Characterization of Seed-derived Vitis davidii Seedings by Principal Component Analysis
-
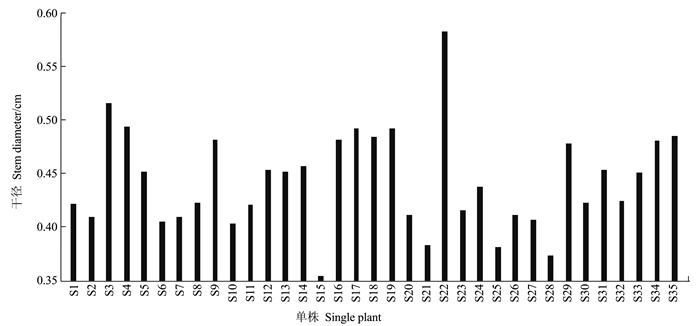
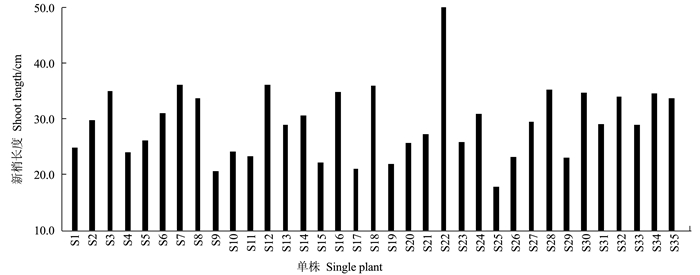
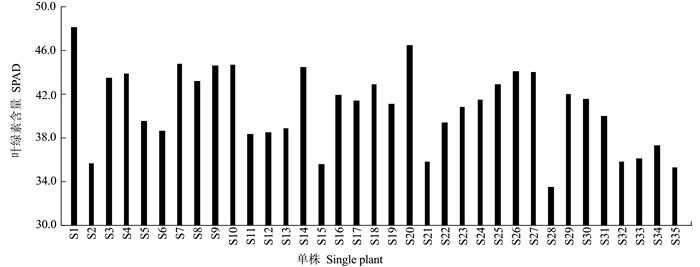
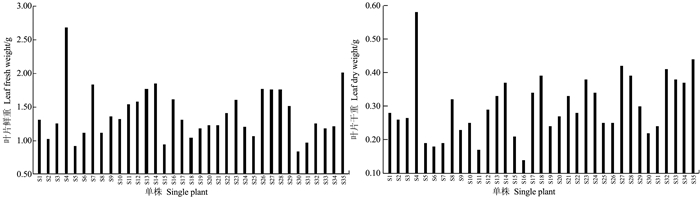
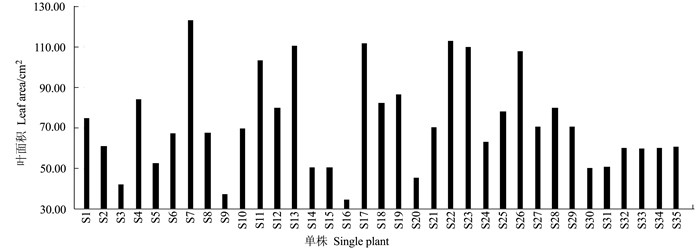
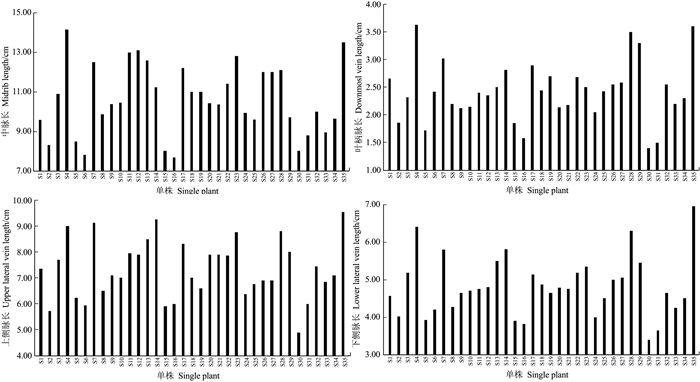
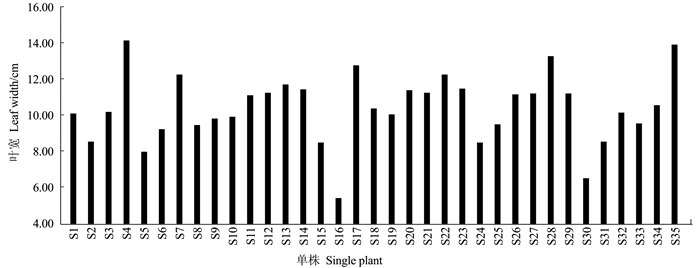
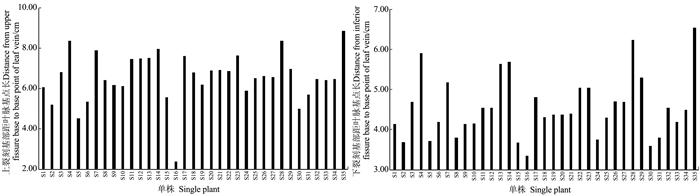
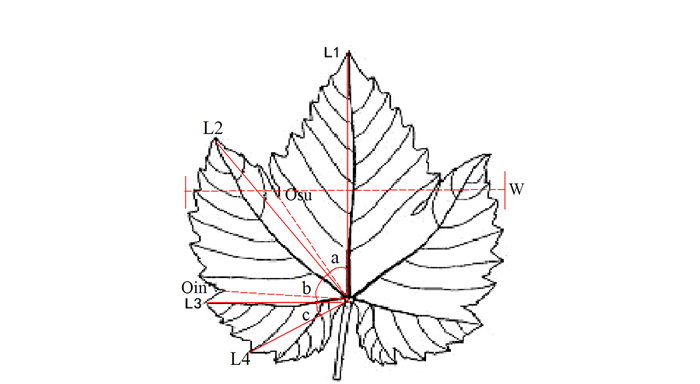
摘要:目的 建立一套适合刺葡萄实生单株苗期性状的评价方法。方法 测定了刺葡萄实生单株干径、新梢长度、叶片叶绿素含量、叶面积、叶片干鲜重、叶片叶形结构参数等16个主要性状,并应用主成分分析法对其进行综合评价。结果 刺葡萄实生单株主要生长性状均出现较大变异,尤其是新梢长度、叶片叶绿素含量、干径等变异较大。选取方差累积贡献率为86.254%的前6个主成分来评价刺葡萄实生单株,决定第1主成分的是干径、新梢长度、叶绿素含量、叶面积、叶片鲜重、叶片干重;决定第2主成分的是中脉长、上侧脉长、下侧脉长、叶柄脉长;决定第3主成分的是叶宽和上中侧脉夹角。结论 以6个主成分及单个主成分所对应的特征值占所提取主成分总的特征值之和的比例作为权重,构建刺葡萄实生单株苗期性状的综合评价模型F综=0.38F1+0.24F2+0.12F3+0.10F4+0.09F5+0.06F6,综合得分排名前两位的单株分别为S4和S35。Abstract:Objective To establish a method for evaluating the characteristics of seed-derived Vitis davidii seedlings.Method Sixteen characteristics including stem girth, shoot length, leaf chlorophyll content, leaf area, leaf dry and fresh weight, and blade structure of the seedlings were determined for a comprehensive evaluation by principal component analysis.Result Significant variations were found on the growth of the seedlings, especially on shoot length, leaf chlorophyll content, and stem girth. The first 6 principal components made up 86.254% of the total contribution. The first principal component was determined by the stem girth, shoot length, chlorophyll content, leaf area, and fresh and dry weights of the leaves; the second principal component by the lengths of midrib, upper lateral vein, lower lateral vein, and downmost vein; and, the third principal component by the leaf width and the angle between upper lateral vein and midrib.Conclusion Using the eigenvalues corresponding to the 6 principal components and the ratio of single to extracted principal component, a comprehensive evaluation model for the seed-derived V.davidii seedlings was established. Accordingly, S4 and S35 scored the highest among the specimens. A rapid method to screen V.davidii resources at seedling stage for cultivar selection and new variety breeding had thus become available.
-
-
表 1 刺葡萄苗期性状的特征值和累计方差贡献率
Table 1 Eigenvalues and accumulative contribution of various characteristics of V. davidii seedlings
主成分
The principal components特征值
The eigenvalue方差贡献率
Variance contribution rate/%累计方差贡献率
Cumulative variance contribution rate/%1 5.177 32.359 32.359 2 3.265 20.409 52.768 3 1.614 10.085 62.853 4 1.430 8.937 71.790 5 1.308 8.176 79.966 6 1.006 6.288 86.254 表 2 主成分在各苗期性状指标上的因子荷载矩阵
Table 2 Rotated component matrix of principal components
性状
Characters主成分The principal components 1 2 3 4 5 6 干径Stem diameter 0.930 0.057 0.184 0.110 -0.028 0.253 新梢长度New shoots length 0.890 -0.219 0.272 0.223 0.505 -0.114 叶绿素含量Chlorophyll content 0.888 0.189 0.409 -0.091 -0.624 0.191 叶片鲜重Leaf fresh weight 0.864 -0.096 -0.133 -0.008 -0.105 0.143 叶片干重Leaf dry weight 0.663 0.064 -0.233 -0.015 0.385 0.268 叶面积Leaf area 0.568 -0.074 0.275 -0.089 -0.283 -0.619 中脉长Midrib length 0.089 0.905 0.150 -0.089 -0.090 -0.080 上侧脉长Upper lateral vein length 0.077 0.860 0.060 -0.125 0.071 0.026 下侧脉长Lower lateral vein length 0.338 0.800 0.001 -0.145 0.146 0.087 叶柄脉长Downmost vein length 0.285 0.559 -0.100 -0.175 0.087 0.013 叶宽Leaf width 0.249 -0.185 0.661 0.132 -0.102 -0.147 上裂刻基部距叶脉基点长Distance from upper fissure base to point of leaf vein 0.265 -0.215 -0.299 0.758 -0.094 -0.060 下裂刻基部距叶脉基点长Distance from inferior fissure to base point of leaf vein 0.319 -0.161 -0.343 0.646 -0.100 -0.054 上中侧脉夹角Angle between upper lateral and midrib veins 0.092 -0.106 0.690 -0.099 0.100 -0.225 上下侧脉夹角Angle between upper and lower later 0.061 0.540 -0.163 -0.142 0.284 0.554 下侧脉与叶柄脉夹角Angle between lower lateral veins and downmost veins -0.257 0.488 -0.080 -0.486 0.511 0.130 表 3 刺葡萄苗期性状评价结果
Table 3 Evaluation on characteristics of V. davidiii seedings
编号
Serial numberF1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F综 排名
RankingS1 -0.17 2.69 2.69 -0.91 -1.39 0.75 0.74 13 S2 -6.93 0.26 0.53 -0.88 2.15 -0.37 -2.43 30 S3 -0.83 -1.76 2.15 0.91 1.05 1.73 -0.17 19 S4 14.42 4.13 -2.11 0.39 -0.76 1.44 6.29 1 S5 -5.06 8.44 1.35 0.26 0.54 -0.70 0.29 16 S6 -5.80 -0.96 -2.29 -0.62 -0.38 -1.05 -2.88 32 S7 5.20 -4.11 1.91 -0.80 -1.25 -1.20 0.94 10 S8 -2.75 2.01 -0.19 -0.05 0.63 0.44 -0.50 23 S9 -2.91 -1.91 -1.33 -0.07 -1.58 1.73 -1.75 28 S10 -2.08 0.24 1.35 -1.47 -0.82 0.53 -0.76 25 S11 2.40 1.45 0.26 -0.30 -1.93 -2.38 0.92 11 S12 0.52 -10.54 0.25 1.37 -0.55 -0.23 -2.23 29 S13 5.27 -1.18 0.17 0.41 -0.78 -1.12 1.63 6 S14 5.18 0.85 -0.66 0.01 0.29 1.93 2.26 5 S15 -8.74 -3.52 -1.29 -1.64 0.29 -0.65 -4.51 35 S16 -6.12 -1.22 -1.85 3.05 -1.42 0.84 -2.61 31 S17 2.94 -5.68 0.55 -0.48 -1.43 -0.13 -0.36 21 S18 0.83 -0.11 0.34 1.31 -0.71 0.17 0.41 15 S19 0.76 5.52 -0.90 0.35 -1.00 -0.55 1.41 8 S20 -1.87 0.38 1.54 -1.32 -0.42 1.56 -0.50 22 S21 -1.03 1.34 -1.30 -1.48 1.59 -0.67 -0.28 20 S22 4.33 0.96 4.05 4.05 1.63 -1.16 2.83 3 S23 5.32 2.13 1.11 -1.24 -0.22 -1.30 2.43 4 S24 -2.38 3.87 -0.24 0.52 0.38 0.11 0.09 18 S25 -3.53 0.98 -0.19 -2.96 -0.43 0.19 -1.45 27 S26 2.57 1.05 -0.45 -0.66 -2.44 -0.67 0.84 12 S27 2.00 0.76 1.32 -1.58 0.93 1.19 1.11 9 S28 5.91 -2.45 -1.21 -1.69 2.86 -1.02 1.53 7 S29 2.65 -0.94 -0.67 -0.14 -0.86 0.51 0.64 14 S30 -8.88 0.09 1.30 1.72 -0.42 -0.03 -3.07 34 S31 -7.73 -1.04 1.33 0.14 0.73 0.44 -2.92 33 S32 -1.05 -2.64 -0.57 -0.08 2.17 -0.14 -0.92 26 S33 -1.95 1.14 -3.77 1.41 0.46 -0.26 -0.76 24 S34 -0.35 1.50 -2.54 2.41 0.51 -0.48 0.18 17 S35 9.88 -1.71 -0.66 0.05 2.57 0.55 3.54 2 -
[1] 王美军, 黄乐, 蒋建雄, 等.刺葡萄花粉形态观察[J].果树学报, 2014, 31(4):610-616. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gskx201404012 WANG M J, HUANG L, JIANG J X, et al. Observation on pollen morphology of thorn grape[J]. Journal of Fruit Trees, 2014, 31(4):610-616.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gskx201404012
[2] ARTLIP T S, WISNIEWSKI M E, NORELLI J L. Field evaluation of apple overexpressing a peach CBF gene confirms its effect on cold hardiness, dormancy, and growth[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2013, 106:79-86. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=931b92be070023300fa29b6e2db9bc54
[3] NUNES S, SANTOS C, MOUTINHO-PEREIRA J, et al. Physiological characterization and true-to-typeness evaluation of in vitro and ex vitro seedlings of Pinus elliottii:A contribution to breeding programs[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2016, 107:222-227. DOI: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.05.039
[4] DARBYSHIRE R, FARRERA I, MARTINEZ-LVSCHER J, et al. A global evaluation of apple flowering phenology models for climate adaptation[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2017, 240-241:67-77. DOI: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2017.03.021
[5] 徐丰, 石雪晖, 杨国顺, 等.湖南不同类型刺葡萄植物学性状研究[J].中外葡萄与葡萄酒, 2010(2):8-12. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwptyptj201003002 XU F, SHI X H, YANG G S, et al. Study on botanical characters of different types of thorn grape in hunan[J]. Chinese and Foreign Grapes and Wine, 2010(2):8-12.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwptyptj201003002
[6] 李若兰, 熊闻, 鞠延轮, 等.野生刺葡萄叶片度量性状研究[J].西北林学院学报2017, 32(1):172-178, 217. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2017.01.27 LI R L, XIONG W, JU Y L, et al. Study on leaf metric characters of wild thorn grape[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry College, 2017, 32(1):172-178, 217.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2017.01.27
[7] 王美军, 黄乐, 刘昆玉, 等.刺葡萄叶与花和果实及种子的表型性状研究[J].湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 42(5):489-495. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hunannydx201605005 WANG M J, HUANG L, LIU K Y, et al. Studies on phenotypic characters of leaves and flowers, fruits and seeds of grape thorn[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 42(5):489-495.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hunannydx201605005
[8] 宋军阳, 于大永, 王西平.葡萄叶片数量化研究[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 43(2):142-148. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbnydxxb201502021 SONG J Y, YU D Y, WANG X P. Quantitative study on grape leaves[J]. Journal of Northwest Agricultural and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(2):142-148.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbnydxxb201502021
[9] WU J F, ZHANG C Y, CHEN J Z, et al. Morphological diversity within litchi (Litchi chinensisSonn.) based on leaf and branch traits[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2016, 207:21-27. DOI: 10.1016/j.scienta.2016.05.004
[10] CHASHNIDELA B, HAJNAJARI H. Relationships of morphological traits and ripening time during juvenile phase in apple[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2012, 144:29-35. DOI: 10.1016/j.scienta.2012.06.034
[11] MLWAT A, MAGUIRE K. Canopy Management and Dry Matter of 'Hayward' Kiwifruit[J]. Acta Horticulturae, 2007, 753(753):333-340. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=7cc821d27913a2df2cf6bb36db1cd6ab
[12] 高建昌, 郭广君, 国艳梅, 等.平台扫描仪结合ImageJ软件测定番茄叶面积[J].中国蔬菜, 2011(2):73-77. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgsc201101013 GAO J C, GUO G J, GUO Y M, et al. The platform scanner and ImageJ software were used to measure tomato leaf area[J]. Chinese Vegetables, 2011(2):73-77.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgsc201101013
[13] GALET P. Précis d'A mpélographie Pratique[M]. Charles DEHAN, Monptellier France, 1985, 130.
[14] GOMES M P, MANAC'H S G L, MACCARIO S, et al. Differential effects of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) on photosynthesis and chlorophyll metabolism in willow plants[J]. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 2016, 130:65-70. DOI: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2015.11.010
[15] 周香艳, 杨江伟, 唐勋, 等. amiRNA技术沉默C-3氧化酶编码基因StCPD对马铃薯抗旱性的影响[J].作物学报, 2018, 44(4):512-521. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zuowxb201804006 ZHOU X Y, YANG J W, TANG X, et al. Effects of amiRNA silencing StCPD gene encoding c-3 oxidase on drought resistance of potato[J]. Journal of Crops, 2018, 44(4):512-521.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zuowxb201804006
[16] LEROY C, SAINT-ANDRE L, AUCLAIR D. Practical methods for nondestructive measurement of tree leaf area[J]. Agro Forest Systems, 2007, 71(2):99-108.
[17] 张万红.基于图像分割的苹果叶片几何参数计算[J].中国农业大学学报, 2018, 23(8):101-108. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgnydxxb201808011 ZHANG W H. Geometric parameter calculation of apple leaves based on image segmentation[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2018, 23(8):101-108.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgnydxxb201808011
[18] 王聚辉, 程子祥, 修文雯, 等.玉米茎叶夹角与根系入土角度相关性研究[J].华北农学报, 2015, 30(S1):173-178. DOI: 10.7668/hbnxb.2015.S1.031 WANG J H, CHENG Z X, XIU W W, et al. Study on the correlation between maize stem and leaf Angle and root penetration Angle[J]. North China Agricultural Journal, 2015, 30(S1):173-178.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7668/hbnxb.2015.S1.031
[19] 陈秀娟, 糜林, 陈卫平, 等.种苗地径对草莓生长发育及产量和品质的影响[J].南京农业大学学报, 2011, 34(4):129-132. CHEN X J, MI L, CHEN W P, et al. Effect of seedling diameter on growth, yield and quality of strawberry[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2011, 34(4):129-132.(in Chinese)
[20] 温维亮, 王勇健, 李超, 等.葡萄树形态结构与生长发育过程数字化表达方法研究[J].中国农业科学, 2015, 48(11):2143-2151. DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2015.11.006 WEN W L, WANG Y J, LI C, et al. Study on digital expression methods of grape tree morphological structure and growth process[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science, 2015, 48(11):2143-2151.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2015.11.006
[21] WANG Y, JIN G, SHI B, et al. Empirical models for measuring the leaf area and leaf mass across growing periods in broadleaf species with two life histories[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2019, 102:289-301. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.02.041
[22] 曾小平, 姚睿, 蔡锡安, 等.底泥养分富集条件下11种水生植物的光合氮利用效率[J].生态学报, 2018, 38(14):4923-4931. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201814001 ZENG X P, YAO R, CAI X A, et al. Photosynthetic nitrogen use efficiency of 11 aquatic plants under nutrient enrichment of sediment[J]. Acta ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(14):4923-4931.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201814001
[23] 魏书精, 罗碧珍, 魏书威, 等.森林生态系统土壤呼吸测定方法研究进展[J].生态环境学报, 2014, 23(3):504-514. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.03.021 WEI S J, LUO B Z, WEI S W, et al. Advances in soil respiration assay for forest ecosystems[J]. Journal of Ecological Environment, 2014, 23(3):504-514.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.03.021
[24] 仇占南, 张茹阳, 彭明朗, 等.北京野生软枣猕猴桃果实品质综合评价体系[J].中国农业大学学报, 2017, 22(2):45-53. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgnydxxb201702005 QIU Z N, ZHANG R Y, PENG M L, et al. Comprehensive quality evaluation system of Beijing wild jujube kiwi fruit[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2017, 22(2):45-53.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgnydxxb201702005
[25] 李伟, 郜海燕, 陈杭君, 等.基于主成分分析的不同品种杨梅果实综合品质评价[J].中国食品学报, 2017, 17(6):161-171. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgspxb201706022 LI W, HAO H Y, CHEN H J, et al. Comprehensive quality evaluation of waxberry fruits of different varieties based on principal component analysis[J]. Chinese Food Journal, 2017, 17(6):161-171.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgspxb201706022
[26] LI J, LUO W, WANG Z, et al. Early detection of decay on apples using hyperspectral reflectance imaging combining both principal component analysis and improved watershed segmentation method[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 2019, 149:235-246. DOI: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.12.007
[27] COELHO I, MATOS A S, TEIXEIRA R, et al. Combining multielement analysis and chemometrics to trace the geographical origin of Rocha pear[J].Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 2019, 77:1-8. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfca.2018.12.005
[28] WANG Y, HU Y, CHEN B, et al. Physiological mechanisms of resistance to cold stress associated with 10 elite apple rootstocks[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2018, 17(4):857-866. DOI: 10.1016/S2095-3119(17)61760-X
[29] KALAYCLOǦLU Z, KAYGUSUZ H, DÖKER S, et al. Characterization of Turkish honeybee pollens by principal component analysis based on their individual organic acids, sugars, minerals, and antioxidant activities[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 2017, 84:402-408. DOI: 10.1016/j.lwt.2017.06.003




 下载:
下载: