Study on the aroma components of the juice of Guanximiyou and its bud-mutation varieties of Hongroumiyou and Sanhongmiyou
-
摘要:目的 研究探明琯溪蜜柚及其芽变新品种果汁的香气组分种类、相对含量与差异,以及引起香气组分变化的可能分子机理。方法 以琯溪蜜柚及其芽变品种红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚果实为试材,采用气相色谱质谱法(GC-MS)测定果汁香气组分;通过转录组分析,筛选差异表达显著的基因,并采用FPKM值的趋势分析这些基因的表达模式。结果 供试3个果汁样品中共检出150种香气组分,占组分数量较多的香气化合物为芳香烃类、倍半萜烯类、醛类、醇类、酮类等;各品种的香气组分数量与含量相差较大,琯溪蜜柚、红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚分别检出59种、129种和67种香气化合物,其总相对含量分别为4.56、8.02和9.90,说明芽变显著引起了香气组分和总相对含量的变化。香气组分中醛类相对含量最高,己醛为3个品种的共同主要香气组分;醇类、酮类相对含量次之,呋喃类、芳香烃类、倍半萜烯类、酯类、单萜类化合物相对含量较少;此外还检出相对含量很低或微量的其他类的香气组分32种,且均为未见报道的未知化合物。利用转录组分析筛选获得新基因(Citrus_maxima_newGene_12651)1个,表达差异显著的脂肪氧化酶(Lipoxidase)LOX2.1基因7个(cg2g001970、cg2g001980、cg2g002000、cg2g002010、cg2g002030、cg2g002040、cg2g002080)、LOX3.1基因1个(cg1g010660)和乙醇脱氢酶(Alcohol dehydrogenase)ADH1基因2个(cg3g017900、cg3g017890),采用FPKM值的趋势分析,初步推测3个品种的果汁香气组分差异与脂肪酸途径、异戊二烯途径中的基因差异表达有关。结论 醛类、醇类、酮类是琯溪蜜柚及其芽变品种红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚的主要香气组分,己醛为3个品种的共同主要香气化合物;供试3个品种果汁香气组分差异显著,初步推测与脂肪酸途径、异戊二烯途径等途径中的基因差异表达有关。Abstract:Objective The aim of this study is to investigate the types, relative contents and differences in the aroma components of the juice of Guanximiyou and its new bud variants, as well as the possible molecular mechanisms causing the changes in the aroma components.Methods Fruits juice of Guanximiyou and its bud-variant varieties Hongroumiyou and Sanhongmiyou were used as test materials to determine the aroma components by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The genes that were significantly differentially expressed were screened by transcriptome analysis, and the expression patterns of these genes were analyzed using the trend of FPKM values.Results A total of 150 aroma components were detected in the three juice samples, and the aroma compounds that accounted for a large number were aromatic hydrocarbons, sesquiterpenes, aldehydes, alcohols and ketones. Guanximiyou, Hongroumiyou and Sanhongmiyou detected 59, 129 and 67 aroma compounds respectively, with their total relative contents of 4.56, 8.02 and 9.90 respectively, indicating that bud changes significantly caused changes in the aroma components and total relative content. The relative content of aldehydes was the highest, with hexanal being the main aroma component common to all three species; alcohols and ketones were the next most abundant, while furans, aromatic hydrocarbons, sesquiterpenes, esters and monoterpenes were less abundant; 32 other aroma components were also detected at very low or trace levels, all of which were unknown and unreported compounds. Transcriptome analysis was used to screen for one new gene (Citrus_maxima_newGene_12651), seven genes with significant differences in expression of Lipoxidase (LOX2.1) (cg2g001970, cg2g001980, cg2g002000, cg2g002010, cg2g002030, cg2g002040, cg2g002080 cg2g002030, cg2g002040, cg2g002080), one LOX3.1 gene (cg1g010660) and two Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH1) genes (cg3g017900, cg3g017890), using trend analysis of FPKM values. It was tentatively hypothesized that the differences in the aroma components of the juices of the three varieties were related to the differential expression of genes in the fatty acid pathway and the isoprene pathway.Conclusion Aldehydes, alcohols and ketones were the main aroma components of Guanximiyou and its bud varieties, and hexanal was the main aroma compound common to the three varieties; The significant differences in the aroma components of the fruit juices of the three varieties tested were initially hypothesized to be related to the differential expression of genes in the fatty acid pathway and isoprene pathway.
-
Keywords:
- pomelo /
- Guanximiyou /
- bud-mutation varieties /
- aroma component /
- differentially expressed gene
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】柑橘是我国广泛栽培,面积和产量均居前茅的果树种类,主要包括宽皮橘类、甜橙类、柚类、杂柑类、金柑类和枸橼等,其中以宽皮橘类、甜橙类、柚类栽培最为广泛。柚子是中国的特产水果,果实硕大,挥发性物质含量较高,芸香味浓郁。琯溪蜜柚以果大色美味佳、皮薄汁多耐贮而闻名海内外,堪称“柚中之冠”,香气是琯溪蜜柚果实品质的重要指标之一。【前人研究进展】已有研究报道,在柚子[1-4]、葡萄柚[5,6]、甜橙[7-12]、酸橙[11,12]、血橙[10,13,14,]、宽皮柑橘[11,15-18]、柠檬[19-21]、枸橼[22]、杂柑[23-26]上均有果实香气物质的研究。不同种类、不同品种之间存在基因型差异,其果实香气成分也存在较大的差异,且因检测分析方法不同,已有研究的结果不尽一致。【本研究切入点】柚类不同种类和品种的果实主要香气成分存在差异,而琯溪蜜柚及其芽变品种红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚果实的香气成分如何,尚未见深入研究;也未见对引起琯溪蜜柚芽变品种香气组分差异的分子机理进行研究。【拟解决的关键问题】研究探明琯溪蜜柚及其芽变新品种果汁的香气组分种类、相对含量与差异,以及引起香气组分变化的可能分子机理,以期为高品质蜜柚的选育和产品深度开发提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
供试材料为琯溪蜜柚[Citrus maxima(Burm.)Merr]及其芽变1代品种红肉蜜柚、芽变2代品种三红蜜柚,样品采自于平和县厝坵村福建平和祥红红肉蜜柚开发有限公司果园,8年生结果树,取成熟果实果汁为供试样品。
主要试剂C8-C20烷烃混标(40 mg·L−1,Sigma),3-己酮(0.815 g·mL−1,Sigma),正己烷(色谱纯,罗恩),超纯水,氯化钠(色谱纯,Sigma)。
1.2 试验仪器
气相色谱质谱仪器(7890B,Agilent),自动进样架(GERSTEL MPS),飞行时间质谱(Pegasus HT-C- LECO),毛细管色谱柱(0.25 μm ×0.25 mm × 30 m,RESTEK Rxi-5 Sil MS),分析天平(赛多利斯科学仪器北京有限公司 d = 0. 1 mg),纯水系统(Millipore,Elix Essential 5,Milli-Q Advan-tage A10),纤维针(1 cm,50/30 μm,DVB/CAR/PDMS,Supelco,Bellefonte, PA, USA),称量纸,药匙,试管架,移液枪。
1.3 试验方法
1.3.1 香气组分分析
采用气相色谱质谱法。称取1.5 g NaCl粉末,吸取6 ml果汁,加入6 μl内标3-己酮(0.163 g·L−1)于20 mL顶空瓶中,盖上带有硅胶/聚四氟乙烯隔膜(18 mm,GERSTEL)的螺旋卷曲帽,迅速混匀。备好的样品于−20 ℃保存。每个基因型设3个生物学重复。采用固相微萃取(SPME)法进行香气物质的提取时,样品于室温下解冻,放置于气相色谱质谱仪(7890B,Agilent)支架上,以待检测。分析时,果汁样品在40 ℃下温育30 min后,由1 cm纤维针(50/30 μm,DVB/CAR/PDMS,Supelco,Bellefonte, PA, USA)暴露在顶空瓶上方吸附60 min,再经由纤维针将吸附的香气化合物注入气相色谱质谱仪(7890B,Agilent)注入器端口,释放5 min。GC设备设置为:色谱柱,Rxi-5 Sil MS;进样口温度:250 ℃;传输线温度:270 ℃;载气:氦气;氦气流速:1 mL·min−1;程序升温:40 ℃保持5 min,以3 ℃·min−1的速率升至230 ℃,保持3 min,以15 ℃·min−1的速率升至260 ℃;不分流进样。MS条件:溶剂延迟,5 min;扫描范围:45~600;采集速率:10谱图/s;检测器电压:1530 V;EI电离能量:70 eV;离子源温度:250 ℃。每天进样前,先跑一针C8-C20烷烃混标(10 mg·L−1,Sigma),通过自动解卷积与鉴定系统(AMDIS)计算正构烷烃C8-C20数据文件得到正构烷烃保留指数(RI)。采用各组分在图谱库NIST05.L中匹配度大于99%的鉴定结果进行定性分析,并与文献资料中相关化合物保留指数进行比对分析。采用内标法对样品的峰面积进行校正。
1.3.2 转录组分析
材料 以琯溪蜜柚及其芽变品种红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚果实为材料。每个品种选取3株8年长势一致的蜜柚树,分别采集花后80 、120 和180 d的果实,每株树采3个果,共27个样品;取果肉液氮速冻,−80 ℃低温冰箱贮存备用。
方法 采用BioTeKe总RNA抽提试剂盒提取柚果实总RNA;委托广州华大生物科技有限公司建库、测序(Illumina HiSeqTM 2500)、De novo组装和注释等生物信息学分析;差异表达基因筛选与FPKM趋势分析参照文献[27]~[28]。
1.3.3 数据处理与统计
试验结果为3次重复的平均值,试验数据采用Microsoft Excel软件进行处理和图表制作,采用JMP 13.0统计软件进行主成分分析,采用prism软件进行FPKM值趋势预测。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 供试3个品种果汁香气组分与相对含量
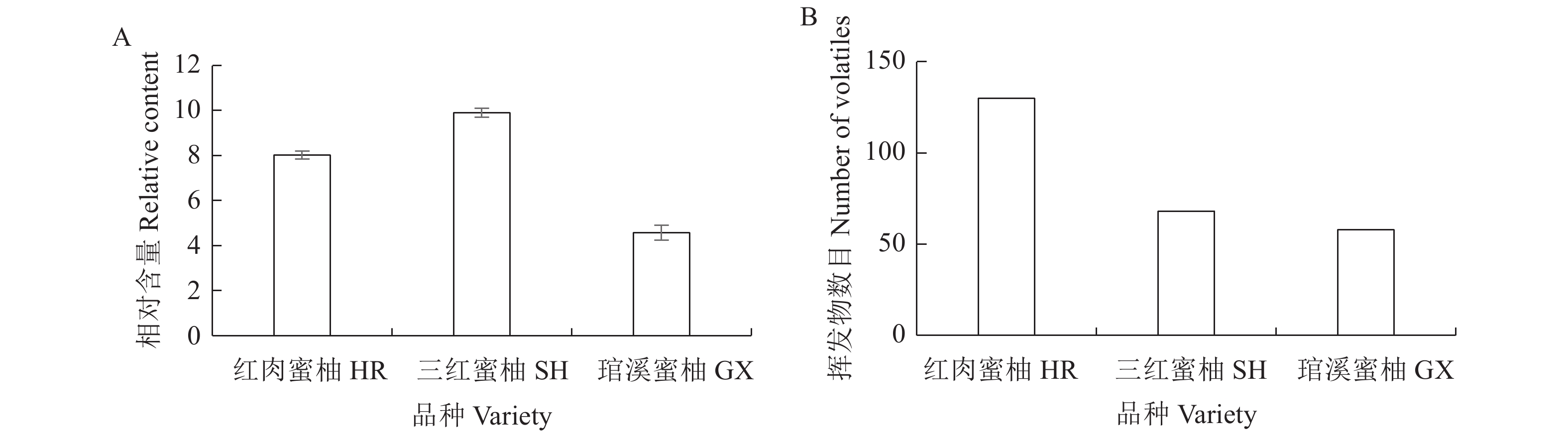
图1-A、B和表1至表8显示,琯溪蜜柚及其芽变品种红肉蜜柚、三红蜜柚果汁样品中共检出150种香气组分,各品种的香气组分数量与含量相差较大。
表 1 琯溪蜜柚、红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚果汁样品中的醛类香气组分Table 1. Aroma volatiles(Aldehydes)in juice samples of Guanximiyou, Hongroumiyou and Sanhongmiyou化合物
Compound保留指数 RI
(计算Calculated)相对含量
Relative contentHR SH GX 反-2-戊烯醛
(E)-2-Pentenal735.43(748)* 0.02 0.10 0.02 顺-3-己烯醛
(Z)-3-Hexenal764.01(793) 0.31 0.26 0.08 己醛 Hexanal 766.26(787) 3.65 5.77 2.24 2-己烯醛 2-Hexenal 807.38(854) 0.04 0.03 0.01 反-2-己烯醛
(E)-2-Hexenal814.59(844) 0.38 0.23 0.13 4-甲基-己醛
4-methyl-Hexanal840.57(889) tr 0.01 0.71 庚醛 Heptanal 867.56(899) 0.07 0.35 nd 反-2-庚醛
(E)-2-Heptanal932.46(946) 0.01 0.12 nd 辛醛 Octanal 989.86(998) 0.01 0.10 tr 反-2-辛烯醛
(E)-2-Octenal1055.85(1059) tr 0.15 nd 壬醛 Nonanal 1112.22(1109) 0.01 0.05 nd 反-2-壬烯醛
(E)-2-Nonenal1175.83(1160) nd 0.02 tr 正葵醛 Decanal 1228.75(1228) nd tr nd 注:数据均为内标峰面积的相对定量值,且为3个生物学重复的平均值。RI:保留指数Retention index,*:括号内数字为已发表的保留指数RI;tr :表示此处有被识别的峰,但值小于0.0095;nd:表示未检测到峰;GX:琯溪蜜柚,HR:红肉蜜柚,SH:三红蜜柚。下同。
Note: The data are all relative quantitative values of internal standard peak areas and are the average of three biological replicates. RI: Retention index, *: the number in parentheses is the published retention index(RI). tr: there is an identified peak here, but the value is less than 0.009 5. nd: no peak was detected. GX: Guanximiyou, HR: Hongroumiyou, SH: Sanhongmiyou. Same as below.
琯溪蜜柚果汁中共检测到59种香气化合物,总相对含量4.56,占多数的化合物种类为芳香烃类、倍半萜烯类、醛类、醇类、酮类等。红肉蜜柚果汁中共检测到129种香气化合物,总相对含量8.02,占多数的化合物种类为芳香烃类。三红蜜柚果汁中共检测到67种香气化合物,总相对含量9.90,占多数的化合物种类为芳香烃类、醛类、醇类等。相对含量较高的主要香气组分为醛类、醇类、酮类,相对含量较低的有呋喃类、芳香烃类、倍半萜烯类、酯类、单萜类化合物,此外还检出相对含量很低或微量的其他类的香气组分32种,且均为未见报道的未知化合物。
表1表明,3个供试品种果汁共检出13种醛类香气组分,其中1种相对含量为微量(虽有被识别的峰,但相对值小于0.0095);琯溪蜜柚共检出8种醛类香气组分,其中6种内标峰面积的相对定量值>0.0095,总相对含量为3.19;微量2种、未检出5种;红肉蜜柚共检出11种醛类香气组分,其中9种内标峰面积的相对定量值>0.0095,总相对含量为4.5;微量2种、未检出2种;三红蜜柚共检出13种醛类香气组分,其中12种内标峰面积的相对定量值>0.0095,总相对含量为7.19;微量1种。己醛在醛类香气组分中的相对含量最高,是3个品种果汁的共同主要香气组分,但芽变品种红肉蜜柚(3.65)和三红蜜柚(5.77)均显著高于琯溪蜜柚(2.24)。
表2表明,3个供试品种果汁共检出12种醇类香气组分,其中,2种未见研究报道,3种仅含微量;2种为未知醇类香气物质。琯溪蜜柚共检出10种醇类香气组分,其中5种内标峰面积的相对定量值>0.0095,总相对含量为0.13;微量5种,未检出2种;红肉蜜柚共检出10种醇类香气组分,其中8种内标峰面积的相对定量值>0.0095,总相对含量为2.29;微量2种,未检出2种;三红蜜柚共检出12种醇类香气组分,其中9种内标峰面积的相对定量值>0.0095,总相对含量为1.64;微量3种。正己醇和3-己烯-1-醇在醇类香气组分中相对含量最高,是3个品种的共同香气组分,但芽变品种红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚均显著高于琯溪蜜柚。
表 2 琯溪蜜柚、红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚果汁样品中的醇类香气组分Table 2. Aroma volatiles (Alcohols) in juice samples of Guanximiyou, Hongroumiyou and Sanhongmiyou化合物
Compound保留指数RI
(计算Calculated)相对含量
Relative contentHR SH GX 正戊醇 1-Pentanol 743.08(761 d) 0.04 0.07 0.04 顺-2-戊烯-1-醇
(Z)-2-Penten-1-ol744.78(767 c) 0.03 0.03 0.02 3-己烯-1-醇
(E)-3-Hexen-1-ol819.22(851 b) 0.95 0.74 tr 反-2-己烯-1-醇
(E)-2-Hexen-1-ol829.79(858 g) 0.05 0.02 tr 正己醇 1-Hexanol 835.19(865 b) 1.17 0.66 0.03 RI 949 948.98 tr tr tr 反-2-庚烯-1-醇
(E)-2-Hepten-1-ol949.04(958 g) 0.01 0.03 0.02 正庚醇 1-Heptanol 952.49(967 g) 0.02 0.04 nd 1-辛烯-3-醇(蘑菇醇)
1-Octen-3-ol963.78(974 a) 0.02 0.04 0.02 RI 1032 1032.38 nd tr tr 芳樟醇 Linalool 1106.80(1 104 d) tr tr tr 正辛醇 1-Octanol 1075.06(1 068 e) nd 0.01 nd 表3表明,3个品种共检出12种酮类香气组分,其中8种未见研究报道,3种为微量,6种为未知酮类香气物质。琯溪蜜柚共检出10种酮类香气组分,其中5种内标峰面积的相对定量值>0.0095,总相对含量为0.21;微量5种,未检出2种;红肉蜜柚共检出6种酮类香气组分,其中2种内标峰面积的相对定量值>0.0095,总相对含量为0.18;微量4种、未检出6种;三红蜜柚共检出10种酮类香气组分,其中6种内标峰面积的相对定量值>0.0095,总相对含量为0.62;微量4种、未检出2种。6-甲基-5-庚烯-2-酮在酮类香气组分中相对含量最高;以三红蜜柚相对含量最高,为0.49,红肉蜜柚次之,为0.17,琯溪蜜柚最低,仅0.01。
表 3 琯溪蜜柚、红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚果汁样品中的酮类香气组分Table 3. Aroma volatiles (Ketone) in juice samples of Guanximiyou, Hongroumiyou and Sanhongmiyou化合物
Compound保留指数RI
(计算Calculated)相对含量
Relative contentHR SH GX RI 733 732.77 tr tr tr RI 854 854.02 tr 0.03 tr 甲基己基甲酮 2-Octanone 909.18(984) tr nd tr RI 919 919.31 nd 0.01 tr 1-辛烯-3-酮 1-Octen-3-one 957.95(972) tr 0.03 0.01 6-甲基-5-庚烯-2-酮
6-methyl-5-Hepten-2-one967.70(981) 0.17 0.49 0.01 2-庚酮 2-Heptanone 973.40(889) nd 0.04 0.01 RI 1096 1095.97 nd tr 0.17 RI 1138 1138.24 nd 0.02 tr RI 1154 1153.82 nd tr 0.01 4-庚烯-2-酮 (E)-4-Hepten-2-one 1478.28 nd tr nd 异丙基三级丁基酮
2,2,4-Trimethyl-3-pentanone1755.93 0.01 nd nd 表4表明,3个品种共检出40种芳香烃类香气组分,其中,38种未见研究报道,14种相对含量仅为微量,27种为未知芳香烃类香气物质。琯溪蜜柚共检出7种芳香烃类香气组分,其中4种内标峰面积的相对定量值>0.0095,总相对含量为0.79;微量3种、未检出33种。红肉蜜柚检出芳香烃类香气组分最多,达37种,其中23种内标峰面积的相对定量值>0.0095,总相对含量为0.32;微量14种、未检出3种。三红蜜柚共检出10种芳香烃类香气组分,其中3种内标峰面积的相对定量值>0.0095,总相对含量为0.06;微量7种、未检出30种。芳香烃类香气组分的相对含量都较低,以RI 820相对含量最高,琯溪蜜柚为0.68,而其芽变品种红肉蜜柚仅含微量,三红蜜柚则未检出;RI 1029次之,琯溪蜜柚相对含量0.07,红肉蜜柚未检出,三红蜜柚仅含微量;甲苯和RI 1446再次之,红肉蜜柚相对含量仅为0.04,三红蜜柚仅含微量,琯溪蜜柚则未检出。
表 4 琯溪蜜柚、红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚果汁样品中的芳香烃类香气组分Table 4. Aroma volatiles(Aromatic hydrocarbons)in juice samples of Guanximiyou, Hongroumiyou and Sanhongmiyou化合物
Compound保留指数RI
(计算Calculated)相对含量
Relative contentHR SH GX RI 731 730.67 tr tr nd 甲苯 Toluene 741.71(773) 0.04 0.04 0.03 RI 820 820.07 tr nd 0.68 1,3-二甲基苯
1,3-dimethyl-Benzene853.57(862) tr tr tr RI 999 999.25 nd 0.01 0.01 RI 1020 1020.01 0.01 0.01 nd RI 1029 1028.87 nd tr 0.07 RI 1054 1053.85 tr tr tr RI 1272 1272.38 tr tr nd RI 1296 1295.64 nd tr tr RI 1355 1355.35 tr nd nd 3,3′-联[环己烯]
Bi-2-cyclohexen-1-yl1404.24 tr nd nd RI 1446 1445.87 0.04 tr nd RI 1470 1470.38 tr nd nd α-罗勒烯
3,7-dimethyl-1,3,7-Octatriene1480.44 tr nd nd RI 1573 1573.43 0.01 nd nd 2,5-dimethyl-3-methylene-1,5-Heptadiene 1576.62 tr nd nd RI 1578 1578.15 0.01 nd nd 4-甲基-十三烷
Tridecane, 4-methyl-1583.55 0.01 nd nd 正十三烷烃 Tridecane 1628.07 0.02 nd nd RI 1631 1631.10 0.01 nd nd RI 1634 1634.29 0.01 nd nd 2,3,3-三甲基戊烷
2,3,3-trimethyl-Pentane1640.04 0.01 nd nd RI 1645 1645.49 0.01 nd nd RI 1652 1651.53 tr nd nd 2,2-二甲基丁烷
2,2-dimethyl-Butane1661.20 0.02 nd nd RI 1663 1663.38 0.02 nd nd 2-甲基辛烷
2-methyl-Octane1666.62 0.01 nd nd RI 1672 1671.95 0.01 nd nd RI 1677 1677.41 0.01 nd nd 2-溴(正)壬烷
2-Bromononane1683.40 0.01 nd nd RI 1709 1708.83 tr nd nd RI 1718 1717.58 tr nd nd RI 1722 1722.38 tr nd nd 3,3-二甲基己烷
3,3-dimethyl-Hexane1725.56 0.01 nd nd RI 1732 1731.85 0.01 nd nd RI 1745 1744.63 0.01 nd nd (1 -甲基乙基)-环己烷
(1-methylethyl)-Cyclohexane1756.23 0.01 nd nd RI 1791 1791.04 0.01 nd nd RI 1824 1823.79 0.01 nd nd 表5表明,3个品种果汁共检出5种呋喃类香气组分,其中,1种未见研究报道,1种仅含微量。琯溪蜜柚共检出5种呋喃类香气组分,其中3种内标峰面积的相对定量值>0.0095,总相对含量为0.08;微量2种;红肉蜜柚共检出3种呋喃类香气组分,其中2种内标峰面积的相对定量值>0.0095,总相对含量为0.29;微量1种,未检出2种;三红蜜柚共检出5种呋喃类香气组分,其中3种内标峰面积的相对定量值>0.0095,总相对含量为0.22;微量2种。其中,2,2,6-三甲基-6-乙烯基四氢-2H-呋喃-3-醇相对含量最高,芽变品种红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚分别为0.22和0.16,而琯溪蜜柚仅含微量。
表 5 琯溪蜜柚、红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚果汁样品中的呋喃类香气组分Table 5. Aroma volatiles(Furan)in juice samples of Guanximiyou, Hongroumiyou and Sanhongmiyou化合物
Compound保留指数RI
(计算Calculated)相对含量
Relative contentHR SH GX 2-propyl-Furan 756.60(793) tr tr tr 2-正丁基呋喃 2-n-Butyl furan 854.77(892) nd 0.01 0.01 2,2,6-三甲基-6-乙烯基四氢-
2H-呋喃-3-醇
cis-Linalool oxide1069.21(1070) 0.22 0.16 tr 反-氧化芳樟醇
trans-Linalool oxide(furanoid)1088.26(1088) 0.07 0.05 0.02 2-丁基四氢呋喃
2-butyltetrahydro-Furan1100.32 nd tr 0.05 表6表明,3个品种果汁共检出10种酯类香气组分,均为未见研究报道;其中1种仅含微量,8种为未知酯类香气物质。琯溪蜜柚共检出2种未知酯类香气组分,其中1种内标峰面积的相对定量值>0.0095,总相对含量为0.08;微量1种。红肉蜜柚共检出10种酯类香气组分,3种内标峰面积的相对定量值>0.0095,总相对含量为0.03,其中2种为未知酯类香气物质;微量7种,其中6种为未知酯类香气物质。三红蜜柚仅检出2种微量的未知酯类香气组分。酯类香气组分相对含量都较低,其中,RI 896相对含量在琯溪蜜柚果汁中为0.08,而红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚均为微量;草酸烯丙基壬酯、RI 1761和RI 1767只有在红肉蜜柚果汁中检出,仅为0.01。
表 6 琯溪蜜柚、红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚果汁样品中的酯类香气组分Table 6. Aroma volatiles(Ester)in juice samples of Guanximiyou, Hongroumiyou and Sanhongmiyou化合物
Compound保留指数RI
(计算Calculated)相对含量
Relative contentHR SH GX RI 896 895.70 tr tr 0.08 RI 988 987.64 tr nd tr RI 1048 1047.57 tr tr nd RI 1687 1687.01 tr nd nd RI 1761 1761.19 0.01 nd nd RI 1767 1767.03 0.01 nd nd RI 1794 1794.40 tr nd nd 草酸环丁基壬酯
Oxalic acid, cyclobutyl nonyl ester1801.61 tr nd nd 草酸烯丙基壬酯
Oxalic acid, allyl nonyl ester1812.18 0.01 nd nd RI 1847 1846.74 tr nd nd 表7表明,3个品种果汁共检出24种倍半萜烯类香气组分;其中18种未见研究报道,1种仅含微量,18种为未知倍半萜烯类香气物质。琯溪蜜柚共检出4种未知倍半萜烯类香气组分,但均含微量。红肉蜜柚共检出24种倍半萜烯类香气组分;9种内标峰面积的相对定量值>0.0095,总相对含量为0.26,其中5种为未知倍半萜烯类香气物质;微量15种,其中13种为未知倍半萜烯类香气物质。三红蜜柚共检出4种未知倍半萜烯类香气组分,但均含微量。倍半萜烯类香气组分是供试3个品种中红肉蜜柚果汁特有的香气组分。
表 7 琯溪蜜柚、红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚果汁样品中的倍半萜烯类香气组分Table 7. Aroma volatiles(Sesquiterpene)in juice samples of Guanximiyou, Hongroumiyou and Sanhongmiyou化合物
Compound保留指数RI
(计算Calculated)相对含量
Relative contentHR SH GX RI 1360 1360.07 tr nd nd RI 1364 1363.78 0.01 tr nd 荜澄茄烯 β-Cubebene 1375.92(1387) tr nd nd RI 1397 1397.35 tr nd tr RI 1404 1403.94 tr nd nd β-波旁烯(-)-β-Bourbonene 1411.29(1417) 0.03 nd nd RI 1419 1418.70 tr nd nd RI 1457 1456.54 tr nd nd RI 1472 1472.33 tr nd nd RI 1475 1475.20 tr nd nd RI 1486 1485.94 tr nd nd RI 1487 1487.46 tr nd nd RI 1498 1497.97 tr nd nd 大牛儿烯 D Germacrene D 1501.39(1487) 0.02 nd nd RI 1506 1505.71 0.08 tr nd RI 1513 1512.73 tr nd nd RI 1518 1517.58 0.01 nd tr RI 1522 1522.08 tr nd nd (1S,4aS,8aR)-1-异丙基-4,7-
二甲基-1,2,4A,5,6,8A-六氢萘
α-Muurolene1524.06(1523) 0.01 nd nd RI 1528 1527.99 tr nd nd RI 1537 1536.66 0.03 tr nd δ杜松烯 δ-Cadinene 1542.61(1540) 0.06 tr nd 4-diene Cadina-1(2) 1554.56(1533) tr nd tr RI 1559 1558.55 0.01 nd tr 表8表明,3个品种果汁共检出2种单萜类香气组分,相对含量都很低。琯溪蜜柚检出2种单萜类香气组分,均含微量。红肉蜜柚检出2种单萜类香气组分,相对含量较低,总相对含量为0.02。三红蜜柚检出2种单萜类香气组分,总相对含量为0.08。
表 8 琯溪蜜柚、红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚果汁样品中的单萜类香气组分Table 8. Aroma volatiles(Monoterpene)in juice samples of Guanximiyou, Hongroumiyou and Sanhongmiyou化合物
Compound保留指数RI
(计算Calculated)相对含量
Relative contentHR SH GX β-月桂烯 β-Myrcene 973.26(988) 0.01 0.06 tr 柠檬烯 Limonene 1018.06(1024) 0.01 0.02 tr 此外,研究结果还表明,3个品种果汁共检出32种其他类香气组分,均为未见研究报道的未知物质;其中24种仅含微量。琯溪蜜柚共检出11种其他类香气组分,均为未知物质,总相对含量为0.03;其中9种仅含微量。红肉蜜柚共检出26种其他类香气组分,均为未知物质,总相对含量为0.06;其中21种仅含微量。三红蜜柚共检出9种其他类香气组分,均为未知物质,总相对含量为0.05;其中7种仅含微量。
综上所述,3个品种果汁中香气化合物中相对含量最多的化合物是醛类香气组分。其中己醛相对含量为最高,三红蜜柚果汁中的己醛相对含量最多,分别是琯溪蜜柚和红肉蜜柚的2.76倍和1.58倍。3-己烯醛和2-己烯醛在红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚中含量较高,而在琯溪蜜柚中相对含量很低,分别仅有0.08和0.13。而4-甲基己醛,在琯溪蜜柚中含量较高,为0.71,在其他两个芽变品种中均为微量。
醇类、酮类化合物的相对含量次之。反式-3-己烯-1-醇在红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚中的相对含量较高,分别为0.95和0.74,而在琯溪蜜柚中仅含微量。正己醇则在红肉蜜柚中含量较高,为1.17,分别是三红蜜柚(0.66)和琯溪蜜柚(0.03)的1.77倍和39倍。六甲基五庚烯二酮在三红蜜柚中含量为0.49,而在琯溪蜜柚中仅有0.01。
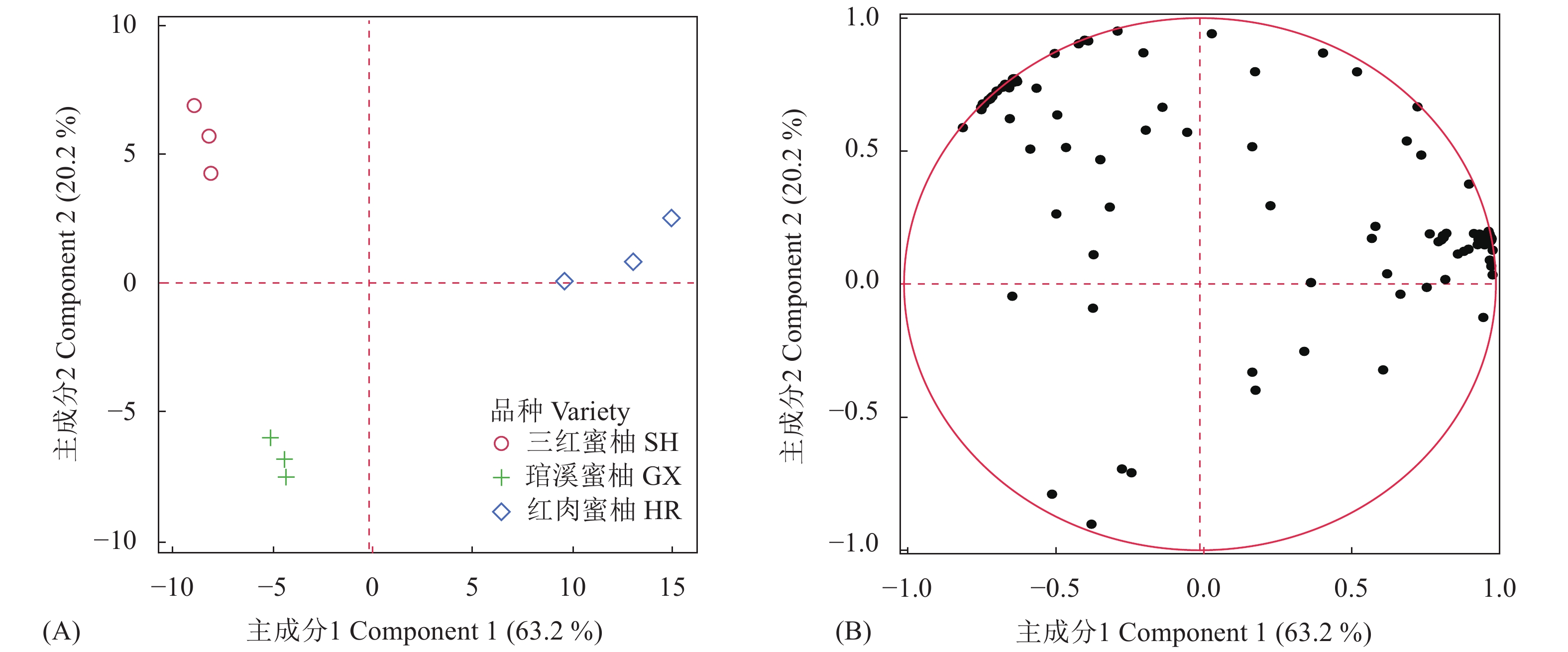
2.2 三个品种果实果汁样品中香气组分的主成分分析
图2显示,红肉蜜柚、三红蜜柚和琯溪蜜柚果汁样品中的主成分差异较大。图2(A)中,主成分1从横轴上看显示出3种基因型63.2%的差异,主成分2从纵轴上看显示出3种基因型20.2%的差异。图2(B)中,每个数字代表了一种化合物,从直观上看化合物两极分化明显,大部分特征值均接近于1,说明这些化合物在3种基因型果实果汁中的含量差异较大,为3种基因型特有的化合物;但也有一些化合物如己醛,特征值接近于1,在3种基因型的柚子果汁中的含量均为最大,故己醛应为3种基因型柚子的共同化合物。而根据3种基因型特有的化合物,推测其合成途径及相关差异表达基因,可用来比较3种基因型柚子的差异。
图2(A)与图2(B)还显示,多数化合物较集中于红肉蜜柚,此结果与图1相同,说明红肉蜜柚果汁中化合物种类较多。最终结论显示,红肉蜜柚、三红蜜柚和琯溪蜜柚这3种基因型的果实果肉香气组分差异较大,虽红肉蜜柚化合物种类较三红蜜柚多,但总相对含量却低于三红蜜柚,故三红蜜柚香气较红肉蜜柚和琯溪蜜柚更为浓郁,这个发现对于柚子品种的选育上具有一定意义。
2.3 与香气组分代谢相关的差异基因转录组分析
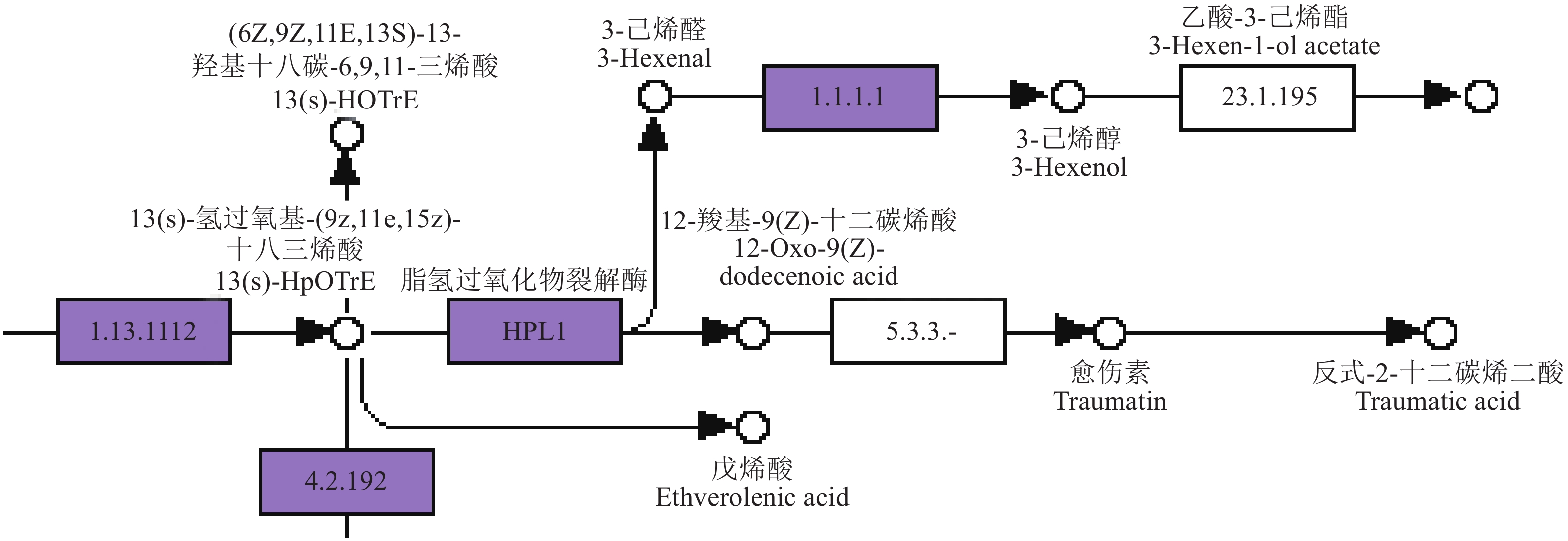
上述试验结果表明,供试3个品种果汁中香气组分种类和相对含量差异明显,说明这与芽变引起的变异关系密切。供试3个品种果汁中香气组分以醛类的相对含量最高,其次为醇类和酮类,相对含量最高的香气化合物为己醛。因此,根据课题组的转录组数据[27,28]对α-亚麻酸代谢途径(α-linolenic acid metabolism)中的相关基因进行KEGG差异表达分析,发现新基因(Citrus_maxima_newGene_12651)1个,表达差异显著的脂肪氧化酶(Lipoxidase)LOX2.1基因7个(cg2g001970、cg2g001980、cg2g002000、cg2g002010、cg2g002030、cg2g002040、cg2g002080)、LOX3.1基因1个(cg1g010660)和乙醇脱氢酶(Alcohol dehydrogenase)ADH1基因2个(cg3g017900、cg3g017890),并对其进行FPKM值趋势分析,预测差异表达基因的表达模式,以研究供试3个品种形成香气差异的分子机理。
据转录组分析显示,顺式-3-己烯醛(3-Hexenal)的合成受到脂氧合酶LOX2S(1.13.11.12)等酶的调控(图3)。在HPL1通路中发现了1个与3-Hexenal的合成相关的新基因(Citrus_maxima_newGene_12651),根据KEGG注释,该新基因是细胞色素P450家族的一员,可能是氢过氧化物裂解酶(Hydroperoxide lyase,HPL)基因。HPL和丙二烯氧化合酶(allene oxide synthase,AOS)、联乙烯醚合酶(divinyl ether synthase,DES)属于同一个细胞色素P450亚家族,与C6醛或醇及相应酯的形成有关[29,30]。而在脂氧合酶(1.13.11.12)代谢通路上,筛选获得表达差异显著的7个LOX2.1和1个LOX3.1基因。另外,3-Hexenal通过P类醇脱氢酶通路醇脱氢酶(alcohol dehydrogenase,ADH)合成3-己烯-1-醇,经过分析也筛选获得2个参与了合成3-Hexen-1-ol过程的ADH1基因。
根据FPKM值的趋势分析(图4),新基因Citrus_maxima_newGene_12651在果实发育期的表达差异极其显著,影响了顺式-3-己烯醛合成。3个品种果实膨大期(花后120-180 d)以红肉蜜柚的表达最为突出。在开花后180 d时的果肉中,红肉蜜柚的表达水平最高,三红蜜柚次之,琯溪蜜柚最低,这与3个品种成熟果实果汁香气中顺式-3-己烯醛的浓度高低趋势相符,说明它们可能呈正相关调控。
分析结果还显示,在脂氧合酶(LOX,1.13.11.12)代谢通路中的3个LOX基因Cg2g002010(LOX2.1)、Cg2g002080(LOX2.1)和Cg1g010660(LOX3.1)差异表达明显,花后180 d时,Cg2g002010(LOX2.1)和Cg2g002080(LOX2.1)基因在红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚果实中表达水平较高,在琯溪蜜柚中较低,这两个基因可能与顺式-3-己烯醛合成呈正相关调控,而Cg1g010660(LOX3.1)则相反;而其他5个LOX基因在花后120 d和花后180 d时果实中基本不表达。
在α-亚麻酸代谢途径(α-linolenic acid metabolism)中,P类醇脱氢酶ADH1通路(1.1.1.1)影响了乙烯醇和3-己烯-1-醇的合成,其中有2个ADH1基因(图4)参与其中,并且在180 d时,表达差异极其显著。Cg3g017890(ADH1)基因表达水平以红肉蜜柚最高,琯溪蜜柚只有其一半,三红蜜柚则最低。Cg3g017900(ADH1)基因则相反,琯溪蜜柚的表达水平最高,红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚都只有琯溪蜜柚的一半。在3个品种成熟果实果汁香气中,红肉蜜柚的正己醇和3-己烯浓度最高,三红蜜柚其次,琯溪蜜柚只有微量。说明上述基因参与了α-亚麻酸代谢途径中代谢的调控。
3. 讨论与结论
据已有研究报道,柚果实的主要香气物质是柠檬烯、α-蒎烯、β-蒎烯、月桂烯、诺卡酮、芳樟醇等[1]。苍南四季柚果实中的主要香气物质为月桂烯、柠檬烯、努特卡酮、β-蒎烯、喇叭茶萜醇[4]。在玉环柚果实中,鉴定出柠檬烯、α-蒎烯、月桂烯等29种香气物质[3]。与果皮组织相比,α-蒎烯和月桂烯在柚果实果肉中香气更强[2]。
另有研究报道,葡萄柚果实的香气物质以γ-松油烯、柠檬烯为主[2]。采用GC-MS方法对葡萄柚香气活性成分进行鉴定。鉴别出了13种风味成分,这些成分之前从未在柚子油中报告过。香气最强的化合物包括:1,8-桉叶素、辛醛、十二醛、反式-4,5-环氧-(E)-2-癸醛、-辛烯醛和诺酮。而硫化合物(如4-巯基-4-甲基-2-戊醇和甲硫醇)的香气活性令人惊讶地低,两种假定的柚子香气影响化合物(4-巯基-4-甲基-2-戊酮和1-p-薄荷-8-硫醇)均未检测到。葡萄柚油中含有200多种挥发物,但只有38种挥发物具有显著的香气活性,其中22种挥发物被认为是主要的香气影响化合物[31]。Alberto J.Nunez等采用SDE法结合GC-MS分析了葡萄柚果汁,鉴定了58种化合物组分,其中25种是当时的首次报道,发现同时采收的来自相同产地、不同时间的葡萄柚其风味化合物的组分上差别不大,但含量差别显著[6]。
本研究结果表明,琯溪蜜柚及其芽变红肉蜜柚、三红蜜柚3个品种果实香气物质含量最多的化合物均为己醛,这与嵇海峰等的研究结果一致[32]。但芽变品种红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚的己醛等醛类香气化合物含量显著高于琯溪蜜柚,可见,这是红肉突变体的果实风味优于琯溪蜜柚的原因。本研究还显示,虽然红肉蜜柚香气化合物种类较三红蜜柚多,但总相对含量却低于后者,所以,己醛类物质总相对含量高是三红蜜柚香气较红肉蜜柚更为浓郁的原因。研究还表明,醇类和酮类香气物质也是琯溪蜜柚及其芽变品种的主要香气物质。
转录组分析发现,在α-亚麻酸代谢途径中出现1个新基因(Citrus_maxima_newGene_12651),属于细胞色素P450的一个亚家族,推测为HPL基因。可见,琯溪蜜柚芽变导致了香气形成基因的突变。转录组分析筛选获得7个LOX2.1、1个LOX3.1和2个ADH1与香气形成相关的11个显著差异表达的基因。据FPKM值的趋势分析,可初步推测供试3个品种的果汁香气组分差异,与脂肪酸途径、异戊二烯途径中的基因差异表达有关。供试3个品种的挥发性物质与已报道的柚子、葡萄柚等柚类果实存在较大差异,这可能是由基因型差异引起的。在供试3个琯溪蜜柚及其芽变品种果汁中,也存在倍半萜烯类物质的差异,说明在芽变的过程中,倍半萜烯类等途径也出现异常。在植物中,单萜和倍半萜具有挥发性,他们是果实重要的芳香物质,这两类物质分别由MVA和MEP途径形成的。此外,本研究还发现了不少香气组分未知的化合物。这些都值得今后进一步研究、验证,以探明芽变引起香气差异的分子机理。
-
表 1 琯溪蜜柚、红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚果汁样品中的醛类香气组分
Table 1 Aroma volatiles(Aldehydes)in juice samples of Guanximiyou, Hongroumiyou and Sanhongmiyou
化合物
Compound保留指数 RI
(计算Calculated)相对含量
Relative contentHR SH GX 反-2-戊烯醛
(E)-2-Pentenal735.43(748)* 0.02 0.10 0.02 顺-3-己烯醛
(Z)-3-Hexenal764.01(793) 0.31 0.26 0.08 己醛 Hexanal 766.26(787) 3.65 5.77 2.24 2-己烯醛 2-Hexenal 807.38(854) 0.04 0.03 0.01 反-2-己烯醛
(E)-2-Hexenal814.59(844) 0.38 0.23 0.13 4-甲基-己醛
4-methyl-Hexanal840.57(889) tr 0.01 0.71 庚醛 Heptanal 867.56(899) 0.07 0.35 nd 反-2-庚醛
(E)-2-Heptanal932.46(946) 0.01 0.12 nd 辛醛 Octanal 989.86(998) 0.01 0.10 tr 反-2-辛烯醛
(E)-2-Octenal1055.85(1059) tr 0.15 nd 壬醛 Nonanal 1112.22(1109) 0.01 0.05 nd 反-2-壬烯醛
(E)-2-Nonenal1175.83(1160) nd 0.02 tr 正葵醛 Decanal 1228.75(1228) nd tr nd 注:数据均为内标峰面积的相对定量值,且为3个生物学重复的平均值。RI:保留指数Retention index,*:括号内数字为已发表的保留指数RI;tr :表示此处有被识别的峰,但值小于0.0095;nd:表示未检测到峰;GX:琯溪蜜柚,HR:红肉蜜柚,SH:三红蜜柚。下同。
Note: The data are all relative quantitative values of internal standard peak areas and are the average of three biological replicates. RI: Retention index, *: the number in parentheses is the published retention index(RI). tr: there is an identified peak here, but the value is less than 0.009 5. nd: no peak was detected. GX: Guanximiyou, HR: Hongroumiyou, SH: Sanhongmiyou. Same as below.
表 2 琯溪蜜柚、红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚果汁样品中的醇类香气组分
Table 2 Aroma volatiles (Alcohols) in juice samples of Guanximiyou, Hongroumiyou and Sanhongmiyou
化合物
Compound保留指数RI
(计算Calculated)相对含量
Relative contentHR SH GX 正戊醇 1-Pentanol 743.08(761 d) 0.04 0.07 0.04 顺-2-戊烯-1-醇
(Z)-2-Penten-1-ol744.78(767 c) 0.03 0.03 0.02 3-己烯-1-醇
(E)-3-Hexen-1-ol819.22(851 b) 0.95 0.74 tr 反-2-己烯-1-醇
(E)-2-Hexen-1-ol829.79(858 g) 0.05 0.02 tr 正己醇 1-Hexanol 835.19(865 b) 1.17 0.66 0.03 RI 949 948.98 tr tr tr 反-2-庚烯-1-醇
(E)-2-Hepten-1-ol949.04(958 g) 0.01 0.03 0.02 正庚醇 1-Heptanol 952.49(967 g) 0.02 0.04 nd 1-辛烯-3-醇(蘑菇醇)
1-Octen-3-ol963.78(974 a) 0.02 0.04 0.02 RI 1032 1032.38 nd tr tr 芳樟醇 Linalool 1106.80(1 104 d) tr tr tr 正辛醇 1-Octanol 1075.06(1 068 e) nd 0.01 nd 表 3 琯溪蜜柚、红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚果汁样品中的酮类香气组分
Table 3 Aroma volatiles (Ketone) in juice samples of Guanximiyou, Hongroumiyou and Sanhongmiyou
化合物
Compound保留指数RI
(计算Calculated)相对含量
Relative contentHR SH GX RI 733 732.77 tr tr tr RI 854 854.02 tr 0.03 tr 甲基己基甲酮 2-Octanone 909.18(984) tr nd tr RI 919 919.31 nd 0.01 tr 1-辛烯-3-酮 1-Octen-3-one 957.95(972) tr 0.03 0.01 6-甲基-5-庚烯-2-酮
6-methyl-5-Hepten-2-one967.70(981) 0.17 0.49 0.01 2-庚酮 2-Heptanone 973.40(889) nd 0.04 0.01 RI 1096 1095.97 nd tr 0.17 RI 1138 1138.24 nd 0.02 tr RI 1154 1153.82 nd tr 0.01 4-庚烯-2-酮 (E)-4-Hepten-2-one 1478.28 nd tr nd 异丙基三级丁基酮
2,2,4-Trimethyl-3-pentanone1755.93 0.01 nd nd 表 4 琯溪蜜柚、红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚果汁样品中的芳香烃类香气组分
Table 4 Aroma volatiles(Aromatic hydrocarbons)in juice samples of Guanximiyou, Hongroumiyou and Sanhongmiyou
化合物
Compound保留指数RI
(计算Calculated)相对含量
Relative contentHR SH GX RI 731 730.67 tr tr nd 甲苯 Toluene 741.71(773) 0.04 0.04 0.03 RI 820 820.07 tr nd 0.68 1,3-二甲基苯
1,3-dimethyl-Benzene853.57(862) tr tr tr RI 999 999.25 nd 0.01 0.01 RI 1020 1020.01 0.01 0.01 nd RI 1029 1028.87 nd tr 0.07 RI 1054 1053.85 tr tr tr RI 1272 1272.38 tr tr nd RI 1296 1295.64 nd tr tr RI 1355 1355.35 tr nd nd 3,3′-联[环己烯]
Bi-2-cyclohexen-1-yl1404.24 tr nd nd RI 1446 1445.87 0.04 tr nd RI 1470 1470.38 tr nd nd α-罗勒烯
3,7-dimethyl-1,3,7-Octatriene1480.44 tr nd nd RI 1573 1573.43 0.01 nd nd 2,5-dimethyl-3-methylene-1,5-Heptadiene 1576.62 tr nd nd RI 1578 1578.15 0.01 nd nd 4-甲基-十三烷
Tridecane, 4-methyl-1583.55 0.01 nd nd 正十三烷烃 Tridecane 1628.07 0.02 nd nd RI 1631 1631.10 0.01 nd nd RI 1634 1634.29 0.01 nd nd 2,3,3-三甲基戊烷
2,3,3-trimethyl-Pentane1640.04 0.01 nd nd RI 1645 1645.49 0.01 nd nd RI 1652 1651.53 tr nd nd 2,2-二甲基丁烷
2,2-dimethyl-Butane1661.20 0.02 nd nd RI 1663 1663.38 0.02 nd nd 2-甲基辛烷
2-methyl-Octane1666.62 0.01 nd nd RI 1672 1671.95 0.01 nd nd RI 1677 1677.41 0.01 nd nd 2-溴(正)壬烷
2-Bromononane1683.40 0.01 nd nd RI 1709 1708.83 tr nd nd RI 1718 1717.58 tr nd nd RI 1722 1722.38 tr nd nd 3,3-二甲基己烷
3,3-dimethyl-Hexane1725.56 0.01 nd nd RI 1732 1731.85 0.01 nd nd RI 1745 1744.63 0.01 nd nd (1 -甲基乙基)-环己烷
(1-methylethyl)-Cyclohexane1756.23 0.01 nd nd RI 1791 1791.04 0.01 nd nd RI 1824 1823.79 0.01 nd nd 表 5 琯溪蜜柚、红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚果汁样品中的呋喃类香气组分
Table 5 Aroma volatiles(Furan)in juice samples of Guanximiyou, Hongroumiyou and Sanhongmiyou
化合物
Compound保留指数RI
(计算Calculated)相对含量
Relative contentHR SH GX 2-propyl-Furan 756.60(793) tr tr tr 2-正丁基呋喃 2-n-Butyl furan 854.77(892) nd 0.01 0.01 2,2,6-三甲基-6-乙烯基四氢-
2H-呋喃-3-醇
cis-Linalool oxide1069.21(1070) 0.22 0.16 tr 反-氧化芳樟醇
trans-Linalool oxide(furanoid)1088.26(1088) 0.07 0.05 0.02 2-丁基四氢呋喃
2-butyltetrahydro-Furan1100.32 nd tr 0.05 表 6 琯溪蜜柚、红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚果汁样品中的酯类香气组分
Table 6 Aroma volatiles(Ester)in juice samples of Guanximiyou, Hongroumiyou and Sanhongmiyou
化合物
Compound保留指数RI
(计算Calculated)相对含量
Relative contentHR SH GX RI 896 895.70 tr tr 0.08 RI 988 987.64 tr nd tr RI 1048 1047.57 tr tr nd RI 1687 1687.01 tr nd nd RI 1761 1761.19 0.01 nd nd RI 1767 1767.03 0.01 nd nd RI 1794 1794.40 tr nd nd 草酸环丁基壬酯
Oxalic acid, cyclobutyl nonyl ester1801.61 tr nd nd 草酸烯丙基壬酯
Oxalic acid, allyl nonyl ester1812.18 0.01 nd nd RI 1847 1846.74 tr nd nd 表 7 琯溪蜜柚、红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚果汁样品中的倍半萜烯类香气组分
Table 7 Aroma volatiles(Sesquiterpene)in juice samples of Guanximiyou, Hongroumiyou and Sanhongmiyou
化合物
Compound保留指数RI
(计算Calculated)相对含量
Relative contentHR SH GX RI 1360 1360.07 tr nd nd RI 1364 1363.78 0.01 tr nd 荜澄茄烯 β-Cubebene 1375.92(1387) tr nd nd RI 1397 1397.35 tr nd tr RI 1404 1403.94 tr nd nd β-波旁烯(-)-β-Bourbonene 1411.29(1417) 0.03 nd nd RI 1419 1418.70 tr nd nd RI 1457 1456.54 tr nd nd RI 1472 1472.33 tr nd nd RI 1475 1475.20 tr nd nd RI 1486 1485.94 tr nd nd RI 1487 1487.46 tr nd nd RI 1498 1497.97 tr nd nd 大牛儿烯 D Germacrene D 1501.39(1487) 0.02 nd nd RI 1506 1505.71 0.08 tr nd RI 1513 1512.73 tr nd nd RI 1518 1517.58 0.01 nd tr RI 1522 1522.08 tr nd nd (1S,4aS,8aR)-1-异丙基-4,7-
二甲基-1,2,4A,5,6,8A-六氢萘
α-Muurolene1524.06(1523) 0.01 nd nd RI 1528 1527.99 tr nd nd RI 1537 1536.66 0.03 tr nd δ杜松烯 δ-Cadinene 1542.61(1540) 0.06 tr nd 4-diene Cadina-1(2) 1554.56(1533) tr nd tr RI 1559 1558.55 0.01 nd tr 表 8 琯溪蜜柚、红肉蜜柚和三红蜜柚果汁样品中的单萜类香气组分
Table 8 Aroma volatiles(Monoterpene)in juice samples of Guanximiyou, Hongroumiyou and Sanhongmiyou
化合物
Compound保留指数RI
(计算Calculated)相对含量
Relative contentHR SH GX β-月桂烯 β-Myrcene 973.26(988) 0.01 0.06 tr 柠檬烯 Limonene 1018.06(1024) 0.01 0.02 tr -
[1] MINH TU N T, THANH L X, UNE A, et al. Volatile constituents of Vietnamese pummelo, orange, tangerine and lime peel oils [J]. Flavour and Fragrance Journal, 2002, 17(3): 169−174. DOI: 10.1002/ffj.1076
[2] CHUNG H, CHUNG W Y, YOO E S, et al. Characterization of volatile aroma-active compounds in Dangyooja (Citrus grandis Osbeck) [J]. Journal of the Korean Society for Applied Biological Chemistry, 2012, 55(1): 133−136. DOI: 10.1007/s13765-012-0023-2
[3] 张捷莉, 车奋勇, 李学成, 等. 玉环柚果皮中香气成分的GC-MS分析 [J]. 食品科学, 2008, 29(10):480−482. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2008.10.113 ZHANG J L, CHE F Y, LI X C, et al. Analysis of volatiles in Yuhuan shaddock peel by GC-MS [J]. Food Science, 2008, 29(10): 480−482.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2008.10.113
[4] 王贤亲, 林滨, 林丹, 等. 苍南四季柚果皮挥发油成分的气相色谱-质谱联用分析 [J]. 药物分析杂志, 2009, 29(12):2044−2046. WANG X Q, LIN B, LIN D, et al. GC-MS analysis of chemical constituents of volatile oil from peels of Cangnan Sijiyou [J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 2009, 29(12): 2044−2046.(in Chinese)
[5] 李悦, 侯滨滨, 静宝元. 葡萄柚精油的气相色谱-质谱分析 [J]. 食品研究与开发, 2009, 30(12):128−131. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2009.12.037 LI Y, HOU B B, JING B Y. The analysis of grapefruit essential oil by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry [J]. Food Research and Development, 2009, 30(12): 128−131.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2009.12.037
[6] ABERTO J N, HEN M, JO M H B. Volatile flavor components of grapefruit juice (Citrus paradise Mascfadyen) [J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 1985, 36(8): 757−763. DOI: 10.1002/jsfa.2740360818
[7] PIILIP E S, MANUEL G M. Quantification of volatile constituents in orange juice drinks and its use for comparison with pure juice by multivariate analysis [J]. LWT - Food Science and Technology,, 1997, 30: 497−501. DOI: 10.1006/fstl.1996.0207
[8] REGA B, FOURNIER N, GUICHARD E. Solid phase microextraction (SPME) of orange juice flavor: odor representativeness by direct gas chromatography olfactometry (D-GC-O) [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2003, 51(24): 7092−7099. DOI: 10.1021/jf034384z
[9] MACCARONE E, CAMPISI S, FALLICO B, et al. Flavor components of Italian orange juices [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 1998, 46(6): 2293−2298. DOI: 10.1021/jf970949d
[10] MOUFIDA S, MARZOUK B. Biochemical characterization of blood orange, sweet orange, lemon, bergamot and bitter orange [J]. Phytochemistry, 2003, 62(8): 1283−1289. DOI: 10.1016/S0031-9422(02)00631-3
[11] 周海燕. 柑橘果汁特征香气组成及其在贮藏中的变化[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2006. ZHOU H Y. Characteristic aroma component of orange juice and its variation during storage[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2006. (in Chinese).
[12] ARENA E, GUARRERA N, CAMPISI S, et al. Comparison of odour active compounds detected by gas-chromatography–olfactometry between hand-squeezed juices from different orange varieties [J]. Food Chemistry,, 2006, 98(1): 59−63. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.04.035
[13] 乔宇, 谢笔钧, 柴倩, 等. 血橙果实香气成分的气相色谱-质谱分析 [J]. 质谱学报, 2008, 29(1):1−5, 9. QIAO Y, XIE B J, CHAI Q, et al. Analysis of aroma components in blood orange fruit by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Chinese Mass Spectrometry Society, 2008, 29(1): 1−5, 9.(in Chinese)
[14] 杨菜冬, 张晓鸣. 不同品种甜橙芳香物质的SPME分析 [J]. 食品研究与开发, 2006, 27(11):162−166. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2006.11.054 YANG C D, ZHANG X M. Analysis of aroma compounds of different varieties of sweet orange with spme [J]. Food Research and Development, 2006, 27(11): 162−166.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2006.11.054
[15] SHARON-ASA L, SHALIT M, FRYDMAN A, et al. Citrus fruit flavor and aroma biosynthesis: isolation, functional characterization, and developmental regulation of Cstps1, a key gene in the production of the sesquiterpene aroma compound valencene [J]. The Plant Journal, 2003, 36(5): 664−674. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01910.x
[16] NJOROGE S M, UKEDA H, KUSUNOSE H, et al. Volatile components of the essential oils from Kabosu, Daidai, and Yuko, Japanese sour citrus fruits [J]. Flavour & Fragrance Journal,, 2010, 9(6): 289−297.
[17] SAWAMURA M, THI MINH TU N, ONISHI Y, et al. Characteristic odor components of Citrus reticulata blanco (ponkan) cold-pressed oil [J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2004, 68(8): 1690−1697. DOI: 10.1271/bbb.68.1690
[18] MIYAZAWA N, FUJITA A, KUBOTA K. Aroma character impact compounds in kinokuni mandarin orange (Citrus kinokuni) compared with Satsuma mandarin orange (Citrus unshiu) [J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2010, 74(4): 835−842. DOI: 10.1271/bbb.90937
[19] ALLEGRONE G, BELLIARDO F, CABELLA P. Comparison of volatile concentrations in hand-squeezed juices of four different lemon varieties [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2006, 54(5): 1844−1848. DOI: 10.1021/jf051206s
[20] ROBERT J C, ARKADIUSZ K, NICOLE L C, et al. Identification, synthesis, and characterization of novel sulfur-containing volatile compounds from the in-depth analysis of lisbon lemon peels (Citrus limon L. Burm. f. cv. Lisbon). [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2015, 63: 1915−1931. DOI: 10.1021/jf505177r
[21] 杨荣华. 白柠檬果皮油特征香气成分的评价 [J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2000, 26(3):31−34. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-990X.2000.03.007 YANG R H. Haracteristic flavor compounds in peel oil of lime [J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2000, 26(3): 31−34.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-990X.2000.03.007
[22] VENTURINI N, CURK F, DESJOBERT J M, et al. Chemotaxonomic investigations of peel and petitgrain essential oils from 17 citron cultivars [J]. Chemistry & Biodiversity, 2010, 7(3): 736−751.
[23] KATUMI U, YUKIO H A, SHIBAMOTO T. Volatile Chemicals Identified in Extracts from Newly Hybrid Citrus, Dekopon (Shiranuhi mandarin Suppl. J.) [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2002, 50(19): 5355−5359. DOI: 10.1021/jf0203951
[24] DHARMAWAN J, KASAPIS S, SRIRAMULA P, et al. Evaluation of aroma-active compounds in Pontianak orange peel oil (Citrus nobilis Lour. var. microcarpa Hassk.) by gas chromatography-olfactometry, aroma reconstitution, and omission test. [J]. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry, 2009, 57(1): 239−244.
[25] 赵雪梅, 叶兴乾, 朱大元. 常山胡柚皮中挥发性成分分析 [J]. 果树学报, 2007, 24(1):109−112. ZHAO X M, YE X Q, ZHU D Y. Study on the volatile oils and volatile components in the rind of Changshan Huyou pomelo cultivar [J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2007, 24(1): 109−112.(in Chinese)
[26] 尚雪波, 张菊华, 单杨, 等. GC-MS法分析杂柑皮中挥发性精油成分 [J]. 食品科学, 2010, 31(2):175−178. SHANG X B, ZHANG J H, SHAN Y, et al. GC-MS analysis of peel volatile oils of three hybrid cultivars of Citrus [J]. Food Science, 2010, 31(2): 175−178.(in Chinese)
[27] 潘鹤立. 琯溪蜜柚芽变株系果实性状的研究——基于基因组学和转录组学[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2019. PAN H L. Study on fruit Characters of pomelo [Citrus grandis (L.)Osbeck] bud mutant strain based on genomics and transcriptome[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2019.
[28] 潘鹤立, 潘腾飞, 佘文琴, 等. 柚芽变株系类胡萝卜素代谢差异基因的转录组学分析 [J]. 热带作物学报, 2020, 41(11):2165−2175. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2020.11.004 PAN H L, PAN T F, SHE W Q, et al. Transcriptome analysis of carotenoid metabolism differential genes in pomelo bud strain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2020, 41(11): 2165−2175.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2020.11.004
[29] BLÉE E. Phytooxylipins and plant defense reactions [J]. Progress in Lipid Research, 1998, 37(1): 33−72. DOI: 10.1016/S0163-7827(98)00004-6
[30] HOWE G A, SCHILMILLER A L. Oxylipin metabolism in response to stress [J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2002, 5(3): 230−236. DOI: 10.1016/S1369-5266(02)00250-9
[31] LIN J, ROUSEFF R L. Characterization of aroma-impact compounds in cold-pressed grapefruit oil using time-intensity GC-olfactometry and GC-MS [J]. Flavour & Fragrance Journal, 2001, 16(6): 457−463.
[32] 嵇海峰, 朱艳冰, 蔡慧农, 等. 3种福建省柚子汁挥发性成分及香气分析 [J]. 集美大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 19(4):266−273. JI H F, ZHU Y B, CAI H N, et al. Analysis of the volatiles and aroma of the juice of three varieties of pummelo in Fujian Province [J]. The Editorial Board of Jimei University (Natural Science), 2014, 19(4): 266−273.(in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 孔令硕,樊丁宇,靳娟,杨磊,田嘉,郝庆. 灰枣及其六个芽变材料生物学特性. 北方园艺. 2024(07): 35-42 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王鑫,毕海鑫,修伟业,遇世友,韩春然. 发酵蓝靛果果汁的工艺优化及香气成分分析. 食品工业科技. 2023(13): 176-185 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李巍,石媛真,郭嘉,黄小玉,林香信,张江周,吴良泉. 不同贮藏时间琯溪蜜柚果肉营养及香气成分研究. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2023(17): 185-195 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李娟,陈巧玲,胡泳华. 同时蒸馏萃取法提取红肉蜜柚果皮精油的工艺优化研究. 新余学院学报. 2022(05): 32-36 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王丹,江芊,胡璇,范佐旺,赵海鹏,元超,陈晓鹭,于福来. 基于HS-SPME-GC/MS的海南万宁产诺丽鲜果、干果和发酵液挥发性成分分析. 中国调味品. 2022(12): 162-167+185 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)




 下载:
下载: