Chemistry and In Vitro Immunological Activity of Polysaccharides from Sparassis latifolia
-
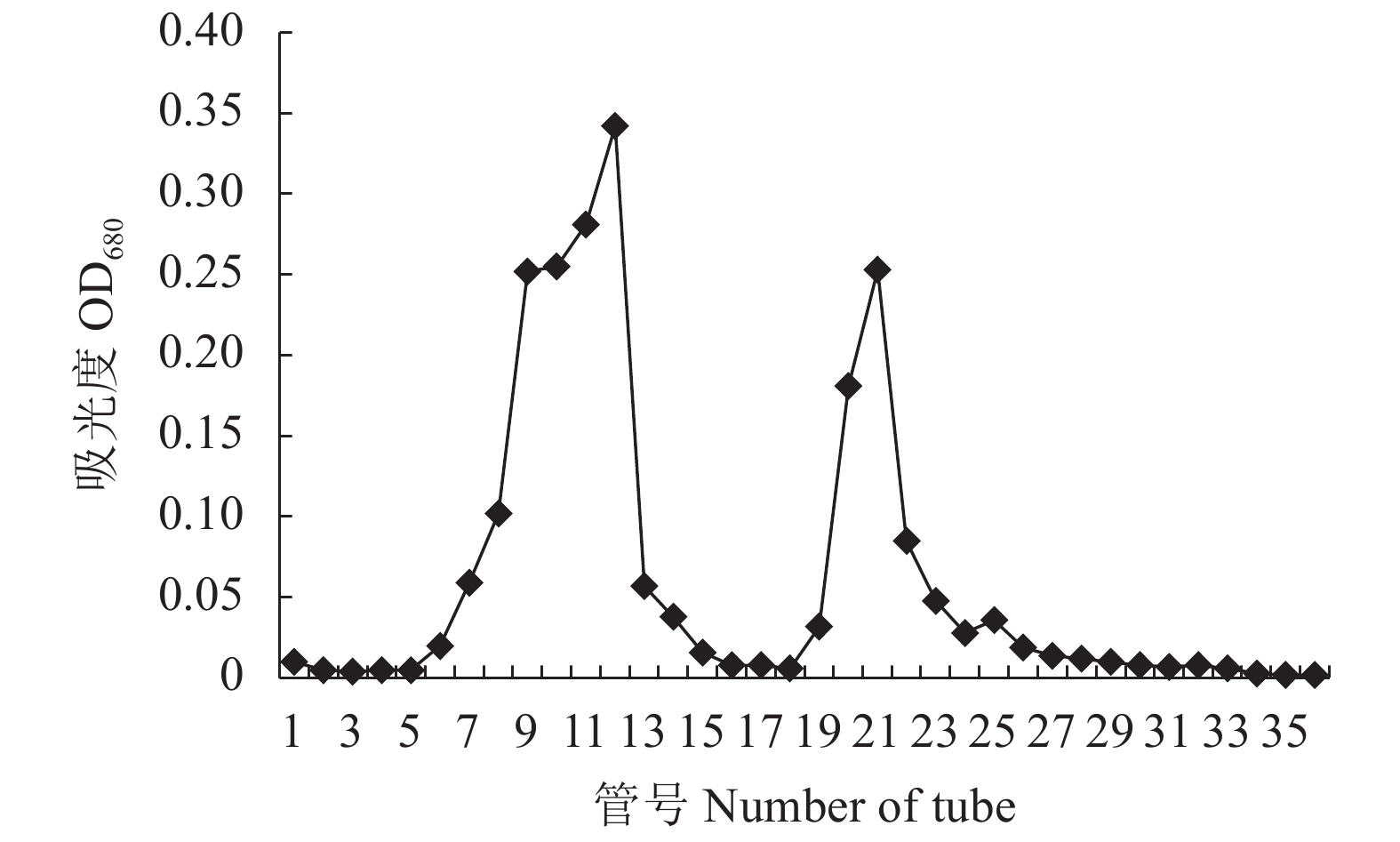
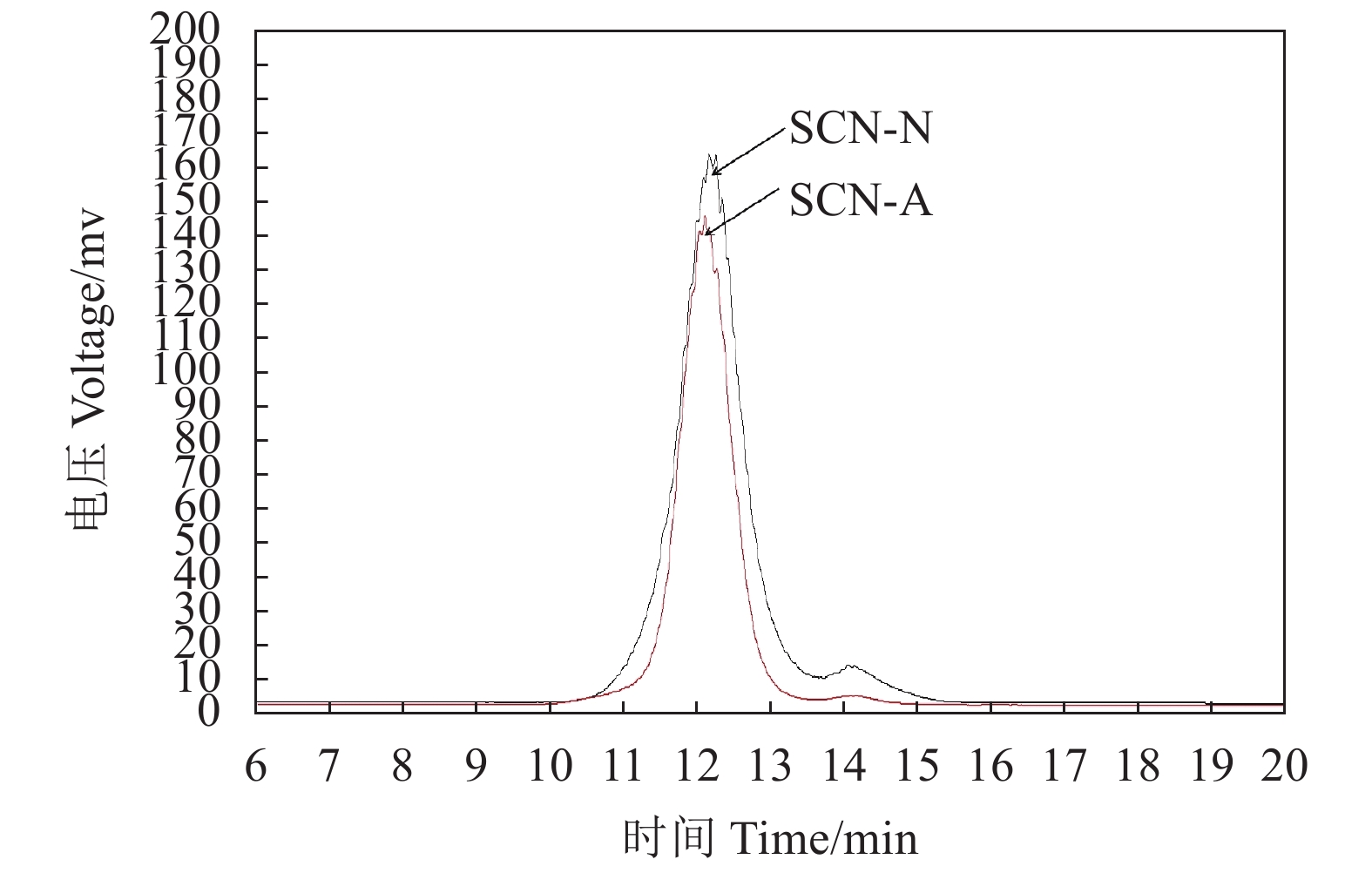
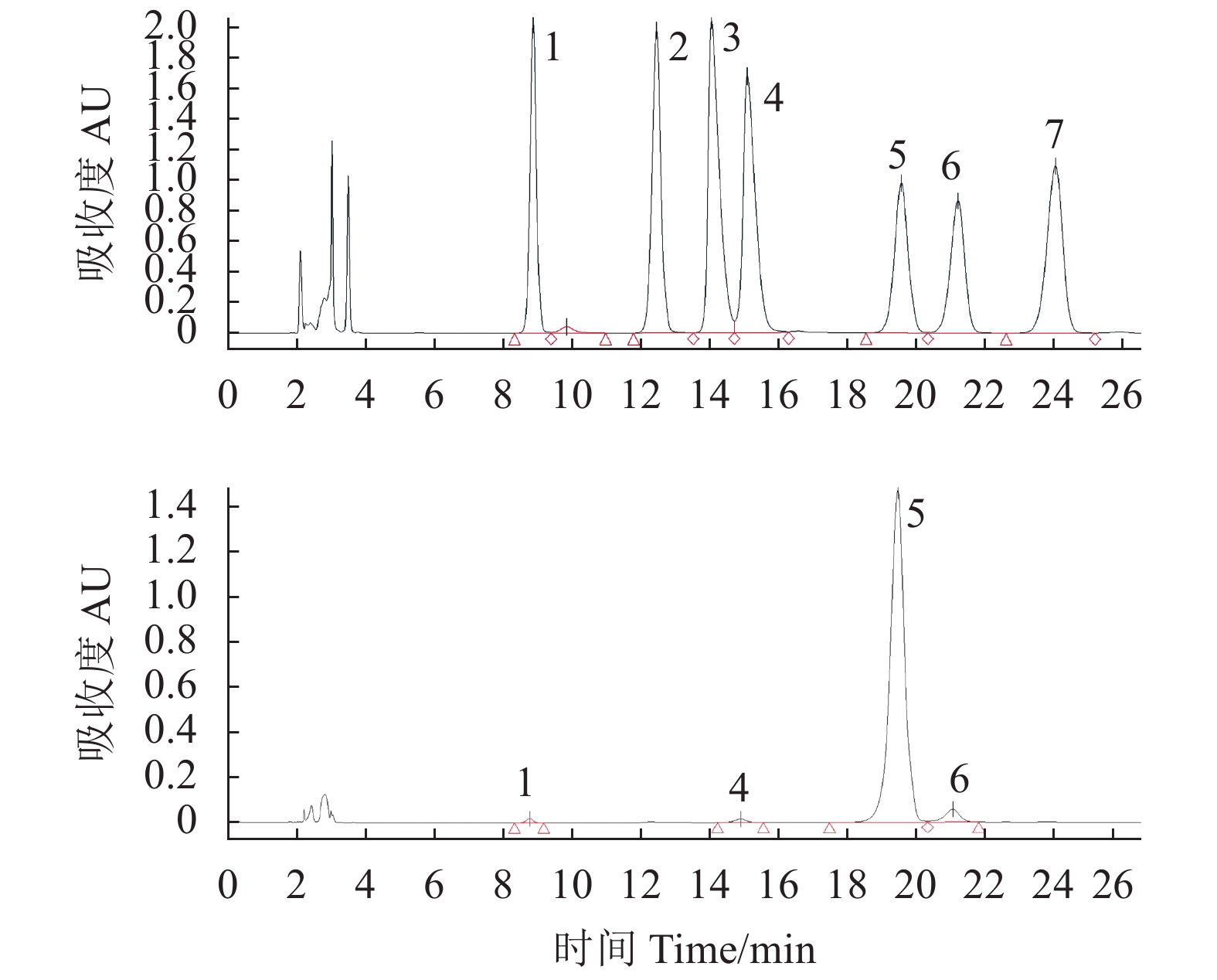
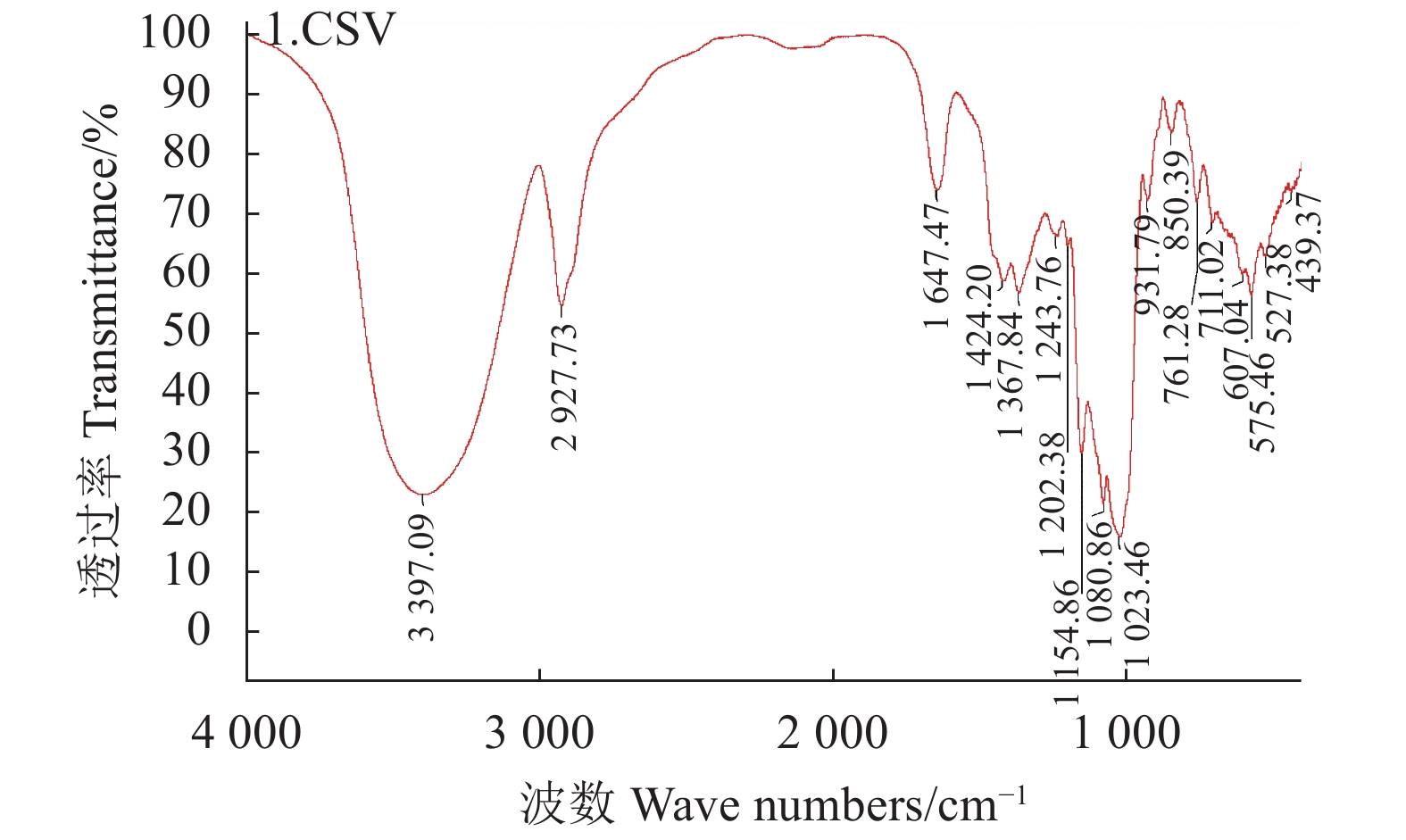
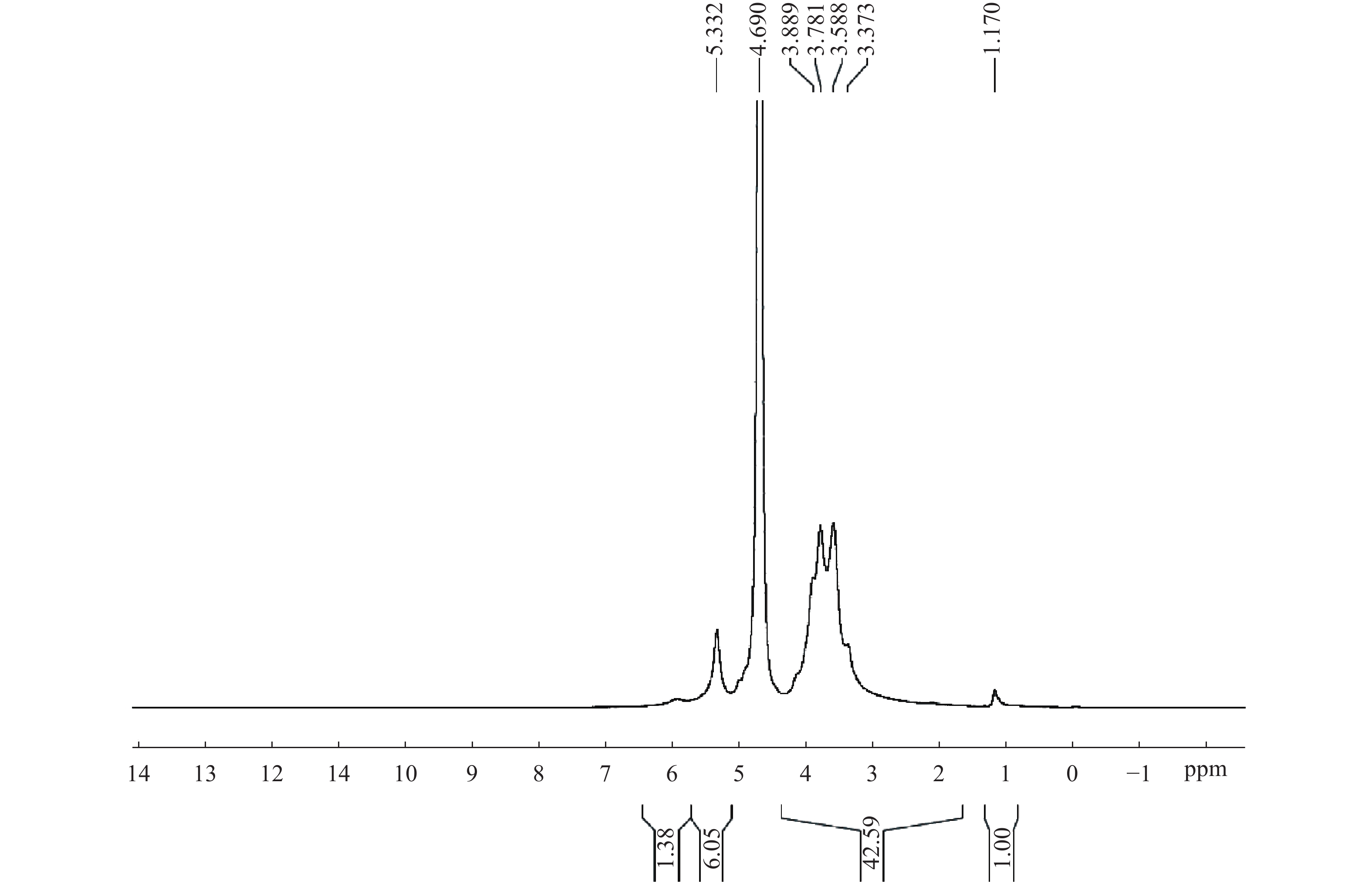
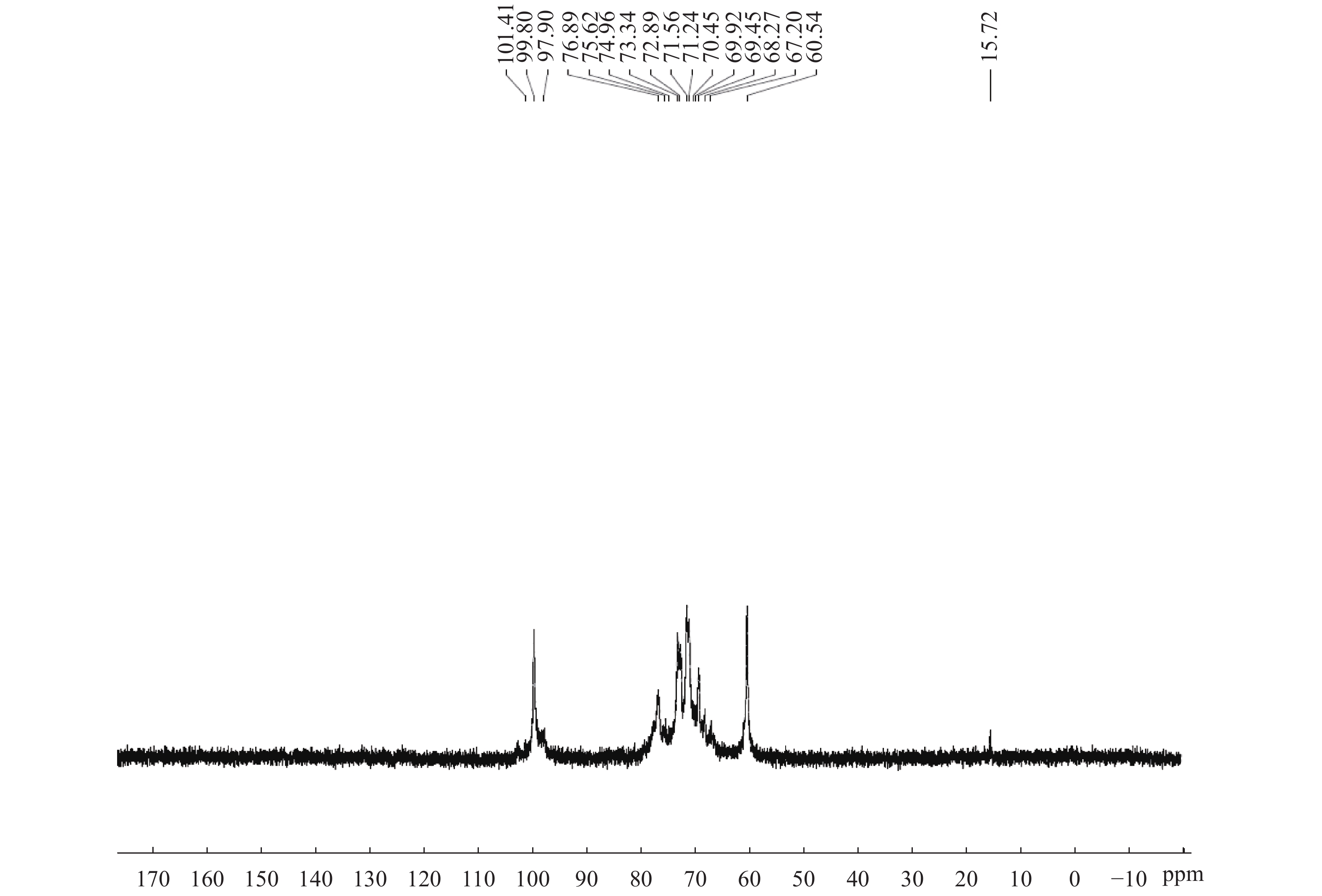
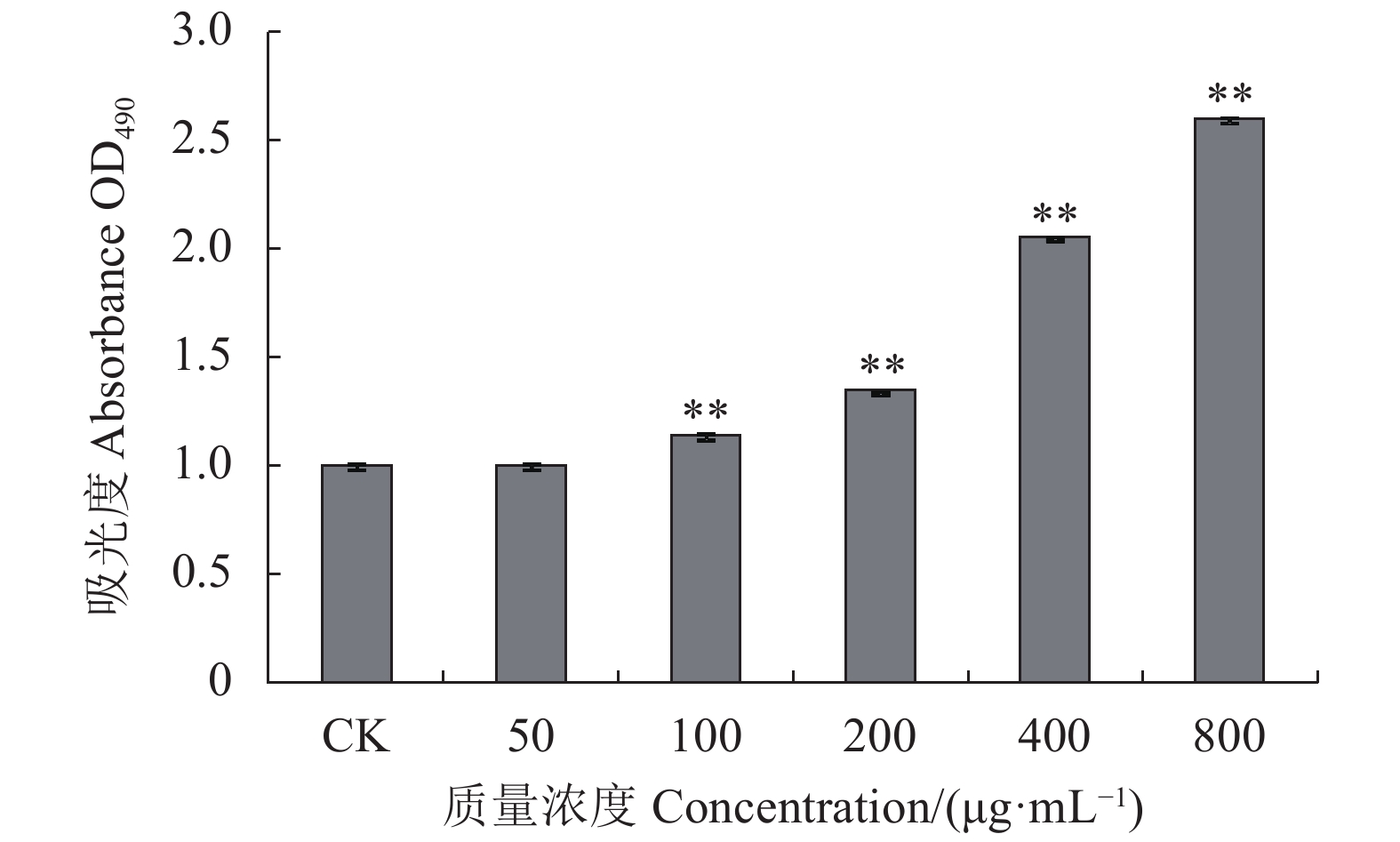
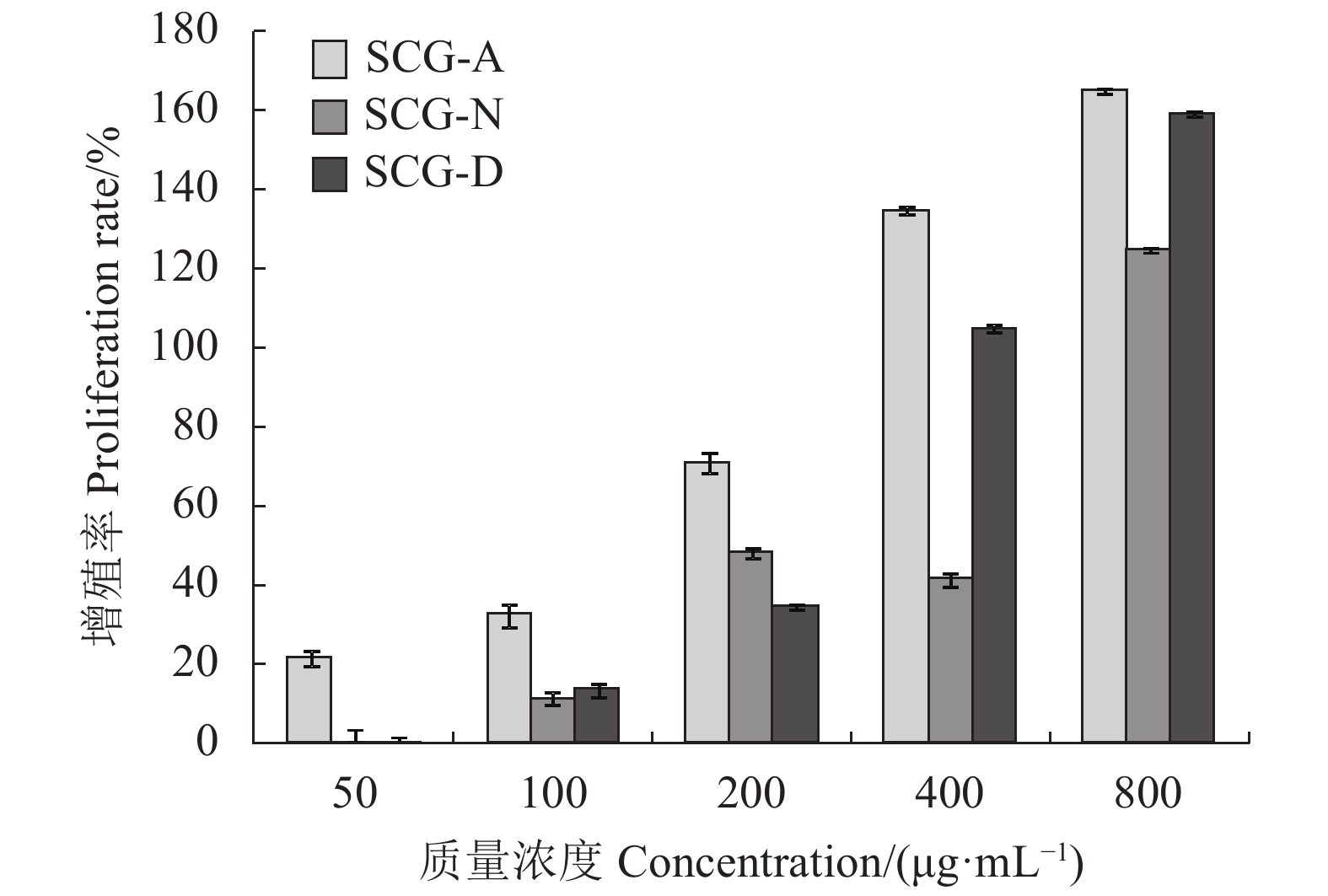
摘要:目的 分析绣球菌水溶性多糖的结构与免疫活性。方法 采用热水提取法从广叶绣球菌Sparassis latifolia的真空冷冻干燥品中提取得到绣球菌水溶性多糖SCG-D,然后通过DEAE Sepharose Fast Flow离子交换层析对其进行分离,获得SCG-N和SCG-A两个多糖组分,并对SCG-A组分进行HPSEC、单糖组成分析、红外光谱、1H-NMR和13C-NMR核磁共振的结构分析。通过大鼠脾淋巴细胞体外刺激活性测试比较了SCG-D及其组分SCG-A、SCG-N的体外免疫活性差异。结果 绣球菌水溶性多糖SCG-D具有促进鼠脾淋巴细胞增殖的活性,其酸性多糖组分SCG-A促进作用最强,其100 μg·mL−1 72 h处理组的增殖率为32.7%,而SCG-N多糖组分的活性较SCG-A低,其100 μg·mL−1 72 h处理组增殖率为11.66%。结构分析结果表明SCG-A的重均分子量为4.30×105 Da,其主链结构为α-1,4-D-葡聚糖,主要由葡萄糖和半乳糖构成,并且还含有一定量的1-6分支结构。结论 绣球菌冻干品的水溶性多糖及其组分具有促进大鼠脾淋巴细胞体外增殖的免疫活性,其中活性最强的酸性多糖组分SCG-A是一种具有1-6分支结构的α-1,4-葡聚糖。Abstract:Objective Chemical structure and in vitro immunological activity of the water soluble polysaccharides from Sparassis latifolia were studied .Method The lyophilized powder of S. latifolia fruiting bodies was extracted by hot water to obtain polysaccharides SCG-D. From the extract, the SCG-N and SCG-A fractions were isolated by the DEAE-Sepharose Fast Flow ion exchange chromatography. The structure of SCG-A was analyzed using HPSEC, monosaccharide composition analysis, FT-IR, and NMR. The in vitro immunological activities of the extract and the fractions were determined by a test on rat spleen lymphocytes.Result SCG-D was found active in promoting the lymphocyte proliferation. SCG-A exhibited the strongest activity with a proliferation rate of 32.7% at the concentration of 100 μg/mL in 72h, while SCG-N activity was lower at 11.66%. The molecular weight of SCG-A was 4.30×105Da with an α-1,4-D-glucan as its main chain consisting primarily of glucose and galactose with some 1-6-branches.Conclusion The water-soluble polysaccharides and its fractions obtained from the lyophilized S. latifolia powder showed varying in vitro immune activities of promoting the proliferation of rat spleen lymphocytes. The acidic SCG-A had a main chain structure of α-1,4-glucan with 1-6-branches and showed the greatest immunological activity among the 3 polysaccharide materials.
-
Keywords:
- Sparassis latifolia /
- polysaccharide /
- spleen lymphocyte /
- immunity
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】畜牧业生产中抗生素的滥用和超级耐药菌不断涌现,给畜牧业生产和我国食品安全带来很大危害。为促进畜牧业生产的发展和保障食品安全,应用微生物的功能性作用,开发具有安全高效的复合微生物菌剂,成为当前畜牧业生产的一种趋势[1-6]。而依据猪的胃肠道微生物功能而开发的微生物菌剂,在生猪的养殖中应用广泛[7-8]。【前人研究进展】有研究证实饲料中添加微生物菌剂饲喂育肥猪,平均日增重可提高6.7%,肉料比可降低11.7%,饲喂微生物添加剂的要比未饲喂的猪每头节约饲料成本21.6~27.2元,效果较显著[9];也有报道使用芽孢杆菌添加到饲料中,饲喂哺乳仔猪,提高增重22%以上,耗料指数下降1%~6%,具有较好的经济效益;还有报道证实,添加微生物菌剂,能改善小猪胃肠菌群[10],可明显减少哺乳仔猪、仔猪的拉稀[11],增强机体免疫作用[12],改善猪舍环境[13],减少粪便中有害气体的产量等[14-15]。尽管之前的研究证实微生物菌剂不仅能改善断奶小仔猪的拉稀,还能改善育肥猪的生产性能。但实际生产中的应用还是较少。一方面是因为之前的研究添加菌剂相对单一,对生猪生产性能的改善相对有限,临床应用也相对有限。另一方面,是因为微生物菌剂功能的发挥是多菌种相互配合的复杂系统,详细的作用机理尚待深入揭示,进一步限制了微生物菌剂在畜牧业生产中的应用。【本研究切入点】为进一步推动微生物菌剂在生产中的应用,改善生猪的生产性能,本研究采用多菌种的复合菌添加模式,进一步探讨复合菌剂对育肥猪的生长、发育的影响。【拟解决的关键问题】通过运用复合微生物菌(包括芽孢菌、放线菌、乳酸菌、酵母菌、粪肠菌、光合菌等多种菌),进行为期90 d的添加饲喂试验,以期揭示长期添加复合微生物菌对生猪生产性能、胃肠道绒毛和微生物结构影响,从而推动复合微生物菌剂在生猪生产中的应用。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
1.1.1 试验动物
60日龄的杜×长×大育肥猪共300头购自福建龙岩上杭某养殖公司,体重(25.0±1.6)kg。
1.1.2 复合微生物菌
本试验中复合菌华惠一号由福建省农业科学院畜牧兽医研究所和泉州华惠生物科技有限公司共同分离培养,包括1.25×108 cfu·g−1以上的芽孢菌、放线菌、乳酸菌、酵母菌、粪肠菌、光合菌等。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 试验处理设置
饲养地点在福建龙岩上杭某养殖公司,采用常规的水泥面养殖猪舍,平均气温22℃,养殖周期90 d。育肥猪300头,随机分成2组,每组15个重复,每个重复10头。试验组饲喂添加复合微生物菌活菌饲料,对照组饲喂常规的饲料。正式饲喂试验前7 d进行预试验。饲喂管理按照自由采食方法进行,提供充足清洁饮水,每天进行一次猪舍清扫,定时观察记录试验猪的采食、体重、粪便、精神状况,常规疫苗接种。
1.2.2 饲料的基础日粮、营养成分及制备
将复合菌液按1:12.5比列添加至玉米粉,在25~38℃密闭发酵5~7 d。试验组按基础原料组成配方:发酵玉米16 kg,玉米粉634 kg,豆粕280 kg,麦麸30 kg,预混料40 kg进行混匀饲喂。对照组则按基础原料组成配方:玉米粉650 kg,豆粕280 kg,麦麸30 kg,预混料40 kg混匀饲喂。试验饲料的原料基础日粮及其营养成分见表1。
表 1 基础日粮组成及营养成分Table 1. Basic diet and nutritional composition of forage组成 Composition 含量 Contain 玉米 Corn/% 65 麦皮 Wheat bran/% 3 豆粕 Soybean meal/% 28 预混料 Premix/%(每千克日粮) 4 总计 Total/% 100 消化能 Digestive energy(DE)/(MJ·kg−1) 13.87 粗蛋白 Crude protein(CP)/% 19.5 赖氨酸 Lysine(Lys)/% 1.1 钙 Calcium(Ca)/% 0.9 有效磷 Available phosphorus(AP)/% 0.45 注:预混料组成:石粉40%,磷酸氢钙30%,碘酸钙0.25%,亚硒酸钠0.75%,一水硫酸亚铁1.85%,一水硫酸锌1.5%,五水硫酸铜2.2%,一水硫酸锰0.85%,维生素A0.05%,维生素B1(98%)0.004%,维生素B2(96%)0.02%,维生素B6(98%)0.012%,维生素B12(1%)0.005%,维生素D3 0.09%,维生素E(50%)0.1%,氯化胆碱(50%)3.5%,生物素(2%)0.013%,烟酸(99%)0.076%,叶酸(97%)0.002%,泛酸(98%)0.051%,维生素K3(25%)0.1%,食盐6.0%,蛋氨酸(99%)1.0%,赖氨酸(98%)5.0%,抗氧化剂0.1%,载体(沸石粉)6.558%。
Note:The composition of premix is 40% stone powder, 30% calcium hydrogen phosphate, 0.25% calcium iodate, 0.75% sodium selenite, 1.85% ferrous sulfate monohydrate, 1.5% zinc sulfate monohydrate, 2.2% copper sulfate pentahydrate, 0.85% manganese sulfate monohydrate, 0.05% vitamin A, 0.004% vitamin B1 (98%), 0.02% vitamin B2 (96%), 0.012% vitamin B6 (98%), Vitamin B12 (1%) 0.005%, vitamin D3 0.09%, vitamin E (50%) 0.1%, choline chloride (50%) 3.5%, biotin (2%) 0.013%, niacin (99%) 0.076%, folic acid (97%) 0.002%, pantoic acid (98%) 0.051%, vitamin K3 (25%) 0.1%, salt 6.0%, methionine (99%) 1.0%, lysine (98%) 5.0%, antioxidant 0.1%, carrier (zeolite powder) 6.558%.1.3 生产性能指标测定
试验前,对所有猪进行称重,然后添加复合菌,并分别在15、30、60、90 d进行称重、统计采食量,并计算每头日均增重、头均耗料以及耗料增重比,分析复合菌对育肥猪生产性能的影响。
1.4 肠道绒毛结构测定
饲喂试验结束后,各处理分别选择18头体重相近且生长状况良好、未发生过消化道疾病的育肥猪,空腹处死,取0.25 cm的胃、结肠、盲肠,放入多聚甲醛固定,经酒精脱水,二甲苯透明,然后将已透明的组织块置于已溶化的石蜡中浸蜡、包埋;再将包埋好的组织块切片,然后脱蜡、至水、染色;染色后的切片经纯酒精脱水,再经二甲苯使切片透明;将已透明的切片滴上树胶,盖上盖玻片封固;待树胶略干后镜检。
1.5 16S rRNA基因测序
1.5.1 微生物组总DNA提取和目标片段PCR扩增
试验结束时,通过安乐死处理试验组和对照组猪(每组10只),分别取处死猪的胃和结肠黏液进行微生物组总DNA提取,然后通过1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳验证提取DNA的纯度,同时运用紫外分光光度方法对提取的胃和结肠黏液DNA进行定量。接着再根据肠道微生物序列中的保守片段设计引物,对肠道微生物的基因可变区(单个或连续的多个)或特定基因片段进行PCR扩增。
1.5.2 扩增产物纯化和定量
PCR扩增产物通过2%琼脂糖凝胶电泳进行检测,并对目标片段进行切胶回收,回收采用AXYGEN公司的凝胶回收试剂盒。参照电泳初步定量结果,将PCR扩增回收产物进行荧光定量,荧光试剂为Quant-iT PicoGreen dsDNA Assay Kit,定量仪器为Microplate reader(BioTek,FLx800)。根据荧光定量结果,按照每个样本的测序量需求,对各样本按相应比例进行混合。
1.5.3 测序文库制备和高通量测序
采用Illumina公司的TruSeq Nano DNA LT Library Prep Kit试剂盒制备测序的基因文库。将验证合格的测序文库进行梯度稀释,按相应比例混合文库,混合后再采用碱变性为单链进行上机测序;使用MiSeq Reagent Kit V3 (600 cycles)和MiSeq测序仪进行2×300 bp的双端测序。
首先进行初步筛查高通量测序的原始下机数据的序列质量;再按照引物和Barcode信息,将通过质量初筛的序列,分配入对应样本,并去除嵌合体;然后使用QIIME软件,调用UCLUST这一序列比对工具,对前述获得的序列按97%的序列相似度进行归并和OTU划分,并选取每个OTU中丰度最高的序列作为该OTU的代表序列。随后,根据每个OTU在每个样本中所包含的序列数,构建OTU在各样本中丰度的矩阵文件(即OTU table),该矩阵文件可转换为“BIOM(Biological Observation Matrix)”这一更便于传输、储存并兼容于其他分析工具的文件格式。OTU归并划分获得的序列,然后根据每个OTU的代表序列进行序列的分类地位鉴定以及系统发育学分析;接着再根据OTU在不同样本中的丰度分布,对每个样本的多样性水平进行评估,并根据样本的稀疏曲线来评估测序深度;随后根据不同分类水平分析各样本(组)并检验组间各自的统计学意义;然后对OTU丰度矩阵中的全体样本在90%的最低测序深度水平,统一进行随机重抽样(即“序列量拉平处理”),从而校正测序深度引起的多样性差异。随后,使用QIIME软件分别对每个样本计算上述4种多样性指数,再通过α和β多变量统计学分析工具,分析不同样本间及组间的菌群结构差异及与相关的物种差异;接着根据微生物肠道菌群的基因测序结果,预测各样本的菌群相关代谢功能。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 复合微生物菌剂对育肥猪生产性能的影响
如表2所示,试验组的育肥猪在15、30、60、90 d平均日增重显著高于对照组,F/G显著低于对照组。表明在育肥猪日粮中添加复合菌能提高育肥猪日增重,降低料肉比。
表 2 添加复合菌对育肥猪生产性能的影响Table 2. Effect of compound microbial agent addition in forage on weight-gain of pigs at fattening stage试验时间
Time试验处理
Treatments平均日采食量
Average daily feed intake(ADFI)/(kg·头−1)平均增重
Average head gain/(kg·头−1)平均日增重
Average daily gain(ADG)
/(kg·头−1)料/肉比(F/G)
Feed/weight gainF/G与对照组比较
F/G compared with control15 d 复合菌组 Treatment 1.60±0.28 a 9.5±0.48 a 0.63±0.15 a 2.53 a −8.38% 对照组 Control 1.60±0.39 a 8.72±1.29 b 0.52±0.14 b 2.73 b 30 d 复合菌组 Treatment 1.86±0.98 a 10.01±2.84 a 0.67±0.17a 2.76 a −2.81% 对照组 Control 1.88±0.40 a 9.92±1.48 b 0.61±0.10 b 2.84 b 60 d 复合菌组 Treatment 2.43±0.52 a 25.86±1.24 a 0.86±0.15 a 2.82 a −11.74% 对照组 Control 1.97±0.19 b 25.08±1.29 b 0.84±0.34 b 3.15 b 90 d 复合菌组 Treatment 3.35±0.76 a 28.65±1.24 a 0.95±0.15 a 3.52 a −2.63% 对照组 Control 3.36±0.55 a 27.78±1.29 b 0.93±0.34 b 3.63 b 注:不同小写字母表示同一时间不同处理之间差异显著(P<0.05),相同字母表示差异不显著(P>0.05)。
Note: Different letters in the same row means significant difference between treatments(P<0.05).2.2 胃肠道结构及绒毛变化
添加复合菌组的猪胃壁纵肌层和横肌层较厚;胃壁绒毛比对照组长,差异极显著(P<0.01);结肠绒毛和盲肠绒毛比对照组长,差异显著(P<0.05)或极显著(P<0.01)。此外,对照组的胃壁纵肌层和横肌层较薄(图1)。说明复合微生物菌的添加促进了胃肠肠绒毛的发育,减少了损伤。
![]() 图 1 胃肠道结构及绒毛变化注:箭头标注为胃肠道绒毛结构;*表示差异显著(P<0.05),**表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。Figure 1. Changes on structure and villi in gastrointestinal tractsNote:The arrow is marked as the gastrointestinal villi structure; * indicates significant difference (P<0.05), ** indicates extremenly significant difference (P<0.01).
图 1 胃肠道结构及绒毛变化注:箭头标注为胃肠道绒毛结构;*表示差异显著(P<0.05),**表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。Figure 1. Changes on structure and villi in gastrointestinal tractsNote:The arrow is marked as the gastrointestinal villi structure; * indicates significant difference (P<0.05), ** indicates extremenly significant difference (P<0.01).2.3 胃和结肠的微生组成结构
试验结束时,各采集18只育肥猪的胃液和结肠的黏液进行16S rRNA基因测序。结果如图2、3所示:试验组育肥猪的胃黏液属水平的乳酸菌丰度(平均67.81%)比试验组高(13.54%)(P<0.05),胃黏液属水平的艰难梭菌属(4.51%)比对照低(5.55%),差异显著(P<0.05)。结肠黏液属水平的乳酸菌丰度(平均6.51%)比试验组高(3.17%),差异显著(P<0.05),结肠黏液属水平艰难梭菌属(2.32%)比对照低(3.73%),差异显著(P<0.05)。结果表明,在育肥猪日粮中添加复合菌有促进乳酸菌属丰度、降低艰难梭菌属丰度的作用。
3. 讨论
3.1 饲喂复合微生物菌对育肥猪生产性能的影响
育肥猪生产性能的改善,主要体现在日增重增加、耗料增重比的下降等多个方面。本研究结果表明,饲用复合微生物菌明显增加日增重,降低耗料增重比,与任瑞兰等[15]、马雪花等[16]、何志刚等[17]和文廷富等[18]的试验结果较为一致。此外,从15 d开始,一直持续到90 d,育肥猪的日增重明显增加,耗料增重比也明显降低。本研究中使用的复合菌剂包括了6大类菌,充分考虑到育肥猪胃肠道的不同位置对于微生物菌提供的不同生长条件,胃和十二指肠相对开放,需氧菌多于厌氧菌,而结肠和盲肠相对密闭,大部分是厌氧菌。之前很多的研究报道,都证实了微生物菌的添加功效[19-21],但极少考虑不同位置的胃肠道菌群差异,因此很多研究结果与实际应用存在一定差异。本试验充分考虑胃肠道不同位置菌群分布,通过复合菌添加,让不同菌定植于不同位置,从而保证了外来菌群能够有效影响内在菌群平衡。从研究结果看,添加复合菌剂的效果确实持续存在,具体的机理尚待进一步的研究。
3.2 饲喂复合微生物菌对胃肠道绒毛结构影响
胃肠道绒毛结构影响营养物质的消化吸收,添加微生态制剂是否能改善生产性能,首要考察其对胃肠道绒毛结构生长是否有促进作用[22]。本试验比较分析添加复合菌剂组胃、结肠和盲肠的肠道形态及绒毛长度。结果发现,添加复合菌组结肠和盲肠的绒毛比对照组长,与李长军等[23]、孙媛等[24]用微生态制剂饲喂仔猪促进猪肠道绒毛发育,以及欧阳志周[25]通过添加丁酸梭菌可促进猪肠道绒毛发育的结果较接近。此外,本次试验也发现,饲喂复合微生物菌的育肥猪的胃壁肌层较厚,绒毛长度比对照组长。从胃动力学可知,胃壁肌层厚度越厚,越有利于饲料在胃里的初级消化。而胃的绒毛长度可延长营养物质在胃壁的滞留时间,同时也延长微生物在胃壁的作用时间,进一步促进了营养物质在胃里的消化吸收,从而对生产性能进行改善[26]。
3.3 饲喂复合微生物菌对育肥猪肠道微生物的影响
育肥猪肠道微生物是宿主营养物质消化和吸收的关键,对宿主免疫及疾病等起着重要的调控作用。同时肠道微生物菌群结构又受到宿主胃肠道内环境以及日粮、品种、外界环境等的影响[27]。本试验中添加的复合微生物菌剂,明显增加胃和结肠的乳酸菌属的丰度。胃里的乳酸菌不仅可促进乳糖、蛋白质、单糖及钙、镁等营养物质的吸收,产生B族维生素等大量有益物质;同时还可增加肠道有益菌群,改善胃肠道功能,恢复肠道内菌群平衡,形成抗菌生物屏障,维护宿主健康;还可抑制腐败菌的繁殖,消解腐败菌产生的毒素,清除肠道垃圾等。因此,推测胃、结肠的乳酸菌属的丰度增加是改善育肥猪生产性能的重要因素。
此外,本研究也证实,添加复合益生菌可减少艰难梭菌为主的有害梭菌的增殖。有害梭菌的减少可促进菌群平衡,维护肠道结构功能,提高营养物质的消化吸收,从而改善生产性能。本试验和杨红萍等[28]添加复合微生态制剂可显著增加盲肠、结肠、直肠中乳酸杆菌、双歧杆菌数量以及杜泓明等[29]添加复合益生菌培养物影响断奶仔猪的盲肠微生物区系的结果较为一致。
4. 结论
复合菌剂可增加育肥猪胃、结肠和盲肠的肠壁绒毛长度,增加胃和结肠的乳酸菌属的丰度,同时减少以艰难梭菌为主的有害梭菌的增殖,维护肠道结构功能,保证菌群平衡,促进生产性能的提升,可作为饲料添加剂在生产中应用。
-
-
[1] KIMURA T. Natural products and biological activity of the pharmacologically active cauliflower mushroom Sparassis crispa [J]. BioMed Research Intermational, 2013, 8(3): 501−508.
[2] CHANDRASEKARAN G, OH D S, SHIN H J. Properties and potential applications of the culinary-medicinal cauliflower mushroom, Sparassis crispa (Wulf.: Fr.) (Aphyllophoromycetideae): a review [J]. International Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms, 2011, 13(2): 177−183. DOI: 10.1615/IntJMedMushr.v13.i2.100
[3] KIM H S, KIM J Y, RYU H S, et al. Induction of dendritic cell maturation by β-glucan isolated from Sparassis crispa [J]. International Immunopharmacology, 2010, 10(10): 1284−1294. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2010.07.012
[4] KIM H H, LEE S, SINGH T S, et al. Sparassis crispa Suppresses mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation: Role of calcium, mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-κB [J]. Intermational Journal of Molecular Medicine, 2012, 30(2): 344−350. DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2012.1000
[5] 白晨, 宋文荣, 杨剑飞, 等. 绣球菌子实体干燥条件与多糖保留率相关性研究 [J]. 食品科学, 2012, 33(20):119−122. BAI C, SONG W R, YANG J F, et al. Effect of Drying Methods on Retention Rate of Polysaccharides in Sparassia crispa Fruit Bodies [J]. Food Science, 2012, 33(20): 119−122.(in Chinese)
[6] 朱美静, 童群义. 猴头多糖脱蛋白方法的研究 [J]. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 26(4):25−27. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2383.2005.04.007 ZHU M J, TONG Q Y. Study on Removal of Proten from Hericium erinaceus Polysaccharides [J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2005, 26(4): 25−27.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2383.2005.04.007
[7] 金丽琴, 薛胜霞, 吕建新, 等. 牛膝多糖衍生物对小鼠脾淋巴细胞增殖及诱生IL-2和TNF-α的影响 [J]. 中国生化药物杂志, 2008, 29(5):312−314. JIN L Q, XUE S X, LU J X, et al. Effect of derivatives of Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharides on lymphocyte proliferation and induction of IL-2 and TNF- [J]. Chinese Journal of Biochemical Pharmaceutics, 2008, 29(5): 312−314.(in Chinese)
[8] JAMAS S, EASSON D, STROFF GRO, et al. Method for producing soluble glucan: United States Patent, 5633369[P]. 1997.
[9] TZIANABOS A O. Polysaccharide immunomodulators as therapeutic agents: structural aspects and biologic function [J]. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 2000, 13(4): 523−533. DOI: 10.1128/CMR.13.4.523
[10] 张迪, 王宏雨, 林衍铨. 不同干制方法对广叶绣球菌多糖提取率和分子量分布的影响 [J]. 中国食用菌, 2017, 36(3):54−56. ZHANG D, WANG H Y, LIN Y Q. Effects of Different Drying Methods on Extraction Rate and Molecular Weight Distribution of Polysaccharides from Sparassis latifolia [J]. Edible Fungi of China, 2017, 36(3): 54−56.(in Chinese)
[11] 钱正明, 李文庆, 孙敏甜, 等. 冬虫夏草化学成分分析 [J]. 菌物学报, 2016, 35(4):476−490. QIAN Z M, LI W Q, SUN M T, et al. Analysis of chemical compounds in Chinese cordyceps [J]. Mycosystema, 2016, 35(4): 476−490.(in Chinese)
[12] 马晓丽, 孟磊, 孙莲, 等. HPLC分析大蒜多糖中的单糖 [J]. 中国现代应用药学杂志, 2009, 26(7):585−587. MA X L, MENG L, SUN L, et al. Determination of Monosaccharide Compositions and Contents in Polysaccharide of Garlic by HPLC [J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy, 2009, 26(7): 585−587.(in Chinese)
[13] 李平厉. 硫酸化可德兰多糖的制备、体外免疫调节、抗乙肝病毒感染活性及体内用作乙肝疫苗[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2014. LI P L. Studies on the preparation, in vitro immunoregulatory andanti-hepatitis B virus infection activities and invivo action as a hepatitis B vaccine adjuvant of curdlan sulfate[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2014. (in Chinese)
[14] 陈晓兰, 杨海峰, 瞿静雯, 等. 不同桑叶提取物对小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞增殖能力的影响 [J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2017, 44(12):3598−3604. CHEN X L, YANG H F, QU J W, et al. Effect of Different Mulberry Leaf Extracts on Spleen Lymphocyte Proliferation in Mice [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2017, 44(12): 3598−3604.(in Chinese)
[15] RUI TADA, TOSHIE HARADA, NORIKO NAGI-MIUR, et al. NMR characterization of the structure of a b-(1, 3)-D-glucan isolate from cultured fruit bodies of Sparassis crispa [J]. Carbohydrate Research, 2007, 342: 2611−2618. DOI: 10.1016/j.carres.2007.08.016
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 陆东,王燕,周化鹏,陆璐,寇建新. 奇台县基于宽膜种植的不同玉米品种比较研究. 粮油与饲料科技. 2024(11): 25-27 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: