Reference Gene Selection for RT-qPCR Analysis on Cucumis melo
-
摘要:目的 筛选可分别在甜瓜不同组织器官和不同胁迫处理下稳定表达的内参基因,用于对靶基因表达量的实时荧光定量分析,保证相关试验的准确性及可靠性。方法 以甜瓜品种新银辉为试验材料,通过实时荧光定量PCR技术分析18s rRNA、TUA、EF1a、Actin1、Actin2、Actin3、Actin4、CYC和UBI-ep共9个候选内参基因在甜瓜不同组织器官及不同胁迫处理下的表达稳定性,包括甜瓜根、叶、种子和果实4种不同组织材料,以及水分胁迫、肉桂酸胁迫、盐碱胁迫和ABA胁迫4种处理。同时使用Best-Keeper、Norm Finder和ge Norm软件对9个候选内参基因进行稳定性分析。结果 对不同组织器官而言,Best-Keeper评估排名前5的内参基因依次为CYC>18s rRNA>UBI-ep>EF1a>TUA;Norm Finder计算排名前5的内参基因依次为EF1a>UBI-ep>Actin4>CYC>Actin3;ge Norm分析排名前5的基因依次为Actin4=Actin3>Actin1>EF1a>UBI-ep。不同胁迫处理中,Best-Keeper计算排名前5的基因依次为18s rRNA>Actin3>Actin4>EF1a>UBI-ep;Norm Finder分析排名前5的基因依次为EF1a>UBI-ep>Actin4>CYC>18s rRNA;ge Norm分析排名前5的基因依次为EF1a=UBI-ep>Actin4>CYC>Actin1。总体而言EF1a在不同组织器官和不同胁迫处理中的综合排名均较为稳定;Actin4、Actin3、Actin1和EF1a是不同组织器官中较为稳定的内参基因组合;EF1a和UBI-ep是4种胁迫条件下较稳定的内参基因组合。结论 EF1a在甜瓜不同组织器官及不同胁迫条件下均可稳定表达,是较为合适的内参基因;同时可通过设置双内参基因进一步降低试验误差。Abstract:Objective In search for internal reference genes of Cucumis melo L. that could stably express in different tissues and under stress conditions to warrant accuracy and reliability of the RT-qPCR analysis on target gene expression.Method Expression stabilities of 9 candidate genes, 18srRNA, TUA, EF1a, Actin1, Actin2, Actin3, Actin4, CYC, and UBI-ep, from the roots, leaves, seeds, and fruits of Xinyinhui melon being treated by water, cinnamic acid, saline alkali or ABA were determined by RT-qPCR and analyzed using the BestKeeper, NormFinder, and geNorm software.Result In different tissues, the top 5 choice genes identified by BestKeeper ranked as CYC>18s rRNA>UBI-ep>EF1a>TUA, those by NormFinder EF1a>UBIep>Actin4>CYC>Actin3, and those by geNorm Actin4=Actin3>Actin1>EF1a>UBI-ep. Under various stresses, they were 18s rRNA>Actin3>Actin4>EF1a>UBI-ep as ranked by BestKeeper, EF1a>UBI-ep>Actin4>CYC>18s rRNA by NormFinder, and EF1a=UBI-ep>Actin4>CYC>Actin by geNorm. Overall, EF1a appeared to be most stable among the 9 genes. Insofar as variety of tissues is concerned, Actin4, Actin3, Actin1, and EF1a were more stable than the others; and, under stress, EF1a and UBI-ep tended to be superior.Conclusion Stably expressed in the tissues under the stresses as tested, EF1a was selected as the reference gene for studies on C. melo to reduce experimental errors. To further ensure accuracy, application of dual reference genes in RT-qPCR analysis might be considered.
-
Keywords:
- Cucumis melo L. /
- reference gene /
- RT-qPCR /
- Tissuestissues and organs /
- stress
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】菌糠是栽培各种食用菌后剩下的培养基废料,每生产1 kg食用菌约产生3.25 kg菌糠[1]。我国是食用菌生产大国,随着我国对食用菌需求量的增多,每年产生的菌糠数量也随之增加[2]。随着食用菌产业生产规模的不断扩大,每年产生菌糠8.36×107t [3]。未经处理的菌糠因所含纤维比例较高,存在适口性较差和消化率偏低等问题。研究表明,经生物发酵和酶解作用的菌糠,其纤维素和木质素等成分都得到很大程度的降解,粗蛋白、粗脂肪含量都高于未经发酵的基质[4]。平菇作为我国栽培和消费量最大的菌种之一,栽培后产生的培养基废料量也相对较多。平菇菌糠中含有丰富的氨基酸、蛋白质、多糖、钙、镁及微量元素等[5],具有很大的开发潜力。因此,探讨添加乳酸菌对提高平菇菌糠发酵饲料品质和发酵进程的促进作用,具有重要的现实意义。【前人研究进展】李志香等[6]把多种饲料酵母加入由醋糟和棉籽壳构成的废弃菌糠中,对比分析原菌糠和发酵菌糠后,发现不同基质的菌糠发酵饲料的粗蛋白质含量均高于20%。曹启民等[7]在猪的基本饲料中加入20%的发酵灵芝菌糠后,发现对猪的生长并没有产生显著的影响,但每千克增重饲料成本下降5.19%,瘦肉率显著提高。罗茂春等[8]研究发现,白玉菇菌糠发酵后粗蛋白、无氮浸出物显著提高,粗纤维显著降低,pH值下降,乳酸含量升高,菌糠感官品质得到较大改善。菌糠经过某些微生物的发酵作用,粗纤维中的一些成分被不同程度地降解,同时产生多种糖类尤其是还原糖,提高了菌糠内营养物质的消化利用率[9]。郑有坤等[10]研究表明,微生物发酵处理会降低香菇菌糠的中性洗涤纤维、酸性洗涤纤维和可溶性碳水化合物含量,提高粗蛋白和氨基酸含量,以酵母菌和乳酸菌混合发酵处理的效果最好。同时,微生物还可产生有机酸类等营养物质,提高菌糠的饲用价值[11]。在发酵饲料中添加足够的乳酸菌,可使发酵过程中乳酸菌繁殖的启动时间更早、繁殖速度更快,从而占据主导地位,能有效抑制不良菌的繁殖,减少饲料消耗,提高发酵品质[12]。【本研究切入点】迄今为止,比较不同乳酸菌对平菇菌糠发酵饲料品质改善效果的研究鲜见报道。【拟解决的关键问题】探明不同乳酸菌对平菇菌糠发酵饲料品质和发酵进程的影响,为生产优质菌糠发酵饲料提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验原料
平菇菌糠:平菇培养基由73%五节芒、25%麸皮和2%石灰组成,含水率为60%左右。以福建农林大学国家菌草工程技术研究中心栽培平菇采收一茬后的菌糠作为本试验发酵原料。
乳酸菌:由华南农业大学草业科学系饲草加工与贮藏实验室提供的专利菌。其中乳酸菌CCZZ1(Lactic acid bacteria,CCZZ1)为耐低温乳酸菌株,乳酸菌HT1(Lactic acid bacteria,HT1)为耐高温乳酸菌株。
1.2 试验设计
试验设4个处理:添加乳酸菌CCZZ1处理(记为CCZZ1处理)、添加乳酸菌HT1处理(记为HT1处理)、添加乳酸菌CCZZ1+乳酸菌HT1处理(记为MIX处理),以不添加乳酸菌为空白对照(CK)。每个处理最初均设18个重复,装有约100 g菌糠的塑料袋为一个重复。分别在不同发酵天数(1、3、7、15、30、60 d)开封,每个处理的每个开封期均调查3个重复。乳酸菌CCZZ1和乳酸菌HT1单独添加处理的添加量均按每克发酵原料(鲜重)添加1×108 cfu进行;复合添加处理两种乳酸菌的添加量各半,均为5×107 cfu。
1.3 发酵饲料的调制
将收集的菌棒开包后去除其中霉变的部分,捣碎后混合均匀,分别称取300 g菌糠,装入塑料袋内并做好标记。对照处理喷洒蒸馏水5 mL,其余处理各喷洒配制好的添加剂和蒸馏水共计5 mL,混拌均匀后大致分为3等份作为同一天开封的重复处理。每个处理组制作18个这样的菌糠料,分别装入真空袋内并做好标记,用真空泵抽气使其真空后密封。室温下贮存,分别于发酵1、3、7、15、30、60 d后开袋检测。
1.4 项目的测定与检测方法
取代表性的样本20 g装入100 mL备有刻度的广口锥形瓶内,加入80 mL蒸馏水,放入4 ℃冰箱中,18 h后过滤,制浸提液,取50 mL浸提液测定pH值(pHS-3D型酸度计),检测浸提液的氨态氮(AN)含量(苯酚-次氯酸钠比色法) [13];采用岛津LC-20AT型高效液相色谱(色谱柱:Shodex Rspak KC-811 S-DVB gel Column 300×8 mm,检测器:SPD-M10AVp,流动相:3 mmol·L−1高氯酸)测定浸提液的乳酸(LA)、乙酸(AA)、丙酸(PA)、丁酸(BA)含量[14]。氨态氮(AN)用AN/TN的值表示,即测定的氨态氮(AN)占原料总氮(TN)的比例(苯酚-次氯酸钠比色法[13]检测)。乳酸(LA)、乙酸(AA)、丙酸(PA)和丁酸(BA)均用新鲜(FM)基础表示。
新鲜样本在65 ℃恒温箱中烘干48 h,放置常温回潮30 min后粉碎称重,计算含水率,并立即将烘干样粉碎装入密闭的棕色玻璃瓶中备用。采用常规法[15]测定干物质(DM)和粗蛋白质(CP)含量;采用Anthrone比色法[16]测定可溶性碳水化合物(WSC)含量;采用Van Soest 等[16]的方法测定中性洗涤纤维(NDF)和酸性洗涤纤维(ADF)含量;半纤维素(HC)含量通过测定中性洗涤纤维(NDF)和酸性洗涤纤维(ADF)含量,计算二者的差值,即HC=中性洗涤纤维(NDF)–酸性洗涤纤维(ADF);粗灰分(Ash)含量采用灼烧法[17]测定。CP、WSC、NDF、ADF、HC和Ash用干物质(DM)基础表示。
参考傅彤[18]报道的方法测定原料的乳酸菌、细菌、酵母菌和霉菌数量。
1.5 数据分析
用Excel 2003软件初步处理原始数据后,再用SPSS 13.0统计软件对数据进行方差统计分析。相同发酵时间不同添加剂、相同添加剂不同发酵时间对菌糠发酵饲料品质所有项目的影响使用单因子方差分析。单因子方差分析采用Duncan’s多重比较法。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 平菇菌糠的化学成分和微生物组成
从表1看出,供试菌糠的pH值为5.42,呈弱酸性;可溶性碳水化合物含量较低,仅为3.63%;粗蛋白含量为9.62%;中性洗涤纤维和酸性洗涤纤维含量较高,分别为76.03%和64.01%;半纤维素含量为12.02%。
表 1 菌糠的化学成分Table 1. Chemical composition of spent mushroom culture substratepH DM/ % WSC/% CP /% NDF/% ADF/% HC/% 5.42 39.89 3.63 9.62 76.03 64.01 12.02 注:(1)表中营养成分均为菌糠干物质(DM)测定值;(2)WSC:可溶性碳水化合物,CP:粗蛋白,NDF:中性洗涤纤维,ADF:酸性洗涤纤维,HC:半纤维素。
Note:(1)all nutrients in the table are measured by bacterial bran dry matter(DM).(2)WSC: Soluble carbohydrate, CP: Crude protein, NDF: Neutral detergent fiber, ADF: Acid detergent fiber, HC:Hemicellulose.从表2看出,菌糠的微生物组成中好气性细菌数量较多,可与乳酸菌争夺养分,影响乳酸菌的生长繁殖。
表 2 菌糠的微生物组成及数量Table 2. Microorganisms and microbial counts in spent mushroom culture substrate[单位:lg(cfu·g−1)] 乳酸菌
Lactic acid bacteria好气性细菌
Aerobic bacteria酵母菌
Yeast霉菌
Mold2.23 4.98 2.35 1.23 2.2 乳酸菌对平菇菌糠发酵饲料品质和发酵进程的影响
由图1可知,总体而言,平菇菌糠发酵饲料的pH值随发酵时间的增加而降低。在发酵3~30 d的4个发酵时间点上,3个添加乳酸菌处理组(以下简称:添加组)的pH值均显著低于对照组(CK)(P<0.05),同一时间点均以MIX处理组的pH值最低,且在发酵15 d时复合添加组(MIX组)显著低于2个单独添加组(P<0.05);3个添加组的pH值在发酵7 d时均降到4.2以下(一般发酵饲料的pH值在4.2以下品质较优),而CK组的pH值在发酵30 d时才降到4.2以下。也就是说,3个添加组的pH值比CK组提前23 d下降到4.2以下,且以MIX组下降速度最快。
![]() 图 1 不同处理、不同发酵时间的菌糠发酵饲料pH值注:①图中每个时间点不同处理差异显著性标注从上到下依次是CK、CCZZI、HT1、MIX处理组;②( )内无相同字母表示同一时间点不同处理组间差异显著(P<0.05),有相同字母者表示差异不显著(P>0.05);( )外无相同字母表示同一处理组不同时间点间差异显著(P<0.05),有相同字母者表示差异不显著(P>0.05)。图2~3、表3~12同。Figure 1. Effect of treatments on pH of fermented feed materialNote:①The significant markers of different treatments at each time point in the figure from top to bottom are CK, CCZZI, HT1 and MIX treatment groups.(same as Figure1-3)②Different letters in "( )" indicate that there are significant differences among different treatment groups at the same time(P<0.05), the same letters or not marked letters show no significant difference(P>0.05).The different letters outside "( )" indicated that there were significant differences at different time points in the same treatment group(P<0.05), the same letters or not marked letters show no significant difference(P>0.05). Figure 2-3 and table 3-12 are the same.
图 1 不同处理、不同发酵时间的菌糠发酵饲料pH值注:①图中每个时间点不同处理差异显著性标注从上到下依次是CK、CCZZI、HT1、MIX处理组;②( )内无相同字母表示同一时间点不同处理组间差异显著(P<0.05),有相同字母者表示差异不显著(P>0.05);( )外无相同字母表示同一处理组不同时间点间差异显著(P<0.05),有相同字母者表示差异不显著(P>0.05)。图2~3、表3~12同。Figure 1. Effect of treatments on pH of fermented feed materialNote:①The significant markers of different treatments at each time point in the figure from top to bottom are CK, CCZZI, HT1 and MIX treatment groups.(same as Figure1-3)②Different letters in "( )" indicate that there are significant differences among different treatment groups at the same time(P<0.05), the same letters or not marked letters show no significant difference(P>0.05).The different letters outside "( )" indicated that there were significant differences at different time points in the same treatment group(P<0.05), the same letters or not marked letters show no significant difference(P>0.05). Figure 2-3 and table 3-12 are the same.由图2可知,在发酵7~30 d的3个发酵时间点上,3个添加组的LA含量均高于CK组(P<0.05);在发酵60 d时,3个添加组LA含量开始下降,3个添加组LA含量均显著低于CK组(P<0.05)。
由图3可知,在发酵1 d和3 d,CK组的AA含量均高于3个添加组,但差异不显著;在发酵7 d和30 d,CK组AA含量均显著低于3个添加组(P<0.05);在发酵的整个过程中,CCZZ1处理组的AA含量一直呈上升趋势。
由表3可知,从发酵3 d开始,平菇菌糠发酵饲料的AN含量随发酵天数的增加而升高。在发酵15 d及之后,CK组的AN含量一直最高;在发酵15 d和30 d时,MIX组的AN含量显著低于CK组(P<0.05);在发酵60 d时,3个添加组的AN含量均显著低于CK组(P<0.05)。
表 3 不同处理、不同发酵时间的菌糠发酵饲料氨态氮AN(AN/TN)含量Table 3. Effect of treatments on ammonia nitrogen AN (AN/TN) in fermented feed material(单位:%) 发酵时间 Fermentation Time/d CK CCZZ1 HT1 MIX 1 0.08±0.01(a)b 0.07±0.01(a)b 0.08±0.00(a)b 0.04±0.00(b)c 3 0.03±0.00(b)f 0.04±0.00(a)e 0.03±0.00(b)f 0.04±0.00(a)c 7 0.04±0.00(a)e 0.04±0.00(a)e 0.04±0.00(a)e 0.04±0.00(a)c 15 0.06±0.01(a)d 0.05±0.00(ab)d 0.05±0.01(ab)d 0.04±0.00(b)c 30 0.07±0.00(a)c 0.06±0.00(ab)c 0.06±0.00(ab)c 0.05±0.01(b)b 60 0.14±0.03(a)a 0.08±0.00(b)a 0.09±0.01(b)a 0.10±0.01(b)a 由表4可知,总体而言,平菇菌糠发酵饲料的PA含量随发酵天数的增加而升高。在发酵1~15 d时段,4个处理之间差异不显著(P>0.05);在发酵到30~60 d时,3个添加组的PA含量与之前相比显著增加(P<0.05),3个添加组处理间差异不显著(P>0.05)。
表 4 不同处理、不同发酵时间的菌糠发酵饲料丙酸PA(FM)含量Table 4. Effect of treatments on propionic acid PA (FM) in fermented feed material(单位:%) 发酵时间 Fermentation Time/d CK CCZZ1 HT1 MIX 1 0.02±0.00(a)a 0.02±0.00(a)b 0.02±0.00(a)b 0.02±0.01(a)b 3 0.01±0.01(a)a 0.02±0.01(a)b 0.02±0.00(a)b 0.02±0.01(a)b 7 0.02±0.00(a)a 0.02±0.00(a)b 0.01±0.01(a)b 0.02±0.01(a)b 15 0.02±0.00(a)a 0.02±0.01(a)b 0.01±0.01(a)b 0.02±0.00(a)b 30 0.03±0.00(b)a 0.04±0.00(a)a 0.04±0.01(a)a 0.04±0.01(a)a 60 0.04±0.04(a)a 0.04±0.01(a)a 0.04±0.01(a)a 0.04±0.02(a)a 由表5可知,CCZZ1组的BA含量在发酵3 d时,显著低于CK组和MIX组(P<0.05);MIX组的BA含量在发酵的1~7 d显著高于15~60 d(P<0.05);在发酵60 d时,CCZZ1组的BA含量最高。
表 5 不同处理、不同发酵时间的菌糠发酵饲料丁酸BA(FM)含量Table 5. Effect of treatments on butyric acid BA (FM) in fermented feed material(单位:%) 发酵时间 Fermentation Time/d CK CCZZ1 HT1 MIX 1 0.04±0.01(a)a 0.04±0.01(a)a 0.03±0.02(a)a 0.03±0.00(a)a 3 0.03±0.01(a)a 0.01±0.01(b)b 0.02±0.00(ab)a 0.03±0.01(a)a 7 0.01±0.00(a)b 0.01±0.01(a)b 0.02±0.02(a)a 0.03±0.02(a)a 15 0.01±0.01(a)b 0.03±0.02(a)ab 0.02±0.01(a)a 0.01±0.00(a)b 30 0.01±0.00(a)b 0.01±0.01(a)b 0.01±0.01(a)a 0.01±0.01(a)b 60 0.01±0.01(b)b 0.03±0.01(a)ab 0.02±0.01(ab)a 0.01±0.01(b)b 由表6可知,在发酵7 d 和15 d,CK组的DM含量均低于3个添加组;在发酵7 d时CK组的DM含量显著低于3个添加组(P<0.05);在发酵30 d和60 d,CK组DM含量显著高于3个添加组(P<0.05);在发酵60 d 时,2个单独添加组DM含量显著高于MIX组(P<0.05)。
表 6 不同处理、不同发酵时间的菌糠发酵饲料干物质DM含量Table 6. Effect of treatments on dry matters (DM) in fermented feed material(单位:%) 发酵时间 Fermentation Time/d CK CCZZ1 HT1 MIX 1 36.09±0.72(a)c 36.18±0.61(a)b 36.10±0.32(a)bc 36.47±0.18(a)bc 3 35.91±0.35(a)c 35.34±0.25(a)c 36.04±0.76(a)c 36.32±0.21(a)cd 7 34.96±0.24(b)d 35.67±0.28(a)bc 35.96±0.44(a)c 35.69±0.44(a)d 15 37.05±0.21(a)b 37.39±0.71(a)a 37.38±1.39(a)ab 37.15±0.56(a)a 30 37.09±0.15(a)b 36.12±0.20(bc)b 36.39±0.23(b)bc 35.87±0.03(c)cd 60 40.25±0.66(a)a 38.06±0.15(b)a 38.20±0.02(b)a 37.04±0.33(c)ab 由表7可知,总体而言,随着发酵时间的增加,各处理组Ash含量的变化较小。发酵3~15 d,CK组、MIX组的Ash含量均低于2个单独添加组;在发酵7 d,MIX组的Ash含量显著低于2个单独添加组(P<0.05);在发酵60 d时,CK组Ash含量显著高于3个添加组(P<0.05)。
表 7 不同处理、不同发酵时间的菌糠发酵饲料粗灰分Ash含量Table 7. Effect of treatments on ash (DM) in fermented feed material(单位:%) 发酵时间 Fermentation Time/d CK CCZZ1 HT1 MIX 1 11.87±0.07(b)b 12.08±0.16(ab)b 12.35±0.23(a)a 11.98±0.16(b)a 3 11.72±0.11(b)b 12.22±0.24(a)ab 12.69±0.08(a)a 11.85±0.05(b)a 7 11.78±0.29(c)b 12.31±0.06(b)ab 12.66±0.19(a)a 11.78±0.07(c)a 15 11.89±0.56(b)b 12.36±0.24(a)ab 12.56±0.14(a)a 11.76±0.30(b)a 30 12.30±0.38(ab)b 12.46±0.12(ab)a 12.70±0.30(a)a 11.98±0.28(b)a 60 14.02±0.70(a)a 10.94±0.08(b)c 10.52±0.19(b)b 11.23±0.19(b)b 由表8可知,在发酵7 d时,CCZZ1组CP含量最高。发酵15 d 后勤工作各处理的CP含量开始减少;在发酵15 d时CK组CP含量显著低于3个添加组(P<0.05);在发酵60 d时,CK组CP含量显著高于3个添加组(P<0.05)。
表 8 不同处理、不同发酵时间的菌糠发酵饲料粗蛋白CP含量Table 8. Effect of treatments on crude protein CP (DM) in fermented feed material(单位:%) 发酵时间 Fermentation Time/d CK CCZZ1 HT1 MIX 1 7.01±0.09(a)ab 7.08±0.08(a)b 6.90±0.13(a)b 6.98±0.10b(a)b 3 6.81±0.11(a)bc 7.05±0.14(a)b 6.90±0.10(a)b 6.97±0.60(a)b 7 7.12±0.11(b)a 7.34±0.10(a)a 7.13±0.14(b)a 7.02±0.07(b)b 15 6.98±0.05(b)abc 7.17±0.07(a)b 7.15±0.08(a)a 7.27±0.03(a)a 30 6.79±0.11(a)c 6.86±0.07(a)c 6.80±0.14(a)b 6.81±0.11(a)c 60 6.79±0.19(a)c 6.37±0.11(b)d 6.38±0.08(b)c 6.20±0.01(b)d 由表9可知,在发酵15 d时,HT1组的WSC含量最低,显著低于MIX组(P<0.05);在发酵30 d和60 d时,MIX组的WSC含量显著低于其他3个处理组(P<0.05)。
表 9 不同处理、不同发酵时间的菌糠发酵饲料可溶性碳水化合物WSC含量Table 9. Effect of treatments on water soluble carbohydrate WSC (DM) in fermented feed material(单位:%) 发酵时间 Fermentation Time/d CK CCZZ1 HT1 MIX 1 0.60±0.14(a)ab 0.48±0.04(a)b 0.49±0.05(a)bc 0.56±0.14(a)ab 3 0.68±0.12(a)a 0.67±0.18(a)a 0.69±0.32(a)a 0.66±0.07(a)a 7 0.53±0.06(a)ab 0.48±0.04(a)b 0.61±0.17(a)ab 0.48±0.02(a)bc 15 0.46±0.04(b)b 0.47±0.01(b)b 0.42±0.04(c)c 0.51±0.03(a)bc 30 0.58±0.04(a)ab 0.63±0.08(a)ab 0.60±0.02(a)ab 0.48±0.05(b)bc 60 0.57±0.11(a)ab 0.66±0.04(a)a 0.55±0.08(a)abc 0.38±0.01(b)c 由表10可知,总体而言,平菇菌糠发酵饲料的ADF含量随着发酵时间的增加而有所升高。在发酵3~15 d时段,同一时间点各处理组间的ADF含量差异不显著(P>0.05);在发酵30 d,CK组、MIX组的ADF含量显著低于HT1处理组(P<0.05);在发酵60 d时,CCZZ1组的ADF含量显著高于HT1处理组(P<0.05)。
表 10 不同处理、不同发酵时间的菌糠发酵饲料酸性洗涤纤维ADF含量Table 10. Effect of treatments on acid washing fiber ADF (DM) in fermented feed material(单位:%) 发酵时间 Fermentation Time/d CK CCZZ1 HT1 MIX 1 49.30±1.67(b)b 49.97±3.33(b)e 55.53±2.23(a)cd 56.65±1.76(a)d 3 51.35±7.27(a)b 56.48±0.82(a)d 51.89±3.44(a)d 54.50±2.53(a)d 7 59.32±3.31(a)a 62.66±2.48(a)bc 60.36±4.26(a)bc 61.25±1.48(a)bc 15 61.12±2.06(a)a 58.94±1.64(a)cd 58.53±3.16(a)bc 59.71±0.82(a)c 30 63.34±0.77(b)a 64.70±2.02(ab)ab 66.59±1.16(a)a 62.92±1.67(b)ab 60 64.19±0.91(ab)a 66.84±1.69(a)a 63.77±1.92(b)ab 65.55±1.20(ab)a 由表11可知,在发酵1~15 d,各处理组之间差异不显著(P>0.05);在发酵30 d时,CK组、CCZZ1组的NDF含量均显著低于 HT1处理组(P<0.05);在发酵60 d时,CK组、HT1组的NDF含量显著低于CCZZ1组(P<0.05)。
表 11 不同处理、不同发酵时间菌糠发酵饲料的中性洗涤纤维NDF含量Table 11. Effect of treatments on neutral washing fiber NDF (DM) in fermented feed material(单位:%) 发酵时间 Fermentation Time/d CK CCZZ1 HT1 MIX 1 60.56±4.86(a)c 61.05±4.11(a)c 66.96±4.26(a)c 62.37±0.92(a)d 3 67.00±3.47(a)b 71.17±1.18(a)b 67.18±5.35(a)c 67.50±2.44(a)c 7 76.61±0.85(a)a 78.25±2.12(a)a 74.95±2.93(a)ab 74.88±2.35(a)ab 15 75.10±2.13(a)a 70.88±3.98(a)b 72.22±3.51(a)bc 75.25±5.35(a)ab 30 75.47±1.58(b)a 75.64±2.05(b)ab 79.43±0.60(a)a 76.85±1.50(ab)a 60 69.93±1.59(b)b 72.95±1.43(a)b 69.44±1.28(b)bc 71.27±1.55(ab)bc 由表12可知,各处理组在发酵结束时的HC含量均最低。在发酵1 d时,MIX组的HC含量显著低于其他3组(P<0.05);在发酵3~60 d时段,同一时间点各处理组之间差异不显著(P>0.05);发酵60 d时,CK组、CCZZ1组和HT1组的HC含量均显著低于其他发酵时间点(P<0.05),MIX组的HC含量也显著低于3~30 d的4个发酵时间点。
表 12 不同处理、不同发酵时间的菌糠发酵饲料半纤维素HC含量Table 12. Effect of treatments on hemicellulose HC (DM) in fermented feed material(单位:%) 发酵时间 Fermentation Time/d CK CCZZ1 HT1 MIX 1 11.26±3.22(a)b 11.08±0.93(a)c 11.43±2.50(a)a 5.72±0.85(b)b 3 15.65±3.99(a)ab 14.68±0.59(a)ab 15.29±4.56(a)a 13.00±0.22(a)a 7 17.29±3.29(a)a 15.59±0.66(a)a 14.60±1.34(a)a 13.63±2.37(a)a 15 13.98±1.95(a)ab 11.93±3.00(a)bc 13.68±0.43(a)a 15.55±4.79(a)a 30 12.12±0.84(a)b 10.95±2.33(a)c 12.84±0.58(a)a 13.93±3.16(a)a 60 5.74±1.39(a)c 6.12±0.40(a)d 5.67±0.84(a)b 5.72±0.46(a)b 3. 讨论
3.1 菌糠的化学成分和微生物组成
供试材料平菇菌糠的pH值为5.42,偏酸性;中性洗涤纤维和酸性洗涤纤维所占比例偏高,分别为76.03 %和64.01 %;菌糠粗蛋白含量较高(9.62 %)。其纤维和粗蛋白含量与陆亚珍等[19]的测定结果相近,与中等质量粗饲料相当。食用菌的菌丝残体和通过食用菌生命活动产生的纤维素、半纤维素、木质素,以及丰富的矿物元素、氨基酸等营养物质,具有很高的营养价值[20]。采集食用菌子实体后,菌糠具有浓厚的芳香气味,更易粉碎,禽畜的适口性更好,可直接作为饲料喂养大型禽畜[21]。
由表2可知,平菇菌糠的微生物组成中乳酸菌数量(FM)为2.23 lg (cfu·g−1),好气性细菌数量(FM)为4.98 lg (cfu·g−1),酵母菌和霉菌数量(FM)分别为2.35 lg (cfu·g−1)和1.23 lg (cfu·g−1)。在发酵初期,酵母菌和霉菌会过多消耗饲料的营养物质,霉菌会使饲料发霉变质并产生酸败味,降低其品质。在平菇菌糠的微生物组成中乳酸菌数未占据优势地位,不能满足良好的乳酸发酵需要。在自然发酵条件下,附着在原材料上的乳酸菌数量会使发酵初期的pH值下降,菌糠附着的菌数量越多,pH值下降越快[22]。由于前人的研究大多过于笼统,为了更深入研究乳酸菌对菌糠发酵饲料品质的影响,本试验选用更适宜用作动物饲料开发的平菇菌糠,通过筛选不同菌糠发酵菌种和完善发酵工艺,对菌糠发酵不同时间各成分进行测定、分析和比较研究。本研究结果可为生产优质菌糠发酵饲料提供理论依据,为菌糠资源的合理利用开辟新途径。
3.2 乳酸菌对平菇菌糠发酵饲料品质和发酵进程的影响
3.2.1 乳酸菌对平菇菌糠发酵饲料品质的影响
平菇菌糠发酵过程中,随着乳酸菌发酵生产乳酸,pH值下降至4.2以下时,平菇菌糠内的微生物的活动会受到抑制,从而减少平菇菌糠内营养物质的损耗,3个添加乳酸菌的处理组pH值比CK组更快降到4.2以下,说明发酵前添加乳酸菌可增加发酵初期的乳酸菌数量,促进乳酸发酵,加快生成大量的乳酸,迅速降低pH值,抑制有害微生物的活性,从而减少发酵过程中营养物质的损失,这与 Mcdonald等[23]的试验结果一致。伴随着后期的进一步发酵,平菇菌糠饲料中氨态氮含量,以及乳酸、乙酸、丙酸的含量均呈上升趋势,pH值 呈下降趋势,这与陈鑫珠[24-25]的试验结果一致。但在发酵进程结束时,酸性洗涤纤维、中性洗涤纤维含量有所升高,粗蛋白含量有所下降。究其原因:①乳酸菌发酵到一定程度,由于发酵底物逐渐消耗,乳酸菌生长繁殖速度变慢,从而减弱了其对有害微生物的抑制作用,导致有害微生物异常发酵。②伴随着发酵的进程,菌糠内部温度升高,耐低温的乳酸菌活动减弱或停止,也使有害微生物活性增强并对菌糠中蛋白质产生降解作用。
3.2.2 乳酸菌对平菇菌糠发酵饲料发酵进程的影响
王英超等[22]的研究结果表明,平菇菌糠发酵初期,在菌糠上接种一定量的乳酸菌可加速发酵。在本试验的4个处理组中,添加乳酸菌的3个处理组在发酵7 d时pH值均降到4.2以下,而未添加乳酸菌的对照组则是在30 d时pH值才下降到4.2以下。4个处理组在发酵的1~30 d,菌糠的pH值持续降低,添加乳酸菌的3个处理组的pH值与未添加的对照组相比下降更明显,其中又以复合添加乳酸菌组pH值下降最快。这与侯建建[26] 对苜蓿青贮饲料的试验结果相似。说明,平菇菌糠中添加乳酸菌可以加快其pH值的下降,从而加快平菇菌糠的发酵进程。
4. 结论
单一或复合添加乳酸菌CCZZ1、HT1可使平菇菌糠发酵过程的pH值迅速降低,加快发酵进程,减少菌糠营养物质损失,对提升菌糠发酵品质有积极作用。在本试验条件下平菇菌糠在发酵第15 d开封效果最好。
-
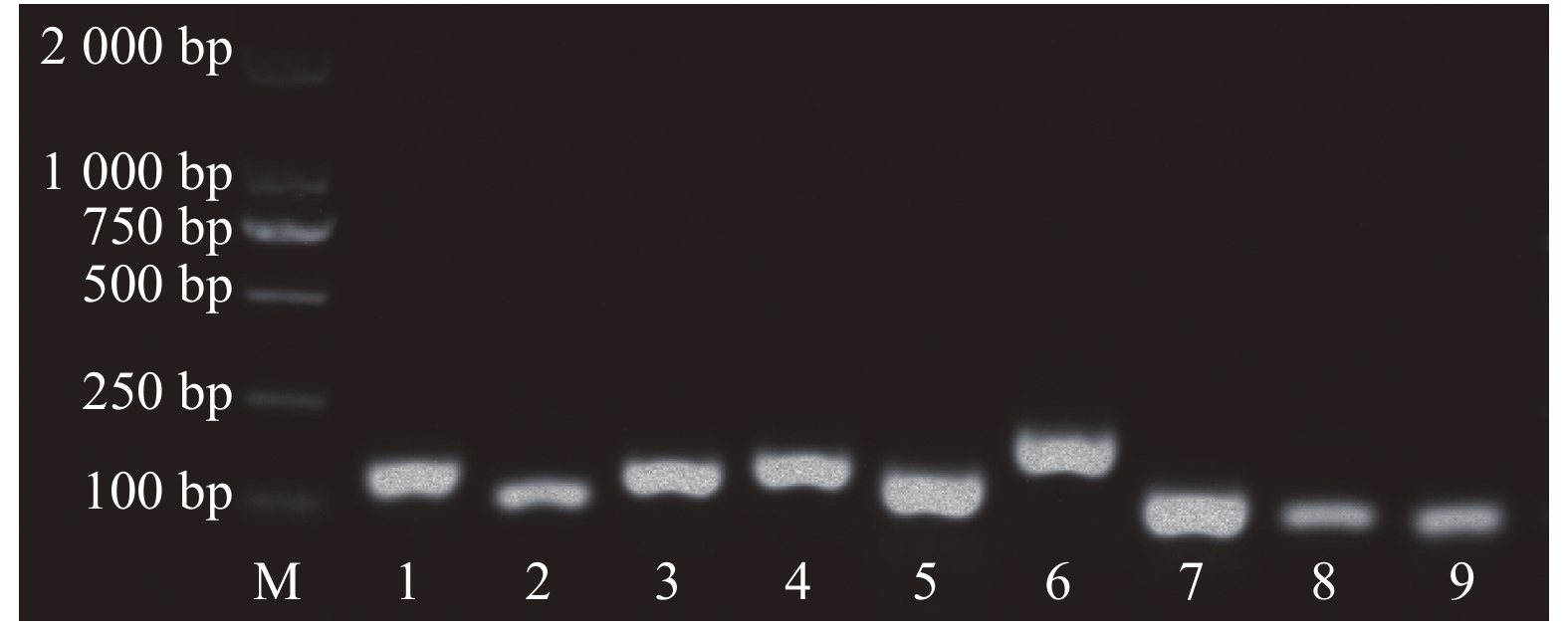
图 1 9个候选内参基因的引物扩增特异性与扩增长度
注:M:Marker;1~9分别为内参基因Actin1、Actin2、Actin3、Actin4、CYC、UBI-ep、TUA、18s rRNA、EF1a。
Figure 1. Amplification specificities and lengths of 9 candidate reference genes
Note: M: marker; 1–9: candidate reference genes, Actin1, Actin2, Actin3, Actin4, CYC,UBI-ep, TUA, 18s rRNA, and EF1a, respectively.
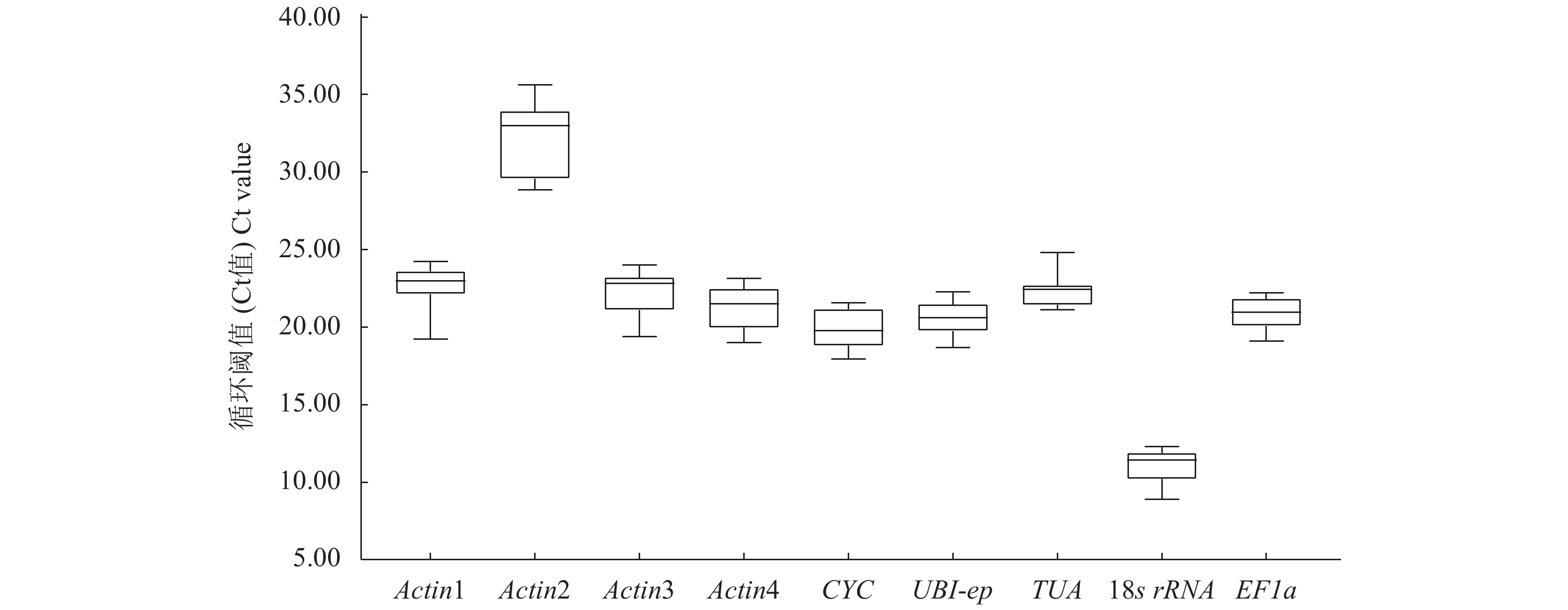
图 3 9个候选内参基因Ct值箱线图
注:箱线图箱体代表Ct值主要集中范围;上边表示上四分线;中线表示中位数;下边表示下四分线;上边缘表示本组数据最大值;下边缘表示本组数据最小值。
Figure 3. Box plot of Ct values of 9 reference genes
Note: Box: range of concentrated Ct values; top line: upper quarter line; middle line: median value; bottom line: lower quarter line; top edge: maximum value of group; bottom edge: minimum of group.
表 1 9个候选内参基因RT-qPCR引物序列及其扩增效率
Table 1 RT-qPCR primer sequences and amplification efficiency of 9 candidate reference genes
登录号
GenBank ID基因
Gene引物序列(5′-3′)
Primer sequence F/R(5′-3′)产物大小
Product size/bp扩增效率
Efficiency(E)AF206894.1 18s rRNA TCTGCCCGTTGCTCTGATG 130 2.05 TCACCCGTCACCACCATAG XM_008456199.2 TUA ACGCTGTTGGTGGTGGTAC 106 2.06 GAGAGGGGTAAACAGTGAATC XM_008459007.2 EF1a ACTGTGCTGTCCTCATTATTG 98 1.98 AGGGTGAAAGCAAGAAGAGC LN713255.1 CYC GATGGAGCTCTACGCCGATGTC 153 1.97 CCTCCCTGGCACATGAAATTAG NM_001282241.1 UBI-ep CACCAAGCCCAAGAAGATC 220 2.10 TAAACCTA ATCACCACCAGC XM_008442791.2 Actin1 TTCTGGTGATGGTGTGAGTC 149 2.09 GGCAGTGGTGGTGAACATG XM_008449644.2 Actin2 GAAGGAATAACCACGCTCAG 117 2.02 ACACAGTTCCCATCTACGAG XM_008449644.2 Actin3 GGCAGTGGTGGTGAACATG 149 1.99 TTCTGGTGATGGTGTGAGTC LN713262.1 Actin4 TGGAAGCTGCAGGAATCCACGA 165 2.04 TGCTGGGAGCAAGGGCTGTG 表 2 Best-Keeper软件分析9个候选内参基因稳定性
Table 2 Stabilities of 9 reference genes analyzed by BestKeeper software
样品分组
Sample group基因
Gene几何平均值
Geometric
mean value最大值
Max最小值
Mix标准差
Stardand
deviaton(SD)变异差
Coefficient
ofvariation(CV)稳定性排名
Ranking of
stable value不同组织器官
Different tissuesCYC 20.88 21.55 19.72 0.57 2.72 1 18s rRNA 10.21 11.46 8.90 0.77 7.55 2 UBI-ep 20.12 22.10 18.69 0.94 4.67 3 EF1a 20.42 22.03 19.11 0.95 4.65 4 TUA 22.69 24.80 21.10 0.98 4.31 5 Actin1 21.92 23.98 19.23 1.37 6.21 6 Actin4 20.63 23.14 18.99 1.38 6.65 7 Actin3 21.61 24.03 19.39 1.50 6.92 8 Actin2 31.38 33.95 29.40 1.86 5.92 9 不同胁迫处理
Different stress conditions18s rRNA 11.82 12.31 11.16 0.22 1.86 1 Actin3 22.85 23.30 21.54 0.37 1.62 2 Actin4 21.85 22.77 21.23 0.43 1.97 3 EF1a 21.24 22.20 20.36 0.46 2.18 4 UBI-ep 21.38 22.29 20.49 0.46 2.14 5 Actin1 23.20 24.22 22.28 0.54 2.35 6 CYC 18.87 19.89 17.95 0.59 3.44 7 TUA 22.05 23.35 21.27 0.60 2.71 8 Actin2 36.68 35.63 28.84 1.86 5.67 9 表 3 Norm Finder和ge Norm软件分析候9个选内参基因稳定性
Table 3 Stabilities of 9 reference genes analyzed by NormFinder and geNorm software
样品分组
Sample groupNorm Finder ge Norm 基因
Gene稳定值
Stability value稳定性排名
Ranking of stable value基因
Gene稳定值
Stability value稳定性排名
Ranking of stable value不同组织器官
Different tissuesEF1a 0.107 1 Actin4 0.526 1 UBI-ep 0.153 2 Actin3 0.526 2 Actin4 0.228 3 Actin1 0.640 3 CYC 0.243 4 EF1a 0.794 4 Actin3 0.291 5 UBI-ep 0.894 5 18s rRNA 0.315 6 18s rRNA 0.961 6 Actin1 0.319 7 CYC 1.101 7 TUA 0.345 8 TUA 1.318 8 Actin2 0.423 9 Actin2 1.462 9 不同胁迫处理
Different stress conditionsEF1a 0.023 1 EF1a 0.138 1 UBI-ep 0.053 2 UBI-ep 0.138 2 Actin4 0.059 3 Actin4 0.145 3 CYC 0.078 4 CYC 0.207 4 18s rRNA 0.128 5 TUA 0.242 5 TUA 0.128 6 18s rRNA 0.321 6 Actin1 0.214 7 Actin1 0.373 7 Actin3 0.236 8 Actin3 0.445 8 Actin2 0.264 9 Actin2 0.781 9 表 4 9个选内参基因稳定性综合排名
Table 4 Overall ranking on expression stabilities of 9 reference genes
样品分组
Sample group基因
GeneBest-Keeper Norm-Finder ge Norm 几何平均值
Geometric mean value综合排名
Comprehensive rankings不同组织器官
Different tissuesEF1a 4 1 4 2.520 1 Actin4 7 3 1 2.759 2 CYC 1 4 7 3.037 3 UBI-ep 3 2 5 3.107 4 18s rRNA 2 6 6 4.160 5 Actin3 8 5 2 4.309 6 Actin1 6 7 3 5.013 7 TUA 5 8 8 6.840 8 Actin2 9 9 9 9.000 9 不同胁迫处理
Different stress conditionsEF1a 4 1 1 1.587 1 UBI-ep 5 2 2 2.714 2 Actin4 3 3 3 3.000 3 18s rRNA 1 5 6 3.107 4 CYC 7 4 4 4.820 5 Actin3 2 8 8 5.040 6 TUA 8 6 5 6.214 7 Actin1 6 7 7 6.649 8 Actin2 9 9 9 9.000 9 -
[1] GINZINGER D G. Gene quantification using real-time quantitative PCR: An emerging technology hits the mainstream [J]. Experimental Hematology, 2002, 30(6): 503−512. DOI: 10.1016/S0301-472X(02)00806-8
[2] ZHANG Z Z, FAN J R, WU J H, et al. Alleviating effect of silicon on melon seed germination under autotoxicity stress [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 188: 109901. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109901
[3] PFAFFL M W, TICHOPAD A, PRGOMET C, et al. Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper - Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2004, 26(6): 509−515. DOI: 10.1023/B:BILE.0000019559.84305.47
[4] VANDESOMPELE J, DE PRETER K, PATTYN F, et al. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes [J]. Genome Biology, 2002, 3(7): 1−12.
[5] TANG X, ZHANG N, SI H J, et al. Selection and validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis in potato under abiotic stress [J]. Plant Methods, 2017, 13: 85. DOI: 10.1186/s13007-017-0238-7
[6] LUO H L, LUO L P, GUAN B C, et al. Evaluation of candidate reference genes for RT-qPCR in lily (Lilium brownii) [J]. The Journal of Horticultural Science and Biotechnology, 2014, 89(3): 345−351. DOI: 10.1080/14620316.2014.11513089
[7] 吕运舟, 董筱昀, 黄利斌. 黄山栾树实时荧光定量PCR内参基因的筛选 [J]. 分子植物育种, 2019, 17(2):553−560. LÜ Y Z, DONG X Y, HUANG L B. The screening of reference genes for real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR of Koelreuteria bipinnata [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2019, 17(2): 553−560.(in Chinese)
[8] 任锐, 戴鹏辉, 李萌, 等. 珙桐实时定量PCR内参基因的筛选及稳定性评价 [J]. 植物生理学报, 2016, 52(10):1565−1575. REN R, DAI P H, LI M, et al. Selection and stability evaluation of reference genes for real-time quantitative PCR in dove tree (Davidia involucrata) [J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 2016, 52(10): 1565−1575.(in Chinese)
[9] GOPALAM R, RUPWATE S D, TUMANEY A W. Selection and validation of appropriate reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR analysis in Salvia hispanica [J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(11): e0186978. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186978
[10] 蒋婷婷, 高燕会, 童再康. 石蒜属植物实时荧光定量PCR内参基因的选择 [J]. 园艺学报, 2015, 42(6):1129−1138. JIANG T T, GAO Y H, TONG Z K. Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR in Lycoris [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2015, 42(6): 1129−1138.(in Chinese)
[11] 王彦杰, 董丽, 张超, 等. 牡丹实时定量PCR分析中内参基因的选择 [J]. 农业生物技术学报, 2012, 20(5):521−528. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7968.2012.05.008 WANG Y J, DONG L, ZHANG C, et al. Reference gene selection for real-time quantitative PCR normalization in tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa andr.) [J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2012, 20(5): 521−528.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7968.2012.05.008
[12] FAUSTO A K S, SILVA T D F, ROMANEL E, et al. microRNAs as reference genes for quantitative PCR in cotton [J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(4): e0174722. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174722
[13] 潘红, 赖呈纯, 张静, 等. 不同光质条件下刺葡萄红色愈伤组织的RT-qPCR内参基因筛选 [J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2019, 25(6):1407−1413. PAN H, LAI C C, ZHANG J, et al. Selection of reference genes for RT-qPCR from the red callus of Vitis davidii (Rom. Caill.) Fo(ë)x under different light qualities [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 2019, 25(6): 1407−1413.(in Chinese)
[14] GONZÁLEZ-VERDEJO C I, DIE J V, NADAL S, et al. Selection of housekeeping genes for normalization by real-time RT–PCR: Analysis of Or-MYB1 gene expression in Orobanche ramosa development [J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 2008, 379(2): 176−181. DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2008.05.003
[15] 史兴青. 甜瓜生长发育和胁迫条件下实时荧光定量PCR内参基因的筛选 [D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2016. SHI X Q. Selection of suitable reference genes for quantitative real-time RT-PCR studies in Cucumis melo under growth and development process, biotic and abiotic stresses[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2016. (in Chinese).
[16] ANDERSEN C L, JENSEN J L, ØRNTOFT T F. Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: A model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets [J]. Cancer Research, 2004, 64(15): 5245−5250. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0496
[17] SUDHAKAR REDDY P, SRINIVAS REDDY D, SIVASAKTHI K, et al. Evaluation of Sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.)] reference genes in various tissues and under abiotic stress conditions for quantitative real-time PCR data normalization [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 529. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00529
[18] LI L, WANG K Y, ZHAO M Z, et al. Selection and validation of reference genes desirable for gene expression analysis by qRT-PCR in MeJA-treated ginseng hairy roots [J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(12): e0226168. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226168
[19] 乔永刚, 王勇飞, 曹亚萍, 等. 药用蒲公英低温和高温胁迫下内参基因筛选与相关基因表达分析 [J]. 园艺学报, 2020, 47(6):1153−1164. QIAO Y G, WANG Y F, CAO Y P, et al. Reference genes selection and related genes expression analysis under low and high temperature stress in Taraxacum officinale [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2020, 47(6): 1153−1164.(in Chinese)
[20] 宋晓波, 常英英, 刘昊, 等. 核桃不定根发生阶段内参基因筛选与关键基因表达分析 [J]. 园艺学报, 2019, 46(10):1907−1918. SONG X B, CHANG Y Y, LIU H, et al. Reference gene selection and genes expression analysis during adventitious root formation in walnut [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2019, 46(10): 1907−1918.(in Chinese)
[21] 刘涛, 熊青, 许颖妍, 等. 夜香树花期荧光定量PCR内参基因的筛选 [J]. 植物科学学报, 2017, 35(4):534−542. DOI: 10.11913/PSJ.2095-0837.2017.40534 LIU T, XIONG Q, XU Y Y, et al. Selection of reference genes for qRT-PCR normalization in Cestrum nocturnum during flowering [J]. Plant Science Journal, 2017, 35(4): 534−542.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11913/PSJ.2095-0837.2017.40534
[22] 胡宁宁, 郭慧琴, 李西良, 等. 羊草不同组织实时定量PCR 内参基因的筛选 [J]. 草业科学, 2017, 34(7):1434−1441. DOI: 10.11829/j.issn.1001-0629.2016-0510 HU N N, GUO H Q, LI X L, et al. Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR of Leymus chinensis in different tissues [J]. Pratacultural Science, 2017, 34(7): 1434−1441.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11829/j.issn.1001-0629.2016-0510
[23] 黄文华. 蒙古冰草干旱胁迫下内参基因的筛选及P5CS基因定量表达分析 [D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2014. HUANG W H. Selection of control gene in quantitative PCR and analysis of differential expression of P5CS gene in Agropyron mongolicum Keng under drought stress [D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese).
[24] 张燕梅, 王瑞芳, 杨子平, 等. 剑麻内参基因筛选与稳定表达分析 [J]. 热带作物学报, 2019, 40(11):2166−2173. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2019.11.010 ZHANG Y M, WANG R F, YANG Z P, et al. Screening of suitable reference genes for qRT-PCR normalization in sisal [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2019, 40(11): 2166−2173.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2019.11.010
[25] XIAO Z, SUN X B, LIU X Q, et al. Selection of reliable reference genes for gene expression studies on Rhododendron molle G. don [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 1547.
[26] HU R, QI G, KONG Y, et al. Comprehensive analysis of NAC domain transcription factor gene family in Populus trichocarpa [J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2010, 10(1): 145−158. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-145
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 张艺,何军,张宝龙,赵帆,陈祖梅. 蓄雨型间歇灌溉模式下缓释肥配施生物炭对水稻产量及水分利用的影响. 核农学报. 2025(05): 1040-1049 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 郭颂,杨卫君,李廷宇,杨梅,陈雨欣,宋世龙,惠超,耿洪伟. 生物炭用量与灌水量对北疆灌区春小麦籽粒产量和品质综合评价. 麦类作物学报. 2024(05): 658-666 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 劳洁玉,郑铭洁,黄永材,任震,吴家森,傅伟军. 紫云英及氮肥减量下配施生物质炭对土壤理化性质和水稻产量的影响. 江西农业大学学报. 2024(02): 289-301 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 熊家欢,张义凯,向镜,陈惠哲,徐一成,王亚梁,王志刚,姚坚,张玉屏. 覆膜稻田施用炭基肥对水稻产量及氮素利用的影响. 中国水稻科学. 2024(05): 567-576 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘慧,焦岩,窦婉毓,张文龙,裴巍. 减氮配施生物炭对土壤肥力和水稻产量的补偿效应与机制. 农业机械学报. 2024(09): 391-401+469 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 李廷宇,申毅,童俊飞,路顺凤,李琴,郭颂,杨卫君. 施用生物炭并减少灌水量对麦田土壤团聚结构及冬小麦产量的影响. 中国农学通报. 2024(36): 110-116 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 孙靓楠,红雨,王伶瑞,薛转转,吴艳玲. 生物炭对高粱根际土壤线虫的影响. 内蒙古师范大学学报(自然科学汉文版). 2023(06): 551-558+567 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)




 下载:
下载: