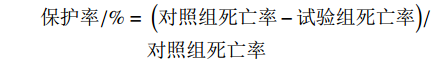Effects of Feeding Schizochytrium on Anti-Vibrio vulnificus Infection in Zebrafish
-
摘要:目的 研究饲料中添加裂殖壶菌对鱼类抗细菌感染能力的影响,为裂殖壶菌作为饲料添加剂的应用提供理论基础。方法 以6个月的成年斑马鱼为研究对象,以基础颗粒饲料为对照组(C组),试验组在基础饲料中添加干重3%的裂殖壶菌(S组),进行28 d饲喂试验。28 d后以创伤弧菌Vibrio vulnificus菌株FJ03-X2对斑马鱼进行攻毒,统计免疫保护率,并收集斑马鱼的肾脏组织提取RNA,逆转录成cDNA,通过Real-time RT-PCR检测相关基因lysozyme和tnfb的表达。结果 饲料中添加3%裂壶菌能够显著提高斑马鱼感染创伤弧菌后的存活率,相对保护率为42.8%;Real-time RT-PCR检测的结果发现S组的斑马鱼肾脏中溶菌酶Lysozyme的mRNA水平极显著高于对照组(P<0.01),而肿瘤坏死因子TNFb的mRNA水平则极显著低于对照组(P<0.01)。结论 裂殖壶菌作为营养添加剂可以提高斑马鱼抗创伤弧菌感染的能力。Abstract:Objective A feeding experiment was conducted in order to study the effects of feeding Schizochytrium on the resistance of fish to bacterial infection.Methods Six-month adult zebrafishes were fed with diety added 3% Schizochytrium(Group S) for 28 days in a laboratory culture system, and the control with only basic diety(Group C). Then Vibrio vulnificus FJ03-X2 was applied for infection, and the relative survival percent of zebrafishes were analyzed. And RNA was extracted from the kidney tissues and reverse transcribed into cDNA to detect the experison of lysozyme and tnfb.Results The survival rate of Group S was significantly increased with immune protective rate reaching 42.8%. The mRNA level of Lysozyme in the kidney of zebrafish in Group S was significantly higher than that in the control (P<0.01), while the mRNA level of TNFb was significantly lower than that in the control group (P<0.01).Conclusion As a nutrient additive, Schizochytrium could improve the ability of zebrafish to resist bacterial infection, which provided a theoretical basis for the application of Schizochytrium in fishery industry.
-
Keywords:
- Schizochytrium /
- zebrafish /
- Vibrio vulnificus /
- feed additive
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】脂肪酸是构成动物日粮油脂的主要组成部分。目前大量的研究表明,脂肪酸作为一种调节因子,参与众多细胞的功能、炎症反应及免疫力的调节[1]。其中研究较多的脂肪酸是多不饱和脂肪酸(poly unsaturated fatty acids,PUFAs)。PUFAs来源较广,但高度不饱和脂肪酸(HUFAs)则只在深海鱼类和海藻中含量较高。绝大部分动物不能新合成ω-3 PUFAs和ω-6 PUFAs,动物体只能通过日粮摄取补充。目前较主流的方法就是在饲料中添加含有大量不饱和脂肪酸的鱼油或藻类[2]。相对于鱼油容易氧化、会污染水质等不足,来自于海水的微藻是更理想的饲料添加剂。通过在基础饲料中添加富含PUFAs的裂殖壶菌,了解其对斑马鱼的免疫力特别是抗菌能力的影响,可为开发新型富含多不饱和脂肪酸的饲料添加剂提供理论基础,也为养殖业的病害综合防治提供参考。【前人研究进展】裂殖壶菌(Schizochytrium)又称裂壶藻,是一类海洋真菌。营养成分研究分析表明其中脂肪酸含量相当高,甚至可占细胞干重50%以上,总脂肪酸中DHA含量高达35%–40%,其他脂肪酸含量低[3-4]。PUFA暴露在空气中容易氧化,但是在裂殖壶菌中是包被于细胞内而不易氧化,而且细胞内的DHA含量还可以通过培养基的优化来控制。PUFAs具有许多特殊的生理功能,如调节肠道健康以及具有抗菌活性,还具有抗炎及调节免疫的活性。有研究表明:ω-3PUFAs与炎症反应密切相关,能有效降低促炎症因子FGE2和白三烯B4的生成,同时对IL-6、IL-8和TNF-α等促炎症因子也有一定抑制作用[5]。给注射脂多糖LPS的动物或烧伤的动物饲喂含有大量PUFAs的鱼油后,其循环血液中TNF-α、IL-1及IL-6浓度相应降低,从而降低迟发超敏反应的强度[6-7]。大鼠或小鼠饲以缺乏多不饱和脂肪酸ω-3PUFAs或ω-6PUFAs的日粮后,巨噬细胞介导的吞噬作用和细胞毒性作用以及中性粒细胞的趋化性都出现减弱[8]。此外,研究发现ω-3PUFAs还能促进细胞凋亡以及其他形式的细胞死亡而具有抗肿瘤的活性[9]。此外,裂殖壶菌的细胞内还含有丰富的维生素、必需氨基酸等其他营养成分,与酵母、鱼油相比有更高的实用价值。创伤弧菌(Vibrio vulnificus)是一种常见的、分布广泛的嗜盐性革兰氏阴性病原菌[10]。它是一种人兽共患的致病菌,能引起原发性败血症和软组织感染,曾导致日本和欧美等国鳗鲡产业的巨大经济损失[11]。创伤弧菌也是近年来在福建沿海水产养殖中较为常见、危害较大的病原菌。【本研究切入点】以往对裂殖壶菌作为饲料添加剂的研究主要集中于对动物生长性能的提高,对其影响动物尤其是水生动物免疫性能方面的探索并不深入,主要检测相关生化指标或免疫相关酶的活性[12-14]。本研究以常见的水产病原菌对斑马鱼进行攻毒试验,更为直接地研究裂殖壶菌添加对动物的抗菌能力的影响,并检测了相关免疫因子,对其中的机制进行探索。【拟解决的关键问题】为了解裂殖壶菌作为饲料添加剂的作用效果,本课题组以斑马鱼为研究对象,在基础饲料中添加裂殖壶菌。饲喂28 d后,以福建省常见的水产病原菌创伤弧菌进行攻毒试验,计算免疫保护率并检测斑马鱼的相关炎症因子的表达变化,以此来评估裂殖壶菌作为饲料添加剂在提高鱼类抗菌能力方面的作用,了解以DHA为代表的多不饱和脂肪酸是通过何种途径影响斑马鱼抗菌能力,为裂殖壶菌作为饲料添加剂的应用提供研究基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
1.1.1 菌株
裂殖壶菌(资源编号ATCC MYA-1381)由福建师范大学生命科学学院惠赠。创伤弧菌FJ03-X2是福建省农业科学院生物技术研究所鱼病研究室于2003年在福建省长乐某养殖场分离到的一株鳗源创伤弧菌[15],保存于−80℃。
1.1.2 试验动物
斑马鱼亲鱼购自国家斑马鱼资源中心,6个月大的成年野生型AB系斑马鱼由本实验室自主繁殖,平均体重约为0.2 g,健康状况良好。
1.1.3 主要试剂
酵母提取物、蛋白胨、D-葡萄糖均购自上海生工生物工程有限公司;海盐(益尔Yier);培养基TSA、TSB均购自广东环凯微生物科技有限公司;0.1%DEPC处理水;氯仿;异丙醇;无水乙醇;Trizol试剂(Invitrogen,Cat. No. 15596026);试剂盒PrimeScript™ RT reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser(Perfect Real Time)和SYBR® Premix Ex Taq™ II(RR820A)均购自大连宝生物工程有限公司(TaKaRa)。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 裂殖壶菌培养及冷冻干燥
培养基参考ATCC Medium 790 By+ Medium:每升中含酵母提取物1.0 g,蛋白胨1.0 g,D-葡萄糖5.0 g,海盐27.5 g。锥形瓶加盖可通气瓶塞培养60 h,温度20℃,摇床转速220 r·min−1。无需光照。
收集裂殖壶菌,室温8 000 r·min−1离心10 min,去除上清,将收集的沉淀置于冷冻干燥仪中冻干24 h,样品的脂肪酸含量经福建省农业科学院农业质量标准与检测技术研究所测定(检测标准GB 5009.168-2016)。用研钵将冻干的裂殖壶菌磨成粉末,以3%的比例添加入基础饲料中,充分混匀,放置于阴凉干燥处备用。
1.2.2 裂殖壶菌对斑马鱼的养殖投喂
试验用水族箱大小约为15 cm×25 cm×40 cm,带自动循环控温及紫外消毒过滤系统。净水器过滤自来水,曝气24 h作为循环水源,控制水温(28±1)℃,盐度0.05%,每个水族箱放养斑马鱼20尾。斑马鱼每天上、下午各饲喂1次,投饵量为体重的1%,对照组饲喂基础饲料,试验组饲喂上述添加干重3%的裂殖壶菌的基础饲料,攻毒试验前一天禁食。基础饲料为台湾海丰宝赠红小型鱼饲料,基础营养成分见表1。
表 1 基础饲料的营养成分Table 1. Nutrient composition of basic feed成分 Ingredient 含量 Content/% 粗蛋白质 Crude protein ≥40.0 粗纤维 Crude fiber ≤4.0 氨基酸 Amino acid ≥30.0 粗灰分 Crude ash ≤16.0 水分 Water content ≤11.0 盐分 Salt ≤3.0 总磷 Total phosphorus content ≥0.9 钙 Calcium ≥1.5 1.2.3 斑马鱼创伤弧菌攻毒试验
创伤弧菌FJ03-X2的培养、复苏及活化参考文献[15]的方法进行。创伤弧菌对斑马鱼半致死剂量的测定方法参考文献[16]的方法。
对照组(C组)和试验组(S组)的斑马鱼各15尾以MS-222麻醉后,分别以上述半致死量的创伤弧菌进行攻毒。每天观察记录死亡情况,试验持续1周,统计保护率。攻毒试验重复3次。
保护率/%=(对照组死亡率−试验组死亡率)/对照组死亡率 1.2.4 Real-time RT-PCR检测斑马鱼相关基因的表达
总RNA的提取:在FJ03-X2攻毒24 h后,分别解剖各组存活和死亡的斑马鱼肾脏组织(每组随机选取3尾),参照TRIzol® Reagent说明书,提取总RNA。以NanoDrop Spectrophotometer ND-1000进行RNA的浓度测定。
逆转录反应:严格按照PrimeScript RT reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser试剂盒说明书的操作步骤,将上述总RNA进行逆转录,合成cDNA。反应结束后,将制备的cDNA保存于−40℃,待用。
SYBR Green Real-time RT-PCR:采用SYBR Green Ⅰ嵌合荧光法,按SYBR® Premix Ex Taq™ II(RR820A)说明书配制反应体系。反应体系为20 μL:10 μL SYBR Premix Ex Taq (2×),1 μL上游引物,1 μL下游引物,0.4 μL ROX Reference DyeⅡ(50×),1 μL cDNA模板,6.6 μL ddH2O。Real-time PCR在ABI 7500实时荧光定量PCR 仪上进行,反应程序:95℃预变性30 s;95℃变性5 s、退火温度60℃下退火34 s;40个循环用于检测PCR扩增特异性的熔解曲线反应程序为:95℃ 15 s,60℃ 60 s,95℃ 15 s。实时荧光定量测定方法参照文献[16],以β-actin作为内参基因,以未添加模板的反应体系作为空白对照,Real-time RT-PCR引物由上海生工生物工程有限公司合成(表2),每个样品3个平行。反应结束后,通过熔解曲线分析产物的单一性,并利用2−△△Ct来确定每个基因的相对表达量。公式如下:
表 2 PCR引物序列Table 2. PCR primer sequence目的基因 Objective gene 正向引物序列(5′-3′)Forward primer sequence(5′-3′) 反向引物序列(5′-3′)Reverse primer sequence(5′-3′) actb1 CACTTCACGCCGACTCAAAC TCGGGGATGCTTATTTGCCA tnfb GCCAACCCATTTCAGCGATTG GGCATGTGATGAAGCCAAACGAA lysozyme CCGTAGTCCTTCCCCGTATCA GATTTGAGGGATTCTCCATTGG △Ct=Ct(目的基因)− Ct(β-actin基因)。目的基因在试验组中相对于对照组的表达差异倍数用2−△△Ct计算表示,而−△△Ct=−(△Ct试验组−△Ct对照组)。
1.3 数据分析
利用Excel 2010软件对数据进行统计分析。基因表达结果采用相对表达量的形式,所有数值以平均值±标准差表示,以P<0.01为差异极显著标准,P<0.05为差异显著标准。应用Excel 2010和SPSS16.0软件对数据进行统计分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 裂殖壶菌的脂肪酸含量及各脂肪酸组成
经测定,裂殖壶菌总脂肪酸含量占干重的25.2%,其中DHA含量占总脂肪酸的39.62%,EPA含量占总脂肪酸的1.25%,详细结果见表3。
表 3 裂殖壶藻ATCC MYA-1381的脂肪酸组成Table 3. Fatty acid composition of Schizochytrium ATCC MYA-1381脂肪酸 Fatty acid 百分比 Percentage% C14∶0 3.81 C15∶0 0.95 C16∶0 43.22 C16∶1n7c 0.16 C17∶0 0.38 C17∶1n7c 0.13 C18∶0 0.74 C18∶1n9c 0.08 C18∶2n6c 0.04 C18∶3n3c 0.07 C20∶0 0.19 C20∶3n6c 0.67 C20∶4n6c 0.17 C20∶5n3c 1.25 C23∶0 0.08 C24∶0 0.08 C22∶6n3c 39.62 其他 Others 8.35 2.2 斑马鱼创伤弧菌攻毒试验结果
创伤弧菌以半致死量攻毒12 h后,部分斑马鱼开始出现腮、腹部、尾鳍出血以及腹水等典型的败血症症状,陆续死亡。攻毒后24 h–7 d各组斑马鱼均未再出现死亡。C组(对照组)的死亡率为46.7%,接近半致死量;S组(试验组)的平均死亡率为26.7%,保护率达到42.8%(表4)。
表 4 斑马鱼创伤弧菌攻毒试验Table 4. Infection test of zebrafish with Vibrio vulnificus组别 Groups 攻毒尾数 Total number 死亡尾数 Dead number 死亡率 Death rate(24 h) 免疫保护率 Relative survival percent(RPS) 对照组 Control group 15 7 46.7% — 试验组 Experimental group 15 4 26.7% 42.8% 2.3 免疫相关基因lysozyme和tnfb在斑马鱼肾脏中的表达
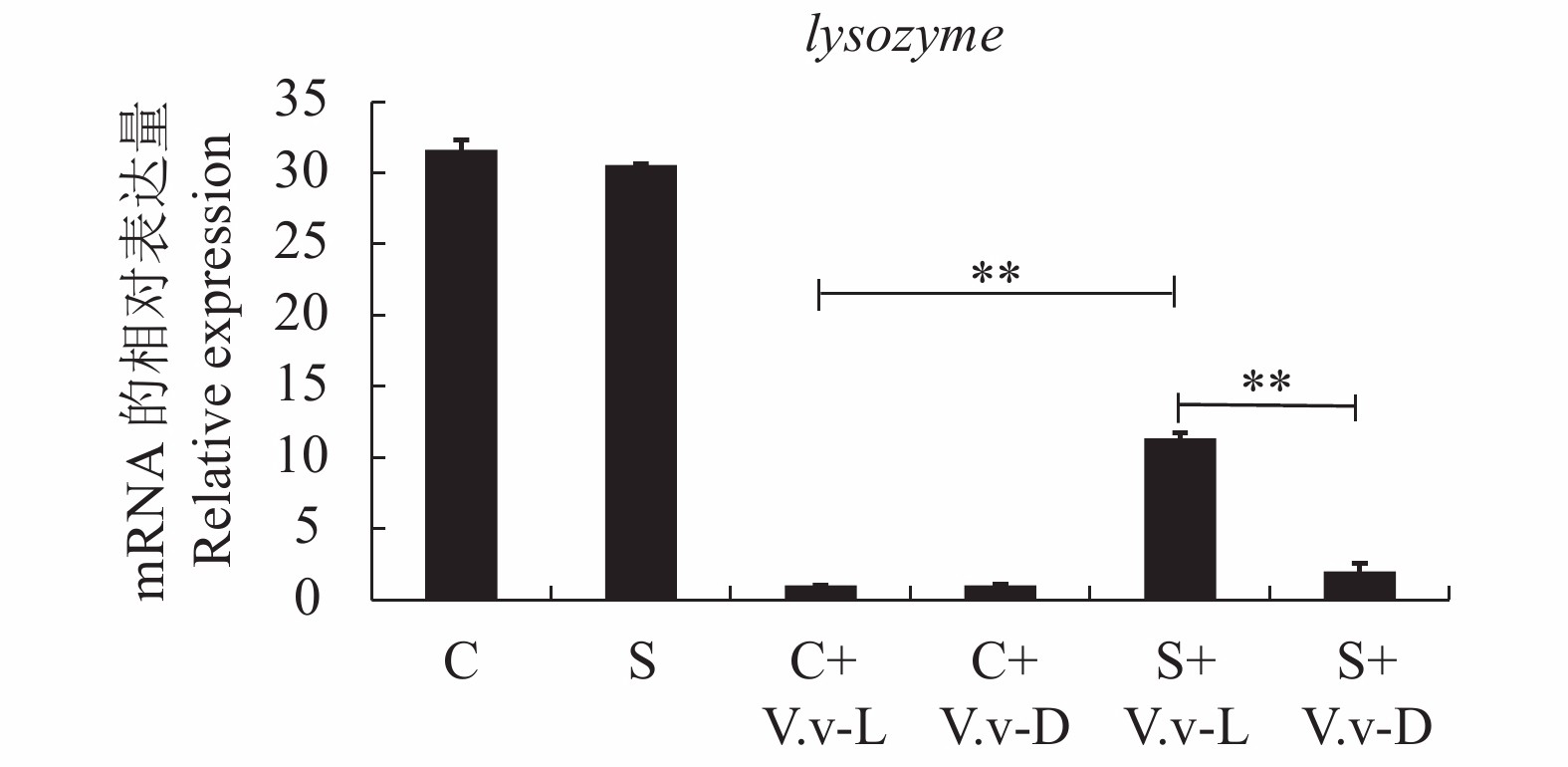
创伤弧菌攻毒前后C组和S组斑马鱼肾脏中lysozyme和tnfb的mRNA水平如图1、2所示。lysozyme的检测结果(图1)显示:1)创伤弧菌攻毒后,斑马鱼肾脏中lysozyme表达急剧降低,尤其是攻毒后死亡的斑马鱼;2)S组lysozyme表达水平高于C组,其中S组存活的斑马鱼中lysozyme的表达水平极显著高于C组存活的斑马鱼(P<0.01);3)S组内存活的斑马鱼lysozyme的表达极显著高于死亡的斑马鱼(P<0.01)。表明饲料中添加裂殖壶菌可通过提高lysozyme的表达水平来抵抗细菌的感染,从而对斑马鱼产生保护作用,提高其存活率。
![]() 图 1 Real-time RT-PCR检测创伤弧菌感染后肾脏中lysozyme的mRNA水平注:C为对照组攻毒前;S为试验组攻毒前;C+V.v-L为对照组创伤弧菌攻毒存活的斑马鱼;C+V.v-D为对照组创伤弧菌攻毒死亡的斑马鱼;S+V.v-L为试验组创伤弧菌攻毒存活的斑马鱼;S+V.v-D为试验组创伤弧菌攻毒死亡的斑马鱼;**表示试验组与对照组存在极显著性差异P<0.01。图2同。Figure 1. mRNA level of lysozyme in the kidney of zebrafish under infection by Vibrio vulnificusNote: C-Zebrafish in the control group before challenge; S-Zebrafish in the experimental group before challenge; C+V.v-L-Survival zebrafish in the control group challenged by Vibrio vulnificus; C+V.v-D-Dead zebrafish in the control group challenged by Vibrio vulnificus; S+V.v-L- Survival zebrafish in the experimental group challenged by Vibrio vulnificus; S+V.v-D- Dead zebrafish in the experimental group challenged by Vibrio vulnificus; **-The value indicates significant difference,P<0.01. The same as Fig. 2.
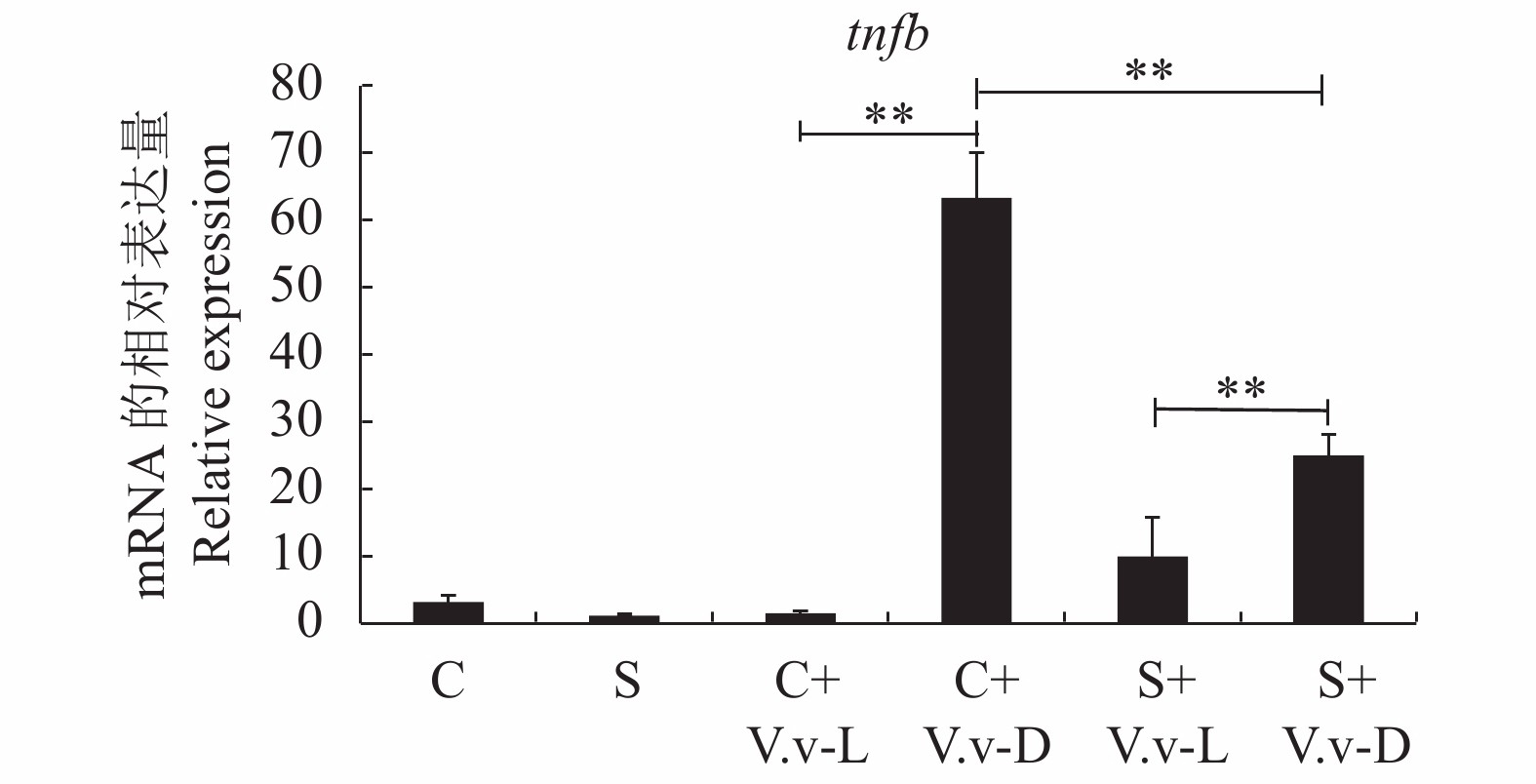
图 1 Real-time RT-PCR检测创伤弧菌感染后肾脏中lysozyme的mRNA水平注:C为对照组攻毒前;S为试验组攻毒前;C+V.v-L为对照组创伤弧菌攻毒存活的斑马鱼;C+V.v-D为对照组创伤弧菌攻毒死亡的斑马鱼;S+V.v-L为试验组创伤弧菌攻毒存活的斑马鱼;S+V.v-D为试验组创伤弧菌攻毒死亡的斑马鱼;**表示试验组与对照组存在极显著性差异P<0.01。图2同。Figure 1. mRNA level of lysozyme in the kidney of zebrafish under infection by Vibrio vulnificusNote: C-Zebrafish in the control group before challenge; S-Zebrafish in the experimental group before challenge; C+V.v-L-Survival zebrafish in the control group challenged by Vibrio vulnificus; C+V.v-D-Dead zebrafish in the control group challenged by Vibrio vulnificus; S+V.v-L- Survival zebrafish in the experimental group challenged by Vibrio vulnificus; S+V.v-D- Dead zebrafish in the experimental group challenged by Vibrio vulnificus; **-The value indicates significant difference,P<0.01. The same as Fig. 2.斑马鱼肾脏中tnfb的表达情况(图2)可以看出:1)攻毒前S组斑马鱼肾脏的tnfb表达水平低于C组;2)攻毒后S组与C组存活的斑马鱼相较于死亡的斑马鱼,其肾脏中tnfb的表达极显著降低(P<0.01),而与各自攻毒前的表达水平差异不大;3)死亡的斑马鱼中S组的tnfb表达相对于C组也极显著降低(P<0.01)。这一结果暗示:短时间内tnfb的过量表达有可能对斑马鱼造成不利影响,导致感染后死亡;饲料中添加裂殖壶菌可以抑制tnfb的过量表达,从而提高斑马鱼急性感染后的存活率。
3. 讨论与结论
本研究中应用的菌株ATCC MYA-1381经测定总脂肪酸含量占干重的25.2%,其中多不饱和脂肪酸DHA含量占总脂肪酸的39.62%,EPA含量占总脂肪酸的1.25%,与文献报道的结果一致[4]。
大量研究表明,饲料中添加裂殖壶菌能提高动物的生长性能,并且随着添加量的提高,其生长速度也随之增加:例如Matthew等[17]的研究表明,在大西洋鲑鱼的饮食中用裂殖壶菌油替代鱼油,可以显著提高鱼肉组织中的DHA含量;裂殖壶菌作为鱼油DHA替代资源在金头海鲷养殖上也显示出的巨大潜力[18];以正常商品饲料作对照,用1%的裂殖壶菌投喂对虾,其生长率、成活率有显著性差异[12];焦建刚等[13]的研究表明,在对虾基础饲料中添加0.5%的裂殖壶菌发酵粉,可明显地促进其生长,降低饲料系数(FCR),提高肌肉中蛋白质及DHA的含量,改善了对虾的品质。本研究选择的是6个月的成年斑马鱼,发现饲喂28 d后,试验组和对照组的体重、体长并没有显著差异。后期将会对3个月以下的幼鱼进行饲喂,以便更好地了解裂殖壶菌的添加对斑马鱼生长发育的影响。
本研究试验发现C组(基础饲料组)的平均死亡率为46.7%,接近半致死量。S组(裂殖壶菌添加组)的平均死亡率为26.7%,保护率达到42.8%。说明饲料中添加裂殖壶菌具能够有效提高斑马鱼的抗创伤弧菌感染的能力。研究表明饲料中添加裂殖壶菌可显著提高对虾组织中超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、溶菌酶(LZM)、丙二醛(MDA)等免疫指标(P<0.05)[12];黄亮华等[14]发现在饲料中添加裂殖壶菌除了可以提高刺参的特定生长率(SGR),还可以明显提高其体腔液中的SOD、LZM、酸性磷酸酶(ACP)、碱性磷酸酶(AKP)等的活性。说明裂殖壶菌作为一种天然的海洋真菌,对水生生物机体具有明显的免疫刺激作用。
鱼类具有特异性和非特异性免疫反应,但与哺乳动物相比,其特异性免疫机制发育尚不完全。非特异性免疫是鱼类免疫系统的第一道防线,具有作用范围广,反应快,遗传性等特点,是一切免疫防御的基础[19-20]。为了进一步探究添加裂殖壶菌对鱼类的非特异免疫调节的机理,本研究通过荧光定量PCR技术,检测了斑马鱼肾脏组织中免疫相关基因lysozyme和tnfb的表达情况。
溶菌酶(Lysozyme)作为非特异性免疫的重要因子,在抵御病原菌入侵过程中发挥重要作用,是机体免疫机能的重要评价指标之一[21-22]。本研究中,创伤弧菌攻毒后,斑马鱼肾脏中lysozyme表达急剧降低,特别是攻毒后死亡的斑马鱼,说明lysozyme的表达水平与斑马鱼的抗菌能力密切相关。值得注意的是:S组与C组相比lysozyme表达水平上调,其中S组存活的斑马鱼中lysozyme的表达较C组存活的斑马鱼显著上调。这一结果提示饲料中添加裂殖壶菌可能通过提高斑马鱼的lysozyme表达水平来抵抗细菌的感染,从而产生保护作用,提高其存活率。
肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)不仅具有杀伤和抑制肿瘤细胞的作用,同时也是重要炎症介质之一,具有抗感染,促进细胞增殖和分化等作用。TNF常被称为一把双刃剑,它与细菌感染的关系是两方面的:一方面适量TNF有助于增强中性粒细胞和单核巨噬细胞的吞噬杀伤功能,促进病原菌的消除,增强局部组织的抗感染能力,从而保护机体[23];另一方面过量的TNF则介导组织炎症损伤,引起多器官功能损害、循环衰竭,是高死亡率的重要病理机制之一[24]。本研究中,攻毒前S组斑马鱼肾脏的tnfb表达水平低于C组;攻毒后这两组存活的斑马鱼肾脏中tnfb的表达显著低于死亡的;死亡的斑马鱼中S组的tnfb表达也显著相低于C组。提示细菌感染后短时间内tnfb的过量表达可能对斑马鱼造成不利影响,导致其死亡;饲料中添加裂殖壶菌可能通过抑制tnfb的过量表达,从而提高斑马鱼急性感染后的存活率。这一结果与DHA可以抑制斑马鱼炎症因子如TNF、IL-1β以及NF-κB等的表达,从而提高斑马鱼在病原菌攻毒后的存活率相一致[25]。
在下一步的研究中,我们将检测斑马鱼中更多的免疫相关因子,特别是IL-1β、NF-κB、IL-6以及IL-8等炎症因子的表达情况,并检测SOD、MDA、ACP、AKP、CAT等免疫指标,从而进一步了解裂殖壶菌提高斑马鱼抗感染能力的作用机制。
综上所述,饲料中添加裂殖壶菌可以提高斑马鱼抵抗创伤弧菌感染的能力,提高其存活率。本研究提供了一种新的思路:养殖业病害的防控可以从病原入手,如使用有效的药物或疫苗,也可以从饲料入手,通过有效的添加剂增强动物的免疫力,减轻症状,提高生存率。
-
图 1 Real-time RT-PCR检测创伤弧菌感染后肾脏中lysozyme的mRNA水平
注:C为对照组攻毒前;S为试验组攻毒前;C+V.v-L为对照组创伤弧菌攻毒存活的斑马鱼;C+V.v-D为对照组创伤弧菌攻毒死亡的斑马鱼;S+V.v-L为试验组创伤弧菌攻毒存活的斑马鱼;S+V.v-D为试验组创伤弧菌攻毒死亡的斑马鱼;**表示试验组与对照组存在极显著性差异P<0.01。图2同。
Figure 1. mRNA level of lysozyme in the kidney of zebrafish under infection by Vibrio vulnificus
Note: C-Zebrafish in the control group before challenge; S-Zebrafish in the experimental group before challenge; C+V.v-L-Survival zebrafish in the control group challenged by Vibrio vulnificus; C+V.v-D-Dead zebrafish in the control group challenged by Vibrio vulnificus; S+V.v-L- Survival zebrafish in the experimental group challenged by Vibrio vulnificus; S+V.v-D- Dead zebrafish in the experimental group challenged by Vibrio vulnificus; **-The value indicates significant difference,P<0.01. The same as Fig. 2.
表 1 基础饲料的营养成分
Table 1 Nutrient composition of basic feed
成分 Ingredient 含量 Content/% 粗蛋白质 Crude protein ≥40.0 粗纤维 Crude fiber ≤4.0 氨基酸 Amino acid ≥30.0 粗灰分 Crude ash ≤16.0 水分 Water content ≤11.0 盐分 Salt ≤3.0 总磷 Total phosphorus content ≥0.9 钙 Calcium ≥1.5 表 2 PCR引物序列
Table 2 PCR primer sequence
目的基因 Objective gene 正向引物序列(5′-3′)Forward primer sequence(5′-3′) 反向引物序列(5′-3′)Reverse primer sequence(5′-3′) actb1 CACTTCACGCCGACTCAAAC TCGGGGATGCTTATTTGCCA tnfb GCCAACCCATTTCAGCGATTG GGCATGTGATGAAGCCAAACGAA lysozyme CCGTAGTCCTTCCCCGTATCA GATTTGAGGGATTCTCCATTGG 表 3 裂殖壶藻ATCC MYA-1381的脂肪酸组成
Table 3 Fatty acid composition of Schizochytrium ATCC MYA-1381
脂肪酸 Fatty acid 百分比 Percentage% C14∶0 3.81 C15∶0 0.95 C16∶0 43.22 C16∶1n7c 0.16 C17∶0 0.38 C17∶1n7c 0.13 C18∶0 0.74 C18∶1n9c 0.08 C18∶2n6c 0.04 C18∶3n3c 0.07 C20∶0 0.19 C20∶3n6c 0.67 C20∶4n6c 0.17 C20∶5n3c 1.25 C23∶0 0.08 C24∶0 0.08 C22∶6n3c 39.62 其他 Others 8.35 表 4 斑马鱼创伤弧菌攻毒试验
Table 4 Infection test of zebrafish with Vibrio vulnificus
组别 Groups 攻毒尾数 Total number 死亡尾数 Dead number 死亡率 Death rate(24 h) 免疫保护率 Relative survival percent(RPS) 对照组 Control group 15 7 46.7% — 试验组 Experimental group 15 4 26.7% 42.8% -
[1] STROBEL C, JAHREIS G, KUHNT K. Survey of n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids in fish and fish products [J]. Lipids in Health and Disease, 2012, 11(1): 144. DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-11-144
[2] BELL J G, HENDERSON R J, TOCHER D R, et al. Substituting fish oil with crude palm oil in the diet of Atlantic salmon(Salmo salar) affects muscle fatty acid composition and hepatic fatty acid metabolism [J]. The Journal of Nutrition, 2002, 132(2): 222−230. DOI: 10.1093/jn/132.2.222
[3] 李美玉, 李健, 陈萍, 等. 维生素E和裂壶藻对中国对虾生长及TLR/NF-κB表达水平的影响 [J]. 中国渔业质量与标准, 2012, 2(2):37−44. LI M Y, LI J, CHEN P, et al. Effects of VE and Schizochytrium on growth and TLR / NF -κB expression level of Fenneropenaeus chinensis [J]. China Fishery Quality And Standards, 2012, 2(2): 37−44.(in Chinese)
[4] 朱路英, 张学成, 王淑芳, 等. 一种海洋真菌: 裂殖壶菌的营养成分分析 [J]. 食品科学, 2009, 30(24):272−275. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2009.24.058 ZHU L Y, ZHANG X C, WANG S F, et al. Analysis of nutritional components of a marine fungus: Schizochytrium limanium [J]. Food Science, 2009, 30(24): 272−275.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2009.24.058
[5] CALDER P C. N-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids, inflammation, and inflammatory diseases [J]. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2006, 83(6): 1505S−1519S. DOI: 10.1093/ajcn/83.6.1505S
[6] SADEGHI S, WALLACE F A, CALDER P C. Dietary lipids modify the cytokine response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide in mice [J]. Immunology, 1999, 96(3): 404−410. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00701.x
[7] HAYASHI N, TASHIRO T, YAMAMORI H, et al. Effects of intravenous ω-3 and ω-6 fat emulsion on cytokine production and delayed type hypersensitivity in burned rats receiving total parenteral nutrition [J]. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition, 1998, 22(6): 363−367. DOI: 10.1177/0148607198022006363
[8] KELLEY D S, DAUDU P A. Fat intake and immune response [J]. Progress in Food & Nutrition Science, 1993, 17(1): 41−63.
[9] SAWYER M B, FIELD C J. Possible mechanisms of ω-3 PUFA anti-tumour action[C]//Dietary Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Cancer. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, 2009: 3-38.
[10] FARMER J J III. vibrio (" beneckea”) vulnificus, the bacterium associated with Sepsis, septicæmia, and the Sea [J]. The Lancet, 1979, 314(8148): 903.
[11] BIOSCA E G, AMARO C, ESTEVE C, et al. First record of Vibrio vulnificus biotype 2 from diseased European eel, Anguilla anguilla L [J]. Journal of Fish Diseases, 1991, 14(1): 103−109. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2761.1991.tb00581.x
[12] 冯伟. 维生素C、E和裂壶藻对中国对虾非特异性免疫功能影响的研究[D]. 海: 上海海洋大学, 2011. FENG W. Effects of supplemental different level Vc, Ve and Schizochytrium on non-specific immunity of Chinese shrimp (Fenneropenaeus Chinensis)[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2011. (in Chinese)
[13] 焦建刚, YUAN Kathy, THABUIS Clémentine, 等. 裂殖壶藻发酵粉对南美白对虾生长性能和肌肉营养成分的影响 [J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 2014, 23(4):523−527. JIAO J G, KATHY Y, THABUIS C, et al. The effect of dried algae Schizochytrium sp. on growth performance and nutrients in the muscle of white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) [J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2014, 23(4): 523−527.(in Chinese)
[14] 黄亮华, 李浩洋, 李彬, 等. 裂壶藻对刺参生长、免疫及消化酶的影响 [J]. 渔业科学进展, 2014, 35(3):91−97. DOI: 10.11758/yykxjz.20140313 HUANG L H, LI H Y, LI B, et al. Effects of dietary Schizochytrium limacinum on the growth, immunity and digestion enzyme activity of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus [J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2014, 35(3): 91−97.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11758/yykxjz.20140313
[15] 许斌福, 林天龙, 董传甫. 鳗鲡创伤弧菌的分子鉴定 [J]. 中国人兽共患病杂志, 2005, 11(21):995−997. XU B F, LIN T L, DONG C F. Molecular identification of Vibrio vulnificus isolated from the diseased European eels in mainland China [J]. Chinese Journal of Zoonoses, 2005, 11(21): 995−997.(in Chinese)
[16] 陈华, 李素一, 张丽娟, 等. CpG-ODN 2006对斑马鱼抗创伤弧菌感染的作用 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2018, 33(1):1−6. CHEN H, LI S Y, ZHANG L J, et al. Functions of CpG-ODN 2006 on Resistance of Zebra Fish against Vibrio vulnificus [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 33(1): 1−6.(in Chinese)
[17] MILLER M R, NICHOLS P D, CARTER C G. Replacement of fish oil with thraustochytrid Schizochytrium sp. L oil in Atlantic salmon parr(Salmo salar L.) diets [J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology, 2007, 148(2): 382−392.
[18] GANUZA E, BENÍTEZ-SANTANA T, ATALAH E, et al. crypthecodinium cohnii and Schizochytrium sp. as potential substitutes to fisheries-derived oils from seabream(Sparus aurata) microdiets [J]. Aquaculture, 2008, 277(1/2): 109−116.
[19] 吉红, 周继术, 曹福余, 等. DHA对鲤抗氧化能力影响的初步研究 [J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 2009, 18(2):2142−2149. JI H, ZHOU J S, CAO F Y, et al. Effect of DHA on anti-oxidation capacity in common carp(Cyprinus carpio L.) [J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2009, 18(2): 2142−2149.(in Chinese)
[20] 王桂芹, 牛小天, 闫先春, 等. 饲料中添加维生素E和二十二碳六烯酸对鲤鱼生长和抗病力的影响 [J]. 上海交通大学学报(农业科学版), 2010, 28(2):124−128. WANG G Q, NIU X T, YAN X C, et al. Effect of dietary vitamin E and DHA levels on growth and disease resistance of Cyprinus carpio juvenile [J]. Journal of Shanghai JiaoTong University(Agricultural Science), 2010, 28(2): 124−128.(in Chinese)
[21] 刘然然. 大鲵c-型和g-型溶菌酶基因的生物信息学分析和表达研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2018. LIU R R. Bioinformatics analysis and expression research of c-style lysozyme gene and g-style lysozyme gene from Chinese giant salamander[D]. Yangling, China: Northwest A & F University, 2018. (in Chinese)
[22] 邱本丹. 大黄鱼溶菌酶对鳗弧菌胁迫的响应研究[D]. 舟山: 浙江海洋大学, 2016. QIU B D. The response of c-type and g-type lysozyme in large yellow croaker(Larimichthys crocea) to Vibrio anguillarum[D]. Zhoushan: Zhejiang Ocean University, 2016. (in Chinese)
[23] PFEFFER K. Biological functions of tumor necrosis factor cytokines and their receptors [J]. Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews, 2003, 14(3/4): 185−191.
[24] 胡梦平, 刘巧刿. 肿瘤坏死因子-α在铜绿假单胞菌肺炎中的变化及意义 [J]. 海南医学院学报, 2009, 15(8):864−866. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1237.2009.08.013 HU M P, LIU Q G. The role of tumor necrosis factor alpha in Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia [J]. Journal of Hainan Medical University, 2009, 15(8): 864−866.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1237.2009.08.013
[25] CHENG C L, HUANG S J, WU C L, et al. Transgenic expression of Omega-3 PUFA synthesis genes improves zebrafish survival during Vibrio vulnificus infection [J]. Journal of Biomedical Science, 2015, 22: 103. DOI: 10.1186/s12929-015-0208-1
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 张新明,赵璐,胡晓文. 裂壶藻营养价值及其在动物生产中的应用进展. 河南农业科学. 2021(03): 1-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: