Effects of Salicylic Acid on Growth and Physiology of Non-heading Chinese Cabbage Seedlings under Cadmium Stress
-
摘要:目的 探讨水杨酸(Salicylic acid,SA)诱导不结球白菜抗镉(Cadmium,Cd)胁迫的响应及对Cd吸收积累和转运差异,为利用SA减轻Cd胁迫对不结球白菜的伤害提供理论依据。方法 以华冠不结球白菜为试验材料,研究Cd胁迫(50 mg·L−1 CdCl·2.5H2O)及喷施SA(0.01~0.5 mmol·L−1)对幼苗生长、光合色素含量、根系活力、渗透调节物质、丙二醛(MDA)含量、抗氧化酶活性和Cd积累的影响。结果 与空白对照(CK1)相比,Cd胁迫对照组(50 mg·L−1 CdCl·2.5H2O,CK2)显著抑制不结球白菜幼苗的生长,降低光合色素含量、根系活力、蛋白质含量、脯氨酸(Pro)含量和抗氧化酶活性,提高丙二醛(MDA)含量。在Cd胁迫下,喷施0.01~0.05 mmol·L−1SA可以促进不结球白菜幼苗生长,以0.05 mmol·L−1SA处理效果最好;在Cd胁迫10 d时,不结球白菜幼苗的根冠比、脯氨酸含量、POD、CAT活性较CK2提高140%、44.98%、118.18%、70.43%,且显著降低幼苗地上部分Cd含量和转运系数;而喷施0.1~0.5 mmol·L−1SA幼苗生长受抑。结论 0.05 mmol·L−1SA是最适宜的喷施浓度,能有效缓解Cd对不结球白菜幼苗的毒害,提高幼苗的耐Cd性。Abstract:Objective Growth and physiological responses of non-heading Chinese cabbage to salicylic acid (SA) spraying under Cd-stress were studied.Method Huaguan non-heading Chinese cabbage (Brassica chinensis L.) seedlings under an imposed stress of 50 mg CdCl·2.5H2O·L−1 were sprayed with SA at a rate of 0.01-0.5 mmol·L−1. Growth, root activity, osmotic regulators, photosynthetic pigment content, malondialdehyde (MDA) content, and antioxidant enzyme activity as well as the Cd absorption, accumulation, and transportation of the separately treated seedlings were determined.Result The seedlings under the Cd-stress control (CK2) grew significantly slower with reduced root vitality, contents of photosynthetic pigments, protein, and proline (Pro), and antioxidant enzyme activities but increased MDA in comparison to the blank control (CK1). Under the Cd-stress, SA spraying in the range of 0.01-0.05 mmol·L−1 rejuvenated the seedling growth, with the greatest effect observed when 0.05 mmol·L−1 SA was applied. The seedlings of CK1 had their root/shoot ratio increased by 140%, proline content by 44.98%, POD by 118.18%, and CAT by 70.43% over those of CK2 10d under the Cd-stress, while the aboveground parts of the plants had the Cd content and transport coefficient significantly reduced. On the other hand, when higher SA concentrations in the range of 0.1-0.5 mmol·L−1 was applied, the seedling growth was significantly inhibited.Conclusion At a concentration of 0.05 mmol SA·L−1, the spraying could effectively alleviate the Cd toxicity and improve the Cd tolerance of the non-heading Chinese cabbage seedlings.
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】镉(Cadmium,Cd)是环境中毒性最强的重金属元素之一,被联合国环境规划署列为具有全球意义的危险物质之首[1]。随着城市化、工业化的迅速发展,福州市城区土壤和农田土壤均受到重金属Cd污染,研究发现城区土壤和农田土壤中的Cd含量均超过福建省土壤背景值,相对于其他重金属元素,Cd元素存在严重积累现象[2-3]。不结球白菜作为Cd超富集蔬菜,在Cd胁迫下不结球白菜呈现叶片黄化、植株矮小的毒害症状[4-5],不结球白菜幼苗叶绿素的含量显著降低,光合作用受到抑制,同时产生过量的活性氧,造成膜质过氧化损伤[6],Cd在蔬菜中富集积累,可通过食物链传递危害人体健康[7]。【前人研究进展】水杨酸(Salicylic acid,SA)是植物体内广泛存在的一种酚类化合物,它不仅参与调节植物生长发育的生理过程,还能诱导植物对低温、盐碱、重金属等胁迫产生抗性[8]。近年来,关于SA缓解植物Cd胁迫的研究较为广泛,研究表明,SA能缓解Cd对花椰菜种子萌发和幼苗生长的抑制[9];外施SA可降低小麦根部Cd含量,提高光合速率,增强小麦的耐Cd能力[10];外源SA处理莴苣幼苗后,可以有效缓解Cd对莴苣幼苗生长的抑制作用[11];SA预处理可以缓解Cd胁迫对番茄生长的毒害作用,降低番茄根、叶中的Cd积累量[12]。【本研究切入点】不结球白菜(Brassica chinensis L.)为十字花科芸薹属芸薹种白菜亚种,原产于我国,种质资源丰富[13],生长快速、口感清爽、营养丰富[14],是福建省栽培最广的绿叶蔬菜之一。不结球白菜作为Cd敏感植物,更容易从土壤中吸收Cd并转移至可食部位[15]。目前,关于将SA用于缓解Cd对不结球白菜毒性效应的研究鲜见报道。【拟解决的关键问题】本试验以不结球白菜为材料,采用穴盘育苗,研究Cd胁迫下不同质量浓度SA处理对不结球白菜幼苗形态、生理及Cd富集量的影响,探讨SA诱导不结球白菜抗Cd胁迫的响应及对Cd吸收积累和转运差异,为利用SA减轻Cd胁迫对不结球白菜的伤害提供理论依据,在生产上为提高作物抗重金属栽培提供新方法。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
以华冠不结球白菜为供试材料,产地为日本株式会社武藏野种苗园,该品种生育期短、属矮脚种、叶柄深绿肥厚,具有耐暑、耐病及耐雨等特性。以珍珠岩、草炭作为育苗基质。
1.2 试验方法
试验于2018年12月19日至2019年1月28日在福建省农业科学院中以示范农场玻璃温室和生理生化实验室进行。不结球白菜播种时间为12月19日,出苗时间为12月21日,试验共设6个处理,每个处理重复3次。将草炭与珍珠岩以2∶1体积比例(V/V)配成复合基质,将基质装入72孔穴盘中。不结球白菜播种后置于玻璃温室植物工厂育苗,采用的营养液配方为每200 L添加A:Ca(NO3)2 16 kg,KNO3 6 kg;B:KHPO4 3 kg,MgSO4 10 kg,EDTA-Fe 460 g,MnSO4 120 g,ZnSO4 60 g,CuSO4 4 g,NH4Mo 1.5 g,HBO3 60 g[16]。不结球白菜幼苗长至两叶一心时,于每天上午9:00,对幼苗进行以下处理:(1)空白对照(CK1)和Cd胁迫对照组(CK2),叶面均喷施去离子水;(2)叶面喷施去离子水配制的0.01 mmol·L−1SA溶液;(3)叶面喷施去离子水配制的0.05 mmol·L−1SA溶液;(4)叶面喷施去离子水配制的0.1 mmol·L−1SA溶液;(5)叶面喷施去离子水配制的0.5 mmol·L−1SA溶液。连续喷施3 d,叶片以正反两面全部湿润且无液体滴下为准。3 d后开始Cd胁迫处理,除CK1用正常营养液培养,其余处理用含50 mg·L−1 CdCl·2.5H2O营养液培养。分别在Cd胁迫处理的第5 d、第10 d取样测定不结球白菜幼苗的形态指标和生理指标。
1.3 测定项目与方法
1.3.1 形态指标
株高:用直尺测量植株基部到顶端生长点的长度;茎粗:用游标卡尺测定植株子叶下2 cm的直径;根长采用WinRHIZO加拿大根系分析系统测定;叶面积用YMJ-B型叶面积测定仪(浙江托普云农科技股份有限公司)测量;地上/地下部鲜干重:用JJ223BC型电子天平(感量为0.1 mg)进行测量;壮苗指数=(茎粗/株高+地下部干质量/地上部干质量)×植株干质量[17];根冠比=地下部鲜质量/地上部鲜质量。取样时,每个处理分别选取10株长势一样且具有代表性的植株。
1.3.2 叶片生理指标
叶绿素(Chl)含量采用张宪政[18]的丙酮乙醇混合液法,可溶性蛋白含量的测定采用杨晴[19]的考马斯亮蓝G-250染色法;脯氨酸(Pro)含量采用磺基水杨酸法,丙二醛(MDA)含量采用硫代巴比妥酸法,根系活力采用TTC法,超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性采用氮蓝四唑(NBT)法,过氧化物酶(POD)活性采用愈创木酚法,过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性采用紫外吸收比色法[20]。取样时,每个处理随机选取长势一致的植株,撕取相同部位的叶片,去除叶脉后,剪碎混匀,重复测试3次。叶片生理指标测定的部位均以鲜重(FW)计算。
1.3.3 镉含量测定
将不结球白菜幼苗从基质中取出,依次用自来水、超纯水洗涤,将地上与地下部分分开,于105 ℃杀青30 min,70 ℃烘干至恒重,用不锈钢粉碎机粉碎备用。取1 g烘干样品,经混合酸高温消煮成透明或淡黄色液体,用火焰原子吸收光谱法测定茎叶和根Cd含量[21],并计算转运系数。
转运系数=地上部分镉含量/地下部分镉含量[22]
1.4 数据处理
试验数据采用Excel、DPS v7.05 数据处理软件进行统计和分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 外源SA对Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗生长的影响
从表1可以看出,Cd胁迫5 d,与CK1相比,CK2的不结球白菜幼苗生长受到抑制,其株高、茎粗、根长、叶面积、根冠比和壮苗指数分别下降6.88%、16.88%、5.58%、4.91%、42.31%和30.50%;0.01 mmol·L−1、0.05 mmol·L−1SA处理的不结球白菜各生长指标均高于CK2,但与CK1相比,株高、茎粗差异不显著,根长、叶面积显著高于CK1,根冠比、壮苗指数显著降低;SA质量浓度高于0.05 mmol·L−1,幼苗生长量反而下降。Cd胁迫10 d,CK2处理的不结球白菜幼苗的生长量依旧低于CK1,其中根冠比下降幅度达到62.27%;0.01 mmol·L−1、0.05 mmol·L−1SA处理的不结球白菜幼苗各生长量均高于CK2;与CK1相比,幼苗的株高、茎粗均升高,而根长、叶面积、根冠比、壮苗指数均下降;当SA质量浓度高于0.05 mmol·L−1,幼苗生长呈下降趋势。
表 1 外源SA对Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗生长的影响Table 1. Effect of exogenous SA on growth of non-heading Chinese cabbage seedlings under Cd-stress处理时间
Processing time/dSA/(mmol·L−1) 株高
Plant height/cm茎粗
Stem thickness/cm根长
Root length/cm叶面积
Leaf area/cm2根冠比
Root shoot ratio壮苗指数
seedling index5 0(CK1) 10.67±0.35 ab 0.28±0.02 a 8.37±0.32 de 12.99±1.00 b 0.12±0.02 a 0.69±0.03 a 0(CK2) 9.93±0.40 b 0.23±0.02 b 7.90±0.46 e 12.35±0.73 b 0.07±0.02 c 0.48±0.04 b 0.01 11.57±0.80 a 0.28±0.03 a 9.70±0.10 b 15.19±1.60 a 0.09±0.00 bc 0.52±0.03 b 0.05 10.63±0.85 ab 0.27±0.03 a 11.83±0.21 a 16.33±0.62 a 0.09±0.01 b 0.50±0.09 b 0.1 10.37±0.65 b 0.21±0.02 bc 9.17±0.29 c 11.25±1.32 bc 0.08±0.01 bc 0.48±0.01 b 0.5 8.43±0.32 c 0.17±0.01 c 8.60±0.17 d 9.89±0.18 c 0.08±0.00 bc 0.53±0.04 b 10 0(CK1) 10.87±0.10 b 0.29±0.03 ab 12.00±1.13 a 17.31±0.55 a 0.20±0.02 a 0.61±0.01 a 0(CK2) 10.23±0.25 c 0.26±0.02 bc 8.90±0.36 b 13.29±1.45 b 0.08±0.04 c 0.42±0.06 b 0.01 11.77±0.21 a 0.33±0.02 a 9.17±0.58 b 16.65±0.34 a 0.12±0.00 bc 0.50±0.07 ab 0.05 10.80±0.26 b 0.32±0.02 a 9.60±0.36 b 16.55±1.41 a 0.18±0.08 ab 0.44±0.04 b 0.1 10.47±0.15 bc 0.22±0.01 cd 9.33±1.26 b 12.26±0.32 b 0.09±0.03 c 0.43±0.09 b 0.5 10.27±0.25 c 0.20±0.01 d 9.50±0.50 b 12.18±1.06 b 0.10±0.01 c 0.41±0.05 b 注:同列同处理数值不同字母表示处理间差异达到0.05显著水平;表2、3同。
Note: Data with different letters on same column under same treatment indicate significant difference at level of 0.05. Same for below.2.2 外源SA对Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗叶片光合色素的影响
从表2可以看出,Cd胁迫5 d和10 d,与CK1相比,CK2的不结球白菜幼苗叶片的叶绿素含量和类胡萝卜素含量均降低。Cd胁迫5 d,不同浓度SA处理均能提高幼苗叶片的叶绿素含量,以0.05 mmol·L−1SA处理的叶绿素含量和类胡萝卜素含量最高,其叶绿素a、叶绿素b和叶绿素(a+b)含量较CK2分别增加40.47%、117.28%和55.10%,类胡萝卜素含量增加36.30%。Cd胁迫10 d,0.01 mmol·L−1SA、0.05 mmol·L−1SA处理的幼苗叶片叶绿素含量和类胡萝卜素含量与CK1相比差异不显著。当SA浓度高于0.05 mmol·L−1,叶绿素含量、类胡萝卜素含量均下降。
表 2 外源SA对Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗叶片光合色素的影响Table 2. Effect of exogenous SA on photosynthetic pigment in non-heading Chinese cabbage seedling leaves under Cd-stress处理时间
Processing time/dSA/(mmol·L−1) 叶绿素a
Chlorophyll a/(mg·g−1)叶绿素b
Chlorophyll b/(mg·g−1)叶绿素(a+b)
Total chlorophyll content/(mg·g−1)类胡萝卜素
Carotenoid/(mg·g−1)5 0(CK1) 0.43±0.01 de 0.16±0.00 c 0.59±0.01 c 0.12±0.01 ab 0(CK2) 0.42±0.01 e 0.10±0.01 e 0.52±0.01 d 0.10±0.00 c 0.01 0.59±0.00 a 0.21±0.01 a 0.80±0.01 a 0.13±0.01 a 0.05 0.56±0.01 b 0.18±0.01 b 0.74±0.03 b 0.12±0.02 ab 0.1 0.44±0.00 cd 0.15±0.01 c 0.59±0.00 c 0.11±0.01 bc 0.5 0.46±0.02 c 0.12±0.01 d 0.58±0.02 c 0.09±0.01 c 10 0(CK1) 1.06±0.01 a 0.35±0.03 a 1.41±0.04 a 0.28±0.00 ab 0(CK2) 0.97±0.01 b 0.28±0.01 b 1.25±0.01 b 0.24±0.01 c 0.01 1.09±0.01 a 0.35±0.01 a 1.44±0.02 a 0.27±0.02 b 0.05 1.06±0.02 a 0.35±0.02 a 1.40±0.02 a 0.30±0.01 a 0.1 0.84±0.02 c 0.26±0.00 bc 1.10±0.02 c 0.25±0.00 c 0.5 0.77±0.04 d 0.23±0.01 c 1.00±0.05 d 0.21±0.00 d 2.3 外源SA对Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗根系活力、可溶性蛋白、脯氨酸和MDA含量的影响
2.3.1 外源SA对Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗根系活力的影响
由图1可以看出,CK2的不结球白菜幼苗根系活力显著低于CK1;Cd胁迫5 d 和10 d,外源SA处理的幼苗根系活力均高于CK2;Cd胁迫5 d,0.05 mmol·L−1SA处理的根系活力较CK2显著增加29.44%;Cd胁迫10 d,0.01 mmol·L−1SA处理的根系活力最高,较CK2显著提高103.28%,但不同浓度SA处理之间差异不显著。
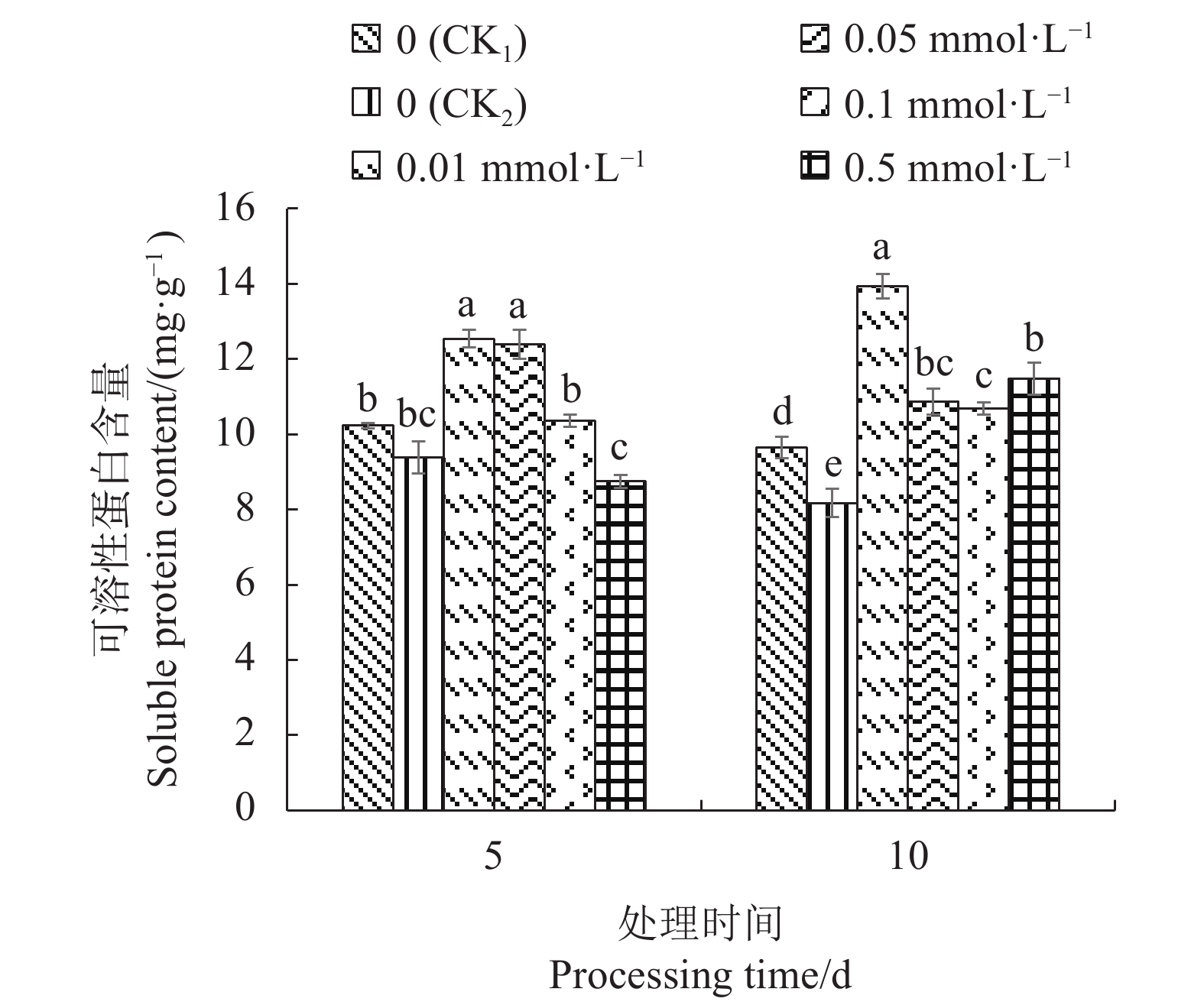
2.3.2 外源SA对Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗叶片可溶性蛋白含量的影响
由图2可知,CK2的幼苗叶片可溶性蛋白含量低于CK1;Cd胁迫5 d,0.01 mmol·L−1SA、0.05 mmol·L−1SA处理的幼苗叶片可溶性蛋白含量显著高于各个处理,0.1 mmol·L−1SA、0.5 mmol·L−1SA处理的可溶性蛋白含量出现下降;Cd胁迫10 d,SA处理显著提高可溶性蛋白含量,以0.01 mmol·L−1SA处理的可溶性蛋白含量升高最多,较CK1和CK2分别增加44.45%和70.74%。
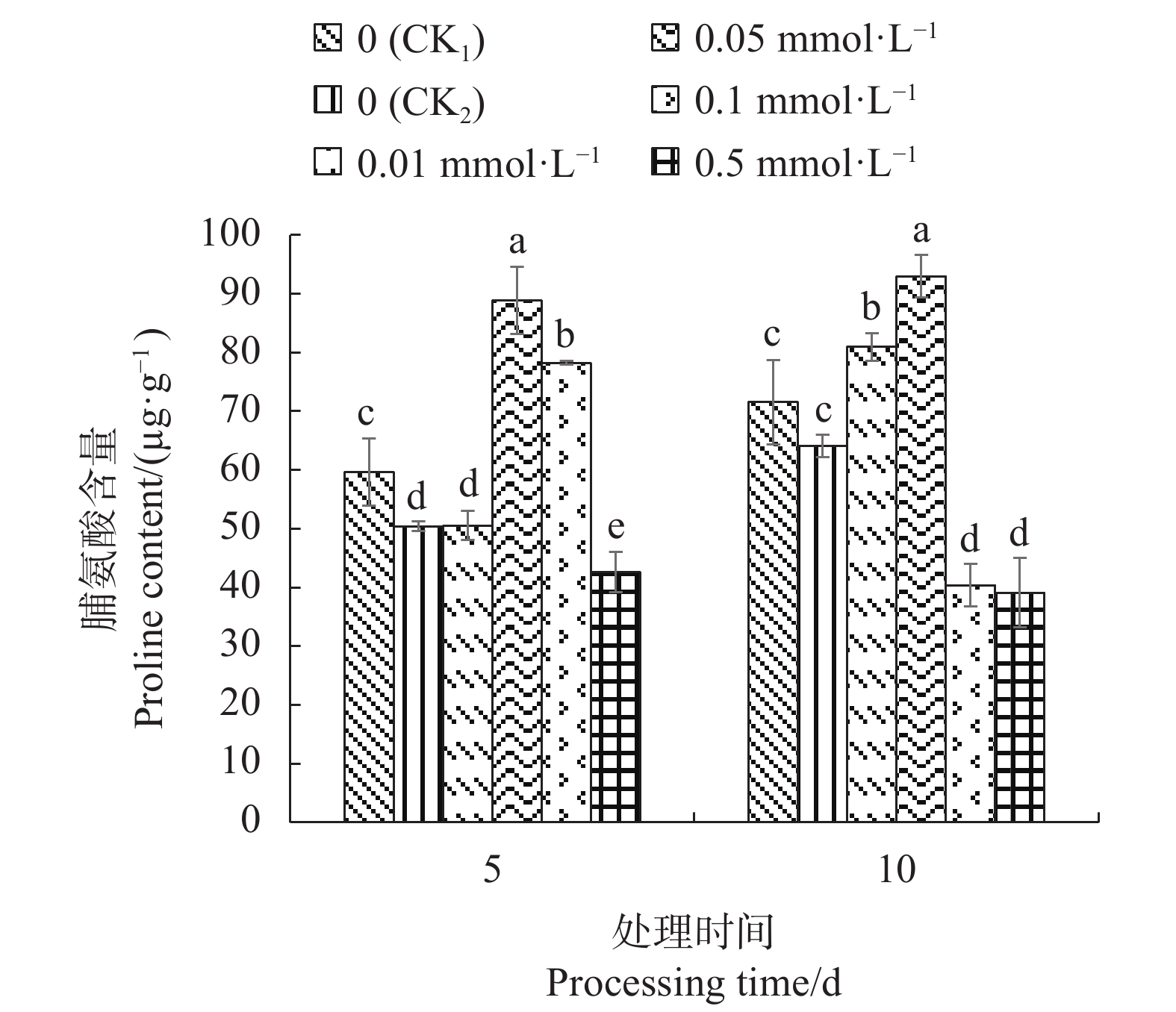
2.3.3 外源SA对Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗叶片脯氨酸含量的影响
从图3可知,CK2的幼苗叶片脯氨酸含量均低于CK1;处理5 d后,0.01 mmol·L−1SA处理的脯氨酸含量与CK2差异不显著,0.05 mmol·L−1SA、0.1 mmol·L−1SA处理的脯氨酸含量显著高于各个处理,0.5 mmol·L−1SA处理显著低于其余处理;处理10 d后,0.01 mmol·L−1SA、0.05 mmol·L−1SA处理的脯氨酸含量显著高于其余处理,其中0.05 mmol·L−1SA处理较CK1和CK2分别提高29.96%和44.98%;而0.1 mmol·L−1SA、0.5 mmol·L−1SA处理的脯氨酸含量显著降低,与其余处理之间差异显著。
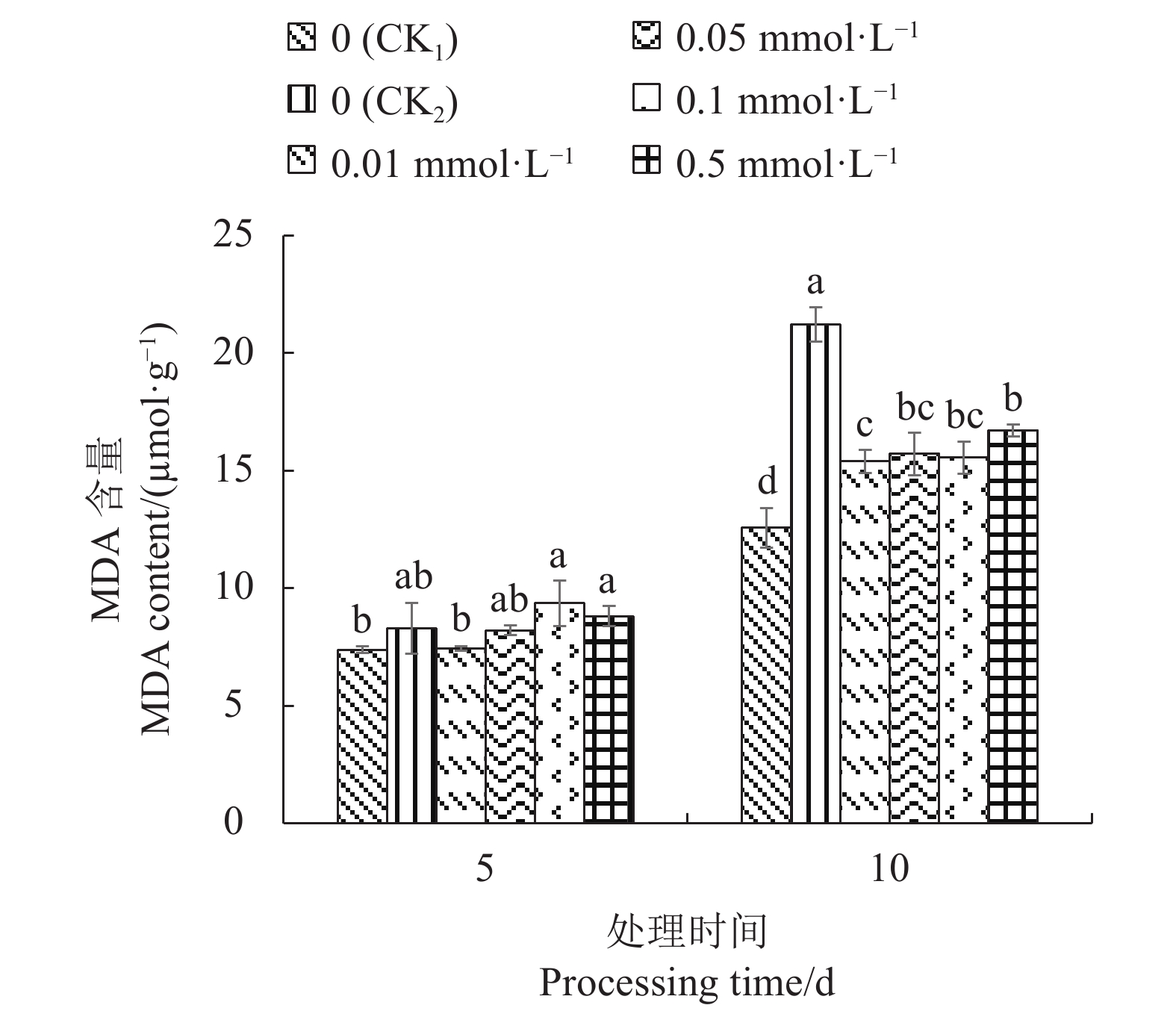
2.3.4 外源SA对Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗叶片丙二醛含量的影响
由图4可知,Cd胁迫5 d,CK1的不结球白菜幼苗叶片MDA含量最低,但与CK2、0.01 mmol·L−1SA、0.05 mmol·L−1SA处理之间差异不显著;胁迫10 d后,CK2的幼苗叶片MDA含量上升幅度最大,较CK1显著增加68.83%;不同浓度SA处理均能降低幼苗叶片MDA含量,但含量仍显著高于CK1,其中0.01 mmol·L−1SA处理下降幅度最大,较CK2显著降低27.50%。
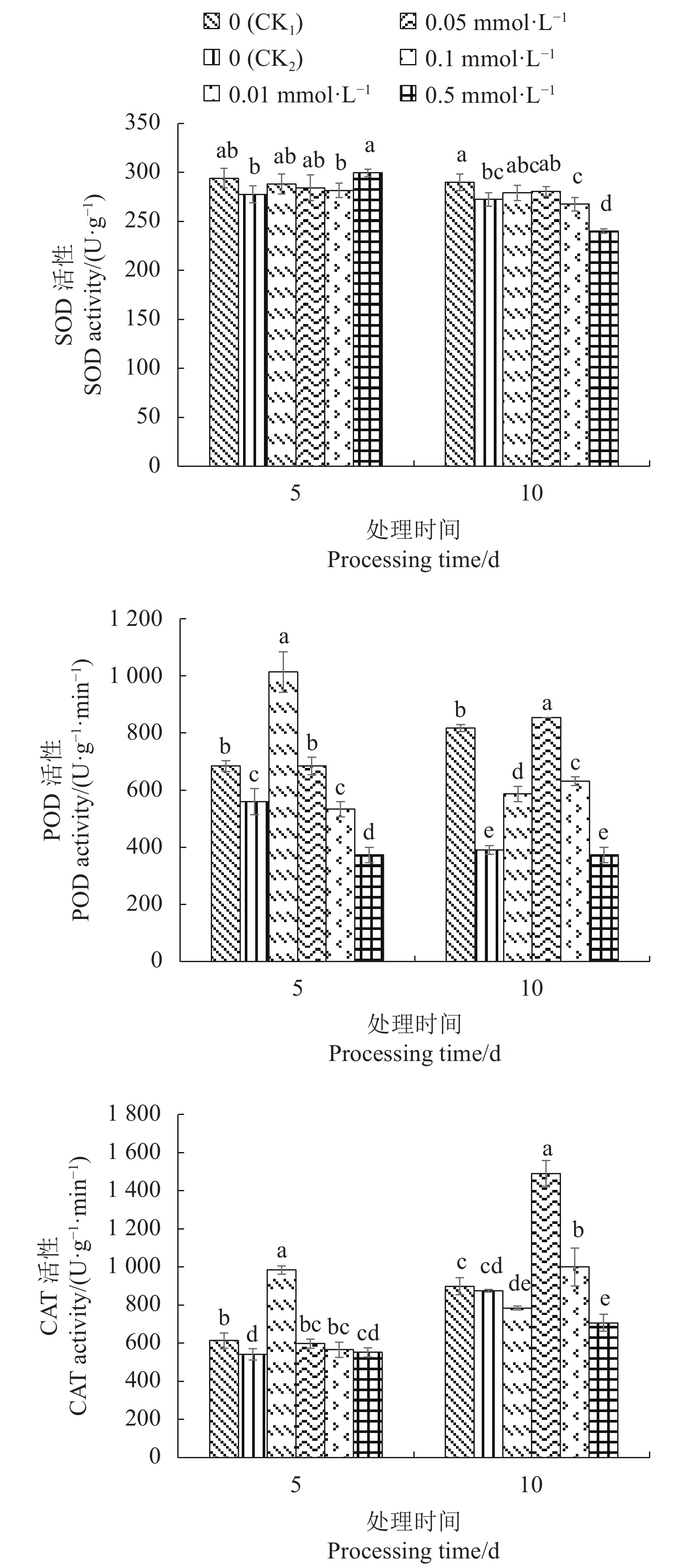
2.4 外源SA对Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗叶片抗氧化酶活性的影响
从图5可以看出,CK2的不结球白菜幼苗叶片SOD、POD、CAT活性均低于CK1。Cd胁迫5 d,CK2的不结球白菜幼苗叶片SOD活性与0.5 mmol·L−1 SA处理相比差异显著,与其余处理之间差异不显著;Cd胁迫10 d,CK2的幼苗叶片SOD活性显著低于CK1,0.01 mmol·L−1SA、0.05 mmol·L−1SA处理的幼苗叶片SOD活性略有增加。
Cd胁迫5 d,0.01 mmol·L−1SA、0.05 mmol·L−1SA处理显著提高幼苗叶片POD活性,以0.01 mmol·L−1SA处理表现最好,而0.1 mmol·L−1SA、0.5 mmol·L−1SA处理POD活性下降;Cd胁迫10 d,0.05 mmol·L−1SA处理的幼苗叶片POD活性较CK2显著提高1.18倍,当SA浓度超过0.05 mmol·L−1POD活性出现下降。
Cd胁迫5 d,不同浓度SA处理均能提高幼苗叶片CAT活性,以0.01 mmol·L−1SA处理的CAT活性最高,与其余处理之间差异显著;Cd胁迫10 d,0.05 mmol·L−1SA、0.1 mmol·L−1SA处理叶片的CAT活性得到提高,其中0.05 mmol·L−1SA处理的CAT活性较CK2显著提高70.43%,与各处理之间差异显著;当SA超过0.05 mmol·L−1CAT活性出现下降。
2.5 外源SA对Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗地上、地下部分Cd含量及转运系数的影响
由表3可知,不结球白菜幼苗地上部分Cd含量高于地下部分,CK2的不结球白菜幼苗地上、地下部分Cd含量显著高于其余处理,外源SA处理能显著降低幼苗体内Cd含量;Cd胁迫5 d,CK2的转运系数显著高于其余处理,转运系数随SA浓度的增加呈先降低后升高的趋势,其中0.05 mmol·L−1SA处理的转运系数最小。
表 3 外源SA对Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗地上、地下部分Cd含量及转运系数的影响Table 3. Effect of exogenous SA on Cd Content and transport coefficient of aboveground and underground parts of non-heading Chinese cabbage seedlings under Cd-stress处理时间
Processing time/dSA/mmol·L−1 地上部分Cd含量
Cd content in above ground/(mg·kg−1)地下部分Cd含量
Cd content in underground part/(mg·kg−1)转运系数
Transport coefficient5 0(CK2) 483.33±7.02 a 215.97±4.80 a 2.24±0.02 a 0.01 319.03±5.67 c 185.97±4.28 b 1.72±0.07 c 0.05 251.87±3.48 e 167.53±4.28 d 1.50±0.03 d 0.1 269.23±3.00 d 175.37±4.11 c 1.54±0.02 d 0.5 334.87±4.45 b 174.40±4.75 cd 1.92±0.03 b 10 0(CK2) 677.70±2.33 a 397.73±3.00 a 1.70±0.01 b 0.01 534.33±3.52 c 348.10±2.98 c 1.54±0.02 c 0.05 503.47±2.34 d 375.77±4.98 b 1.34±0.02 d 0.1 594.07±4.44 b 338.67±4.77 d 1.75±0.04 a 0.5 598.13±3.44 b 350.77±3.31 c 1.71±0.02 b 3. 讨论与结论
3.1 外源SA对Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗生长的影响
生物量是植物生长状况的直接反映,是确定其对环境耐性的重要指标之一[23]。本研究结果表明,Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗生物量积累受到抑制,较CK1表现出下降趋势,其中根冠比下降幅度最大,说明根系生长受抑制程度最大;0.01~0.05 mmol·L−1 SA处理不结球白菜幼苗后,可以有效缓解Cd胁迫对不结球白菜幼苗生长的抑制作用,当SA浓度高于0.05 mmol·L−1,缓解效果减弱甚至表现出抑制作用,这可能是高浓度SA与Cd共同作用对不结球白菜幼苗根系产生了双重的毒害有关,这与任艳芳等[11]的研究结果一致。
3.2 外源SA对Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗叶片光合色素的影响
叶绿素是植物进行光合作用时吸收和传递光能的主要色素,其含量高低不仅反映植物的光合能力强弱,亦能反映出植物在逆境下受伤害的程度[24]。本试验中,不结球白菜幼苗叶片叶绿素含量在Cd胁迫后显著下降,可能出现的原因:一是Cd2+在幼苗叶片细胞内积累后,取代叶绿素中的Zn2+、Mg2+、Fe2+,或与叶绿体中蛋白质上的-SH结合,导致叶绿体的结构和功能被破坏;二是叶绿素合成所必需的酶活性受抑,导致叶绿素合成受阻;三是活性氧和MDA的产生,致使叶绿素受到破坏[25]。0.01~0.05 mmol·L−1SA处理的幼苗叶片叶绿素含量和类胡萝卜素含量显著增加,说明外源SA通过提高幼苗叶片叶绿素含量来维持Cd胁迫下光合作用的正常进行,从而提高其对Cd胁迫的抗性,这与张永平等[26]的研究结果相一致。
3.3 外源SA对Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗根系活力、可溶性蛋白、脯氨酸和丙二醛含量的影响
根系是植物吸收和合成的重要器官,根的生长状况和活力水平直接影响植株地上部的生长和营养吸收及产量高低,因此根系活力是衡量根系功能的重要指标[20]。本次试验中,CK2的不结球白菜幼苗根系活力显著低于CK1,可能是土壤中的Cd2+使根系受到损伤,导致根系活力下降,幼苗生长受抑;而SA处理的幼苗根系活力显著升高,说明喷施SA能够缓解Cd对不结球白菜幼苗的伤害,维持根系吸收和运输功能,促进植株生长,这与邵小杰等[27]的研究结果相似。
植物体内可溶性蛋白、脯氨酸在逆境胁迫下可作为渗透调节剂,通过调节渗透压,维持细胞内环境的稳定;当植物遇到逆境胁迫时,植物体内可溶性蛋白、脯氨酸的含量会迅速积累[28]。本研究结果表明,Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗叶片的可溶性蛋白、脯氨酸含量表现出下降,可能是较高浓度的Cd2+抑制蛋白质的合成和脯氨酸的积累;外源SA处理后不结球白菜幼苗叶片的可溶性蛋白、脯氨酸含量显著升高,说明SA能促进Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗叶片可溶性蛋白的合成和脯氨酸的积累,通过调节渗透压、维持细胞膜的稳定性,缓解Cd2+对膜的伤害,这与张芬琴等[29]的研究结果一致。
MDA是膜脂过氧化作用的主要产物,可与蛋白质、核酸等发生反应,干扰细胞内正常的生命活动,抑制植物生长发育,故MDA含量可以反映细胞膜脂过氧化水平和细胞膜受伤害程度[30]。本研究中,Cd胁迫10 d时,CK2的不结球白菜幼苗叶片MDA含量迅速上升,这可能是因为植物根系不断吸收Cd2+,导致Cd2+在植物体内富集量增加,从而对植物的伤害更为严重;外源SA均可降低不结球白菜幼苗叶片MDA含量,这与任艳芳等[11]的研究结果一致。证明外施SA能减轻Cd胁迫对膜的过氧化损伤,降低膜的透性,稳定膜的结构,促进Cd胁迫下幼苗的生长。
3.4 外源SA对Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗叶片抗氧化酶活性的影响
SOD、POD、CAT是植物体内具有协同作用的抗氧化酶,在逆境胁迫下清除细胞内过量的活性氧,维持活性氧代谢的平衡,减轻逆境胁迫对植物细胞造成的伤害[31]。本试验发现,Cd胁迫下,不结球白菜幼苗叶片SOD、POD和CAT活性较CK1均有不同程度降低,可能是Cd2+诱导氧化毒害的主要原因[32]。适宜浓度的SA处理可提高不结球白菜幼苗叶片的抗氧化酶活性,Cd胁迫5 d时以0.01 mmol·L−1SA处理效果较佳,Cd胁迫10 d时0.05 mmol·L−1SA处理抗氧化酶活性最高,这与赵新月等[33]研究玉米在镉胁迫下喷施SA的最适宜浓度为 50~100 μmol·L−1的结果一致。本试验中,当SA浓度大于0.05 mmol·L−1,明显抑制不结球白菜幼苗叶片的酶活性,可能是因为高浓度的SA 降低相应的酶活性,说明SA只能在一定范围内对植物的抗氧化酶活性产生促进作用,超过这个范围将产生抑制作用。
3.5 外源SA对Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗地上、地下部分Cd含量及转运系数的影响
通常情况下,植物通过将重金属截留于根系,减少重金属由根部向地上部分转运,从而减轻镉对地上部分的毒害[34]。本试验中,不结球白菜幼苗对Cd的吸收表现为地上部分>地下部分,说明不结球白菜幼苗从土壤中吸收的Cd主要积累于茎叶,向地上部茎叶中转移较多,这与任艳军等[35]的研究一致。外源SA处理可以显著降低不结球白菜幼苗地上、地下部分Cd含量,其中0.01 mmol·L−1SA、0.05 mmol·L−1SA处理能有效降低幼苗的转运系数,说明0.01~0.05 mmol·L−1SA处理的不结球白菜幼苗对重金属Cd的根际阻控效应较强,减少Cd向幼苗地上部分的转运。
综上所述,Cd胁迫会对不结球白菜幼苗生长造成伤害,添加外源SA可有效缓解Cd胁迫的伤害,本研究结果认为SA为0.05 mmol·L−1时,不结球白菜幼苗的根长、根冠比最高,同时能显著提高幼苗脯氨酸含量和POD、CAT活性,降低不结球白菜幼苗地上部分的Cd累积量,提高不结球白菜幼苗的抗Cd能力。
-
图 1 外源SA对Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗根系活力的影响
注:同处理数值不同字母表示处理间差异达到0.05显著水平;图2~5同.
Figure 1. Effect of exogenous SA on root activity of non-heading Chinese cabbage seedlings under Cd-stress
Note: :Different letters of the same treatment indicated that the difference was significant at 0.05 level. The same as Fig. 2-5.
表 1 外源SA对Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗生长的影响
Table 1 Effect of exogenous SA on growth of non-heading Chinese cabbage seedlings under Cd-stress
处理时间
Processing time/dSA/(mmol·L−1) 株高
Plant height/cm茎粗
Stem thickness/cm根长
Root length/cm叶面积
Leaf area/cm2根冠比
Root shoot ratio壮苗指数
seedling index5 0(CK1) 10.67±0.35 ab 0.28±0.02 a 8.37±0.32 de 12.99±1.00 b 0.12±0.02 a 0.69±0.03 a 0(CK2) 9.93±0.40 b 0.23±0.02 b 7.90±0.46 e 12.35±0.73 b 0.07±0.02 c 0.48±0.04 b 0.01 11.57±0.80 a 0.28±0.03 a 9.70±0.10 b 15.19±1.60 a 0.09±0.00 bc 0.52±0.03 b 0.05 10.63±0.85 ab 0.27±0.03 a 11.83±0.21 a 16.33±0.62 a 0.09±0.01 b 0.50±0.09 b 0.1 10.37±0.65 b 0.21±0.02 bc 9.17±0.29 c 11.25±1.32 bc 0.08±0.01 bc 0.48±0.01 b 0.5 8.43±0.32 c 0.17±0.01 c 8.60±0.17 d 9.89±0.18 c 0.08±0.00 bc 0.53±0.04 b 10 0(CK1) 10.87±0.10 b 0.29±0.03 ab 12.00±1.13 a 17.31±0.55 a 0.20±0.02 a 0.61±0.01 a 0(CK2) 10.23±0.25 c 0.26±0.02 bc 8.90±0.36 b 13.29±1.45 b 0.08±0.04 c 0.42±0.06 b 0.01 11.77±0.21 a 0.33±0.02 a 9.17±0.58 b 16.65±0.34 a 0.12±0.00 bc 0.50±0.07 ab 0.05 10.80±0.26 b 0.32±0.02 a 9.60±0.36 b 16.55±1.41 a 0.18±0.08 ab 0.44±0.04 b 0.1 10.47±0.15 bc 0.22±0.01 cd 9.33±1.26 b 12.26±0.32 b 0.09±0.03 c 0.43±0.09 b 0.5 10.27±0.25 c 0.20±0.01 d 9.50±0.50 b 12.18±1.06 b 0.10±0.01 c 0.41±0.05 b 注:同列同处理数值不同字母表示处理间差异达到0.05显著水平;表2、3同。
Note: Data with different letters on same column under same treatment indicate significant difference at level of 0.05. Same for below.表 2 外源SA对Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗叶片光合色素的影响
Table 2 Effect of exogenous SA on photosynthetic pigment in non-heading Chinese cabbage seedling leaves under Cd-stress
处理时间
Processing time/dSA/(mmol·L−1) 叶绿素a
Chlorophyll a/(mg·g−1)叶绿素b
Chlorophyll b/(mg·g−1)叶绿素(a+b)
Total chlorophyll content/(mg·g−1)类胡萝卜素
Carotenoid/(mg·g−1)5 0(CK1) 0.43±0.01 de 0.16±0.00 c 0.59±0.01 c 0.12±0.01 ab 0(CK2) 0.42±0.01 e 0.10±0.01 e 0.52±0.01 d 0.10±0.00 c 0.01 0.59±0.00 a 0.21±0.01 a 0.80±0.01 a 0.13±0.01 a 0.05 0.56±0.01 b 0.18±0.01 b 0.74±0.03 b 0.12±0.02 ab 0.1 0.44±0.00 cd 0.15±0.01 c 0.59±0.00 c 0.11±0.01 bc 0.5 0.46±0.02 c 0.12±0.01 d 0.58±0.02 c 0.09±0.01 c 10 0(CK1) 1.06±0.01 a 0.35±0.03 a 1.41±0.04 a 0.28±0.00 ab 0(CK2) 0.97±0.01 b 0.28±0.01 b 1.25±0.01 b 0.24±0.01 c 0.01 1.09±0.01 a 0.35±0.01 a 1.44±0.02 a 0.27±0.02 b 0.05 1.06±0.02 a 0.35±0.02 a 1.40±0.02 a 0.30±0.01 a 0.1 0.84±0.02 c 0.26±0.00 bc 1.10±0.02 c 0.25±0.00 c 0.5 0.77±0.04 d 0.23±0.01 c 1.00±0.05 d 0.21±0.00 d 表 3 外源SA对Cd胁迫下不结球白菜幼苗地上、地下部分Cd含量及转运系数的影响
Table 3 Effect of exogenous SA on Cd Content and transport coefficient of aboveground and underground parts of non-heading Chinese cabbage seedlings under Cd-stress
处理时间
Processing time/dSA/mmol·L−1 地上部分Cd含量
Cd content in above ground/(mg·kg−1)地下部分Cd含量
Cd content in underground part/(mg·kg−1)转运系数
Transport coefficient5 0(CK2) 483.33±7.02 a 215.97±4.80 a 2.24±0.02 a 0.01 319.03±5.67 c 185.97±4.28 b 1.72±0.07 c 0.05 251.87±3.48 e 167.53±4.28 d 1.50±0.03 d 0.1 269.23±3.00 d 175.37±4.11 c 1.54±0.02 d 0.5 334.87±4.45 b 174.40±4.75 cd 1.92±0.03 b 10 0(CK2) 677.70±2.33 a 397.73±3.00 a 1.70±0.01 b 0.01 534.33±3.52 c 348.10±2.98 c 1.54±0.02 c 0.05 503.47±2.34 d 375.77±4.98 b 1.34±0.02 d 0.1 594.07±4.44 b 338.67±4.77 d 1.75±0.04 a 0.5 598.13±3.44 b 350.77±3.31 c 1.71±0.02 b -
[1] 孙丽娟, 秦秦, 宋科, 等. 镉污染农田土壤修复技术及安全利用方法研究进展 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2018, 27(7):1377−1386. SUN L J, QIN Q, SONG K, et al. The remediation and safety utilization techniques for Cd contaminated farmland soil: A review [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2018, 27(7): 1377−1386.(in Chinese)
[2] 陈雯, 龙翔, 王宁涛, 等. 福州市土壤重金属污染现状评价与分析 [J]. 安全与环境工程, 2015, 22(5):68−72. CHEN W, LONG X, WANG N T, et al. Pollution evaluation and analysis of heavy metals in soils of Fuzhou City [J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2015, 22(5): 68−72.(in Chinese)
[3] 张鹏帅, 朱旭彬, 苏雪玲, 等. 福州市郊农田土壤与蔬菜重金属污染状况分析 [J]. 福建师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 34(3):85−94. ZHANG P S, ZHU X B, SU X L, et al. Analysing the pollution of heavy metal contamination in soils and vegetables in Fuzhou suburb [J]. Journal of Fujian Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 34(3): 85−94.(in Chinese)
[4] 王苗苗, 强沥文, 王伟, 等. 纳米二氧化钛对镉胁迫下小白菜毒性效应的影响 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(6):1185−1195. DOI: 10.11654/jaes.2019-1422 WANG M M, QIANG L W, WANG W, et al. Effects of nano titanium dioxide on the toxicity of Chinese cabbage under cadmium stress [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(6): 1185−1195.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11654/jaes.2019-1422
[5] 肖旭峰, 李猛, 龙俊敏, 等. 镉诱导小白菜活性氧及抗氧化酶活性与自噬关系分析 [J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2019, 41(5):873−880. XIAO X F, LI M, LONG J M, et al. Relationship of active oxygen, antioxidant enzyme activity and autophagy under Cd stress in pakchoi [J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2019, 41(5): 873−880.(in Chinese)
[6] 刘自力, 黄一凡, 朱正波, 等. 叶面喷施褪黑素对小白菜幼苗镉耐性的影响 [J]. 植物生理学报, 2018, 54(4):660−668. LIU Z L, HUANG Y F, ZHU Z B, et al. Effects of foliar feeding of melatonin on cadmium tolerance of Chinese cabbage seedlings [J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2018, 54(4): 660−668.(in Chinese)
[7] CHUNG T, PHILLIPS A R, VIERSTRA R D. ATG8 lipidation and ATG8-mediated autophagy in Arabidopsis require ATG12 expressed from the differentially controlled ATG12A AND ATG12B loci [J]. The Plant Journal, 2010, 62(3): 483−493. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04166.x
[8] 谢玉英. 水杨酸与植物抗逆性的关系 [J]. 生物学杂志, 2007, 24(4):12−15, 20. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1736.2007.04.004 XIE Y Y. Relationship between salicylicacid and anti-adversity in plants [J]. Journal of Biology, 2007, 24(4): 12−15, 20.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1736.2007.04.004
[9] 陈珍. 水杨酸对镉胁迫下花椰菜种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响 [J]. 种子, 2009, 28(2):39−43. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4705.2009.02.012 CHEN Z. Effects of salicylic acid on seeds germination and seedlings growth of cauliflower under cadmium stress [J]. Seed, 2009, 28(2): 39−43.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4705.2009.02.012
[10] 王瑞波. 水杨酸对镉胁迫小麦叶绿素荧光参数的影响 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2017, 33(7):96−99. WANG R B. Effect of salicylic acid on chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in wheat under cadmium stress [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2017, 33(7): 96−99.(in Chinese)
[11] 任艳芳, 何俊瑜, 王思梦, 等. 水杨酸对镉胁迫下莴苣幼苗生长和氧化胁迫的缓解效应 [J]. 西南农业学报, 2009, 22(6):1567−1570. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4829.2009.06.015 REN Y F, HE J Y, WANG S M, et al. Relieving effect of exogenous salicylic acid on seedling growth and oxidative stress of lettuce under cadmium stress [J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2009, 22(6): 1567−1570.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4829.2009.06.015
[12] 王小红, 郭军康, 贾红磊, 等. 外源水杨酸缓解镉对番茄毒害作用的研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(12):2705−2714. DOI: 10.11654/jaes.2019-0754 WANG X H, GUO J K, JIA H L, et al. The effect of exogenous salicylic acid on alleviating cadmium toxicity in tomato plants [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(12): 2705−2714.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11654/jaes.2019-0754
[13] 叶静渊. 我国油菜的名实考订及其栽培起源 [J]. 自然科学史研究, 1989, 8(2):158−165. YE J Y. The name and reality of the rape (brassjca campestris and Brassica juncea) in China [J]. Studies in the History of Natural Sciences, 1989, 8(2): 158−165.(in Chinese)
[14] 侯喜林, 宋小明. 不结球白菜种质资源的研究与利用 [J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2012, 35(05):35−42. HOU X L, SONG X M. Research and utilization of Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis Makino(non-heading Chinese cabbage)germplasm resources [J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2012, 35(05): 35−42.(in Chinese)
[15] ZHOU H, YANG W T, ZHOU X, et al. Accumulation of heavy metals in vegetable species planted in contaminated soils and the health risk assessment [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2016, 13(3): E289. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph13030289
[16] 陈永快, 王涛, 黄语燕, 等. 不同品种叶用莴苣营养液膜栽培性状及产量分析 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2019, 34(10):1158−1166. CHEN Y K, WANG T, HUANG Y Y, et al. Greenhouse nutrient film technique cultivation and production of lettuce [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 34(10): 1158−1166.(in Chinese)
[17] 秦伟, 刘震, 王民乾, 等. 复配基质对西瓜幼苗光合能力、壮苗指数及根系活力的影响 [J]. 天津农业科学, 2020, 26(6):21−24. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6500.2020.06.006 QIN W, LIU Z, WANG M Q, et al. Effect of compound substrate on the photosynthetic capacity, seedling strength index and root activity of watermelon seedlings [J]. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 26(6): 21−24.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6500.2020.06.006
[18] 张宪政. 植物叶绿素含量测定: 丙酮乙醇混合液法 [J]. 辽宁农业科学, 1986(3):26−28. ZHANG X Z. Determination of plant chlorophyll content-acetone-ethanol mixture method [J]. Liaoning Agricultural Science, 1986(3): 26−28.(in Chinese)
[19] 杨晴, 郭守华. 植物生理生化实验[M]. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2010: 9. [20] 王学奎. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006. [21] ZAYED A, GOWTHAMAN S, TERRY N. Phytoaccumulation of trace elements by wetland plants: I. duckweed [J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 1998, 27(3): 715−721.
[22] 刘俊祥, 魏树强, 翟飞飞, 等. Cd2+胁迫下多年生黑麦草的生长与生理响应 [J]. 核农学报, 2015, 29(3):587−594. DOI: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2015.03.0587 LIU J X, WEI S Q, ZHAI F F, et al. Growth and physiology response of perennial ryegrass to Cd2+Stress [J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 29(3): 587−594.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2015.03.0587
[23] RIZWAN M, ALI S, QAYYUM M F, et al. Use of Maize (Zea mays L.) for phytomanagement of Cd-contaminated soils: A critical review [J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2017, 39(2): 259−277. DOI: 10.1007/s10653-016-9826-0
[24] 贺国强, 刘茜, 郭振楠, 等. 镉胁迫对烤烟叶片光合和叶绿素荧光特性的影响 [J]. 华北农学报, 2016, 31(S1):388−393. DOI: 10.7668/hbnxb.2016.S1.065 HE G Q, LIU Q, GUO Z N, et al. Effects of cadmium stress on photosynthetic and characteristics, chlorophyll fluorescence in leaves of flue-cured tobacco [J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2016, 31(S1): 388−393.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7668/hbnxb.2016.S1.065
[25] 王红霞, 施国新, 徐勤松, 等. Cr6+胁迫对槐叶苹叶片光合生理特征及超微结构的影响 [J]. 西北植物学报, 2008(11):2244−2250. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4025.2008.11.017 WANG H X, SHI G X, XU Q S, et al. Photosynthetic physiological characteristics and ultrastructure of Salvinia natans leaves under Cr6+ stress [J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2008(11): 2244−2250.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4025.2008.11.017
[26] 张永平, 陈幼源, 杨少军, 等. 外源水杨酸对镉胁迫甜瓜幼苗生长与光合气体交换和叶绿素荧光特性的影响 [J]. 西北植物学报, 2014, 34(04):778−785. ZHANG Y P, CHEN Y Y, YANG S J, et al. Effects of exogenous salicylic acid on seedling growth, photosynthetic and chlorophyll fluorescent parameters in melon seedlings under cadmium stress [J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2014, 34(04): 778−785.(in Chinese)
[27] 邵小杰, 杨洪强, 冉昆, 等. 水杨酸对镉胁迫下葡萄根系质膜ATPase和自由基的影响 [J]. 中国农业科学, 2010, 43(7):1441−1447. DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2010.07.015 SHAO X J, YANG H Q, RAN K, et al. Effects of salicylic acid on plasma membrane ATPase and free radical of grape root under cadmium stress [J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2010, 43(7): 1441−1447.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2010.07.015
[28] 钟鹏, 刘杰, 王建丽, 等. 花生对低温胁迫的生理响应及抗寒性评价 [J]. 核农学报, 2018, 32(6):1195−1202. ZHONG P, LIU J, WANG J L, et al. Physiological responses and cold resistance evaluation of peanut under low-temperature stress [J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 32(6): 1195−1202.(in Chinese)
[29] 张芬琴, 李晓利, 马斌山, 等. 水杨酸对镉胁迫下玉米幼苗生理特性的影响 [J]. 湖北农业科学, 2006(5):567−569. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0439-8114.2006.05.015 ZHANG F Q, LI X L, MA B S, et al. Effects of SA on physiological characteristics of maize seedling under Cd2+ stress [J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2006(5): 567−569.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0439-8114.2006.05.015
[30] PARIDA A K, JHA B. Antioxidative defense potential to salinity in the euhalophyte Salicornia brachiata [J]. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2010, 29(2): 137−148. DOI: 10.1007/s00344-009-9129-0
[31] LIANG Y C, CHEN Q, LIU Q, et al. Exogenous silicon (Si) increases antioxidant enzyme activity and reduces lipid peroxidation in roots of salt-stressed barley (Hordeum vulgareL.) [J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2003, 160(10): 1157−1164. DOI: 10.1078/0176-1617-01065
[32] CHO U H, SEO N H. Oxidative stress in Arabidopsis thaliana exposed to cadmium is due to hydrogen peroxide accumulation [J]. Plant Science, 2005, 168(1): 113−120. DOI: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.07.021
[33] 赵新月, 何茂, 石辉, 等. 外源水杨酸对镉胁迫下玉米幼苗的叶氮素代谢和根系抗氧化酶的影响 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2013, 32(10):1950−1958. DOI: 10.11654/jaes.2013.10.007 ZHAO X Y, HE M, SHI H, et al. Role of exogenous salicylic acid in alleviating nitrogen metabolism in leaves and antioxidase in root by cadmium stress in maize seedling [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2013, 32(10): 1950−1958.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11654/jaes.2013.10.007
[34] 李君, 葛跃, 王明新, 等. 镉对蓖麻耐性生理及营养元素吸收转运的影响 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(8):3081−3087. LI J, GE Y, WANG M X, et al. Effect of Cd on tolerance physiology, nutrients uptake and translocation in Ricinus communis L [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2016, 36(8): 3081−3087.(in Chinese)
[35] 任艳军, 任学军, 马建军, 等. Cd/Cr复合胁迫下不同品种蔬菜对Cd和Cr积累与转运的差异研究 [J]. 核农学报, 2018, 32(5):993−1002. DOI: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2018.05.0993 REN Y J, REN X J, MA J J, et al. Study on the variety difference of Cd and Cr accumulation and translocation in vegetable under Cd/Cr combination stress [J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 32(5): 993−1002.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2018.05.0993
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 龙丽,刘克,张莉莉,冯仕清,郑勇,赵长春. 镉胁迫对不同品种白菜生长生理及亚细胞分布的影响. 地球与环境. 2024(01): 65-75 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 翟佳悦,宁伊,刘丽媛,王全伟. 大豆GmALMT33基因在镉胁迫应答中的功能分析. 植物遗传资源学报. 2024(06): 1014-1026 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陈锦平,黄太庆,邢颖,曾成城,廖青,潘丽萍,梁潘霞,刘永贤. 外源植物激素对小白菜硒、镉富集及生理特性的影响. 生态学杂志. 2023(05): 1083-1089 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李亮,辛在军,王玺洋,李晓晖,孙小艳. 褪黑素对镉胁迫下紫苏根系特征的影响. 农业环境科学学报. 2022(02): 257-266 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李金龙,贾云鹤,李岩,许春梅,刘思宇. 土壤含水量对镉胁迫下油豆角生长发育及镉积累的影响. 黑龙江农业科学. 2022(05): 54-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 于永昂,张夏冰,张蕾,睢晓湉. 小麦TaAlaAT基因的克隆及镉胁迫下表达分析. 江苏农业科学. 2022(18): 48-53 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 李芹梅,李文祥,曹孟会,刘松,张天谣,汪琼,黄美娟,黄海泉. 铜离子对滇水金凤花色变化的生理生化研究. 福建农业学报. 2021(11): 1323-1329 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: