Optimization of Seed Sterilization and Rooting Medium for Regeneration of Brassica napus
-
摘要:目的 植物的种子灭菌和生根培养是组织培养的重要步骤。目前已报道的用于甘蓝型油菜种子灭菌的次氯酸钠(NaClO)浓度、灭菌时间和生根培养基的植物生长调节剂种类及其浓度均存在较大的差异,因此,本研究旨在筛选出甘蓝型油菜种子的最佳NaClO灭菌处理方法和生根培养基最适的植物生长调节剂及其浓度。方法 比较了甘蓝型油菜的种子经不同浓度(浓度范围为0.1% ~ 30.0%)NaClO灭菌后的发芽率、健康芽率和菌落率,筛选出最适的种子灭菌NaClO浓度,再在该最适NaClO浓度基础上找出了最适的种子灭菌时间;通过比较不同质量浓度(0.1 ~ 2.0 mg·L−1)的植物生长调节剂萘乙酸(NAA)或吲哚丁酸(IBA)对甘蓝型油菜再生根的促进作用,找出油菜生根培养最适的植物生长调节剂种类及其浓度。结果 甘蓝型油菜种子的最佳灭菌NaClO浓度为2.0%或3.0%,在3.0% NaClO下的最适灭菌时间为15 min,种子经该灭菌方法处理后的发芽率和健康芽率分别可达97.4%和85.9%,且菌落发生率最少。该油菜种子灭菌的方法也适用于其他9个植物品种,尤其适合于甘蓝型油菜、大白菜和拟南芥的种子灭菌。在生根培养基中添加0.1 mg·L−1 NAA对甘蓝型油菜再生根的促进作用最强,油菜培养7 d后即有92.5%的累积生根率,再生根从切点处生长,且再生的须根数最多。结论 本研究优化了甘蓝型油菜种子的NaClO灭菌方法和生根培养基的植物生长调节剂及其浓度,为高效的油菜组织培养研究奠定了基础。Abstract:Objective Seed sterilization and rooting culture are important steps in plant tissue culture. At present, there is considerable variation in the concentration of sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) and seed sterilization time of Brassica napus, as well as the type and concentration of hormone in the rooting media. The purpose of this study was to optimize the method of seed sterilization with NaClO and the formula of rooting medium for B. napus regeneration.Method The optimum concentration of NaClO for seed sterilization was screened by comparing the growth status (such as germination rate, healthy shoot rate and rate of colonies) of seeds treated with different concentrations (0.1%–30.0%) of NaClO, and the appropriate sterilization time was optimized based on the growth status of seeds treated with the optimal concentration of NaClO for 10—30 min. Moreover, the optimum formula of rooting media was screened by comparing the rooting regeneration of seedlings in the media containing 0.1–2.0 mg·L−1 naphthylacetic acid (NAA) / indolebutyric acid (IBA).Result The optimum concentration of NaClO for seed sterilization was 2.0% or 3.0%, and the best time for seed sterilization with 3.0% NaClO was 15 min, causing the 97.4% of germination rate and 85.9% of healthy shoot rate with least rate of colonies. Moreover, this method of seed sterilization is applicable to other 9 plants, especially for B. napus, B. pekinensis and Arabidopsis thaliana. The root regenerated best in the rooting medium containing 0.1 mg·L−1 NAA, in which 92.5% of root regenerated from the cutting point on the 7th day with the most lateral roots.Conclusion This study optimized the method of seed sterilization and the formula of rooting medium, which laid a foundation for efficient plant tissue culture of B. napus.
-
Keywords:
- Brassica napus /
- seed sterilization /
- sodium hypochlorite /
- rooting /
- NAA /
- IBA
-
食用菌蕴藏着丰富的天然抗氧化物质成分,显示出较高的抗氧化能力[1-4],如具有抑制羟自由基(·OH)氧化的功能[4]。·OH是一种氧化能力很强的自由基,它能够很容易地氧化各种有机物和无机物,氧化效率高,反应速率快,可造成组织脂质过氧化、核酸断裂、蛋白质和多糖分解,与机体的衰老、肿瘤、辐射损伤和细胞吞噬有关[4-5]。由于·OH的反应活性大、寿命短、存在浓度低,所以准确、便捷、快速检测·OH的方法就显得特别重要,特别是在测定及筛选抗羟自由基物质和研究羟自由基导致的各种疾病方面具有重要意义。近年来,国内外检测羟自由基的主要方法有分光光度法、荧光法、高效液相色谱法、化学发光分析法、电化学分析法、电子自旋共振法等[5]。其中分光光度法具有检测效率高、经济性好、可重复性强、高通量等优势。而文献报道以Fenton反应作为·OH源的分光光度法检测抗氧化力的主要方法有:番红显色法[6-8]、甲基紫显色法[4, 9]、邻二氮菲-Fe2+氧化法[10]、水杨酸钠显色法[11-12]和二甲亚砜探针显色法[13-14]。
采用番红花红T作为氧化还原指示剂,用分光光度法测定Fenton反应产生的·OH,具有操作简便、费用低,易于广泛使用的优点。本试验在按照参考文献[6, 15],采用Fenton番红显色法测定茶薪菇发酵产物对Fenton反应产生羟自由基的清除率时,发现对照管在520 nm的吸光值(以下简称Ack)有两个问题:(1)Ack<0.1,无法测出茶薪菇发酵液对·OH清除率;(2)测定结果不稳定。根据Fenton反应原理,试验通过调整番红、样品的加入用量及比例等主要影响因素,解决无法测出检测茶薪菇发酵产物对·OH清除率的问题;筛选反应体系的酸碱度,提高吸光值的稳定性,并用维生素C作为·OH清除剂的阳性对照品,验证测定方法的准确性以及作为茶薪菇发酵产物抗氧化力测定的标准,验证改进后的Fenton反应法在检测茶薪菇发酵产物·OH清除率测定上的实用性以及应用效果的准确性。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
1.1.1 茶薪菇菌株Agrocybe chaxingu Huang
由福建省农业科学院农产品加工研究中心提供。
1.1.2 茶薪菇发酵液的制备
首先,采用PDA平板法、25℃活化培养茶薪菇菌种。接着,采用液体培养手段,接入直径为8 mm的菌块,于(25±0.5)℃、150 r·min-1培养7 d,制备茶薪菇液体菌种。最后,将液体菌种接种于不同的液体发酵培养基中,每瓶接种量为培养基装液量的10%(V/V),与茶薪菇液体菌种相同条件培养7 d,制备茶薪菇发酵液。茶薪菇发酵液的液体培养基配方如下,配方Ⅰ:马铃薯20%,玉米粉3%,麦麸3%,蔗糖2%,酵母粉0.3%,磷酸二酸钾0.1%,硫酸镁0.05%,维生素B1 0.01%;配方Ⅱ~Ⅳ:在配方Ⅰ的基础上添加2%、4%、8%油茶树枝粉。配方Ⅴ~Ⅷ:在配方Ⅰ基础上去掉“麦麸3%”作为配方Ⅴ(麦麸和油茶枝粉的空白对照),在配方Ⅰ基础上去掉“玉米粉3%”作为配方Ⅵ(玉米粉和油茶枝粉的空白对照),在配方Ⅴ的基础上分别添加2%、4%油茶枝粉作为配方Ⅶ和配方Ⅷ(2%、4%油茶枝粉组)。将液体菌种接种于冷却至常温的灭菌液体发酵培养基中,每瓶接种量为培养基装液量的10%(V/V),相同条件培养7 d。菌丝体提取方法参见文献[16]。
1.2 主要仪器
电子天平,德国Sartrius;高速冷冻离心机,上海安亭科学仪器厂;765P型紫外可见分光光度计,上海光谱仪器有限公司;HH-6电热恒温水浴锅,国华电器有限公司;立式压力蒸汽灭菌器,上海申安医疗器械厂;漩涡混合器,海门市其林贝尔仪器制造有限公司;HZP-150型全温振荡培养箱,上海精宏实验设备有限公司。
1.3 主要试剂
番红、乙二胺四乙酸二钠、磷酸二氢钠、磷酸氢二钠均为分析纯。实验用水为超纯水。
1.4 Fenton法检测茶薪菇液体发酵产物在Fenton体系中的抗氧化性
1.4.1 Fenton法反应原理、反应体系及清除率计算
(1) 番红显色法反应原理。H2O2+Fe2+→·OH+OH-+Fe3+,Fe2+催化H2O2产生·OH,·OH与番红(氧化还原指示剂,最大吸收波长520 nm)作用后可使番红褪色,使体系吸光度降低;利用吸光度值的变化间接测定·OH。样品管的吸光度反映其作为抗氧化剂抑制·OH对番红的褪色作用,空白管的吸光值反映番红被·OH完全褪色的吸光度,样品的抗氧化力越强,可清除的羟自由基越多;羟自由基的含量小,番红褪色少,吸光值越大。
(2) 反应体系加样调整。改进前的Fenton体系加样[6, 15]:在10 mL的带盖螺口试管中分别加入1.0 mL磷酸缓冲液(0.15 mol·L-1,pH 7.4)、0.2 mL番红溶液(520 μg·mL-1)、1.0 mL EDTA-Na2-Fe2+(6 mmol·L-1)、0.8 mL H2O2(体积分数0.3%),再加入7 mL样液(或羟自由基清除剂),40℃水浴30 min,冷却后于520 nm处测定其吸光度A样品。改进后的Fenton体系加样:在10 mL的带盖螺口试管中分别加入4.7 mL超纯水、1.0 mL磷酸缓冲液(0.15 mol·L-1,pH 7.4),2.0 mL番红溶液(520 μg·mL-1)、1.0 mL EDTA-Na2-Fe2+(6 mmol·L-1),再分别加入不同浓度0.5 mL的样品溶液,最后加入0.8 mL H2O2(体积分数0.3%),混匀后于40℃水浴30 min,冷却后于520 nm处测吸光度A样品。
(3) 清除率的计算。以等体积超纯水代替样品溶液,其吸光度为A空白;以等体积超纯水代替样品溶液和H2O2溶液,其吸光度为A对照。羟自由基清除率计算公式:清除率=(A样品-A空白)/(A对照-A空白) ×100%。
1.4.2 试剂用量、茶薪菇发酵液用量对体系吸光度的影响
在反应体系中只留下一种有颜色的试剂(或样品),定容至10 mL,通过测定不同试剂用量的吸光值,研究试剂颜色对反应体系吸光值的影响。
1.4.3 番红与茶薪菇发酵液2个较适宜的体积组合对清除率的影响
计算清除率的比值:除茶薪菇发酵液与番红外其他试剂按照改进后的Fenton体系添加,采用单因素法研究,当茶薪菇发酵液体积一定,理论上番红2个较适宜的体积加入Fenton体系后测得的清除率之比应该接近或等于1;当番红体积一定,比较茶薪菇发酵液2个较适宜的体积加入Fenton体系后测得的清除率之比等于茶薪菇发酵液的体积比。
1.4.4 酸碱度对吸光值的影响
依次加入1.0 mL磷酸缓冲液(pH 5.5、6.0、6.5、7.0、7.4、7.5、8.0、8.5),2.0 mL的番红溶液,1.0 mL的EDTA-Na2-Fe2+,0.5 mL 90 mmol·L-1的维生素C溶液,0.8 mL H2O2溶液,用不同酸碱度的磷酸缓冲液调节pH,超纯水加至10 mL,此为水浴前体系的pH0。40℃水浴30 min,冷却,测得水浴后体系的pH1和520 nm处的吸光值。△pH= pH1-pH0,不同pH点的A520的均值为A,△A=A520-A。
1.4.5 稳定性试验
40℃水浴30 min,冷却,室温下测定某样品管在0、5、10、15、20、25、30 min的吸光值,观察吸光值的稳定性。
1.4.6 维生素C对羟自由基清除率的测定
按照1.4.1改进后的反应体系加样,用一系列不同浓度的维生素C溶液替代等体积的样液,40℃水浴30 min,冷却,测得520 nm处的吸光值。
1.4.7 茶薪菇胞内、胞外产物对羟自由基清除率的测定
按照1.4.1改进后的反应体系加样,样液分别为茶薪菇胞内产物(即液体配方Ⅰ~Ⅳ发酵的茶薪菇菌丝体的水提液)和胞外产物(即液体配方Ⅴ~Ⅷ发酵的茶薪菇发酵液)。计算维生素C当量(即与样品羟自由基清除率相等时维生素C的浓度),作为样品抗氧化力的标准。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 番红用量与样品茶薪菇发酵液用量对体系吸光度的影响
2.1.1 番红用量对体系吸光度的影响
反应体系中番红、EDTA-Na2-Fe2+试剂的颜色影响体系的吸光度,在改进前的反应体系中二者吸光值之和(Ack=A番红+A EDTA-Na2-Fe2+=0.046+0.002=0.048)较小,说明番红用量对体系吸光度的影响较大,EDTA-Na2-Fe2+对体系吸光度的影响较小。因此,本试验主要研究番红用量对体系吸光度的影响。
由图 1可知,Fenton体系的吸光值A与520 μg·mL-1番红溶液体积呈线性关系,线性回归方程为:y = 0.2098x-0.1501,R2=0.9699,其中y为吸光度值,x为番红溶液体积(520 μg·mL-1)。结果表明,番红溶液在2.0~8.0 mL体积范围内线性关系良好。根据番红显色Fenton法的反应原理番红用量需要满足以下条件:(1)番红用量足够多,以至于抗氧化剂清除·OH后,·OH残余量的褪色作用能够反映为一定的吸光值;(2)同时满足在没有抗氧化剂的保护时番红的颜色能够被完全褪去。需要提高反应体系番红用量,当番红溶液(520 μg·mL-1)体积为2.0 mL和3.0 mL时同时满足了以上要求。同时其吸光值处于分光光度法较佳的取值范围0.2~0.8。
2.1.2 茶薪菇发酵液对体系吸光度的影响
测定方法见1.4.2,由图 2可知,茶薪菇发酵液的体积与吸光值呈线性关系,线性回归方程为:y = 0.0196x-0.0023,R2=0.9948,其中y为吸光度值,x为茶薪菇发酵液体积。表明茶薪菇发酵液体积在0.5~7.0 mL体积范围内线性关系良好。在改进前的反应体系中,茶薪菇发酵液体积占改进前反应体系总体积的70%,说明样液的颜色、酸碱度对吸光值的影响很大,必然干扰反应体系的呈色及·OH的清除率结果。
试验研究茶薪菇发酵液对吸光度的影响,以减少体系中茶薪菇发酵液体积:当茶薪菇发酵液体积为0.5或1.0 mL时的吸光值小于0.531(番红体积2.0 mL时的吸光值)的5%,也小于0.826(番红体积3.0 mL时的吸光值)的2%,处于可接受误差范围,可以不设置样品的空白对照,减少试验操作环节,降低工作量。因此确定适宜的茶薪菇发酵液体积为0.5或1.0 mL。
2.1.3 番红用量与茶薪菇发酵液用量对体系吸光度的影响
筛选的2个番红体积水平2.0、3.0 mL与2个样品茶薪菇发酵液体积水平为0.5、1.0 mL交叉组合,找出最适组合。测定方法见1.4.3,清除率及其比值见表 1。
表 1 不同样液、番红体积的羟自由基清除率Table 1. Hydroxyl radical scavenging rates with application of varied sample and saffron volumes项目 番红体积2.0 mL 番红体积3.0 mL 清除率比值R1 发酵液体积0.5 mL 36.79 39.49 1.07 发酵液体积1.0 mL 66.03 60.47 0.92 清除率比值R2 1.79 1.53 注:清除率比值R1为番红体积3.0 mL时清除率与番红体积2.0 mL时清除率的比值,R1的理论值为1;清除率比值R2为发酵液体积1.0 mL时清除率与发酵液体积0.5 mL时清除率的比值,R2的理论值为2。 相同体积的茶薪菇发酵液样品,在不同番红体积下清除率理论值相等,其清除率比值越接近1越好。当茶薪菇发酵液体积为0.5 mL,番红体积3.0 mL与2.0 mL时的清除率比值为1.07,比值差为0.07;同理可得,当茶薪菇发酵液体积为1.0 mL时,清除率比值差为0.08,说明茶薪菇发酵液体积为0.5 mL的清除率结果更准确。
相同浓度、体积的番红与不同体积的茶薪菇发酵液清除率的比值等于茶薪菇发酵液体积比(1.0 mL: 0.5 mL=2),实际操作中越接近理论值2越好。由表 1可知,当番红体积为2.0 mL时,清除率比值1.79;番红的体积为3.0 mL时,清除率比值1.53,番红的体积为2.0 mL时更准确。
2.2 酸碱度对体系吸光值的影响
ΔpH、△A按照1.4.4的方法计算,结果见表 2。加入H2O2启动Fenton反应,生成了大量的·OH和OH-,但抗氧化剂阻止·OH对番红的氧化褪色,中和了OH-,使Fenton体系的pH下降。Fenton体系的pH太低,电离出大量的H+与OH-反应,促进Fenton反应产生大量·OH,番红迅速褪色,不利于抗氧化剂发挥保护作用。Fenton体系的pH太高,电离出大量的OH-不利于反应的进行,当pH=7.0时,可以维持H+与OH-电离平衡。所以为了保证测定结果的准确性和稳定性,体系的pH稳定在一定范围内,即△pH较小;同时反应结束后体系的酸碱度接近中性,H+与OH-电离平衡使吸光值更稳定。试验测定了体系pH在5.5~8.5范围内不同酸度溶液的ΔpH。从表 2可以看出,ΔpH<0.5的有pH6.5、pH7.0、pH7.4、pH7.5、pH8.0等5个点。其中当pH7.4时,Fenton反应前后pH均接近7,ΔpH也小。
表 2 酸碱度对体系吸光值的影响Table 2. Effect of pH on absorbance measurementΔpH 5.5 6.0 6.5 7.0 7.4 7.5 8.0 8.5 pH0 5.50 6.00 6.50 7.00 7.39 7.49 8.02 8.51 pH1 4.43 5.05 6.08 6.78 7.05 7.23 7.69 7.86 pH 1.07 0.95 0.42 0.22 0.34 0.26 0.33 0.65 A520 0.163 0.212 0.253 0.322 0.341 0.345 0.365 0.384 ΔA 0.138 0.089 0.048 0.021 0.040 0.044 0.064 0.083 注:A=0.301;ΔA=|A520-A|;ΔpH=pH1-pH0。 尽管体系pH不同,样液均为90 mmol·L-1的维生素C溶液,对羟自由基的清除能力的抗氧化力相同,其理论上吸光值相等。将9个不同pH点的吸光值均值=0.301作为90 mmol·L-1的维生素C溶液的理论吸光值,9个不同pH点的吸光值分别与之比较偏差△A,△A最小区间是pH=7.0~7.5。
2.3 显色稳定性试验
稳定性试验根据1.4.5的方法,室温下A值变化见表 3,30 min内吸光值的变异度均未超过吸光值平均值的1.5%,可见本方法稳定性较好。
表 3 显色稳定性Table 3. Stability of reaction color for spectrophotometry measurement吸光值 放置时间/min 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 A520 0.342 0.337 0.334 0.333 0.332 0.331 0.331 A520 0.459 0.449 0.447 0.445 0.444 0.442 0.442 2.4 维生素C的羟自由基清除率标准曲线
维生素C是常用的羟自由基清除剂,羟自由基清除率在40 ~100 mmol·L-1(维生素C标准品浓度)范围内保持线性关系,线性回归方程为:y = 0.9549x-20.726,R2=0.9858,其中y为羟自由基清除率,x为维生素C标准品浓度。从图 3结果可以看出,维生素C标准品浓度与羟自由基清除作用具有良好的量效关系。
2.5 茶薪菇胞内、外产物的羟自由基清除率
茶薪菇菌丝体提取液的羟自由基清除率结果见表 4,配方Ⅰ与油茶枝粉不同添加水平试验三组(配方Ⅱ-Ⅳ)菌丝体对羟自由基清除率都较高,其中配方Ⅰ菌丝体提取液的羟自由基清除率最高,达65.43%,维生素C当量为90.22 mmol·L-1,显著高于其他3组。Ⅱ组显著高于Ⅲ、Ⅳ组,Ⅲ、Ⅳ组没有显著差异。菌丝体提取液的羟自由基清除率随着油茶枝粉添加水平提高而降低。
表 4 茶薪菇菌丝体提取液的羟自由基清除率Table 4. Hydroxyl radical scavenging rate of hot water extracts of A. chaxingu mycelia项目 配方Ⅰ 配方Ⅱ 配方Ⅲ 配方Ⅳ 清除率/% 65.43±2.96a 55.84±2.75b 51.06±0.97c 48.62±1.57c 维生素C当量/(mmol·L-1) 90.22 80.18 75.18 72.62 注:(1)配方Ⅱ~Ⅳ为在液体培养基配方Ⅰ基础上,添加2%、4%、8%油茶枝粉浸提液;(2)同行中不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);(3)维生素C当量:与样品羟自由基清除率相等时维生素C的浓度,下表同。 茶薪菇发酵液的羟自由基清除率结果见表 5,4种不同液体培养基配方的茶薪菇发酵液均具有一定的羟自由基清除率,其中玉米粉+2%茶树枝粉组的羟自由基清除率达72.87%,维生素C当量为72.82 mmol·L-1。
表 5 茶薪菇发酵液的羟自由基清除率Table 5. Hydroxyl radical scavenging rate of extracellular metabolites of A.chaxingu项目 配方Ⅴ 配方Ⅵ 配方Ⅶ 配方Ⅷ 清除率/% 69.18±5.28a 57.59±2.76b 72.82±3.87a 60.22±5.13a 维生素C当量/(mmol·L-1) 94.16 82.02 97.96 84.77 注:配方Ⅴ、Ⅵ为在液体培养基配方Ⅰ的基础上分别去掉麦麸、玉米粉,Ⅶ、Ⅷ在Ⅴ的基础上添加2%、4%油茶枝粉浸提液。 3. 讨论
3.1 番红用量对吸光度的影响
本试验选择番红作为氧化还原指示剂,是根据文献[6]报道的试验结果,通过比较番红花红T(番红)、甲基橙、次甲基兰、溴酚蓝、甲基红、铬黑T、溴甲酚紫、溴百里香酚蓝、靛红、结晶紫、甲基蓝、考马斯亮蓝等12种染料的全波长图谱,筛选出番红花红T作为氧化还原指示剂。本研究根据反应机理提高了番红用量,方法改进后可测定茶薪菇菌丝体及发酵液对羟自由基清除率。
3.2 pH对吸光度的影响
试验结果显示,当番红检测羟自由基的体系在pH 7.0~7.5时,反应前后体系的pH和吸光度变量最小,最稳定。与前人报道[6, 15]的结果一致。而与樊琛等[7]报道不一致:番红花红T检测羟自由基的体系在酸性环境pH 2.0~6.4范围内稳定。
3.3 方法的准确性和实用性
维生素C为羟自由基清除剂,维生素C的羟自由基清除率呈现明显的量效关系(R2=0.985 8),与文献[17]报道一致,验证了改进后的番红显色Fenton法的准确性;30 min内吸光值稳定,提高了显色稳定性;同时茶薪菇液体发酵产物的抗氧化力测定结果证实了改进后的番红显色法Fenton法的实用性[16]。
-
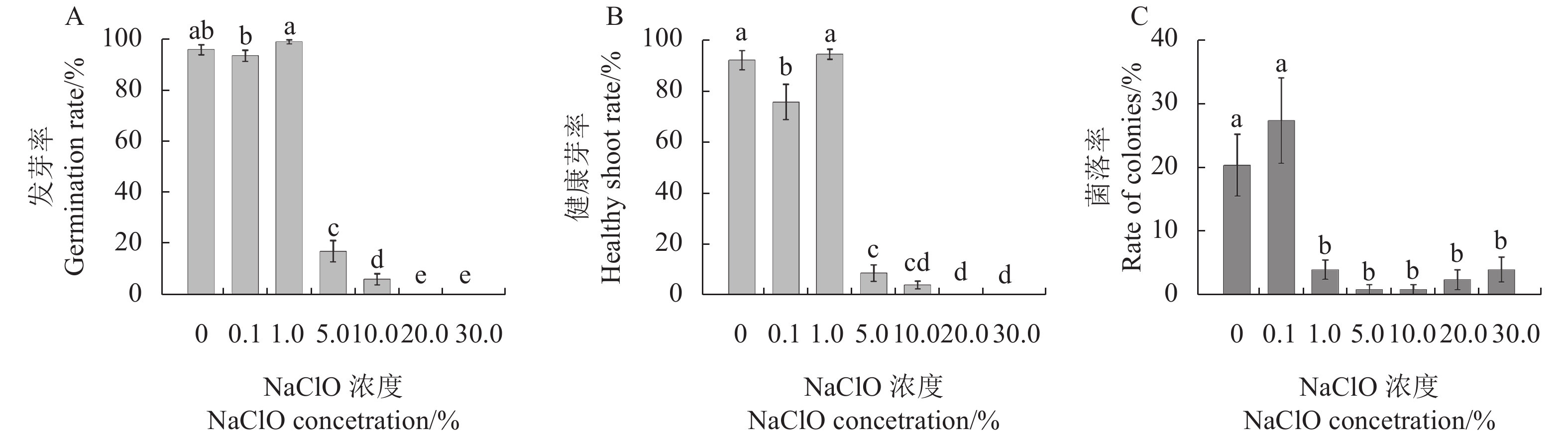
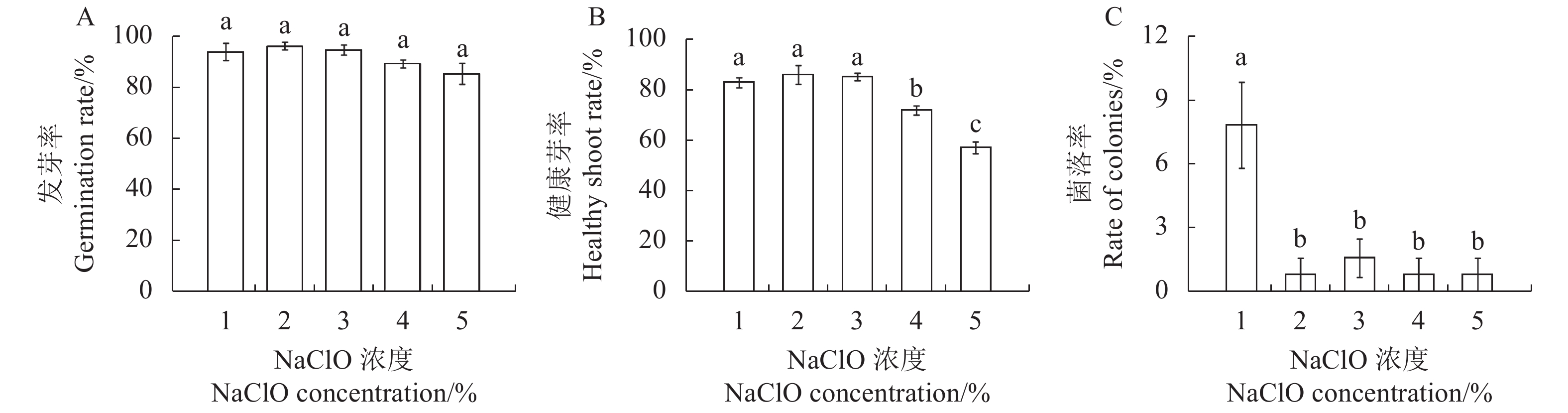
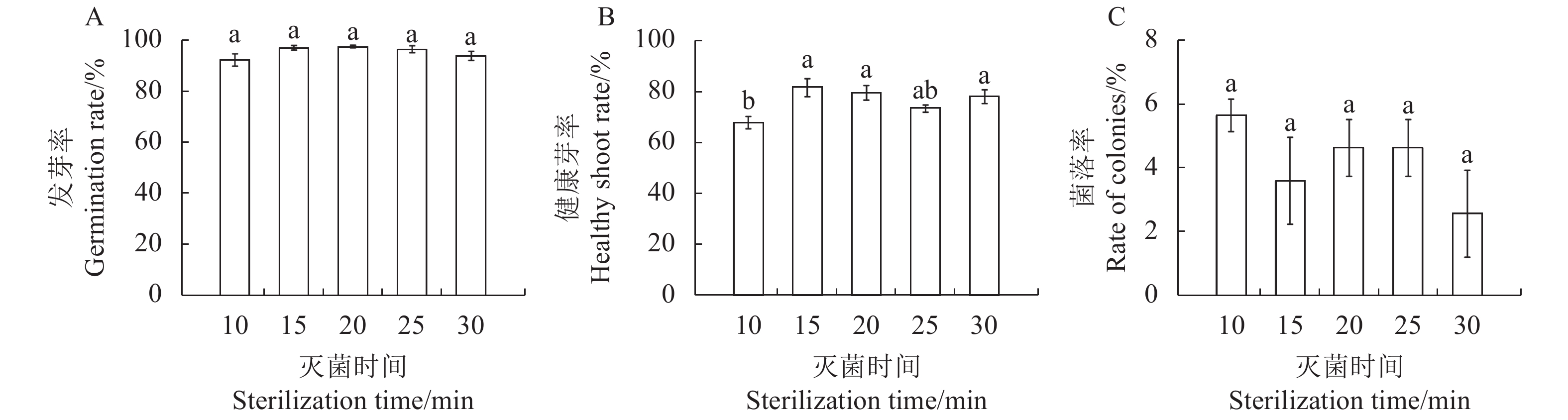
图 1 甘蓝型油菜种子灭菌的NaClO大范围浓度初步筛选
注:A, 发芽率; B, 健康芽率; C, 菌落率。同一图中的不同字母表示处理间具有显著性差异(P ≤ 0.05),数值表示“平均值 ± 标准误”。图2~3同。
Figure 1. Preliminary screening of large-scale concentration of NaClO for seed sterilization in B. napus
Note: A, germination rate; B, healthy shoot rate; C, rate of colonies. Different lowercase letters represent significant difference between treatments (P ≤ 0.05), the value means “mean ± standard error”. The same as Fig.2~3.
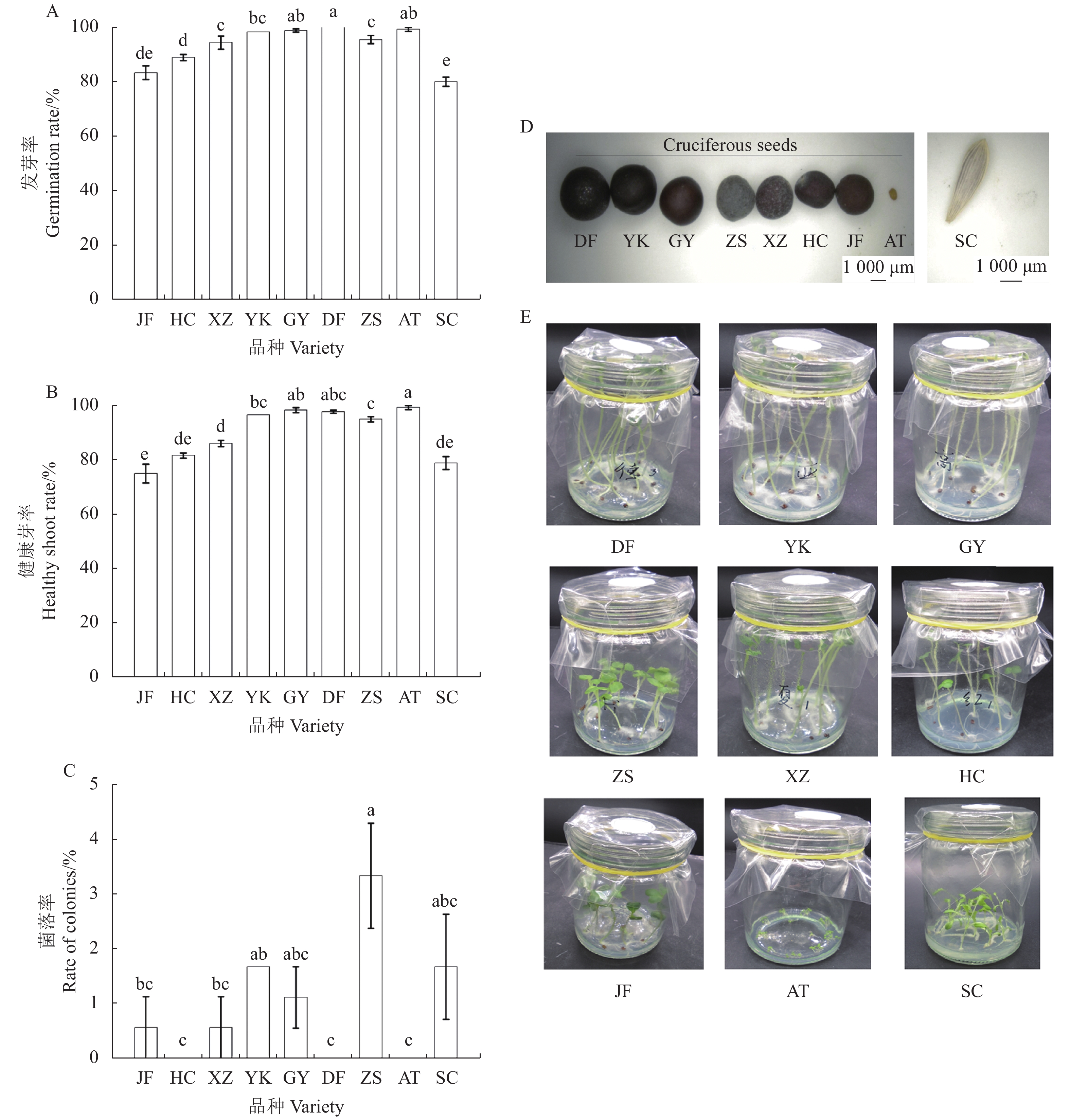
图 4 种子灭菌方法对其他芸苔属作物种子的灭菌效果
注:A, 发芽率;B,健康芽率;C,菌落率;D,9种植物品种的种子;E,9种植物品种的种子灭菌7 d后的苗生长情况。JF,甘蓝B. oleracea ‘京丰一号’;HC,白菜型油菜B. compestris ‘红菜苔’;XZ,小白菜B. campestris ‘夏尊’;YK,甘蓝型油菜B. napus ‘亚科油68’;GY,甘蓝型油菜B. napus ‘高油605’;DF,甘蓝型油菜B. napus ‘德丰油’;ZS,大白菜B. pekinensis ‘F1早熟五号’;SC,莴苣Lactuca sativa ‘意大利全年生菜王’;AT,拟南芥Arabidopsis thaliana。同一小图中的不同字母表示处理间有显著性差异(P ≤ 0.05),数值表示“平均值 ± 标准误”。
Figure 4. The effects of seed sterilization for other Brassica crops with the screened optimal method
Note: A, germination rate; B, healthy shoot rate; B, rate of colonies; D, seeds of 9 plant species; E, seedling growth status of 9 plant species after seed sterilization and sowing for 7 days. JF (B. oleracea ‘Jing Feng 1’), HC (B. compestris ‘Hong Cai Tai’), XZ (B. campestris ‘Xia Zun’), YK (B. napus ‘Ya Ke’), GY (B. napus ‘Gao You’), DF (B. napus ‘De Feng’), ZS (B. pekinensis ‘Zao Shou 5’), SC (Lactuca sativa) and AT (Arabidopsis thaliana). Different lowercase letters represent significant difference between treatments (P ≤ 0.05), the value means “mean ± standard error”.
图 5 不同质量浓度NAA/IBA对油菜再生根的累积生根率、生根部位、主根长和须根数的影响
注:A、累积生根率;B、生根部位(再生根位置与切点处之间的距离);C、主根长;D、须根数。CK、培养基内未添加植物植物生长调节剂; 0.1 NAA, 0.1 mg·L−1 NAA; 0.5 NAA, 0.5 mg·L−1 NAA; 1.0 NAA, 1.0 mg·L−1 NAA; 2.0 NAA, 2.0 mg·L−1 NAA; 0.1 IBA, 0.1 mg·L−1 IBA; 0.5 IBA, 0.5 mg·L−1 IBA; 1.0 IBA, 1.0 mg·L−1 IBA; 2.0 IBA, 2.0 mg·L−1 IBA。图中的不同字母表示处理间具有显著性差异(P ≤ 0.05),数值表示“平均值 ± 标准误”。
Figure 5. Effects of different concentrations of NAA / IBA on cumulative rooting rate, rooting position, taproot length and number of lateral roots of regenerative roots of B. napus
Note: A, cumulative rooting rate; B, rooting position (the distance between root regenerated position and cut point); C, number of lateral roots; D, taproot length. CK, media without plant hormone; 0.1 NAA, 0.1 mg·L−1 NAA; 0.5 NAA, 0.5 mg·L−1 NAA; 1.0 NAA, 1 mg·L−1 NAA; 2.0 NAA, 2.0 mg·L−1 NAA; 0.1 IBA, 0.1 mg·L−1 IBA; 0.5 IBA, 0.5 mg·L−1 IBA; 1.0 IBA, 1.0 mg·L−1 IBA; 2.0 IBA, 2.0 mg·L−1 IBA. Different lowercase letters represent significant difference between treatments (P ≤ 0.05), the value means “mean ± standard error”.
-
[1] OYEBANJI O, NWEKE O, ODEBUNMI O, et al. Simple, effective and economical explant-surface sterilization protocol for cowpea, rice and sorghum seeds [J]. African Journal of Biotechnology, 2009, 8(20): 5395−5399.
[2] YILDIZ M, EKIZ H. The effect of sodium hypochlorite solutions on in vitro seedling growth and regeneration capacity of sainfoin (Onobrychis viciifolia Scop.) hypocotyl explants [J]. Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 2014, 94(7): 1161−1164. DOI: 10.4141/cjps2013-250
[3] 郝梦宇, 丁炳莉, 李超, 等. 甘蓝型油菜组培苗生根培养体系的优化 [J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2018, 40(3):352−358. DOI: 10.7505/j.issn.1007-9084.2018.03.006 HAO M Y, DING B L, LI C, et al. Optimization of rooting medium for in vitro transgenic shoots in Brassica napus [J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 2018, 40(3): 352−358.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7505/j.issn.1007-9084.2018.03.006
[4] ZIAEI M, MOTALLEBI M, ZAMANI M R, et al. Co-expression of chimeric chitinase and a polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein in transgenic canola (Brassica napus) confers enhanced resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2016, 38(6): 1021−1032. DOI: 10.1007/s10529-016-2058-7
[5] BHALLA P L, SINGH M B. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Brassica napus and Brassica oleracea [J]. Nature Protocols, 2008, 3(2): 181−189. DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2007.527
[6] RADKE S E, ANDREWS B M, MOLONEY M M, et al. Transformation of Brassica napus L. using Agrobacterium tumefaciens: developmentally regulated expression of a reintroduced napin gene [J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 1988, 75(5): 685−694. DOI: 10.1007/BF00265588
[7] FAN Y, DU K, GAO Y, et al. Transformation of LTP gene into Brassica napus to enhance its resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum [J]. Russian Journal of Genetics, 2013, 49(4): 380−387. DOI: 10.1134/S1022795413040042
[8] SONNTAG K. Genotype and procedure dependence of Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Brassica napus [J]. Journal of Consumer Protection and Food Safety, 2007, 2(1): 113.
[9] ENGELKE T, HIRSCHE J, ROITSCH T. Metabolically engineered male sterility in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) [J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2011, 122(1): 163−174. DOI: 10.1007/s00122-010-1432-4
[10] KONG F, LI J, TAN X, et al. New time-saving transformation system for Brassica napus [J]. African Journal of Biotechnology, 2009, 8(11): 2497−2502.
[11] WANG Y Q, ZHANG Y, WANG F, et al. Development of transgenic Brassica napus with an optimized cry1C* gene for resistance to diamondback moth (Plutella xylostella) [J]. Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 2014, 94(8): 1501−1506. DOI: 10.4141/cjps-2014-099
[12] LIU H B, GUO X, NAEEM M S, et al. Transgenic Brassica napus L. lines carrying a two gene construct demonstrate enhanced resistance against Plutella xylostella and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum [J]. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture, 2011, 106(1): 143−151. DOI: 10.1007/s11240-010-9902-6
[13] ELHITI M, YANG C, CHAN A, et al. Altered seed oil and glucosinolate levels in transgenic plants overexpressing the Brassica napus SHOOTMERISTMLESS gene [J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2012, 63(12): 4447−4461. DOI: 10.1093/jxb/ers125
[14] MCALLISTER C H, WOLANSKY M, GOOD A G. The impact on nitrogen-efficient phenotypes when aspartate aminotransferase is expressed tissue-specifically in Brassica napus [J]. New Negatives in Plant Science, 2016, 3: 1−9.
[15] WANG Y, XU H, KOU J J, et al. Dual effects of transgenic Brassica napus overexpressing CS gene on tolerances to aluminum toxicity and phosphorus deficiency [J]. Plant Soil, 2013, 362: 231−246. DOI: 10.1007/s11104-012-1289-1
[16] JIANG Y Z, FU X L, WEN M L, et al. Overexpression of an nsLTPs-like antimicrobial protein gene (LJAMP2) from motherwort (Leonurus japonicus) enhances resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in oilseed rape (Brassica napus) [J]. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 2013, 82: 81−87. DOI: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2012.11.001
[17] KHAN M R, RASHID H, ANSAR M, et al. High frequency shoot regeneration and Agrobacterium-mediated DNA transfer in Canola (Brassica napus) [J]. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture, 2003, 75(3): 223−231. DOI: 10.1023/A:1025869809904
[18] MASHAYEKHI M, SHAKIB A M, AHMADRAJI M, et al. Gene transformation potential of commercial canola (Brassica napus L.) cultivars using cotyledon and hypocotyl explants [J]. African Journal of Biotechnology, 2008, 7(24): 4459−4463.
[19] ORLIKOWSKA T, NOWAK K, REED B. Bacteria in the plant tissue culture environment [J]. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture, 2017, 128(3): 487−508. DOI: 10.1007/s11240-016-1144-9
[20] 杜燕, 蒋海玉, 刘其宁. 贮存过期油菜种子消毒方法的研究 [J]. 种子, 2003(2):39−40. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4705.2003.02.016 DU Y, JIANG H Y, LIU Q L. Studies on rescue and propagation of rape germplasm resources exceeding the effective storage duration the collection of sterilization methods [J]. Seed, 2003(2): 39−40.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4705.2003.02.016
[21] 耿思宇, 张姗姗, 徐培林, 等. 激素组合等在甘蓝型油菜下胚轴再生中的作用 [J]. 山西农业科学, 2019, 47(5):730−733, 760. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2481.2019.05.07 GENG S Y, ZHANG S S, XU P L, et al. Role of hormone combinations on hypocotyls regeneration in Brassica napus [J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(5): 730−733, 760.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2481.2019.05.07
[22] 杨长友, 袁中厚, 郑小敏, 等. 甘蓝型油菜高效离体再生体系的建立 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2013(1):111−115. YANG C Y, YUAN Z H, ZHENG X M, et al. Establishment of effective regeneration system of Brassica napus L. in vivo [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2013(1): 111−115.(in Chinese)
[23] 黄昌蓉. 甘蓝型油菜早熟基因遗传转化体系的建立及转基因植株初步鉴定[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2013. HUANG C R. Establishment of genetic transformation with earliness gene and preliminary identification of transgenic plant in Brassica napus[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2013. (in Chinese)
[24] BIJANZADEH E, NOSRATI K, EGAN T. Influence of seed priming techniques on germination and emergence of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) [J]. Seed Science and Technology, 2010, 38: 242−247. DOI: 10.15258/sst.2010.38.1.26
[25] HATZIG S V, FRISCH M, BREUER F, et al. Genome-wide association mapping unravels the genetic control of seed germination and vigor in Brassica napus [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2015(6): 221.
[26] LINDSEY B, RIVERO L, CALHOUN C S, et al. Standardized method for high-throughput sterilization of Arabidopsis seeds [J]. Journal of Visualized Experiments, 2017, 128: e56587.
[27] JOVIČIČ D, POPOVIČ B M, JEROMELA A M, et al. The interaction between salinity stress and seed ageing during germination of Brassica napus seeds [J]. Seed Science and Technology, 2019, 47(1): 47−52. DOI: 10.15258/sst.2019.47.1.05
[28] HAO Z P, HUANG F, HOU S M, et al. Varietal differences in response to imidacloprid seed treatment in germination and early seedling growth of oilseed rape [J]. Seed Science and Technology, 2019, 47(1): 1−12. DOI: 10.15258/sst.2019.47.1.01
[29] MALEK M, GHADERI-FAR F, TORABI B, et al. The influence of seed priming on storability of rapeseed (Brassica napus) seeds [J]. Seed Science and Technology, 2019, 47(1): 87−92. DOI: 10.15258/sst.2019.47.1.09
[30] MAGRINI S, VITIS M D. In vitro reproduction of three Limodorum species (Orchidaceae): impacts of scarification methods and nitrogen sources on mature seed germination and seedling development [J]. Plant Biosystems, 2017, 151(3): 419−428. DOI: 10.1080/11263504.2016.1179698
[31] YADAV K, SINGH N. Effect of seed harvesting season and sterilization treatments on germination and in vitro propagation of Albizia lebbeck (L.) Benth [J]. Analele Universitatii din Oradea, Fascicula Biologie, 2011, 18(2): 151−156.
[32] DING H, FU T J, SMITH M A. Microbial contamination in sprouts: how effective is seed disinfection treatment? [J]. Journal of Food Science, 2013, 78(4): 495−501. DOI: 10.1111/1750-3841.12064
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 陆珠,任梓铭,王月,纪淑娟,杨阳,王欢,于延申. 玉木耳乙醇提取物的抗氧化活性及其部分有效部位含量分析. 特产研究. 2023(04): 8-12 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李浇,覃韶华,张雪欣,贤观妙,蒋羽,袁芳. 基于模糊数学感官评价法优化桑葚火龙果复合咀嚼片的制作研究. 大众科技. 2022(08): 30-35 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 吴俐,翁敏劼,李怡彬,汤葆莎,赖谱富,郑恒光,沈恒胜. 茶薪菇酚类提取物的抗氧化功效评价. 中国食品学报. 2021(01): 96-102 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 罗娅,刘小裕,邓俊林,司风玲. 玉木耳总黄酮的提取工艺及抗氧化活性分析. 重庆师范大学学报(自然科学版). 2020(02): 126-133 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载: