Cold-injury Indicator for Camellia sinensis cv. Fuding-dabaicha in Guizhou Province
-
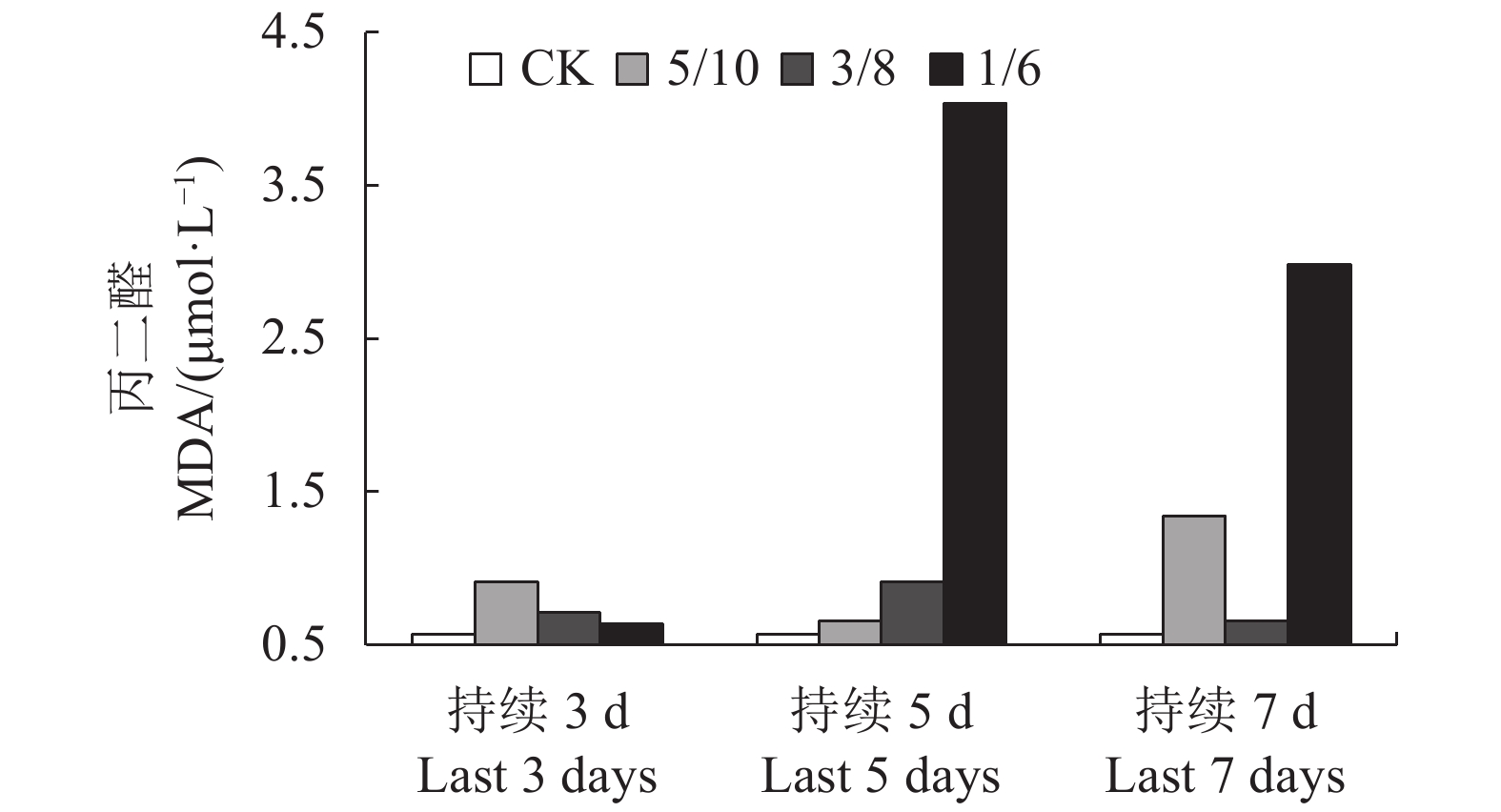
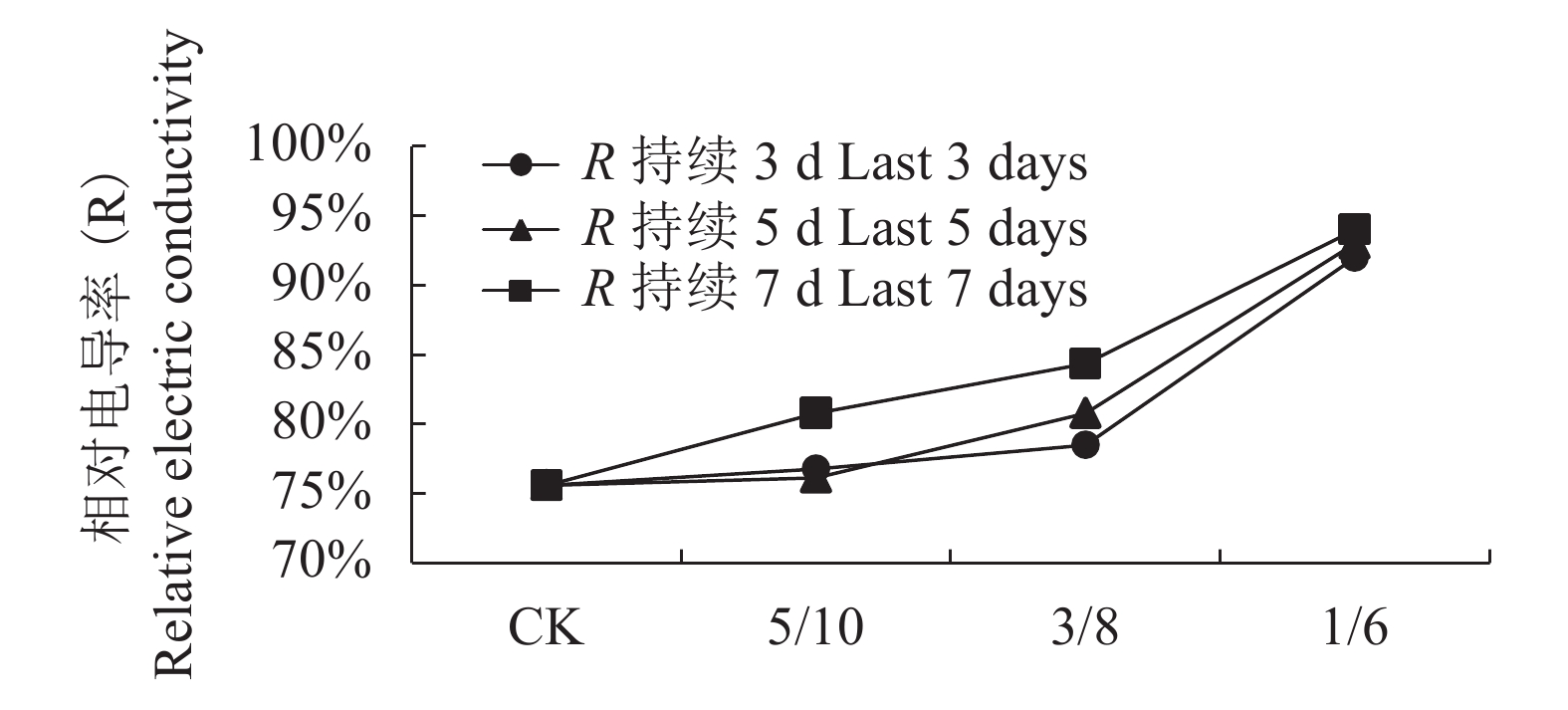
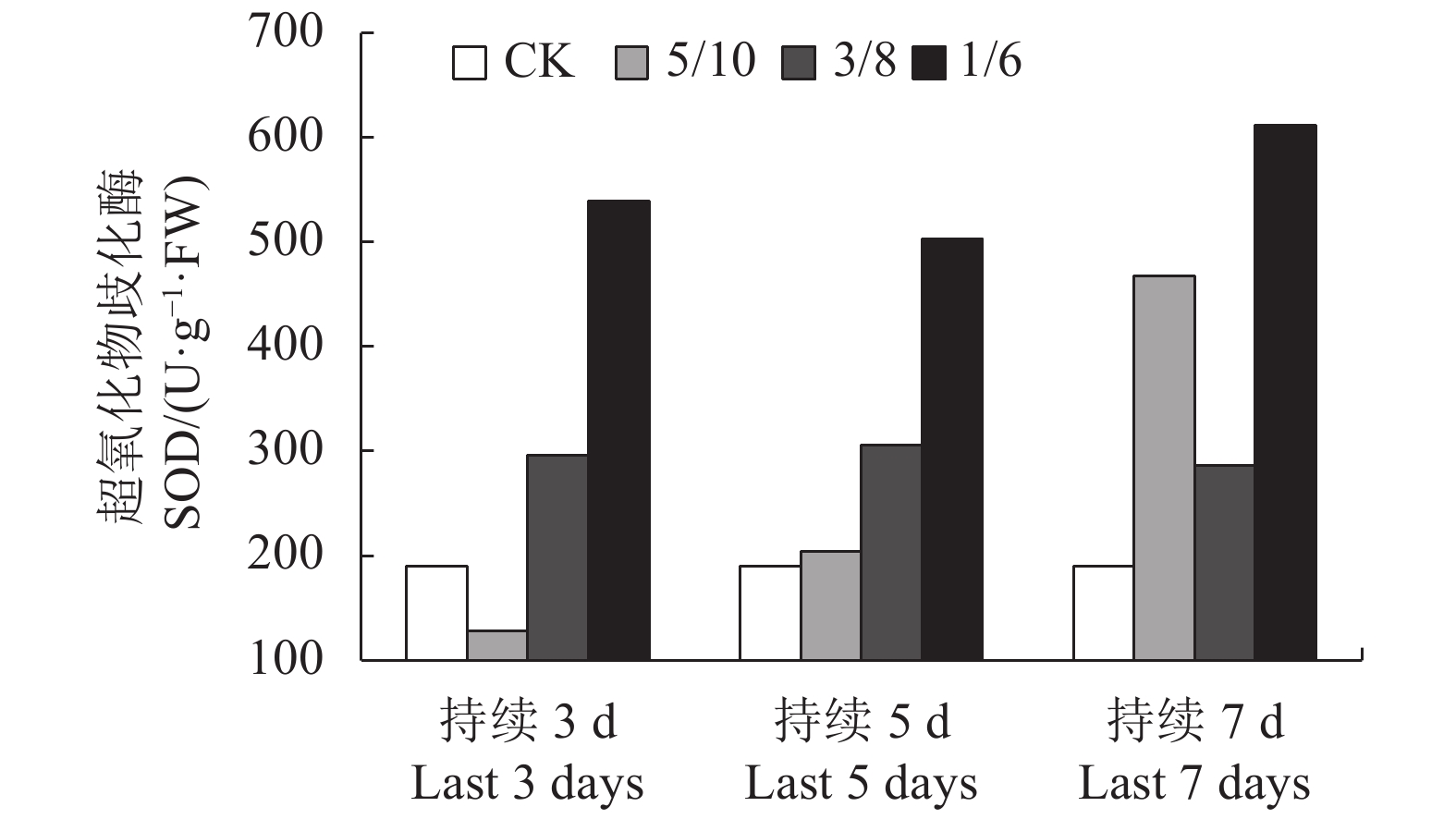
摘要:目的 探明贵州茶叶主栽品种福鼎大白茶的低温冷害指标,为精准茶叶气象指数保险和茶叶农业气象服务提供科学指导。方法 利用人工气候室模拟贵州低温冷害天气过程,测定茶叶不同低温冷害过程中生理指标以反映茶叶低温环境下的生长状态;拟合细胞伤害率与低温胁迫之间的Logistic函数关系,确定茶树生长的低温半致死温度,以量化不同低温冷害天气过程中茶叶的冷害指标。结果 随低温程度的加重,SOD活性大致呈上升趋势,MDA含量大致呈先升高后下降趋势,相对电导率R呈持续上升趋势;低温冷害持续日数不同,对应低温半致死温度不同,低温持续时间越长低温半致死温度越高,低温冷害天气持续3、5和7 d时,低温半致死温度分别为1.5 、1.8 和2.6℃。结论 福鼎大白茶冷害生长响应特征与低温冷害程度和持续天数密切相关:最低温度3℃以下的低温危害比3℃以上大;低温过程持续7 d的低温危害比持续3、5 d时严重;低温半致死温度随冷害持续时间的延长而升高,因此低温冷害指标的制定应依据当地倒春寒冷害气候特征进行量化。Abstract:Objective A cold-injury index for Camellia sinensis cv. Fuding-dabaicha, the major tea cultivars in Guizhou, was established to provide the meteorological information for precision insurance actuary and agro services on the crop.Method Physiological indices that reflect the growth of the tea plants under simulated low-temperatures in an artificial climate chamber were monitored. Semi-lethal temperature of the plants by cold stress was mathematically determined on a logistic function between the rate of injured cell and treatment temperature.Result With the lowering temperature, the physiological responses of the plants showed a gradually increased SOD activity, initially raised and then declined MDA, and continuously increased relative electric conductivity. The semi-lethal temperature of the plants differed depending upon the duration of cold treatment. The longer the plants were exposed to the chill, the higher the semi-lethal temperature became. When the cold lasted for 3 d, 5 d, and 7 d, the semi-lethal temperatures rose to 1.5℃, 1.8℃, and 2.6℃, respectively.Conclusion The growth responses of C. sinensis under low-temperature closely related to severity as well as duration of the exposure. At a temperature below 3℃, the harm imposed on the plant was more serious than above 3℃. And, a severe cold-injury would likely to incur if the treatment lasted for 7 days than 3 d or 5 d on the plants. The semi-lethal temperature of a plant increased with prolonged cold exposure. Thus, the cold-injury index should be applied with a consideration of local climatic conditions.
-
-
表 1 不同低温冷害持续时间下的茶叶Logistic函数参数及低温半致死温度
Table 1 Parameters in logistic function and semi-lethal temperature of tea plants in response to duration of low-temperature exposure
低温冷害持续时间
Chilling damage durationa b 相关系数R2
Correlation coefficient低温半致死温度/℃
Lethal temperature3 d 0.26 0.92 0.93* 1.5℃ 5 d 0.12 1.18 0.99** 1.8℃ 7 d 0.21 0.61 0.95** 2.6℃ 注:**拟合度达<0.05的显著性水平;*拟合度达<0.1的显著性水平。
Note: **indicates the significance level is 0.05; * indicates significance level is 0.1. -
[1] HAZELL P B R, HESS U. Drought insurance for agricultural development and food security in dryland areas [J]. Food Security, 2010, 2(4): 395−405. DOI: 10.1007/s12571-010-0087-y
[2] 毛裕定, 吴利红, 苗长明, 等. 浙江省柑桔冻害气象指数保险参考设计 [J]. 中国农业气象, 2007, 28(2):226−230. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2007.02.027 MAO Y D, WU L H, MIAO C M, et al. A reference design for Citrus freeze damage insurance by using meteorological index in Zhejiang Province [J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2007, 28(2): 226−230.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2007.02.027
[3] 娄伟平, 吴利红, 陈华江, 等. 柑橘气象指数保险合同费率厘定分析及设计 [J]. 中国农业科学, 2010, 43(9):1904−1911. DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2010.09.017 LOU W P, WU L H, CHEN H J, et al. Analysis and design of premium rates determined for weather-based index insurance contract of Citrus [J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2010, 43(9): 1904−1911.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2010.09.017
[4] 刘映宁, 贺文丽, 李艳莉, 等. 陕西果区苹果花期冻害农业保险风险指数的设计 [J]. 中国农业气象, 2010, 31(1):125−129, 136. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2010.01.025 LIU Y N, HE W L, LI Y L, et al. A study on the risk index design of agricultural insurance on apple florescence freezing injury in Shaanxi fruit zone [J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2010, 31(1): 125−129, 136.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2010.01.025
[5] 沈翼辉, 李俊, 郑健雄, 等. 宁波市杨梅气象灾害风险分析与气象指数保险产品设计 [J]. 中国保险, 2017(4):52−55. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4489.2017.04.012 SHEN Yi-hui, LI Jun, ZHENG Jian-jian, et al. Meteorological disaster risk analysis and meteorological index insurance product design of Yangmei in Ningbo [J]. China Insurance, 2017(4): 52−55.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4489.2017.04.012
[6] 杨帆, 刘布春, 刘园, 等. 气候变化对东北玉米干旱指数保险纯费率厘定的影响 [J]. 中国农业气象, 2015, 36(3):346−355. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2015.03.013 YANG F, LIU B C, LIU Y, et al. Impact of climate change on pure premium rating of drought index insurance for maize in northeast China [J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2015, 36(3): 346−355.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2015.03.013
[7] 吴利红, 娄伟平, 姚益平, 等. 水稻农业气象指数保险产品设计: 以浙江省为例 [J]. 中国农业科学, 2010, 43(23):4942−4950. DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2010.23.021 WU L H, LOU W P, YAO Y P, et al. Design of products for rice agro-meteorological index insurance: a case in Zhejiang Province [J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2010, 43(23): 4942−4950.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2010.23.021
[8] 李亚春, 王友美, 巫丽君, 等. 2013年春季低温霜冻对苏南茶树影响的评估 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2014(8):248−250. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1302.2014.08.091 LI LI Y C, WANG Y M, WU L J,, et al. Evaluation of the impact of spring frost on tea trees in south jiangsu province in 2013 [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2014(8): 248−250.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1302.2014.08.091
[9] 姜燕敏, 金志凤, 李仁忠, 等. 浙南春茶早春霜冻的时空分布特征 [J]. 气象科技, 2016, 44( 6):1066−1070. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6345.2016.06.032 JIANG Y M, JIN Z F, LI R Z, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution of early spring frost for spring tea in southern Zhejiang [J]. Meteorological Science and Technology, 2016, 44( 6): 1066−1070.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6345.2016.06.032
[10] 吴宜宣. 勉县优质绿茶低温冻害指标确定及防御补救措施 [J]. 陕西农业科学, 2017, 63(3):73−74, 94. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0488-5368.2017.03.022 WU Y X. Determination of low-temperature damage index of high-quality green tea in mianxian county and defense and remedy measures [J]. Shaanxi agricultural science, 2017, 63(3): 73−74, 94.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0488-5368.2017.03.022
[11] 时慧, 王玉, 周克福, 等. 低温胁迫下茶树叶片活性氧代谢及渗透调节物质含量的变化规律 [J]. 山东农业科学, 2012, 44(7):22−25. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4942.2012.07.007 SHI H, WANG Y, ZHOU K F, et al. Variation of active oxygen metabolism and osmotic regulators contents in Camellia sinensis leaves under low-temperature stress [J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 44(7): 22−25.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4942.2012.07.007
[12] 朱政, 蒋家月, 江昌俊, 等. 低温胁迫对茶树叶片SOD、可溶性蛋白和可溶性糖含量的影响 [J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2011, 38(1):24−26. ZHU Z, JIANG J Y, JIANG C J, et al. Effects of low temperature stress on SOD activity, soluble protein content and soluble sugar content in Camellia sinensis leaves [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2011, 38(1): 24−26.(in Chinese)
[13] 李仁忠, 金志凤, 杨再强, 等. 浙江省茶树春霜冻害气象指标的修订 [J]. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(10):2659−2666. LI R Z, JIN Z F, YANG Z Q, et al. Revision on meteorological indices of spring frost Disaster for Camellia sinensis in Zhejiang Province [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2016, 35(10): 2659−2666.(in Chinese)
[14] 李清声, 梁月荣. 低温对茶树叶片生理特性与相关基因表达的研究进展[M]//中国科协年会——分12茶学青年科学家论坛集, 中国科学技术协会学会学术部, 2014: 1-3. [15] 李叶云, 庞磊, 陈启文, 等. 低温胁迫对茶树叶片生理特性的影响 [J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 40(4):134−138, 145. LI Y Y, PANG L, CHEN Q W, et al. Effects of low temperature stress on physiological characteristics of tea leaves(Camellia sinensis L.) [J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(4): 134−138, 145.(in Chinese)
[16] 程艳, 陈璐, 米艳华, 等. 水稻抗氧化酶活性测定方法的比较研究 [J]. 江西农业学报, 2018, 30(2):108−111. CHENG Y, CHEN L, MI Y H, et al. Comparative study on various methods for determination of activity of antioxidant enzymes in rice [J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2018, 30(2): 108−111.(in Chinese)
[17] 李鹏程, 苏学德, 王晶晶, 等. 8种葡萄砧木品种的低温半致死温度与抗寒性综合评价 [J]. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2017, 52(1):92−96. LI P C, SU X D, WANG J J, et al. Semi-lethal temperature and comprehensive evaluation of hardiness on eight kinds of grape rootstock [J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2017, 52(1): 92−96.(in Chinese)
[18] 许瑛, 陈发棣. 菊花8个品种的低温半致死温度及其抗寒适应性 [J]. 园艺学报, 2008, 35(4):559−564. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0513-353X.2008.04.015 XU Y, CHEN F D. low temperature semilethal temperature and cold resistance of 8 varieties of chrysanthemum [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2008, 35(4): 559−564.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0513-353X.2008.04.015
[19] 孙波, 刘光玲, 杨丽涛, 等. 甘蔗幼苗根系形态结构及保护系统对低温胁迫的响应 [J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2014, 19(6):71−80. SUN B, LIU G L, YANG L T, et al. Response of chilling stress on root morphology and protection systems of sugarcane seedlings [J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2014, 19(6): 71−80.(in Chinese)
[20] 尹航, 王欣亚, 金大翔, 等. 低温诱导胁迫下不同烟草品种电导率及抗氧化酶活性的变化 [J]. 延边大学农学学报, 2018, 40(1):46−52. YIN H, WANG X Y, JIN D X, et al. Changes of antioxidant enzyme activity and conductivity of different tobacco varieties under low temperature induced stress [J]. Agricultural Science Journal of Yanbian University, 2018, 40(1): 46−52.(in Chinese)
[21] 田丹青, 葛亚英, 潘刚敏, 等. 低温胁迫对3个红掌品种叶片形态和生理特性的影响 [J]. 园艺学报, 2011, 38(6):1173−1179. TIAN D Q, GE Y Y, PAN G M, et al. Morphological and physiological characteristics of different cultivars of Anthurium andraenum under chilling stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2011, 38(6): 1173−1179.(in Chinese)
[22] 马艳青, 戴雄泽. 低温胁迫对辣椒抗寒性相关生理指标的影响 [J]. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2000, 26(6):461−462. MA Y Q, DAI X Z. effects of low temperature stress on physiological indexes related to chilli cold resistance [J]. Journal of hunan agricultural university (Natural Science Edition), 2000, 26(6): 461−462.(in Chinese)
[23] 姜会飞, 段若溪. 农业气象学[M].北京: 气象出版社, 2018: 63-64. [24] 张倩, 赵艳霞, 王春乙. 我国主要农业气象灾害指标研究进展 [J]. 自然灾害学报, 2010, 19(6):40−54. ZHANG Q, ZHAO Y X, WANG C Y. Advances in research on major agro-meteorological Disaster indexe in China [J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2010, 19(6): 40−54.(in Chinese)
[25] 王瑞, 马凤鸣, 李彩凤, 等. 低温胁迫对玉米幼苗脯氨酸、丙二醛含量及电导率的影响 [J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2008, 39(5):20−23. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9369.2008.05.005 WANG R, MA F M, LI C F, et al. Effect of low temperature stress on proline, malondialdehyde contents and electric conductivity of maize seedling [J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2008, 39(5): 20−23.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9369.2008.05.005
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 周姣,聂祥,李刚,罗亚楠,蔡曦. 毕节市七星关区引种安吉白茶的气候适应性分析. 南方农业. 2023(07): 104-108 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘义富,王加真,周玲艳. 荧光灯、LED灯对福鼎大白茶树叶片光合生理及茶叶品质的影响. 江苏农业科学. 2023(21): 133-139 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王培娟,唐俊贤,金志凤,马玉平,陈惠. 中国茶树春霜冻害研究进展. 应用气象学报. 2021(02): 129-145 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王加真,刘义富,肖尧,周玲艳,曾一霞,宋世霞,赵蛾,秦中. 不同光配比对福鼎大白茶叶片生理和主要氨基酸积累的影响. 食品工业科技. 2021(19): 29-35 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: