Study on Bacteriostatic Characteristics of Lactobacillus plantarum LV02 and Optimization of Fermentation Medium
-
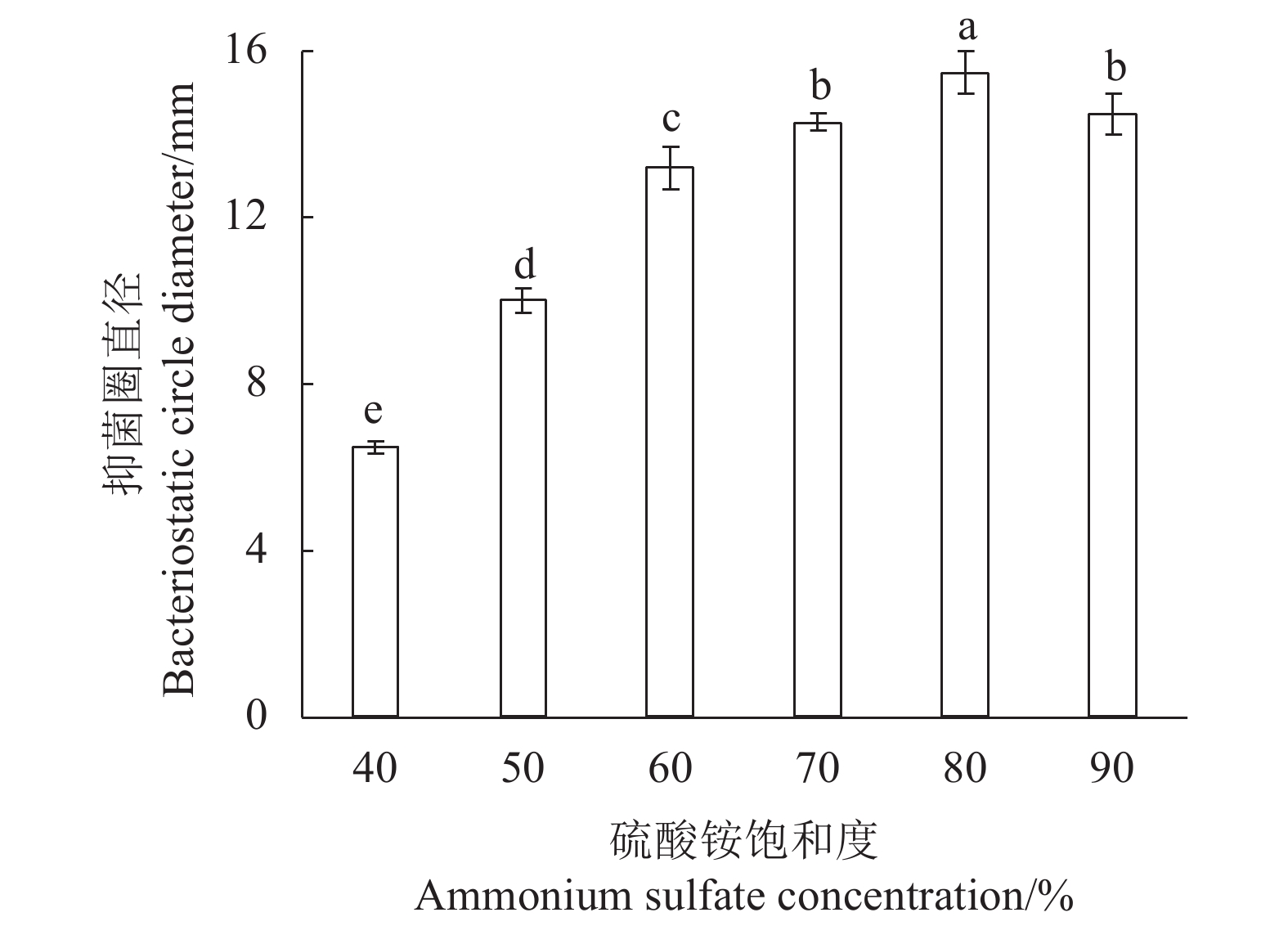
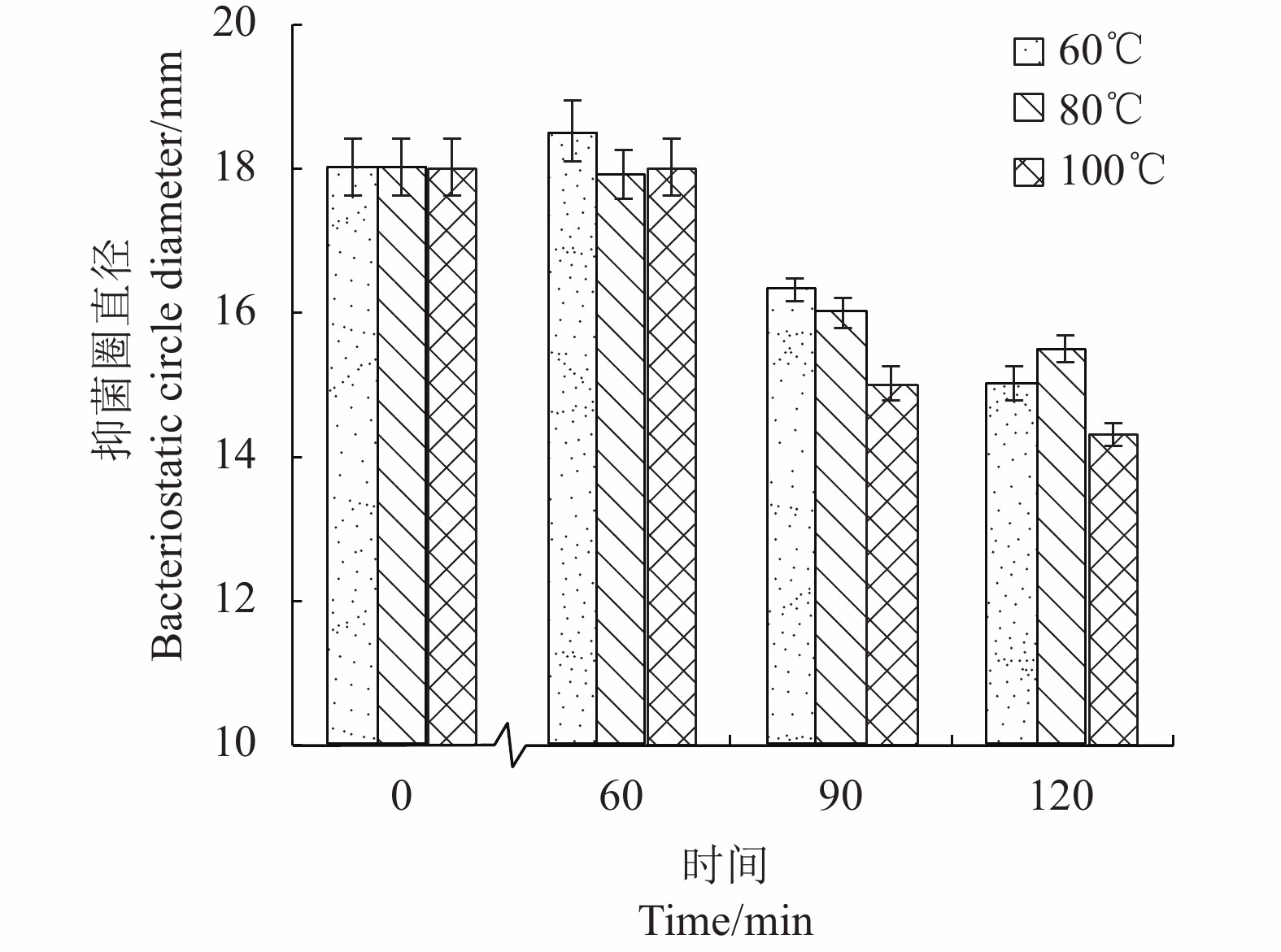
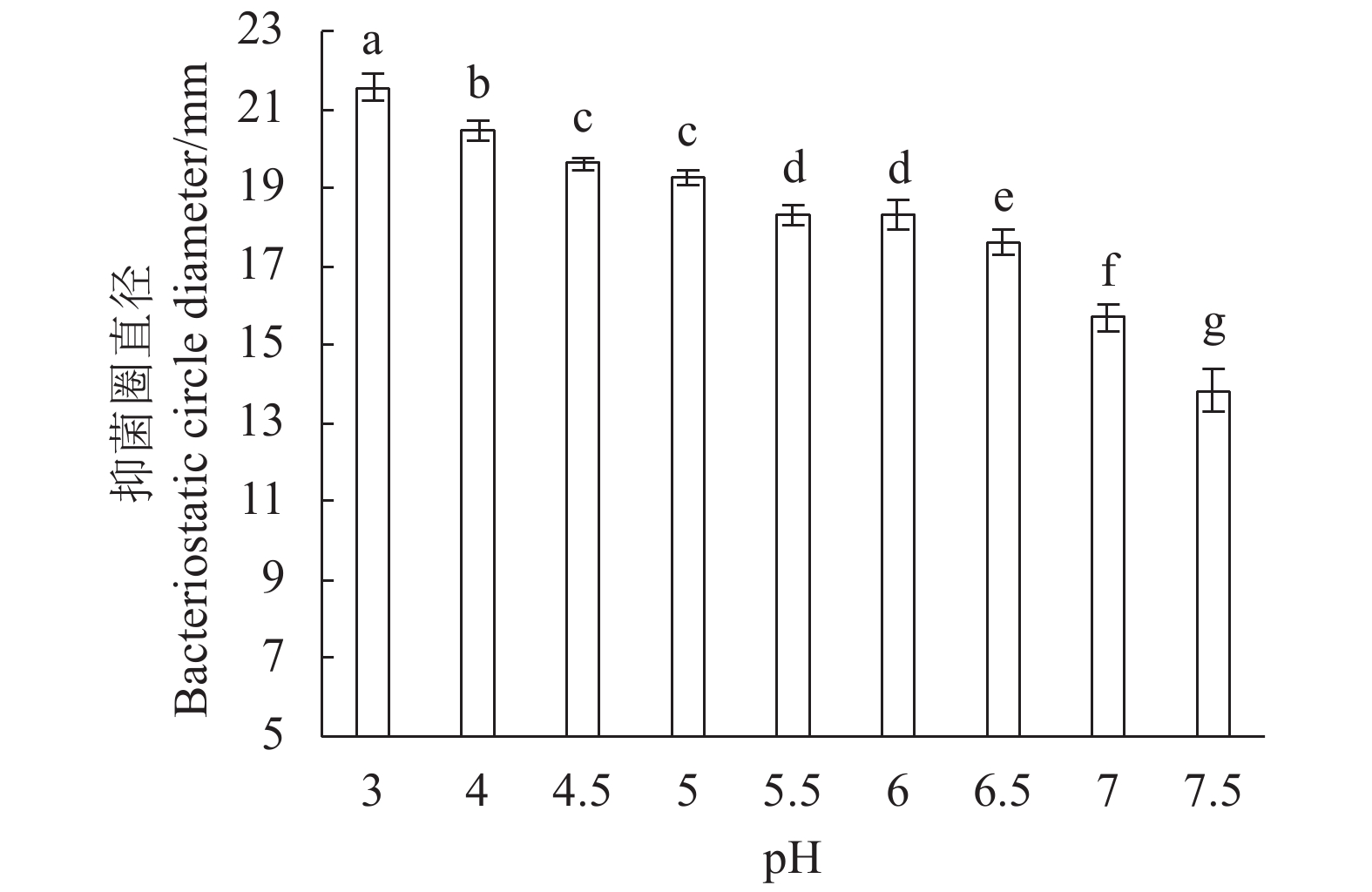
摘要:目的 优化植物乳杆菌LV02发酵培养基,研究其抑菌特性,为开发抗菌保鲜类产品提供技术参考。方法 以大肠杆菌YS为指示菌,抑菌圈直径及生物量OD600为评价指标。在单因素试验的基础上,采用PB试验初步确定各因素的高低水平,接着采用最陡爬坡试验进一步确定步长及方向来接近最大产值,确定CCD试验中心点。最后,采用CCD设计试验,研究各影响因素及其交互作用对植物乳杆菌LV02抑菌性及生物量OD600的影响,确定各影响因素的最佳水平。并通过牛津杯法研究LV02的抑菌特性,来确定应用环境的设定范围。结果 LV02的优化发酵培养基配方为:葡萄糖34.07 g·L−1、酵母浸粉18.12 g·L−1、磷酸氢二钾2 g·L−1、硫酸锰0.16 g·L−1、乙酸钠5 g·L−1、硫酸镁0.20 g·L−1、柠檬酸铵1 g·L−1、吐温80 1 mL·L−1、胡萝卜汁50 mL·L−1,蒸馏水1 L。以5%接种,37 ℃培养24 h,结果为对大肠杆菌YS的抑菌圈直径比未优化前提高了近26%,OD600提高了12%。通过抑菌特性的分析,确定了粗提植物乳杆菌LV02的细菌素所需硫酸铵饱和度为80%,证明了植物乳杆菌LV02具有热稳定性(100 ℃,120 min)、酸碱稳定性(pH 3.0~7.5)及抑菌性。结论 采用CCD试验优化植物乳杆菌LV02发酵培养基,可有效提高生物量OD600及对大肠杆菌YS的抑菌性。通过牛津杯法研究LV02的抑菌特性,确定了pH、温度具稳定性的设定范围。Abstract:Objective Bacteriostatic property of Lactobacillus plantarum LV02 bacteriocin produced on an optimized fermentation medium was determined.Method Based on a single-factor design, the PB and the steepest ascent experiments were conducted to locate the center point of the step length and direction of the influencing factors for a CCD test. Subsequently, effects of different media on the bacteriostatic property and OD600 of the cultured L. plantarum LV02 were evaluated for formulation optimization. The Oxford cup method was employed to determine the bacteriostatic capacity and stability under application conditions of the resulting LV02 bacteriocin produced on the optimized medium.Result The optimized formula for the LV02 fermentation medium in 1 L of water constituted 34.07 g of glucose, 18.12 g of yeast extract, 2 g of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 0.16 g of manganese sulfate, 5 g of sodium acetate, 0.20 g of magnesium sulfate, 1 g of ammonium citrate, 1 mL of Tween 80, and 50 mL of carrot juice. On the optimized medium, LV02 grew to yield a 12% increase on OD600 and bacteriocin with a 26% increase on the diameter of inhibition zone against Escherichia coli YS. For the crude LV02 bacteriocin extraction, 80% saturation concentration of ammonium sulfate was used. The
antibacterial LV02 bacteriocin was stable under 100 ℃ for 120 m and pH 3.0~7.5. Conclusion L. plantarum LV02 cultured on the optimized fermentation medium was bacteriostatic against E. coli YS. The fermentation produced bacteriocin with desirable stabilities to heat, acid, and slight alkaline condition and was considered promising for the development of an antibacterial agent. -
0. 引言
【研究意义】云南山茶是山茶科(Theaceae)山茶属(Camellia)的常绿乔木或灌木,又称滇山茶、云南红花油茶等。云南山茶原产于中国的西南地区,是中国特有种,也是国家二级濒危植物[1−4]。云南山茶因树形高大、花色艳丽且花期长,被誉为云南八大名花之首。其花可入药,种子含油量较高,被誉为“东方橄榄油”,是优质的食用油,且可食药兼用[5]。因此,云南山茶具有广阔的开发利用前景。云南山茶主要分布于西南山区,这些区域土壤瘠薄,干燥少雨,虽然经过多年进化,云南山茶对西南山区环境有了一定适应性。但随着气候环境变化,西南山区近年来旱灾频发,致使云南山茶面临着干旱胁迫的风险[6]。山茶属植物的正常生长发育对水分需求量大,在干旱环境,山茶属植物可通过渗透调节、活性氧清除、植物激素代谢等一系列生理反应来响应干旱胁迫[7],因此研究云南山茶渗透调节物质和植物激素对干旱胁迫的响应,对提高云南山茶抗旱途径,增强其抵御干旱的能力提供理论依据。【前人研究进展】脱落酸(abscisic acid, ABA)是一种重要的植物非生物胁迫应急激素,在植物生长发育和应对各种逆境胁迫中起到重要的调节作用。研究表明,ABA在植物干旱胁迫响应中发挥着重要作用。干旱导致植物中ABA含量大幅提高,从而激活ABA信号转导通路,实现适应干旱环境的生理生化响应[8]。当植物遇到干旱胁迫时,根尖较地上部更为敏感,能合成大量的ABA,经木质部运输和激素信号转导,导致蒸腾速率降低、气孔关闭[9,10]。林先玉等[11,12]发现云南山茶在重度干旱胁迫及复水过程中,云南山茶抗氧化酶系统及叶绿素荧光指标受到影响,喷施外源ABA的云南山茶叶片失水量减少,干旱得到了有效的缓解。郭安红等[13]发现玉米(Zea mays L.)在应对干旱胁迫时,其根、茎、叶中各内源激素积累情况有显著差异。植物内源激素彼此之间是相互作用、相互调节的,而外界环境的影响导致植物内源激素的变化比较复杂,目前,国内外学者对内源激素在干旱胁迫下响应规律尚未统一,即便是同一植物不同时期内源激素的变化也有差别。【本研究切入点】干旱下植物不同组织部位内源激素应对逆境的差异,外源ABA如何影响其他内源激素进而提高植株的耐旱力,还需进一步研究。【拟解决的关键问题】以云南山茶幼苗为材料,研究喷施外源ABA对干旱胁迫下云南山茶幼苗根和叶内源激素代谢的影响,为云南山茶耐旱力研究提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
选取6棵生长状况良好、长势一致、无病虫害的两年生(嫁接苗)云南山茶品种苗紫袍为研究材料,平均株高约45 cm,单株定植于塑料花盆(上口径25 cm、下口径20 cm)中,置于西南林业大学后山树木园培养,培养基质为黄壤土、腐质土、珍珠岩、蛭石,质量比为2∶6∶1∶1。
1.2 试验设计
本试验采用 PEG 模拟干旱法进行干旱胁迫。将筛选好的苗从盆中取出,洗净,分为两组,分别标记为D1、D2,培养于装有10 L pH5.5营养液(配方由中国科学院南京土壤研究所提供)的塑料箱中,用带孔硬质泡沫板和海绵固定植株。每天充分供氧,缓苗3 d后,将以上两组苗进行如下处理:①D1(重度干旱)在营养液加入20%(质量分数)PEG_6000,模拟严重干旱胁迫条件作为对照组;②D2(重度干旱+脱落酸)在营养液加入20%(质量分数) PEG_6000,模拟严重干旱胁迫条件,并于干旱胁迫前3 d直至干旱胁迫结束每天早晚8:00叶面喷施质量浓度为100 mg·L−1的脱落酸作为处理组,喷施程度为叶片正反面均匀喷洒至饱和水滴开始滴落。D1组喷施等量蒸馏水,干旱胁迫后将两组苗重新培养于营养液中进行复水处理。在胁迫开始的第0、24、48、72 h以及复水后24、72 h分别对各根和叶进行取样,采样时选取云南山茶自顶芽第3~5片完全舒展开的功能叶及植株须根,每个时间点取3个重复,样品使用液氮速冻后置于−80 ℃冰箱保存备用(表1)。
表 1 试验处理组别代表符号Table 1. Symbols for various treatments处理组
Treatment group组织部位
Tissue site干旱胁迫时长
Drought stress duration复水后24 h(R24 h)
24 h after rehydration复水后72 h(R72 h)
72 h after rehydration0 h 24 h 48 h 72 h D1 根(G1) G0 h G24 h G48 h G72 h GR24 h GR72 h 叶(Y1) Y0 h Y24 h Y48 h Y72 h YR24 h YR72 h D2 根(G2) G0 hA G24 hA G48 hA G72 hA GR24 hA GR72 hA 叶(Y2) Y0 hA Y24 hA Y48 hA Y72 hA YR24 hA YR72 hA 1.3 生理指标测定
渗透调节物质等参考李合生[14]的方法测定:可溶性糖(Soluble sugar,SS)采用蒽酮比色法;可溶性蛋白(Soluble protein,SP)采用考马斯亮蓝显色法;游离脯氨酸(Free proline,Pro)含量采用茚三酮显色法。
1.4 代谢组检测
选取D1、D2组胁迫 0、72 h 以及恢复 72 h 根和叶的样本,每个时间点3 个生物学重复,共36个样本,由武汉迈维生物科技有限公司进行靶向内源激素代谢检测。根和叶的处理方法参照Li[15]、 Floková[16]等的方法。数据采集仪器系统主要包括超高效液相色谱(Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography, UPLC)(ExionLC™ AD,https://sciex.com.cn/)和串联质谱(Tandem Mass Spectrometry, MS/MS)(QTRAP® 6500+,https://sciex.com.cn/)[17,18]。液相条件为色谱柱:Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 C18柱(1.8 µm,100 mm×2.1 mm i.d.);流动相:A相,超纯水(加入0.04%的乙酸);B相,乙腈(加入0.04%的乙酸);梯度洗脱程序:0 min A/B为95∶5(V/V),1.0 min A/B为95∶5(V/V),8.0 min为5∶95(V/V),9.0 min为5∶95(V/V),9.1 min为95∶5(V/V),12.0 min为95∶5(V/V);流速0.35 mL·min−1;柱温40 °C;进样量2 μL。质谱条件:电喷雾离子源(Electrospray Ionization, ESI)温度 550 °C,正离子模式下质谱电压
5500 V,负离子模式下质谱电压−4500 V,气帘气(Curtain Gas, CUR)35 psi。在Q_Trap 6500+中,每个离子对是根据优化的去簇电压(declustering potential, DP)和碰撞能(collision energy, CE)进行扫描检测。采用Analyst 1.6.3软件采集质谱数据,基于标准品构建MWDB(Metware Database)数据库,对质谱检测的数据进行定性分析。定量分析是利用三重四级杆质谱的多反应监测模式(Multiple Reaction Monitoring, MRM)分析完成。获得不同样本的质谱分析数据后,采用MultiQuant 3.0.3软件处理质谱数据,对所有目标物的色谱峰进行积分,通过标准曲线进行定量分析[19]。1.5 数据处理
结合单变量统计分析和多变量统计分析的方法,采用差异倍数(Fold change, FC)分析、正交偏最小二乘判别分析(OPLS_DA)模型,对于两组比较:根据 fold change ≥ 2或fold change ≤ 0.5 筛选差异代谢物。采用Origin 2022、TBtools、Excel、SPSS、GraphPad Prism 8、迈维云平台(https://cloud.metware.cn/)、联川生物云平台(https://www.omicstudio.cn/)绘制相关图表进行可视化分析;采用KEGG进行代谢通路富集分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 脱落酸对干旱胁迫下云南山茶渗透调节物质的影响
在干旱胁迫及复水处理下云南山茶根系和叶片中可溶性糖、可溶性蛋白、游离脯氨酸含量均发生了显著变化,且叶片中的含量均显著高于根系(图1)。在云南山茶叶片中,可溶性蛋白和可溶性糖含量表现为D2<D1,其中可溶性蛋白含量仅在48 h和72 h 表现为D2>D1,可溶性糖含量仅在72 h表现为D2>D1;游离脯氨酸含量表现为D2>D1且变化显著。在云南山茶根系中,可溶性蛋白和可溶性糖含量表现为D2>D1,可溶性蛋白和可溶性糖在72 h后逐渐表现为D2<D1;游离脯氨酸含量表现为D2<D1且变化显著。
![]() 图 1 云南山茶根和叶渗透调节物质含量不同小写字母表示云南山茶根和叶不同时间处理间的差异显著性(P<0.05)。不同大写字母表示同一时间云南山茶根和叶处理间的差异显著性(P<0.05)。图5同。Figure 1. Contents of osmoregulatory substances in roots and leaves of C. reticulataData with different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at sampling times (P<0.05); those with different capital letters indicate significant differences at same sampling time (P<0.05). Same for Fig. 5.
图 1 云南山茶根和叶渗透调节物质含量不同小写字母表示云南山茶根和叶不同时间处理间的差异显著性(P<0.05)。不同大写字母表示同一时间云南山茶根和叶处理间的差异显著性(P<0.05)。图5同。Figure 1. Contents of osmoregulatory substances in roots and leaves of C. reticulataData with different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at sampling times (P<0.05); those with different capital letters indicate significant differences at same sampling time (P<0.05). Same for Fig. 5.2.2 内源激素代谢组分析
在D1组和D2组中共检测到88种激素化合物,包括2种ABA、26种IAA、36种CKs、10种GA、9种JA、2种SA、1种乙烯类化合物(Ethylene, ETH)、2种独角金内酯(Strigolactones, SL)(图2a)。基于云南山茶幼苗不同处理组根和叶两个部位与内源激素含量进行主成分分析,绘制PCA散点图(图2b)。结果表明,各处理样品组内聚集情况良好,表明样品具有良好的生物学重复。根和叶两个不同组织之间明显分离,表明在样品不同部位中,根和叶两个处理组各时间段内源激素具有明显差异。特别是叶片的几组处理,分离最为显著,这表明喷施了外源脱落酸后,干旱胁迫下的山茶叶片中内源激素的变化最为显著。
2.3 内源激素差异代谢物筛选
本研究可分为胁迫期(0 h_vs_72 h)和复水期(72 h_vs_R72 h)两个时期。在胁迫期D1组和D2组根系中分别筛选到16、22种内源激素差异代谢物,G0 h_vs_G72 h中10种表达上调,6种表达下调;G0 hA_vs_G72 hA中17种表达上调,5种表达下调(图3a),D1组和D2组之间存在10种共有差异代谢物(图3b)。在胁迫期D1组和D2组叶片中分别筛选到24、21种差异代谢物,Y0 h_vs_Y72 h中22种表达上调,2种表达下调;Y0 hA_vs_Y72 hA中18种表达上调,3种表达下调(图3a),D1组和D2组之间存在16种共有差异代谢物(图3b)。在复水期D1组和D2组根系中分别筛选到26、17种内源激素差异代谢物,G72 h_vs_GR72 h中10种表达上调,16种表达下调;G72 hA_vs_GR72 hA中3种表达上调,14种表达下调(图3c),D1组和D2组之间存在11种共有差异代谢物(图3d)。在复水期D1组和D2组叶片中分别筛选到22、25种差异代谢物,Y72 h_vs_YR72 h中19种表达上调,3种表达下调;Y72 hA_vs_YR72 hA中21种表达上调,4种表达下调(图3c),D1组和D2组之间存在17种共有差异代谢物(图3d)。
2.4 内源激素差异代谢物KEGG富集分析
为了探究外源ABA对干旱及复水下云南山茶根和叶两个组织部位内源激素代谢影响的差异,对D2组的差异显著代谢物进行KEGG通路富集分析,发现其富集在玉米素生物合成(Zeatin biosynthesis)、代谢途径(Metabolic pathway)、次生代谢物的生物合成(Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites)、植物激素信号转导(Plant hormone signal transduction)、二萜生物合成(Diterpene biosynthesis)、色氨酸代谢(Tryptophan metabolism)、多种生物碱的生物合成(Biosynthesis of various alkaloids)、氨酰生物合成(Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis)、辅因子生物合成(Biosynthesis of cofactor)、2-氧羧酸代谢(2-oxycarboxylic acid metabolism)等多种代谢通路中。但云南山茶幼苗的根部和叶部的差异显著代谢物显著富集通路不一致(图4)。其中,根部的胁迫期和复水期差异代谢物均显著富集在二萜生物合成通路;叶部胁迫期差异代谢物显著富集在植物激素信号转导途径,复水期显著富集在玉米素生物合成通路。
![]() 图 4 差异代谢物的KEGG富集横坐标表示每个通路对应的富集因子,纵坐标为通路名称,点的颜色为P值,越红表示富集越显著。点的大小代表富集到的差异代谢物的个数多少。a:G0 hA_vs_G72 hA,b:Y0 hA_vs_Y72 hA,c:G72 hA_vs_GR72 hA,d:Y72 hA_vs_YR72 hA。Figure 4. KEGG enrichment map of differential metabolitesHorizontal coordinate: rich factor corresponding to each pathway; vertical coordinate: path name; dot color: P value, the deeper the red color, the more significant the enrichment; dot size: number of differentiated metabolites enriched; a: G0hA_vs_G72hA; b: Y0hA_vs_Y72hA; c: G72hA_vs_GR72hA; d: Y72hA_vs_YR72hA.
图 4 差异代谢物的KEGG富集横坐标表示每个通路对应的富集因子,纵坐标为通路名称,点的颜色为P值,越红表示富集越显著。点的大小代表富集到的差异代谢物的个数多少。a:G0 hA_vs_G72 hA,b:Y0 hA_vs_Y72 hA,c:G72 hA_vs_GR72 hA,d:Y72 hA_vs_YR72 hA。Figure 4. KEGG enrichment map of differential metabolitesHorizontal coordinate: rich factor corresponding to each pathway; vertical coordinate: path name; dot color: P value, the deeper the red color, the more significant the enrichment; dot size: number of differentiated metabolites enriched; a: G0hA_vs_G72hA; b: Y0hA_vs_Y72hA; c: G72hA_vs_GR72hA; d: Y72hA_vs_YR72hA.2.5 主要内源激素差异代谢物变化规律
2.5.1 脱落酸(ABA)和水杨酸(SA)
云南山茶在胁迫期及复水期,根和叶中发生显著差异(|Log2FC|>1)的ABA仅有2种,SA仅有1种,且SA仅在叶片中发生了显著差异(图5)。在胁迫期,D2组的内源ABA显著高于D1组,根中ABA显著高于叶片(图5a),其中ABA-GE仅在D2组的根部积累,叶部无积累(图5b);D2组叶片中SA呈逐渐降低的趋势,D1组趋势与D2组相反(图5c)。在复水期,D2组和D1组叶片中SA均呈逐渐增加的趋势,而ABA与ABA-GE呈现下降或缓慢增长的趋势。
2.5.2 赤霉素(GA)和茉莉酸(JA)
云南山茶根和叶在胁迫期及复水期表现显著差异(|Log2FC|>1)的GA有3种,JA有8种,GA和JA分别在植物的根系和叶片中发生显著变化(图6)。在胁迫期,GA3和GA53在植株根部的积累均显著高于叶部,且GA3和GA53在D2组中的水平著高于D1组,GA1在D2组中的积累显著低于D1组,GA3和GA53随着胁迫时间的推移逐渐升高。JA在D1组和D2组中主要呈增加趋势,D1组和D2组中共有的差异代谢物变化趋势基本一致,且H2JA、JA-ILE在D2组中的积累高于D1组。在复水处理下,植株根和叶两个组织中GA3和GA53均呈下降的趋势,根部GA1水平逐渐降低至0;JA在D1组和D2组中主要呈增加趋势,D1组和D2组中共有的差异代谢物变化趋势基本一致,只有H2JA在D1组呈上调,在D2组中却呈下调,H2JA、OPDA、JA-Val、JA-ILE在D2组中的积累显著低于D1组。
![]() 图 6 胁迫期及复水期3种赤霉素含量变化及茉莉酸热图上下调图中蓝色柱状为D1组,红色柱状为D2组,蓝色方框框选的代谢物为D1组和D2组共有的差异代谢物,未框选的即为特有差异代谢物,下同。a、b、c:3种赤霉素含量变化;d:胁迫期叶片中茉莉酸热图,e:复水期叶片中茉莉酸热图。Figure 6. GA and JA heat map of plant under stress and after rehydrationIn upper and lower diagrams, blue bar: Group D1; red bar: Group D2; metabolites in blue box: differential metabolites shared by D1 and D2; unselected metabolites: unique differential metabolites. Same for below. a, b, c: contents of 3 kinds of GA; d: heat map of JA in leaves under stress; e: heat map of JA in leaves after rehydration.
图 6 胁迫期及复水期3种赤霉素含量变化及茉莉酸热图上下调图中蓝色柱状为D1组,红色柱状为D2组,蓝色方框框选的代谢物为D1组和D2组共有的差异代谢物,未框选的即为特有差异代谢物,下同。a、b、c:3种赤霉素含量变化;d:胁迫期叶片中茉莉酸热图,e:复水期叶片中茉莉酸热图。Figure 6. GA and JA heat map of plant under stress and after rehydrationIn upper and lower diagrams, blue bar: Group D1; red bar: Group D2; metabolites in blue box: differential metabolites shared by D1 and D2; unselected metabolites: unique differential metabolites. Same for below. a, b, c: contents of 3 kinds of GA; d: heat map of JA in leaves under stress; e: heat map of JA in leaves after rehydration.2.5.3 生长素(IAA)和细胞分裂素(CKs)
干旱及复水处理下,有15种IAA和27种CKs在云南山茶中发生了显著(|Log2FC|>1)改变(图7)。在胁迫期根系中,IAA在D1组呈下调趋势,在D2组呈上调趋势;而CKs在D1组和D2组中主要呈上升趋势。其中IAA-Ala、TRA仅在D1组呈显著下调,ILA仅在D2组呈显著上调,且IAA-Ala、IAA-Leu、ILA在D2组中水平显著高于D1组(图7a);2MeScZR、IPR、cZR、BAP、IP、oT、tZ、DHZR、cZ在D2组中的激素水平显著高于D1组(图7b)。在胁迫期叶片中,IAA和CKs在D1组和D2组均呈上调趋势。其中ICA、MEIAA仅在D1组显著上调,且OxIAA、IAN、IAA-Glc、IAA-Asp、ICA、MEIAA在D2组中水平显著低于D1组(图7c);mT9G、IPR、DZ、DHZR等仅在D1组显著上调,且IP、cZR、cZ、pT9G、mT9G、IPR、DZ、DHZR在D2组中的水平显著低于D1组(图7d)。
![]() 图 7 胁迫期及复水期生长素、细胞分裂素热图及上下调图a:胁迫期根系中生长素热图,b:胁迫期根系中细胞分裂素热图,c:胁迫期叶片中生长素热图,d:胁迫期叶片中细胞分裂素热图,e:复水期期根系中生长素热图,f:复水期根系中细胞分裂素热图,g:复水期叶片中生长素热图,h:复水期叶片中细胞分裂素热图。Figure 7. Heat and up-down maps of IAA and cytokinin in plant under stress and after rehydrationa: IAA heat map in roots under stress; b: cytokinin heat map in roots under stress; c: IAA heat map in leaves under stress; d: cytokinin heat map in leaves under stress; e: IAA heat map in roots after rehydration; f: cytokinin heat map in roots after rehydration; g: IAA heat map in leaves after rehydration; h: cytokinin heat map in leaves after rehydration.
图 7 胁迫期及复水期生长素、细胞分裂素热图及上下调图a:胁迫期根系中生长素热图,b:胁迫期根系中细胞分裂素热图,c:胁迫期叶片中生长素热图,d:胁迫期叶片中细胞分裂素热图,e:复水期期根系中生长素热图,f:复水期根系中细胞分裂素热图,g:复水期叶片中生长素热图,h:复水期叶片中细胞分裂素热图。Figure 7. Heat and up-down maps of IAA and cytokinin in plant under stress and after rehydrationa: IAA heat map in roots under stress; b: cytokinin heat map in roots under stress; c: IAA heat map in leaves under stress; d: cytokinin heat map in leaves under stress; e: IAA heat map in roots after rehydration; f: cytokinin heat map in roots after rehydration; g: IAA heat map in leaves after rehydration; h: cytokinin heat map in leaves after rehydration.在复水期根系中,IAA在D1组和D2组主要呈升高趋势,而CKs在D1组和D2组主要呈降低趋势。其中IAA-Glu、ICAlD仅在D1组显著下调,IAA-Asp仅在D2组显著上调,且IAA-Leu、ICAld、IAA-Asp在D2组中的水平高于D1组(图7e);2MeSip、cZ、DHZR、K9G等仅在D1组显著上调,IPR、DHZROG、IP等仅在D2组显著下调,且cZROG、2MeSip、DHZR、K9G、DHZROG在D2组中的水平显著低于D1组(图7f)。在复水期叶片中,IAA和CKs在D1组和D2组主要呈上调趋势。其中OxIAA、IAA-Glc、IAA-Phe仅在D2组显著上调,且ILA、MEIAA、IAA-Asp、OxIAA、IAA-Glc、IAA-Phe在D2组中的积累显著高于D1组(图7g);BAP、iP7G、IPR、tZR等仅在D2组中呈显著上调,且DHZR、cZR、BAP、iP7G、tZR在D2组中的含量显著高于D1组(图7 h)。
2.5.4 生理指标与差异代谢物相关性分析
将检测出的ABA、GA、SA、JA、CKs、IAA中的各自不同种激素含量相加并与渗透调节物质进行相关性分析,结果表明云南山茶幼苗根部(表2)SP、SS与IAA、GA、SA;SS与SP;IAA与GA、SA均呈显著正相关;叶部(表3)SS与IAA、CKs、GA、JA、SA;IAA与CKs、GA、JA;GA与CKs、JA、SA;CKs与SA均呈显著正相关。
表 2 云南山茶幼苗根部生理指标、内源激素的相关系数Table 2. Correlation coefficient of physiological indexes and endogenous hormones of C. reticulata roots生理指标/激素
Physiological indicators/Hormone生理指标/激素
Physiological indicators/Hormone相关性
CorrelationSP IAA 0.948** SP GA 0.831* SP SA 0.976** SP SS 0.954* SS IAA 0.917* SS GA 0.844* SS SA 0.907* IAA GA 0.917* IAA SA 0.875* **表示极显著相关(P<0.01),*表示显著相关(P<0.05)。下同。
**: extremely significant correlation at P<0.01; *: significant correlation at P<0.05. Same for below.表 3 云南山茶幼苗叶部生理指标、内源激素间的相关系数Table 3. Correlation coefficient between physiological indexes and endogenous hormones of C. reticulata leaves生理指标/激素
Physiological indicators/Hormone生理指标/激素
Physiological indicators/Hormone相关性
CorrelationSS IAA 0.902* SS CKs 0.914* SS GA 0.944** SS JA 0.886* SS SA 0.958** IAA CKs 0.841* IAA GA 0.899* IAA JA 0.944** GA CKs 0.936** GA JA 0.915* GA SA 0.896* CKs SA 0.879* 3. 讨论
3.1 云南山茶幼苗根和叶对干旱胁迫及复水处理的差异响应
本试验中云南山茶渗透调节物质在叶片中的含量积累显著高于根系,干旱胁迫下叶片中渗透物质的变化较根系更为显著,这可能由于叶片是渗透调节物质主要产生部位,干旱胁迫下渗透物质的主要调节部位以叶片为主,与季杨等[20]关于在干旱下鸭矛(Dactylis glomerata)叶片渗透物质积累高于根系的结果一致。本研究发现在胁迫期,云南山茶根系通过积累ABA、GA含量,降低IAA含量来响应干旱胁迫,叶片通过提高ABA、JA、SA、IAA含量来应对干旱胁迫。ABA不仅参与植物生长发育调控,还可作为关键调节因子参与非生物胁迫应答,增强植物防御能力和耐旱性[21]。项洪涛等[22]研究表明ABA主要通过调节叶片气孔开闭实现植物对体内水分平衡的控制,提高植物在干旱环境下的耐受力。本研究中,干旱胁迫下云南山茶根系和叶片中ABA含量均发生了明显积累,其中根系中ABA含量积累显著高于叶部,这与任敏等[23]关于根对ABA的反应比地上部敏感,根尖在干旱环境下能合成大量ABA的研究结果一致。路萍[24]研究发现,在干旱胁迫下,植株会抑制IAA从地上部向根系转运,导致IAA在地上部大量积累,使植物叶片IAA含量升高。本研究发现在干旱胁迫下云南山茶根系IAA含量呈下降趋势,而植株叶片IAA含量随着胁迫时间延长呈上升趋势,与上述研究结果一致。胡晓健等[25]研究表明GA能改变植物对水分的利用效率,促使叶片气孔关闭,减少蒸腾作用。本研究发现GA仅在云南山茶根系中发生了显著上升,在叶部呈现小幅度上升,这说明云南山茶在干旱胁迫下根系通过提高GA含量进而响应干旱胁迫。唐子贻等[26]研究发现茶树在干旱下叶片中的GA3呈显著下降趋势,与本研究结果相反。植物抗旱性是一个复杂的综合性状,受多方面因素的影响,这可能是不同物种植物之间存在的差异。SA可以作为信号分子来调控植物的基因表达从而影响其生理特性,在植物的生长发育和抵御逆境胁迫过程中也发挥着重要调控作用[27]。研究证明[28],柑橘(Citrus reticulata Blanco)在受到干旱胁迫后内源JA含量快速增加。本研究同样发现云南山茶叶片中JA和SA含量均随着胁迫时间的推移呈上升趋势而响应干旱胁迫。
王荣荣等[29]研究发现小麦(Triticum aestivum L.)在干旱复水后,植株体内ABA含量逐渐下降到正常水平,IAA含量逐渐上升,发生补偿效应。本研究也发现云南山茶在复水后胁迫症状得到缓解,植株体内水势逐渐恢复,根系和叶片均逐渐降低合成ABA,促进合成IAA,这可能是植株根系和叶片中ABA合成信号转导通路对复水条件做出响应,植株体内水势升高后促进IAA积累发生补偿效应,与上述研究结果一致。牛俊义等[30]研究发现豌豆(Pisum sativum L.)干旱后复水可引起其叶片CKs含量增加,王晓凌等[31]研究表明,玉米在干旱后复水中叶片CKs含量有增长,玉米根系中CKs会向地上部分转移,加速生长导致补偿性生长的发生,弥补干旱胁迫所减少的生长量。本研究同样发现,在复水期云南山茶根系中CKs含量大多都呈下降趋势,叶片中CKs含量呈上升趋势,说明干旱得到缓解后,根系CKs逐渐向地上部分转移,叶片持续积累CKs来响应复水处理,产生补偿效应。
魏晓芸[32]研究发现,干旱胁迫显著影响了红砂(Reaumuria songarica P.)幼苗根部次生代谢物(萜类、酚类、生物碱类、黄酮类等)的合成通路。黎运[33]研究发现油茶(Camellia oleifera A.)在干旱胁迫下,根部差异代谢物显著富集在次生代谢物合成途径上,而叶部差异代谢物显著富集在植物激素信号转导途径上。本研究KEGG富集分析同样发现,云南山茶根部在胁迫期和复水期的差异代谢物均显著富集在二萜生物合成通路;叶部在胁迫期的差异代谢物显著富集在植物激素信号转导途径,在复水期的差异代谢物显著富集在玉米素生物合成通路。
3.2 渗透调节物质与内源激素相互协作响应干旱
在植物经历干旱胁迫时,植物激素作为信号分子可以促进抗氧化酶、渗透调节物质合成,多方协调植物中对非生物胁迫的响应机制[34]。本研究发现干旱胁迫下云南山茶根系中IAA和GA与可溶性蛋白、可溶性糖均呈显著正相关,叶片中IAA、CKs、GA与可溶性糖均呈显著正相关。说明云南山茶在干旱下内源激素促进渗透调节物质合成,与张丽杰[35]和李安[36]等发现干旱下内源激素与渗透调节物质呈正相关的结果一致。
环境信号会诱导植物内源激素合成并通过单一或相互作用调控植物生长发育及新陈代谢[37]。SA不仅可独立地发挥生理作用,也可与其他植物激素(如JA、GA、IAA、CKs等)协同作用,构成植物应答环境胁迫的信号网络,从而提高植物对环境胁迫适应能力[38]。本研究也发现干旱及复水处理下根部的SA与IAA呈显著正相关,叶片中SA与GA、CKs也存在着协同作用。王霞等[39]表明GA对IAA的调节作用为干旱胁迫下GA含量增加,相应地也促进IAA含量增加,本研究干旱及复水处理下植株叶部的GA与IAA也存在着正相关,但干旱胁迫下IAA和GA都增加的机制尚需进一步研究。在干旱下JA含量会快速积累,研究表明JA与IAA、GA均存在着相互协同作用[28],对干旱下欧洲垂枝桦(Betula pendula)叶片内源激素的研究发现,CKs与干旱调节有关,且IAA与CKs的含量随着胁迫时间的推移而增加[35],CKs与IAA之间存在着相互协同的作用。本研究也发现干旱胁迫下叶片CKs与IAA,JA与IAA、GA呈显著正相关。
3.3 施用外源ABA可提高云南山茶耐旱力
植物在受到逆境胁迫时会提高渗透物质的合成能力,降低细胞渗透势,从而缓解胁迫损伤[40]。本试验发现喷施外源ABA能有效提升植株叶部游离脯氨酸的含量,根部可溶性蛋白、可溶性糖的含量,说明外源ABA可降低细胞渗透势,缓解了干旱引起的细胞水分散失,与谢静静等[41]关于外源ABA缓减小麦花后干旱胁迫的效应结果一致。张建生[42]研究发现,施用外源ABA可促进内源ABA合成,而内源ABA可有效缓解干旱,黄小珍[43]研究指出CKs信号可能依赖于ABA信号途径来调控植物对逆境胁迫的响应。本研究发现在干旱胁迫下,D2组中ABA、CKs含量显著高于D1组,说明施用外源ABA可促进植株根系和叶片合成ABA、CKs,提高植株的耐旱力,与上述研究结果一致。在干旱胁迫下D2组根系中GA的含量显著高于D1组,D2组叶片中JA的含量显著高于D1组,说明外源ABA可促进内源GA、JA的合成,这与吴萍民等[44]关于外源ABA可促进GA3含量合成,进而提高植物的耐旱力,马超[45]关于ABA与JA在干旱胁迫下相互协同,相互促进的研究结果一致。本研究表明施用外源ABA在干旱胁迫下可促进云南山茶植株根系ABA、GA、CKs积累和植株叶片ABA、JA积累,进而提高耐旱力。本研究发现在复水处理中,D2组与D1组根系中IAA的含量均呈上升趋势,CKs的含量均呈下降的趋势,且D2组根系中IAA含量高于D1组,D2组根系中CKs含量低于D1组。表明复水后,植株体内水势逐渐升高,根系中IAA含量逐渐升高发生补偿效应,CKs逐渐从根系向地上部转运。施用外源ABA可促进植株根系IAA合成,促进CKs从根系向地上部转移,进而促进植株在复水后恢复。本研究发现,在复水期D1组叶片中JA含量持续上升,D2组中JA含量显著低于D1组。表明施用外源ABA在复水期可抑制植株叶片中JA积累,减缓植株衰老,与前人研究结果一致[46]。上述结果表明施用外源ABA在复水期可促进云南山茶根系IAA的积累,降低根系中CKs含量,降低植株叶片中JA含量而调控自身机制,促进植株的恢复。
4. 结论
本研究以云南山茶幼苗作为材料,测定渗透调节物质及内源激素代谢组,通过比较分析发现云南山茶幼苗根和叶生理指标及内源激素对干旱及复水的响应不一致。干旱及复水处理下渗透调节的关键部位是在叶部。干旱胁迫下云南山茶幼苗的根部促进积累ABA、GA、CKs含量,降低IAA含量,而叶部则是促进积累ABA、JA、SA、IAA、CKs的含量。复水处理下云南山茶幼苗根部ABA、GA、CKs各激素水平逐渐下降,IAA含量逐渐上升,而叶部通过积累JA、SA、IAA、CKs含量调控自身机制。差异显著代谢物KEGG富集分析表明,根部显著富集在二萜生物合成通路中,叶部显著富集在植物激素信号转导途径和玉米素生物合成通路中。渗透调节物质与内源激素的相关性分析表明两者之间存在显著正相关。施用外源ABA在干旱胁迫下可分别提升云南山茶根部可溶性蛋白、可溶性糖、ABA、GA、CKs和叶部游离脯氨酸、ABA、JA的含量,进而提高耐旱力;在复水期可分别降低根部CKs和叶部JA的含量,促进根部和叶部IAA的合成,进而促进植株的恢复。本试验为有关逆境中植物体内各种激素之间的关系和变化规律及KEGG富集通路的分析提供理论依据。
-
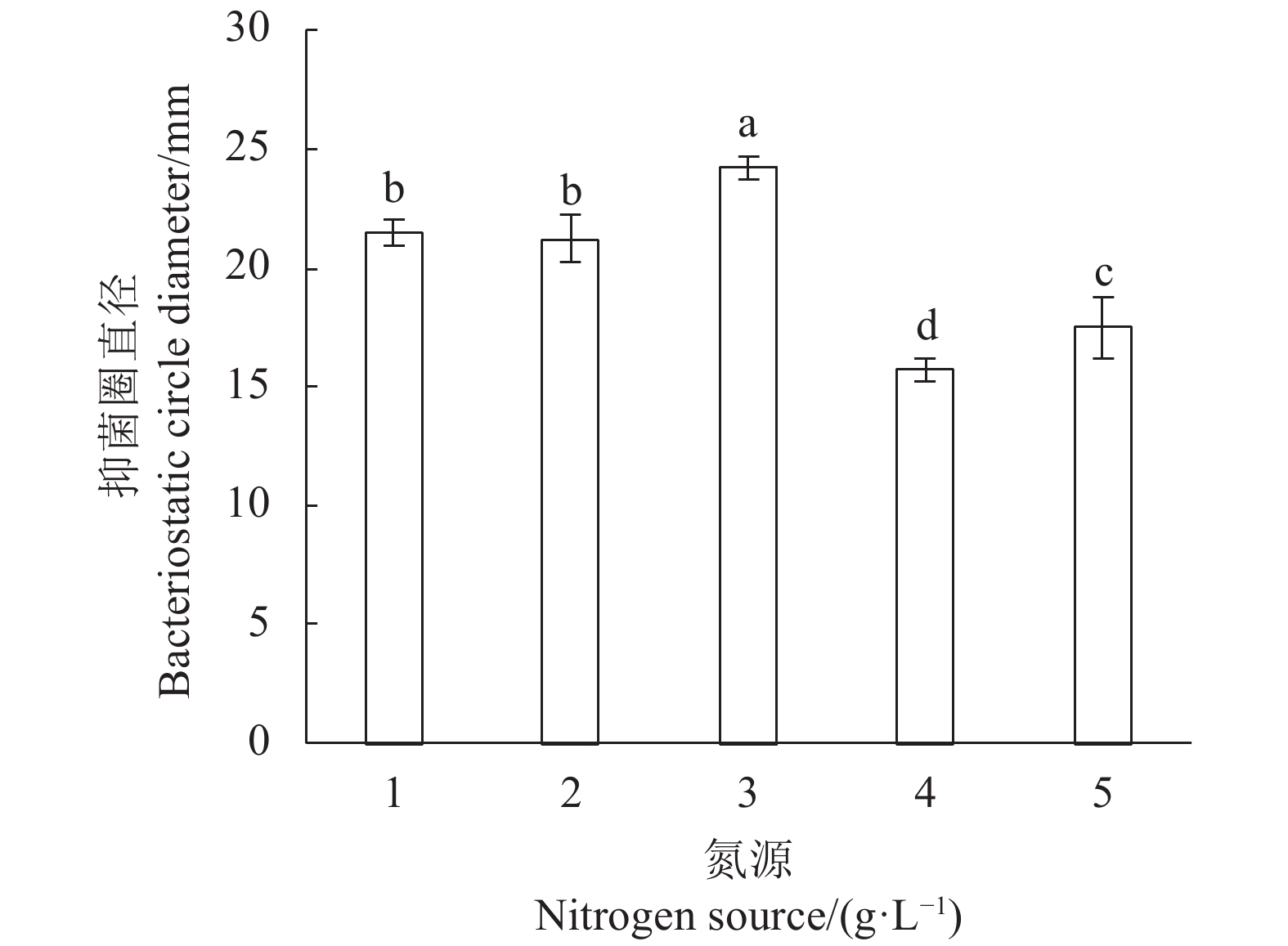
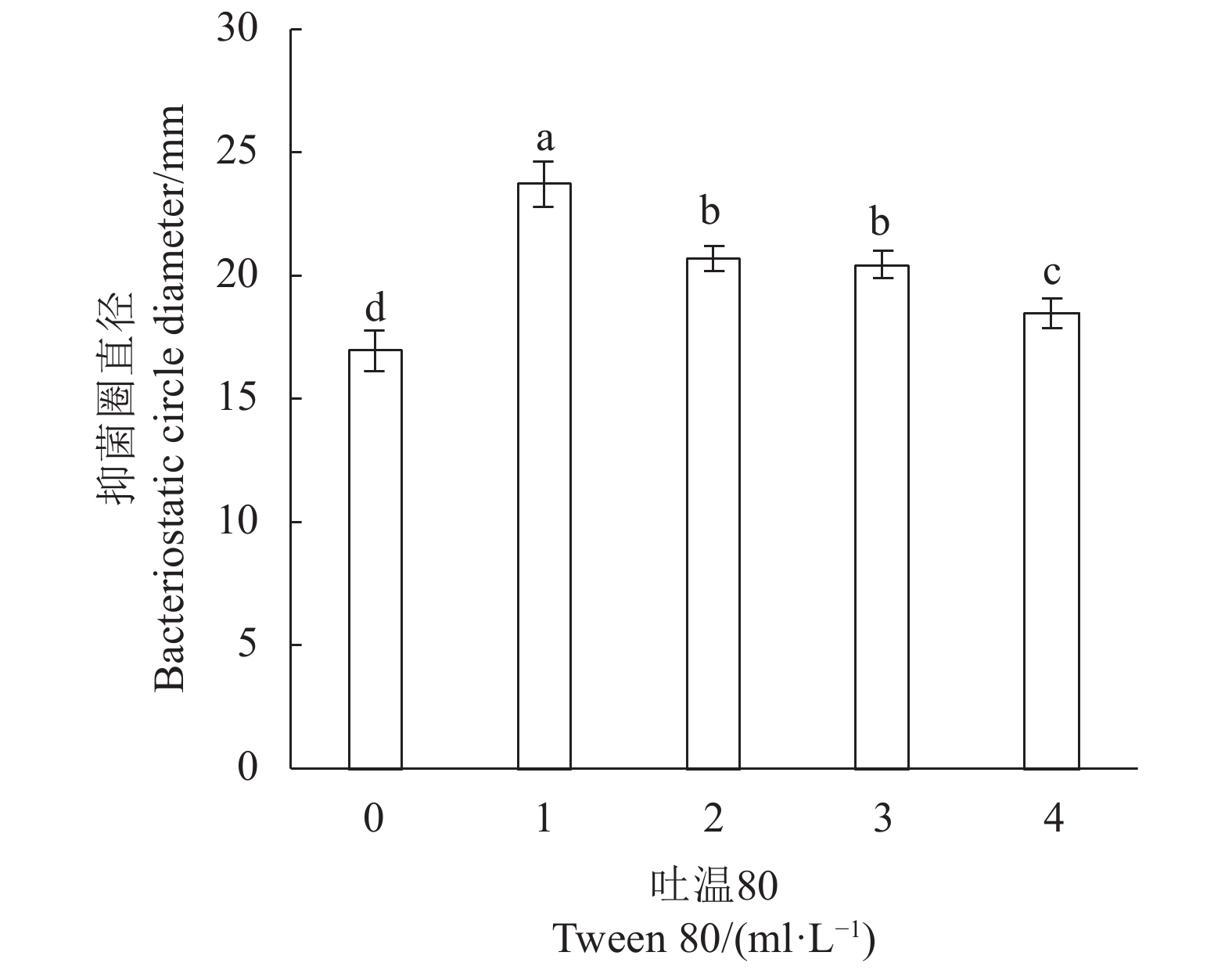
图 10 吐温对LV02的细菌素抗菌效果的影响
注:结合 Duncan 氏法做多重比较,图中标有不同小写字母者表示组间差异显著(P<0.05);相同字母则表示组间差异不显著(P>0.05)。
Figure 10. Effect of Tween-80 in medium on antibacterial activity of LV02 bacteriocin
Note: Combined with Duncan's method for multiple comparisons; those marked with different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between groups (P<0.05); those with same letter indicate no significant differences between groups (P>0.05).
表 1 Plackett-Burman 设计因子水平及编码
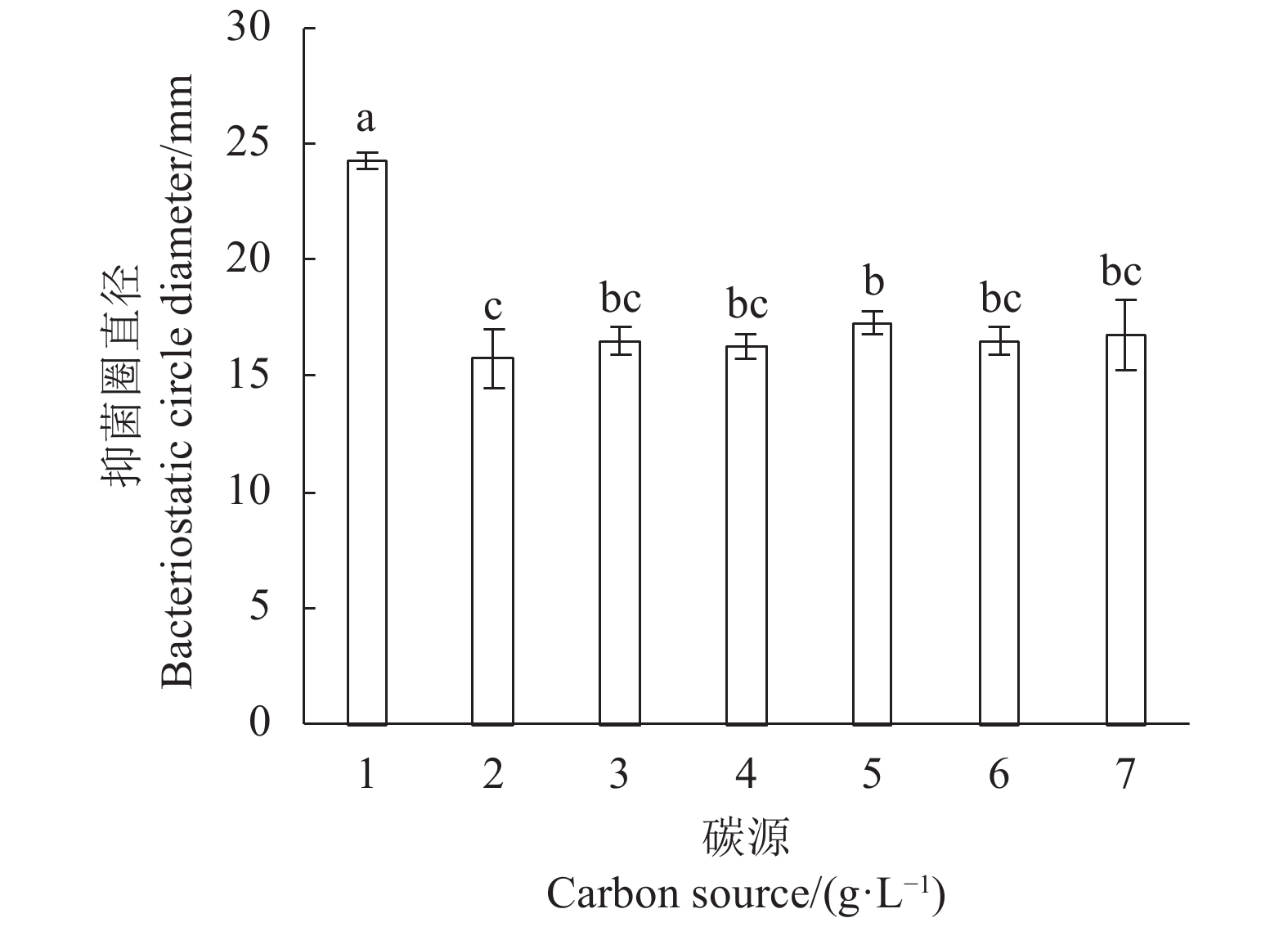
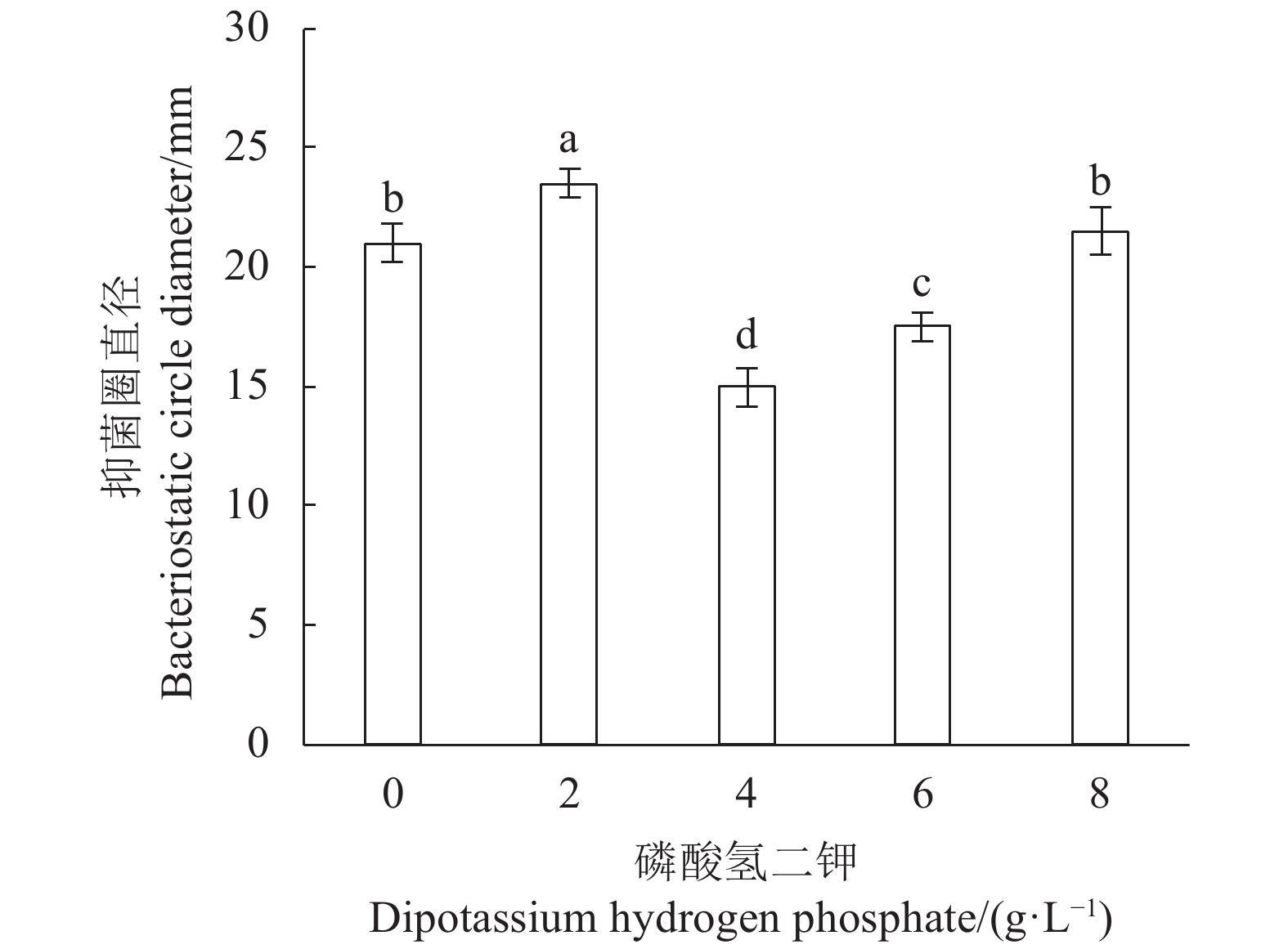
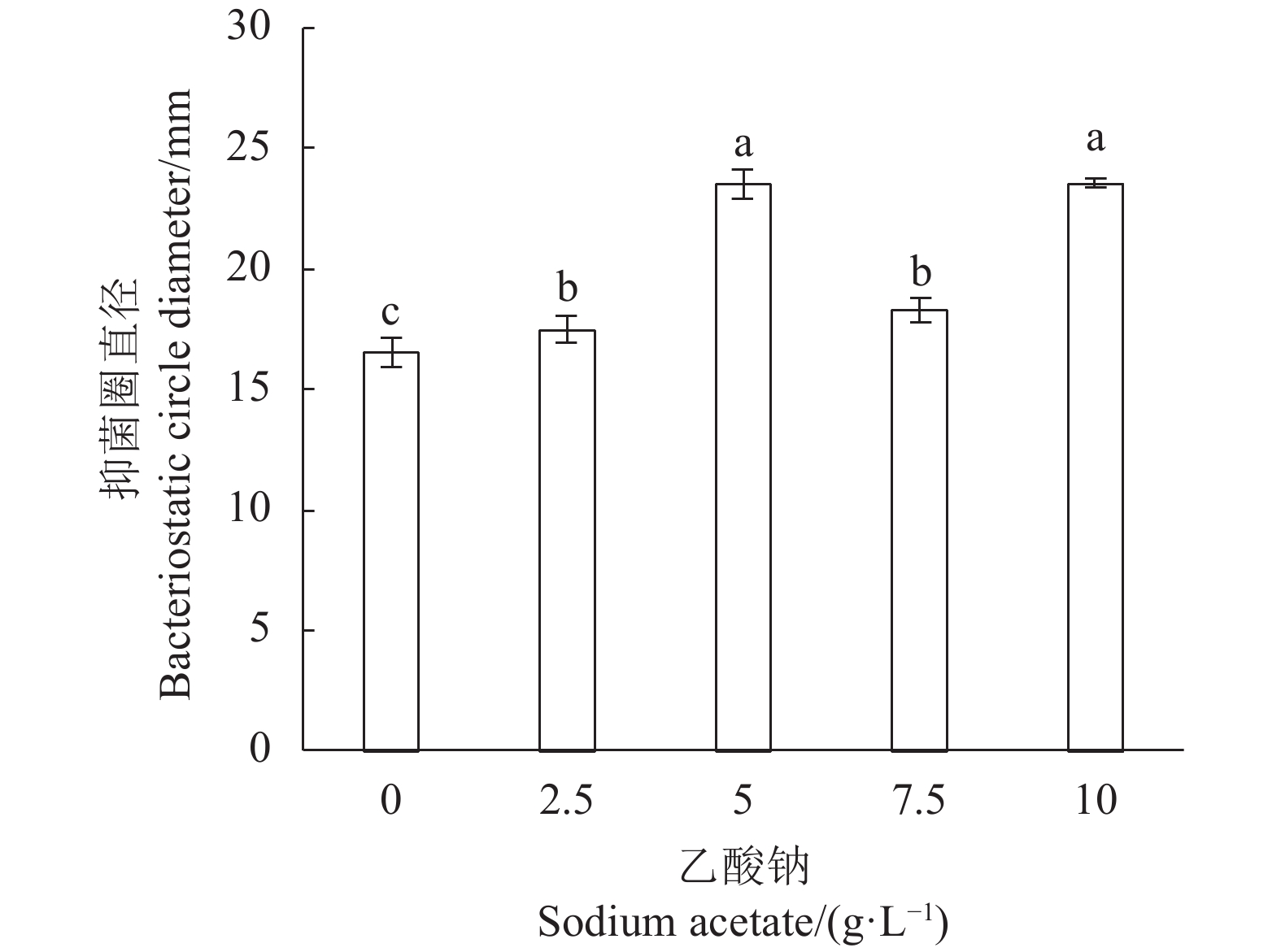
Table 1 Factors, levels, and codes of Plackett-Burman experimental design
变量
Variable实际变量
Actual variable单位
Unit低水平
Low level高水平
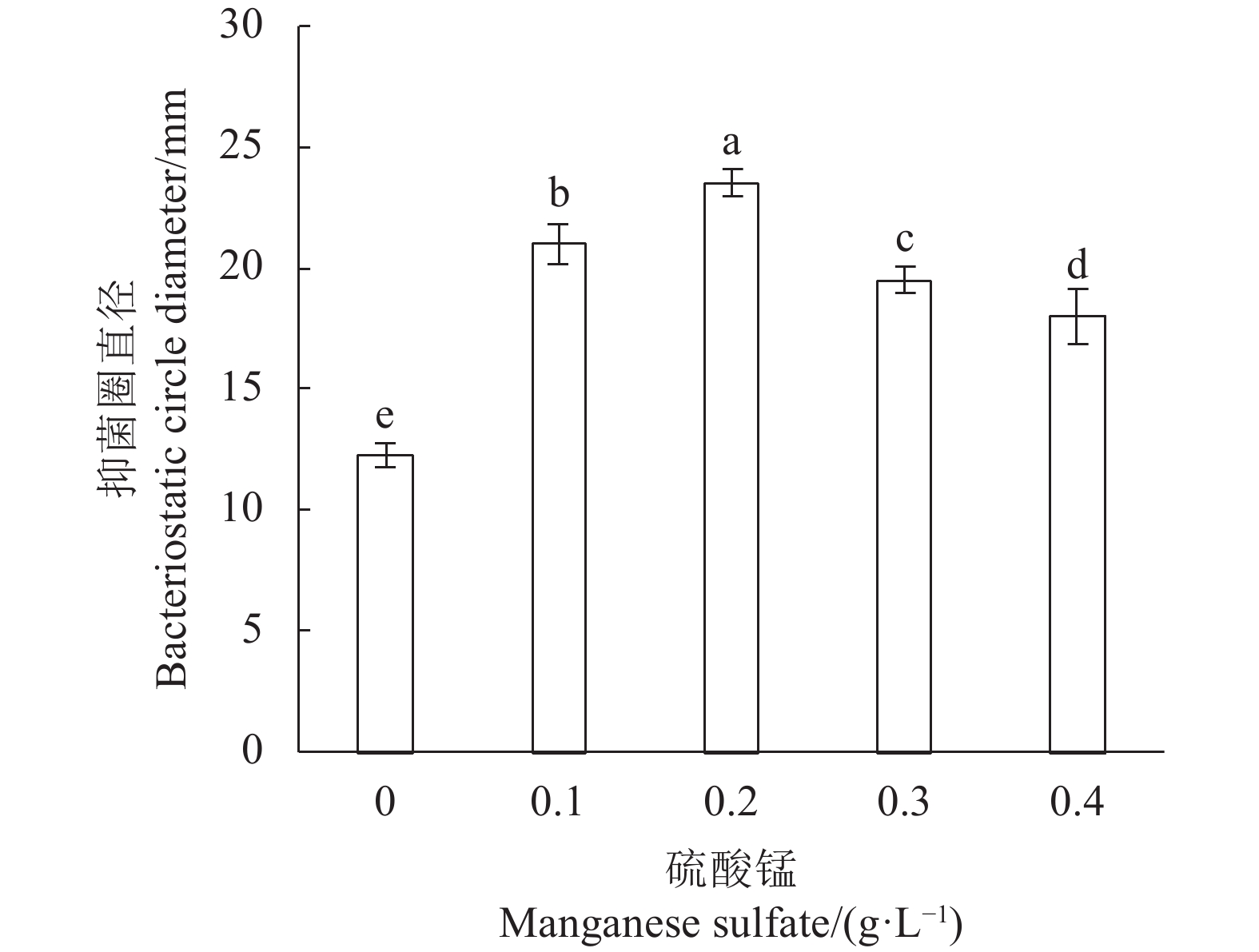
High Level−1 +1 X1 葡萄糖 Glucose g·L−1 15.00 25.00 X2 酵母浸粉 Yeast extract g·L−1 14.00 24.00 X3 硫酸镁 Magnesium sulfate g·L−1 0.15 0.25 X4 乙酸钠 Sodium acetate g·L−1 3.00 7.00 X5 吐温80 Tween 80 ml·L−1 0.50 1.50 X6 胡萝卜汁 Carrot juice ml·L−1 25.00 75.00 X7 硫酸锰 Manganese sulfate g·L−1 0.15 0.25 表 2 CCD试验各因子水平数
Table 2 Levels for each factor on CCD experiment
变量
Variable实际变量
Actual variable/(g·L−1)水平 Level −1.682 −1 0 +1 +1.682 X1 葡萄糖 Glucose 21.55 27.00 35.00 43.00 48.45 X2 酵母浸粉 Yeast extract 14.64 16.00 18.00 20.00 21.36 X7 硫酸锰 Manganese sulfate 0.06 0.10 0.16 0.22 0.26 表 3 LV02对3种指示菌的抑菌结果
Table 3 Antibacterial results of LV02 against three kinds of ndicator bacteria
指示菌名称
Indicator bacteria保菌编号/
NCBI登录号
Bacteria
number/
NCBI
registration
numberLV02抑菌
圈直径
LV02
inhibition
zone
diameter/
mm大肠杆菌YS Escherichia coli YS MN153456.1 19.41 ± 0.34 猪霍乱沙门氏菌 Salmonella choleraesuis ATCC10708 24.74 ± 0.51 单增李斯特氏菌 Listeria monocytogenes ATCC54001 22.30 ± 0.33 表 4 Plackett-Burman试验结果
Table 4 Results of Plackett-Burman experiment
试验序号
Experiment serial number因子 Factor 抑菌圈直径
Bacteriostatic circle diameter/mmX1 X2 X3 X4 X5 X6 X7 1 +1 +1 −1 +1 +1 +1 −1 23.50 2 −1 +1 +1 −1 +1 +1 +1 18.67 3 +1 −1 +1 +1 −1 +1 +1 23.67 4 −1 +1 −1 +1 +1 −1 +1 18.33 5 −1 −1 +1 −1 +1 +1 −1 20.67 6 −1 −1 −1 +1 −1 +1 +1 20.67 7 +1 −1 −1 −1 +1 −1 +1 21.33 8 +1 +1 −1 −1 −1 +1 −1 21.33 9 +1 +1 +1 −1 −1 −1 +1 20.67 10 −1 +1 +1 +1 −1 −1 −1 21.33 11 +1 −1 +1 +1 +1 −1 −1 23.67 12 −1 −1 −1 −1 −1 −1 −1 21.67 表 5 各因子贡献率及效应值
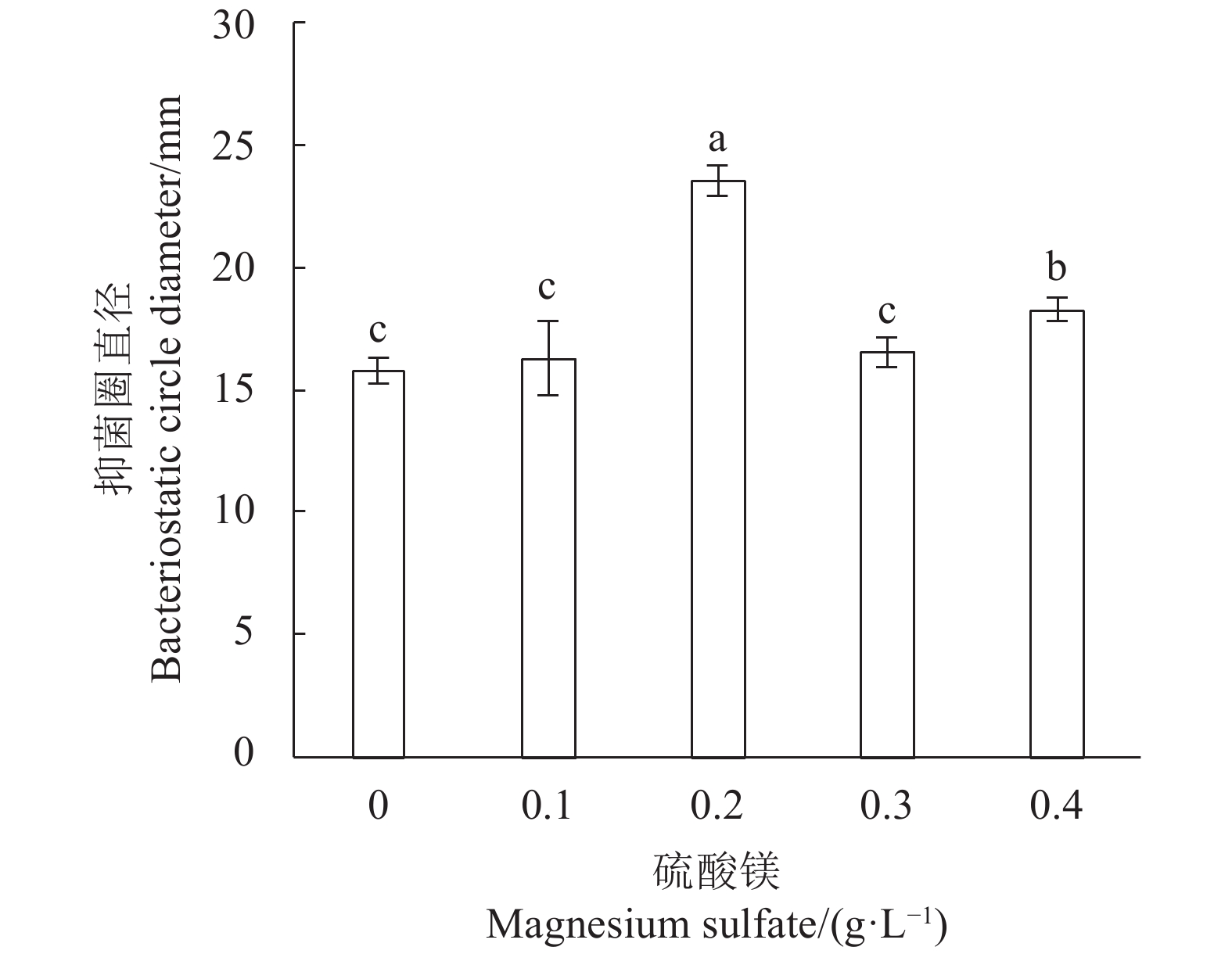
Table 5 Contribution rates and effect values of individual factors
变量
VariableP值
P value效应值
Effect value贡献率
Contribution rate/%重要性
ImportanceX1 0.0100* 1.07 41.39 1 X2 0.0480* −0.65 15.41 3 X3 0.5433 −0.65 0.86 6 X4 0.0705 0.57 11.73 4 X5 0.3190 −0.26 2.53 5 X6 0.6169 0.13 0.57 7 X7 0.0340* −0.74 19.61 2 注: * :该因子效应显著(P<0.05); * *:该因子效应极显著(P<0.01)。表8、9同。
Note: *: significant at P<0.05; **: extremely significant at P<0.01. The same as table 8、9.表 6 最陡爬坡试验结果
Table 6 Results of steepest ascent experiment
试验组号
Experiment
group
number葡萄糖
Glucose/
(g·L−1)硫酸锰
Manganese
sulfate/
(g·L−1)酵母浸粉
Yeast
extract/
(g·L−1)抑菌圈直径
Bacteriostatic
circle diameter/
mm1 11.00 0.34 24.00 20.87 2 19.00 0.28 22.00 22.00 3 27.00 0.22 20.00 22.47 4 35.00 0.16 18.00 24.50 5 43.00 0.10 16.00 22.42 表 7 中心组合设计及结果
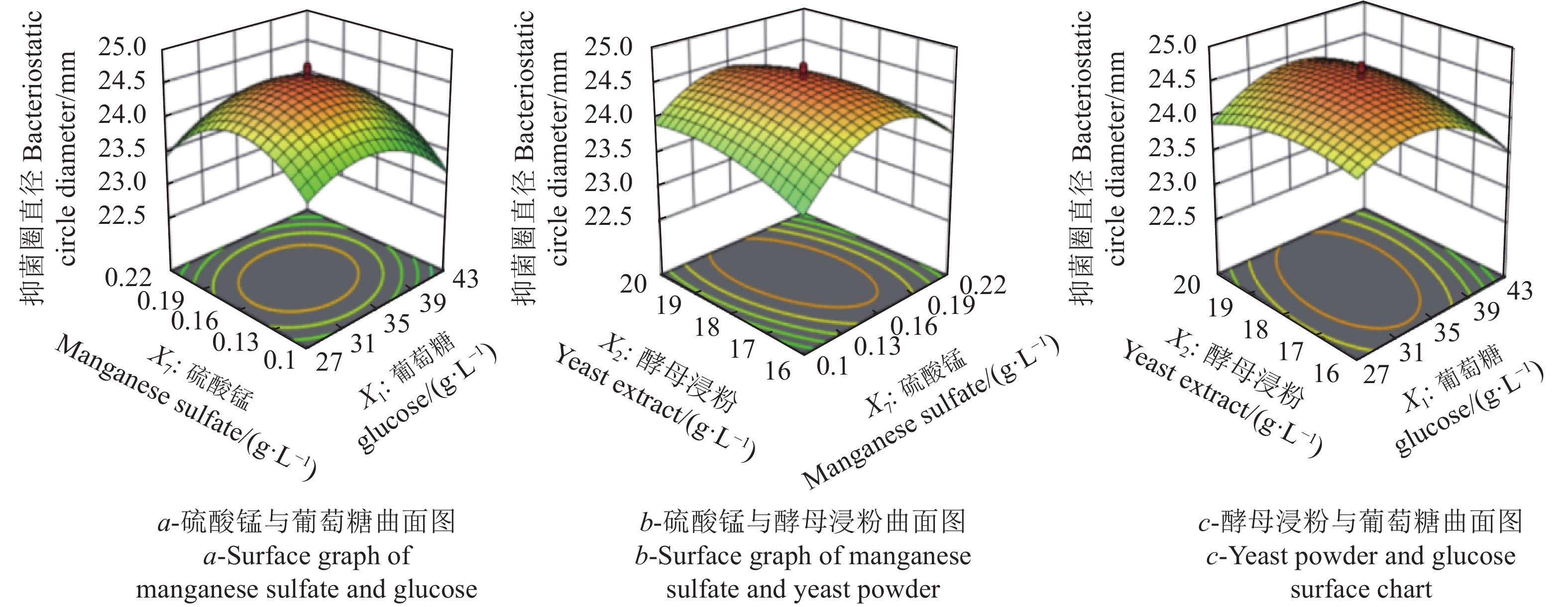
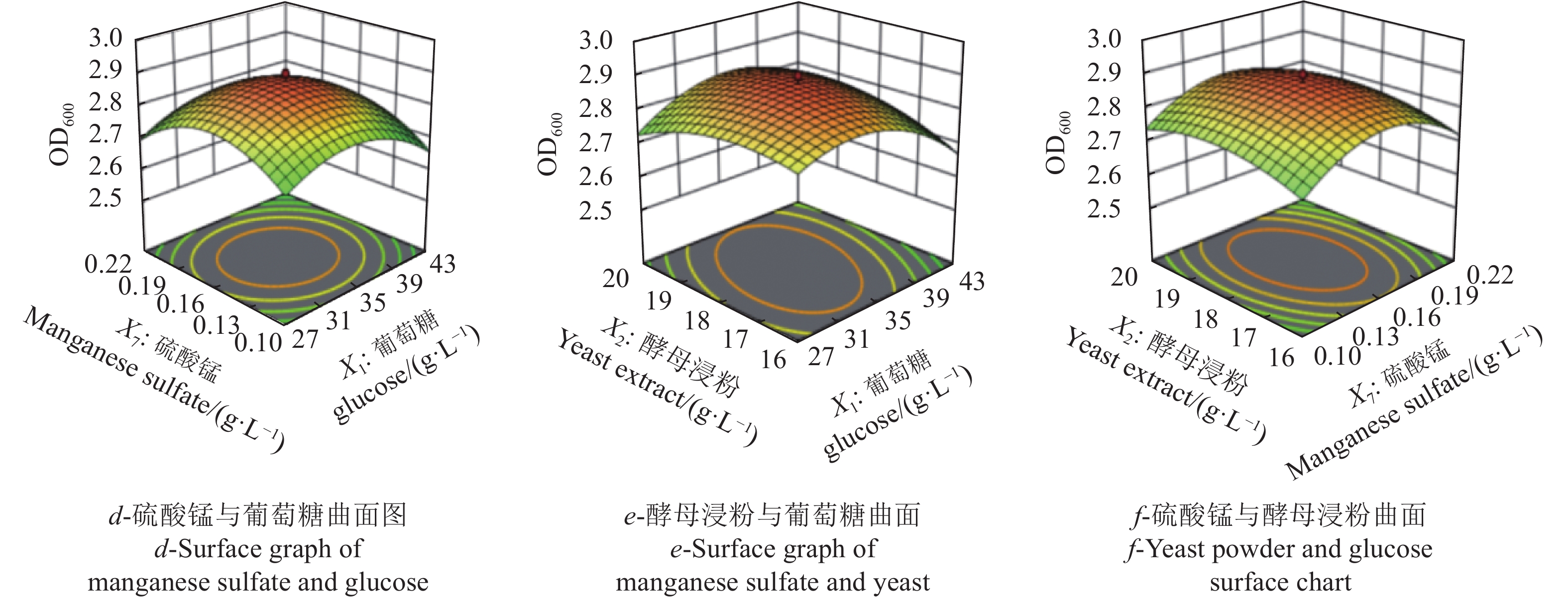
Table 7 CCD design and response values
试验组号
Experiment group number因子
Factor抑菌圈直径
Bacteriostatic circle diameter/mmOD600 葡萄糖X1
Glucose X1硫酸锰X7
Manganese sulfate X7酵母浸粉X2
Yeast extract X2实际值
Actual value预测值
Predictive value实际值
Actual value预测值
Predictive value1 −1 −1 −1 23.55 23.44 2.680 2.690 2 +1 −1 −1 22.80 22.65 2.598 2.560 3 −1 +1 −1 23.43 23.48 2.690 2.680 4 +1 +1 −1 23.40 23.13 2.620 2.580 5 −1 −1 +1 23.40 23.53 2.620 2.640 6 +1 −1 +1 23.52 23.33 2.682 2.660 7 −1 +1 +1 23.00 23.01 2.600 2.610 8 +1 +1 +1 23.33 23.25 2.700 2.660 9 −1.682 0 0 23.53 23.38 2.684 2.650 10 +1.682 0 0 22.58 22.92 2.510 2.580 11 0 −1.682 0 22.67 22.76 2.580 2.590 12 0 +1.682 0 22.62 22.73 2.550 2.580 13 0 0 −1.682 23.73 23.92 2.700 2.730 14 0 0 +1.682 24.10 24.11 2.750 2.760 15 0 0 0 24.63 24.56 2.852 2.880 16 0 0 0 24.72 24.56 2.895 2.880 17 0 0 0 24.75 24.56 2.903 2.880 18 0 0 0 24.00 24.56 2.850 2.860 19 0 0 0 24.60 24.56 2.860 2.850 20 0 0 0 24.70 24.56 2.900 2.900 表 8 以抑菌圈直径为响应值的回归方程方差分析
Table 8 Analysis of variance for regression model based on bacteriostatic zone diameter as response value
方差来源
Source of
variance平方和
Sum of
square自由度
Degree of
freedomF值
F valueP值
P value模型 Model 9.5300 9 13.9700 0.000 1** X1 0.2600 1 3.4100 0.094 7 X7 1.520×10−3 1 0.0200 0.890 2 X2 0.0400 1 0.5300 0.482 4 X1*X7 0.0970 1 1.2800 0.284 8 X1*X2 0.0170 1 2.3000 0.160 7 X7*X2 0.1600 11 2.0740 0.180 9 X12 3.5700 11 7.0600 <0.000 1** X72 5.9500 1 78.4800 <0.000 1** X22 0.5400 1 7.1200 0.023 6* 残差 Residual 0.7600 10 失拟项 Missing item 0.3600 5 0.8900 0.549 4 表 9 以OD600为响应值的回归方程方差分析
Table 9 Analysis of variance for regression model based on OD600 as response value
方差来源
Source of
variance平方和
Sum of
square自由度
Degree of
freedomF值
F valueP值
P value模型 Model 0.2800 9 17.6700 <0.000 1** X1 12.9020 1 3.3100 0.098 8 X7 3.065×10−5 1 0.0170 0.897 8 X2 7.046×10−4 1 0.4000 0.541 8 X1*X7 3.125×10−4 1 0.1800 0.682 9 X1*X2 0.0120 1 6.9800 0.024 7* X7*X2 1.445×10−4 1 0.0820 0.780 7 X12 0.1200 1 68.5700 <0.000 1** X72 0.1500 1 86.5400 <0.000 1** X22 0.0310 1 17.5800 0.0019** 残差 Residual 0.0180 10 失拟项 Missing item 0.0140 5 4.3200 0.067 0 表 10 LV02发酵培养基验证试验结果
Table 10 Verification of LV02 fermentation medium
试验组别
Test Group葡萄糖
glucose/
(g·L−1)酵母浸粉
Yeast extract/(g·L−1)牛肉膏+蛋白胨+
酵母粉
Beef extract+
peptone+
yeast powder/
(g·L−1)硫酸锰
Manganese sulfate/
(g·L−1)胡萝卜汁
Carrot juice/
(mL·L−1)抑菌圈直径
Bacteriostaticcircle
diameter/mmOD600 对照组 Control group 20.00 — 19.00 0.20 — 19.36 ± 0.27 2.435 ± 0.030 预测组 Forecast Group 34.07 18.12 — 0.16 50.00 24.58 2.877 实验组 Test group 34.07 18.12 — 0.16 50.00 24.50 ± 0.31 2.877 ± 0.230 -
[1] SON S H, JEON H L, JEON E B, et al. Potential probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum Ln4 from kimchi: Evaluation of β-galactosidase and antioxidant activities [J]. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 2017, 85: 181−186. DOI: 10.1016/j.lwt.2017.07.018
[2] 杨永亮. 泡菜中植物乳杆菌的分离鉴定及其应用[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2013. YANG Y L. Isolation and identification of the Lactobacillus Plantarum strain from pickles and its application[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2013.(in Chinese)
[3] 金银卡编辑部. 乳酸菌素在饲料中应用研究 [J]. 广东饲料, 2016, 25(12):32−34. Editorial Department of Gold and Silver Cards. Study on the application of lactobacteriocin in feed [J]. Guangdong Feed, 2016, 25(12): 32−34.(in Chinese)
[4] KUMAR V, SHEORAN P, GUPTA A, et al. Antibacterial property of bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum LD4 isolated from a fermented food [J]. Annals of Microbiology, 2016, 66(4): 1431−1440. DOI: 10.1007/s13213-016-1230-6
[5] 刘彩琴, 陆胤, 王石磊,等. 黄酒米浆水中抗菌乳酸菌的筛选及特性分析[J]. 食品工业科技, 2020(9):115 − 118 . LIU C Q, LU Y, WANG S L, et al. Screening and characteristics analysis of antibacterial lactic acid bacteria from rice pulp of huangjiu[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2019: 115 − 118.(in Chinese)
[6] 姜旭德, 张春华. 乳酸菌素及其乳酸链球菌素在食品中的应用 [J]. 中国乳业, 2017(2):60−62. JIANG X D, ZHANG C H. The application of lactobacteriocin and nisin in food processing [J]. China Dairy, 2017(2): 60−62.(in Chinese)
[7] 张敏. pH对植物乳杆菌KDFR27生长的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2016. ZHANG M. Effect of pH on the growth of Lactobacillus plantarum KDFR27[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2016.(in Chinese)
[8] 刘伦伦, 刘焱, 瞿朝霞, 等. 植物乳杆菌发酵盐渍辣椒汁培养基的优化 [J]. 中国酿造, 2014, 33(2):32−36. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5071.2014.02.008 LIU L L, LIU Y, QU Z X, et al. Optimization of pepper juice medium for Lactobacillus plantarum [J]. China Brewing, 2014, 33(2): 32−36.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5071.2014.02.008
[9] 王瑶, 李琪, 李平兰. 植物乳杆菌LPL-1产细菌素发酵培养基优化 [J]. 农业机械学报, 2018, 49(9):311−317. DOI: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2018.09.036 WANG Y, LI Q, LI P L. Optimization of fermentation medium of Lactobacillus plantarum LPL-1 for plantaricin LPL-1 production by response surface methodology [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(9): 311−317.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2018.09.036
[10] 王瑶, 李琪, 李平兰. 响应面法优化植物乳杆菌LPL-1产细菌素发酵条件及细菌素理化性质分析 [J]. 食品科学, 2018, 39(22):101−109. DOI: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201822016 WANG Y, LI Q, LI P L. Optimization of fermentation conditions for plantaricin production by Lactobacillus plantarum LPL-1 by response surface methodology and its physicochemical properties [J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(22): 101−109.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201822016
[11] 徐珑倩, 胡凯弟, 张艾青, 等. 植物乳杆菌P158产细菌素培养基及培养条件的优化 [J]. 食品科学, 2017, 38(22):109−116. DOI: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201722017 XU L Q, HU K D, ZHANG A Q, et al. Optimization of medium and culture conditions for bacteriocin production by Lactobacillus plantarum P158 [J]. Food Science, 2017, 38(22): 109−116.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201722017
[12] ZHAO S M, HAN J Z, BIE X M, et al. Purification and characterization of plantaricin JLA-9: A novel bacteriocin against Bacillus spp. produced by Lactobacillus plantarum JLA-9 from Suan-tsai, a traditional Chinese fermented cabbage [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2016, 64(13): 2754−2764. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b05717
[13] 许女, 史改玲, 张浩, 等. 植物乳杆菌KF1对奶牛乳房炎金黄色葡萄球菌的抑茵机制 [J]. 中国食品学报, 2016, 16(10):19−27. XU N, SHI G L, ZHANG H, et al. Antibacterial mechanism of Lactobacillus plantarum KF1 on Staphylococcus aureus isolated from subclinical mastitis milk [J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2016, 16(10): 19−27.(in Chinese)
[14] YOO H, RHEEM I, RHEEM S, et al. Optimizing medium components for the maximum growth of Lactobacillus plantarum JNU 2116 using response surface methodology [J]. Korean Journal for Food Science of Animal Resources, 2018, 38(2): 240−250.
[15] 高秀芝, 康建依, 易欣欣, 等. 一种发酵蔬菜的混合益生菌、发酵蔬菜及其制备方法: 中国, 110106112A[P]. 2019−08−09. [16] 沈菲儿. 乳酸菌发酵对莲藕泡菜质构和风味影响的研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2016. SHEN F E. Study on the effect of lactic acid bacteria fermentation on the texture and flavor of lotus root kimchi[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2016(in Chinese)
[17] 张子豪. 高效抑制大肠埃希氏菌的芽孢杆菌筛选及其抑菌特性研究[D]. 北京: 北京农学院, 2018. ZHANG Z H. Optimization of fermentation culture medium and conditions of Bacillus with high antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Agriculture, 2018.(in Chinese)
[18] 赵玉鉴. 益生性植物乳杆菌 C88 直投式发酵剂的制备及其应用[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2014. ZHAO Y J. Preparation and application of probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum C88 direct vat set culture[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2014.(in Chinese)
[19] 汤夏安, 刘彩莲, 邓业成, 等. 广西地不容内生真菌DBR-9产橘霉素的发酵条件优化 [J]. 河南农业科学, 2019, 48(7):81−87. TANG X A, LIU C L, DENG Y C, et al. Optimization of Fermentation Conditions for the Production of Citrinin from Endophytic Fungus DBR-9 of Stephania kwangsiensis [J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 48(7): 81−87.(in Chinese)
[20] 杨慧娟. 具有抑制甜瓜枯萎病菌的植物乳杆菌筛选及其抑菌特性研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2014. YANG H J. Selection of fusarium oxysporum Inhibitory L. plantarum strains and characterization of their antifungal activity[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese)
[21] 姜晶, 敖日格乐, 王纯洁, 等. 酸马奶提取植物乳杆菌DSM20174细菌素的理化特性研究 [J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2016, 43(2):444−449. JIANG J, AORIGELE, WANG C J, et al. Study on physicochemical properties of Lactobacillus plantarum DSM20174 bacteriocin from koumiss [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2016, 43(2): 444−449.(in Chinese)
[22] 唐坚. 生菜的冰温保鲜及微生物预测模型的初步建立[D]. 上海: 上海师范大学, 2015. TANG J. Freezing-pointstorage of lettuce and thepreliminary establishment of predictionmodel of microorganisms[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Normal University, 2015.(in Chinese)
[23] KORDEL M, SAHL H G. Susceptibility of bacterial, eukaryotic and artificial membranes to the disruptive action of the cationic peptides Pep 5 and nisin [J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 1986, 34(2): 139−144. DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1986.tb01393.x
[24] 章检明. 植物乳杆菌 B23 合成细菌素发酵条件优化及诱导调控研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2015. ZHANG J M. Optimization of fermentationconditions and research of inductionregulation for bacteriocin productionby Lactobacillus plantarum B 23[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2015.(in Chinese)
[25] 王莉. 食品营养学[M]. 第三版. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2018: 93. [26] 王帅. 植物乳杆菌培养及冻干技术研究[D]. 西安: 陕西科技大学, 2016. WANG S. Study on cultivation and cryoprotectant of Lactobacillus plantarum[D]. Xian: Shaanxi Universityof Science and Technology, 2016.(in Chinese)
[27] 施铜铃, 卢烨, 梁金钟. 嗜酸乳杆菌HUC-La-0812菌株高密度生长培养基的优化 [J]. 乳业科学与技术, 2009, 32(6):271−274. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5187.2009.06.007 SHI T L, LU Y, LIANG J Z. Optimization of high-density growth medium of Lactobacillus acidophilus strain HUC-La-0812 [J]. Journal of Dairy Science and Technology, 2009, 32(6): 271−274.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5187.2009.06.007
[28] 赵静. 直投式微生物菌剂及发芽谷物发酵饮品的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨商业大学, 2015. ZHAO J. Researched on direct vat set(dvs) microbial starter and sprouting grains fermented beverages[D]. Harbin: Harbin University of Commerce, 2015.(in Chinese)
[29] 杨杰, 谷新晰, 李晨, 等. 响应面法优化植物乳杆菌绿豆乳增殖培养基 [J]. 中国食品学报, 2015, 15(12):83−90. YANG J, GU X X, LI C, et al. Optimization of multiplying culture of mungbean milk of Lactobacillus plantarum by response surface method [J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2015, 15(12): 83−90.(in Chinese)
[30] 刘正奇. 植物乳杆菌WLPL04的胞外多糖结构与益生功能研究及其发酵工艺优化[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2018. LIU Z Q. Research on structure and probiotic function of exopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus plantarum WLPL04 and optimization of its fermentation processes[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2018. (in Chinese)




 下载:
下载: