Spectrum-effect Relationship between HPLC Fingerprints and DPPH-scavenging Activities of Tea Catechins
-
摘要:目的 研究茶叶儿茶素HPLC指纹图谱与其自由基清除活性的关系。方法 采用70%甲醇对绿茶、白茶、闽北乌龙、闽南乌龙、红茶5类共25批次样本进行提取;以福林酚法测定总酚含量;以1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH)法研究自由基清除活性;同时通过高效液相色谱法(HPLC)获取指纹图谱数据并对所获取的指纹图谱数据进行主成分分析;采用偏最小二乘回归分析研究HPLC指纹图谱与DPPH清除活性的谱效关系,结合皮尔逊(Pearson)相关性分析对偏最小二乘回归模型进行验证。结果 获取25批次样本的HPLC指纹图谱,确定了8个儿茶素类化合物,成功构建了偏最小二乘回归方程,其决定系数R2=0.900 9。结果表明表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(EGCG)、表没食子儿茶素(EGC)、表儿茶素没食子酸酯(ECG)与DPPH清除力相关性最强,均呈极显著正相关;没食子酸(GA)与DPPH清除力呈负相关。Pearson相关性分析结果与偏最小二乘回归模型结果基本一致。结论 本研究通过HPLC指纹图谱信息可预测抗氧化活性。
-
关键词:
- 儿茶素 /
- 抗氧化 /
- 高效液相色谱(HPLC) /
- 谱效关系
Abstract:Objective Correlation between the high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) fingerprints and the DPPH radical scavenging activities of catechins from varieties of teas was studied.Method From 5 categories of teas including green tea, white tea, northern Fujian oolong, southern Fujian oolong, and black tea, 25 specimens were collected and extracted with 70% methanol. The extracts were used to determine polyphenols content by the Folin-Ciocalteu method, the free radical scavenging activity by [1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazylradical2,2-Diphenyl-1-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl) hydrazyl, DPPH] assay, and the fingerprints by HPLC for a principal component analysis. A correlation model between the HPLC fingerprints and DPPH radical scavenging activity was established by a partial least squares regression analysis and validated by the Pearson analysis.Result The HPLC fingerprints of the 25 specimens had 8 common compounds. The established regression model showed a coefficient of determination of R2=0.900 9. The 3 compounds, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), epigallocatechin (EGC), and epicatechin gallate (ECG), exhibited the strongest and significant correlations with DPPH radical scavenging activity. On the other hand, gallic acid (GA) correlated inversely with the scavenging activity. The Pearson analysis showed a result consistent with what the partial least squares regression test did.Conclusion It appeared that the antioxidant activity of catechins in the various teas could be satisfactorily predicted by HPLC fingerprints. -
0. 引言
【研究意义】类受体胞质激酶(Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase,RLCK)是一类只含有胞内激酶域、缺少胞外受体域和跨膜结构域的类受体蛋白激酶(Receptor-like protein kinase,RLKs)[1]。研究显示,RLCK家族基因通过参与PTI(Pattern-triggered immunity,PTI)信号通路,发挥了从激活PRRs(Pattern-recognition receptors,PRRs)向下游传递免疫信号的功能,并且RLCK是植物识别多种病原菌效应蛋白的潜在联接点,同时RLCK还可作为宿主蛋白或支架蛋白参与ETI( Effector-triggered immunity ,ETI)信号,增加识别特异性及扩大植物免疫系统网络[2]。水稻中RLCK家族基因全基因组分析表明,不同发育阶段,379个RLCK基因中有100个差异表达,表明RLCK家族基因参与多种发育过程[3]。棉花是世界上最大的天然纤维作物和重要的油料作物,在其生长过程中RLCK家族基因的第六亚家族成员(RLCK VI)是否参与调控生长发育和逆境适应等过程未见报道。因此,针对棉花RLCK VI家族基因进行全基因组分析,探讨该家族基因在其生长发育和逆境胁迫响应中的潜在作用,对揭示棉花RLCK VI蛋白的生物学功能具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】研究表明,植物RLCK家族基因的RLCK VI在拟南芥和水稻中广泛参与植物的抗病、抗逆、生长发育等多种生物过程[3-5]。拟南芥和水稻中分别含有147个、379个RLCK家族成员[6,7],研究显示,在拟南芥中,RLCK VI家族分为A和B两组,每组7个成员[8];水稻中,RLCK VI家族共13个成员,其中A组7个,B组6个[9]。拟南芥中,RLCK VI家族基因AtSTU(Stunted)缺失后,植株表现出生长迟缓[10]。当拟南芥的RLCK VI_A2基因缺失,导致细胞扩增和幼苗生长受限[11]。研究表明,ROPs(Rho-related GTPases from plants)可以激活拟南芥中的AtRLCK VI_A3基因的表达,当AtRLCK VI_A3基因缺失后,拟南芥突变体表现出植株矮小,高分枝数的毛状体比例增加,对白粉病的抗性降低[4,12]。AtBIK1(Botrytis-induced kinase 1)基因参与了FLS2介导植物的免疫反应,也是BR(Brassinosteroid,BR)介导的信号通路中的关键因子[13,14]。在病原体感染后,拟南芥AtRBK1(RLCK VI_A4)和AtRBK2(RLCK VI_A6)基因的表达增强,进一步说明RLCK VI_A组基因在病原体反应中起重要作用[15]。定位于细胞质中的OsRRK1(Rop-interacting receptor-like kinase 1)蛋白是水稻中第一个被研究的类胞质受体激酶RLCK Ⅵ家族蛋白,是一个多效性基因,在调控水稻叶片的卷曲和对褐飞虱的防御中都起关键作用[5,16,17]。OsGUDK(Growth under drought kinase)基因在幼根、营养叶和旗叶中能被干旱诱导表达,该基因突变体在幼苗期对盐较敏感,营养生长时期在干旱条件下光合作用和生物量下降,生殖生长时期在干旱条件下产量显著降低,分析表明,GUDK基因通过磷酸化并激活转录因子OsAP37基因,从而激活下游与胁迫相关基因的转录,提高植株抗干旱能力[18,19]。大豆GsRLCK基因转录受盐和干旱诱导,将其转入拟南芥中过表达,提高了转基因拟南芥植株抗盐和抗干旱能力[1,20]。RLCK VI家族基因RBK1(Rop binding protein kinase1)和RBK2在花粉中表达,参与微管结构形成[21]。近期研究表明,ROP(Rho-related GTPases from plants)蛋白是高等植物中的信号小 G 蛋白,被称为“分子开关”,而拟南芥中的RLCK Ⅵ_A组基因能够被ROP蛋白特异激活,从而调控植物生长发育、抗病、抗逆等过程[1,22]。例如:AtRLCKⅥ_A3 基因通过与 ROP4和 ROP6相互作用阻碍十字花科白粉菌感染拟南芥以及影响毛状体形成过程中的细胞分化[1,4]。【本研究切入点】目前,关于RLCK VI家族基因的研究主要集中于模式植物拟南芥与水稻中,该家族基因在参与植物生长发育、逆境胁迫响应过程中扮演重要角色;但棉花中RLCK VI基因家族的研究却鲜有报道。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究基于最新发布的海岛棉Hai7124基因组[22],利用生物信息学方法鉴定 RLCK VI基因家族成员,并对海岛棉RLCK VI家族基因的理化性质、染色体分布、基因结构、系统进化关系、基因复制进行分析,并基于转录组测序(RNA-Seq)数据分析其在不同组织及在黄萎病胁迫、干旱胁迫和盐胁迫处理下的表达模式,为后续棉花中RLCK VI基因家族的功能研究及棉花遗传性状改良提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 海岛棉RLCK VI家族基因鉴定
海岛棉全基因组数据下载自棉花基因组数据库(https://www.cottongen.org/)[23],从拟南芥数据库(The arabidopsis information resource,TAIR)和水稻基因组数据库(Rice Phylogenomics Database)(https://ricephylogenomics.ucdavis.edu/)下载RLCK VI蛋白序列信息,利用TBtools软件[24]与海岛棉基因组数据建立本地数据库,利用TBtools软件的BLAST SeveralSequencestoa Big Database程序鉴定含有RLCK VI家族保守结构域的海岛棉蛋白序列。将所获得的RLCK VI家族保守结构域的海岛棉蛋白序列提交NCBI 网站的保守结构域数据库(Conserved domain database,CDD)和Pfam数据库进行保守结构域分析,对海岛棉RLCK VI家族基因进行鉴定。
1.2 海岛棉RLCK VI蛋白序列理化性质、亚细胞定位及结构域分析
利用ExPASy(https://web.expasy.org/protparam/)在线工具对鉴定出的海岛棉RLCK VI家族蛋白序列进行理化性质分析;利用ProtComp 9.0 在线工具(http://www.softberry.com/)预测海岛棉RLCK VI家族成员的亚细胞定位;使用 ClustalX2.1 (http://www.clustal.org/clustal2/)软件进行蛋白序列多重比对;利用NCBI 网站的保守结构域数据库(Conserved domain database,CDD)进行保守域分析,利用TBtools软件绘制海岛棉RLCK VI保守区域氨基酸序列的保守情况。
1.3 海岛棉RLCK VI蛋白系统进化树构建和基因结构分析
将海岛棉RLCK VI蛋白序列和已经分类的拟南芥RLCK VI 蛋白序列进行Clustal X 多序列比对,利用MEGA 7.0 软件基于最大似然法(Neighbor-joining method)对比结果构建系统进化树,Bootstrap设为 1 000 次[25]。利用在线软件工具 GSDS 2.0(http://gsds.cbi.pku.edu.cn/)对 RLCK VI 基因家族的基因结构进行可视化。利用 MEME在线软件分析海岛棉RLCK VI 保守基序,参数设置为基序最大发现数目为 10,基序最大长度为 100 nt(Nucleotide,核苷酸)。
1.4 染色体定位和基因复制分析
利用海岛棉基因组注释文件信息提取海岛RLCK VI 基因家族染色体物理位置信息,利用TBtools软件进行RLCK VI 基因染色体定位;利用TBtools工具中的MCScanX检测海岛棉基因组复制基因对,检测标准:蛋白比对 E值小于 1×10−10,至少 50%序列相似度;共线性区段内至少有5个复制基因。利用TBtools工具中的Ka/Ks_Calculator 2.0程序计算海岛棉复制基因对的非同义突变率(Ka)和同义突变率(Ks)。
1.5 海岛棉RLCK VI基因家族表达谱分析
从 NCBI SRA 数据库下载最新的海岛棉根、茎、叶、花药、苞片、花丝、花瓣、雌蕊、萼片、花托等10个组织,以及盐、PEG6000 模拟干旱逆境胁迫和黄萎病菌胁迫处理下的不同时期的转录组数据,项目数据登录号为PRJNA490626和PRJNA234454。利用TBtools工具软件进行有参比对并计算表达量TPM(Transcripts per kilobase million)[26],利用 log2(TPM+1)计算表达量,并将结果导入 R 包pheatmap绘制表达量热图。
1.6 胁迫处理及相关基因表达分析
对海岛棉品种海7124三周龄幼苗进行PEG、NaCl和黄萎病菌胁迫处理,PEG、NaCl处理时间为0、1、3、6、12、24 h,黄萎病菌胁迫处理时间为0、2、6、12、24、48、72 h,收集处理不同时间后棉花根部组织,液氮速冻后保存于−80 ℃冰箱。EASYspin Plus 植物 RNA 快速提取试剂盒购自北京艾德莱生物科技有限公司。cDNA 第一链合成试剂盒购自宝日医生物技术(北京)有限公司。Trans start Tip Green qPCR Super Mix荧光定量试剂购自北京全式金生物技术股份有限公司,qRT-PCR反应体系及程序严格按照试剂盒说明书操作。试验设3个重复,以GhUBQ7作为内参基因,采用2−∆∆CT法计算基因的相对表达量,qRT-PCR引物见表1。
表 1 荧光定量 PCR引物序列Table 1. Sequences of primers for quantitative PCR基因名称
Gene name基因序列(5′-3′)
Primer sequence (5′-3′)GB_A11G2234-F AATGAAGAATGAGAAACAA GB_A11G2234-R GAGGTGAAAACTGAAGTAC GB_A12G0061-F AAACTGGACTCACCACAAC GB_A12G0061-R AGTACACCAAAGGCAAACA GB_D01G2010-F GCAATATGGGGACCAACTG GB_D01G2010-R AGAACAACACCGAAAGCGT GB_D03G0730-F CATAAACGAAATAGCTTGC GB_D03G0730-R CCTTGGTCTCATAGGAAAC GhUBQ7-F GAAGGCATTCCACCTGACCAAC GhUBQ7-R CTTGACCTTCTTCTTCTTGTGCTTG 2. 结果与分析
2.1 海岛棉RLCK VI家族成员鉴定及系统进化分析
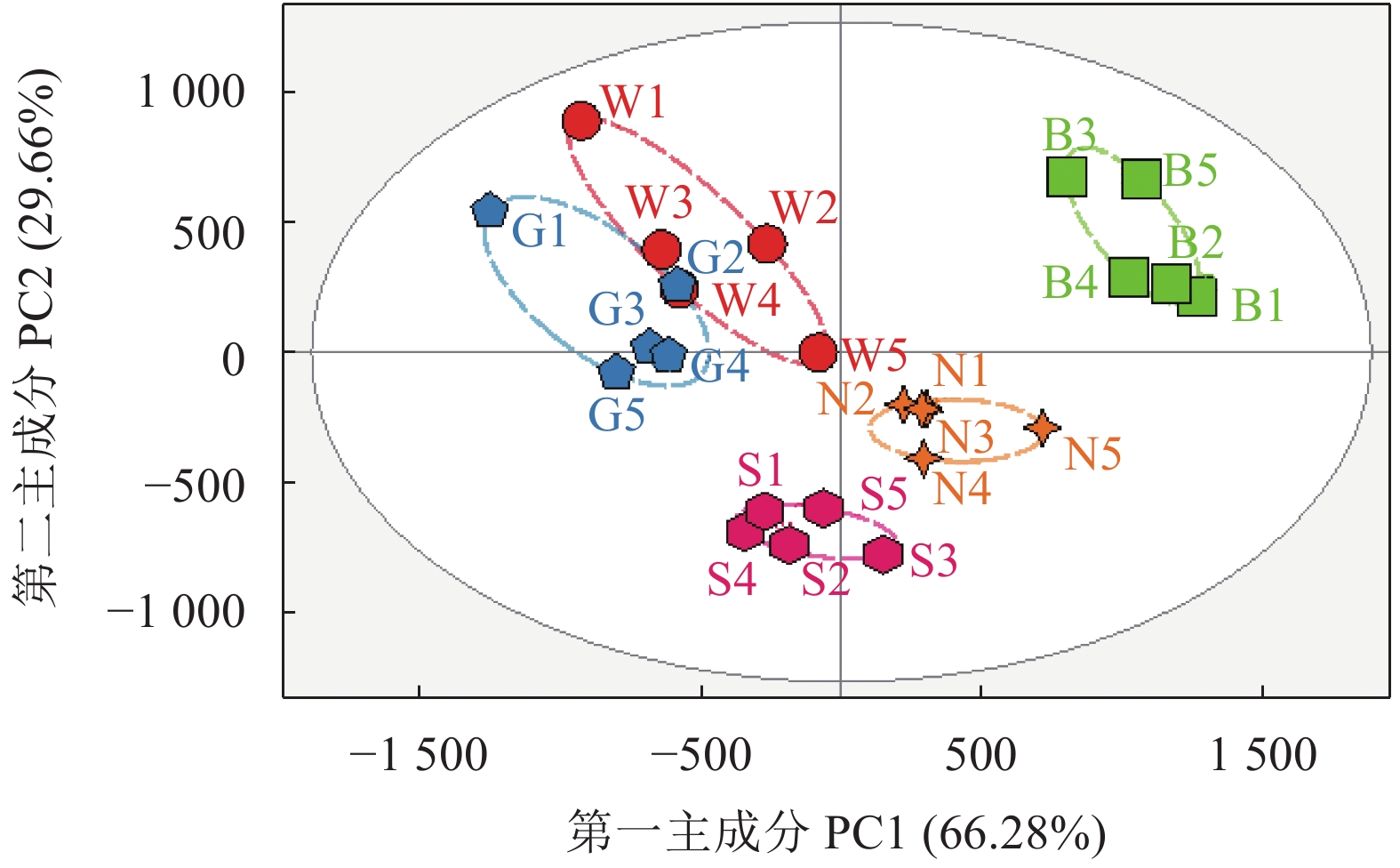
利用海岛棉基因组(Hai7124_V1.1)数据建立本地数据库,以拟南芥和水稻RLCK VI家族基因为探针序列,利用TBtools软件中的BLAST Several Sequences to a Big Database程序进行序列比对,获得与拟南芥和水稻RLCK VI家族基因同源序列,利用NCBI 中Conserved domain database(CDD)和Pfam数据库进行保守结构域分析,选取均含RLCK VI家族保守结构域的海岛棉蛋白序列,采用MEGA7.0软件最大似然法程序构建进化树,利用同源聚类的原理进行序列筛选,获得39个海岛棉RLCK VI 家族成员(图1)。
![]() 图 1 拟南芥、水稻与海岛棉RLCK VI家族基因系统进行分析红色方块为RLCK VI_A亚家族;绿色方块为RLCK VI_B亚家族;At:拟南芥,LOC_Os:水稻,GB:海岛棉。Figure 1. Phylogenetic evolution of RLCK VI family genes in Arabidopsis thaliana, Oryza sativa, and G. barbadenseRed square indicates RLCK VI_A subfamily group; green square, RLCK VI_B subfamily group; At: Arabidopsis thaliana; LOC_Os: Oryza sativa; GB: G. barbadense.
图 1 拟南芥、水稻与海岛棉RLCK VI家族基因系统进行分析红色方块为RLCK VI_A亚家族;绿色方块为RLCK VI_B亚家族;At:拟南芥,LOC_Os:水稻,GB:海岛棉。Figure 1. Phylogenetic evolution of RLCK VI family genes in Arabidopsis thaliana, Oryza sativa, and G. barbadenseRed square indicates RLCK VI_A subfamily group; green square, RLCK VI_B subfamily group; At: Arabidopsis thaliana; LOC_Os: Oryza sativa; GB: G. barbadense.2.2 海岛棉 RLCK VI家族成员编码蛋白理化性质、染色体分布及亚细胞定位分析
对RLCK VI家族成员编码的蛋白质进行理化性质分析,其编码的氨基酸序列长度为389~776 aa,蛋白质分子量为44313.24~84629.22 Da,理论等电点(Theoretical isoelectric point,pI)5.3~9.51,pI<7.0 的酸性蛋白质共计25个,其中17个为GbRLCK VI_A亚族成员;pI>7.0的碱性蛋白共计14个,其中10个为GbRLCK VI_A亚族成员(表2)。亚细胞定位分析显示,位于细胞质中有12个基因,位于胞外有10个基因,位于质膜上的基因共计17个(表2)。基于海岛棉全基因组数据,共鉴定RLCK VI家族基因成员39个基因均含有1个激酶结构域,分析该家族基因在染色体上的位置信息,结果表明(表2),在A04、A06、A07、A13号染色体和D02、D05、D06、D07、D08、D13号染色体无RLCK VI家族基因成员分布,其他每条染色体上至少含有1个RLCK VI家族基因,其中位于A、D的11、12号染色体的最多,每条染色体均包含5个RLCK VI家族基因;统计发现A、D染色体分别含有RLCK VI家族基因20个、19个,由此说明,GbRLCK VI家族基因在 A染色体和 D染色体的进化历程可能是不对称的(表2)。
表 2 GbRLCK VI亚族成员蛋白理化性质及亚细胞定位分析Table 2. Physicochemical properties and subcellular localizations of proteins in GbRLCK VI subfamily members基因编号
Gene ID分类
Classification理论等电点
pI相对分子质量
Relative molecular
mass/Da染色体
Chromosome位置
Location/bp开放阅读
框长度
ORF/bp氨基酸
Amino
acids/aa亚细胞定位
Subcellular
localizationGB_A01G0260 RLCK VI_A 5.30 62875.09 A 2206175~2210244 1683 561 细胞质 Cytoplasmic GB_A01G1081 RLCK VI_B 8.18 83349.28 A 20600106~20603458 2214 738 胞外 Extracellular GB_A01G1914 RLCK VI_B 5.97 75989.42 A 103561645~103564486 2046 682 胞外 Extracellular GB_A02G1246 RLCK VI_B 6.94 84611.20 A 63519857~63524024 2325 775 胞外 Extracellular GB_A02G1740 RLCK VI_A 5.94 50565.48 A 97801526~97803417 1362 454 质膜 Plasma membrane GB_A03G0311 RLCK VI_A 5.95 44313.24 A 3766673~3768994 1167 389 质膜 Plasma membrane GB_A05G3702 RLCK VI_A 8.52 67781.48 A 84140713~84143610 1815 605 细胞质 Cytoplasmic GB_A08G1010 RLCK VI_A 9.08 65230.47 A 33774846~33777243 1749 583 细胞质 Cytoplasmic GB_A09G2643 RLCK VI_A 5.6 58175.80 A 77782790~77786063 1554 518 细胞质 Cytoplasmic GB_A10G1115 RLCK VI_A 6.01 54570.32 A 22829603~22832184 1470 490 质膜 Plasma membrane GB_A11G0540 RLCK VI_A 6.03 50910.97 A 4885422~4887763 1362 454 质膜 Plasma membrane GB_A11G1251 RLCK VI_A 9.25 47356.59 A 12738544~12740333 1269 423 质膜 Plasma membrane GB_A11G2234 RLCK VI_A 6.09 52234.38 A 51930366~51932808 1395 465 质膜 Plasma membrane GB_A11G2998 RLCK VI_A 6.98 54619.72 A 102734569~102739375 1455 485 质膜 Plasma membrane GB_A11G3462 RLCK VI_A 8.39 54509.86 A 111382556~111386884 1455 485 细胞质 Cytoplasmic GB_A12G0061 RLCK VI_A 9.54 44738.44 A 770437~772212 1197 399 质膜 Plasma membrane GB_A12G0366 RLCK VI_B 5.53 51025.69 A 6110842~6112604 1365 455 质膜 Plasma membrane GB_A12G0580 RLCK VI_B 8.94 57833.28 A 12489405~12491904 1566 522 胞外 Extracellular GB_A12G0837 RLCK VI_B 6.28 72794.02 A 35264457~35267552 1959 653 胞外 Extracellular GB_A12G1016 RLCK VI_A 6.08 55330.70 A 58620348~58623557 1470 490 细胞质 Cytoplasmic GB_D01G0255 RLCK VI_A 5.61 54753.77 D 2136137~2138668 1461 487 质膜 Plasma membrane GB_D01G1159 RLCK VI_B 8.62 82638.79 D 16772231~16775594 2193 731 胞外 Extracellular GB_D01G2010 RLCK VI_B 5.87 75966.19 D 54299320~54302161 2049 683 胞外 Extracellular GB_D03G0345 RLCK VI_A 5.94 50468.36 D 3912795~3914684 1359 453 质膜 Plasma membrane GB_D03G0730 RLCK VI_B 6.52 84629.22 D 19203868~19208089 2328 776 胞外 Extracellular GB_D03G1685 RLCK VI_A 5.86 44338.23 D 49960463~49962648 1167 389 质膜 Plasma membrane GB_D04G0916 RLCK VI_A 8.82 67857.57 D 17923478~17926392 1824 608 细胞质 Cytoplasmic GB_D09G2477 RLCK VI_A 5.54 58118.73 D 52528068~52531290 1554 518 细胞质 Cytoplasmic GB_D10G1818 RLCK VI_A 6.1 58069.37 D 46511912~46514475 1569 523 细胞质 Cytoplasmic GB_D11G0554 RLCK VI_A 5.96 51742.65 D 4472367~4474758 1386 462 质膜 Plasma membrane GB_D11G1285 RLCK VI_A 9.37 50810.57 D 11385965~11387753 1347 449 细胞质 Cytoplasmic GB_D11G2293 RLCK VI_A 6.17 52301.37 D 30637528~30639969 1395 465 质膜 Plasma membrane GB_D11G2991 RLCK VI_A 7.67 54466.53 D 60438857~60443672 1455 485 质膜 Plasma membrane GB_D11G3433 RLCK VI_A 8.39 54454.82 D 67010248~67014591 1455 485 细胞质 Cytoplasmic GB_D12G0064 RLCK VI_A 9.51 44758.54 D 777708~781902 1197 399 质膜 Plasma membrane GB_D12G0350 RLCK VI_B 5.54 51097.86 D 4562988~4564741 1365 455 质膜 Plasma membrane GB_D12G0573 RLCK VI_B 9.04 57727.16 D 9309237~9311733 1563 521 胞外 Extracellular GB_D12G0968 RLCK VI_A 5.73 53551.68 D 20078236~20080755 1425 475 细胞质 Cytoplasmic GB_D12G0998 RLCK VI_B 6.62 79099.37 D 16414879~16417975 2133 711 胞外 Extracellular 2.3 海岛棉RLCK VI家族基因结构和基序(motif)预测分析
利用39条海岛棉RLCK VI家族基因的氨基酸序列构建系统进化树并对家族基因结构和保守基序进行可视化分析,结果显示(图2),39个RLCK VI家族基因分为A、B两个组;通过比较RLCK VI家族基因外显子-内含子,基因外显子数6~9个;利用 MEME 在线软件分析海岛棉RLCK VI 家族蛋白序列保守 motif,分析发现B组基因成员均含有motif1~motif8,而A组基因成员除GB_A12G0580和GB_D12G0573外,其他成员均含有motif1~motif7,motif9或motif10只存在部分RLCK VI家族成员。
2.4 海岛棉RLCK VI基因家族共线性分析
为了进一步探索海岛棉RLCK VI家族基因的进化过程,本研究分析了海岛棉RLCK VI 家族不同基因间的共线性关系,共发现36对RLCK VI基因存在共线性关系(图3),除A 染色体和 D染色体上的RLCK VI基因之间存在共线性关系外,A 、D染色体内分别有2对和7对RLCK VI基因也存在共线性关系,而且RLCK VI基因家族存在单个基因对应多个基因的情况,说明该家族在进化过程中发生了染色体片段复制事件。
为研究海岛棉GbRLCK_VI家族基因在染色体区段上的进化复制关系,利用TBtool软件中的MCScanX软件检测复制基因。在海岛棉A 染色体间、D 染色体间及 A和D 染色体间分别检测到了2对、5对和24对全基因组复制基因,采用KaKs_Calculator对海岛棉复制基因对进行 Ka/Ks分析(表3)。研究发现所有基因对的 Ka/Ks 均小于 1,表明海岛棉GbRLCK VI家族基因在进化过程中可能经历了严格的纯化选择作用,暗示了复制基因在进化上的保守,结构稳定,可能具有一致性功能。
表 3 串联重复基因Ka/Ks计算Table 3. Calculation of Ka/Ks for tandem repeat gene基因编号
Gene ID基因编号
Gene ID非同义替换
Ka同义替换
Ks非同义替换/同义替换
Ka/KsGB_A01G1914 GB_A12G0366 0.104312114 0.45263137 0.230457101 GB_A01G0260 GB_D01G0255 0.028943225 0.046322927 0.624814254 GB_A01G1081 GB_D01G1159 0.020977245 0.054445666 0.385287692 GB_A01G1914 GB_D01G2010 0.013406752 0.02845499 0.471156428 GB_A01G1914 GB_D12G0350 0.109277637 0.473782321 0.230649461 GB_A02G1740 GB_D03G0345 0.005691277 0.03053857 0.186363574 GB_A02G1246 GB_D03G0730 0.006776517 0.037543027 0.18050001 GB_A02G1740 GB_D11G2293 0.197554085 1.040010514 0.18995393 GB_A05G3702 GB_D04G0916 0.023308504 0.056770511 0.410574135 GB_A09G2643 GB_D09G2477 0.012551719 0.050376868 0.249156396 GB_A10G1115 GB_D09G2477 0.250706504 0.744111803 0.336920478 GB_A10G1115 GB_D10G1818 0.010688224 0.02700967 0.395718402 GB_A11G1251 GB_A12G0061 0.103086568 0.88836622 0.116040621 GB_A11G0540 GB_D11G0554 0.01383297 0.035350161 0.391312788 GB_A11G1251 GB_D11G1285 0.012356552 0.038946803 0.31726743 GB_A11G2998 GB_D11G2991 0.01397591 0.054049622 0.258575533 GB_A11G3462 GB_D11G3433 0.013455287 0.069780882 0.192821966 GB_A11G0540 GB_D11G2293 0.239191447 0.679802163 0.351854496 GB_A11G2234 GB_D11G2293 0.009270106 0.04321328 0.214519851 GB_A11G1251 GB_D12G0064 0.108697399 0.818974304 0.132723821 GB_A12G0366 GB_D01G2010 0.110134899 0.497372712 0.221433336 GB_A12G0061 GB_D11G1285 0.102473606 0.89384392 0.114643735 GB_A12G0061 GB_D12G0064 0.017583223 0.05245583 0.335200547 GB_A12G0580 GB_D12G0573 0.006683419 0.045728447 0.146154523 GB_A12G0366 GB_D12G0350 0.01232937 0.026976777 0.457036417 GB_A12G1016 GB_D12G0968 0.014602332 0.065561783 0.222726282 GB_D01G2010 GB_D12G0350 0.116240086 0.513096743 0.22654614 GB_D03G0345 GB_D11G2293 0.19515733 1.062230892 0.18372402 GB_D09G2477 GB_D10G1818 0.254053518 0.74467519 0.341160175 GB_D11G0554 GB_D11G2293 0.210367409 0.660727812 0.318387398 GB_D11G1285 GB_D12G0064 0.106823583 0.823959217 0.129646687 2.5 海岛棉GbRLCK VI家族基因在不同组织的表达分析
由于基因的表达和功能的执行具有组织特异性,利用转录组数据分析了GbRLCK VI家族成员在根、茎、叶、花药、苞片、花丝、花瓣、雌蕊、萼片、花托等10个组织的表达模式(图4),以TPM>1 作为基因表达的筛选标准。结果表明,4个基因在所有组织中的TPM数值均小于1,因此认为它们在组织中不表达或者表达量极少。只在其中1个组织中表达的基因共9个,根中表达的基因2个(GB_D04G0916、GB_A05G3702),花药中表达的基因6个(GB_D10G1818、GB_A02G1740、GB_A12G1016、GB_D09G2477、GB_A11G0540、GB_A10G1115),GB_D11G3433只在花丝中表达。只在两个组织中表达的基因有3个,包括GB_D11G2991(根、花丝)、GB_A01G0260(根、花托)、GB_D03G0345(花药、苞片)。在3个组织(根、花丝、雌蕊)中表达的基因有4个(GB_D11G1285、GB_A11G1251、GB_A12G0366、GB_D11G0554)。在4个组织(根、花丝、雌蕊、花托)中表达的只有GB_D12G0350基因。在根、茎、花药、苞片、花瓣、雌蕊、萼片7个组织中表达的基因仅有GB_A01G1081。 GB_A11G2234、GB_A12G0837、GB_D01G1159、GB_D11G2293在8个组织(根、叶、花药、苞片、花丝、花瓣、雌蕊、萼片、花托)中表达。GB_D12G0064、GB_A12G0061、GB_D01G2010在9个组织(根、茎、叶、花药、苞片、花瓣、雌蕊、萼片、花托)中表达。9个基因(GB_A01G1914、GB_D12G0998、GB_D12G0573、GB_A12G0580、GB_A03G0311、GB_D03G0730、GB_D03G1685、GB_D01G0255、GB_A02G1246)在10个组织(根、茎、叶、花药、苞片、花丝、花瓣、雌蕊、萼片、花托)中均表达(图4)。
2.6 海岛棉GbRLCK VI家族基因在逆境胁迫下表达分析
利用海岛棉在盐、干旱与黄萎病菌胁迫下的转录组数据,分析GbRLCK VI家族基因在不同逆境中的表达规律,聚乙二醇(Polyethylene glycol,PEG)模拟干旱胁迫处理后,以TPM>1 作为基因表达的筛选标准,发现20个基因在对照中TPM值均小于1,22个基因在处理1、3、6、12、24 h的TPM值均小于1,认为它们在CK和处理时间点不表达或表达量极低。与CK相比,各处理时间点均高于CK的基因3个(GB_D12G0064、GB_A12G0061、GB_A03G0311),而各处理时间点均低于CK的基因有2个(GB_D01G2010、GB_D12G0998);除上述基因表达特征外,GB_A01G1914表达值在处理6、12、24 h高于CK,但在处理1、3 h表达值低于CK;GB_D11G2293只在12 h表达值高于CK,由此推测GbRLCK_VI家族的部分基因参与了干旱胁迫响应(图5)。
盐胁迫处理后,发现17个基因在对照组和处理组中TPM值均小于1,除此之外,3个基因(GB_D03G0345、GB_A11G2998、GB_A10G1115)在对照组中TPM值均小于1,但在处理组不同时间点TPM值大于1。盐胁迫处理后,5个基因(GB_D12G0064、GB_A12G0061、GB_A03G0311、GB_D03G0730、GB_A02G1246)上调表达,4个基因(GB_A01G1914、GB_A01G1081、GB_A12G0837、GB_A01G0260)下调表达, GB_D11G2293、GB_A11G2234、GB_D03G1685在处理24 h后上调表达,其余时间点下调表达,GB_D01G0255处理1 h后上调表达,其余时间点下调表达(图5)。
黄萎病菌胁迫后,发现17个基因在对照组和处理组中TPM值均小于1,表明这些基因几乎不参与黄萎病菌胁迫相响应。GB_A02G1740只在对照组中TPM值小于1,但在处理组不同时间点TPM值大于1;3个基因(GB_A11G0540、GB_D12G0350、GB_A12G0366)在对照组中TPM值大于1,黄萎病菌处理后,TPM值小于1;与对照相比,处理组中5个基因(GB_D01G2010、GB_A01G1914、GB_A11G0540、GB_A12G0580、GB_D01G2010)在处理时间点下调,10个基因(GB_D12G0064、GB_A12G0061、GB_A02G1246、GB_A02G1740、GB_D01G1159、GB_A01G1081、GB_D03G0345、GB_D03G0370、GB_A03G0311、GB_D03G1685)在处理时间点上调表达,以上分析结果显示GbRLCK VI家族成员在棉花应对逆境胁迫时发挥着重要作用(图5)。
2.7 胁迫处理相关基因表达PCR验证
在上述数据基础上,从响应干旱、盐和黄萎病菌胁迫的GbRLCK VI家族中挑选4个基因GB_A12G0061、GB_A11G2234、GB_D01G2010、GB_D03G0730进行qRT-PCR验证,结果如图6所示,GB_A11G2234基因均能响应干旱、盐和黄萎病菌胁迫,胁迫处理24 h时,表达量最高。GB_A12G0061基因在3种胁迫处理后,随处理时间的延长,在不同处理时间点相对表达量均高于对照,干旱胁迫后,该基因在处理24 h时表达量最高,而盐和黄萎病菌胁迫后,该基因在处理12 h时表达量最高。GB_D01G2010基因的表达特正与转录组数据结果一致,该基因对干旱和盐胁迫响应随处理时间推移,较对照而言,表达量下降,但黄萎病菌处理后,在处理12 h表达量达到最高值。GB_D03G0730基因在盐和黄萎病菌胁迫处理后,在不同处理时间点相对表达量均高于对照,干旱胁迫后,该基因在处理1 h时表达量最高,较其他3个基因而言,该基因对干旱胁迫响应时间较早,上述结果显示,GB_A12G0061、GB_A11G2234、GB_D03G0730基因在盐和黄萎病菌处理的时间点中,表达量高于对照;GB_A12G0061基因在干旱胁迫后,各处理时间点表达量均高于对照,表明它们参与了棉花对逆境胁迫(干旱、盐和黄萎病菌)的响应过程。
3. 讨论
棉花是重要的纤维和油料作物[27]。目前,新疆是我国的棉花主产区,但地处干旱荒漠地带,水资源短缺,盐碱重且分布广,棉田枯黄萎病蔓延,严重制约棉花可持续发展,积极开发抗病、抗旱、耐盐碱地植棉潜力,将成为棉花生产保持相对稳定的重要应对策略。因此培育多抗棉花品种是当前棉花育种的主要目标[18]。研究表明,RLCK家族基因广泛参与植物的抗逆、生长发育等多种生物过程[2,27],而棉花全基因组测序完成,为我们从全基因组水平研究基因家族奠定了基础。本研究从海岛棉全基因组中鉴定出39个RLCK VI 家族基因,该亚家族基因数量明显高于拟南芥(14个)和水稻(13个),但从植物基因组大小相比,棉花基因组较大,约2.22 Gb[28],远高于拟南芥(164 Mb)[29]、水稻(441 Mb)的基因组[29],推测棉花中RLCK VI家族成员数量与基因组大小有明显相关性,其原因可能由于棉花中RLCK VI家族基因发生了基因组复制事件,从而引起该家族基因扩展。
依据拟南芥和水稻中RLCK VI家族基因的进化关系及分组方法[8],将海岛棉的39个RLCK VI基因分为A、B亚家族,数量分别为27个和12个,而拟南芥中的RLCK VI_A和RLCK VI_B亚家族成员均为7个[8],水稻中的RLCK VI_A、RLCK VI_B亚家族成员分别为7个、6个,除基因数量存在差异外,其结果与拟南芥和水稻中的RLCK VI家族分组结果一致。对海岛棉RLCK VI家族基因结构分析结果显示,该家族基因成员均有内含子,该结论与拟南芥和水稻RLCK VI家族基因结构相似 [8]。
组织表达分析表明,海岛棉不同器官中RLCK VI家族基因表达模式不同,B组基因在植物组织中的表达高于量A组基因,统计显示,共计9个基因在10个组织均表达,说明这些基因可能在棉花整个生长发育中都发挥作用。在拟南芥中,AtRLCK VI A2(At2g18890)缺失后,严重影响细胞扩增和幼苗生长[11],而与该基因同源的GB_A03G0311和GB_D03G1685在10个组织中均高表达;RLCK VI家族基因AtRBK1(At5g10520)通过磷酸化调控生长素应答调节细胞的生长[15],海岛棉中与AtRBK1基因同源性较高的基因有8个,其中,GB_D03G0345、 GB_A02G1740、 GB_A11G0540、 GB_D11G0554仅在花药组织中表达量较高, GB_D11G2293仅在根组织中表达量较高, GB_A11G2234在根和花药组织中表达量较高, GB_A12G1016、 GB_D12G0968在10个组织中均不表达;RLCK VI_B4(At2g16750)为发育迟缓(Stunted)基因,当该基因缺失后,拟南芥突变体发育的许多方面表现出生长迟缓;在营养生长期,突变体幼苗比野生型幼苗的叶子更小、根更短[10], 海岛棉中与RLCK VI_B4同源的基因有4个,GB_A01G1914与GB_D01G2010在10个组织中均表达,但GB_A12G0366仅在根、花丝和雌蕊中表达,通过转录组数据推测海岛棉中RLCK VI家族基因参与了生长发育调控,且在组织中表达具有多样性,后续进行相关研究仍需进行分析和验证。
前人研究证实RLCK-VI家族蛋白成员在拟南芥和水稻中广泛参与植物的生物胁迫和非生物胁迫生物过程[3-5]。通过分析不同胁迫(干旱、盐、黄萎病)处理下海岛棉RLCK VI家族基因的表达模式,统计发现,B组中参与胁迫响应的基因多于A组基因,研究表明,AtRLCK VI A3(At5g65530)不仅能提高拟南芥对白粉病的抗性,而且能调控拟南芥中的毛状体分支生长[4],而与之同源的基因(GB_A11G2234、GB_A12G1016、GB_D11G2293和GB_D12G0968)共4个,其中,GB_A11G2234、GB_D11G2293能够被干旱、盐及黄萎病胁迫诱导表达,但GB_A12G1016、GB_D12G0968均不能被干旱、盐及黄萎病胁迫诱导表达;水稻中,OsRRK1基因是第一个被研究的类胞质受体激酶RLCK Ⅵ家族基因,在调控水稻叶片的卷曲和对褐飞虱的防御中都起关键作用[5],在海岛棉中与该基因同源性较高的基因为GB_A03G0331、 GB_D03G1685,两个基因在盐、干旱、黄萎病菌胁迫下均能表达,但在盐、干旱胁迫下表达量较高,表明GB_A03G0331、 GB_D03G1685、GB_A11G2234、GB_D11G2293基因能够参与逆境胁迫,以上结果与已有的研究结果相似,但GB_A12G1016、GB_D12G0968基因虽然与AtRLCK VI A3有较高的同源性,但均不能被干旱、盐及黄萎病胁迫诱导表达。挑选4个基因GB_A12G0061、GB_A11G2234、GB_D01G2010、GB_D03G0730进行qRT-PCR验证,表达分析结果显示,4个基因在干旱、盐或黄萎病菌胁迫下的表达趋势与转录组数据一致,表明它们参与了棉花对逆境胁迫(干旱、盐和黄萎病菌)的响应过程,目前RLCK VI家族基因相关研究主要集中于拟南芥和水稻,但研究成果仍然较少,因此,海岛棉RLCK VI家族基因的生物学功能仍需深入研究。
综上,本研究从海岛棉基因组中鉴定出39 个GbRLCK_VI基因家族成员,分A、B两组, GbRLCK VI家族基因的表达具有组织特异性,且多数基因能被盐、干旱、黄萎病胁迫诱导表达。
-
图 1 茶样的总酚含量及其DPPH清除活性
注:G、W、N、S、B分别代表绿茶、白茶、闽北乌龙、闽南乌龙、红茶。图2同。
Figure 1. Polyphenol contents and DPPH radical scavenging activities of tea specimens
Note:G, W, N, S, and B represent samples of green tea, white tea, northern Fujian oolong, southern Fujian oolong, and black tea, respectively. The same for Fig.2.
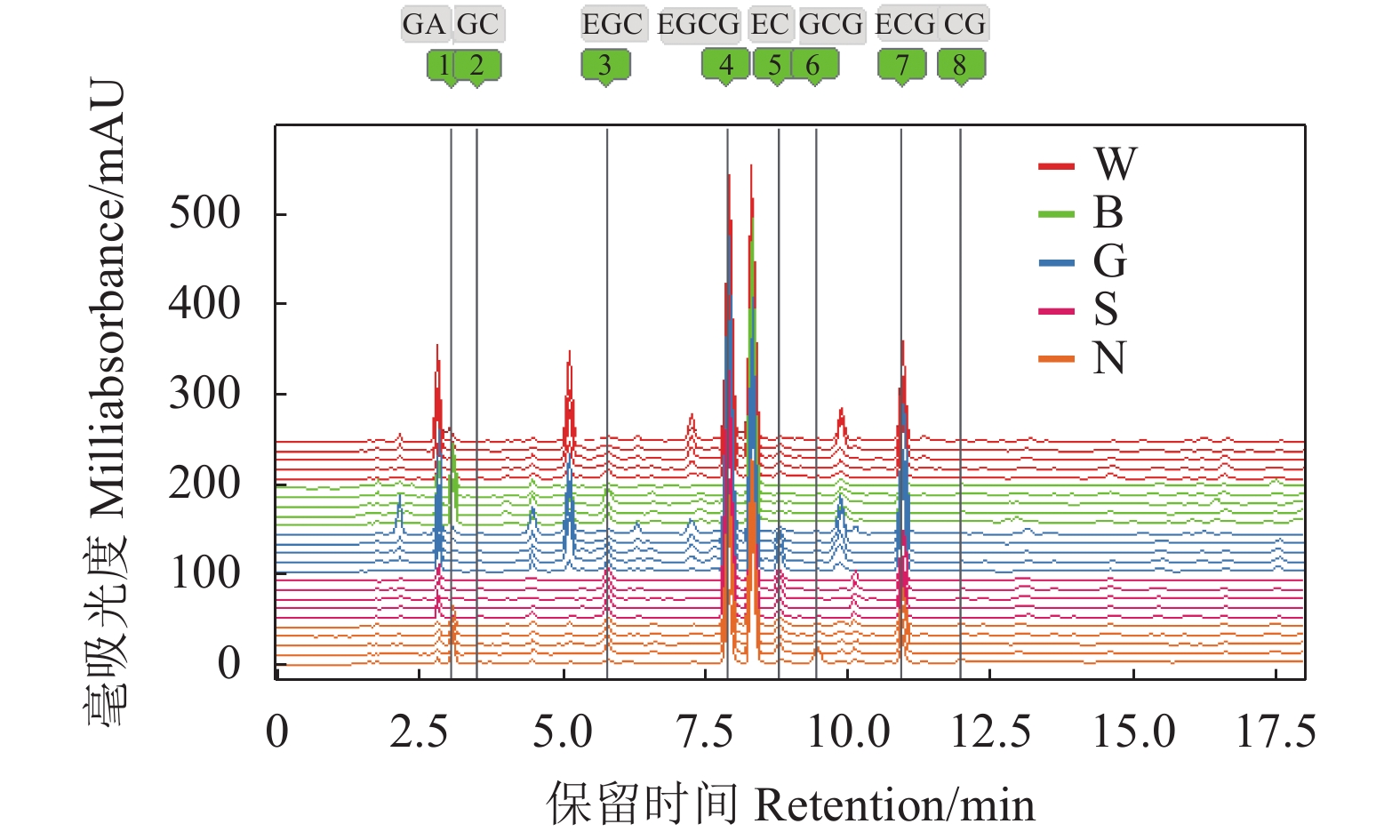
图 3 25个样品的HPLC指纹图谱
注:图中各样品编号由上至下分别为W1、W2、W3、W4、W5、B1、B2、B3、B4、B5、G1、G2、G3、G4、G5、S1、S2、S3、S4、S5、N1、N2、N3、N4、N5。
Figure 3. HPLC fingerprints from 25 samples
Note:The sample numbers from the top to the bottom are: W1, W2, W3, W4, W5, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, G1, G2, G3, G4, G5, S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, N1, N2, N3, N4, N5, respectively.
表 1 25个样品HPLC指纹图谱共有峰峰面积
Table 1 Average areas of common peaks on HPLC fingerprints from 25 samples
样品
Samples25个样品共有峰的峰面积 mAU*S
Average peak area of every common peak mAU*SGA GC EGC EGCG EC GCG ECG CG G1 40.13±1.40 18.22±2.25 65.87±3.57 2 227.66±13.35 49.54±1.15 32.02±1.95 995.88±9..90 8.77±5.70 G2 25.03±1.54 8.54±0.57 74.24±0.11 1637.85±3.57 121.59±0.92 12.23±1.27 768.66±5.20 10.52±1.24 G3 21.94±0.46 17.81±0.64 80.63±0.67 1716.19±1.63 147.59±1.70 18.96±1.38 769.49±3.11 8.59±1.70 G4 21.11±1.15 14.70±3.50 79.25±3.20 1653.04±13.25 150.69±3.20 10.51±0.20 765.03±15.75 10.56±2.65 G5 13.18±1.15 13.06±0.45 91.82±4.33 1894.60±6.30 169.08±1.10 20.26±0.40 952.57±3.51 14.85±5.45 W1 41.36±0.90 4.55±3.05 111.84±5.55 2038.52±68.95 34.36±3.85 20.29±0.55 875.54±16.45 5.64±2.30 W2 43.63±1.10 10.71±1.70 89.49±2.95 1382.64±43.60 57.11±3.35 12.58±0.50 569.71±12.55 6.08±1.20 W3 41.22±0.35 5.80±0.55 91.56±0.45 1836.79±4.55 50.96±8.95 14.19±0.65 642.15±2.20 7.49±0.10 W4 27.76±1.10 8.32±0.80 95.98±5.95 1814.42±94.35 58.06±4.00 9.37±2.35 545.45±22.70 6.22±0.55 W5 47.33±1.30 7.55±0.30 70.44±0.15 1326.74±9.80 36.01±2.40 7.29±1.15 412.72±1.70 6.11±1.00 N1 106.43±0.50 6.64±0.45 64.66±0.30 965.38±67.50 79.93±11.40 16.89±4.35 321.53±39.65 16.39±1.05 N2 94.12±0.65 9.42±1.30 78.55±1.40 1037.62±2.00 91.03±1.5 22.86±0.75 313.46±5.20 15.66±1.30 N3 102.94±0.35 8.44±5.22 79.80±2.60 983.68±22.30 87.01±1.82 20.98±0.60 298.41±9.28 10.53±1.83 N4 70.68±0.85 10.03±1.83 69.03±0.70 955.95±2.85 93.20±1.65 22.93±3.45 303.44±0.60 14.65±0.99 N5 155.18±0.45 15.98±1.55 65.33±0.75 578.92±9.85 19.10±0.10 154.82±0.25 212.88±4.50 40.47±2.20 S1 4.20±0.90 16.01±3.05 94.03±5.55 1523.93±68.95 86.89±3.85 8.96±0.55 368.55±16.45 10.68±2.30 S2 5.38±1.10 12.29±1.70 70.83±2.95 1361.34±43.60 109.65±2.35 9.23±1.95 402.72±12.4 11.26±0.45 S3 6.53±0.35 11.52±0.50 65.74±0.45 1066.28±4.50 125.36±8.95 5.74±0.65 319.91±2.20 8.80±0.10 S4 4.93±1.10 11.48±0.80 70.38±5.95 1423.13±94.35 83.51±4.00 13.15±2.35 373.80±22.50 8.54±0.55 S5 6.43±1.30 15.79±0.11 65.66±0.15 1298.71±9.80 74.57±2.40 8.64±1.15 335.69±1.72 7.32±1.12 B1 203.94±17.35 0.48±0.07 45.49±2.35 11.04±0.39 2.85±0.09 3.24±0.12 71.26±7.35 8.22±1.84 B2 210.96±0.050 ND 50.50±1.25 110.06±3.46 3.21±0.12 3.16±0.32 119.59±3.52 15.38±3.10 B3 228.05±2.65 ND 70.50±4.55 434.56±3.45 15.89±2.80 5.83±2.35 343.13±4.00 12.55±2.65 B4 180.05±0.65 ND 61.54±3.55 221.03±0.90 15.74±0.43 1.63±0.020 233.35±13.25 8.37±0.86 B5 219.56±4.70 ND 63.60±7.00 155.15±4.15 9.92±0.30 4.38±1.25 261.40±7.30 19.73±4.05 注:ND指未检出。
Note:ND means undetected.表 2 偏最小二乘回归方程假设检验结果
Table 2 Hypothetic result of partial least squares regression equation
方差来源 Variance Source 自由度 df 方差 SS 均方差 MS F P 回归 Regress 8 1491 186 18 0 残差 Residual 16 164 10 总变异数 Total variation 24 1 655 表 3 偏最小二乘回归方程预测结果
Table 3 Predicted result from partial least squares regression equation
模型检验
Model test样品
Sample预测值
Predictive实测值
Measured相对标准偏差
Relative standard deviation/%内部验证
Internal testG1 57.45 60.87 5.62 B3 40.90 39.28 4.12 N4 48.48 50.58 4.15 W3 56.25 58.19 3.33 S5 49.92 48.25 3.46 外部验证
External testR1 47.41 53.25 10.97 R2 62.15 58.34 6.53 R3 58.83 61.46 4.28 R4 47.93 45.16 6.13 R5 46.17 43.05 7.25 表 4 茶样中共同峰与其DPPH清除活性之间的关系
Table 4 Correlation coefficients between DPPH radical scavenging activities and common peaks
化合物 Composition GA GC EGC EGCG EC GCG ECG CG 相关系数 Correlation −0.723** 0.609** 0.808** 0.899** 0.427* 0.174 0.771** −0.170 注:**表示在0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关,*表示在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关。
Note: ** indicates a significant correlation at 0.01 level (double sides); * shows a significant correlation at 0.05 1evel (double sides). -
[1] CHEN X Y, GOU S H, SHI Z Q, et al. Spectrum-effect relationship between HPLC fingerprints and bioactive components of Radix Hedysari on increasing the peak bone mass of rat [J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 2019, 9(4): 266−273. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2018.10.004
[2] SHEN C H, LIU C T, SONG X J, et al. Evaluation of analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of Rubia cordifolia L. by spectrum-effect relationships [J]. Journal of Chromatography B, 2018, 1090: 73−80. DOI: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.05.021
[3] ZHAO Y, YOU X M, JIANG H, et al. Spectrum-effect relationships between high-performance liquid chromatography fingerprints and anti-inflammatory activities of Leontopodium leontopodioides (Willd.) Beauv [J]. Journal of Chromatography B, 2019, 1104: 11−17. DOI: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.11.001
[4] 李秋月. 延胡索生物碱谱-效关系及相互作用研究[D]. 北京: 北京协和医学院, 2014. [5] 吕邵娃, 董书羽, 郭玉岩, 等. 数据分析技术在中药谱效关系中的应用进展 [J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2015, 21(15):226−230. LV S W, DONG S Y, GUO Y Y, et al. Advance in application of data analysis technique in spectrum-effect relationship of traditional Chinese medicines [J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2015, 21(15): 226−230.(in Chinese)
[6] 曾令军, 林兵, 宋洪涛. 中药谱效关系研究进展及关键问题探讨 [J]. 中国中药杂志, 2015, 40(8):1425−1432. ZENG L J, LIN B, SONG H T. Progress in study of spectrum-effect relationship of traditional Chinese medicine and discussions [J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2015, 40(8): 1425−1432.(in Chinese)
[7] 徐晶晶, 刘斌. 基于DPPH、FRAP法的薄荷药材抗氧化谱效关系研究 [J]. 北京中医药大学学报, 2015, 38(6):405−410. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2157.2015.06.009 XU J J, LIU B. Spectrum-effect relation in antioxidant activity of Menthae haplocalycis Herba based on DPPH and FRAP assay [J]. Journal of Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 38(6): 405−410.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2157.2015.06.009
[8] ZHU C S, ZHANG B, LIN Z J, et al. Relationship between high-performance liquid chromatography fingerprints and uric acid-lowering activities of Cichorium intybus L [J]. Molecules, 2015, 20(5): 9455−9467. DOI: 10.3390/molecules20059455
[9] 谭庆龙, 欧筱争, 谢丽霞, 等. 藏方甲嘎松汤挥发油体外抗氧化活性的谱效关系研究 [J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2015, 26(3):360−364. TAN Q L, OU X Z, XIE L X, et al. Study on spectrum-effect relationship between fingerprints and antioxidant activities of essential oil from Tibetan medicine jiagasong decoction in vitro [J]. Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology, 2015, 26(3): 360−364.(in Chinese)
[10] XU G L, XIE M, YANG X Y, et al. Spectrum-effect relationships as a systematic approach to traditional Chinese medicine research: current status and future perspectives [J]. Molecules, 2014, 19(11): 17897−17925. DOI: 10.3390/molecules191117897
[11] 王媛媛, 马飞祥, 李凤英, 等. 在线色谱联用技术检测天然产物抗氧化活性的研究进展 [J]. 北方药学, 2016, 13(9):123−125. WANG Y Y, MA F X, LI F Y, et al. Progress in the determination of antioxidant activity of natural products by on-line chromatography [J]. Journal of North Pharmacy, 2016, 13(9): 123−125.(in Chinese)
[12] 韦献雅, 殷丽琴, 钟成, 等. DPPH法评价抗氧化活性研究进展 [J]. 食品科学, 2014, 35(9):317−322. DOI: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201409062 WEI X Y, YIN L Q, ZHONG C, et al. Advances in the DPPH radical scavenging assay for antioxidant activity evaluation [J]. Food Science, 2014, 35(9): 317−322.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201409062
[13] ZHANG C, SUEN CLAIREL C, YANG C, et al. Antioxidant capacity and major polyphenol composition of teas as affected by geographical location, plantation elevation and leaf grade [J]. Food Chemistry, 2018, 244: 109−119. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.09.126
[14] LV H P, ZHANG Y, SHI J, et al. Phytochemical profiles and antioxidant activities of Chinese dark teas obtained by different processing technologies [J]. Food Research International, 2017, 100: 486−493. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodres.2016.10.024
[15] 林清霞, 项丽慧, 王丽丽, 等. 茶多酚高通量检测技术研究进展 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(3):146−153. LIN Q X, XIANG L H, WANG L L, et al. High throughput test of tea polyphenols: a review [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2019, 35(3): 146−153.(in Chinese)
[16] 周卫龙, 徐建峰, 黄伙水. 茶叶中茶多酚和儿茶素类含量的检测方法: GB/T 8313-2018[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018: 1-7. [17] 王丽丽, 陈键, 宋振硕, 等. 茶叶中没食子酸、儿茶素类和生物碱的HPLC检测方法研究 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2014, 29(10):987−994. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2014.10.011 WANG L L, CHEN J, SONG Z S, et al. Simultaneous HPLC determination of Gallic acid, catechins and alkaloids in tea [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 29(10): 987−994.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2014.10.011
[18] 王丽丽, 杨军国, 宋振硕, 等. 鲜叶、绿茶和白茶化学组分比较及清除DPPH自由基研究 [J]. 茶叶学报, 2015, 56(4):214−222. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4872.2015.04.004 WANG L L, YANG J G, SONG Z S, et al. Compositional differences and DPPH radical scavenging of fresh tea leaves, green tea and white tea [J]. Acta Tea Sinica, 2015, 56(4): 214−222.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4872.2015.04.004
[19] 陈金娥, 丰慧君, 张海容. 红茶、绿茶、乌龙茶活性成分抗氧化性研究 [J]. 食品科学, 2009, 30(3):62−66. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2009.03.013 CHEN J N, FENG H J, ZHANG H R. Effects of active ingredients in black tea, green tea and oolong tea on antioxidant capability [J]. Food Science, 2009, 30(3): 62−66.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2009.03.013
[20] 林玲, 龚志华, 袁冬寅, 等. 相同加工原料下的6类茶体外抗氧化性能比较 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2018, 34(2):107−112. DOI: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb16120045 LIN L, GONG Z H, YUAN D Y, et al. Comparison of antioxidative activity in vitro among six kinds of tea made from the same raw material [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2018, 34(2): 107−112.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb16120045
[21] ZHAO C N, TANG G Y, CAO S Y, et al. Phenolic profiles and antioxidant activities of 30 tea infusions from green, black, oolong, white, yellow and dark Teas [J]. antioxidants, 2019, 8: 215−228. DOI: 10.3390/antiox8070215
[22] 杨伟丽, 肖文军, 邓克尼. 加工工艺对不同茶类主要生化成分的影响 [J]. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2001, 27(5):384−386. YANG W L, XIAO W J, DENG K N. Effects of processing technology of different teas on the main biochemistry components [J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University(Natural Sciences Editon), 2001, 27(5): 384−386.(in Chinese)
[23] 龙海林, 李强, 司银楚, 等. 虎杖的功效成分组研究Ⅲ: 对血浆黏度影响的谱效分析研究 [J]. 现代医药卫生, 2012, 28(20):3080−3082. LONG H L, LI Q, SI Y C, et al. Spectrum-effect relationship study on influence of effective compositions research Ⅲ of polygoni Cuspidation plasma viscosity [J]. Journal of Modern Medicine & Health, 2012, 28(20): 3080−3082.(in Chinese)
[24] 肖遂. 基于谱效关系的中药铁苋菜抑菌物质辨识方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2013. XIAO S. A method for research of antibacterial constituent recognition of traditional Chinese medicine(Acalypha australis linn.) by spectrum-effect relationship[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2013. (in Chinese)
[25] 邓书鸿, 聂磊. 中药谱效关系的分析方法及数据处理技术研究进展 [J]. 中药材, 2010, 33(11):1819−1823. DENG S H, NIE L. Advances in analytical methods and data processing techniques for the relationship between the spectrum and effect of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2010, 33(11): 1819−1823.(in Chinese)
[26] DOU Q P. Recent advances on tea polyphenols [J]. Frontiers in Bioscience, 2012, E4(1): 111−131. DOI: 10.2741/e363
[27] 卢怡雯, 李晓芬, 项朋志, 等. 没食子酸清除DPPH自由基的紫外-可见吸收光谱研究 [J]. 食品工业科技, 2014, 35(2):124−126, 130. LU Y W, LI X F, XIANG P Z, et al. Study on UV-Vis absorption spectrometric investigation of the gallic acid against DPPH free radicals [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2014, 35(2): 124−126, 130.(in Chinese)
[28] 马慧, 茹鑫, 王津, 等. 4种茶叶水提物及茶多酚的体外抗氧化性能研究 [J]. 食品研究与开发, 2019, 40(8):65−70. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2019.08.011 MA H, RU X, WANG J, et al. Study on the antioxidant capacity of four tea water extracts and tea polyphenols in vitro [J]. Food Research and Development, 2019, 40(8): 65−70.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2019.08.011
-
期刊类型引用(16)
1. 李禹,段斌,杨代云,周艳宾,朱宏强,刘凯义,褚建忠,王戈,王娜,白羽祥,杜宇,代惠娟,周鹏. 有机肥配施微生物菌剂对土壤理化特性及烤烟产质量的影响. 江苏农业科学. 2025(02): 81-87 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 汤宏,王建伟,曾掌权,刘伦沛,阮运飞,梁春华,冷丽娟. 连作烤烟土壤特征及连作障碍防控技术研究进展. 黑龙江农业科学. 2024(08): 109-117 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王晓园,黄瑞寅,刘意旋,何经纬,和锐敏,李宙文,何岸,安玉兴,罗莎莎. 施用生物炭对烟叶品质和土壤及其细菌群落结构的影响. 西南农业学报. 2024(06): 1171-1179 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 鲍子薇,李朝阳,贾豫钊,张迎迎,刘飞. 甜瓜连作障碍及其调控措施研究进展. 南方农业. 2024(13): 50-58+64 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李青,李其胜,谢昶琰,张苗,陈川,章安康,孙春梅. 生物有机肥与生物质灰渣配施对连作甜瓜生长及土壤性质的影响. 土壤通报. 2024(05): 1386-1394 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 乔中华,周游,杨青山,王丹,郭子晗,许凌峰,祁俊生,张孟雁,周浓. 不同产地栽培滇重楼根际土壤酚酸类物质的测定与评价. 中国野生植物资源. 2024(S1): 7-14 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 韦秋芳,梁健仪,黄继川,李珠娴,钟文亮,涂玉婷. 生物炭-过氧化尿素对酚酸胁迫下广藿香扦插苗生长及生理生化指标的影响. 广东农业科学. 2024(12): 120-130 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 胡沙沙,胡海军,吴映霞,张家春,金小珍,周清莲. 生物炭对连作障碍影响的研究进展. 黑龙江农业科学. 2023(09): 143-147 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 胡骞予,赵娅红,吕怡颖,邓晨宵,肜磊,卢超,余磊,戴利利,齐颖,高鹏华,蔡宪杰,闫鼎,黄飞燕,韩天华. 生物炭不同施用量对烟草根际土壤真菌群落结构的影响. 西南农业学报. 2023(10): 2254-2260 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 谭雪莲,郭天文,胡新元,张平良,曾骏,刘晓伟. 黄土高原旱作区马铃薯连作根际土壤微生物群落变化特征. 作物学报. 2022(03): 682-694 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 李忱昊. 生物炭修复污染土壤的研究进展. 资源节约与环保. 2022(02): 91-93 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 张义杰,徐杰,陆仁窗,叶辰,黄惠川,杨敏,何霞红,朱书生. 生石灰对林下酸化土壤的调控作用及三七生长的影响. 应用生态学报. 2022(04): 972-980 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 孔明,王铎,李杰,李正伟,张智俊,孔德旬,杨松兵,陈燕,白羽祥,王戈. 烟秆生物质炭对烤烟连作障碍的消减作用初探. 山东农业科学. 2021(01): 87-93 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 杨晋燕,赵永伟,董宁禹,李佳颖,刘新源,李洪臣,常剑波,陈彦春,杨军杰. 烟草连作障碍产生的原因及防治方法. 现代农业科技. 2021(04): 101-103 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 王启宇,邓小鹏,张留臣,封幸兵,王皓,李庆鹏,周彬,陈峰,王津军,张晗,李卫,陈小龙,黄飞燕,刘佳妮,余磊,童文杰. 烟草根结线虫感病烟株根际土壤酚酸类物质变化的研究. 安徽农业科学. 2021(13): 153-157+160 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 李松伟,王发展,陈彪,谢俊明,史久长. 生物炭配施海藻肥对连作植烟土壤理化特性及烤烟生长的影响. 河南农业大学学报. 2021(05): 852-861 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(14)




 下载:
下载: