Assessment on Anthracnose-resistance of 590 Soybean Cultivars in China
-
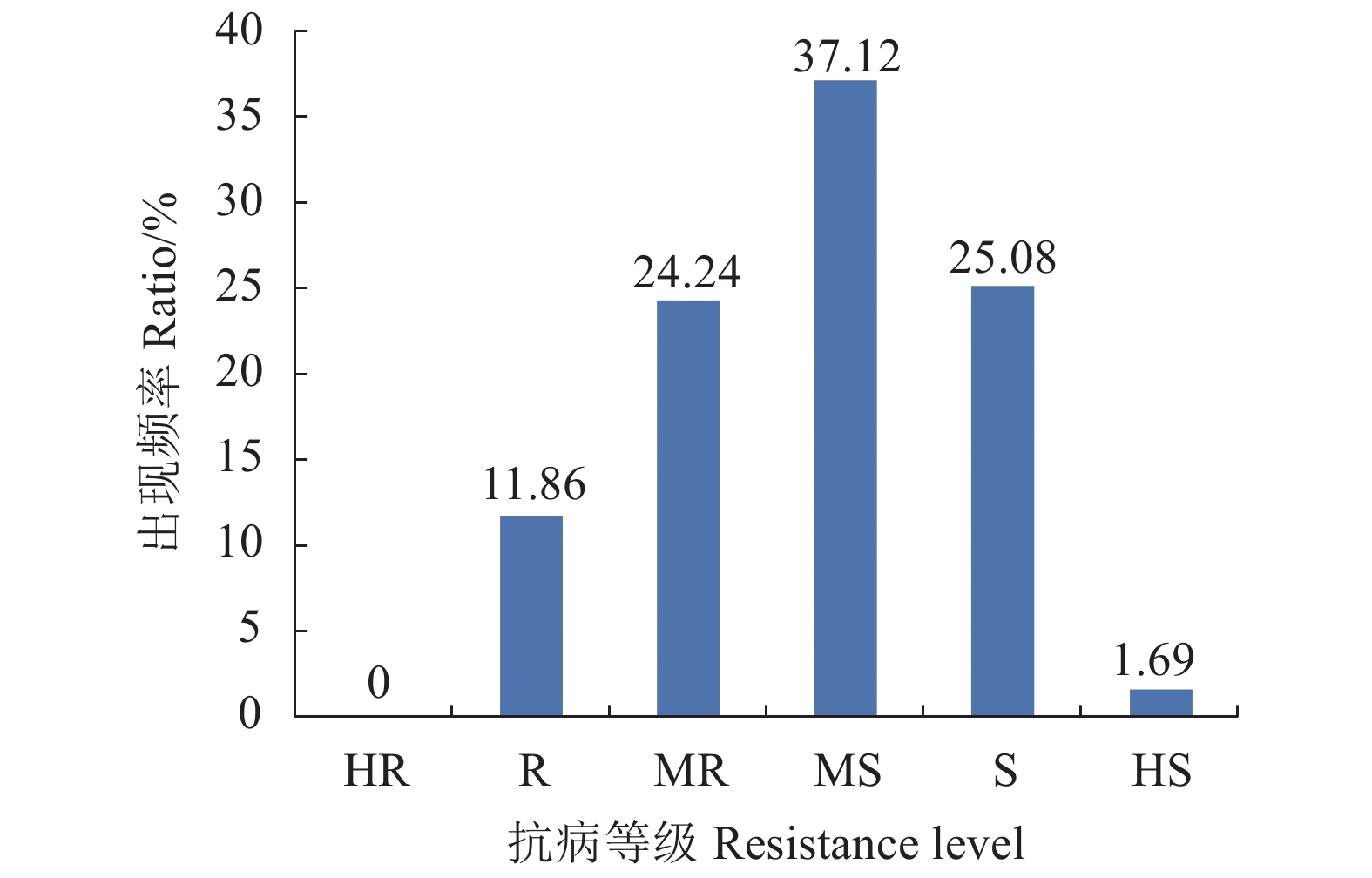
摘要:目的 开展大豆品种炭疽病抗性鉴定,为筛选抗病品种和抗病育种提供科学依据。方法 采用人工接种法鉴定了2011—2019年共590份大豆品种(系)对炭疽病的抗病性。结果 鉴定出高抗品种(HR)、抗病品种(R)、中抗品种(MR)、中感品种(MS)、感病品种(S)和高感品种(HS)的数量分别为0、70、143、219、148和10份,比率分别为0、11.86%、24.24%、37.12%、25.08%和1.69%。不同年份间抗性品种比率(RR)范围为13.64%~68.00%,其中:2013年抗性品种的比率最高,为68.00%;其次的2012年抗性品种比率为52.00%;2016年抗性品种比率最低,为13.64%。国家热带亚热带地区春大豆组(S1)、国家热带亚热带地区夏大豆组(S2)、国家鲜食大豆春播组(S3)、国家鲜食大豆夏播组(S4)、国家长江流域春大豆组(S5)、福建省大豆新品种组(S6)和其他新品种组(S7)抗性品种的比率范围为5.89%~69.23%,其中:国家热带亚热带地区夏大豆组(S2)抗性品种比率最高,为69.23%;其次为国家鲜食大豆夏播组(S4),抗性品种比率为57.69%;国家鲜食大豆春播组(S3)抗性品种比率最低,为5.89%。结论 鉴定结果表明,590份大豆品种(系)中,抗病和中抗品种占比为36.10%,没有对炭疽病高抗的品种;春播鲜食大豆缺乏对炭疽病抗性较好的品种。Abstract:Objective Anthracnose-resistance of varieties of soybean in China was assessed and classified to facilitate the breeding of resistant cultivars.Method From 2011 to 2019, 590 varieties of domestic soybean cultivars were collected and challenged by an artificial inoculation of Colletotrichum truncatum to determine their degrees of resistance to anthracnose.Result The test showed 70 of the varieties belonged to the resistant (R), 143 to the medium resistant (MR), 219 to the medium susceptible (MS), 148 to the susceptible (S), and 10 to the highly susceptible (HS) categories, representing 11.86%, 24.24%, 37.12%, 25.08%, and 1.69%, respectively, of the entire sampled population. The overall disease resistant rate (RR) in a particular year varied from year to year, ranging from 13.64% to 68.00%, with the highest shown in 2013, followed by 52% in 2012 and the lowest in 2016. The RRs of the spring varieties in the tropical and subtropical areas (S1), the summer varieties in the tropical and subtropical areas (S2), the spring-sowing green varieties (S3), the summer-sowing green varieties (S4), the spring soybean from Yangtze river basin (S5), the new variety from Fujian (S6), and the new varieties from other regions (S7) ranked from the lowest of S3 at 5.89% to the highest of S2 at 69.23%, while S4 being the second highest at 57.69%.Conclusion Out of the 590 varieties, 36.10% were only resistant or moderately resistant to anthracnose with none exhibited high resistance. And, there was no spring-sowing green soybeans for fresh consumption being substantially resistant to the disease.
-
Keywords:
- soybean /
- anthracnose /
- resistance evaluation /
- Colletotrichum truncatum
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】大豆是一种重要的油料、粮食和饲料作物,是植物蛋白和油脂的主要来源,是全球食物链的重要组成部分[1]。主要由平头炭疽菌(Colletotrichum truncatum)侵染引起的大豆炭疽病是世界大豆产区重要的真菌性病害之一,可侵染大豆子叶、叶片、叶柄、茎秆、荚果和种子[2],一般田块豆荚发病率为30%,重病田块豆荚发病率达50%以上[3]。选育和合理利用抗病品种是防治大豆炭疽病最经济、有效、安全的措施。因此,鉴定并利用大豆抗炭疽病遗传资源,选育抗性品种对大豆产业具有重要意义[4]。【前人研究进展】1992年我国大豆种质资源专题组对全国各省、市已入国家库的2 034份大豆品种材料进行苗期抗炭疽病鉴定的结果表明,我国菜用大豆品种资源对炭疽病抗性的差异非常明显,其变异系数高达269.02。绝大多数品种或材料为感病型,但也具有一定数量的抗病材料,如蔓生品种和龙油豆、紫花皮和矮生品种Lamaniere等[5]。1995年,Ghimire等鉴定了美国33个大豆品种对炭疽病的抗性,IBRN-6、IBRN-11等6个品种抗性较好[6]。Sharma等对85个大豆品种进行炭疽病抗性鉴定,AB136和G2333等12个品种表现为抗病[7]。【本研究切入点】作物抗病性鉴定是选育、获得抗性品种不可或缺的重要环节。为此,针对我国大豆品种(系)对炭疽病抗性缺乏系统、客观评价的问题,笔者于2011—2019年连续9年开展大豆新品种(系)抗炭疽病鉴定。【拟解决的关键问题】明确我国大豆品种对炭疽病的抗病性变化情况,分析不同组别大豆品种对炭疽病的抗性状况,以期为我国大豆品种的抗病育种和种植品种的区域布局提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 供试材料
1.1.1 菌株
平头炭疽菌菌株FJLH12、FJPT08、FJSM09、FJLY18分别采集自福建省龙海市榜山镇芦州村、莆田市庄边镇泮洋村、三明市梅列区洋溪镇上街村、龙岩市上杭县茶地镇茶地村,均由福建省农业科学院植物保护研究所分离保存,并进行致病性测定。
1.1.2 培养基
马铃薯葡萄糖琼脂培养基(PDA培养基):将马铃薯200 g切片,加水煮沸30 min,用四层纱布过滤,取上清液加入葡萄糖20 g、琼脂粉16 g,加热至琼脂粉完全溶解,加水定容至1 000 mL,在121℃下高压湿热灭菌25 min。马铃薯葡萄糖培养基(PDB培养基):将马铃薯200 g切片,加水煮沸30 min,用四层纱布过滤,取上清液加入葡萄糖20 g,加水定容至1 000 mL,250 mL三角瓶中装入150 mL培养基,在121℃下高压湿热灭菌25 min。
1.1.3 大豆品种(系)
2011—2019年累计鉴定7组(代号S1至S7)、590份大豆品种(系)。S1:国家热带亚热带地区春大豆组(Spring soybean group of tropical and subtropical areas)91份、S2:国家热带亚热带地区夏大豆组(Summer soybean group of tropical and subtropical areas)13份、S3:国家鲜食大豆春播组(Fresh soybean spring sowing group)85份、S4:国家鲜食大豆夏播组(Fresh soybean summer sowing group)52份、S5:国家长江流域春大豆组(Spring soybean group of Yangtze river basin)78份,以上种质材料均由农业农村部全国农业技术推广服务中心提供;S6:福建省大豆新品种组(New soybean varieties group of Fujian province)156份,由福建省农业厅种子管理总站提供;S7:其他新品种组(Other new variety groups)115份,由四川省农业科学院经济作物研究所、浙江省种子管理总站、山西省农业科学院经济作物研究所、湖北省种子管理局等单位提供。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 大豆炭疽病菌接种体制备
将保存在滤纸片上的各供试菌株转至PDA培养基平板上,28 ℃培养5 d,用直径5 mm的打孔器在菌落边缘打取菌饼,将菌饼转入PDB液体培养基中,每瓶转5个菌饼,于150 r·min−1、28 ℃黑暗振荡培养7 d,过滤后用血球计数板检测分生孢子浓度,制成浓度为1×105 CFU·mL−1的悬浮液,将各供试菌株孢子悬浮液按相同比例混合后作为接种体,备用[8]。
1.2.2 大豆品种种植
参鉴大豆品种种植在福建省莆田市庄边镇吉云村试验基地。各参鉴品种露地播种5行,每行6株,行距30 cm,株距15 cm,品种采用随机排列,3次重复。每个重复四周种植感病品种2行,作为保护行。全生育期内不使用杀菌剂,杀虫剂的使用根据鉴定圃内害虫发生种类和程度而定,接种前后15 d不施用任何药剂。
1.2.3 接种方法
于大豆始荚期,将鉴定圃土壤浇水至湿润,然后在接种体中加入0.1%的吐温80,于大豆幼嫩豆荚上进行喷雾接种,每100株植株喷1 000 mL孢子悬浮液,于25~30 ℃覆膜保湿2 d后打开薄膜两端通风,接种3~5 d后移去薄膜。
1.2.4 病情调查
对照品种为感病品种毛豆75和毛豆3号,发病程度达到感病等级(S),于病情稳定时开始调查各参鉴品种所有植株的结实豆荚(不少于200个豆荚)。病情分级标准如下,0级:豆荚无病斑;1级:豆荚上有褐点型小病斑,病斑面积≤整个豆荚面积的5%;3级:豆荚上出现典型病斑,整个豆荚面积的5%<病斑面积≤整个豆荚面积的10%;5级:豆荚上出现典型病斑,整个豆荚面积的10%<病斑面积≤整个豆荚面积的25%;7级:豆荚上出现典型病斑,整个豆荚面积的25%<病斑面积≤整个豆荚面积的50%;9级:豆荚上出现典型病斑,病斑面积占整个豆荚面积的50%以上。
调查记录参鉴品种炭疽病的病情,利用下列公式计算各品种病情指数,根据病情指数评价各参鉴品种的抗性水平,抗病程度分为5级,高抗(HR):DI=0,抗病(R):0<DI<10,中抗(MR):10≤DI<20,中感(MS):20≤DI<40,感病(S):40≤DI<60,高感(HS):DI≥60[9]。计算不同年份、不同组别抗性品种占供试品种的比例,即抗性品种比率(RR)。
病情指数(DI)=∑[(各级病荚数×相对病荚数值)÷(调查总荚数×9)]×100
抗性品种比率(RR)=[(高抗品种数+抗病品种数+中抗品种数)÷总品种数]×100%
2. 结果与分析
2.1 大豆品种对炭疽病抗性鉴定结果
2011—2019年累计鉴定590份大豆品种(系),共鉴定出抗病品种70个,比率为11.86%;中抗品种143个,比率为24.24%;中感品种219个,比率为37.12%;感病品种148个,比率为25.08%;高感品种10个,比率为1.69%;没有出现高抗品种(图1)。
2.2 不同年份抗炭疽病鉴定结果
2011—2019年参鉴品种抗病品种(R)比率范围为0~36.00%,其中:2012年比率最高;其次为2013年,为32.00%;2016年最低。2011—2019年中抗品种(MR)比率范围为13.64%~36.00%,其中:2013年比率最高;其次为2015年,为34.09%;2016年最低。2011—2019年中感品种(MS)比
率范围为4.26%~50.47%,其中:2018年比率最高;其次为2017年,为50.00%;2011年最低。2011—2019年感病品种(S)比率范围为8.00%~40.91%,其中:2016年比率最高;其次为2012年,为40.00%;2013年最低。 在连续9年的鉴定中,抗性品种比率(RR)范围为13.64%~68.00%,各年度病情指数均值分别为36.92、23.49、18.41、28.79、27.58、37.33、28.01、28.00和30.34。2013年抗性品种比率最高(68.00),病情指数均值最小(18.41);其次是2012年,抗性品种比率为52.00%,病情指数均值为23.49;2016年抗性品种比率最低,仅为13.64%,病情指数均值为37.33(表1)。
表 1 不同年份大豆品种抗炭疽病鉴定结果Table 1. Anthracnose-resistance of soybean shown in different years年份
Year品种数
Number of soybean varieties合计
Total比率
Ratio/%抗性品种比率
Ratio of resistant varieties/%病指均值
Disease indexHR R MR MS S HS HR R MR MS S HS 2011 0 10 9 2 18 8 47 0.00 21.28 19.15 4.26 38.30 17.02 40.43 36.92 2012 0 18 8 4 20 0 50 0.00 36.00 16.00 8.00 40.00 0.00 52.00 23.49 2013 0 16 18 12 4 0 50 0.00 32.00 36.00 24.00 8.00 0.00 68.00 18.41 2014 0 6 19 23 18 0 66 0.00 9.09 28.79 34.85 27.27 0.00 37.88 28.79 2015 0 1 15 19 9 0 44 0.00 2.27 34.09 43.18 20.45 0.00 36.36 27.58 2016 0 0 6 20 18 0 44 0.00 0.00 13.64 45.45 40.91 0.00 13.64 37.33 2017 0 5 10 24 9 0 48 0.00 10.40 20.83 50.00 18.75 0.00 31.25 28.01 2018 0 10 25 54 17 1 107 0.00 9.35 23.36 50.47 15.89 0.93 32.71 28.00 2019 0 4 33 61 35 1 134 0.00 2.99 24.63 45.52 26.12 0.75 27.62 30.34 合计 Total 0 70 143 219 148 10 平均值 average 0.00 13.71 24.05 33.97 26.19 2.08 37.77 — 2.3 不同组别品种抗炭疽病鉴定结果
由表2看出,2011—2019年590份参鉴品种抗病品种(R)、中抗品种(MR)、中感品种(MS)、感病品种(S)、高感品种(HS)的比率范围分别为1.18%~30.77%、4.71%~40.38%、28.21%~51.30%、0~50.59%和0~5.88%。S1、S2、S3、S4、S5、S6和S7组别大豆品种的病情指数均值分别为19.86、15.75、41.22、20.27、29.49、30.85和28.78,S2组和S1组的病情指数均值明显低于其他组别。各组别的抗性品种比率范围为5.89%~69.23%,其中:S2组比率最高,其次为S4组(57.69%),S3组比率最低。
表 2 不同组别大豆品种抗炭疽病鉴定结果Table 2. Anthracnose-resistance of soybean from different crop groups组别
Group品种数
Number of soybean varieties合计
Total比率
Ratio/%抗性品种比率
Ratio of resistant varieties/%病指均值
Disease indexHR R MR MS S HS HR R MR MS S HS S1 0 21 31 34 5 0 91 0.00 23.08 34.07 37.36 5.49 0.00 57.15 19.86 S2 0 4 5 4 0 0 13 0.00 30.77 38.46 30.77 0.00 0.00 69.23 15.75 S3 0 1 4 32 43 5 85 0.00 1.18 4.71 37.65 50.59 5.88 5.89 41.22 S4 0 9 21 18 4 0 52 0.00 17.31 40.38 34.62 7.69 0.00 57.69 20.27 S5 0 6 17 28 26 1 78 0.00 7.69 21.79 35.90 33.33 1.28 29.48 29.49 S6 0 23 38 44 47 4 156 0.00 14.74 24.36 28.21 30.13 2.56 39.10 30.85 S7 0 6 27 59 23 0 115 0.00 5.22 23.48 51.30 20.00 0.00 28.70 28.78 合计 Total 0 70 143 219 148 10 平均值 average 0.00 14.28 26.75 36.54 21.03 1.39 41.03 — S1组累计鉴定出抗病品种(R)、中抗品种(MR)共52份,桂0521-2、桂H49、莆豆11、粤春2010-1等21份品种为抗病品种,桂605、泉豆12、中黄39等31份品种为中抗品种(表3)。S2组累计鉴定出抗病品种(R)、中抗品种(MR)共9份,贡夏369-37、桂166、粤夏2011-4、粤夏2013-2为抗病品种,南夏豆25、圣豆16、粤夏2012-1等5份品种为中抗品种(表4)。S3组累计鉴定出抗病品种(R)、中抗品种(MR)共5份,桂610为抗病品种,中黄19、K丰77-2、科力源12号、苏春15-2为中抗品种(表5)。S4组累计鉴定出抗病品种(R)、中抗品种(MR)共30份,苏菜13-009、苏菜201、苏菜50016、苏鲜豆19号等9份品种为抗病品种,油11-57、福豆9号、衢鲜5号等21份品种为中抗品种(表6)。S5组累计鉴定出抗病品种(R)、中抗品种(MR)共23份,贡6140、科豆2号、南充9707-23-2、浙H0634等6份品种为抗病品种,鄂豆010、鄂豆012、浙H0431等17份品种为中抗品种(表7)。S6组累计鉴定出抗病品种(R)、中抗品种(MR)共61份,福豆71、惠豆1号、莆豆5号等23份品种为抗病品种,闽豆06B12-1、福豆1014、莆豆11等38份品种为中抗品种(表8)。S7组累计鉴定出抗病品种(R)、中抗品种(MR)共33份,衢0811-2、苏豆18号等6份品种为抗病品种,川鲜1802、川鲜1804、浙农1801等27份品种为中抗品种(表9)。
表 3 国家热带亚热带地区春大豆组(S1)抗病品种Table 3. Resistant varieties in S1 group序号
Serial number品种
Variety name病情指数
Disease index抗病等级
Disease-resistant grade鉴别年份
Identification year1 桂0521-2 Gui 0521-2 0.86 抗病 R 2011 2 桂605 Gui605 15.10 中抗 MR 2011 3 桂H49 GuiH49 2.21 抗病 R 2011 4 华春6号 Huachun 6 (CK) 12.50 中抗 MR 2011 5 莆豆11 Pudou 11 8.95 抗病 R 2011 6 泉豆12 Quandou 12 12.00 中抗 MR 2011 7 泉豆7号 Quandou 7 (CK) 8.78 抗病 R 2011 8 粤春2010-1 Yuechun 2010-1 5.71 抗病 R 2011 9 粤春2010-2 Yuechun 2010-2 3.80 抗病 R 2011 10 中黄39 Zhonghuang 39 17.50 中抗 MR 2011 11 福豆2128 Fudou 2128 13.71 中抗 MR 2012 12 桂0381-2 Gui 0381-2 3.77 抗病 R 2012 13 桂0717-1 Gui 0717-1 16.97 中抗 MR 2012 14 莆豆5号 Pudou 5 4.80 抗病 R 2012 15 泉豆7号 Quandou 7 (CK) 4.58 抗病 R 2012 16 粤春2010-1 Yuechun 2010-1 9.69 抗病 R 2012 17 粤春2011-1 Yuechun 2011-1 7.51 抗病 R 2012 18 粤春2011-2 Yuechun 2011-2 9.14 抗病 R 2012 19 桂0737-1 Gui 0737-1 11.70 中抗 MR 2013 20 桂147 Gui 147 19.12 中抗 MR 2013 21 华春2号 Huachun 2 (CK) 10.19 中抗 MR 2013 22 华春6号 Huachun 6 (CK) 16.10 中抗 MR 2013 23 南农56-10 Nannong 56-10 7.34 抗病 R 2013 24 莆豆21 Pudou 21 8.52 抗病 R 2013 25 泉豆1号 Quandou 1 19.44 中抗 MR 2013 26 泉豆5号 Quandou 5 6.41 抗病 R 2013 27 泉豆7号 Quandou 7 (CK) 9.84 抗病 R 2013 28 瓦密黄豆 Wami soybean 6.05 抗病 R 2013 29 粤春2010-1 Yuechun 2010-1 8.56 抗病 R 2013 30 粤春2011-1 Yuechun 2011-1 15.78 中抗 MR 2013 31 粤春2012-1 Yuechun 2012-1 15.91 中抗 MR 2013 32 贡595 Gong 595 8.86 抗病 R 2014 33 华春2号 Huachun 2 (CK) 17.85 中抗 MR 2014 34 泉豆14 Quandou 14 16.44 中抗 MR 2014 35 泉豆5号 Quandou 5 19.36 中抗 MR 2014 43 华春2号 Huachun 2 (CK) 16.60 中抗 MR 2015 44 莆豆041 Pudou 041 10.77 中抗 MR 2015 45 泉豆5号 Quandou 5 18.12 中抗 MR 2015 46 圣豆40 Shengdou 40 11.58 中抗 MR 2015 47 粤春2013-2 Yuechun 2013-2 13.26 中抗 MR 2015 36 桂春豆107 Guichundou 107 9.67 抗病 R 2017 37 华春10号 Huachun 10 19.20 中抗 MR 2017 38 华春2号 Huachun 2 (CK) 17.10 中抗 MR 2017 39 泉豆17 Quandou 17 12.50 中抗 MR 2017 40 圣豆40 Shengdou 40 8.70 抗病 R 2017 41 华春7号 Huachun 7 14.69 中抗 MR 2018 42 中黄306 Zhonghuang 306 18.00 中抗 MR 2018 48 桂春豆112 Guichundou 112 15.09 中抗 MR 2019 49 华春14号 Huanchun 14 17.70 中抗 MR 2019 50 华春15号 Huachun 15 11.11 中抗 MR 2019 51 齐黄34 Qihuang 34 19.14 中抗 MR 2019 52 泉豆20 Quandou 20 19.28 中抗 MR 2019 表 4 国家热带亚热带地区夏大豆组(S2)抗病品种Table 4. Resistant varieties in S2 group序号
Serial number品种
Variety name病情指数
Disease index抗病等级
Disease-resistant grade鉴别年份
Identification year1 贡夏369-37 Gongxia 369-37 6.99 抗病 R 2014 2 桂166 Gui 166 7.52 抗病 R 2014 3 华夏9号 Huaxia 9 (CK) 15.89 中抗 MR 2014 4 南夏豆25 Nanxiadou 25 16.05 中抗 MR 2014 5 圣豆16 Shengdou 16 15.52 中抗 MR 2014 6 粤夏2011-4 Yuexia 2011-4 6.35 抗病 R 2014 7 粤夏2012-1 Yuexia 2012-1 15.14 中抗 MR 2014 8 粤夏2013-1 Yuexia 2013-1 18.32 中抗 MR 2014 9 粤夏2013-2 Yuexia 2013-2 9.03 抗病 R 2014 表 5 国家鲜食大豆春播组(S3)抗病品种Table 5. Resistant varieties in S3 group序号
Serial number品种
Variety name病情指数
Disease index抗病等级
Disease-resistant grade鉴别年份
Identification year1 桂610 Gui 610 5.74 抗病 R 2012 2 中黄19 Zhonghuang 19 16.81 中抗 MR 2012 3 K丰77- 2 Kfeng 77-2 16.20 中抗 MR 2013 4 科力源12号 Keliyuan 12 19.07 中抗 MR 2015 5 苏春15-2 Suchun 15-2 17.41 中抗 MR 2015 表 6 国家鲜食大豆夏播组(S4)抗病品种Table 6. Resistant varieties in S4 group序号
Serial number品种
Variety name病情指数
Disease index抗病等级
Disease-resistant grade鉴别年份
Identification year1 HD0032 17.41 中抗 MR 2013 2 绿宝珠 Lvbaozhu (CK) 9.54 抗病 R 2013 3 衢鲜3号 Quxian 3 (CK) 2.85 抗病 R 2013 4 苏菜13-009 Sulai 13-009 8.09 抗病 R 2013 5 苏菜201 Sulai 201 2.51 抗病 R 2013 6 苏菜50016 Sulai 50016 0.77 抗病 R 2013 7 苏鲜豆19号 Suxiandou 19 3.56 抗病 R 2013 8 油11-57 You 11-57 10.32 中抗 MR 2013 9 粤夏2012-2 Yuexia 2012-2 5.30 抗病 R 2013 10 福豆9号 Fudou 9 19.66 中抗 MR 2014 11 绿宝珠 Lvbaozhu (CK) 16.38 中抗 MR 2014 12 衢鲜3号 Quxian 3 (CK) 18.66 中抗 MR 2014 13 衢鲜5号 Quxian 5 19.49 中抗 MR 2014 14 苏7辐选 Su 7 fuxuan 14.36 中抗 MR 2014 15 浙夏002 Zhexia 002 16.15 中抗 MR 2014 16 淮鲜12-07 Huaixian 12-07 18.91 中抗 MR 2016 17 绿宝珠 Lvbaozhu (CK) 10.93 中抗 MR 2016 18 南农46 Nannong 46 12.38 中抗 MR 2016 19 苏7辐选 Su 7 fuxuan 18.41 中抗 MR 2016 20 绿宝珠 Lvbaozhu (CK) 11.51 中抗 MR 2017 21 衢鲜3号 Quxian 3 (CK) 19.87 中抗 MR 2017 22 苏豆22号 Sudou 22 19.75 中抗 MR 2017 23 浙鲜0840 Zhexian 0840 5.48 抗病 R 2017 24 浙鲜85 Zhexian 85 18.60 中抗 MR 2017 25 华夏18 Huaxia 18 9.26 抗病 R 2018 26 淮鲜豆9号 Huaixiandou 9 18.96 中抗 MR 2018 27 南农46 Nannong 46 19.09 中抗 MR 2018 28 南农52 Nannong 52 17.22 中抗 MR 2018 29 衢鲜3号 Quxian 3 (CK) 19.35 中抗 MR 2019 30 晋科2号 Jinke 2 19.38 中抗 MR 2019 表 7 国家长江流域春大豆组(S5)抗病品种Table 7. Resistant varieties in S5 group序号
Serial number品种
Variety name病情指数
Disease index抗病等级
Disease-resistant grade鉴别年份
Identification year1 鄂豆010 Edou 010 12.90 中抗 MR 2011 2 鄂豆012 Edou 012 10.90 中抗 MR 2011 3 浙H0431 Zhe H0431 11.90 中抗 MR 2011 4 贡6140 Gong 6140 8.87 抗病 R 2012 5 冀豆17 Jidou 17 11.90 中抗 MR 2012 6 科豆2号 Kodou 2 6.84 抗病 R 2012 7 南充9707-23-2 Nanchong 9707-23-2 6.13 抗病 R 2012 8 天隆一号 Tianlong 1 11.47 中抗 MR 2012 9 浙H0634 Zhe H0634 8.74 抗病 R 2012 10 赣05-2 Gan 05-2 18.09 中抗 MR 2013 11 圣贡617-2 Shenggong 617-2 14.03 中抗 MR 2013 12 天隆一号 Tianlong 1 (CK) 10.33 中抗 MR 2013 13 天隆一号 Tianlong 1 (CK) 13.66 中抗 MR 2014 14 天隆一号 Tianlong 1 (CK) 15.93 中抗 MR 2015 15 赣豆10号 Gandou 10 11.30 中抗 MR 2017 16 中豆4601 Zhongdou 4601 13.40 中抗 MR 2017 17 赣豆10号 Gandou 10 9.24 抗病 R 2018 18 南农49 Nannong 49 15.44 中抗 MR 2018 19 湘春2701 Xiangchun 2701 8.96 抗病 MR 2018 20 浙春1024 Zhechun 1024 16.99 中抗 MR 2018 21 湘春豆26 Xiangchundou 26 (CK) 16.97 中抗 MR 2019 22 赣豆10号 Gandou 10 10.44 中抗 MR 2019 23 南农49 Nannong 49 10.59 中抗 MR 2019 表 8 福建省大豆新品种(系)组(S6)抗病品种Table 8. Resistant varieties in S6 group序号
Serial number品种
Variety name病情指数
Disease index抗病等级
Disease-resistant grade鉴别年份
Identification year1 101 9.79 抗病 R 2011 2 103 10.10 中抗 MR 2011 3 104 7.40 抗病 R 2011 4 105 16.30 中抗 MR 2011 5 106 3.90 抗病 R 2011 6 107 5.85 抗病 R 2011 7 福豆310 Fudou 310 (CK) 13.58 中抗 MR 2012 8 福豆71 Fudou 71 4.44 抗病 R 2012 9 惠豆1号 Huidou 1 0.33 抗病 R 2012 10 闽豆06B12-1 Mindou 06B12-1 16.67 中抗 MR 2012 11 莆豆 17 Pudou 17 7.22 抗病 R 2012 12 莆豆12 Pudou 12 15.56 中抗 MR 2012 13 莆豆5号 Pudou 5 9.51 抗病 R 2012 14 泉豆12号 Quandou 12 5.56 抗病 R 2012 15 泉豆13号 Quandou 13 9.17 抗病 R 2012 16 泉豆7号 Quandou 7 (CK) 4.58 抗病 R 2012 17 福豆1014 Fudou 1014 18.04 中抗 MR 2013 18 莆 豆11 Pudou 11 16.41 中抗 MR 2013 19 莆豆019 Pudou 019 17.59 中抗 MR 2013 20 莆豆5号 Pudou 5 15.13 中抗 MR 2013 21 泉豆12号 Quandou 12 9.43 抗病 R 2013 22 泉豆13号 Quandou 13 3.77 抗病 R 2013 23 泉豆1号 Quandou 1 11.48 中抗 MR 2013 24 泉豆7号 Quandou 7 9.84 抗病 R 2013 25 福豆310 Fudou 310 18.71 中抗 MR 2014 26 南农NF19 Nannong NF19 8.76 抗病 R 2014 27 泉豆5号 Quandou 5 15.73 中抗 MR 2014 28 圣豆8号 Shengdou 8 13.42 中抗 MR 2014 29 粤春2011-3 Yuechun 2011-3 14.78 中抗 MR 2014 30 福豆10号 Fudou 10 16.85 中抗 MR 2015 31 福豆234 Fudou 234 (CK) 17.22 中抗 MR 2015 32 华春4号 Huachun 4 16.48 中抗 MR 2015 33 华春7号 Huachun 7 12.41 中抗 MR 2015 34 毛豆3号 Maodou 3 (CK) 15.11 中抗 MR 2015 35 南农15-2 Nannong 15-2 13.52 中抗 MR 2015 36 莆豆041 Pudou 041 9.07 抗病 R 2015 37 泉豆15 Quandou 15 16.67 中抗 MR 2015 38 福豆11 Fudou 11 18.34 中抗 MR 2016 39 莆豆047 Pudou 047 16.73 中抗 MR 2016 40 莆豆610 Pudou 610 8.29 抗病 R 2017 41 泉豆15 Quandou 15 8.11 抗病 R 2017 42 泉豆17 Quandou 17 16.09 中抗 MR 2017 43 福豆12号 Fudou 12 16.50 中抗 MR 2018 44 福豆234 Fudou 234 (CK) 12.73 中抗 MR 2018 45 交大23号 Jiaoda 23 10.63 中抗 MR 2018 46 莆豆704 Pudou 704 11.81 中抗 MR 2018 47 泉豆17 Quandou 17 4.87 抗病 R 2018 48 苏豆28号 Sudou 28 6.35 抗病 R 2018 49 苏豆29号 Sudou 29 15.20 中抗 MR 2018 50 福农春豆2号 Funongchundou 2 18.59 中抗 MR 2019 51 华春8号 Huachun 8 19.02 中抗 MR 2019 52 交大24 Jiaoda 24 18.67 中抗 MR 2019 53 闽豆10号 Mindou 10 17.21 中抗 MR 2019 54 南农1821 Nannong 1821 9.50 抗病 R 2019 55 南农88026 Nannong 88026 5.50 抗病 R 2019 56 泉豆20 Quandou 20 12.83 中抗 MR 2019 57 兴化豆3号 Xinghuadou 3 12.15 中抗 MR 2019 58 福农夏豆2号 Funongxiadou 2 17.86 中抗 MR 2019 59 华夏10号 Huaxia 10 10.85 中抗 MR 2019 60 闽诚豆8号 Minchengdou 8 15.20 中抗 MR 2019 61 苏闽夏2号 Suminxia 2 8.11 抗病 R 2019 表 9 其他新品种(系)组(S7)抗病品种Table 9. Resistant varieties in S7 group序号
Serial number品种
Variety name病情指数
Disease index抗病等级
Disease-resistant grade鉴别年份
Identification year1 川鲜1802 Chuanxian 1802 13.79 中抗 MR 2018 2 川鲜1804 Chuanxian 1804 14.69 中抗 MR 2018 3 南752-44 Nan 752-44 9.36 抗病 R 2018 4 浙农1801 Zhenong 1801 12.84 中抗 MR 2018 5 浙农1803 Zhenong 1803 13.00 中抗 MR 2018 6 绿秋王 Lvqiuwang 19.32 中抗 MR 2018 7 衢0811-2 Qu 0811-2 6.71 抗病 R 2018 8 衢鲜1号 Quxian 1 (CK) 11.21 中抗 MR 2018 9 衢鲜6号 Quxian 6 12.15 中抗 MR 2018 10 苏豆18号 Sudou 18 6.47 抗病 R 2018 11 夏丰2008 Xiafeng 2008 12.85 中抗 MR 2018 12 浙农1204 Zhenong 1204 11.49 中抗 MR 2018 13 浙农1619 Zhenong 1619 9.88 抗病 R 2018 14 浙农1620 Zhenong 1620 13.17 中抗 MR 2018 15 浙农18-6 Zhenong 18-6 14.62 中抗 MR 2018 16 浙农18-7 Zhenong 18-7 13.10 中抗 MR 2018 17 浙农18-9 Zhenong 18-9 7.07 抗病 R 2018 18 浙鲜86 Zhexian 86 12.27 中抗 MR 2018 19 C3 15.98 中抗 MR 2019 20 C4 18.44 中抗 MR 2019 21 C7 18.14 中抗 MR 2019 22 油春13-10 Youchun 13-10 16.83 中抗 MR 2019 23 贡鲜豆3号 Gongxiandou 3 19.77 中抗 MR 2019 24 绿秋8号 Lvqiu 8 12.52 中抗 MR 2019 25 ZC08 18.79 中抗 MR 2019 26 ZC09 13.38 中抗 MR 2019 27 ZC10 19.24 中抗 MR 2019 28 ZC11 17.93 中抗 MR 2019 29 ZC12 15.45 中抗 MR 2019 30 ZC13 19.56 中抗 MR 2019 31 衢鲜1号 Quxian 1 15.84 中抗 MR 2019 32 H0427 18.50 中抗 MR 2019 33 浙鲜豆5号 Zhexian 5 11.92 中抗 MR 2019 3. 讨论与结论
炭疽菌属(Colletotrichum Corda)真菌种类多,是一类重要的植物病原菌,是子囊菌中最常见和最重要的一个属,在超过460种木本和草本植物上引起炭疽病[10-14]。炭疽菌具有繁殖快、产孢量大、潜伏侵染和多次再侵染等特性,导致炭疽病难以防治,常造成巨大的经济损失。基于其科学和经济价值,炭疽菌属在世界上重要的植物病原真菌中位列第八[15]。据报道,造成大豆炭疽病的病原菌有很多种,包括平头炭疽菌(C. truncatum)[2]、毁灭炭疽菌(C. destructivum)[16]、胶胞炭疽菌(C. gloeosporioides)[17]、禾生炭疽菌(C. graminicola)[18]、黑线炭疽菌(C. dematium)[19]、辣椒炭疽菌(C. capsici)[20]和C. chlorophyti[21-22],而造成我国大豆炭疽病的主要病原菌为平头炭疽菌[23-25]。林敬州等用平头炭疽菌孢子悬浮液作为接种体采用喷雾接种法对76份大豆种质资源进行抗性鉴定,抗性品种占供试材料比例为38.16%[23]。徐晶用平头炭疽菌孢子悬浮液作为接种体采用离体叶片点滴法对浙江59份大豆品种进行炭疽病的抗性鉴定,大部分品种对JS11-32菌株表现出抗性,抗性品种的比例高达96.61%;33份品种对TB8-15菌株表现出抗性,抗性品种比例为55.93%[24]。可见,不同接种方法、不同接种体对试验结果影响较大。本研究在豆荚形成初期采用喷雾接种法接种豆荚,连续9年感病对照品种(毛豆75和毛豆3号)病情指数均达到感病等级,获得了较稳定的鉴定结果。
本研究结果表明,2011—2019年不同年份间大豆炭疽病抗性品种比率为13.64%~68.00%,其中2016年最低,2013年最高,其余年份间抗性品种比率范围为28.70%~57.69%,这表明我国部分大豆种质资源对炭疽病具有较好抗性。在不同组别大豆品种对比中,国家热带亚热带地区夏大豆组和春大豆组病情指数均值低于其他组别,其抗性品种比率较高,分别为69.23%和57.15%,这可能与国家热带亚热带地区大豆炭疽病发病严重,品种选育过程中经过自然筛选有关。鲜食大豆春播组抗性品种比率较低,仅为5.89%,这表明我国春播鲜食大豆品种中缺乏抗病品种,仍需加强春播鲜食大豆抗病材料和品种的选育研究。
-
表 1 不同年份大豆品种抗炭疽病鉴定结果
Table 1 Anthracnose-resistance of soybean shown in different years
年份
Year品种数
Number of soybean varieties合计
Total比率
Ratio/%抗性品种比率
Ratio of resistant varieties/%病指均值
Disease indexHR R MR MS S HS HR R MR MS S HS 2011 0 10 9 2 18 8 47 0.00 21.28 19.15 4.26 38.30 17.02 40.43 36.92 2012 0 18 8 4 20 0 50 0.00 36.00 16.00 8.00 40.00 0.00 52.00 23.49 2013 0 16 18 12 4 0 50 0.00 32.00 36.00 24.00 8.00 0.00 68.00 18.41 2014 0 6 19 23 18 0 66 0.00 9.09 28.79 34.85 27.27 0.00 37.88 28.79 2015 0 1 15 19 9 0 44 0.00 2.27 34.09 43.18 20.45 0.00 36.36 27.58 2016 0 0 6 20 18 0 44 0.00 0.00 13.64 45.45 40.91 0.00 13.64 37.33 2017 0 5 10 24 9 0 48 0.00 10.40 20.83 50.00 18.75 0.00 31.25 28.01 2018 0 10 25 54 17 1 107 0.00 9.35 23.36 50.47 15.89 0.93 32.71 28.00 2019 0 4 33 61 35 1 134 0.00 2.99 24.63 45.52 26.12 0.75 27.62 30.34 合计 Total 0 70 143 219 148 10 平均值 average 0.00 13.71 24.05 33.97 26.19 2.08 37.77 — 表 2 不同组别大豆品种抗炭疽病鉴定结果
Table 2 Anthracnose-resistance of soybean from different crop groups
组别
Group品种数
Number of soybean varieties合计
Total比率
Ratio/%抗性品种比率
Ratio of resistant varieties/%病指均值
Disease indexHR R MR MS S HS HR R MR MS S HS S1 0 21 31 34 5 0 91 0.00 23.08 34.07 37.36 5.49 0.00 57.15 19.86 S2 0 4 5 4 0 0 13 0.00 30.77 38.46 30.77 0.00 0.00 69.23 15.75 S3 0 1 4 32 43 5 85 0.00 1.18 4.71 37.65 50.59 5.88 5.89 41.22 S4 0 9 21 18 4 0 52 0.00 17.31 40.38 34.62 7.69 0.00 57.69 20.27 S5 0 6 17 28 26 1 78 0.00 7.69 21.79 35.90 33.33 1.28 29.48 29.49 S6 0 23 38 44 47 4 156 0.00 14.74 24.36 28.21 30.13 2.56 39.10 30.85 S7 0 6 27 59 23 0 115 0.00 5.22 23.48 51.30 20.00 0.00 28.70 28.78 合计 Total 0 70 143 219 148 10 平均值 average 0.00 14.28 26.75 36.54 21.03 1.39 41.03 — 表 3 国家热带亚热带地区春大豆组(S1)抗病品种
Table 3 Resistant varieties in S1 group
序号
Serial number品种
Variety name病情指数
Disease index抗病等级
Disease-resistant grade鉴别年份
Identification year1 桂0521-2 Gui 0521-2 0.86 抗病 R 2011 2 桂605 Gui605 15.10 中抗 MR 2011 3 桂H49 GuiH49 2.21 抗病 R 2011 4 华春6号 Huachun 6 (CK) 12.50 中抗 MR 2011 5 莆豆11 Pudou 11 8.95 抗病 R 2011 6 泉豆12 Quandou 12 12.00 中抗 MR 2011 7 泉豆7号 Quandou 7 (CK) 8.78 抗病 R 2011 8 粤春2010-1 Yuechun 2010-1 5.71 抗病 R 2011 9 粤春2010-2 Yuechun 2010-2 3.80 抗病 R 2011 10 中黄39 Zhonghuang 39 17.50 中抗 MR 2011 11 福豆2128 Fudou 2128 13.71 中抗 MR 2012 12 桂0381-2 Gui 0381-2 3.77 抗病 R 2012 13 桂0717-1 Gui 0717-1 16.97 中抗 MR 2012 14 莆豆5号 Pudou 5 4.80 抗病 R 2012 15 泉豆7号 Quandou 7 (CK) 4.58 抗病 R 2012 16 粤春2010-1 Yuechun 2010-1 9.69 抗病 R 2012 17 粤春2011-1 Yuechun 2011-1 7.51 抗病 R 2012 18 粤春2011-2 Yuechun 2011-2 9.14 抗病 R 2012 19 桂0737-1 Gui 0737-1 11.70 中抗 MR 2013 20 桂147 Gui 147 19.12 中抗 MR 2013 21 华春2号 Huachun 2 (CK) 10.19 中抗 MR 2013 22 华春6号 Huachun 6 (CK) 16.10 中抗 MR 2013 23 南农56-10 Nannong 56-10 7.34 抗病 R 2013 24 莆豆21 Pudou 21 8.52 抗病 R 2013 25 泉豆1号 Quandou 1 19.44 中抗 MR 2013 26 泉豆5号 Quandou 5 6.41 抗病 R 2013 27 泉豆7号 Quandou 7 (CK) 9.84 抗病 R 2013 28 瓦密黄豆 Wami soybean 6.05 抗病 R 2013 29 粤春2010-1 Yuechun 2010-1 8.56 抗病 R 2013 30 粤春2011-1 Yuechun 2011-1 15.78 中抗 MR 2013 31 粤春2012-1 Yuechun 2012-1 15.91 中抗 MR 2013 32 贡595 Gong 595 8.86 抗病 R 2014 33 华春2号 Huachun 2 (CK) 17.85 中抗 MR 2014 34 泉豆14 Quandou 14 16.44 中抗 MR 2014 35 泉豆5号 Quandou 5 19.36 中抗 MR 2014 43 华春2号 Huachun 2 (CK) 16.60 中抗 MR 2015 44 莆豆041 Pudou 041 10.77 中抗 MR 2015 45 泉豆5号 Quandou 5 18.12 中抗 MR 2015 46 圣豆40 Shengdou 40 11.58 中抗 MR 2015 47 粤春2013-2 Yuechun 2013-2 13.26 中抗 MR 2015 36 桂春豆107 Guichundou 107 9.67 抗病 R 2017 37 华春10号 Huachun 10 19.20 中抗 MR 2017 38 华春2号 Huachun 2 (CK) 17.10 中抗 MR 2017 39 泉豆17 Quandou 17 12.50 中抗 MR 2017 40 圣豆40 Shengdou 40 8.70 抗病 R 2017 41 华春7号 Huachun 7 14.69 中抗 MR 2018 42 中黄306 Zhonghuang 306 18.00 中抗 MR 2018 48 桂春豆112 Guichundou 112 15.09 中抗 MR 2019 49 华春14号 Huanchun 14 17.70 中抗 MR 2019 50 华春15号 Huachun 15 11.11 中抗 MR 2019 51 齐黄34 Qihuang 34 19.14 中抗 MR 2019 52 泉豆20 Quandou 20 19.28 中抗 MR 2019 表 4 国家热带亚热带地区夏大豆组(S2)抗病品种
Table 4 Resistant varieties in S2 group
序号
Serial number品种
Variety name病情指数
Disease index抗病等级
Disease-resistant grade鉴别年份
Identification year1 贡夏369-37 Gongxia 369-37 6.99 抗病 R 2014 2 桂166 Gui 166 7.52 抗病 R 2014 3 华夏9号 Huaxia 9 (CK) 15.89 中抗 MR 2014 4 南夏豆25 Nanxiadou 25 16.05 中抗 MR 2014 5 圣豆16 Shengdou 16 15.52 中抗 MR 2014 6 粤夏2011-4 Yuexia 2011-4 6.35 抗病 R 2014 7 粤夏2012-1 Yuexia 2012-1 15.14 中抗 MR 2014 8 粤夏2013-1 Yuexia 2013-1 18.32 中抗 MR 2014 9 粤夏2013-2 Yuexia 2013-2 9.03 抗病 R 2014 表 5 国家鲜食大豆春播组(S3)抗病品种
Table 5 Resistant varieties in S3 group
序号
Serial number品种
Variety name病情指数
Disease index抗病等级
Disease-resistant grade鉴别年份
Identification year1 桂610 Gui 610 5.74 抗病 R 2012 2 中黄19 Zhonghuang 19 16.81 中抗 MR 2012 3 K丰77- 2 Kfeng 77-2 16.20 中抗 MR 2013 4 科力源12号 Keliyuan 12 19.07 中抗 MR 2015 5 苏春15-2 Suchun 15-2 17.41 中抗 MR 2015 表 6 国家鲜食大豆夏播组(S4)抗病品种
Table 6 Resistant varieties in S4 group
序号
Serial number品种
Variety name病情指数
Disease index抗病等级
Disease-resistant grade鉴别年份
Identification year1 HD0032 17.41 中抗 MR 2013 2 绿宝珠 Lvbaozhu (CK) 9.54 抗病 R 2013 3 衢鲜3号 Quxian 3 (CK) 2.85 抗病 R 2013 4 苏菜13-009 Sulai 13-009 8.09 抗病 R 2013 5 苏菜201 Sulai 201 2.51 抗病 R 2013 6 苏菜50016 Sulai 50016 0.77 抗病 R 2013 7 苏鲜豆19号 Suxiandou 19 3.56 抗病 R 2013 8 油11-57 You 11-57 10.32 中抗 MR 2013 9 粤夏2012-2 Yuexia 2012-2 5.30 抗病 R 2013 10 福豆9号 Fudou 9 19.66 中抗 MR 2014 11 绿宝珠 Lvbaozhu (CK) 16.38 中抗 MR 2014 12 衢鲜3号 Quxian 3 (CK) 18.66 中抗 MR 2014 13 衢鲜5号 Quxian 5 19.49 中抗 MR 2014 14 苏7辐选 Su 7 fuxuan 14.36 中抗 MR 2014 15 浙夏002 Zhexia 002 16.15 中抗 MR 2014 16 淮鲜12-07 Huaixian 12-07 18.91 中抗 MR 2016 17 绿宝珠 Lvbaozhu (CK) 10.93 中抗 MR 2016 18 南农46 Nannong 46 12.38 中抗 MR 2016 19 苏7辐选 Su 7 fuxuan 18.41 中抗 MR 2016 20 绿宝珠 Lvbaozhu (CK) 11.51 中抗 MR 2017 21 衢鲜3号 Quxian 3 (CK) 19.87 中抗 MR 2017 22 苏豆22号 Sudou 22 19.75 中抗 MR 2017 23 浙鲜0840 Zhexian 0840 5.48 抗病 R 2017 24 浙鲜85 Zhexian 85 18.60 中抗 MR 2017 25 华夏18 Huaxia 18 9.26 抗病 R 2018 26 淮鲜豆9号 Huaixiandou 9 18.96 中抗 MR 2018 27 南农46 Nannong 46 19.09 中抗 MR 2018 28 南农52 Nannong 52 17.22 中抗 MR 2018 29 衢鲜3号 Quxian 3 (CK) 19.35 中抗 MR 2019 30 晋科2号 Jinke 2 19.38 中抗 MR 2019 表 7 国家长江流域春大豆组(S5)抗病品种
Table 7 Resistant varieties in S5 group
序号
Serial number品种
Variety name病情指数
Disease index抗病等级
Disease-resistant grade鉴别年份
Identification year1 鄂豆010 Edou 010 12.90 中抗 MR 2011 2 鄂豆012 Edou 012 10.90 中抗 MR 2011 3 浙H0431 Zhe H0431 11.90 中抗 MR 2011 4 贡6140 Gong 6140 8.87 抗病 R 2012 5 冀豆17 Jidou 17 11.90 中抗 MR 2012 6 科豆2号 Kodou 2 6.84 抗病 R 2012 7 南充9707-23-2 Nanchong 9707-23-2 6.13 抗病 R 2012 8 天隆一号 Tianlong 1 11.47 中抗 MR 2012 9 浙H0634 Zhe H0634 8.74 抗病 R 2012 10 赣05-2 Gan 05-2 18.09 中抗 MR 2013 11 圣贡617-2 Shenggong 617-2 14.03 中抗 MR 2013 12 天隆一号 Tianlong 1 (CK) 10.33 中抗 MR 2013 13 天隆一号 Tianlong 1 (CK) 13.66 中抗 MR 2014 14 天隆一号 Tianlong 1 (CK) 15.93 中抗 MR 2015 15 赣豆10号 Gandou 10 11.30 中抗 MR 2017 16 中豆4601 Zhongdou 4601 13.40 中抗 MR 2017 17 赣豆10号 Gandou 10 9.24 抗病 R 2018 18 南农49 Nannong 49 15.44 中抗 MR 2018 19 湘春2701 Xiangchun 2701 8.96 抗病 MR 2018 20 浙春1024 Zhechun 1024 16.99 中抗 MR 2018 21 湘春豆26 Xiangchundou 26 (CK) 16.97 中抗 MR 2019 22 赣豆10号 Gandou 10 10.44 中抗 MR 2019 23 南农49 Nannong 49 10.59 中抗 MR 2019 表 8 福建省大豆新品种(系)组(S6)抗病品种
Table 8 Resistant varieties in S6 group
序号
Serial number品种
Variety name病情指数
Disease index抗病等级
Disease-resistant grade鉴别年份
Identification year1 101 9.79 抗病 R 2011 2 103 10.10 中抗 MR 2011 3 104 7.40 抗病 R 2011 4 105 16.30 中抗 MR 2011 5 106 3.90 抗病 R 2011 6 107 5.85 抗病 R 2011 7 福豆310 Fudou 310 (CK) 13.58 中抗 MR 2012 8 福豆71 Fudou 71 4.44 抗病 R 2012 9 惠豆1号 Huidou 1 0.33 抗病 R 2012 10 闽豆06B12-1 Mindou 06B12-1 16.67 中抗 MR 2012 11 莆豆 17 Pudou 17 7.22 抗病 R 2012 12 莆豆12 Pudou 12 15.56 中抗 MR 2012 13 莆豆5号 Pudou 5 9.51 抗病 R 2012 14 泉豆12号 Quandou 12 5.56 抗病 R 2012 15 泉豆13号 Quandou 13 9.17 抗病 R 2012 16 泉豆7号 Quandou 7 (CK) 4.58 抗病 R 2012 17 福豆1014 Fudou 1014 18.04 中抗 MR 2013 18 莆 豆11 Pudou 11 16.41 中抗 MR 2013 19 莆豆019 Pudou 019 17.59 中抗 MR 2013 20 莆豆5号 Pudou 5 15.13 中抗 MR 2013 21 泉豆12号 Quandou 12 9.43 抗病 R 2013 22 泉豆13号 Quandou 13 3.77 抗病 R 2013 23 泉豆1号 Quandou 1 11.48 中抗 MR 2013 24 泉豆7号 Quandou 7 9.84 抗病 R 2013 25 福豆310 Fudou 310 18.71 中抗 MR 2014 26 南农NF19 Nannong NF19 8.76 抗病 R 2014 27 泉豆5号 Quandou 5 15.73 中抗 MR 2014 28 圣豆8号 Shengdou 8 13.42 中抗 MR 2014 29 粤春2011-3 Yuechun 2011-3 14.78 中抗 MR 2014 30 福豆10号 Fudou 10 16.85 中抗 MR 2015 31 福豆234 Fudou 234 (CK) 17.22 中抗 MR 2015 32 华春4号 Huachun 4 16.48 中抗 MR 2015 33 华春7号 Huachun 7 12.41 中抗 MR 2015 34 毛豆3号 Maodou 3 (CK) 15.11 中抗 MR 2015 35 南农15-2 Nannong 15-2 13.52 中抗 MR 2015 36 莆豆041 Pudou 041 9.07 抗病 R 2015 37 泉豆15 Quandou 15 16.67 中抗 MR 2015 38 福豆11 Fudou 11 18.34 中抗 MR 2016 39 莆豆047 Pudou 047 16.73 中抗 MR 2016 40 莆豆610 Pudou 610 8.29 抗病 R 2017 41 泉豆15 Quandou 15 8.11 抗病 R 2017 42 泉豆17 Quandou 17 16.09 中抗 MR 2017 43 福豆12号 Fudou 12 16.50 中抗 MR 2018 44 福豆234 Fudou 234 (CK) 12.73 中抗 MR 2018 45 交大23号 Jiaoda 23 10.63 中抗 MR 2018 46 莆豆704 Pudou 704 11.81 中抗 MR 2018 47 泉豆17 Quandou 17 4.87 抗病 R 2018 48 苏豆28号 Sudou 28 6.35 抗病 R 2018 49 苏豆29号 Sudou 29 15.20 中抗 MR 2018 50 福农春豆2号 Funongchundou 2 18.59 中抗 MR 2019 51 华春8号 Huachun 8 19.02 中抗 MR 2019 52 交大24 Jiaoda 24 18.67 中抗 MR 2019 53 闽豆10号 Mindou 10 17.21 中抗 MR 2019 54 南农1821 Nannong 1821 9.50 抗病 R 2019 55 南农88026 Nannong 88026 5.50 抗病 R 2019 56 泉豆20 Quandou 20 12.83 中抗 MR 2019 57 兴化豆3号 Xinghuadou 3 12.15 中抗 MR 2019 58 福农夏豆2号 Funongxiadou 2 17.86 中抗 MR 2019 59 华夏10号 Huaxia 10 10.85 中抗 MR 2019 60 闽诚豆8号 Minchengdou 8 15.20 中抗 MR 2019 61 苏闽夏2号 Suminxia 2 8.11 抗病 R 2019 表 9 其他新品种(系)组(S7)抗病品种
Table 9 Resistant varieties in S7 group
序号
Serial number品种
Variety name病情指数
Disease index抗病等级
Disease-resistant grade鉴别年份
Identification year1 川鲜1802 Chuanxian 1802 13.79 中抗 MR 2018 2 川鲜1804 Chuanxian 1804 14.69 中抗 MR 2018 3 南752-44 Nan 752-44 9.36 抗病 R 2018 4 浙农1801 Zhenong 1801 12.84 中抗 MR 2018 5 浙农1803 Zhenong 1803 13.00 中抗 MR 2018 6 绿秋王 Lvqiuwang 19.32 中抗 MR 2018 7 衢0811-2 Qu 0811-2 6.71 抗病 R 2018 8 衢鲜1号 Quxian 1 (CK) 11.21 中抗 MR 2018 9 衢鲜6号 Quxian 6 12.15 中抗 MR 2018 10 苏豆18号 Sudou 18 6.47 抗病 R 2018 11 夏丰2008 Xiafeng 2008 12.85 中抗 MR 2018 12 浙农1204 Zhenong 1204 11.49 中抗 MR 2018 13 浙农1619 Zhenong 1619 9.88 抗病 R 2018 14 浙农1620 Zhenong 1620 13.17 中抗 MR 2018 15 浙农18-6 Zhenong 18-6 14.62 中抗 MR 2018 16 浙农18-7 Zhenong 18-7 13.10 中抗 MR 2018 17 浙农18-9 Zhenong 18-9 7.07 抗病 R 2018 18 浙鲜86 Zhexian 86 12.27 中抗 MR 2018 19 C3 15.98 中抗 MR 2019 20 C4 18.44 中抗 MR 2019 21 C7 18.14 中抗 MR 2019 22 油春13-10 Youchun 13-10 16.83 中抗 MR 2019 23 贡鲜豆3号 Gongxiandou 3 19.77 中抗 MR 2019 24 绿秋8号 Lvqiu 8 12.52 中抗 MR 2019 25 ZC08 18.79 中抗 MR 2019 26 ZC09 13.38 中抗 MR 2019 27 ZC10 19.24 中抗 MR 2019 28 ZC11 17.93 中抗 MR 2019 29 ZC12 15.45 中抗 MR 2019 30 ZC13 19.56 中抗 MR 2019 31 衢鲜1号 Quxian 1 15.84 中抗 MR 2019 32 H0427 18.50 中抗 MR 2019 33 浙鲜豆5号 Zhexian 5 11.92 中抗 MR 2019 -
[1] 齐照明, 侯萌, 韩雪, 等. 东北地区大豆主栽品种油份蛋白含量的关联分析 [J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2014, 36(2):168−174. DOI: 10.7505/j.issn.1007-9084.2014.02.005 QI Z M, HOU M, HAN X, et al. Association analysis of soybean oil and protein content for Northeast soybean cultivar in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 2014, 36(2): 168−174.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7505/j.issn.1007-9084.2014.02.005
[2] 汪涛, 钟荣顺, 高智谋. 大豆炭疽菌的营养生理研究 [J]. 菌物研究, 2006, 4(3):91−93. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3538.2006.03.021 WANG T, ZHONG R S, GAO Z M. Study on nutritional physiology of Colletotrichum truncatum [J]. Journal of Fungal Research, 2006, 4(3): 91−93.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3538.2006.03.021
[3] 王国荣, 孙志峰, 陈吴健, 等. 大豆豆荚炭疽病有效杀菌剂的筛选与防治适期研究 [J]. 浙江农业学报, 2012, 24(2):258−262. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2012.02.015 WANG G R, SUN Z F, CHEN W J, et al. Screening of effective fungicides and optimum period for controlling soybean pod anthracnose [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2012, 24(2): 258−262.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2012.02.015
[4] 王坤, 王晓鸣, 朱振东, 等. 普通菜豆抗炭疽病地方品种的朊蛋白标记分析 [J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2009, 10(2):169−174. WANG K, WANG X M, ZHU Z D, et al. Analysis of phaseolin marker for Chinese common bean landraces with anthracnose resistance [J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2009, 10(2): 169−174.(in Chinese)
[5] 孙志峰. 大豆豆荚炭疽病的发病因子及其防治研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2008: 31-32. SUN Z F. Study on disease factors of soybean pod anthracnose and its control[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2008: 31-32. (in Chinese)
[6] GHIMIRE S R, PRADHANANG P M, LOHAR D P. Use of fungicides and identification of resistant varieties for the management of bean rust and anthracnose diseases in common beans [J]. Working Paper-Lumle Regional Agricultural Research Centre, 1995, 42: 76−95.
[7] SHARMA P N, KUMAR A, SHARMA O P, et al. Pathogenic variability in Colletotrichum lindemuthianum and evaluation of resistance in Phaseolus vulgaris in the north-western Himalayan region of India [J]. Journal of Phytopathology, 1999, 147(1): 41−45.
[8] 阮宏椿, 石妞妞, 甘林, 等. 稻曲病菌对戊唑醇的敏感基线及抗药突变体的生物学性状 [J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 45(6):148−154. RUAN H C, SHI N N, GAN L, et al. Baseline sensitivity of Ustilaginoidea virens against tebuconazole and biological characteristics of resistant mutants [J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(6): 148−154.(in Chinese)
[9] 福建省质量技术监督局. 大豆抗炭疽病鉴定技术规范: DB 35/T 1574—2016[S]. [10] CANNON P F, DAMM U, JOHNSTON P R, et al. Colletotrichum - current status and future directions [J]. Studies in Mycology, 2012, 73: 181−213. DOI: 10.3114/sim0014
[11] DAMM U, BARONCELLI R, CAI L, et al. Colletotrichum: species, ecology and interactions [J]. IMA Fungus, 2010, 1(2): 161−165. DOI: 10.5598/imafungus.2010.01.02.08
[12] DEAN R, VAN KAN J A L, PRETORIUS Z A, et al. The Top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology [J]. Molecular Plant Pathology, 2012, 13(4): 414−430. DOI: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2011.00783.x
[13] WIKEE S, CAI L, PAIRIN N, et al. Colletotrichum species from Jasmine (Jasminum sambac) [J]. Fungal Diversity, 2011, 46: 171−182. DOI: 10.1007/s13225-010-0049-x
[14] ZHANG C, DIAO Y Z, WANG W Z, et al. Assessing the risk for resistance and elucidating the genetics of Colletotrichum truncatum that is only sensitive to some DMI fungicides [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017, 8: 1779. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01779
[15] RAMDIAL H, RAMPERSAD S N. Characterization of Colletotrichum spp. causing anthracnose of bell pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) in Trinidad [J]. Phytoparasitica, 2015, 43(1): 37−49. DOI: 10.1007/s12600-014-0428-z
[16] BAIRD R E, MULLINIX B G, PEERY A B. Diversity and longevity of the soybean debris mycobiota in a no-tillage system [J]. Plant disease, 1997, 81(5): 530−534. DOI: 10.1094/PDIS.1997.81.5.530
[17] CHEN L S, CHU C, LIU C D, et al. PCR-based detection and differentiation of anthracnose pathogens, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and C. truncatum, from vegetable soybean in Taiwan [J]. Journal of Phytopathology, 2006, 154(11-12): 654−662. DOI: 10.1111/j.1439-0434.2006.01163.x
[18] 陈吴健. 大豆豆荚炭疽病的病原鉴定及其防治[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2007. CHEN W J. Identification and control of soybean pod anthracnose[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2007. (in Chinese)
[19] 肖杰文, 刘月廉, 冉俊祥, 等. 巴西大豆中炭疽菌的分离鉴定研究 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(5):333−337. XIAO J W, LIU Y L, RAN J X, et al. Identification of Colletotrichum isolates from Brazil soybean [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2011, 27(5): 333−337.(in Chinese)
[20] DAMM U, SATO T, ALIZADEH A, et al. The Colletotrichum dracaenophilum, C. magnum and C. orchidearum species complexes [J]. Studies in Mycology, 2019, 92: 1−46. DOI: 10.1016/j.simyco.2018.04.001
[21] 李海云, 靳帅, 张学勤, 等. 大豆炭疽病菌Colletotrichum chlorophyti的鉴定 [J]. 植物保护, 2017, 43(2):163−166. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.2017.02.028 LI H Y, JIN S, ZHANG X Q, et al. Identification of Colletotrichum chlorophyti causing soybean anthracnose [J]. Plant Protection, 2017, 43(2): 163−166.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.2017.02.028
[22] YANG H C, STEWART J M, HARTMAN G L. First report of Colletotrichum chlorophyti infecting soybean seed in Arkansas, United States [J]. Plant Disease, 2013, 97(11): 1510.
[23] 林敬州, 姜聪, 汪自强, 等. 大豆种质资源对大豆豆荚炭疽病的抗性评价 [J]. 浙江农业科学, 2013, 54(2):166−168. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0528-9017.2013.02.020 LIN J Z, JIANG C, WANG Z Q, et al. Resistance evaluation of soybean resources to soybean pod anthracnose [J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 54(2): 166−168.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0528-9017.2013.02.020
[24] 徐晶. 平头炭疽菌对大豆抗感品种的致病差异及其MAPK基因CtPMK1的功能研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2013. XU J. Disease differences of Colletotrichum truncatum on resistant and susceptible soybean lines and characterization of a mapk gene CTPMK1in the pathogen[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2013. (in Chinese)
[25] 连金番, 杜宜新, 赵志刚, 等. 宁夏春大豆炭疽病病原菌形态学分类鉴定研究 [J]. 宁夏农林科技, 2019, 60(7):25−26. LIAN J P, DU YX, ZHAO ZG, et al. Morphological classification and identification of spring soybean anthrax pathogens in Ningxia [J]. Ningxia Journal of Agriculture and Forestry Science &Technology, 2019, 60(7): 25−26.(in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 陈敏氡,王彬,林霜霜,朱海生,余文权. 福建省蔬菜种质收集、保存、鉴评与利用. 中国蔬菜. 2025(01): 13-18 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 田鑫,钟程,韩珊. 2种大豆对炭疽病抗性生理的研究. 现代园艺. 2024(01): 45-48+53 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 许涛,胡旭,孙劝劝,章武,贺俐,许廷晨,杨虎彪,吴杨,王志勇. 海雀稗种质资源币斑病抗性鉴定. 分子植物育种. 2024(18): 6090-6100 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 石妞妞,连金番,邱德柱,居骋,张楠,殷越,李本金,杜宜新. 野尻链霉菌9-13对大豆炭疽病病原菌的抑制活性及作用机制. 植物保护学报. 2024(04): 830-840 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李艺阳,吴冕,王幸,顾和平,陈新,崔晓艳. 大豆炭疽病病原鉴定及大豆种质资源抗病性评价. 植物病理学报. 2024(06): 1167-1178 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 李月,林剑浩,年海,饶军华,周而勋. 南方大豆品种炭疽病抗性鉴定及抗病相关基因表达分析. 大豆科学. 2023(01): 12-22 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 廖旺姣,邹东霞,常明山,钟雅婷,黄乃秀. 八角无性系对炭疽病抗性的快速测定. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学). 2023(01): 41-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 陈夕军,陈莹,石童,蒋冬阳,凌焕贵,陈宸. 大豆常见病害症状、病原种类及其生理分化. 大豆科技. 2023(02): 27-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李建飞,王肖肖,舒跃,黄奇,唐桂香. 大豆炭疽病的分类、流行监测与防治研究进展. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版). 2023(04): 463-471 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. SHI Niu-niu,LIAN Jin-pan,QIU De-zhu,CHEN Fu-ru,DU Yi-xin. Resistance risk and molecular mechanism associated with resistance to picoxystrobin in Colletotrichum truncatum and Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Journal of Integrative Agriculture. 2023(12): 3681-3693 .  必应学术
必应学术
11. 张玉梅,蓝新隆,陈伟,滕振勇,陆佩兰,林国强,胡润芳. 鲜食大豆新品种闽豆10号的选育及特征特性. 福建农业学报. 2022(05): 572-577 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(4)




 下载:
下载:
