Identification and Malachite Green-Degrading Ability of Citrobacter Sp., D3
-
摘要:目的 筛选获得可高效降解孔雀石绿的菌株。方法 采用富集驯化的方法对渔业养殖环境中的土著微生物进行分离筛选,获得的降解菌株通过生理生化、扫描电镜和16S rDNA分析进行鉴定,采用单因素试验研究温度、pH及药物初始浓度对菌株降解效率的影响,并对其降解动力学参数进行分析。通过发光细菌法结合高分辨质谱仪对其降解产物的综合毒性和降解途径进行分析。结果 从上海某渔业养殖池塘中分离到一株孔雀石绿降解菌D3,初步鉴定其为柠檬酸杆菌Citrobacter sp.。菌株D3在pH7~8、温度30~35 ℃的环境中具有较好的生长和降解率,在该条件下,菌株对质量浓度为2 mg·L−1的孔雀石绿的降解率为96.32%,半衰期为0.563 0 d,且其代谢产物隐性孔雀石绿无明显累积;孔雀石绿质量浓度超过30 mg·L−1,菌株生长及降解受到明显抑制。菌体降解孔雀石绿可以用一级反应动力学方程描述,拟合曲线的相关系数在0.916 9~0.963 5。菌株对孔雀石绿的降解产物综合毒性降低明显,72 h降解产物对发光细菌的抑制率降低50%以上。从降解产物中解析获得3种特征降解中间产物,分别为4-二甲氨基二苯基甲酮(m/z=226.12)、N,N-二甲基苯胺(m/z=122.10)和4-二甲氨基-苯酚(m/z=138.09),推测D3菌株对孔雀石绿的降解过程为逐步脱掉苯环获得次级代谢产物。结论 D3菌株对孔雀石绿具有很好的降解效果,对解决渔业生态中的孔雀石绿残留具有较高的应用价值。Abstract:Objective A microorganism capable of decomposing malachite green (MG) was identified and its degradation ability studied.Method Indigenous microbes in water samples from aquaculture farms were enriched and domesticated in laboratory to screen for the species that could degrade the organic germicide, MG, a pollutant in aquaculture ponds. Strains showing such capability by physiological and biochemical tests were examined under scanning electron microscopy and identified by a 16S rDNA analysis. A single factor experiment was conducted to determine the effects of temperature, pH, and initial MG concentration on the degradation kinetics of the isolated bacterium. The inoculated culture medium was monitored continuously for the luminescent bacteria toxicity determination and sampled for the high-resolution mass spectrometry analysis to reveal the decomposition pathway.Result An MG-degrading bacterium isolated from the specimens collected at a fish pond in Shanghai was identified as D3 belonging to Citrobacter sp. It exhibited a high rate of growth and MG-degradation on the medium at the pH ranging from 7 to 8 and temperature between 30℃ and 35℃. Its degradation rate under MG 2 mg·L−1 was 96.32% and a half-life of 0.563 0 d with no significant accumulation of leucomalachite green (LMG). Once the MG concentration exceeded 30 mg·L−1, the bacterial growth and degradation effect were significantly hindered. The first-order kinetic degradation function of D3 had a correlation coefficient of 0.916 9–0.963 5. After inoculation for 72 h, the overall toxicity shown on the medium was significantly decreased with more than 50% reduction on the inhibition of the luminescent bacterial growth. Three compounds, 4-dimethylaminodiphenyl ketone (m/z=226.12), N, N-dimethylaniline (m/z=122.10), and 4-dimethylamino-phenol (m/z=138.09), in the metabolites were the degradation intermediates. It appeared that D3 removed the benzene rings in MG step by step to result in those degraded secondary metabolites.Conclusion D3 of Citrobacter sp. might be applied to decontaminate MG in aquaculture ponds.
-
Keywords:
- Malachite green /
- leucomalachite green /
- microbial degradation
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】孔雀石绿(Malachite green,MG)作为工业用染色剂和细胞化学染色剂等被广泛应用[1]。1933年,研究发现孔雀石绿具有抗菌的药效,之后许多国家开始将孔雀石绿广泛用作杀菌剂,主要用于杀灭养殖水体环境中的寄生虫、原生动物和鱼卵中的霉菌等[2]。孔雀石绿会在水生动物体内代谢成无色孔雀石绿(Leucomalachite green,LMG),孔雀石绿和无色孔雀石绿在水生动物体内长时间残留,可产生高度致畸、致癌和突变效应[3]。考虑到孔雀石绿的毒性,各国纷纷将其列入水产养殖的禁用药物名单,然而,由于孔雀石绿价格低廉、抗菌效果显著,而且还没有研制生产出更好的替代药物,因此直到现在,仍不断有违规使用孔雀石绿的情况发生。在水产品抽样检查中发现孔雀石绿仍然存在残留超标现象[4-5],在渔业生态环境监测中,孔雀石绿在养殖底泥中残留现象较为突出[6-7],如何安全有效地去除渔业环境中的孔雀石绿药物残留已成为水产养殖领域待解决的问题。【前人研究进展】目前,国内外研究孔雀石绿药物降解的方式主要有光降解[8]、化学降解[9]和生物降解[10]。相对于物理化学方法费用高、副作用大等不足,生物修复方法具有高效、成本低、无二次污染等优势。然而,目前利用微生物降解药物研究主要集中在堆肥、城市污水、湖泊和土壤等环境领域。吴永利等[11]从印染厂污泥中分离到一株假单孢菌Pseudomonas sp.,该菌株处理化工废水中高浓度孔雀石绿效果理想。熊晶晶等[12]从盐场的盐田中分离了一株耐受高盐环境的菌株,菌株对150 g·L−1的NaCl浓度具有较高的适应性,适用于高盐度条件下孔雀石绿的降解。而对于渔业养殖环境中孔雀石绿残留的积累模式、降解行为和生物修复技术研究较少,有报道利用高锰酸钾去除养殖水体中孔雀石绿效果较好,在非养殖期间通过翻耘、暴晒和泼洒生石灰等方法也可降低养殖底泥中孔雀石绿残留[13]。【本研究切入点】但整体而言,对于渔业养殖环境中孔雀石绿残留的积累模式、降解行为和生物修复技术研究较少,特别是与生物降解相关菌株的筛选。开展养殖环境中孔雀石绿及其代谢产物隐性孔雀石绿的微生物降解行为及生物修复技术研究,不仅对明确生物修复过程中药物的降解途径和机理具有重要的作用,而且对养殖环境的保护、水产品质量安全等具有重要意义。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究从渔业养殖池塘中分离获得一株可高效降解孔雀石绿的菌株,且其降解过程中代谢产物隐性孔雀石绿无明显累积,采用生理生化、扫描电镜及16S rDNA对菌株进行生理生化、菌体形态特征及分子生物学鉴定,同时对其降解特性进行初步研究,并结合生物毒性测试仪及高分辨质谱仪对菌株的降解产物及降解途径进行分析探讨,以期为该菌株在渔业养殖环境中降解孔雀石绿的应用提供理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 仪器与试剂
岛津LC-20AD液相色谱仪、AB SCIEX QTRAP® 6500质谱联用仪、LTQ Orbitrap XL(Thermo Fisher Scientific)、涡旋振荡器(IKA MS3)、超纯水机(美国Millipore公司)、Centrifuge 5810R型离心机(德国Eppendorf公司)、恒温培养摇床(上海一恒THZ-100)、滨松光子水质安全毒性测试仪(BHP9514)。
乙腈和二氯甲烷为色谱纯(TEDIA);PRS固相萃取柱(Agilent Bond Elut);乙酸和乙酸铵等化学纯试剂购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
孔雀石绿标准品:显性孔雀石绿(Malachite green,MG)、隐性孔雀石绿(Leucomalachite green,LMG)购自德国Dr.Ehrenstorfer。氘代显性孔雀石绿(Malachite green-D5,MG-D5)、氘代隐性孔雀石绿(Leucomalachite green-D6,LMG-D6)购自德国WITEGA。
乙酸铵溶液(0.125 mol·L−1):9.635 g乙酸铵溶于1 L H2O,乙酸调pH = 4。
0.2%乙酸铵溶液、标准储备液(500 µg·mL−1)和内标标准储备液(200 µg·mL−1)。
基础培养基:磷酸二氢钾3.0 g,七水硫酸镁0.1 g,硝酸铵2.0 g,无水CaCl2 0.01 g,磷酸氢二钾1.5 g,乙二胺四乙酸二钠0.01 g,过滤养殖水体1 000 mL,pH 7.6~7.8,高压蒸汽灭菌(121 ℃,15 min)后制得。
营养培养基:蛋白胨10.0 g,牛肉粉3.0 g,氯化钠5.0 g,葡萄糖1.0 g,过滤养殖水体1 000 mL,pH 7.6~7.8,高压蒸汽灭菌(121 ℃,15 min)后制得。
富集培养液:在营养培养基中加入孔雀石绿药物,使孔雀石绿药物质量浓度为5 mg·L−1。
孔雀石绿降解液体培养基:99%基础培养基,1%营养培养基,添加孔雀石绿质量浓度为5 mg·L−1。
孔雀石绿琼脂平板:蛋白胨10.0 g,牛肉粉3.0 g,氯化钠5.0 g,琼脂15.0 g,蒸馏水1 000 mL,121 ℃高压灭菌15 min,冷却,添加孔雀石绿溶液,混匀倒平板。
1.2 孔雀石绿降解菌的分离、筛选
上海市郊区某养殖鱼塘采集底泥样品,取适量底泥于无菌状态下,加入含孔雀石绿5 mg·L−1的富集培养液的250 mL三角瓶中,在温度30 ℃、转速160 r·min−1的条件下,驯化培养3 d,待培养液浑浊且颜色变浅后,按10%的接种量转接至下一批次新鲜富集培养液中,并逐步加大孔雀石绿投加浓度,如此重复,投加梯度质量浓度为5、10、15、20、25 mg·L−1。取最后一次获得的培养液,稀释5~8倍后,取100 µL涂布于孔雀石绿琼脂平板上,30 ℃恒温培养24 h,挑选单菌落,连续平板划线3次以上,获得纯化单菌落,将纯化后的各菌落接至孔雀石绿降解液体培养基中振荡培养24 h(30 ℃,160 r·min−1),通过高效液相色谱-串联质谱仪(HPLC-MS/MS)检测降解液体培养液中孔雀石绿残留量,同时检测其代谢产物隐性孔雀石绿累积情况,最后筛选获得对孔雀石绿具有高效降解能力且降解过程中隐性孔雀石绿无明显累积的菌株,降解菌使用20%甘油冻干管于−80 ℃冰箱冷冻保存。
1.3 菌种鉴定
根据细菌分类鉴定标准,从菌株个体形态特征、菌落特征等方面进行初步鉴定。利用常规方法进行革兰氏染色观察,根据细菌鉴定手册对菌株进行生理生化试验,通过扫描电子显微镜观察菌株D3的细胞形态,利用分子生物学手段进行菌株鉴定,提取D3基因组DNA作为模板进行16S rRNA基因的扩增,测序获得完整的16S rRNA基因序列,将菌株D3的16S rRNA基因序列在NCBI上进行同源性比对分析。
1.4 HPLC-MS/MS检测孔雀石绿方法
培养液8 000 r·min−1离心3 min,取100 µL溶液,稀释到10 mL水体中,加入300 µL质量浓度为0.2 µg·mL−1的氘代孔雀石绿和氘代隐性孔雀石绿混合内标,取1 mL样品过PRS固相萃取柱,PRS柱子经过活化(2 mL乙腈、2 mL水),上样,淋洗(2 mL水、2 mL乙腈),最后采用3 mL乙腈∶乙酸铵(V∶V=1∶1)洗脱,取1 mL洗脱液过滤,采用高效液相色谱-串联质谱仪检测。
1.5 降解条件的优化
培养温度:设置培养温度分别为15 、20 、25 、30 、35 和40 ℃,孔雀石绿降解液体培养基初始pH为7.6,摇床转速160 r·min−1,避光,在此培养条件下,测定菌株在48 h后的降解率。
初始pH:设置孔雀石绿降解液体培养基的初始pH分别为4.0、5.0、6.0、7.0、8.0、9.0和10.0,恒定温度30 ℃,摇床转速160 r·min−1,避光,测定菌株在48 h后的降解率。
不同初始浓度:设置孔雀石绿降解液体培养基中孔雀石绿的质量浓度分别为2、5、10、15、20、30 µg·mL−1,分别接入处于对数生长期的菌液,在温度30 ℃、pH 7.6、避光、摇床转速160 r·min−1条件下培养,定时取样测定菌株对孔雀石绿的降解率。
不同条件下的降解,均为孔雀石绿降解液体培养基中接入1%的处于对数生长期的菌液。孔雀石绿在环境中易转化为隐性孔雀石绿,试验同时考查不同温度和pH对隐性孔雀石绿降解的影响。试验设置3个平行重复。
1.6 菌株降解产物综合毒性分析
采用发光细菌法[14],检测降解菌株产物综合毒性。发光细菌为可进行生物发光的一类细菌,该类细菌遇到有毒有害物质,其发光性受到抑制。相关试验显示,毒物浓度同菌体发光强度存在线性负相关关系,因此,发光细菌发光强度可作为毒物毒性大小的测定指标。目前利用发光细菌进行毒性评估已广泛应用于环境科学的各个领域[15]。
将菌株接种于孔雀石绿降解液体培养基中,于30 ℃、160 r·min−1摇床培养,分别于24 h和7 d后取样,菌液8 000 r·min−1离心10 min,取上清液通过水质生物安全测试仪进行毒性分析。发光细菌菌株为明亮发光杆菌,根据仪器获得的发光值,计算发光细菌的抑制率,其抑制率的计算公式如下:
X/%=
(1−RLRL0) ×100式中,X为抑制率;RL为暴露于样品的明亮发光杆菌的发光强度;RL0为暴露于标准品种的明亮发光杆菌的发光强度。
1.7 降解产物及降解途径分析
为满足孔雀石绿降解中间产物达到其在高分辨质谱仪的检出要求,试验过程中,适当提高MG的初始浓度,提高降解产物的回收、富集效率。回收、富集方法如下:分别在投加菌株后的第3、6、12和24 h取样,收集菌株对MG的降解液,采用二氯甲烷大量萃取降解产液中的代谢产物,萃取液合并后旋蒸,使用1 mL甲醇溶解,过滤装瓶,采用LTQ Orbitrap XL高分辨质谱进行降解产物分析,设置无添加菌样品和纯菌体培养液为两个空白对照。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 孔雀石绿降解菌Citrobacter sp. D3的分离、筛选及特性分析
经分离、筛选,获得一株具有高效降解孔雀石绿药物的菌株,命名为D3。其生物学特征为:革兰氏染色阴性,杆菌(图1),鸟氨酸脱羧酶试验、赖氨酸脱羧酶试验、尿素酶试验、精氨酸双水解试验、明胶液化试验阴性,甘露醇试验、山梨醇试验阳性,可以利用葡萄糖、乳糖、蔗糖。在固体培养基上,菌落圆形、凸起,中等大小,边缘整齐光滑,呈灰白色,半透明。
以菌株D3的基因组DNA为模板,以细菌16S rDNA通用引物进行PCR扩增,PCR产物测序后在GenBank上登录,序列号为MG201776,经BLAST同源性比对发现,该菌株的16S rDNA与柠檬酸杆菌属相似度最高,进一步结合形态学和生理生化特征可初步鉴定该菌株为柠檬酸杆菌(Citrobacter sp.)。
2.2 菌株降解条件的优化
2.2.1 温度对菌株D3降解效率的影响
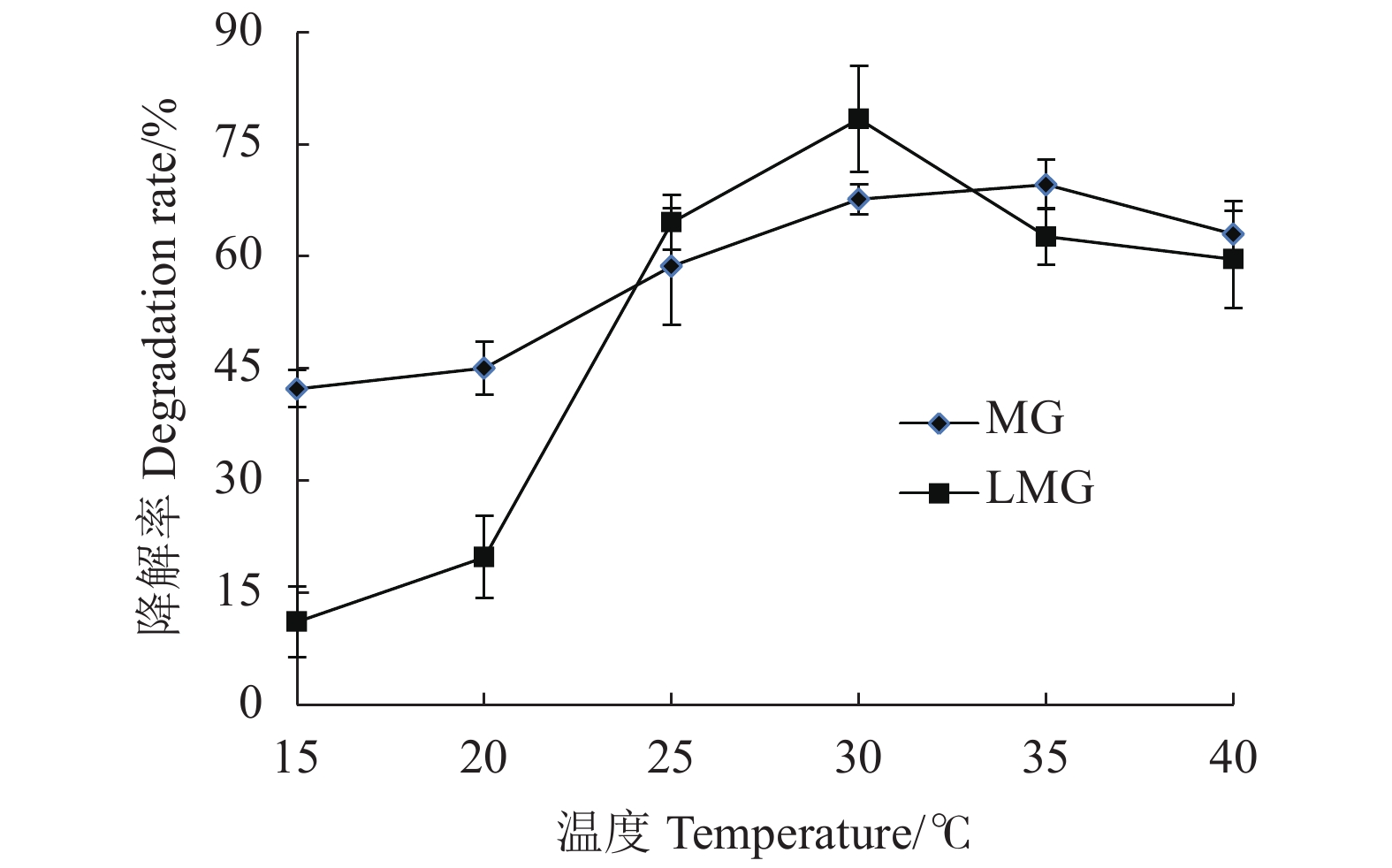
温度作为微生物生长及其代谢的重要因子,在适宜的温度范围内,微生物会表现出较快的生长及代谢速率,因此,试验设置不同的培养温度,考察不同温度下菌株D3对孔雀石绿降解效率的影响,并同时考察降解菌对孔雀石绿代谢产物隐性孔雀石绿降解的影响。
由图2看出,D3菌株在35 ℃时对孔雀石绿具有最高的降解率,在低温条件15~20 ℃对孔雀石绿的降解率较低;菌株对隐性孔雀石绿的最高降解率在30 ℃左右。降解菌对药物的降解整体呈现随着温度的升高降解率提高,温度超过最适降解温度,其降解效率降低,可能由于温度对菌体生长及降解酶活性有影响,间接影响菌株对药物的降解率。因此,选择30~35 ℃作为D3菌株对MG和LMG的最适降解温度。
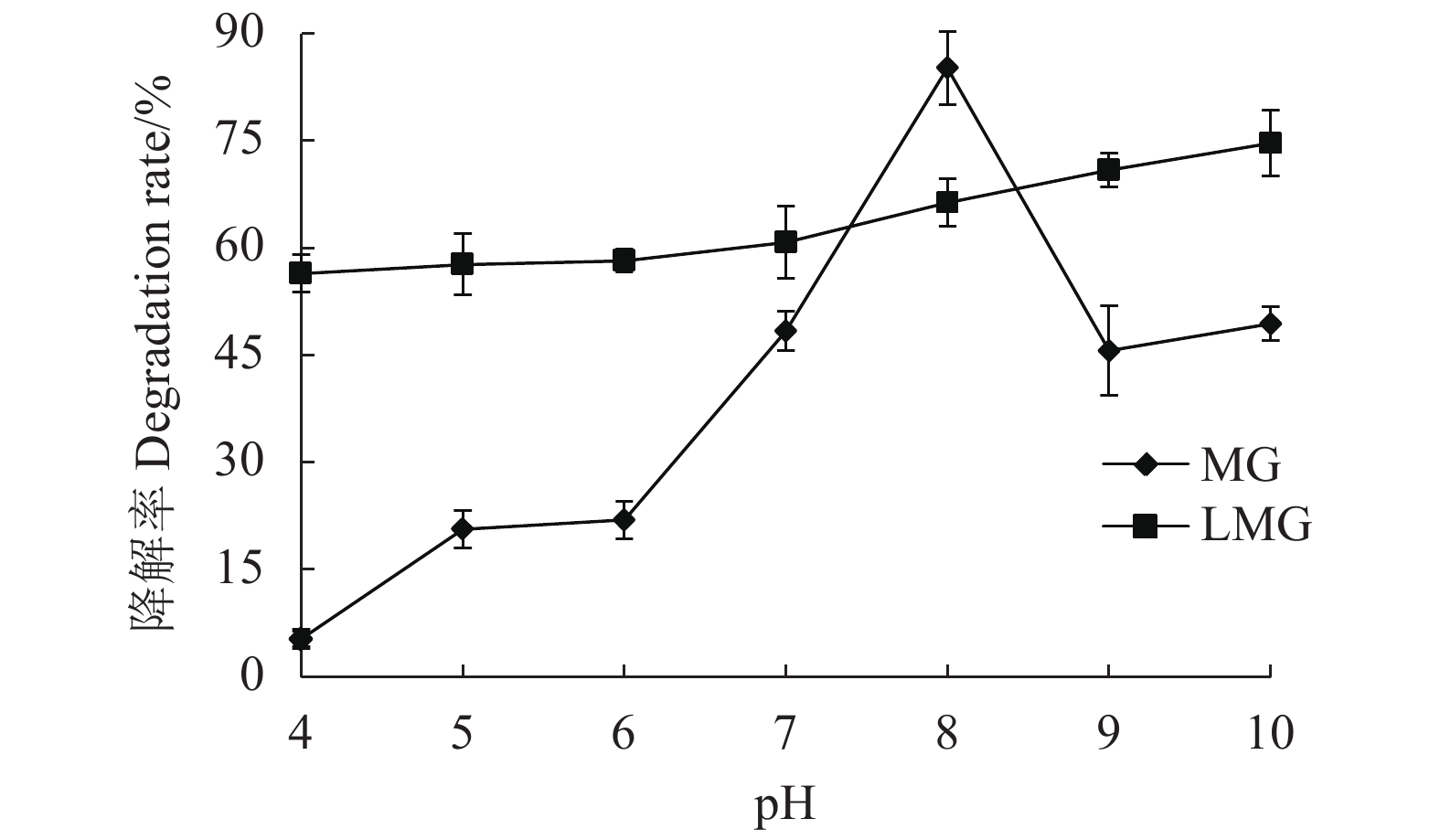
2.2.2 培养液初始pH对菌株D3降解效率的影响
菌株在不同初始pH的培养液中的生长及降解效率如图3所示。从图中可以看出,D3菌株在偏酸性条件下,降解率较低,仅为15%左右,pH为8时获得最高降解率,这与孔雀石绿降解菌Enterobacter B-20[16]和Sphingomonas paucimobilis[17]的最适降解pH较一致,这可能与高pH更适于孔雀石绿降解酶发挥作用有关。随着碱性增强,菌株对孔雀石绿的降解率降低,因为随着pH的升高,菌体生长受到抑制,导致降解率减弱,但其降解效率相对酸性条件仍较高,降解率约为46%。隐性孔雀石绿为孔雀石绿的酸性还原产物,从图中数据显示,D3菌株对隐性孔雀石绿降解的最适pH范围较为宽泛,pH对LMG的降解影响不大,随着pH值的增加,其降解率有所提升,在pH为4~10范围内,降解率较为稳定,维持在60%~75%。综上,选取pH为7~8作为D3菌株对MG和LMG的最适降解pH。
2.2.3 培养液中药物初始浓度对菌株D3降解效率的影响
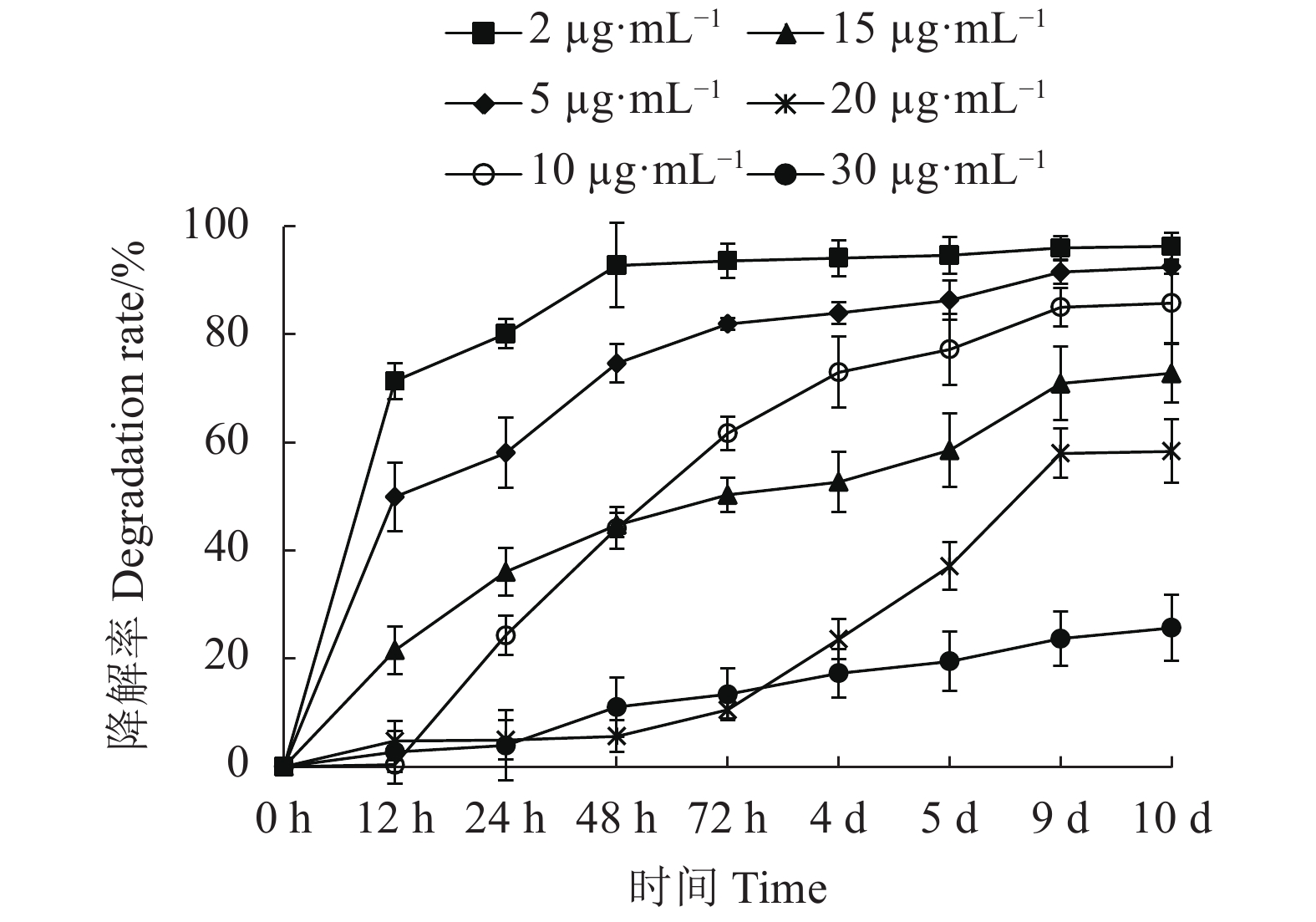
将生长于对数期的菌液以1%的接种量接种至100 mL孔雀石绿药物初始质量浓度分别为2、5、10、15、20、30 µg·mL−1的培养液中,分别在第12、24、48、72、4、5、9、10 d检测孔雀石绿的降解率。
由图4可知,D3菌株对不同初始浓度孔雀石绿的降解率均随时间的延长而增加,降解率达到最大值后随着时间的增加,药物的降解率不再增加,这可能是降解过程中不断累积的代谢物质及环境中营养成分的耗损,对菌体的正常生长代谢产生影响,导致酶活性降低。结果显示,较低初始浓度条件下,菌体在48 h左右降解率达到最大值。随着初始浓度的增加,菌体降解药物的时间延长,且降解率降低,在质量浓度为30 µg·mL−1的条件下,菌体降解率最高为20%左右,菌体OD600值非常低,说明高浓度的孔雀石绿对菌株的生长繁殖产生抑制,进而导致降解率降低。
2.2.4 降解动力学分析
采用一级反应动力学方程描述孔雀石绿降解过程,本试验所用的动力学方程为:
ln(C0 / Ct)= k t,即Ct = C0 e−kt
t1/2 = ln2/k
式中,Ct为降解后t时刻残留孔雀石绿的质量浓度(µg·mL−1),C0代表孔雀石绿的初始质量浓度(µg·mL−1),t为降解反应时间(d),k为孔雀石绿降解速率常数(d−1),t1/2为药物降解半衰期(d)。
采用D3菌株降解不同初始浓度条件下的孔雀石绿,降解试验结果如表1所示。一级动力学方程的拟合度由R2进行评价。结果表明,菌体降解孔雀石绿可以用一级反应动力学方程来描述,拟合曲线的相关系数在0.916 9~0.963 5。不同初始浓度对药物的降解率影响较大,随着初始浓度的提高,药物的降解半衰期增加,且降解率下降。低浓度条件下,D3菌株对MG降解效果理想,降解率在85%以上,降解半衰期较短。在初始质量浓度较高的情况下,菌株降解效率较低,在30 µg·mL−1条件下,药物的降解效率仅为25.7%,且降解半衰期时间延长明显。
表 1 D3菌株在不同初始浓度MG条件下的降解动力学参数Table 1. Parameters on D3 degradation kinetics of varied starting MG concentrations初始质量浓度
Initial concentration/(µg·mL−1)降解动力学方程
Degradation kinetics equation相关系数R2 降解半衰期t1/2/d 降解率
Degradation/%2 Ct=1.485 8e−1.231 1t 0.936 0 0.563 0 96.32 5 Ct=4.192 7e−0.636 5t 0.918 1 1.089 92.49 10 Ct=8.977 2e−0.230 6t 0.916 9 3.005 8 85.80 15 Ct=11.712 4e−0.113 6t 0.922 5 6.101 6 72.81 20 Ct=21.289 9e−0.095 9t 0.963 5 7.227 8 66.70 30 Ct=28.962 4e−0.028 6t 0.917 9 24.235 9 25.70 2.3 菌株降解产物综合毒性分析
本试验采用发光细菌法,研究D3菌株对孔雀石绿降解产物的综合毒性,通过降解产物对明亮发光杆菌发光抑制率评价产物毒性。D3菌株对MG的降解产物在24 h和72 h对发光细菌的抑制率如表2所示。结果显示,菌株对发光细菌的抑制率分别为0.2%和0.5%,说明D3菌株在生长过程中几乎不会产生生物毒性,而初始质量浓度为5 µg·mL−1的MG对发光细菌具有较高的抑制率,抑制率为50%以上,投加D3菌株后,菌株对MG的降解效果, 24 h时药物抑制率降低10.9%,72 h后抑制率再降低17.3%。结果表明,D3菌株在降解MG过程中可有效减弱药物生物毒性,但降解混合液在72 h对发光细菌仍具有约21.9%的抑制率,说明D3菌株在降解MG的过程中产生未完全分解的中间产物,中间产物对发光细菌仍具有抑制作用。
表 2 D3菌株对MG降解产物的综合毒性Table 2. Toxicity of MG degraded by D3 strain样品 Sample 相对发光值 RL0 相对发光值 RL(24 h) 抑制率X (24 h)/% 相对发光值 RL(72 h) 抑制率X (72 h)/% D3 100 99.7 0.2 99.4 0.5 MG 100 49.9 50.1 49.2 50.8 MG+D3 100 60.8 39.2 78.1 21.9 2.4 菌株降解产物及降解途径分析
菌体对药物的降解主要依赖酶的催化作用,由于降解速度较快,降解过程产生的中间降解产物可能被迅速分解,为最大程度收集中间降解产物,获得准确的药物降解途径,分别在菌体投加后的3 h、6 h、12 h和24 h连续取样,不同时间段的降解产物混合后浓缩富集。
采用高分辨质谱仪对富集浓缩的降解产物进行质谱分析,高分辨质谱仪目前被广泛应用于降解产物代谢途径及其降解中间产物的分析[18]。试验结果先经过空白扣除,再进行质谱图分析,初步获得MG的3种中间降解产物,分别为4-二甲氨基二苯基甲酮(m/z=226.12)、N,N-二甲基苯胺(m/z=122.10)和4-二甲氨基-苯酚(m/z=138.09),其质谱图和分子结构如图5所示。根据MG和其3种降解产物的分子结构特征推测D3菌株降解MG的途径如图6所示。MG首先经过羟基化反应生成一个过渡中间产物孔雀石绿甲醇,该过渡中间产物氧化分解,获得4-二甲氨基二苯基甲酮和N,N-二甲基苯胺,中间产物4-二甲氨基二苯基甲酮进一步分解,获得次级代谢产物4-二甲氨基-苯酚和苯甲醛。
3. 讨论
本研究从渔业养殖环境中分离得到的柠檬酸杆菌,可高效降解渔业生态环境中的孔雀石绿药物残留,且其降解过程中代谢产物隐性孔雀石绿无明显累积。该菌株生长温度、pH范围宽泛,具备较强的环境适应性,在pH为7~10、温度为25 ℃~40 ℃条件下,菌株对孔雀石绿具备较高的降解效率,其降解率最高可达95%以上,并同时对孔雀石绿代谢产物隐性孔雀石绿具有较好的去除效果。目前,已有多株孔雀石绿降解菌被筛选出,如芽孢杆菌(Brevibacillus)、肠杆菌(Enterobacter)、拉乌尔菌(Raoultella)及假单胞菌(Pseudomonas)等[19],但尚未见可同时去除孔雀石绿及其代谢产物的菌株报道,柠檬酸杆菌尚属首次。通过对降解菌株的降解动力学分析,获得菌株在不同初始浓度条件下的降解动力学参数,研究发现菌株在2~10 µg·mL−1低浓度范围,对孔雀石绿药物具备较高的降解效率,降解率在85%以上,药物质量浓度提高至30 µg·mL−1时,菌体生长受到抑制,其降解效率明显降低,孔雀石绿在渔业养殖中治病、杀菌用药质量浓度约0.15~2.00 µg·mL−1,用药浓度不高,该降解菌株降解能力可有效解决残留于渔业环境中的孔雀石绿药物残留。本试验通过对降解产物的毒性分析,推测降解菌对孔雀石绿的降解产物仍存在部分毒性,并初步获得3种降解中间产物,其中4-二甲氨基二苯基甲酮是MG脱掉一个苯环结构后主要的特征产物之一,该产物与已报道的多种菌株降解孔雀石绿的降解产物较为一致[20],多数菌株降解MG均有此产物产生,说明其降解途径具有相似性。产物N,N-二甲基苯胺是生产MG的工业原料,也是合成MG的关键前体,该产物的出现可以推断N,N-二甲基苯胺在MG生产上可重复使用。由于部分降解中间产物尚未找到,所以MG详细的降解途径有待进一步研究。目前国内外利用微生物降解孔雀石绿的研究较多,但是在微生物领域仍未有一个全面的关于MG降解途径报告[21],本研究成功分离的3种特征产物可为MG的降解途径研究分析填补理论上的空白。如何将最终的降解产物完全转化为无毒无害的物质,或为环境中的植物、生物菌群吸收代谢,是后期的一个重要研究方向。
-
表 1 D3菌株在不同初始浓度MG条件下的降解动力学参数
Table 1 Parameters on D3 degradation kinetics of varied starting MG concentrations
初始质量浓度
Initial concentration/(µg·mL−1)降解动力学方程
Degradation kinetics equation相关系数R2 降解半衰期t1/2/d 降解率
Degradation/%2 Ct=1.485 8e−1.231 1t 0.936 0 0.563 0 96.32 5 Ct=4.192 7e−0.636 5t 0.918 1 1.089 92.49 10 Ct=8.977 2e−0.230 6t 0.916 9 3.005 8 85.80 15 Ct=11.712 4e−0.113 6t 0.922 5 6.101 6 72.81 20 Ct=21.289 9e−0.095 9t 0.963 5 7.227 8 66.70 30 Ct=28.962 4e−0.028 6t 0.917 9 24.235 9 25.70 表 2 D3菌株对MG降解产物的综合毒性
Table 2 Toxicity of MG degraded by D3 strain
样品 Sample 相对发光值 RL0 相对发光值 RL(24 h) 抑制率X (24 h)/% 相对发光值 RL(72 h) 抑制率X (72 h)/% D3 100 99.7 0.2 99.4 0.5 MG 100 49.9 50.1 49.2 50.8 MG+D3 100 60.8 39.2 78.1 21.9 -
[1] 刘婧, 张建辉, 冷艳丽, 等. 巯基功能化介孔材料对阳离子染料的吸附应用 [J]. 化学试剂, 2019, 41(7):668−674. LIU J, ZHANG J H, LENG Y L, et al. Adsorption of thiol-functionalized mesoporous materials for cationic dyes [J]. <italic>Chemical Reagents</italic>, 2019, 41(7): 668−674.(in Chinese)
[2] ELI A, BRIYAI O F, ABOWEI J F N. A review of some fungi infection in African fish saprolegniasis, dermal mycoses, branchiomyces infection, systemic mycoses and dermocystidium [J]. <italic>Asian Journal of Medical Science</italic>, 2011, 3(5): 198−205.
[3] 胡浩光, 刘少彬, 李绪鹏, 等. 水产品中孔雀石绿残留的毒性作用及风险评估 [J]. 农业与技术, 2016, 36(19):117−119, 126. HU H G, LIU S B, LI X P, et al. Toxicity and risk assessment of malachite green residues in aquatic products [J]. <italic>Agriculture and Technology</italic>, 2016, 36(19): 117−119, 126.(in Chinese)
[4] 宋娟, 毕小玲, 庄晓洪. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定水产品中孔雀石绿及其代谢物残留量 [J]. 理化检验:化学分册, 2016, 52(10):1164−1168. SONG J, BI X L, ZHUANG X H. UHPLC-MS/MS Determination of Residual Amounts of Malachite Green and Its Metabolite in Aquatic Products [J]. <italic>Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis(Part B: Chemical Analysis</italic>, 2016, 52(10): 1164−1168.(in Chinese)
[5] 范芳芳, 樊成, 魏宁果. 2018年陕西省水产品中4种兽药残留的风险分析 [J]. 农产品加工, 2019(11):68−70. FAN F F, FAN C, WEI N G. Risk analysis of four veterinary drug residues in aquatic products in Shaanxi Province in 2018 [J]. <italic>Farm Products Processing</italic>, 2019(11): 68−70.(in Chinese)
[6] 程杏安, 郑子昭, 蒋旭红, 等. 珠江三角洲水域底泥中孔雀石绿、结晶紫及其代谢物分析 [J]. 生态科学, 2015, 34(3):59−64. CHENG X A, ZHENG Z Z, JIANG X H, et al. Analysis of malachite green and crystal violet and its metabolites in water sediment of Pearl River Delta [J]. <italic>Ecological Science</italic>, 2015, 34(3): 59−64.(in Chinese)
[7] 梅光明, 郭远明, 张小军, 等. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定环境底泥中的孔雀石 [J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2014, 40(3):330−337. MEI G M, GUO Y M, ZHANG X J, et al. Determination of malachite green in sediment by ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry [J]. <italic>Journal of Zhejiang University(Agriculture and Life Sciences)</italic>, 2014, 40(3): 330−337.(in Chinese)
[8] 张俊艳, 温裕云, 刘珺, 等. 隐性孔雀石绿在有机溶剂中的光化学降解过程 [J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 50(S1):32−37. ZHANG J Y, WEN Y Y, LIU J, et al. Mechanism studies on the photochemical degradation of leucomalachite green in organic solvent media [J]. <italic>Journal of Xiamen University(Natural Science)</italic>, 2011, 50(S1): 32−37.(in Chinese)
[9] 徐清艳. 铁酸钴催化Na<sub>2</sub>S<sub>2</sub>O<sub>8</sub>降解孔雀石绿的研究 [J]. 山东化工, 2018, 47(22):185−187. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2018.22.084 XU Q Y. The Degradation of malachite green by sodium persulfate with cobalt ferrite [J]. <italic>Shandong Chemical Industry</italic>, 2018, 47(22): 185−187.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2018.22.084
[10] ZHANG C, DIAO H W, LU F X, et al. Degradation of triphenylmethane dyes using a temperature and pH stable spore laccase from a novel strain of <italic>Bacillus vallismortis</italic> [J]. <italic>Bioresource Technology</italic>, 2012, 126: 80−86. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.09.055
[11] 吴永利, 王莉, 范子睿, 等. 孔雀石绿高效脱色菌的鉴定及降解特性研究 [J]. 安徽建筑大学学报, 2017, 25(1):38−43. DOI: 10.11921/j.issn.2095-8382.20170109 WU Y L, WANG L, FAN Z R, et al. Identification and characterization of the highly efficient malachite green decolorization strain [J]. <italic>Journal of Anhui Jianzhu University</italic>, 2017, 25(1): 38−43.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11921/j.issn.2095-8382.20170109
[12] 熊晶晶, 徐敏, 林锦钰, 等. 一株耐盐菌的分离鉴定及其孔雀石绿脱色的研究 [J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2019, 46(1):51−56. XIONG J J, XU M, LIN J Y, et al. Study on decolorization of malachite green by a <italic>Staphylococcus saprophyticus</italic> [J]. <italic>Journal of Anhui Agricultural University</italic>, 2019, 46(1): 51−56.(in Chinese)
[13] 柯江波, 胡鲲, 曹海鹏, 等. 孔雀石绿在养殖水和底泥中的残留消除规律 [J]. 南方农业学报, 2014, 45(12):2274−2279. DOI: 10.3969/j:issn.2095-1191.2014.12.2274 KE J B, HU K, CAO H P, et al. Elimination law of malachite green residue in water and sediment of aquaculture pond [J]. <italic>Journal of Southern Agriculture</italic>, 2014, 45(12): 2274−2279.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j:issn.2095-1191.2014.12.2274
[14] 付萍, 何健龙, 张秀珍, 等. 发光细菌法在浒苔绿潮次生毒性快速检测中的应用 [J]. 科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(1):288−292. FU P, HE J L, ZHANG X Z, et al. The application of luminous bacteria method in rapid detection for secondary toxicity of <italic>Ulva prolifera</italic> green tide decomposition [J]. <italic>Science Technology and Engineering</italic>, 2019, 19(1): 288−292.(in Chinese)
[15] 隋成瑶. 发光细菌法在环境监测中的应用 [J]. 黑龙江环境通报, 2018, 42(3):23−25. SUI C Y. Application of luminescent bacteria method in environment monitoring [J]. <italic>Heilongjiang Environmental Journal</italic>, 2018, 42(3): 23−25.(in Chinese)
[16] 都林娜, 李刚, 杨玉义, 等. <italic>Enterobacter sp</italic>.CV-v对孔雀石绿的脱色特性及机理研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(10):3675−3682. DU L N, LI G, YANG Y Y, et al. Decolorization of malachite green by <italic>Enterobacter sp</italic>. CV-v: characteristics and mechanism [J]. <italic>Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae</italic>, 2016, 36(10): 3675−3682.(in Chinese)
[17] KOBAYASHI T, TAYA H, WILAIPUN P, et al. Malachite-green-removing properties of a bacterial strain isolated from fish ponds in Thailand [J]. <italic>Fisheries Science</italic>, 2017, 83(5): 827−835. DOI: 10.1007/s12562-017-1102-4
[18] JIRAPANJAWAT T, NEY B, TAYLOR M C, et al. The redox cofactor F<sub>420</sub> protects mycobacteria from diverse antimicrobial compounds and mediates a reductive detoxification system [J]. <italic>Applied and Environmental Microbiology</italic>, 2016, 82(23): 6810−6818. DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02500-16
[19] 王亚妮, 宋金龙, 韩刚, 等. 孔雀石绿降解菌群多样性及高效降解菌的降解特性分析 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2019(9):150−155. WANG Y N, SONG J L, HAN G, et al. Analysis of diversity of malachite green-degrading microbial community and degradation characteristics of efficiently-degrading bacteria [J]. <italic>Biotechnology Bulletin</italic>, 2019(9): 150−155.(in Chinese)
[20] YANG J, YANG X D, LIN Y H, et al. Laccase-catalyzed decolorization of malachite green: performance optimization and degradation mechanism [J]. <italic>PLoS One</italic>, 2015, 10(5): e0127714. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127714
[21] WANG J A, GAO F, LIU Z Z, et al. Pathway and molecular mechanisms for malachite green biodegradation in <italic>Exiguobacterium sp</italic>. MG2 [J]. <italic>PLoS One</italic>, 2012, 7(12): e51808. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051808
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 胡佳惠,孙政,许亦飞,贺江. 孔雀石绿降解菌的分离鉴定及特性研究. 湖南文理学院学报(自然科学版). 2023(01): 40-44 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 田小丽,李绪鹏,李春生,陈胜军,薛勇,邓建朝,潘创,王悦齐. 微生物降解孔雀石绿的研究进展. 中国渔业质量与标准. 2021(06): 34-44 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




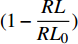

 下载:
下载: