Effect of Different Soil Compaction on Growth and Quality of Anoectochilus roxburghii
-
摘要:目的 明确不同土壤紧实度对金线莲生长发育的影响,筛选出金线莲生长所需的适宜紧实度,为金线莲科学种植、品质提升提供理论依据。方法 通过盆栽试验,采用珍珠岩调控,设置土壤容重分别为0.7、0.8、0.9、1.0和1.1 g·cm−3 共5个处理,测定不同土壤紧实度对金线莲生长、生理与品质的影响。结果 (1)过高或过低的土壤紧实度均不利于金线莲生长和产量提升,土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3处理时金线莲株高、地径、叶片数、根长、鲜重最大,相比其他处理平均显著增加14.97%、8.70%、6.80%、21.04%、28.87%;折干率在土壤容重0.8 g·cm−3时最大,相比其他处理平均增加44.84%;而土壤紧实度对叶长和叶宽影响不明显。(2)适宜的土壤紧实度(0.8~0.9 g·cm−3)提高了金线莲叶片中叶绿素a和类胡萝卜素含量,但对叶绿素b含量影响不明显。(3)过高或过低的土壤紧实度均不利于金线莲C、N、P、K养分积累和品质提升,土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3处理时金线莲多糖、氨基酸、总酚、黄酮、Vc含量最高,相比其他处理平均增加36.65%、41.79%、23.22%、24.10%、13.60%。结论 过高或过低的土壤紧实度均不利于金线莲的生长及产量品质的提升,当红壤与珍珠岩配比(m ∶ m)达到40 ∶ 1,即土壤容重为0.9 g·cm−3时,金线莲生长和品质最佳。Abstract:Objective To clarify the influence of different soil compaction on the growth and development of the Anoectochilus, and to screen out the appropriate compaction required for the growth of the Anoectochilus, to provide a theoretical basis for the scientific planting and quality improvement of the Anoectochilus.Method Through pot experiment, used perlite control, the soil bulk density was set to 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1.0 and 1.1 g·cm−3, a total of 5 treatments to study the effect of soil compaction on the growth and quality of Anoectochilus.Result (1) Too high or too low soil compaction is not conducive to the growth and yield of Anoectochilus. When the soil bulk density is 0.9 g·cm−3, the plant height, ground path, number of leaves, root length and fresh weight of Anoectochilus are was the largest, with a significant increase of 14.97%, 8.70%, 6.80%, 21.04%, and 28.87% on average compared with other treatments; the drying rate is the largest when the soil bulk density is 0.8 g·cm−3, which is an average increase of 44.84% compared with other treatments; The soil compaction has no obvious effect on leaf length and leaf width. (2) Suitable soil compaction (0.8~0.9 g·cm−3) increased the content of chlorophyll a and carotenoids in the leaves of Anoectochilus, but had little effect on the content of chlorophyll b. (3) Too high or too low soil compaction is not conducive to the accumulation of C, N, P, K nutrients and quality improvement of Anoectochilus, when the soil bulk density is 0.9 g·cm−3, the polysaccharides, amino acids, total The content of phenol, flavonoids, and Vc was the highest, and the average increase was 36.65%, 41.79%, 23.22%, 24.10%, 13.60% compared with other treatments.Conclusion Too high or too low soil compaction is not conducive to the growth and yield and quality of the Anoectochilus. When the ratio of red soil to perlite reaches 40 ∶ 1, which is the soil bulk density is 0.9 g·cm−3, the growth and quality of the Anoectochilus is the best.
-
Keywords:
- soil compactness /
- Anoectochilus /
- growth /
- quality
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】金线莲(Anoectochilus roxburghii),又名金草、金蚕,天门冬目兰科,单子叶植物,主要分布于我国东南部福建、台湾、浙江、江西等地[1]。其味道甘甜、药性平和,具有降火、祛湿气、祛毒、镇痛止咳、降低血压血糖、抑制肿瘤等功效,具有极高的药用价值,在民间被誉为“药王” “鸟人参”等[2-3]。金线莲对外界环境要求极高,多生长在环境阴凉、土质良好、水气充足、有良好团粒结构且有充足肥力的土壤[4]。近年来由于人类过度开垦、灌溉、施肥等活动,导致土壤板结、水土流失、土壤质量不断恶化,极大地限制了金线莲产量和品质的提升[5],因此急需寻找一种合适的种植方式。有研究发现通过调控土壤紧实度能改变土壤物理机械结构,进而影响作物产量[6]。土壤紧实度是指土壤抵抗外力的压实和破碎的能力,可通过土壤容重、孔隙度和机械阻力等指标来评价,其中土壤容重是反映土壤紧实度最直接、最常用的指标[7]。土壤容重和土壤紧实度直接相关,土壤容重提高,土壤紧实度也增大[7]。土壤紧实度的大小影响作物根系的穿透能力和矿质元素的转移,进而影响植物生长进程,因此栽培金线莲不仅需要适宜的水肥,还必须有适宜的土壤紧实度[8]。【前人研究进展】多项研究表明,土壤过度疏松或紧实,会影响作物生长,造成作物减产,品质下降。土壤过于松弛,土壤保水持肥能力下降,更容易加快土壤水分和养分的流失。吴晓莲等[9]研究发现,土壤容重过低会影响甘蔗苗期生长,最终导致减产。邹俊等[10]对活血丹设置不同容重处理后发现,土壤容重0.8 g·cm−3处理,活血丹各项生长指标和生物量,以及光合色素、可溶性糖、游离氨基酸含量均显著低于土壤容重1.0 g·cm−3处理。土壤过于紧实,通气性变差,影响根系生长发育及生理代谢。刘永晨等[11]研究发现,土壤紧实胁迫处理抑制甘薯生长,降低块根中干物质分配率和块根产量。Tracy等[12]研究发现,土壤过于紧实,抑制番茄根系生长,降低根系活性,导致番茄产量和品质下降。【本研究切入点】目前,对金线莲生长的研究绝大多数集中在栽培基质材料与配方,而缺乏从栽培基质物理性质-土壤紧实度角度出发,对金线莲生长和品质影响的研究。【拟解决的关键问题】本试验通过改变土壤和珍珠岩用量,设置不同容重处理,研究不同土壤紧实度对金线莲生长和品质的影响,筛选出金线莲生长所需的适宜紧实度,以期为金线莲高产栽培、产量品质提升提供有力的理论支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
供试植物为小叶品种金线莲组培苗,取自福建农林大学自然生物资源保育利用福建省高校工程研究中心。
供试土壤为红壤,0~20 cm土壤pH值5.82、有机质25.40 g·kg−1,碱解氮63.54 mg·kg−1,有效磷35.41 mg·kg−1,速效钾109.28 mg·kg−1。
供试珍珠岩购自市场,粒径大小3~6 mm,容重为100~150 kg·cm−3。
试验于2019年1月13日~6月13日在福建农林大学田间实验室(阳光房)内进行,试验地地理坐标为(25°15′~26°39′N,118°08′~120°31′E),属典型亚热带海洋性季风气候区,年平均气温约20.1 ℃,气温适宜,温暖湿润,光照充沛,适宜金线莲生长。
1.2 试验设计
试验采用盆栽试验,花盆为口径20 cm,底径16 cm,高15 cm的PVC盆,花盆底部放置有塑料网,防止土壤冲刷。试验设置5个土壤容重处理,分别为0.7(T1)、0.8(T2)、0.9(T3)、1.0(T4)、1.1 g·cm−3(T5),每个处理设置5个重复。各处理所需土壤与珍珠岩见表1,选用m(N)∶m(P2O5)∶m(K2O)=15∶15∶15的复合肥,每盆施用量为1.2 g,折合大田施用量为444 kg·hm−2。将土壤、肥料与珍珠岩混合均匀后装入花盆,并压至相应的刻度(距盆顶3 cm),缓慢浇水,放置2 d后,选取长势良好、大小一致的金线莲幼苗,用5 %的多菌灵溶液浸泡10 min进行消毒杀菌,晾干后均匀移栽至PVC花盆中,每盆移栽10株,试验期间水肥、光照、病虫害管理按常规进行。
表 1 各处理土壤和珍珠岩质量Table 1. The quality of soil and perlite for each treatment处理
Treatment红壤
Red soil/g珍珠岩
Perlite/g容重
Bulk density/(g·cm−3)T1 1200 120 0.7 T2 1400 80 0.8 T3 1600 40 0.9 T4 1800 20 1.0 T5 2000 0 1.1 1.3 试验方法
1.3.1 样品采集与处理
金线莲栽培管理150 d后,采收所有地上部金线莲样品,将采收金线莲样品分为两部分,一部分植株样品位于4 ℃冰箱进行冷藏处理,用于植物生长、生理指标测定,另一部分植株样品置于105 ℃鼓风干燥箱杀青2 h,65 ℃烘干至恒重,粉碎至粉末状,过0.149 mm筛,装袋编号,用于植物品质指标测定。
1.3.2 生长指标测定
金线莲采收时对植物生长指标进行测定,每个处理选取5株金线莲,用卷尺测定植株株高、叶长、叶宽和根长(株高以地面到植株最高处为准;叶长、叶宽测定选取金线莲中最大的叶片,以长宽最大处为准;根长测定选取金线莲主根系,以地面到根最底端为准),用电子游标卡尺测定植株地径(距离地面1 cm处),用电子天平称量植株鲜重,计算折干率,折干率(%)=(植株干重/植株鲜重)×100%。
1.3.3 生理指标测定
选用整个植株鲜样进行金线莲生理指标测定,叶绿素a、叶绿素b、类胡萝卜素含量均采用乙醇浸提-分光光度法测定,吸收光波长分别为663、645、470 nm[13]。
1.3.4 品质指标测定
全碳、全氮含量采用全自动微量碳氮元素分析仪(德国ELEMENTAR)测定,全磷含量采用钒钼黄比色法测定,全钾含量采用火焰光度法测定。多糖含量采用苯酚-硫酸法测定,游离氨基酸含量采用茚三酮柱后衍生法测定,Vc含量采用2,6-二氯酚靛酚滴定法测定,总酚含量采用酒石酸亚铁比色法测定,黄酮含量以芦丁为标准品对照,分光光度法测定[13]。
1.4 数据处理与分析
采用Microsoft Excel 2016整理数据与绘图,用SPSS 20.0软件对试验数据进行单因素方差分析和SNK法进行显著性检验(P<0.05)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲生长的影响
由表2可以看出,土壤紧实度对于金线莲的生长影响显著。金线莲株高和地径都随土壤容重的增加呈先增加后减少的趋势,株高在土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3达到最大值12.40 cm,分别是其他处理的1.25、1.10、1.11、1.15倍,与其他处理均达显著性差异(P<0.05);地径在土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3达到最大值2.75 mm,分别是其他处理的1.12、1.01、1.12、1.10倍;表明过高或过低的容重都不利于金线莲株高和地径的增长。金线莲叶片数、叶长、叶宽也受土壤紧实度的影响,叶片数以土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3处理为最大,以土壤容重0.7 g·cm−3处理为最小,两者间相差0.49片;叶长除容重0.7 g·cm−3处理外,其余处理间无显著性差异,都显著大于容重0.7 g·cm−3的处理;各处理叶宽位于1.68~1.77 cm,处理间无显著差异;表明过高过低的容重都不利于金线莲叶片的生长。金线莲根长在土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3达到最大值4.53 cm,分别是其他处理的1.50、1.42、1.06、1.01倍,与土壤容重0.7、0.8 g·cm−3处理间差异较大,表明土壤容重过低会显著影响根系的生长发育。
表 2 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲生长指标的影响Table 2. The effect of different soil compaction on the growth index of Anoectochilus处理
Treatment株高
Plant height/cm地径
Ground path/mm叶数
Number of leaves叶长
Leaf length/cm叶宽
Leaf width/cm根长
Root length/cmT1 9.92±0.32 c 2.46±0.22 b 3.87±0.33 b 2.03±0.19 b 1.74±0.14 a 3.02±0.31 c T2 11.28±0.44 b 2.71±0.20 a 4.34±0.22 a 2.51±0.08 a 1.75±0.07 a 3.20±0.27 c T3 12.40±0.73 a 2.75±0.15 a 4.36±0.37 a 2.63±0.13 a 1.77±0.07 a 4.53±0.34 a T4 11.14±0.51 b 2.45±0.26 b 4.00±0.35 b 2.41±0.13 a 1.71±0.16 a 4.26±0.28 b T5 10.80±0.65 bc 2.50±0.23 b 4.12±0.18 ab 2.41±0.14 a 1.68±0.10 a 4.49±0.45 a 注:表中标注不同小写字母表示在(P<0.05)水平差异显著,下同。
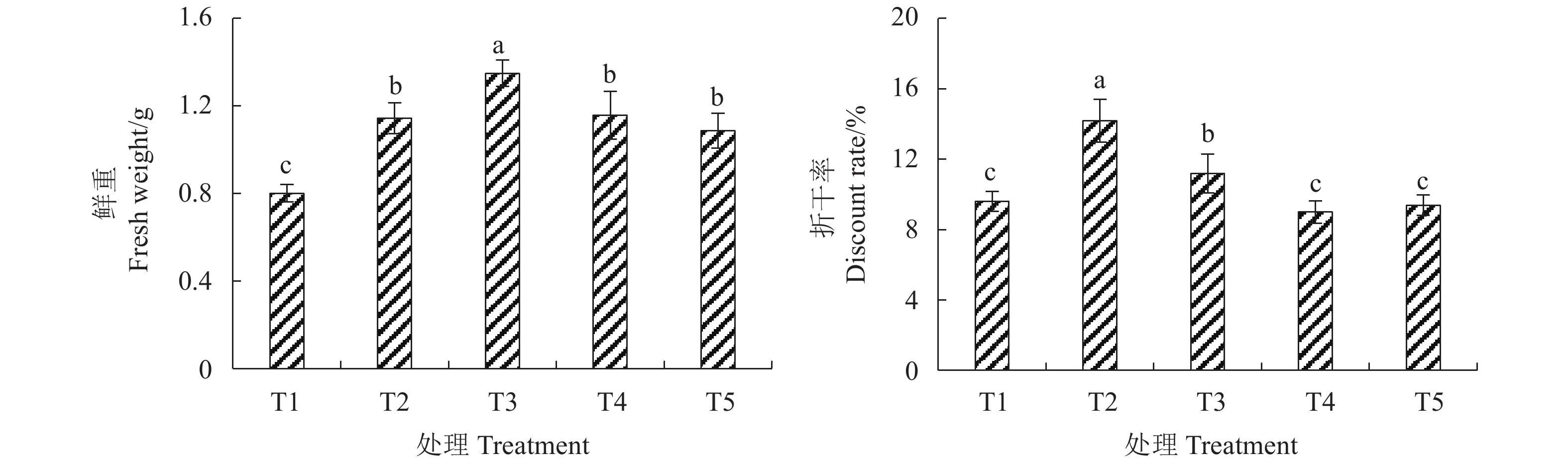
Note: Different lowercase letters in the table indicate significant differences at(P<0.05), the same below.由图1可知,土壤紧实度对金线莲产量有着显著的影响。金线莲鲜重和折干率均随土壤容重的增加呈现先增加后减少的趋势。鲜重在土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3达到最大值1.35 g,相比其他处理显著增加68.51%、18.04%、16.61%、24.13%(P<0.05),在土壤容重0.7 g·cm−3达到最小值0.80 g,与其他各处理间均达显著性差异。折干率在土壤容重0.8 g·cm−3达到最大值14.18%,相比其他处理显著增加47.71%、26.72%、57.73%、51.17%,在土壤容重1.0 g·cm−3达到最小值8.99%,而土壤容重0.7、1.0、1.1 g·cm−3处理下折干率之间无显著差异。表明过高或过低的土壤紧实度均不利于金线莲产量提升和体内干物质的合成与积累。
2.2 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲生理的影响
由表3可知,土壤紧实度对金线莲叶绿素和类胡萝卜素合成有着显著的影响。金线莲叶片中叶绿素及类胡萝卜素随土壤容重总体上均呈现先增加后减少的趋势,叶绿素a含量在土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3达到最大值1.99 mg·g−1,分别是其他处理的1.08、1.02、1.07、1.09倍,土壤容重0.8、0.9 g·cm−3处理间无明显差异。各处理叶绿素b含量平均为0.45 mg·g−1,各处理间差异不显著。各处理类胡萝卜素含量平均为0.56 mg·g−1,在土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3达到最大值0.63 mg·g−1,分别是其他处理的1.24、1.15、1.07、1.19倍,在土壤容重0.7 g·cm−3达到最小值0.51 mg·g−1,与最大值间存在显著性差异(P<0.05),但与其他处理间无显著差异。表明适宜的土壤紧实度会促进金线莲叶绿素和类胡萝卜素的合成,影响植物光合作用。
表 3 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲叶绿素与类胡萝卜素的影响Table 3. The effect of different soil compaction on physiological index of Anoectochilus处理
Treatment叶绿素a
Chlorophyll a/
(mg·g−1)叶绿素b
Chlorophyll b/
(mg·g−1)类胡萝卜素
Carotenoids/
(mg·g−1)T1 1.84±0.12 b 0.43±0.05 a 0.51±0.09 b T2 1.96±0.15 a 0.43±0.02 a 0.55±0.04 b T3 1.99±0.08 a 0.46±0.06 a 0.63±0.05 a T4 1.86±0.17 b 0.47±0.03 a 0.59±0.03 ab T5 1.83±0.13 b 0.46±0.07 a 0.53±0.08 b 2.3 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲养分、品质的影响
各处理间金线莲植株碳、氮、磷、钾养分含量变化趋势相同(见表4),均随土壤容重的增加呈先增加后减少的趋势。金线莲中碳素的含量最多,平均达到348.59 mg·g−1,其次是氮元素,磷元素含量最少,平均为1.15 mg·g−1。碳素含量在土壤容重1.0 g·cm−3达到最大值357.92 mg·g−1,相比其他处理分别增加了18.34、16.37、2.59、9.34 mg·g−1,在土壤容重0.7 g·cm−3达到最小值339.58 mg·g−1,高土壤容重(大于0.9 g·cm−3)处理的金线莲碳素积累量显著大于低土壤容重。氮素含量位于25.79~28.71 mg·g−1,除土壤容重1.1 g·cm−3处理金线莲氮素积累量最低外,其余处理间无显著性差异。磷素含量在土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3达到最大值1.27 mg·g−1,分别是其他处理的1.23、1.10、1.09、1.13倍,与其他处理均达显著差异(P<0.05)。钾素含量也以土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3处理为最大,以土壤容重1.1 g·cm−3处理为最小,两处理间钾素含量差距达到1.80 mg·g−1,达到显著差异。表明适宜的土壤容重可以促进金线莲植株养分积累,对碳、磷、钾素促进作用较为明显,而对氮素促进作用不明显。
表 4 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲养分含量的影响Table 4. The effect of different soil compaction on nutrient content of Anoectochilus处理
Treatment养分含量 Nutrient content/(mg·g−1) C N P K T1 339.58±10.47 b 28.15±1.27 a 1.03±0.04 c 19.27±1.05 b T2 341.55±12.54 b 28.35±1.31 a 1.15±0.08 b 20.62±1.30 a T3 355.33±9.92 a 28.71±0.52 a 1.27±0.07 a 20.77±1.52 a T4 357.92±17.43 a 28.21±1.39 a 1.16±0.12 b 19.13±0.99 b T5 348.58±8.04 a 25.79±0.93 b 1.12±0.09 b 18.97±1.41 b 由表5可知,土壤紧实度显著影响金线莲的品质。多糖含量在土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3达到最大值143.07 mg·g−1,相比其他处理显著增加了30.65%、70.81%、24.83%、29.00%(P<0.05),而在土壤容重0.8 g·cm−3时含量最低。氨基酸含量位于1.44~2.57 mg·g−1,在土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3达到最大值,相比其他处理显著增加了25.37%、29.80%、44.38%、78.47%,在高容重下氨基酸含量下降明显。黄酮含量位于8.65~13.98 mg·g−1,以土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3处理为最大,以土壤容重0.8 g·cm−3处理为最小。总酚和Vc含量均随土壤容重的增加呈先增加后减少的趋势,总酚在土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3达到最大值34.37 mg·g−1,相比其他处理显著增加了27.39%、24.80%、14.68%、26.92%,除土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3处理外,其余处理间无显著差异。Vc含量位于21.77~27.57 mg·g−1,以土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3处理为最大,以土壤容重1.1 g·cm−3处理为最小,两处理间Vc含量差距为5.80 mg·g−1,达到显著性差异。表明中等土壤紧实度的土壤最适于金线莲多糖、氨基酸、Vc等的合成和积累,促进品质提升。
表 5 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲品质指标的影响Table 5. The effect of different soil compaction on the quality index of Anoectochilus处理
Treatment多糖
Polysaccharide/(mg·g−1)氨基酸
Amino acid/(mg·g−1)总酚
Total phenols/(mg·g−1)黄酮
Flavonoids/(mg·g−1)Vc
Vitamin C/(mg·g−1)T1 109.51±3.55 b 2.05±0.13 b 26.98±1.64 b 12.01±0.84 ab 23.36±1.23 b T2 83.76±1.29 c 1.98±0.15 b 27.54±1.47 b 8.65±0.52 c 27.28±2.04 a T3 143.07±4.97 a 2.57±0.21 a 34.37±2.06 a 13.98±1.11 a 27.57±1.84 a T4 114.61±4.25 b 1.78±0.08 bc 29.97±2.34 b 13.74±0.95 a 24.67±1.81 b T5 110.91±3.88 b 1.44±0.17 c 27.08±1.82 b 10.66±0.69 b 21.77±2.45 c 3. 讨论
3.1 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲生长的影响
土壤紧实度作为反映土壤松紧状况的指标,通过影响土壤水分、养分、通气状况、热量以及微生物,进而影响植物的生长[14]。本试验结果表明,通过珍珠岩调控,土壤物理性质发生变化,金线莲株高、地径、叶片数、根长、鲜重等随着土壤容重增加,都呈先增加后减少的趋势。在红壤与珍珠岩配比为40∶1,即土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3时达到最大。表明适宜的土壤容重会促进金线莲的生长,提高作物产量,而过高或过低的土壤容重会影响金线莲生长发育进程。这些与前人的研究结果相似。
刘宪辉[15]研究发现珍珠岩施入蔬菜大棚土壤中能有效改良土壤,增加作物产量。这是因为一方面珍珠岩具有较高的吸附容量和离子交换能力,可有效起到保水保肥、抗渗漏、提高养分生物有效性作用,另一方面它自身含有一定量的钾、磷、钛、锰、硅、铁、钙等植物不可缺少的中微量元素,为农作物提高了良好的生长条件。徐海等[16]研究发现,玉米地上部生长受土壤容重影响显著,土壤过松或过紧均不利于作物的生长。刘兆娜等[17]对花生设置不同容重处理,发现适宜土壤容重在整个生育期都有利于花生各器官干物质积累,有利于增加结果数和荚果饱满度,提高荚果和籽仁产量。土壤紧实度过高,土壤孔隙度降低,土壤板结程度增加,土壤通气透水能力变差,土壤内空气缺乏,进而抑制微生物活动和养分转化进程,根系对水和养分的吸收能力降低;而土壤紧实度过低,土壤孔隙度大,土壤内部空气浓度变高,土壤热量扩散速度加快,植物根系与土壤接触面积变小,土壤对植物根系的支持能力减弱,土壤保水持肥能力下降,养分易随降水或灌溉水流失。因此,只有适宜的土壤紧密度,才能保证土壤水分、养分供应充足、通气状况良好,有助于金线莲的正常生长[18]。
3.2 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲生理的影响
叶绿素和类胡萝卜素作为表征植物光合作用能力的指标,其含量的高低会影响植物光合作用,进而影响植物物质的合成与转运[19]。本试验结果表明,在红壤与珍珠岩配比为40∶1,即土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3时金线莲叶绿素a和类胡萝卜素含量最高,叶绿素b含量无显著差异,表明土壤紧实度会影响金线莲的生理,影响叶绿素和类胡萝卜素的合成,过高或者过低的土壤紧实度均不利于金线莲叶绿素和类胡萝卜素的合成与积累。尚庆文等[20]研究表明,土壤紧实度增加,生姜叶片活性降低,叶绿素含量下降,光合速率下降,光合作用减弱。田树飞等[21]研究表明适宜的土壤紧实度有利于花生叶片光合色素的合成与积累。这些都与本研究结果一致。适宜的土壤紧实度会提高植株中叶绿素和类胡萝卜素含量,促进光合作用。这可能与土壤环境改善、水肥气热环境适宜、植株生长发育良好、植株各项生理活性提高有关[22]。
3.3 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲养分和品质的影响
C、N、P、K含量是间接反映植物生长及物质合成的指标,通过影响植物体内物质转化进程,进而影响物质的合成与积累[23]。多糖、总酚、氨基酸、黄酮、Vc等物质,是反映金线莲营养及药用价值的重要指标,其含量高低能够反映金线莲活性物质含量的高低[24]。
本试验结果表明,金线莲N、P、K含量均在0.9 g·cm−3处理达到最大值,C含量在1.0 g·cm−3处理达到最大值,在0.9 g·cm−3处理与1.0 g·cm−3处理间两者仅相差2.59 mg·g−1,可以得知金线莲生长在红壤与珍珠岩配比为40∶1,即容重为0.9 g·cm−3的土壤中,其养分含量最高。金线莲多糖、氨基酸、总酚、黄酮、Vc含量随土壤容重的增加总体呈先增加后减少的趋势,也均在0.9 g·cm−3处理达到最大值,多糖、氨基酸、总酚含量与其他处理均达显著差异,表明过高过低的土壤紧实度均不利于金线莲品质的提升。张亚如等[25]研究发现,土壤过高或者过低的紧实度都会抑制花生结荚期氮、磷、钾等元素的吸收,影响植株品质。张向东等[26]对桔梗设置不同紧实度处理,发现土壤紧实胁迫下,桔梗根系活力下降,叶绿素含量降低,可溶性蛋白含量减少,植株品质降低。综合分析原因,过高过低的土壤紧实度,会导致金线莲根系对于土壤中营养元素的供给和吸收能力降低,从而使体内物质循环和转化途径效率降低[27]。过高的土壤紧实度,其土壤结构紧实黏重,土层氧气浓度低,土壤胶体对养分和水分的吸附作用强烈,土壤酶活性低,微生物活动弱,根系难以下扎,从而根系难以吸收水分和养分;过低的土壤紧实度,土壤结构松碎易散,土壤保水保肥能力低,土壤水分易通过土面蒸腾而损失,土壤养分易流失,土壤养分和水分供应不足,进而导致金线莲养分积累量降低、品质下降等[28]。
4. 结论
适宜的土壤紧实度会促进金线莲生长和产量提升,对金线莲根、茎、叶生长及物质合成与积累有显著影响,在红壤与珍珠岩配比达到40∶1,土壤容重为0.9 g·cm−3时效果最佳,而土壤紧实度对金线莲叶长和叶宽的增长没有显著影响。
土壤紧实度的高低会影响金线莲的生理,适宜的土壤紧实度促进金线莲叶片中叶绿素a和类胡萝卜素的合成,但对叶绿素b含量没有显著影响。
适宜的土壤紧实度增加金线莲体内C、N、P、K养分含量,提高植株中多糖、氨基酸、总酚、黄酮和Vc含量,在红壤与珍珠岩配比达到40∶1,土壤容重为0.9 g·cm−3时效果最佳,土壤容重过高或者过低均不利于金线莲养分合成积累和品质提升。
综上,土壤紧实度对于金线莲的生长和品质有显著影响。在红壤与珍珠岩配比达到40∶1,即土壤容重为0.9 g·cm−3时金线莲各项生长、品质指标优于其他处理,总体效果最佳,对金线莲科学种植具有一定的指导意义。
-
表 1 各处理土壤和珍珠岩质量
Table 1 The quality of soil and perlite for each treatment
处理
Treatment红壤
Red soil/g珍珠岩
Perlite/g容重
Bulk density/(g·cm−3)T1 1200 120 0.7 T2 1400 80 0.8 T3 1600 40 0.9 T4 1800 20 1.0 T5 2000 0 1.1 表 2 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲生长指标的影响
Table 2 The effect of different soil compaction on the growth index of Anoectochilus
处理
Treatment株高
Plant height/cm地径
Ground path/mm叶数
Number of leaves叶长
Leaf length/cm叶宽
Leaf width/cm根长
Root length/cmT1 9.92±0.32 c 2.46±0.22 b 3.87±0.33 b 2.03±0.19 b 1.74±0.14 a 3.02±0.31 c T2 11.28±0.44 b 2.71±0.20 a 4.34±0.22 a 2.51±0.08 a 1.75±0.07 a 3.20±0.27 c T3 12.40±0.73 a 2.75±0.15 a 4.36±0.37 a 2.63±0.13 a 1.77±0.07 a 4.53±0.34 a T4 11.14±0.51 b 2.45±0.26 b 4.00±0.35 b 2.41±0.13 a 1.71±0.16 a 4.26±0.28 b T5 10.80±0.65 bc 2.50±0.23 b 4.12±0.18 ab 2.41±0.14 a 1.68±0.10 a 4.49±0.45 a 注:表中标注不同小写字母表示在(P<0.05)水平差异显著,下同。
Note: Different lowercase letters in the table indicate significant differences at(P<0.05), the same below.表 3 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲叶绿素与类胡萝卜素的影响
Table 3 The effect of different soil compaction on physiological index of Anoectochilus
处理
Treatment叶绿素a
Chlorophyll a/
(mg·g−1)叶绿素b
Chlorophyll b/
(mg·g−1)类胡萝卜素
Carotenoids/
(mg·g−1)T1 1.84±0.12 b 0.43±0.05 a 0.51±0.09 b T2 1.96±0.15 a 0.43±0.02 a 0.55±0.04 b T3 1.99±0.08 a 0.46±0.06 a 0.63±0.05 a T4 1.86±0.17 b 0.47±0.03 a 0.59±0.03 ab T5 1.83±0.13 b 0.46±0.07 a 0.53±0.08 b 表 4 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲养分含量的影响
Table 4 The effect of different soil compaction on nutrient content of Anoectochilus
处理
Treatment养分含量 Nutrient content/(mg·g−1) C N P K T1 339.58±10.47 b 28.15±1.27 a 1.03±0.04 c 19.27±1.05 b T2 341.55±12.54 b 28.35±1.31 a 1.15±0.08 b 20.62±1.30 a T3 355.33±9.92 a 28.71±0.52 a 1.27±0.07 a 20.77±1.52 a T4 357.92±17.43 a 28.21±1.39 a 1.16±0.12 b 19.13±0.99 b T5 348.58±8.04 a 25.79±0.93 b 1.12±0.09 b 18.97±1.41 b 表 5 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲品质指标的影响
Table 5 The effect of different soil compaction on the quality index of Anoectochilus
处理
Treatment多糖
Polysaccharide/(mg·g−1)氨基酸
Amino acid/(mg·g−1)总酚
Total phenols/(mg·g−1)黄酮
Flavonoids/(mg·g−1)Vc
Vitamin C/(mg·g−1)T1 109.51±3.55 b 2.05±0.13 b 26.98±1.64 b 12.01±0.84 ab 23.36±1.23 b T2 83.76±1.29 c 1.98±0.15 b 27.54±1.47 b 8.65±0.52 c 27.28±2.04 a T3 143.07±4.97 a 2.57±0.21 a 34.37±2.06 a 13.98±1.11 a 27.57±1.84 a T4 114.61±4.25 b 1.78±0.08 bc 29.97±2.34 b 13.74±0.95 a 24.67±1.81 b T5 110.91±3.88 b 1.44±0.17 c 27.08±1.82 b 10.66±0.69 b 21.77±2.45 c -
[1] 郎楷永, 陈心启, 罗毅波, 等. 中国植物志: 第17卷[M]. 北京: 北京科学出版社, 1999: 204−227. [2] 吴丽丽, 梁燕, 许光辉. 金线莲化学成分、药理作用及临床应用研究概述 [J]. 海峡药学, 2014, 26(10):34−36, 37. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3765.2014.10.013 WU L L, LIANG Y, XU G H. Advances on investigation of chemical components, pharmacological ac-tivtties and clinical applications of Anocetochilus roxburghii [J]. Strait Pharmaceutical Journal, 2014, 26(10): 34−36, 37.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3765.2014.10.013
[3] 陈育青, 林艺华, 邹毅辉, 等. 金线莲生药鉴定、活性成分影响因素及药理作用研究进展 [J]. 中成药, 2020, 42(8):2141−2144. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2020.08.033 CHEN Y Q, LIN Y H, ZOU Y H, et al. Research progress on identification of crude drugs, active ingredients and pharmacological effects of Anoectochilus [J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2020, 42(8): 2141−2144.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2020.08.033
[4] YE S Y, SHAO Q S, ZHANG A L. Anoectochilus roxburghii: A review of its phytochemistry, pharmacology, and clinical applications [J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2017, 209: 184−202. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.07.032
[5] 童晨晓, 邹双全, 胡坤, 等. 废菌棒替代泥炭土对金线莲生长和品质的影响 [J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2020, 42(5):915−922. TONG C X, ZOU S Q, HU K, et al. Effect of used bagasse substrate substituting peat soil on growth and quality of Anoectochilus roxburghii [J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis (Natural Sciences Edition), 2020, 42(5): 915−922.(in Chinese)
[6] 张向东, 华智锐, 邓寒霜. 土壤紧实胁迫对黄芩生长、产量及品质的影响 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2014(3):7−11. DOI: 10.11838/sfsc.20140302 ZHANG X D, HUA Z R, DENG H S. Effects of soil compaction stress on growth, quantity and quality of Scutellaria baicalensis [J]. Soils and Fertilizers Sciences in China, 2014(3): 7−11.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11838/sfsc.20140302
[7] 刘文虎, 魏振康, 肖理, 等. 土壤紧实度对裸土侵蚀强度影响的实验与分析 [J]. 中国水土保持科学, 2019, 17(6):52−60. LIU W H, WEI Z K, XIAO L, et al. Experimental analysis of soil compactness on erosion intensity of bare soil [J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 17(6): 52−60.(in Chinese)
[8] YE S Y, SHAO Q S, XU M J, et al. Effects of light quality on morphology, enzyme activities, and bioactive compound contents in Anoectochilus roxburghii [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 857. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00857
[9] 吴晓莲, 林兆里, 张华. 不同土壤紧实度对甘蔗品种福农39号苗期生长的影响 [J]. 广东农业科学, 2014, 41(19):43−46. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2014.19.011 WU X L, LIN Z L, ZHANG H. Influence of soil density on seedling growth of sugarcane variety Funong 39 [J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 41(19): 43−46.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2014.19.011
[10] 邹俊, 刘丽, 郭巧生, 等. 土壤容重对活血丹生长、生理及药材品质的影响 [J]. 中国中药杂志, 2018, 43(19):3848−3854. ZOU J, LIU L, GUO Q S, et al. Effects of soil bulk density on growth, physiology and quality of Glechoma longituba [J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2018, 43(19): 3848−3854.(in Chinese)
[11] 刘永晨, 司成成, 柳洪鹃, 等. 土壤紧实度对甘薯群体结构及产量的影响 [J]. 山东农业科学, 2019, 51(10):99−103. LIU Y C, SI C C, LIU H J, et al. Effects of soil compactness on population structure and yield of sweet potato [J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 51(10): 99−103.(in Chinese)
[12] TRACY S R, BLACK C R, ROBERTS J A, et al. Quantifying the impact of soil compaction on root system architecture in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) by X-ray micro-computed tomography [J]. Annals of Botany, 2012, 110(2): 511−519. DOI: 10.1093/aob/mcs031
[13] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典(2010年版): 一部[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2010. [14] 田孝志, 徐龙晓, 宋建飞, 等. 土壤紧实度对不同砧木苹果幼树根系H_2S及硫代谢酶的影响 [J]. 植物生理学报, 2020, 56(9):1845−1853. TIAN X Z, XU L X, SONG J F, et al. Effects of soil compaction on root H2S and sulfur metabolic enzymes of young apple tree with different rootstocks [J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2020, 56(9): 1845−1853.(in Chinese)
[15] 刘宪辉. 膨胀珍珠岩改良蔬菜大棚土壤理化性质的研究 [J]. 现代农业, 2010(11):25. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0708.2010.11.025 LIU X H. Research on improving physical and chemical properties of vegetable greenhouse soil by expanded perlite [J]. Modern Agriculture, 2010(11): 25.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0708.2010.11.025
[16] 徐海, 王益权, 王永健, 等. 土壤紧实胁迫对玉米苗期生长与钙吸收的影响 [J]. 农业机械学报, 2011, 42(11):55−59, 54. XU H, WANG Y Q, WANG Y J, et al. Effect of soil compaction stress on the growth of corn and calcium absorption at the seedling stage [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2011, 42(11): 55−59, 54.(in Chinese)
[17] 刘兆娜, 田树飞, 邹晓霞, 等. 土壤紧实度对花生干物质积累和产量的影响 [J]. 青岛农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 36(1):34−40. LIU Z N, TIAN S F, ZOU X X, et al. Effects of soil compaction on dry matter accumulation and yield of peanut [J]. Journal of Laiyang Agricultural College, 2019, 36(1): 34−40.(in Chinese)
[18] WANG S B, GUO L L, ZHOU P C, et al. Effect of subsoiling depth on soil physical properties and summer maize (Zea mays L.) yield [J]. Plant, Soil and Environment, 65, 2019(3): 131−137.
[19] 杨喜珍, 杨利, 覃亚, 等. PEG-8000模拟干旱胁迫对马铃薯组培苗叶绿素和类胡萝卜素含量的影响 [J]. 中国马铃薯, 2019, 33(4):193−202. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3635.2019.04.001 YANG X Z, YANG L, QIN Y, et al. Effects of PEG-8000 stres on contents of chlorophyll and carotenoid of potato plantlets in vitro [J]. Chinese Potato Journal, 2019, 33(4): 193−202.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3635.2019.04.001
[20] 尚庆文, 孔祥波, 王玉霞, 等. 土壤紧实度对生姜植株衰老的影响 [J]. 应用生态学报, 2008, 19(4):782−786. SHANG Q W, KONG X B, WANG Y X, et al. Effects of soil compactness on ginger plant senescence [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2008, 19(4): 782−786.(in Chinese)
[21] 田树飞, 刘兆娜, 邹晓霞, 等. 土壤紧实度对花生光合与衰老特性和产量的影响 [J]. 花生学报, 2018, 47(3):40−46. TIAN S F, LIU Z N, ZOU X X, et al. Effects of soil compaction on photosynthesis and senescence characteristics and yield of peanut [J]. Journal of Peanut Science, 2018, 47(3): 40−46.(in Chinese)
[22] 史文卿, 张彬彬, 柳洪鹃, 等. 甘薯块根形成和膨大对土壤紧实度的响应机制及与产量的关系 [J]. 作物学报, 2019, 45(5):755−763. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2019.84084 SHI W Q, ZHANG B B, LIU H J, et al. Response mechanism of sweet potato storage root formation and bulking to soil compaction and its relationship with yield [J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2019, 45(5): 755−763.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2019.84084
[23] 裴雪霞, 党建友, 张定一, 等. 化肥减施下有机替代对小麦产量和养分吸收利用的影响 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(10):1768−1781. DOI: 10.11674/zwyf.20197 PEI X X, DANG J Y, ZHANG D Y, et al. Effects of organic substitution on the yield and nutrient absorption and utilization of wheat under chemical fertilizer reduction [J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(10): 1768−1781.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11674/zwyf.20197
[24] 牛欢, 韦坤华, 徐倩, 等. 不同光照度对金线莲生长、生理特性和药用成分的影响 [J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2020, 29(1):26−36, 43. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7895.2020.01.04 NIU H, WEI K H, XU Q, et al. Effects of different illuminances on growth, physiological characteristics, and medicinal components of Anoectochilus roxburghii [J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 2020, 29(1): 26−36, 43.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7895.2020.01.04
[25] 张亚如, 崔洁亚, 侯凯旋, 等. 土壤容重对花生结荚期氮、磷、钾、钙吸收与分配的影响 [J]. 华北农学报, 2017, 32(6):198−204. DOI: 10.7668/hbnxb.2017.06.029 ZHANG Y R, CUI J Y, HOU K X, et al. Effects of soil bulk density on nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and calcium uptake and distribution in peanut pod bearing stage [J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2017, 32(6): 198−204.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7668/hbnxb.2017.06.029
[26] 张向东, 邓寒霜, 华智锐. 土壤紧实胁迫对桔梗生长、产量及品质的影响 [J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 41(7):177−182. ZHANG X D, DENG H S, HUA Z R. Effects of soil compaction stress on growth, quantity and quality of Platycodon grandiflorum [J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University(Natural Science Edition), 2013, 41(7): 177−182.(in Chinese)
[27] 刘滨硕, 薛洪海, 李明, 等. 土壤紧实度对羊草形态及其生物量的影响 [J]. 科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(2):59−62. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.02.010 LIU B S, XUE H H, LI M, et al. Effects of soil bulk density on morphology and biomass of Leymus chinensis [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19(2): 59−62.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.02.010
[28] 王玉萍, 周晓洁, 卢潇, 等. 土壤紧实度对马铃薯根系、匍匐茎、产量和品质的影响 [J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(6):1590−1596. DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2016.00031 WANG Y P, ZHOU X J, LU X, et al. Effect of soil compaction on root, stolon, yield and quality of potato [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2016, 36(6): 1590−1596.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2016.00031
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 朱兴龙,张佳旭,陈晓妍,黄旭龙,周涛,吴清华,裴瑾. 遂宁川白芷产地变迁过程中土壤质地对药材质量的影响. 世界中医药. 2024(18): 2725-2733 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 潘可可,王克磊,李斌奇,张曦文,陈发兴. 不同比例红蓝光及光照强度对金线莲生理及叶绿素荧光特性的影响. 热带作物学报. 2022(08): 1628-1635 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(9)




 下载:
下载: