ISSR-PCR Optimization and Primer Selection for Analyzing Exserohilum turcicum Isolates Collected in Fujian
-
摘要:目的 明确适用于福建省玉米大斑病菌ISSR分子标记的反应体系和引物。方法 采用单因素水平优化法对ISSR-PCR扩增反应中的Taq聚合酶用量、dNTPs浓度、Mg2+浓度、模板DNA浓度、PCR反应循环数以及引物的最佳退火温度等重要参数进行优化。结果 适合福建省玉米大斑病菌群体遗传多样性分析的ISSR-PCR反应体系(25 μL)为:Taq聚合酶0.55 U、dNTPs 0.30 mmol·L-1、Mg2+ 1.30 mmol·L-1、DNA模板100 ng、引物10 pmol。ISSR-PCR扩增程序为:94℃预变性4 min;94℃变性45 s,51.2~56.0℃退火45 s,72℃延伸1.5 min,35个循环;72℃延伸10 min。利用优化的反应体系从56条ISSR引物中筛选出稳定性好、多态性高的引物10条:UBC117、UBC118、UBC808、UBC835、UBC847、UBC855、UBC856、UBC857、UBC866和UBC887,其最佳退火温度分别为55.6、53.1、51.2、51.2、56.0、53.1、53.1、51.2、51.2和51.2℃。利用优化的ISSR-PCR反应体系对21株供试菌株进行PCR扩增,结果表明,相同地理来源以及不同地理来源菌株间的DNA多态性均不同,表明福建省玉米大斑病菌群体存在丰富的遗传多样性。结论 本研究优化的ISSR-PCR反应体系和筛选的引物可用于福建省玉米大斑病菌群体遗传多样性和遗传结构的研究。
-
关键词:
- 玉米大斑病菌 /
- 反应体系 /
- 简单序列重复区间扩增多态性 /
- 玉米大斑病 /
- 遗传多样性
Abstract:Objective To determine the optimal reaction conditions and primers for the inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) PCR in analyzing isolates of Exserohilum turcicum, a pathogen of the northern corn leaf blight in Fujian.Method Conditions for the ISSR-PCR amplification including Taq polymerase dosage, concentrations of dNTPs, Mg2+ and template DNA and reaction cycle as well as annealing temperatures for selected primers were optimized using a single-factor method.Result For a 25 μL ISSR-PCR genetic diversity analysis on E. turcicum, the following conditions were applied:0.55 U of Taq polymerase, 0.30 mmoL·L-1 of dNTPs, 1.30 mmoL·L-1 of Mg2+, 100 ng of template DNA, and 10 pmol of primer under 94℃ for 4 min followed by 35 cycles of 45 s at 94℃, 45 s at 51.2-56.0℃, and 1.5 min at 72℃, and finally, at 72℃ for 10 min. Ten stable, polymorphic primers, i.e., UBC117, UBC118, UBC808, UBC835, UBC847, UBC855, UBC856, UBC857, UBC866, and UBC887, were selected from 56 ISSR primers, with their optimized annealing temperatures determined to be 55.6, 53.1, 51.2, 51.2, 56.0, 53.1, 53.1, 51.2, 51.2, and 51.2℃, respectively. Regardless of their geographical origins, the 21 E. turcicum isolates differed on DNA polymorphism indicating an abundance on genetic diversity among them.Conclusion The optimized ISSR-PCR reaction conditions and primers could be applied for genetic studies on E. turcicum in Fujian. -
0. 引言
【研究意义】鲜食或加工型玉米是福建省重要的经济作物[1]。由大斑突脐蠕孢菌Exserohilum turcicum (Pass.) Leonard et Suggs(有性态:Setosphaeria turcica Leonard et Suggs)侵染引起的玉米大斑病是玉米生产上的世界性病害,该病可在玉米整个生育期发生,一般减产20%,重者可达50%以上,大斑病的流行严重影响了福建省鲜食玉米的产量和品质[2-4]。玉米大斑病菌具有寄主适应性强、变异频繁和生理分化明显等特点。研究表明玉米大斑病菌可在自然条件下频繁进行有性生殖,不同交配型和寄主适合度的2株室内诱导产生的F1代玉米大斑病菌菌株进行有性杂交形成的F2代菌株群体中,有30%的菌株在产孢量、毒素产量以及致病力上有显著增强[2, 5]。由于玉米大斑病菌频繁地进行有性重组,造成病菌变异频率显著提升和新的生理小种不断出现[4-6],这为病害的长期可持续控制和鲜食玉米的优质、安全生产带来了困扰。最经济、有效的防治玉米大斑病的措施是种植抗病品种[7],但是福建省适宜的气候条件以及高复种指数,致使田间玉米大斑病菌强适应性新小种不断积累,加之该菌的遗传变异性常常导致玉米品种抗病性丧失。因此,深入探讨玉米大斑病菌群体的DNA指纹图谱,揭示病菌流行群体的遗传多样性和遗传结构,对了解病菌群体的变异趋势以及指导抗病玉米品种的选育具有重要的意义。【前人研究进展】已有随机扩增多态性(Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA,RAPD)[2, 8-9]、扩增片段长度多态性(Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism,AFLP)[10]、通用引物聚合酶链式反应(Universally primed polymerase chain reaction,UP-PCR)[11]、简单重复序列标记(Simple Sequence Repeat,SSR)[12-14]、简单序列重复区间扩增多态性(inter-simple sequence repeat,ISSR)[15-17]等多种DNA分子标记技术被应用于国内外玉米大斑病菌群体遗传多样性的研究中。在众多DNA分子标记中,ISSR分子标记技术由于操作简单、稳定性好以及多态性高,且无需知道靶标的任何遗传背景[18-19],使其成为植物病原真菌群体遗传多样性和遗传结构研究的重要工具[20]。近年来,ISSR分子标记技术已被广泛应用于Bipolaris maydis[1]、Puccinia polysora[21]、Cercospora zeina[22]、Sporisorium reilianum[23]、Fusarium graminearum[24]、Bipolaris zeicola[25]和Curvularia lunata[26]等玉米重要真菌病害的分子标记研究中。【本研究切入点】迄今已报道适用于其他地理来源玉米大斑病菌群体的ISSR-PCR反应体系和引物并不适用于福建省玉米大斑病菌种群。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究采用单因素水平优化法对ISSR-PCR扩增反应中的Taq聚合酶用量、dNTPs浓度、Mg2+浓度、模板DNA浓度、PCR反应循环数以及引物的退火温度等重要参数进行优化,并利用优化的反应体系和扩增条件从植物病原真菌基因组DNA重复序列ISSR引物库中筛选重复性好、多态性高的引物,以期建立适合福建省玉米大斑病菌ISSR分子标记的反应体系和引物,为福建省玉米大斑病菌的群体遗传多样性和遗传结构研究奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
马铃薯葡萄糖琼脂(PDA)培养基:新鲜去皮马铃薯200 g、葡萄糖20 g、琼脂粉16 g、去离子水1 000 mL。121℃湿热灭菌20 min。
试剂和引物:Taq酶、dNTPs、MgCl2溶液和5-kb DNA Marker均购自大连宝生物有限公司;其他分析纯生化试剂购自索莱宝(北京)生物有限公司;供试的56个ISSR引物筛选至加拿大哥伦比亚大学设计的植物病原真菌基因组DNA重复序列ISSR引物库(http:/www.michaelsmith.ubc.ca)并结合谷守芹[15]和郭丽媛[16]等文献报道,引物委托上海英潍捷基生物技术有限公司合成。
仪器:C1000TM Thermal Cycler梯度PCR仪(美国Bio-Rad公司)、Nanodrop 2000c核酸定量仪(赛默飞世尔科技公司)、DYY-6C型电泳系统(北京六一仪器厂)、BioDoc-ItTM凝胶成像系统(美国UVP公司)、ZWY-240恒温振荡培养箱(上海智城分析仪器制造有限公司)。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 玉米大斑病菌的分离和保存
2016-2019年从福建省建瓯、松溪、屏南和南靖等县(市)的鲜食玉米田采集具有典型玉米大斑病症状的玉米病叶,切取病健交界处的组织块(0.5 cm × 0.4 cm)依次置于75% (V/V)酒精和0.1% (W/V)氯化汞溶液中消毒2 min和90 s,无菌水清洗3次,28℃黑暗培养4~5 d,通过单孢分离法获取纯培养菌株(表 1)。所有单孢菌株均经过形态学和rDNA-ITS序列分析鉴定,确定供试菌株为玉米大斑病菌[27-28]。分离纯化的单孢菌株采用滤纸片法保存于-20℃冰箱中[29]。
表 1 供试的福建省玉米大斑病菌菌株Table 1. E. turcicum isolates collected in Fujian序号
Number菌株编号
Isolate code采集地
Location年份
Year1 JO1801 建瓯市东游镇Dongyou town of Jian′ou city 2018 2 JO1809 建瓯市东游镇Dongyou town of Jian′ou city 2018 3 JODB1701 建瓯市东游镇Dongyou town of Jian′ou city 2017 4 JODB1702 建瓯市东游镇Dongyou town of Jian′ou city 2017 5 DFDB1901 建瓯市东峰镇Dongfeng town of Jian′ou city 2019 6 DFDB1902 建瓯市东峰镇Dongfeng town of Jian′ou city 2019 7 DFDB1903 建瓯市东峰镇Dongfeng town of Jian′ou city 2019 8 DFDB1905 建瓯市东峰镇Dongfeng town of Jian′ou city 2019 9 SX1801 松溪县Songxi county 2018 10 SX1802 松溪县Songxi county 2018 11 SX1804 松溪县Songxi county 2018 12 PNDB1602a 屏南县Pingnan county 2016 13 PNDB1604b 屏南县Pingnan county 2016 14 PNDB1606a 屏南县Pingnan county 2016 15 PNDB1608a 屏南县Pingnan county 2016 16 PNDB1609a 屏南县Pingnan county 2016 17 NJDB1805 南靖县Nanjing county 2018 18 NJDB1809 南靖县Nanjing county 2018 19 NJDB1810 南靖县Nanjing county 2018 20 NJDB1816 南靖县Nanjing county 2018 21 NJDB1830 南靖县Nanjing county 2018 1.2.2 玉米大斑病菌DNA的提取
玉米大斑病菌的DNA提取方法采用改良的CTAB法[30]。用无菌手术刀刮取PDA平板上培养6 d的菌丝置于2 mL无菌离心管中,向管中加入800 μL提取液[2% CTAB (w/v),100 mmol·L-1 Tris-HCl (pH 8.0),20 mmol·L-1 EDTA,1.4 mol·L-1 NaCl]、80 μL 10%的SDS和880 μL酚/氯仿/异戊醇(25:24:1),轻柔混匀,37℃、180 r·min-1摇床上振荡1.0 h,12 000 r·min-1离心20 min,将600 μL上清液移至无菌1.5 mL离心管中,加入600 μL异丙醇,轻柔混匀,-20℃冰箱中沉淀30 min,12 000 r·min-1离心20 min,沉淀用800 μL 75%冰乙醇洗涤2次,12 000 r·min-1离心15 min,无菌操作台上室温干燥20 min。DNA用100 μL TE缓冲液(10 mmol·L-1 Tris-HCl,1 mmol·L-1 EDTA,pH 8.0)溶解,再加入2 μL RNA降解酶(20 mg·mL-1)于37℃酶解1 h。所有菌株的DNA样品均通过核酸定量仪测定DNA浓度和质量,OD260/OD280值在1.8左右说明DNA纯度达到实验要求。提取的DNA样品保存于-20℃冰箱中。
1.2.3 ISSR-PCR反应体系的优化
用TE缓冲液分别将玉米大斑病菌JO1801、DFDB1901、SX1801、PNDB1602a和NJDB1805菌株的基因组DNA浓度稀释到200 ng·μL-1,作为ISSR-PCR的模板。ISSR引物为UBC847。25 μL ISSR-PCR反应体系:Taq聚合酶用量分别为0.25、0.35、0.45、0.55、0.65(推荐剂量)、0.75、0.85和0.95 U;dNTPs浓度梯度为0.07、0.10、0.14、0.17、0.20(推荐剂量)、0.23、0.26、0.30 mmol·L-1;Mg2+浓度梯度为0.5、0.8、1.0、1.3、1.5(推荐剂量)、1.7、2.0、2.2 mmol·L-1;DNA模板浓度梯度为50、100、150、200 ng。
ISSR-PCR扩增程序为:94℃预变性4 min;94℃变性45 s,退火温度梯度为56.0、55.6、54.7、53.1、51.2、49.6、48.5和48.0℃退火45 s,72℃延伸90 s,25、30、35或40个循环;72℃延伸10 min;4℃保存。PCR结束后取7 μL扩增产物用含有EB的1.5%琼脂糖凝胶在120 V恒定电压下电泳约35 min,用凝胶成像系统检测并照相。
1.2.4 ISSR-PCR引物的筛选
利用上述优化的反应体系和扩增条件,通过梯度PCR扩增对56条ISSR引物进行筛选,退火温度梯度为56.0、55.6、54.7、53.1、51.2、49.6、48.5和48.0℃。最终筛选扩增条带清晰、多态性好的引物,同时确定引物的最佳退火温度。
1.2.5 ISSR-PCR扩增
利用优化的ISSR-PCR反应体系及扩增条件和筛选的多态性好的引物对21个供试菌株进行ISSR扩增。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 ISSR-PCR反应体系的优化
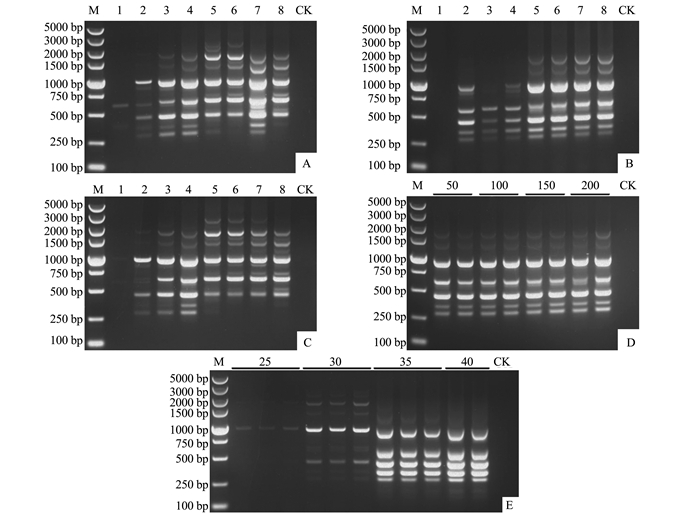
以引物UBC847为例,对Taq聚合酶用量的优化结果表明,25 μL的ISSR-PCR反应体系中0.55 U的Taq聚合酶用量即可扩增出条带清晰、稳定性好的DNA指纹图谱(图 1-A)。设置的8个dNTPs浓度梯度内,7个能扩增出DNA条带,在浓度为0.30 mmol·L-1时扩增出的DNA指纹图谱清晰、重复性好(图 1-B)。Mg2+浓度对ISSR-PCR的扩增结果有较大影响,Mg2+浓度过低或过高,扩增的条带或弱或多态性不丰富,当Mg2+浓度为1.3 mmol·L-1时扩增出的条带较清晰、多态性较好(图 1-C)。本研究设置的50~200 ng模板DNA浓度均能有效地扩增出清晰的DNA指纹图谱(图 1-D),表明本研究设置的DNA模板用量在25 μL ISSR-PCR反应体系中对扩增结果影响不显著。本试验设置的25~40个循环数均能扩增出DNA条带,循环数过少,扩增的条带较少且亮度较暗,循环数越多,扩增的条带越多且亮度越亮。当循环数为35次时,扩增的条带较清晰且亮度适中,当循环数为40次时,扩增的部分条带亮度过强,有覆盖临近的条带的趋势(图 1-E)。当退火温度值为56.0℃时,扩增的条带越多且亮度适中;随着退火温度值的降低,扩增的条带亮度降低或条带数减少(图 2)。
![]() 图 1 引物UBC847的反应体系优化注:M:5-kb DNA Marker;(A) 1~8:Taq酶用量分别为0.25、0.35、0.45、0.55、0.65(推荐剂量)、0.75、0.85和0.95 U;(B) 1~8:dNTPs浓度分别为0.07、0.10、0.14、0.17、0.20(推荐剂量)、0.23、0.26和0.30 mmol·L-1;(C) 1~8:Mg2+浓度分别为0.5、0.8、1.0、1.3、1.5(推荐剂量)、1.7、2.0和2.2 mmol·L-1;(D) 50~200:DNA模板量分别为50、100、150和200 ng;(E) 25~40:循环数分别为25、30、35和40次;CK:空白对照。Figure 1. Reaction condition optimization for primer UBC847Note:M:5-kb DNA Marker; (A) 1-8:the amount of Taq polymerase 0.25, 0.35, 0.45, 0.55, 0.65 (recommended dosages), 0.75, 0.85 and 0.95 U, respectively; (B) 1-8:the concentration of dNTPs 0.07, 0.10, 0.14, 0.17, 0.20 (recommended dosages), 0.23, 0.26 and 0.30 mmol·L-1, respectively; (C) 1-8:the concentration of Mg2+ 0.5, 0.8, 1.0, 1.3, 1.5 (recommended dosages), 1.7, 2.0 and 2.2 mmol·L-1, respectively; (D) 50-200:the concentration of template DNA 50, 100, 150 and 200 ng, respectively; (E) 25-40:the cycle number 25, 30, 35 and 40, respectively; CK:blank control.
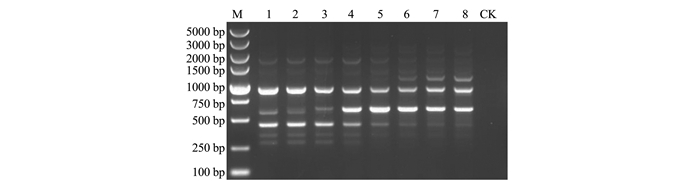
图 1 引物UBC847的反应体系优化注:M:5-kb DNA Marker;(A) 1~8:Taq酶用量分别为0.25、0.35、0.45、0.55、0.65(推荐剂量)、0.75、0.85和0.95 U;(B) 1~8:dNTPs浓度分别为0.07、0.10、0.14、0.17、0.20(推荐剂量)、0.23、0.26和0.30 mmol·L-1;(C) 1~8:Mg2+浓度分别为0.5、0.8、1.0、1.3、1.5(推荐剂量)、1.7、2.0和2.2 mmol·L-1;(D) 50~200:DNA模板量分别为50、100、150和200 ng;(E) 25~40:循环数分别为25、30、35和40次;CK:空白对照。Figure 1. Reaction condition optimization for primer UBC847Note:M:5-kb DNA Marker; (A) 1-8:the amount of Taq polymerase 0.25, 0.35, 0.45, 0.55, 0.65 (recommended dosages), 0.75, 0.85 and 0.95 U, respectively; (B) 1-8:the concentration of dNTPs 0.07, 0.10, 0.14, 0.17, 0.20 (recommended dosages), 0.23, 0.26 and 0.30 mmol·L-1, respectively; (C) 1-8:the concentration of Mg2+ 0.5, 0.8, 1.0, 1.3, 1.5 (recommended dosages), 1.7, 2.0 and 2.2 mmol·L-1, respectively; (D) 50-200:the concentration of template DNA 50, 100, 150 and 200 ng, respectively; (E) 25-40:the cycle number 25, 30, 35 and 40, respectively; CK:blank control.![]() 图 2 引物UBC847的最佳退火温度筛选注:M:5-kb DNA Marker;1~8:退火温度梯度依次为56.0、55.6、54.7、53.1、51.2、49.6、48.5和48.0℃;CK:空白对照。Figure 2. Selection of annealing temperature for primer UBC847Note:M:5-kb DNA Marker; 1-8:the annealing temperature 56.0, 55.6, 54.7, 53.1, 51.2, 49.6, 48.5 and 48.0℃, respectively; CK:blank control.
图 2 引物UBC847的最佳退火温度筛选注:M:5-kb DNA Marker;1~8:退火温度梯度依次为56.0、55.6、54.7、53.1、51.2、49.6、48.5和48.0℃;CK:空白对照。Figure 2. Selection of annealing temperature for primer UBC847Note:M:5-kb DNA Marker; 1-8:the annealing temperature 56.0, 55.6, 54.7, 53.1, 51.2, 49.6, 48.5 and 48.0℃, respectively; CK:blank control.综合上述优化结果,使用引物UBC847,适合福建省玉米大斑病菌ISSR扩增的最适反应体系为:25 μL反应体积中,Taq聚合酶用量0.55 U,dNTPs浓度为0.30 mmol·L-1,Mg2+浓度为1.3 mmol·L-1,模板DNA浓度100 ng,引物终浓度0.4 pmol(Taq酶反应体系推荐用量,本研究未优化);ISSR-PCR扩增程序为:94℃预变性4 min;94℃变性45 s,56.0℃退火45 s,72℃延伸1.5 min,35个循环;72℃延伸10 min。
2.2 ISSR-PCR引物的筛选
利用福建省5个玉米大斑病菌菌株的基因组DNA混合样品为模板和优化的反应体系及扩增条件,最终筛选出UBC117、UBC118、UBC808、UBC835、UBC847、UBC855、UBC856、UBC857、UBC866和UBC887等10条扩增条带清晰、重复性好且多态性丰富的ISSR-PCR引物(表 2)。
表 2 适宜福建省玉米大斑病菌ISSR分子标记的引物及最佳退火温度Table 2. Primers and annealing temperatures for ISSR molecular marker of E. turcicum isolates引物名称
Primer name引物序列(5′-3′)
Primer sequence最适退火温度(℃)
Optimal Tm引物来源
Primer origin是否适合福建种群
Whether suitable for Fujian populationUBC112 (AG)8TA (52) UBC, [15] 不适合unsuitability UBC113 (AG)8TC (54) (52.7) UBC, [15], [16] 不适合unsuitability UBC117 (AGA)7 55.6 (56) (52.7) UBC, [15], [16] 适合suitability UBC118 (GTC)6 53.1 (59.5) (53) UBC, [15], [16] 适合suitability UBC121 (GTGC)4 (61.8) (49) UBC, [15], [16] 不适合unsuitability UBC808 (AG)8C 51.2 (52.7) UBC, [16] 适合suitability UBC835 (AG)8YC 51.2 (53) UBC, [16] 适合suitability UBC847 (CA)8RT 56.0 (49.1) UBC, [16] 适合suitability UBC855 (AC)8YT 53.1 (49.4) UBC, [16] 适合suitability UBC856 (AC)8YA 53.1 UBC 适合suitability UBC857 (AC)8YG 51.2 UBC 适合suitability UBC866 (CTC)6 51.2 UBC 适合suitability UBC887 DVD(TC)7 51.2 UBC 适合suitability 注:① Tm:退火温度,小括弧内的数字为文献中报道的引物最佳退火温度;② UBC:加拿大哥伦比亚大学植物病原真菌基因组DNA重复序列ISSR引物库(http:/www.michaelsmith.ubc.ca)。
Note:①Tm:annealing temperature, numbers in parenthesis are the optimal annealing temperatures for primers reported in the literatures; ② UBC:Primer database for genomic DNA repeat sequence of phytopathogenic fungi established by University of Columbia, Canada (http:/www.michaelsmith.ubc.ca).通过梯度PCR扩增对筛选的UBC117、UBC118、UBC808、UBC835、UBC847、UBC855、UBC856、UBC857、UBC866和UBC887等10条引物的最佳退火温度进行优化,最终确定10条引物的最佳退火温度分别为55.6、53.1、51.2、51.2、56.0、53.1、53.1、51.2、51.2和51.2℃(表 2)。
2.3 ISSR-PCR扩增
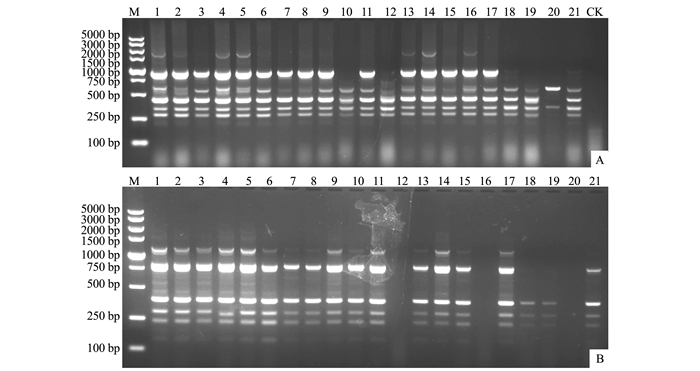
利用优化的ISSR-PCR反应体系和扩增条件对供试的21株玉米大斑病菌进行ISSR-PCR扩增,结果表明,扩增条带的分子量介于100~5 000 bp,引物UBC847从20号菌株DNA中仅扩增出2个条带,而从其他菌株DNA中扩增出4~6个条带,表明不同菌株间的DNA多态性存在明显差异(图 3-A)。引物UBC887从南靖县的菌株DNA(17~21号菌株)中扩增出0~5个条带,而从建瓯市的菌株DNA(1~8号菌株)中扩增出4~5个条带,表明相同地理来源以及不同地理来源菌株间的DNA多态性存在显著差异(图 3-B)。上述结果表明,福建省玉米大斑病菌群体存在丰富的遗传多样性。
![]() 图 3 使用引物UBC847和UBC887对福建省21个玉米大斑病菌株进行ISSR-PCR扩增注:M:5-kb DNA Marker;1~21:福建省玉米大斑病菌的菌株序号与表 1对应;(A)和(B):引物UBC847和UBC887分别对21株玉米大斑病菌的ISSR-PCR扩增结果;CK:空白对照。Figure 3. ISSR-PCR amplification of 21 E. turcicum isolates using primer UBC847 and UBC887Note:M:5-kb DNA Marker; 1-21:isolates of E. turcicum in Fujian Province corresponding with Table 1; (A) and (B):ISSR-PCR amplification results of 21 E. turcicum isolates in Fujian Province using primer UBC847 and UBC887, respectively; CK:blank control.
图 3 使用引物UBC847和UBC887对福建省21个玉米大斑病菌株进行ISSR-PCR扩增注:M:5-kb DNA Marker;1~21:福建省玉米大斑病菌的菌株序号与表 1对应;(A)和(B):引物UBC847和UBC887分别对21株玉米大斑病菌的ISSR-PCR扩增结果;CK:空白对照。Figure 3. ISSR-PCR amplification of 21 E. turcicum isolates using primer UBC847 and UBC887Note:M:5-kb DNA Marker; 1-21:isolates of E. turcicum in Fujian Province corresponding with Table 1; (A) and (B):ISSR-PCR amplification results of 21 E. turcicum isolates in Fujian Province using primer UBC847 and UBC887, respectively; CK:blank control.3. 讨论与结论
对ISSR-PCR反应体系和扩增条件进行优化,是获得扩增图谱清晰、重复性好、多态性高的ISSR分子标记结果的前提。本研究针对影响ISSR-PCR扩增结果的重要参数,如Taq聚合酶用量、dNTPs浓度、Mg2+浓度、模板DNA浓度、扩增循环数以及引物的退火温度等分别进行单因素4~8个水平的系统优化,试验结果表明,Taq聚合酶用量、dNTPs浓度、Mg2+浓度和扩增循环数对ISSR-PCR反应体系均有明显影响,而50~200 ng的模板DNA用量对反应体系的影响不明显。通过单因素优化法建立了适合福建省玉米大斑病菌ISSR分子标记的最适反应体系和扩增条件。该ISSR-PCR反应体系和扩增条件的建立为进一步在DNA分子水平上揭示福建省玉米大斑病菌的遗传变异和遗传结构以及深入探讨病菌的遗传变异、生理分化与致病性之间的关系奠定了基础。
不同地理来源和不同遗传背景的相同物种对ISSR分子标记的引物要求存在一定的差异性。谷守芹等报道适合我国北方地区玉米大斑病菌的ISSR分子标记的引物包括UBC112、UBC113、UBC117、UBC118和UBC121等9条[15]。郭丽媛筛选的适合我国玉米大斑病菌的ISSR分子标记的引物包括UBC112、UBC113、UBC117、UBC118、UBC121、UBC808、UBC835、UBC847、UBC855、UBC887和UBC888等18条[16]。本研究采用优化的ISSR-PCR反应体系从引物库中筛选出UBC117、UBC118、UBC808、UBC835、UBC847、UBC855、UBC856、UBC857、UBC866和UBC887等10条适合福建省玉米大斑病菌ISSR分子标记的引物。而文献中报道的引物UBC112、UBC113和UBC121并不适合福建省玉米大斑病菌种群。
明确ISSR分子标记引物的最佳退火温度是决定试验成败的又一重要因素。一般情况下,退火温度越低,扩增的DNA指纹图谱模糊、弱带多;退火温度越高,不利于长片段的扩增,所以扩增的DNA指纹图谱条带偏少[15]。本研究通过梯度PCR扩增优化出10条ISSR引物的最佳退火温度范围为51.2~56.0℃。引物UBC117的退火温度为55.6℃,与谷守芹等[15]的报道较为一致,但是明显高于郭丽媛的优化结果。UBC118、UBC808、UBC835和UBC855的退火温度,与郭丽媛[16]的优化结果较为一致,但是引物UBC118的退火温度显著低于谷守芹等[15]的报道。这可能是由于不同ISSR反应体系中Mg2+浓度不同以及病菌具有不同的遗传背景所致。
Borchardt等[2]利用RAPD技术研究欧洲玉米大斑病菌群体遗传多样性时发现,病菌群体具有26个不同的RAPD单元型且病菌群体存在丰富的DNA多态性。Tang等[11]通过UP-PCR研究发现,来自中国玉米S. turcica f. sp. zeae和高粱S. turcica f. sp. sorghi上的两个S. turcica致病性专化型群体的DNA多态性高达82%以上,表明不同寄主来源的S. turcica群体存在丰富的遗传多样性,且与地理来源相比,两个S. turcica致病性专化型与遗传多样性的关系更密切。谷守芹等[15]利用ISSR-PCR研究表明,中国玉米大斑病菌的遗传多样性与病菌的交配型存在一定的相关性,而与菌株的地理来源和生理小种没有明显的相关性。本研究发现,相同地理来源以及不同地理来源菌株间的DNA多态性均不同,表明福建省玉米大斑病菌群体存在丰富的遗传多样性。由于本研究主要目的在于建立ISSR-PCR反应体系,群体分析时所用的病菌菌株数量较小,因此,有必要进一步扩大采样的空间范围和样本数量,深入研究福建省玉米大斑病菌群体的遗传多样性和遗传结构,同时揭示病菌群体的遗传多样性和遗传结构与病菌的地理来源、交配型、生理小种以及致病性之间的关系。
-
图 1 引物UBC847的反应体系优化
注:M:5-kb DNA Marker;(A) 1~8:Taq酶用量分别为0.25、0.35、0.45、0.55、0.65(推荐剂量)、0.75、0.85和0.95 U;(B) 1~8:dNTPs浓度分别为0.07、0.10、0.14、0.17、0.20(推荐剂量)、0.23、0.26和0.30 mmol·L-1;(C) 1~8:Mg2+浓度分别为0.5、0.8、1.0、1.3、1.5(推荐剂量)、1.7、2.0和2.2 mmol·L-1;(D) 50~200:DNA模板量分别为50、100、150和200 ng;(E) 25~40:循环数分别为25、30、35和40次;CK:空白对照。
Figure 1. Reaction condition optimization for primer UBC847
Note:M:5-kb DNA Marker; (A) 1-8:the amount of Taq polymerase 0.25, 0.35, 0.45, 0.55, 0.65 (recommended dosages), 0.75, 0.85 and 0.95 U, respectively; (B) 1-8:the concentration of dNTPs 0.07, 0.10, 0.14, 0.17, 0.20 (recommended dosages), 0.23, 0.26 and 0.30 mmol·L-1, respectively; (C) 1-8:the concentration of Mg2+ 0.5, 0.8, 1.0, 1.3, 1.5 (recommended dosages), 1.7, 2.0 and 2.2 mmol·L-1, respectively; (D) 50-200:the concentration of template DNA 50, 100, 150 and 200 ng, respectively; (E) 25-40:the cycle number 25, 30, 35 and 40, respectively; CK:blank control.
图 2 引物UBC847的最佳退火温度筛选
注:M:5-kb DNA Marker;1~8:退火温度梯度依次为56.0、55.6、54.7、53.1、51.2、49.6、48.5和48.0℃;CK:空白对照。
Figure 2. Selection of annealing temperature for primer UBC847
Note:M:5-kb DNA Marker; 1-8:the annealing temperature 56.0, 55.6, 54.7, 53.1, 51.2, 49.6, 48.5 and 48.0℃, respectively; CK:blank control.
图 3 使用引物UBC847和UBC887对福建省21个玉米大斑病菌株进行ISSR-PCR扩增
注:M:5-kb DNA Marker;1~21:福建省玉米大斑病菌的菌株序号与表 1对应;(A)和(B):引物UBC847和UBC887分别对21株玉米大斑病菌的ISSR-PCR扩增结果;CK:空白对照。
Figure 3. ISSR-PCR amplification of 21 E. turcicum isolates using primer UBC847 and UBC887
Note:M:5-kb DNA Marker; 1-21:isolates of E. turcicum in Fujian Province corresponding with Table 1; (A) and (B):ISSR-PCR amplification results of 21 E. turcicum isolates in Fujian Province using primer UBC847 and UBC887, respectively; CK:blank control.
表 1 供试的福建省玉米大斑病菌菌株
Table 1 E. turcicum isolates collected in Fujian
序号
Number菌株编号
Isolate code采集地
Location年份
Year1 JO1801 建瓯市东游镇Dongyou town of Jian′ou city 2018 2 JO1809 建瓯市东游镇Dongyou town of Jian′ou city 2018 3 JODB1701 建瓯市东游镇Dongyou town of Jian′ou city 2017 4 JODB1702 建瓯市东游镇Dongyou town of Jian′ou city 2017 5 DFDB1901 建瓯市东峰镇Dongfeng town of Jian′ou city 2019 6 DFDB1902 建瓯市东峰镇Dongfeng town of Jian′ou city 2019 7 DFDB1903 建瓯市东峰镇Dongfeng town of Jian′ou city 2019 8 DFDB1905 建瓯市东峰镇Dongfeng town of Jian′ou city 2019 9 SX1801 松溪县Songxi county 2018 10 SX1802 松溪县Songxi county 2018 11 SX1804 松溪县Songxi county 2018 12 PNDB1602a 屏南县Pingnan county 2016 13 PNDB1604b 屏南县Pingnan county 2016 14 PNDB1606a 屏南县Pingnan county 2016 15 PNDB1608a 屏南县Pingnan county 2016 16 PNDB1609a 屏南县Pingnan county 2016 17 NJDB1805 南靖县Nanjing county 2018 18 NJDB1809 南靖县Nanjing county 2018 19 NJDB1810 南靖县Nanjing county 2018 20 NJDB1816 南靖县Nanjing county 2018 21 NJDB1830 南靖县Nanjing county 2018 表 2 适宜福建省玉米大斑病菌ISSR分子标记的引物及最佳退火温度
Table 2 Primers and annealing temperatures for ISSR molecular marker of E. turcicum isolates
引物名称
Primer name引物序列(5′-3′)
Primer sequence最适退火温度(℃)
Optimal Tm引物来源
Primer origin是否适合福建种群
Whether suitable for Fujian populationUBC112 (AG)8TA (52) UBC, [15] 不适合unsuitability UBC113 (AG)8TC (54) (52.7) UBC, [15], [16] 不适合unsuitability UBC117 (AGA)7 55.6 (56) (52.7) UBC, [15], [16] 适合suitability UBC118 (GTC)6 53.1 (59.5) (53) UBC, [15], [16] 适合suitability UBC121 (GTGC)4 (61.8) (49) UBC, [15], [16] 不适合unsuitability UBC808 (AG)8C 51.2 (52.7) UBC, [16] 适合suitability UBC835 (AG)8YC 51.2 (53) UBC, [16] 适合suitability UBC847 (CA)8RT 56.0 (49.1) UBC, [16] 适合suitability UBC855 (AC)8YT 53.1 (49.4) UBC, [16] 适合suitability UBC856 (AC)8YA 53.1 UBC 适合suitability UBC857 (AC)8YG 51.2 UBC 适合suitability UBC866 (CTC)6 51.2 UBC 适合suitability UBC887 DVD(TC)7 51.2 UBC 适合suitability 注:① Tm:退火温度,小括弧内的数字为文献中报道的引物最佳退火温度;② UBC:加拿大哥伦比亚大学植物病原真菌基因组DNA重复序列ISSR引物库(http:/www.michaelsmith.ubc.ca)。
Note:①Tm:annealing temperature, numbers in parenthesis are the optimal annealing temperatures for primers reported in the literatures; ② UBC:Primer database for genomic DNA repeat sequence of phytopathogenic fungi established by University of Columbia, Canada (http:/www.michaelsmith.ubc.ca). -
[1] 代玉立, 甘林, 阮宏椿, 等.福建省丙环唑不同敏感性玉米小斑病菌的遗传多样性和致病性[J].植物病理学报, 2019, 49(1):64-74. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zwblxb201901008 DAI Y L, GAN L, RUAN H C, et al. Genetic diversity and pathogenicity of different propiconazole-sensitive isolates of Bipolaris maydis in Fujian Province[J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 2019, 49(1):64-74. (in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zwblxb201901008
[2] BORCHARDT D S, WELZ H G, GEIGER H H. Molecular marker analysis of European Setosphaeria turcica populations[J]. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 1998, 104(6):611-617. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d9123a95d7b6d932dac0b27a8f5d0ff5&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[3] SIMCOX K D, PEDERSEN W L, NICKRENT D L. Isozyme diversity in Setosphaeria turcica[J]. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology, 1993, 15(2):91-96. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1080/07060669309500832
[4] 孙淑琴, 温雷蕾, 董金皋.玉米大斑病菌的生理小种及交配型测定[J].玉米科学, 2005, 13(4):112-113, 123. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ymkx200504032 SUN S Q, WEN L L, DONG J G. Identification of physiological races and mating type of Exserohilum turcicum[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2005, 13(4):112-113, 123. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ymkx200504032
[5] 郭丽媛, 贾慧, 曹志艳, 等.玉米大斑病菌有性杂交后代的交配型与寄生适合度分化[J].中国农业科学, 2013, 46(19):4058-4065. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgnykx201319011 GUO L Y, JIA H, CAO Z Y, et al. Analysis on mating type and parasitic fitness diversity in sexual hybridization offsprings of Setosphaeria turcica[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2013, 46(19):4058-4065. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgnykx201319011
[6] 王玉萍, 王晓鸣, 马青.我国玉米大斑病菌生理小种组成变异研究[J].玉米科学, 2007, 15(2):123-126. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ymkx200702031 WANG Y P, WANG X M, MA Q. Races of Exserohihun turcicum, causal agent of northern leaf blight in China[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2007, 15(2):123-126. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ymkx200702031
[7] CHUNG C L, LONGFELLOW J M, WALSH E K, et al. Resistance loci affecting distinct stages of fungal pathogenesis:use of introgression lines for QTL mapping and characterization in the maize-Setosphaeria turcica pathosystem[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2010(10):103. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-103
[8] 张明会, 徐秀德, 姜钰, 等.玉米大斑病菌种群遗传多样性研究[J].玉米科学, 2009, 17(1):143-146. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ymkx200901035 ZHANG M H, XU X D, JIANG Y, et al. Genetic diversity of Exserohilum turcicum on maize[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2009, 17(1):143-146. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ymkx200901035
[9] FERGUSON L M, CARSON M L. Spatial diversity of Setosphaeria turcica sampled from the Eastern United States[J]. Phytopathology, 2004, 94(8):892-900. http://med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail/PeriodicalPaper_PM18943111
[10] MUIRU W M, KOOPMANN B, TIEDEMANN A V, et al. Evaluation of genetic variability of Kenyan, German and Austrian isolates of Exserohilum turcicum using amplified fragment length polymorphism DNA marker[J]. Biotechnology, 2010, 9(2):204-211. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=Doaj000000780554
[11] TANG L, GAO Z G, YAO Y, et al. Identification and genetic diversity of formae speciales of Setosphaeria turcica in China[J]. Plant Disease, 2015, 99(4):482-487. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=adc7bca21c3bdfa008ec1349ea3c2b8c
[12] HAASBROEK M P, CRAVEN M, BARNES I, et al. Microsatellite and mating type primers for the maize and sorghum pathogen, Exserohilum turcicum[J]. Australasian Plant Pathology, 2014, 43(5):577-581. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=1675359ad74c47ca1d2b84bf23f74c83
[13] WANG H, XIAO Z X, WANG F G, et al. Mapping of HtNB, a gene conferring non-lesion resistance before heading to Exserohilum turcicum (Pass.), in a maize inbred line derived from the Indonesian variety Bramadi[J]. Genetics & Molecular Research, 2012, 11(3):2523-2533. http://med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail/PeriodicalPaper_PM22869072
[14] HUMAN M P, BARNES I, CRAVEN M, et al. Lack of population structure and mixed reproduction modes in Exserohilum turcicum from South Africa[J]. Phytopathology, 2016, 106(11):1386-1392. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=2faa3925ac8299b5ff89f355755139e4
[15] 谷守芹, 范永山, 李坡, 等.玉米大斑病菌ISSR反应体系的优化和遗传多样性分析[J].植物保护学报, 2008, 35(5):427-432. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwbhxb200805009 GU S Q, FAN Y S, LI P, et al. Optimization of ISSR reaction and genetic diversity analysis of Exserohilum turcicum[J]. Acta Phytophylacica Sinica, 2008, 35(5):427-432. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwbhxb200805009
[16] 郭丽媛.中国北方玉米产区玉米大斑病菌生理小种监测及遗传多样性分析[D].保定: 河北农业大学, 2013. GUO L Y. Physiological races monitoring and genetic diversity of Setosphaeria turcica in maize production areas of Northern China[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2013. (in Chinese)
[17] 郭丽婕.中国玉米大斑病菌的遗传多样性及交配型组成分析[D].保定: 河北农业大学, 2015. GUO L J. Genetic diversity and mating type distribution of Setosphaeria turcica in China[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2015. (in Chinese)
[18] FANG D Q, ROOSE M L. Identification of closely related citrus cultivars with inter-simple sequence repeat markers[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 1997, 95(3):408-417. DOI: 10.1007-s001220050577/
[19] TSUMURA Y, OHBA K, STRAUSS S H. Diversity and inheritance of inter-simple sequence polymorphisms in Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii) and sugi (Cryptomeria japonica)[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 1996, 92(1):40-45. http://med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail?id=PeriodicalPaper_JJ0215067698
[20] 秦旭升, 刘学敏, 周艳玲, 等.植物病原真菌中DNA分子鉴定技术[J].植物生理学报, 2000, 36(4):342-347. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwslxtx200004022 QIN X S, LIU X M, ZHOU Y L, et al. DNA molecular marker technique of phytopathogenic fungi[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 2000, 36(4):342-347.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwslxtx200004022
[21] 鄢洪海, 王琰, 张茹琴, 等.基于ISSR-PCR对山东玉米多堆柄锈菌遗传多样性的研究及其初侵染菌源的推测[J].菌物学报, 2018, 37(2):157-165. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jwxt201802003 YAN H H, WANG Y, ZHANG R Q, et al. Genetic diversity and deduction of primary infection source of Puccinia polysora in Shandong Province based on ISSR-PCR[J]. Mycosystema, 2018, 37(2):157-165.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jwxt201802003
[22] 张小飞, 李晓, 崔丽娜, 等.我国玉米灰斑病菌遗传多样性的ISSR分析[J].植物保护学报, 2015, 42(6):908-913. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwbhxb201506007 ZHANG X F, LI X, CUI L N, et al. Genetic diversity analysis of Cercospora spp. by ISSR in China[J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2015, 42(6):908-913.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwbhxb201506007
[23] 张小飞, 高增贵, 庄敬华, 等.利用UP-PCR、ISSR和AFLP标记分析玉米丝黑穗病菌遗传多样性[J].植物保护学报, 2010, 37(3):241-248. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwbhxb201003009 ZHANG X F, GAO Z G, ZHUANG J H, et al. Genetic diversity of Sporisorium reilianum by UP-PCR, ISSR and AFLP analysis[J]. Acta Phytophylacica Sinica, 2010, 37(3):241-248.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwbhxb201003009
[24] 马红霞, 孙华, 郭宁, 等.禾谷镰孢复合种毒素化学型及遗传多样性分析[J].中国农业科学, 2018, 51(1):82-95. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgnykx201801008 MA H X, SUN H, GUO N, et al. Analysis of toxigenic chemotype and genetic diversity of the Fusarium graminearum species complex[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2018, 51(1):82-95.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgnykx201801008
[25] 张小飞, 李晓, 崔丽娜, 等.玉米圆斑病菌(Bipolaris zeicola)遗传多样性ISSR分析[J].植物保护, 2015, 41(3):30-34. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwbh201503006 ZHANG X F, LI X, CUI L N, et al. Genetic diversity analysis of corn leaf spot caused by Bipolaris zeicola with ISSR markers[J]. Plant Protection, 2015, 41(3):30-34.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwbh201503006
[26] 王晓东, 高增贵, 姚远, 等.利用UP-PCR、ISSR标记分析玉米弯孢叶斑病菌遗传多样性[J].华北农学报, 2014, 29(3):227-233. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hbnxb201403041 WANG X D, GAO Z G, YAO Y, et al. Genetic diversity of Curvularia lunata by UP-PCR and ISSR analysis[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2014, 29(3):227-233.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hbnxb201403041
[27] 方中达.植物病理研究方法[M].北京:中国农业出版社, 2007. FANG Z D. Plant Pathology Research Methods[M]. Beijing:China Agriculture Press, 2007.(in Chinese)
[28] INNIS M A, GELFAND D H, SNINSKY J J, et al. PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications[M]//WHITE T J, BRUNS T, LEE S, et al. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. San Diego: Academic Press, 1990: 315-322.
[29] 代玉立, 甘林, 石妞妞, 等.福建省玉米小斑病菌对氟啶胺的敏感性及其与不同杀菌剂间的交互抗性[J].植物保护学报, 2018, 45(6):1374-1380. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwbhxb201806026 DAI Y L, GAN L, SHI N N, et al. Sensitivity of southern corn leaf blight pathogen Cochliobolus heterostrophus to fluazinam and cross-resistance against diverse fungicides in Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2018, 45(6):1374-1380.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwbhxb201806026
[30] 代玉立, 甘林, 阮宏椿, 等.福建省鲜食玉米小型叶斑病的病原菌鉴定[J].福建农业学报, 2017, 32(12):1341-1349. DOI: 10.19303/j.issn.1008-0384.2017.012.013 DAI Y L, GAN L, RUAN H C, et al. Pathogen Identification of small leaf spots on sweet corn plants in Fujian[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 32(12):1341-1349.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.19303/j.issn.1008-0384.2017.012.013
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 高建昊,戴子淙,张小杰,周天旺,王春明,洪流,郭成. 甘肃省玉米大斑病菌交配型组成及遗传多样性分析. 西北农业学报. 2024(04): 736-743 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 代玉立,甘林,刘晓菲,兰成忠,杨秀娟. 福建省玉米大斑病菌对吡唑醚菌酯不同敏感性菌株的遗传多样性与群体遗传结构分析. 农业生物技术学报. 2023(03): 603-616 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 代玉立,甘林,滕振勇,陈伟,卢学松,杨秀娟. 鲜食玉米大斑病经济阈值及品种抗性分级标准. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版). 2021(04): 71-80 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: