Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2013, 33(9):1756-1761.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbzwxb201309007
[18] 陈真勇, 彭正松, 陈卫英.四川晾晒烟的ISSR分析[J].西华师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 33(2):154-160. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/scsfxyxb-zr201202009 CHEN Z Y, PANG Z S, CHEN W Y.Genetic Analysis of Sichuan Sun-Cured Tobacco Germplasm by ISSR[J]Journal of China West Normal University (Natural Sciences), 2012, 33(2):154-160.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/scsfxyxb-zr201202009
[19] 尚志强.分子标记技术在烟草种质资源研究中的应用进展[J].生物技术通报, 2010(3):58-61. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/swjstb201003013 SHANG Z Q.Progress of the Application of Molecular Markers in Tobacco Research Related to Germplasm Resource[J].Biotechnology Bulletin, 2010(3):58-61.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/swjstb201003013
[20] 陈杰, 杨静, 郭鸿雁, 等.DNA分子标记技术在烟草遗传育种中的应用[J].中国农学通报, 2012, 28(7):95-99. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2012.07.018 CHEN J, YANG J, GUO H Y, et al.Advance of Molecular Marker and Its Application in the Tobacco Genetic Breeding[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2012, 28(7):95-99.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2012.07.018




 下载:
下载: