Correlation Between Flavonoids Content and SSR Markers of Tartary Buckwheat
-
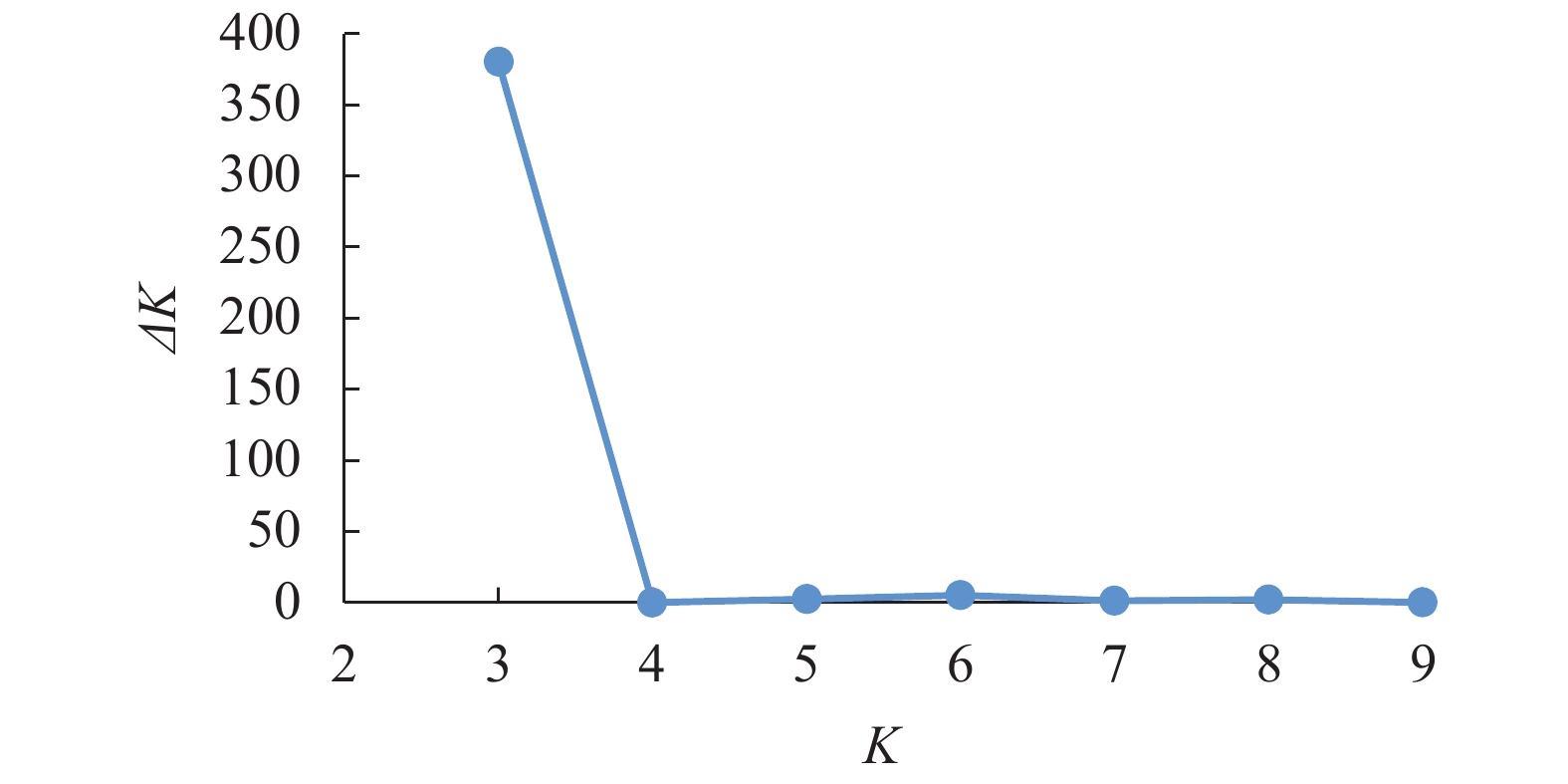
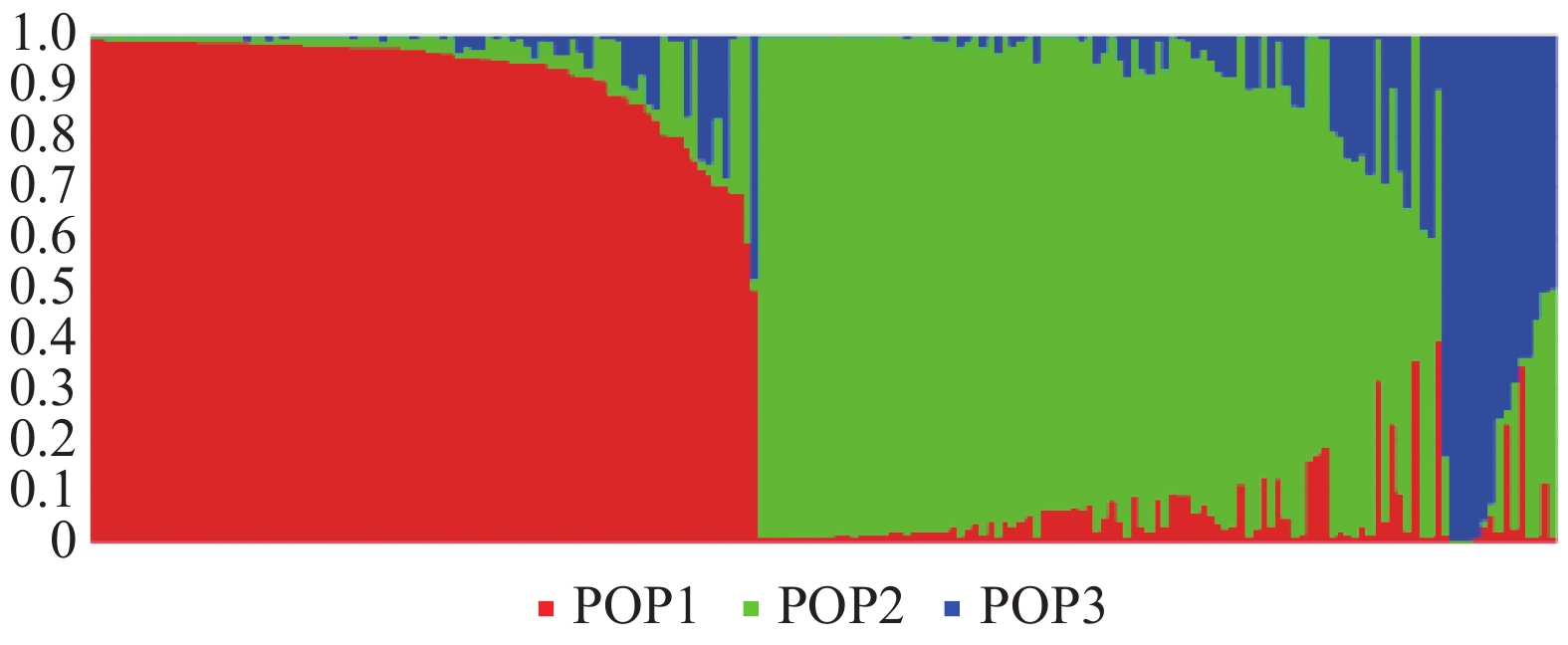
摘要:目的 开展苦荞籽粒总黄酮含量与SSR标记的关联分析,挖掘与黄酮含量相关的分子标记,为高黄酮含量苦荞品种的遗传改良提供依据。方法 以193份苦荞种质为供试材料,基于62对SSR引物分析了供试种质的遗传多样性,对总黄酮含量和SSR标记进行了关联分析。结果 193个种质籽粒总黄酮含量的变幅为1.04%~2.99%,变异系数为27.93%。62对引物在193个种质中共扩增出267个等位基因,每个SSR位点平均检测到2.45个有效等位基因,基因多样性为0.503,Shannon信息指数为0.942,观测杂合度为0.513,引物多态信息量为0.74。群体结构分析将193份种质划分为3个亚群。基于广义线性模型(GLM)共检测到5个与籽粒总黄酮含量显著关联的SSR标记,表型贡献率为6.3%~12.9%,其中标记TatG0124(12.9%)和S6853(8.5%)的表型贡献率较高。结论 供试苦荞种质遗传多样性丰富,可用于苦荞重要农艺和品质性状的关联分析。TatG0124和SSR6853可能是控制籽粒黄酮含量的重要位点,对改良苦荞籽粒黄酮含量具有重要意义。Abstract:Objective Correlation between the flavonoids content and associated markers was analyzed for genetic improvement studies on Tartary buckwheat.Method Sixty-two SSR primer pairs were used to assess the genetic diversity of 193 Tartary buckwheat germplasms. The SSR markers closely related to the total flavonoids content were selected by association analysis.Result The total flavonoids content of 193 Tartary buckwheat germplasms varied from 1.04% to 2.99% with a coefficient variation of 27.93%. Sixty-two pairs of SSR primers amplified 267 polymorphic sites with an average number of effective alleles of 2.45. The mean values of gene diversity, Shannon index, observed heterozygosity and polymorphism information content of SSR markers were 0.503, 0.942, 0.513 and 0.74, respectively. The population structure analysis divided the 193 germplasms into 3 subgroups. Five SSR markers were determined to be significantly associated with flavonoids content by the general linear model (GLM). The phenotypic variations ranged from 6.3% to 12.9% with TatG0124 at 12.9% and S6853 at 8.5% being the higher markers.Conclusion The germplasms used in this study were diverse in genetic variation and feasible for related genome-wide mapping on important traits of Tartary buckwheat. The loci, TatG0124 and S6853, appeared to closely associate with the flavonoids content of Tartary buckwheat and were considered to be potentially useful for breeding new varieties with high content of the functional components.
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】甜樱桃(Prunus avium L.)起源于高加索地区[1],来自于野生甜樱桃的驯化,同时也有部分观点认为甜樱桃起源于欧洲东南部和欧洲西部[2]。我国的甜樱桃主要栽培品种最初从欧美等国家引进,从十九世纪末开始,至今共引进250多个品种[3],而四川甜樱桃产业发展较晚,在20世纪90年代才陆续引进甜樱桃,期间种植规模不断扩大,主要分布在雅安市汉源县和阿坝藏族羌族自治州等高海拔山区,目前已经跻身国内甜樱桃主产区之一,约占全国产量8%[4]。目前大多数甜樱桃主产区都建立了基于适宜当地气候条件和地理环境的种质资源中心,近年来四川的甜樱桃种植面积和产量提升迅速,目前绝大多数品种是外省甚至外国引进。为解决四川独特的高海拔地区存在的樱桃水土不服问题,选育适合当地气候的甜樱桃品种是四川甜樱桃产业发展的长久之计。因此,对所引进的甜樱桃品种进行遗传多样性分析以及开发可以区分特定性状的分子标记很有必要。【前人研究进展】分子标记技术操作方便简单、试验环境要求低,可靠快速的DNA检测技术能够精准地反映物种的遗传多样性和种内(种间)亲缘关系[5]。目前常用的分子标记有RFLP、RAPD、AFLP、SSR等传统分子标记和新型的SRAP和SCoT标记。相关序列扩增多态性 (Sequence-related amplified polymorphism,SRAP) 是由美国加州大学蔬菜作物系Li等[6]提出的利用独特的引物设计对开放阅读框(ORF)进行扩增。上游引物对外显子进行特异扩增,下游引物对内含子区域、启动子区域进行特异扩增。因个体不同以及物种的内含子、启动子与间隔长度不等而产生多态性[7]。目标起始密码子多态性(Start codon targeted,SCoT)标记是基于植物基因ATG起始密码子的一致性及其侧翼的短保守区,开发的一种新的植物DNA标记生成方法[8]。通过设计单引物对基因组进行扩增,可以产生偏向于候选功能基因的显性多态性[9] 。SRAP和SCoT标记都不需要预先知道物种的序列信息,可以直接在不同物种间通用。近年来,SRAP和SCoT标记应用于果树遗传多样性分析越发广泛,SRAP标记引物开发简单便捷,且数量较多,果树育种过程中,文露等[10]就将其应用于鉴定皮球桃芽变品种,刘均[11]将其应用于对鸡蛋李EMS诱变材料选择。SCoT标记更多应用于种质资源的遗传多样性分析,蔡元保等[9]利用SCoT标记和SRAP标记对番木瓜进行遗传多样性分析时发现 SCoT标记检测多态性的能力高于SRAP标记。SRAP和SCoT标记除了兼具传统分子标记的优点外,最突出的特点是扩增位点位于功能基因区,更容易得到与重要性状关联的标记,可以更好地辅助育种。目前在甜樱桃上应用较多的是SSR标记,主要是进行遗传多样性分析[12]和品种鉴定[13]等,关于SRAP和SCoT标记应用相对较少。路娟等[14]利用优化后的SRAP标记体系对45个樱桃种质材料进行遗传多样性分析;Masoud等[15]利用SRAP标记揭示了毛樱桃和甜樱桃之间的内部差异;彭芳芳等[16]建立了樱桃 SCoT标记分析体系,并且对SCoT 分子标记、叶片表型性状遗传多样性进行关联分析,获得了8个与叶片性状极显著相关的特异标记位点。【本研究切入点】SRAP和SCoT两种分子标记在甜樱桃上的成功应用表明了其应用前景,且两种分子标记针对甜樱桃在遗传评价方面的优劣以及更多应用方向值得进一步探究。【拟解决的关键问题】本文首次同时利用SRAP和SCoT分子标记对40个甜樱桃品种进行遗传多样性分析,并且利用两种分子标记基本将甜樱桃按果皮颜色区分开,研究完善优化甜樱桃SRAP和SCoT标记反应体系,并对比分析两种标记在甜樱桃上的应用效果及两种标记与果皮颜色等性状的关联性。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 供试材料
于2020年3~4月,分别从四川省雅安市汉源县和阿坝藏族羌族自治州汶川县、茂县、小金县、金川县、理县等地共采集到40份有明确引种记录的甜樱桃嫩叶样本。经液氮预冷后保存于−80 ℃冰箱,用于后期的基因组DNA提取。40份甜樱桃品种材料具体信息见表1,其中红灯(短柄)同样是红灯,采自汉源县。
表 1 40份甜樱桃品种Table 1. Forty sweet cherry varieties编号
No.名称
Name果实颜色
Fruit color原产地
Origin编号
No.名称
Name果实颜色
Fruit color原产地
Origin1 鲁樱3号 Luying3 红色 Red 中国 China 21 龙冠 Longguan 红色 Red 中国 China 2 拉宾斯 Lapins 紫红色 Purplish red 加拿大 Canada 22 佐藤锦 Satonishiki 黄红色 Yellowish red 日本 3 早甘阳 Zaoganyang 紫红色 Purplish red 中国 China 23 佳红 Jiahong 黄红色 Yellowish red 中国 China 4 齐早 Qizao 紫红色 Purplish red 中国 China 24 琥珀 Hupo 黄红色 Yellowish red 中国 China 5 鲁玉 Luyu 红色 Red 中国 China 25 桑德拉玫瑰 Sandra rose 紫红色 Purplish red 加拿大 Canada 6 美早 Tieton 红色 Red 美国 America 26 彩玉 Caiyu 黄红色 Yellowish red 中国 China 7 布鲁克斯 Brooks 红色 Red 美国 America 27 罗亚明 Royal minnie 紫红色 Purplish red 美国 America 8 桑提娜 Santina 紫红色 Purplish red 加拿大 Canada 28 罗亚理 Royal lee 红色 Red 美国 America 9 萨米脱 Summit 紫红色 Purplish red 加拿大 Canada 29 瑞德 Ruide 红色 Red 美国 America 10 黄蜜 Huangmi 黄红色 Yellowish red 中国 China 30 水晶香槟 Pearl champagne 红色 Red 美国 America 11 雷尼 Rainier 黄红色 Yellowish red 美国 America 31 珊瑚香槟 Coral champagne 红色 Red 美国 America 12 福星 Fuxing 红色 Red 中国 China 32 科迪亚 Kodia 紫黑色 Purplish-black 捷克 Chech 13 明珠 Mingzhu 黄红色 Yellowish red 中国 China 33 那翁 Napoleon 黄色 Yellow 德国 Germany 14 鲁樱1号 Luying1 红色 Red 中国 China 34 艳阳 Sunburst 紫红色 Purplish red 加拿大 Canada 15 黑珍珠 Heizhenzhu 紫黑色 Purplish red 中国 China 35 红蜜 Hongmi 黄红色 Yellowish red 中国 China 16 福晨 Fuchen 红色 Red 中国 China 36 大紫 Black tartarin 紫红色 Purplish red 俄罗斯 Russia 17 早大果 Крупноплодная 紫红色 Purplish red 乌克兰 Ukraine 37 早红宝石 Early ruby 紫红色 Purplish red 乌克兰 Ukraine 18 俄罗斯8号 Russia 8 紫黑色 Purplish red 俄罗斯 Russia 38 宾库 Bing 紫红色 Purplish red 美国 America 19 先锋 Van 紫红色 Purplish red 加拿大 Canada 39 意大利早红 Italian early 紫红色 Purplish red 法国 France 20 红灯 Hongdeng 红色 Red 中国 China 40 红灯(短柄) Hongdeng 红色 Red 中国 China 1.2 甜樱桃基因组DNA提取
采取CTAB法提取基因组DNA,利用紫外分光光度计检测提取的甜樱桃基因组DNA的OD260/OD280值,检验其浓度和纯度,再用1%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测其完整性。最后将提取的基因组DNA用ddH2O稀释至25 ng·µL−1,于−80 ℃保存备用。
1.3 引物筛选
本试验SCoT标记根据Collard等[17,18]公布的80条SCoT引物进行筛选,SRAP标记根据Li等[6]和廖柏勇等[19]设计的28条正向引物和29条反向引物共812种组合进行筛选。共筛选出6对SRAP引物和7条SCoT引物,引物序列见表2、3。本试验中的所有引物均由北京擎科生物科技有限公司成都分公司合成。
表 2 SRAP引物名称及序列Table 2. Names and sequences of SRAP primers名称
Name引物序列5′→3′
Primer Sequence 5′→3′引物序列5′→3′
Primer Sequence 5′→3′me4/em13 TGAGTCCAAACCGGACC GACTGCGTACGAATTCTA me5/em11 TGAGTCCAAACCGGAAG GACTGCGTACGAATTGCA me7/em23 TGAGTCCAAACCGGTCC GACTGCGTACGAATTGGT me8/em4 TGAGTCCAAACCGGTGC GACTGCGTACGAATTTGA me14/em23 TGAGTCCAAACCGGAAC GACTGCGTACGAATTGGT me26/em24 TTCAGGGTGGCCGGATG GACTGCGTACGAATTCAG 1.4 扩增体系
SRAP-PCR扩增体系参考路娟[14]的樱桃SRAP-PCR扩增体系稍作修改,SRAP-PCR反应总体积20 μL,其中正反引物各1 μL(10 µmol·L−1),DNA模板0.6 μL(25 ng·μL−1),2×SanTaq PCR Master Mix10 μL,ddH2O 7.4 μL。2×SanTaq PCR Master Mix从生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司购买。扩增程序为:94 ℃预变性5 min;前5个循环94 ℃变性1 min,35 ℃复性1 min,72 ℃延伸1 min,后30个循环将复性温度提高到50 ℃,其余不变;72 ℃再延伸10 min,于4 ℃下保存20 min。
SCoT-PCR扩增体系参考陈红等[20]的桃SCoT-PCR扩增体系稍作修改,SCoT-PCR反应总体积20 μL,其中引物2 μL(10 µmol·L−1),DNA模板1 μL(25 ng·μL−1),2×Taq PCR Master Mix 10 μL,ddH2O 7 μL。2×Taq PCR Master Mix从康为世纪生物科技股份有限公司购买。扩增程序为:94 ℃预变性4 min、94 ℃变性1 min、50 ℃退火1 min、72 ℃延伸2 min、36个循环、72 ℃延伸10 min、于4 ℃下保存20 min。
表 3 SCoT引物名称及序列Table 3. Names and sequences of SCoT primers名称
Name引物序列5′→3′
Primer Sequence 5′→3′名称
Name引物序列5′→3′
Primer Sequence 5′→3′SCoT12 ACGACATGGCGACCAACG SCoT27 ACCATGGCTACCACCGTG SCoT15 ACGACATGGCGACCGCGA SCoT62 ACCATGGCTACCACGGAG SCoT19 ACCATGGCTACCACCGGC SCoT72 CCATGGCTACCACCGCCC SCoT21 ACGACATGGCGACCCACA 1.5 PCR扩增产物检测及数据统计分析
采用1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳,缓冲液为0.5×TBE,电压120 V,时间50 min,最后在紫外凝胶成像系统上拍照保存。统计条带时以标准样品(Maker)为对照,在同一迁移位置上按条带的有或无进行赋值,有扩增条带记为“1”,无扩增条带记为“0”,从而得到原始的“0/1”矩阵。利用NTSYS 2.1和Popgene 1.32软件进行数据分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 SRAP标记多态性及遗传多样性分析
利用筛选出来的6对SRAP引物对40份甜樱桃品种进行PCR扩增,扩增出的条带稳定且清晰(部分结果见图1)。通过Popgene 1.32软件分析可知(表4),共扩增出DNA位点74个,其中多态性位点67个,平均每个引物组合扩增位点12.3个,平均多态性位点11.2个,多态性百分率90.54%,说明这40份甜樱桃品种的多态性比率较高,遗传背景较为丰富,这6对SRAP引物也能较好揭示甜樱桃的遗传信息。6对SRAP引物的等位基因数(Na)为1.8333~2.0000,平均等位基因数(Na)为1.9100。有效等位基因数(Ne)为1.3245~1.6451,平均有效等位基因数(Ne)为1.4554。Nei's 基因遗传多样性指数(H)为0.2008~0.3587,平均Nei's 基因遗传多样性指数(H)为0.2782。Shannon's 信息指数(I)为0.3134~0.5205,平均Shannon's 信息指数(I)为0.3701。
表 4 不同甜樱桃品种SRAP分子标记多态性及遗传多样性分析Table 4. Polymorphism and genetic diversity of sweet cherry cultivars analyzed based on SRAP markers引物
Primer总条带数
Number of
total bands多态性条带数
Number of
polymorphic bands多态性百分率
Percentage of
polymorphic bands/%等位基因数
Observed number of
alleles (Na)有效等位基因数
Effect
number of
alleles (Ne)Nei's 基因遗传
多样性指数
Nei's gene
diversity (H )Shannon's 信息指数
Shannon's
information
index (I )me4/em13 9 9 100.00 2.0000 1.4506 0.2915 0.4529 me5/em11 16 15 93.75 1.9375 1.4471 0.2684 0.4126 me7/em23 13 12 92.31 1.9231 1.4281 0.2736 0.4263 me8/em4 10 9 90.91 1.9091 1.6451 0.3587 0.5205 me14/em23 12 10 83.33 1.8333 1.3245 0.2008 0.3134 me26/em24 14 12 85.71 1.8571 1.4372 0.2759 0.4250 合计 Total 74 67 均值 Mean 12.3 11.2 90.54 1.9100 1.4554 0.2782 0.3701 2.2 SRAP分子标记UPGMA聚类分析及主坐标分析
基于SRAP分子标记数据,对供试的40份甜樱桃品种利用NTsys软件进行UPGMA(非加权算术平均法)聚类分析,并构建亲缘关系树状图(图2)。由UPGMA聚类分析图可知,40份甜樱桃的遗传相似系数为0.67~0.95。其中,明珠和罗亚理相似系数最大,为0.95,但是这有可能是由于引种时造成品种混乱,而造成了同物异名现象。红蜜和其他39份材料相似系数最小,为0.67,说明红蜜和其他品种的遗传差异较大。
从聚类图(图2)中可以看出,甜樱桃品种之间的亲缘关系非常复杂。相似系数在0.75左右,40份甜樱桃材料可以分为I和II两类。其中I类包含39个品种,II类中只包含红蜜一个品种。在相似系数0.77左右, I类可以分为两个亚组,在相似系数0.78左右,第一个亚组可以分为A、B两组。其中A组包括鲁樱3号、黑珍珠、俄罗斯8号、先锋、萨米脱、艳阳、那翁、鲁樱1号、齐早和福晨。B组只有意大利早红一个品种。在相似系数0.79左右,第二个亚组可以分为C、D、E三组。其中C组包括拉宾斯、早甘阳和桑德拉玫瑰。D组包含品种最多,在相似系数0.85左右,这一组可以分成三个小组,第一小组包括鲁玉、桑提娜和雷尼。第二小组包括福星、明珠、罗亚理、红灯短柄、科迪亚、珊瑚香槟、宾库、水晶香槟、佐藤锦 、琥珀、佳红、彩玉、黄蜜、美早、罗亚明、早大果、布鲁克斯和瑞得。第三小组包括红灯和龙冠,这个结果与这两个品种有着相同的亲本,亲缘关系较近相符。E组包括大紫和早红宝石。
由聚类图可看出,D组共有23个甜樱桃品种,且9个黄色果皮品种中的7个都聚在这一组,只有红蜜和那翁聚类在其他组,佐藤锦、琥珀、佳红、和彩玉单独聚类,遗传相似系数在0.9以上,这表明SRAP分子标记基本可以将黄色品种甜樱桃与红色品种区分开。
利用NTSYS软件对SRAP标记数据进行分析,根据40份甜樱桃品种材料间的相似系数进行主坐标分析(PCoA),如图3-A所示,图中位置远近即表示关系远近,根据SRAP标记主坐标分析结果,第1~3主坐标分别解释总遗传变异的15.87%、8.18%、7.79%,一共占总遗传变异的31.84%。主坐标分析将40个甜樱桃品种分为8类,相对于UPGMA分类中将40个甜樱桃品种分为6类,结果略有差异,主坐标分析可以在侧面验证UPGMA聚类分析(图3-B)。
2.3 SCoT标记多态性及遗传多样性分析
利用筛选出来的7条SCoT引物对40份甜樱桃品种进行PCR扩增,扩增出的条带稳定且清晰(图4)。通过Popgene 1.32软件分析可知(表5),共扩增出DNA位点74个,其中多态性位点69个,平均每个引物组合扩增位点10.6个,平均多态性位点9.9个,多态性百分率93.24%。由表4可知,每个引物的等位基因数(Na)为1.7778~2.0000,平均等位基因数(Na)为1.9278。有效等位基因数(Ne)为1.2752~1.4251,平均有效等位基因数(Ne)为1.3342。Nei's 基因遗传多样性指数(H)为0.1755~0.2493,平均Nei's 基因遗传多样性指数(H)为0.2093。Shannon's 信息指数(I)为0.2765~0.3939,平均Shannon's 信息指数(I)为0.3342。
表 5 不同甜樱桃品种SCoT分子标记多态性及遗传多样性分析Table 5. Polymorphism and genetic diversity of sweet cherry cultivars analyzed based on SCoT markers引物
Primer总条带数
Number of
total bands多态性条带数
Number of
polymorphic bands多态性百分率
Percentage of
polymorphic bands/%等位基因数
Observed number of
alleles (Na)有效等位基因数
Effect number of
alleles (Ne)Nei's 基因遗传
多样性指数
Nei's gene
diversity (H)Shannon's 信息指数
Shannon's information
index (I)SCoT12 9 9 100.00 2.0000 1.3428 0.2262 0.3671 SCoT15 9 9 100.00 2.0000 1.3098 0.2059 0.3380 SCoT19 12 12 100.00 2.0000 1.2752 0.1793 0.3026 SCoT21 13 13 100.00 2.0000 1.4005 0.2493 0.3939 SCoT27 10 8 80.00 1.8000 1.4251 0.2455 0.3693 SCoT62 12 11 91.67 1.9167 1.3015 0.1835 0.2922 SCoT72 9 7 77.78 1.7778 1.2847 0.1755 0.2765 合计 Total 74 69 均值 Mean 10.6 9.9 93.24 1.9278 1.3342 0.2093 0.3342 2.4 SCoT分子标记聚类分析及主坐标分析
基于SCoT分子标记数据,对供试的40份甜樱桃品种利用NTSYS软件进行UPGMA(非加权算术平均法)聚类分析,并构建亲缘关系树状图(图5)。由UPGMA聚类分析图可知,40份甜樱桃品种材料的遗传相似系数数值分布在0.72~0.93。其中,布鲁克斯和桑提娜相似系数最高,为0.93。
由UPGMA聚类图可知,在相似系数0.72时,40份甜樱桃品种材料可以分为I、II两大类,I类包括27个甜樱桃品种,II类包括13个甜樱桃品种。在相似系数0.77左右,I类的27个品种可以分为A、B、C、D四组,A组包括鲁樱3号、佳红、布鲁克斯、桑提娜、那翁、佐藤锦、彩玉、罗亚明、黄蜜、琥珀和先锋11个品种。B组包括拉宾斯、艳阳、宾库、意大利早红和早红宝石5个品种。C组包括早甘阳、大紫、桑德拉玫瑰、珊瑚香槟、鲁玉、罗亚理、红灯短柄和科迪亚8个品种。D组包括了雷尼、水晶香槟和红蜜3个品种。II类13个品种在相似系数0.75左右可以分为E、F两组,其中E组只有齐早一个品种。F组包括美早、黑珍珠、俄罗斯8号、鲁樱1号、福晨、早大果、萨米脱、红灯、龙冠、明珠、瑞得和福星12个甜樱桃品种。
由聚类图可知,佳红、那翁、佐藤锦、彩玉、黄蜜和琥珀,共6个黄色品种聚在A组,遗传相似系数在0.8左右,另外3个黄色品种雷尼和红蜜聚在D组,明珠聚在F组,表明SCoT标记也基本可以区分黄色和红色甜樱桃品种。
利用NTSYS软件对SCoT标记数据进行分析,根据40份甜樱桃品种材料间的相似系数进行主坐标分析(PCoA),如图6-A,根据SCoT标记主坐标分析结果,第1~3主坐标分别解释总遗传变异的14.40%、7.48%、7.24%,一共占总遗传变异的29.12%。主坐标分析将40个甜樱桃品种分为7类(图6-B),相对于UPGMA分类中将40个甜樱桃品种分为6类,结果差异不大。
3. 讨论与结论
3.1 甜樱桃遗传多样性分析
目前分子辅助育种已经成为了解遗传背景、选育新品种必不可少的辅助工具,其目的就是为了在育种前以及育种早期锁定目标性状,提高获得目标性状的可能性。从较早的RAPD和RFLP分子标记到现在应用广泛的SSR分子标记,对于研究甜樱桃遗传多样性提供了更便利的工具。本研究利用的两种分子标记表明,甜樱桃品种之间的遗传相似系数大部分在0.7以上,这表明甜樱桃品种间的遗传距离较低,具有较高的遗传相似度。这个研究结果与前人利用RAPD[21]、AFLP[22]和SSR[23]等分子标记得出结论相近,同时,也有部分研究表明,甜樱桃个别品种间遗传相似系数在0.5左右[24,25],更有研究发现低至0.36[15]。这应该与进行遗传多样性分析所选择的材料相关。大部分研究都会将中国樱桃和甜樱桃一起分析,中国樱桃与甜樱桃之间的遗传相似系数一般在0.5左右[14]。本试验基于SRAP和SCoT标记的扩增位点多态性百分比分别是90.54%和93.24%,均比蔡宇良等[26]利用RAPD标记得到的多态性低,主要是因为其材料中包含了部分中国樱桃。本试验SRAP标记多态性百分比较路娟等[14]的结果84.6%稍高,SCoT标记多态性百分比比彭芳芳等[16]的结果84.4%高,说明本研究中所筛选的引物更适用于甜樱桃遗传多样性分析。
3.2 甜樱桃SRAP与SCoT标记聚类分析
前人利用SSR标记对甜樱桃进行聚类分析时,发现大部分来源于不同地区的甜樱桃可以区分开[27,28],路娟等[14]利用SRAP标记进行甜樱桃聚类分析时也同样可以将大部分品种根据地理来源区分开。本试验中相同来源的甜樱桃品种并没有全部根据地理来源区分开,最主要原因是前人研究中所选用甜樱桃品种是各个地区本土培育,而本研究中的品种是在引种后再进行本土化育种所得到的品种,此时已存在频繁的基因交流。来自美国和加拿大的甜樱桃品种和部分国内新育成的甜樱桃品种并没有按照地理来源区分,很可能是因为国内大部分甜樱桃品种亲本从北美地区引进,因而部分品种具有相同亲本或者亲缘关系较近,这说明目前甜樱桃育种种质资源交流已经很广泛。
综上,本研究采用SRAP和SCoT对40份甜樱桃进行标记聚类,结果大部分黄色甜樱桃品种可以聚在同一组中,说明筛选的引物与甜樱桃果皮颜色性状连锁。王丹丹等[28]利用EST-SSR标记进行遗传多样性聚类分析时也能将黄色系甜樱桃聚为一类。此前高平等[29]利用RAPD、ISSR、SSR标记分析甜樱桃杂交后代遗传多样性及甜樱桃红色果皮性状的QTL,但发现RAPD和SSR标记存在一定局限性,RAPD标记稳定性较差,而SSR可用标记较少。本研究对比两种标记可知,SRAP和SCoT标记聚类结果并不一致,SRAP标记把更多的黄色品种聚为一类且相似系数更高,但同一组的还有另外的红色品种,而SCoT标记可以将9个黄色品种中的6个聚为一类且组内没有红色品种。这表明SCoT标记在区分甜樱桃果皮颜色优于SRAP标记,表明了SCoT标记在性状关联分析等方面的应用潜力更大。
-
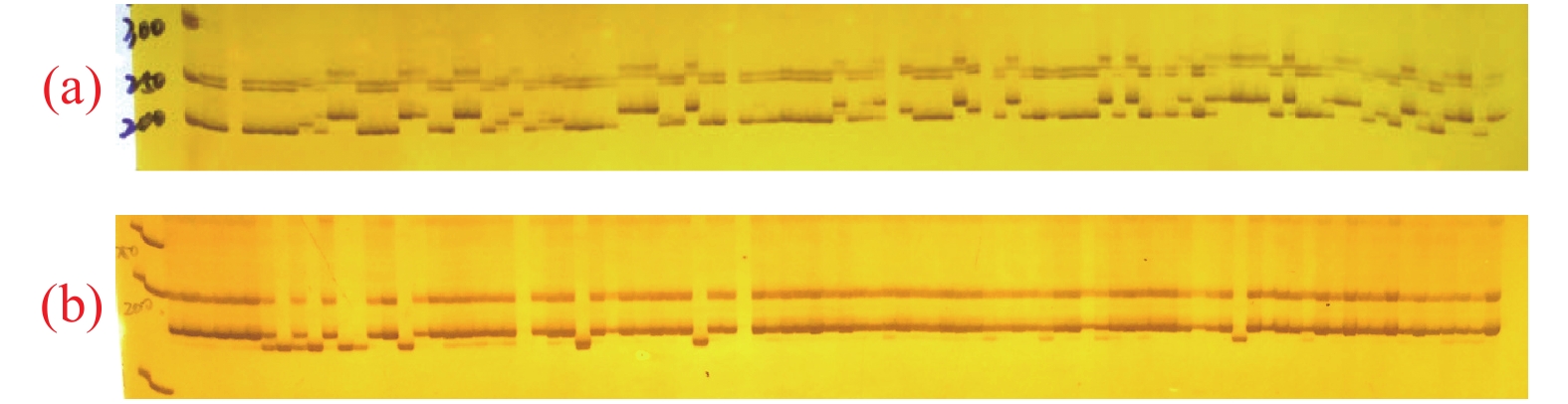
表 1 基于62对SSR引物的193个苦荞种质的遗传多样性参数
Table 1 Genetic diversity indicators of 193 Tartary buckwheat germplasms based on 62 pairs of SSR primers
序号 Index 引物名称 Primer name 等位基因数 Na 有效等位基因数 Ne Shannon信息指数 I 观察杂合度 Ho 基因多样性 He 多态信息量 PIC 1 S7582 4 2.253 0.918 0.932 0.556 0.82 2 S9023 5 4.120 1.497 0.813 0.757 0.90 3 S7676 3 1.451 0.519 0.005 0.311 0.58 4 S7622 3 1.418 0.568 0.130 0.295 0.61 5 S7678 4 3.110 1.224 0.802 0.678 0.77 6 S7642 4 3.501 1.320 0.578 0.714 0.81 7 S8993 3 2.196 0.858 0.865 0.545 0.73 8 S9065 5 2.309 1.002 0.771 0.567 0.79 9 S9095 3 1.442 0.532 0.328 0.307 0.77 10 S8951 3 1.696 0.727 0.151 0.410 0.64 11 S9007 3 2.813 1.063 0.188 0.644 0.73 12 S8983 3 1.759 0.736 0.109 0.432 0.64 13 S9045 3 1.099 0.206 0.000 0.09 0.66 14 S7606 3 2.089 0.802 0.839 0.521 0.73 15 S7662 3 1.709 0.721 0.109 0.415 0.65 16 S2218 5 2.400 1.012 0.844 0.583 0.72 17 S2298 3 1.833 0.753 0.479 0.455 0.80 18 S2314 3 1.241 0.389 0.026 0.194 0.56 19 S2158 5 3.401 1.351 0.797 0.706 0.82 20 S2214 4 3.486 1.314 0.438 0.713 0.81 21 S2252 3 1.840 0.749 0.469 0.457 0.66 22 S2288 4 2.471 1.033 0.875 0.595 0.74 23 S6827 4 1.875 0.814 0.417 0.467 0.67 24 S6865 3 2.038 0.780 0.766 0.509 0.60 25 S2234 5 3.378 1.348 0.870 0.704 0.83 26 S6871 5 2.274 0.938 0.901 0.560 0.77 27 S6821 5 3.136 1.230 0.672 0.681 0.82 28 S6873 4 2.752 1.187 0.266 0.637 0.85 29 S2216 6 2.695 1.193 0.948 0.629 0.87 30 S2310 5 2.173 0.879 0.88 0.540 0.70 31 S2312 7 1.535 0.784 0.094 0.349 0.85 32 S6853 7 3.615 1.453 0.953 0.723 0.88 33 S6805 4 1.350 0.470 0.271 0.259 0.80 34 S6891 3 1.244 0.366 0.000 0.196 0.20 35 S6875 4 2.178 0.863 0.880 0.541 0.78 36 S6789 4 1.505 0.698 0.125 0.335 0.79 37 S6843 3 1.299 0.464 0.078 0.230 0.79 38 S6859 4 1.582 0.664 0.036 0.368 0.72 39 S7654 5 2.811 1.151 0.438 0.644 0.78 40 S7668 4 2.219 0.893 0.813 0.549 0.61 41 S6819 5 3.461 1.325 0.734 0.711 0.80 42 S6811 3 2.105 0.796 0.964 0.525 0.53 43 S5216 3 1.021 0.065 0.000 0.021 0.67 44 S5196 3 2.128 0.82 0.870 0.530 0.57 45 S5166 4 2.300 0.922 0.875 0.565 0.79 46 S5176 3 1.134 0.252 0.000 0.118 0.69 47 S9013 4 2.544 1.026 0.964 0.607 0.73 48 S8963 4 1.065 0.165 0.005 0.061 0.52 49 S8969 3 1.321 0.489 0.135 0.243 0.59 50 S8947 4 1.295 0.412 0.219 0.228 0.71 51 S2304 4 2.228 0.951 0.214 0.551 0.82 52 TatG0242 8 7.283 2.031 0.747 0.863 0.91 53 TatG0164 4 2.248 0.923 0.124 0.555 0.78 54 TatG0227 6 2.625 1.148 0.916 0.619 0.83 55 TatG0272 4 2.391 1.096 0.202 0.582 0.79 56 TatG0188 5 2.542 1.118 0.006 0.607 0.79 57 TatG0124 6 4.437 1.573 0.787 0.775 0.89 58 TatG0004 8 4.684 1.744 0.433 0.787 0.91 59 TatG0156 6 4.370 1.562 0.899 0.771 0.88 60 TatG0214 5 3.526 1.390 0.579 0.716 0.87 61 TatG0184 9 4.248 1.699 0.646 0.765 0.91 62 TatG0175 5 3.851 1.421 0.944 0.740 0.85 表 2 苦荞种质各亚群的遗传多样性指数
Table 2 Genetic diversity indicators for each Tartary buckwheat subgroup
亚群
Subgroup样本数
N等位基因数
Na有效等位基因数
NeShannon信息指数
I观察杂合度
Ho基因多样性
HePOP1 88 4.21 2.42 0.943 0.493 0.513 POP2 90 3.74 2.33 0.870 0.502 0.484 POP3 15 2.95 2.27 0.800 0.576 0.468 表 3 各亚群成对Fst系数(下三角) 和Nei’s遗传距离(上三角)
Table 3 Pairwise estimated Fst (below diagonal) and Nei’s genetic distance (above diagonal) for subgroups
亚群 Subgroup POP 1 POP 2 POP 3 POP1 0.065 0.076 POP2 0.030 0.026 POP3 0.037 0.014 注:全部Fst差异显著(P<0.001)。
Note: All Fst values are significant (P<0.001).表 4 显著LD的SSR标记成对组合数的比例和D'(标准不平衡系数)
Table 4 Percentage and D' (standardized disequilibrium) value of pairs with significant LD
群体与亚群
Population
and
subgroup种质数
No. of germplasmsLD的SSR标记
成对组合数
No. of SSR
marker pairs
in LDLD的SSR标记
成对组合所占比例
Percentage of
SSR marker
pairs in LDD’ 群体 Population 193 644 34.06 0.277 Pop1 88 90 4.76 0.412 Pop2 90 206 10.89 0.304 Pop3 15 97 5.13 0.493 表 5 与苦荞籽粒黄酮含量显著相关的SSR标记
Table 5 SSR markers significantly associated with flavonoids content in Tartary buckwheat grains
SSR标记
SSR markerF值
F value显著水平
P表型贡献率
R2/ %S2310 3.146 0.0095 7.9 S2304 2.423 0.0373 6.3 TatG0124 1.848 0.0401 12.9 S2312 2.157 0.0402 7.7 S6853 2.066 0.0415 8.5 -
[1] 陈庆富. 荞麦属植物科学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012: 10 − 11. [2] 黄凯丰, 李振宙, 王炎, 等. 我国荞麦高产栽培生理研究进展 [J]. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 37(1):115−120. DOI: 10.16614/j.gznuj.zrb.2019.01.019 HUANG K F, LI Z Z, WANG Y, et al. Research progress on physiology of buckwheat under high-yield cultivation [J]. Journal of Guizhou Normal University (Natural Sciences), 2019, 37(1): 115−120.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.16614/j.gznuj.zrb.2019.01.019
[3] 吴韬, 肖丽, 李伟丽. 苦荞的营养与功能成分研究进展 [J]. 西华大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 40(2):91−96, 109. DOI: 10.12198/j.issn.1673-159X.3521 WU T, XIAO L, LI W L. Research progress of chemicals in Tartary buckwheat [J]. Journal of Xihua University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 40(2): 91−96, 109.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.12198/j.issn.1673-159X.3521
[4] LUTHAR Z, GOLOB A, GERM M, et al. Tartary buckwheat in human nutrition [J]. Plants, 2021, 10(4): 700. DOI: 10.3390/plants10040700
[5] 王璐瑗, 荣玉萍, 黄娟, 等. 211份金荞麦收集系根茎黄酮含量的分析评价 [J]. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 37(4):25−30, 48. WANG L Y, RONG Y P, HUANG J, et al. Analysis and evaluation of the flavonoid content of rhizomes of 211 different Golden buckwheat accessions(Fagopyrum cymosum complex) [J]. Journal of Guizhou Normal University (Natural Sciences), 2019, 37(4): 25−30, 48.(in Chinese)
[6] 刘三才, 李为喜, 刘方, 等. 苦荞麦种质资源总黄酮和蛋白质含量的测定与评价 [J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2007, 8(3):317−320. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1810.2007.03.014 LIU S C, LI W X, LIU F, et al. Identificaiton and evaluation of total flavones and protein content in Tartary buckwheat germplasm [J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2007, 8(3): 317−320.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1810.2007.03.014
[7] 吕丹, 黎瑞源, 郑冉, 等. 苦荞种质资源籽粒黄酮含量及籽粒性状的变异分析 [J]. 分子植物育种, 2020, 18(14):4762−4774. LYU D, LI R Y, ZHENG R, et al. Variation analysis of flavonoids content in seeds and seed traits of Tartary buckwheat germplasm resources [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2020, 18(14): 4762−4774.(in Chinese)
[8] 吕丹, 黎瑞源, 郑冉, 等. 苦荞“翅米荞×野苦荞”重组自交系群体籽粒黄酮含量及籽粒性状的分析 [J]. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 37(6):40−46. LYU D, LI R Y, ZHENG R, et al. Analysis of flavonoids content in grains and grain traits on ‘Chimiqiao' and ‘Yekuqiao' recombinant inbred lines population of Tartary buckwheat [J]. Journal of Guizhou Normal University (Natural Sciences), 2019, 37(6): 40−46.(in Chinese)
[9] 郑冉, 黎瑞源, 吕丹, 等. 苦荞重组自交系群体籽粒黄酮含量与产量性状分析 [J]. 广西植物, 2021, 41(2):216−224. DOI: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201906046 ZHENG R, LI R Y, LYU D, et al. Variation analysis of flavonoid contents in seeds and yield traits on recombinant inbred line population of Tartary buckwheat [J]. Guihaia, 2021, 41(2): 216−224.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201906046
[10] MATSUI K, WALKER A R. Biosynthesis and regulation of flavonoids in buckwheat [J]. Breeding Science, 2020, 70(1): 74−84. DOI: 10.1270/jsbbs.19041
[11] SHI T X, LI R Y, ZHENG R, et al. Mapping QTLs for 1000-grain weight and genes controlling hull type using SNP marker in Tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum) [J]. BMC Genomics, 2021, 22: 142. DOI: 10.1186/s12864-021-07449-w
[12] ZHANG L J, LI X X, MA B, et al. The Tartary buckwheat genome provides insights into rutin biosynthesis and abiotic stress tolerance [J]. Molecular Plant, 2017, 10(9): 1224−1237. DOI: 10.1016/j.molp.2017.08.013
[13] ZHANG K X, HE M, FAN Y, et al. Resequencing of global Tartary buckwheat accessions reveals multiple domestication events and key loci associated with agronomic traits [J]. Genome Biology, 2021, 22(1): 23. DOI: 10.1186/s13059-020-02217-7
[14] 马名川, 刘龙龙, 刘璋, 等. 苦荞全基因组SSR位点特征分析与分子标记开发 [J]. 作物杂志, 2021(1):38−46. MA M C, LIU L L, LIU Z, et al. Analysis of SSR loci in whole genome and development of molecular markers in Tartary buckwheat [J]. Crops, 2021(1): 38−46.(in Chinese)
[15] 贺润丽, 尹桂芳, 李春花, 等. 苦荞种皮转录组SSR位点信息分析及其分子标记的开发 [J]. 分子植物育种, 2020, 18(18):6085−6092. HE R L, YIN G F, LI C H, et al. Development of molecular markers and SSR loci information analysis of transcriptome in Tartary buckwheat seed coat [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2020, 18(18): 6085−6092.(in Chinese)
[16] 杜伟, 王东航, 侯思宇, 等. 基于苦荞全长转录组测序开发SSR标记及遗传多样性分析 [J]. 植物生理学报, 2020, 56(7):1432−1444. DU W, WANG D H, HOU S Y, et al. Development of SSR markers based on full-length transcriptome sequencing and its application for genetic diversity analysis in Fagopyrum tataricum [J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2020, 56(7): 1432−1444.(in Chinese)
[17] SHI T X, LI R Y, CHEN Q J, et al. De novo sequencing of seed transcriptome and development of genic-SSR markers in common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum) [J]. Molecular Breeding, 2017, 37(12): 1−15.
[18] 黎瑞源, 潘凡, 陈庆富, 等. 苦荞转录组EST-SSR发掘及多态性分析 [J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2015, 17(4):42−52. LI R Y, PAN F, CHEN Q F, et al. Excavation and polymorphism analysis of EST-SSR from transcriptome of Tartary buckwheat [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2015, 17(4): 42−52.(in Chinese)
[19] 黎瑞源, 石桃雄, 陈其皎, 等. 中国35个苦荞审定品种EST-SSR指纹图谱构建与遗传多样性分析 [J]. 植物科学学报, 2017, 35(2):267−275. LI R Y, SHI T X, CHEN Q J, et al. Construction of EST-SSR fingerprinting and analysis of genetic diversity of thirty-five registered Tartary buckwheat cultivars (Fagopyrum tataricum) in China [J]. Plant Science Journal, 2017, 35(2): 267−275.(in Chinese)
[20] 李春花, 陈蕤坤, 王艳青, 等. 利用SSR标记构建云南苦荞种质资源分子身份证 [J]. 分子植物育种, 2019, 17(5):1575−1582. LI C H, CHEN R K, WANG Y Q, et al. Establishment of the molecular ID for Yunnan Tartary buckwheat germplasm resources based on SSR marker [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2019, 17(5): 1575−1582.(in Chinese)
[21] 屈洋, 周瑜, 王钊, 等. 苦荞产区种质资源遗传多样性和遗传结构分析 [J]. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(11):2049−2062. DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2016.11.002 QU Y, ZHOU Y, WANG Z, et al. Analysis of genetic diversity and structure of Tartary buckwheat resources from production regions [J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(11): 2049−2062.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2016.11.002
[22] 徐笑宇, 方正武, 杨璞, 等. 苦荞遗传多样性分析与核心种质筛选 [J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2015, 33(1):268−277. XU X Y, FANG Z W, YANG P, et al. Genetic diversity analysis of Tartary buckwheat and selection of core collections [J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2015, 33(1): 268−277.(in Chinese)
[23] 杨学文, 丁素荣, 胡陶, 等. 104份苦荞种质的遗传多样性分析 [J]. 作物杂志, 2013(6):13−18. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7283.2013.06.004 YANG X W, DING S R, HU T, et al. Genetic diversity of 104 Tartary buckwheat accessions [J]. Crops, 2013(6): 13−18.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7283.2013.06.004
[24] HOU S Y, SUN Z X, BIN L H, et al. Genetic diversity of buckwheat cultivars (Fagopyrum tartaricum Gaertn.) assessed with SSR markers developed from genome survey sequences [J]. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 2016, 34(1): 233−241. DOI: 10.1007/s11105-015-0907-5
[25] 黎瑞源, 梁龙兵, 石桃雄, 等. 苦荞重组自交系群体F5代SSR遗传图谱的构建 [J]. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 35(4):31−45. LI R Y, LIANG L B, SHI T X, et al. Construction of a microsatellite-based genetic map of Tartary buckwheat using F5 recombinant inbred lines [J]. Journal of Guizhou Normal University (Natural Sciences), 2017, 35(4): 31−45.(in Chinese)
[26] 杨美. 甘蓝型油菜根系形态对低磷胁迫的反应及其QTL分析[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2010. YANG M. Response of root morphology to low phosphorus stress and QTL analysis in Brassica napus[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2010. (in Chinese).
[27] 赵宇慧, 李秀秀, 陈倬, 等. 生物信息学分析方法Ⅰ: 全基因组关联分析概述 [J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(6):715−732. DOI: 10.11983/CBB20091 ZHAO Y H, LI X X, CHEN Z, et al. An overview of genome-wide association studies in plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(6): 715−732.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11983/CBB20091
[28] 徐刚标. 植物群体遗传学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012: 193 − 200. [29] 马名川, 张丽君, 刘璋, 等. 基于SSR标记的山西省不同地区苦荞遗传多样性分析 [J]. 山西农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 41(3):25−31. MA M C, ZHANG L J, LIU Z, et al. Analysis of genetic diversity of Tartary buckwheat from different regions of Shanxi Province based on SSR marker [J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 41(3): 25−31.(in Chinese)
[30] GUPTA N, SHARMA S K, RANA J C, et al. AFLP fingerprinting of Tartary buckwheat accessions (Fagopyrum tataricum) displaying rutin content variation [J]. Fitoterapia, 2012, 83(6): 1131−1137. DOI: 10.1016/j.fitote.2012.04.015
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 黄婉莉,张冬敏,符喜喜,陈心怡,张朝坤. 番石榴杂交F_1代基于SRAP标记的鉴定及果实性状的遗传倾向分析. 果树学报. 2024(09): 1731-1745 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: