Changes on Organic Acids in Chinese Fir Seedlings under Simulated Al-stress
-
摘要:目的 研究铝胁迫对杉木幼苗有机酸含量的影响,以期阐明杉木有机酸对铝胁迫的响应特征。方法 以杉木幼苗为材料,采用营养液培养法,研究不同浓度铝胁迫对杉木幼苗体内有机酸和根尖分泌有机酸含量水平的影响;通过相关性分析,揭示有机酸、铝含量之间的关系。结果 在杉木针叶和根中均检测到草酸、酒石酸、L-苹果酸、抗坏血酸、柠檬酸和富马酸等6种有机酸。针叶中抗坏血酸含量最高,根中则以草酸和抗坏血酸的含量最多。铝胁迫下,针叶中酒石酸、L-苹果酸、抗坏血酸、柠檬酸、富马酸含量呈先升高后降低的变化趋势,草酸的含量则呈升高的趋势。当铝胁迫浓度为1 mmol·L−1时,针叶中L-苹果酸和富马酸的含量显著增加,其他4种有机酸含量则无显著变化。不同浓度铝胁迫下,根中6种有机酸含量均比对照显著降低。根尖分泌有机酸主要以草酸为主,还检测到少量L-苹果酸、抗坏血酸和乳酸。与对照相比,铝胁迫下根尖分泌的草酸含量均显著降低。结论 杉木中不同有机酸以及不同组织对铝胁迫的响应不同。铝胁迫对杉木针叶中L-苹果酸和富马酸含量、根中6种有机酸含量和根尖草酸分泌量有显著影响。杉木根部比针叶对铝胁迫的响应更敏感,胁迫伤害更明显。Abstract:Objective Effect of aluminum (Al)-stress on organic acids in seedlings of Chinese fir, Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb.) Hook, was examined in a simulated study.Method Nutrient culture solutions containing Al in varied concentrations were used to cultivate the seedlings. Organic acids in the plant tissues (i.e., needles and roots) and secreted from the root-tips of the seedlings grown in the media were determined to analyze the effect of Al-stress by a correlation analysis.Result Six organic acids including oxalic acid, tartaric acid, L-malate, ascorbic acid, citric acid, and fumaric acid were found in the needles and roots of the Chinese fir seedlings. Among them, ascorbic acid had the highest content in the needles, while ascorbic acid and oxalic acid in the roots. Under Al-stress, tartaric acid, L-malate, ascorbic acid, citric acid, and fumaric acid increased initially and followed by a decline in the needles, but the oxalic acid on a constant increase trend. At Al concentration of 1 mmol·L−1, L-malic acid and fumaric acid significantly increased, with no significant changes on the other acids, in the needles. The contents of the 6 organic acids in roots of the plants under varied Al-stresses were significantly lower than those of control. Aside from minute amounts of L-malate, ascorbic acid, and lactic acid, oxalic acid was the major organic acids found in the root-tip exudate. It was significantly reduced by the imposition of Al-stress.Conclusion The responses of Chinese fir seedlings to the simulated Al-stress varied with respect to the organic acid contents in the needles or roots and the root-tip secretion. Significant effects were observed on L-malic acid and fumaric acid in the needles and on all 6 organic acids in the roots, as well as oxalic acid exudated from the root-tips. Al-stress appeared to exert greater harm to the roots than the needles on a fir plant.
-
Keywords:
- Chinese fir /
- aluminum stress /
- organic acid /
- root exudates
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】 蝴蝶兰(Phalaenopsis equestris)花型独特、花色淡雅、花期持久,具有较高的观赏价值和市场经济价值,是我国销售量最大的盆花花卉,是目前市场上非常有竞争力和发展潜力的一种价值较高的花卉。但是病毒性病害严重影响和危害了蝴蝶兰的发展前景,已经成为蝴蝶兰产业持续、健康和快速发展的一个巨大绊脚石。福建漳州蝴蝶兰花卉产业在全国具有举足轻重的重要地位。福建漳州作为全国最大的兰花培育集散中心,年产出几千万盆兰花,其中蝴蝶兰约500万~800万盆,投放市场的成品兰占全国兰花市场份额的10%,同时也已成为向美国、日本、韩国和欧洲等国出口蝴蝶兰的重要基地[1]。植物病毒病被称“植物癌症”,一旦发病,尚无有效方法挽救,防治非常困难。近几年,由于全球气候变化、生态环境恶化、农业种植结构、耕种模式改变等原因,蓟马和蚜虫等虫媒传播的花卉病毒病日益严重,对我国蝴蝶兰等重要花卉的安全生产造成了严重的威胁。因此,亟需加强病毒-蝴蝶兰的互作研究,从而为制定防治策略提供理论依据。【前人研究进展】目前,研究表明感染蝴蝶兰植株的病毒种类较多,主要包括建兰花叶病毒(cymbidium mosaic virus, CymMV)[2]、齿兰环斑病毒(odontoglossum ringspot virus, ORSV)[3]、黄瓜嵌纹病毒(cucumber mosaic virus, CMV)[4]、番茄斑萎病毒(tomato spotted wilt virus, TSWV)[5]、建兰环斑病毒(cymbidium ringspot virus, CymRV)、辣椒褪绿病毒(capsicum chlorosis virus, CaCV)[6]、凤仙花坏死斑病毒(impetiens necrotic spot virus, INSV)[7]、兰花斑点病毒(ovrchid fleck rhabdovirus, OFV)[8]、蝴蝶兰黄化斑点病毒 (phalaenopsis chlorosisspot virus, PhCSV)[9]、康乃馨斑驳病毒(carnation mottle virus, CaMV)[10]和石斛兰叶脉坏疽病毒(dendrobium veinnecrosis closterovirus, DVNV) [11]等。其中CymMV和ORSV是蝴蝶兰生产中的主要病毒,且两者经常复合侵染蝴蝶兰植株。CymMV和ORSV分别属于甲型线形病毒科(Alphaflexiviridae) 和帚状病毒科(Virgaviridae)的正单链RNA病毒[12]。病毒感染蝴蝶兰会影响植株的生长发育,具体表现为生长速度减缓,叶片出现规则或者不规则的褪绿黄化、炭疽坏死斑块,花器出现畸形、色泽不均的斑块、提早凋萎等不同症状[13−14],对蝴蝶兰影响巨大。RNA干扰(RNA interference, RNAi)是植物、昆虫和真菌等生物保守的抵御病毒等病原物侵染的免疫防御机制[15−16]。研究表明,病毒侵染模式植物拟南芥后,植物的Dicer-like (DCL)蛋白识别并切割长的病毒来源的双链基因组为21、22、24 nt等不同长度的小干扰RNA(small interference RNA, siRNA),这些病毒来源的siRNA(vsiRNAs)与Argonaute结合形成RNA诱导的沉默复合体,随后复合物中vsiRNAs通过碱基匹配进行基因定位,Argonaute蛋白通过核酸切割活性沉默基因[17],从而沉默外源病毒等病原物基因的表达,由此可知,RNAi免疫途径被激活或者病毒与寄主植物发生互作的一个典型特征是病毒侵染寄主植物细胞后能够诱导产生大量病毒来源的vsiRNAs。由于病原系统的差异,病毒vsiRNAs在丰度、长度分布、5′端碱基偏好性、正负义来源、基因组高低频切割位点等方面呈现广泛的多样性[15]。不同种的病毒侵染不同寄主细胞后产生的 vsiRNAs 丰度存在较大差异,丰度一般在0.1%~20%[15]。vsiRNAs的长度分布主要集中在21 nt和22 nt[15]。vsiRNAs 5′端碱基偏好性根据vsiRNAs结合的AGO蛋白而有所不同[15]。vsiRNAs近乎等比例来源于正负义基因组或者主要来源于正义或负义基因组[15]。vsiRNAs在病毒基因组上呈现连续但不均匀的分布,即形成高低频切割位点[15]。 【本研究切入点】运用深度测序技术,已经在众多不同的植物细胞中鉴定到大量病毒来源的vsiRNAs,vsiRNAs的鉴定已成为研究病毒和寄主互作的有效途径或方法[18−19]。然而关于蝴蝶兰与病毒病原之间的互作尚有待深入探讨。【拟解决的关键问题】通过电镜和PCR等技术鉴定CymMV和ORSV感染蝴蝶兰,并通过深度测序技术鉴定分析病毒来源的vsiRNAs特征来分析CymMV、ORSV和蝴蝶兰寄主之间的相互作用,以期为防治蝴蝶兰病毒病提供依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
病毒侵染和健康的蝴蝶兰样品均由福建漳州台湾农民创业园绿乐园艺有限公司提供。多糖多酚植物总RNA提取试剂盒(RNAprep pure plant plus kit)、一步法RT-PCR试剂盒(fastking one step RT-PCR kit)和DNA Marker分子量标准(MD102)均购自天根生化科技(北京)有限公司。
1.2 RT-PCR
根据CymMV和ORSV外壳蛋白基因序列(Accession登录号分别为: AB693982和AB693988)设计特异扩增引物CymMV-F:ATGGGAGAGCCCACTCCAACT,CymMV-R:TATCCTCCTGGAAACCAGCCT;ORSV-F:ATGTTTTACACTATTACAGA,ORSV-R:TGAGACTTGATTGTACATACCA,两个基因片段大小均约400 bp。用多糖多酚植物总RNA提取试剂盒(RNAprep pure plant plus kit)提取病毒侵染和健康蝴蝶兰叶片总RNA后,根据一步法RT-PCR试剂盒(fastking one step RT-PCR kit)说明进行RT-PCR检测。一步RT-PCR体系(50 μL)为:2×fastking one step RT-PCR mastermix 25 μL,25×RT-PCR Enzyme Mix 2 μL,上下游引物(10 μmol·L−1)各1.25 μL,RNA模版0.01~1.00 μg,ddH2O补至50 μL。RT-PCR程序:42 ℃,30 min;95 ℃,3 min;94 ℃,30 s,55~65 ℃,30 s,72 ℃,30 s,35个循环;72 ℃,5 min。RT-PCR扩增产物用琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测。
1.3 电镜观察
电镜负染观察主要步骤:获取病毒侵染和健康蝴蝶兰叶片的汁液,将汁液滴加在覆有Formvar膜的铜网上,2 min后用滤纸吸去铜网膜上多余的液体,用1%磷钨酸(pH 7.2)进行负染,用透射电子显微镜H-
7650 Hitachi(日立)观察病毒粒体的形态和大小等特征。电镜超薄切片观察主要步骤:病毒侵染和健康蝴蝶兰叶片切成0.5 cm的小块后,依次用2.5%戊二醛进行固定,用酒精梯度脱水,用Spurr试剂进行渗透,用环氧树脂进行包埋;随后在聚合器中70 ℃进行聚合;聚合后的样品在超薄切片机Leica UC7(德国莱卡)上进行切片制备;超薄切片转移至铜网进行染色;最后将铜网置于透射电镜H-
7650 Hitachi (日立)观察病毒粒体的形态和大小等特征。1.4 siRNAs深度测序和特征分析
参照Lan的方法[18]进行siRNAs的深度测序和鉴定分析。主要步骤为:用多糖多酚植物总RNA提取试剂盒(RNA preppure plant plus kit)提取病毒侵染和健康蝴蝶兰叶片总RNA,10 μg总RNA经8%聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳后,回收纯化18~32 nt的siRNAs,用T4 RNA酶分别连接3′接头和5′接头后,SuperScript Ⅱ酶反转录后进行PCR反应,通过聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳回收纯化PCR产物,Illumina HiSeq 2000测序仪(Illumina,美国)进行深度测序。用软件Bowtie将siRNAs与CymMV和ORSV基因组进行匹配,再进行病毒来源vsiRNAs丰度、长度、碱基偏好性和正负义链分布等特征分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 CymMV和ORSV在蝴蝶兰中的侵染
采集蝴蝶兰感病样品(图1A),以蝴蝶兰叶片总RNA为模板,CymMV-F/R和ORSV-F/R为引物,RT-PCR扩增两种病毒的外壳蛋白基因部分片段,经琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测。结果显示,RT-PCR扩增获得了两条特异的目的片段,片段大小约400 bp(图1B),与引物设计预期结果一致,初步表明CymMV和ORSV两种病毒侵染蝴蝶兰。
![]() 图 1 CymMV和ORSV在蝴蝶兰叶片的共侵染鉴定A:病毒侵染的蝴蝶兰样品;B:CymMV和ORSV外壳蛋白基因的RT-PCR扩增产物的琼脂糖凝胶电泳, M为DNA marker MD102;1和2分别为 CymMV和ORSV外壳蛋白基因产物; C:CymMV和ORSV病毒电镜观察的负染图;D:CymMV和ORSV病毒电镜观察的超薄切片图。Figure 1. Identification of CymMV/ORSV co-infections in P. equestrisA: P. equestris plant infected by viruses; B: agarose gel electrophoresis of RT-PCR products of CP genes of CymMV and ORSV; M: DNA marker MD102; 1 and 2: RT-PCR products of CP genes of CymMV and ORSV, respectively; C: electron microscopic negative staining images of CymMV and ORSV; D: electron microscopic images on thin sections of CymMV and ORSV.
图 1 CymMV和ORSV在蝴蝶兰叶片的共侵染鉴定A:病毒侵染的蝴蝶兰样品;B:CymMV和ORSV外壳蛋白基因的RT-PCR扩增产物的琼脂糖凝胶电泳, M为DNA marker MD102;1和2分别为 CymMV和ORSV外壳蛋白基因产物; C:CymMV和ORSV病毒电镜观察的负染图;D:CymMV和ORSV病毒电镜观察的超薄切片图。Figure 1. Identification of CymMV/ORSV co-infections in P. equestrisA: P. equestris plant infected by viruses; B: agarose gel electrophoresis of RT-PCR products of CP genes of CymMV and ORSV; M: DNA marker MD102; 1 and 2: RT-PCR products of CP genes of CymMV and ORSV, respectively; C: electron microscopic negative staining images of CymMV and ORSV; D: electron microscopic images on thin sections of CymMV and ORSV.为了进一步验证RT-PCR结果的准确性和可靠性,采集蝴蝶兰感病叶片进行负染和超薄切片制备,然后用电镜观察结果。电镜结果表明,负染和超薄切片中都能够观察到长约300 nm线状的病毒粒子和长约500 nm杆状的病毒粒子(图1C、D),300 nm线状的病毒粒子和500 nm杆状的病毒粒子分别代表CymMV和ORSV两种病毒,在健康蝴蝶兰叶片样品中并未观察到该种大小和形态特征的病毒,因此电镜结果进一步证实CymMV和ORSV两种病毒侵染了蝴蝶兰。
2.2 CymMV和ORSV来源的vsiRNAs特征分析
2.2.1 siRNAs深度测序总体概况
病毒侵染证实后,提取感病和健康植株的总RNA进行siRNAs的深度测序,鉴定和分析病毒来源的vsiRNAs特征。siRNAs深度测序结果显示,健康和病毒侵染的蝴蝶兰植株分别获得7 563 892和6 133 689个读数的原始种类的小RNA(total siRNAs);将这些total siRNAs匹配到CymMV和ORSV两种病毒基因组后,结果表明,健康和病毒侵染的蝴蝶兰植株中能匹配到病毒基因组的total vsiRNAs读数分别为906和826 682;在病毒侵染的蝴蝶兰样品中,匹配到CymMV和ORSV病毒基因组的total vsiRNAs读数分别为369 524(约44.7%)和457 104(55.3%)。
2.2.2 vsiRNAs的长度特征
获得siRNAs读数后进行特征分析,长度特征分析表明,在健康蝴蝶兰样品中,24、21、22 、23 nt长度的total siRNAs丰度依次较高(图2A),然而在病毒侵染的蝴蝶兰样品中,21、24、22、23 nt长度的total siRNAs丰度依次较高(图2A),total siRNAs最大丰度的差异表明病毒侵染改变了total siRNAs的长度分布形式或特征。另外,在病毒侵染的蝴蝶兰样品中,CymMV和ORSV来源的vsiRNAs长度丰度均主要为21 nt和22 nt(图2B),其中21 nt vsiRNAs丰度均为最高,22 nt vsiRNAs次之,该结果与Pai等的研究结果一致[19]。21 nt vsiRNAs高丰度不仅表明21 nt vsiRNAs在RNAi免疫过程中起主要的抵御病毒作用,还暗示在蝴蝶兰细胞中DCL4和DCL2蛋白可能是vsiRNAs分子形成过程中的主要参与者。vsiRNAs是双链小RNA分子,vsiRNAs 5′或3′端突出的碱基数量称为悬挂(overhang)。对于21 nt的vsiRNAs分子,悬挂的碱基数量=21−碱基匹配数量。21 nt vsiRNAs的overhang分析表明,CymMV和ORSV来源的21 nt的vsiRNAs中,具有2个碱基overhang的vsiRNAs丰度都最高(图2C),暗示在蝴蝶兰细胞中,CymMV和ORSV来源的21 nt的vsiRNAs中具有2个碱基overhang的vsiRNAs可能是RNAi免疫反应最有效的激发者。
![]() 图 2 蝴蝶兰细胞中CymMV和ORSV来源的vsiRNAs特征A:健康蝴蝶兰和病毒侵染蝴蝶兰中siRNAs长度分布;B: 病毒侵染蝴蝶兰中vsiRNAs长度分布; C:病毒侵染的蝴蝶兰中5'端距离为1~21 nt vsiRNAs读数;D: Total vsiRNAs(左)和21 nt vsiRNAs(右) 5'端第一个碱基偏好性。Figure 2. Characterization of CymMV- and ORSV-derived vsiRNAs in P. equestrisA: size distribution of total small RNAs in virus-infected and viruses-free P. equestris plants; B: size distribution of vsiRNAs matching CymMV and ORSV genomes in virus-infected P. equestris plants; C: reads of 21-nt vsiRNAs with 1-21 nt distance between 5′ ends from CymMV and ORSV genome in P. equestris plants; D: relative frequency of 5′-terminal nucleotide of total vsiRNAs (left) and 21 nt vsiRNAs (right).
图 2 蝴蝶兰细胞中CymMV和ORSV来源的vsiRNAs特征A:健康蝴蝶兰和病毒侵染蝴蝶兰中siRNAs长度分布;B: 病毒侵染蝴蝶兰中vsiRNAs长度分布; C:病毒侵染的蝴蝶兰中5'端距离为1~21 nt vsiRNAs读数;D: Total vsiRNAs(左)和21 nt vsiRNAs(右) 5'端第一个碱基偏好性。Figure 2. Characterization of CymMV- and ORSV-derived vsiRNAs in P. equestrisA: size distribution of total small RNAs in virus-infected and viruses-free P. equestris plants; B: size distribution of vsiRNAs matching CymMV and ORSV genomes in virus-infected P. equestris plants; C: reads of 21-nt vsiRNAs with 1-21 nt distance between 5′ ends from CymMV and ORSV genome in P. equestris plants; D: relative frequency of 5′-terminal nucleotide of total vsiRNAs (left) and 21 nt vsiRNAs (right).2.2.3 vsiRNAs的碱基偏好性
vsiRNAs 5′端的第一个碱基种类会影响vsiRNAs结合到哪种Argonaute蛋白。Total vsiRNAs 5′端碱基偏好性分析表明,CymMV和ORSV来源的vsiRNAs 5′端碱基偏好性都是依次偏好于U、A、C和G(图2D,左Panel),该结果表明CymMV和ORSV来源的vsiRNAs因第一个碱基的差异其可能结合各自不同的Argonaute蛋白,进而介导RNAi免疫效应。长度丰度分析表明,21 nt vsiRNAs丰度最高,其可能是蝴蝶兰细胞RNAi免疫途径的主要激发者,因此,进一步分析了21 nt vsiRNAs的5′端第一个碱基偏好性分析,分析结果表明,21 nt vsiRNAs的5′端第一个碱基偏好性也是依次偏好于U、A、C和G(图2D,右Panel),该结果进一步暗示vsiRNAs 5′端第一个碱基的类型与其结合的Argonaute蛋白之间具有密切的联系。
2.2.4 vsiRNAs的正负义链来源
total vsiRNAs正负义链来源(极性)分布表明,CymMV来源的vsiRNAs中,分别有
326662 个读数(88.4%)和42 862个读数(11.6%)的vsiRNAs来自于正义链和负义链病毒基因组(图3A);与此类似,ORSV来源的vsiRNAs中,分别有425 548个读数(93.1%)和31 520个读数(6.9%)的vsiRNAs来自于正义链和负义链病毒基因组(图3A),该结果表明蝴蝶兰细胞中CymMV和ORSV vsiRNAs主要来源都是病毒基因组的正义链。![]() 图 3 CymMV和ORSV vsiRNAs的生成前体分析A:CymMV和ORSV vsiRNAs的正负义链分布;B:vsiRNAs在CymMV基因组上高低频切割位点;C:vsiRNAs在ORSV基因组上高低频切割位点; D:CymMV正链基因组的二级结构预测;E:ORSV正链基因组的二级结构预测。方框I为图3B和图3D中高频切割位点和基因组茎环结构的对应关系。方框II为图3C和图3E中高频切割位点和基因组茎环结构的对应关系。Figure 3. Biogenesis precursors of CymMV and ORSV vsiRNAsA: polarity distribution of vsiRNAs matching CymMV and ORSV genomes from co-infected P. equestris plants; B and C: vsiRNAs hotspots and cold spots distribution along CymMV and ORSV genomes, respectively; D and E: secondary structures of CymMV and ORSV RNAs predicted with RNAfold server. Box I shows the corresponding relationship between the high frequency cutting sites in Figures 3B and the stem ring structure in Figure 3D. Box II shows the corresponding relationship between the high frequency cutting sites in Figures 3C and the stem ring structure in Figure 3E.
图 3 CymMV和ORSV vsiRNAs的生成前体分析A:CymMV和ORSV vsiRNAs的正负义链分布;B:vsiRNAs在CymMV基因组上高低频切割位点;C:vsiRNAs在ORSV基因组上高低频切割位点; D:CymMV正链基因组的二级结构预测;E:ORSV正链基因组的二级结构预测。方框I为图3B和图3D中高频切割位点和基因组茎环结构的对应关系。方框II为图3C和图3E中高频切割位点和基因组茎环结构的对应关系。Figure 3. Biogenesis precursors of CymMV and ORSV vsiRNAsA: polarity distribution of vsiRNAs matching CymMV and ORSV genomes from co-infected P. equestris plants; B and C: vsiRNAs hotspots and cold spots distribution along CymMV and ORSV genomes, respectively; D and E: secondary structures of CymMV and ORSV RNAs predicted with RNAfold server. Box I shows the corresponding relationship between the high frequency cutting sites in Figures 3B and the stem ring structure in Figure 3D. Box II shows the corresponding relationship between the high frequency cutting sites in Figures 3C and the stem ring structure in Figure 3E.2.2.5 高低频切割位点及其与基因组结构的关系分析
将total vsiRNAs定位到CymMV和ORSV病毒基因组具体位点后,高低频切割位点分析表明,vsiRNAs沿着CymMV和ORSV病毒基因组呈现连续但不均匀的分布特征(图3B、C);大部分(95%)total vsiRNAs产生位点位于CymMV和ORSV病毒基因组内部,而不是基因组的5′和3′两端(图3B、3C);在病毒基因组不同位点形成了高频切割点(hotspot)和低频切割点(coldspot)(图3B、C)。
用RNAfold server在线平台预测CymMV和ORSV病毒基因二级结构,结构预测结果表明在CymMV和ORSV病毒基因内部形成了大量的茎环二级结构(图3D、E),且茎环二级结构的形成与高频切割位点是相对应的,表明CymMV和ORSV病毒基因内部茎环二级结构是RNAi免疫途径关键因子DCL蛋白的切割底物,从而形成不同大小的vsiRNAs,即茎环结构是vsiRNAs的主要生成前体。
3. 讨论
蝴蝶兰是具有重要观赏和经济价值的花卉之一。但是病毒性病害已经成为制约蝴蝶兰产业持续健康发展的较大因素。福建漳州蝴蝶兰花卉产业在全国具有举足轻重的重要地位,但是CymMV和ORSV两种病毒对蝴蝶兰危害严重[12−14]。因此,亟需加强蝴蝶兰病毒性病害尤其是CymMV和ORSV两种病毒的检测调查。本研究采集了漳州漳浦农民产业园区的健康和疑似病毒侵染的蝴蝶兰植株,依次采用RT-PCR和传统的电镜技术明确了漳州蝴蝶兰植株感染了CymMV和ORSV两种主要病毒。
植物病毒素有“植物癌症”之称,目前并无有效的防治办法。为了探索有效的防治措施,务必加强病毒和寄主之间相互作用的研究。RNAi是植物、昆虫和真菌等生物保守的抵御病毒等病原物侵染的免疫防御机制[15−16]。RNAi免疫途径被激活的一个典型特征是病毒侵染寄主植物细胞后能够诱导产生大量病毒来源的vsiRNAs。因此,病毒来源的vsiRNAs的鉴定和特征分析已经成为加深理解病毒和寄主相互作用的重要途径和方法。运用高通量深度技术已经在众多的病毒-植物病原系统中鉴定了大量的vsiRNAs[18]。在本研究中,利用siRNAs深度测序技术在CymMV和ORSV复合侵染的蝴蝶兰叶片中获得了大量(约13.48%)病毒来源的vsiRNAs,该结果表明CymMV和ORSV复合侵染蝴蝶兰叶片细胞后激活了寄主植物RNAi免疫途径,病毒与寄主确实存在相互作用。
病毒与寄主互作的具体机制可以通过分析vsiRNAs特征加以理解。研究表明24 nt siRNA主要在miRNA途径中调控寄主本身的生长发育等生命活动中发挥作用,而21 nt的siRNAs主要在siRNA介导的抗病毒免疫途径中发挥作用[15]。本研究中,高丰度值21 nt siRNAs的出现表明CymMV和ORSV的侵染激活了蝴蝶兰细胞中siRNAs介导的抗病毒免疫途径。在拟南芥等模式植物细胞中,21、22、24 nt的vsiRNAs分别由DCL4、DCL2和DCL1蛋白切割底物产生[17],因此推测在蝴蝶兰细胞中该长度的vsiRNAs可能也有其同源蛋白切割底物产生。研究表明许多病原系统产生的21 nt的vsiRNAs中,其5′或3′端具有2个碱基的突出(overhang)siRNAs丰度最高[20−22],与此相似,本研究的蝴蝶兰-病毒系统中,21 nt的vsiRNAs中,5′或3′端具有2个碱基的突出(overhang)vsiRNAs丰度也最高,该结果暗示CymMV和ORSV来源的21 nt的vsiRNAs中具有2个碱基overhang的vsiRNAs可能是RNAi免疫反应最有效的激发者。
研究表明siRNAs 5′端的碱基在介导siRNAs与Argonaute蛋白的结合密切相关[23]。比如,在拟南芥模式植物中,5′端为碱基A的siRNAs 更易与Argonaute2和Argonaute4结合,5′端为碱基U的siRNAs 更易与Argonaute1结合,5′端为碱基C的siRNAs 更易与Argonaute5结合,5′端为碱基G的siRNAs 更易与其他Argonaute结合。本研究中vsiRNAs 5′端碱基偏好性分析表明,CymMV和ORSV来源的vsiRNAs中,5’端碱基偏好性都是依次偏好于U、A、C和G;另外21 nt vsiRNAs 5′端碱基偏好性同样是依次偏好于U、A、C和G,该碱基偏好性结果与其他病原系统的vsiRNAs碱基偏好性一致[24−25];该结果表明CymMV和ORSV来源的vsiRNAs可能结合各自不同的Argonaute蛋白,进而介导RNAi免疫效应,但是由于目前蝴蝶兰基因组无法获得,也就无法获得蝴蝶兰相关的Argonaute蛋白信息,因此后续获得蝴蝶兰基因组中编码Argonaute的基因序列是一项非常重要的工作。
在不同病毒激活寄主RNAi免疫途径中,vsiRNAs产生的前体各不相同[15]。vsiRNAs的形成前体主要通过分析其在病毒基因组正负义链分布、核苷酸产生的位点以及频率分布来推测。在本研究发现,CymMV和ORSV复合侵染的蝴蝶兰细胞中,CymMV和ORSV来源的vsiRNAs主要来自于病毒基因组的正义链,该结果与其他一些正单链RNA病毒在寄主细胞中形成的vsRNAs的正负义偏好性相反,这些病原系统中vsiRNAs大约等比例来源于病毒基因组正负义链,因此他们推测病毒基因组复制过程中形成的双链为vsiRNAs的形成前体[26−29]。进一步将 vsiRNAs定位到CymMV和ORSV病毒基因组具体位点后,高低频切割位点分析表明,vsiRNAs沿着CymMV和ORSV病毒基因组呈现持续但不均匀的分布特征;大部分(95%)total vsiRNAs产生位点位于CymMV和ORSV病毒基因组内部,而不是基因组的5′和3′两端;在病毒基因组不同位点形成了高频切割点和低频切割点。随后用RNAfold server在线平台预测CymMV和ORSV病毒基因二级结构,结构预测结果表明在CymMV和ORSV病毒基因内部形成了大量的茎环二级结构,且茎环二级结构的形成与高频切割位点相对应,因此推测CymMV和ORSV病毒基因组正义链通过碱基匹配自身折叠产生的 pre-miRNA(Precursor miRNA)的茎环结构区域为DCL蛋白的切割底物,即vsiRNAs产生的前体,该预测结果与Flynt和Molnár 等 [30−31] 的研究结果一致。
4. 结论
本研究首先通过电镜和PCR技术鉴定了CymMV和ORSV两种病毒在蝴蝶兰植株中的复合侵染;然后通过深度测序技术鉴定分析了来源于CymMV和ORSV两种病毒基因组的vsiRNAs的丰度、长度、悬挂、碱基偏好性、正负义链分布、Hotspot和Coldspot等特征,从而加深了蝴蝶兰抗病毒RNAi免疫途径防御CymMV和ORSV两种病毒的机制的理解,对研究蝴蝶兰病毒性病害的防治措施具有重要的理论意义。
-
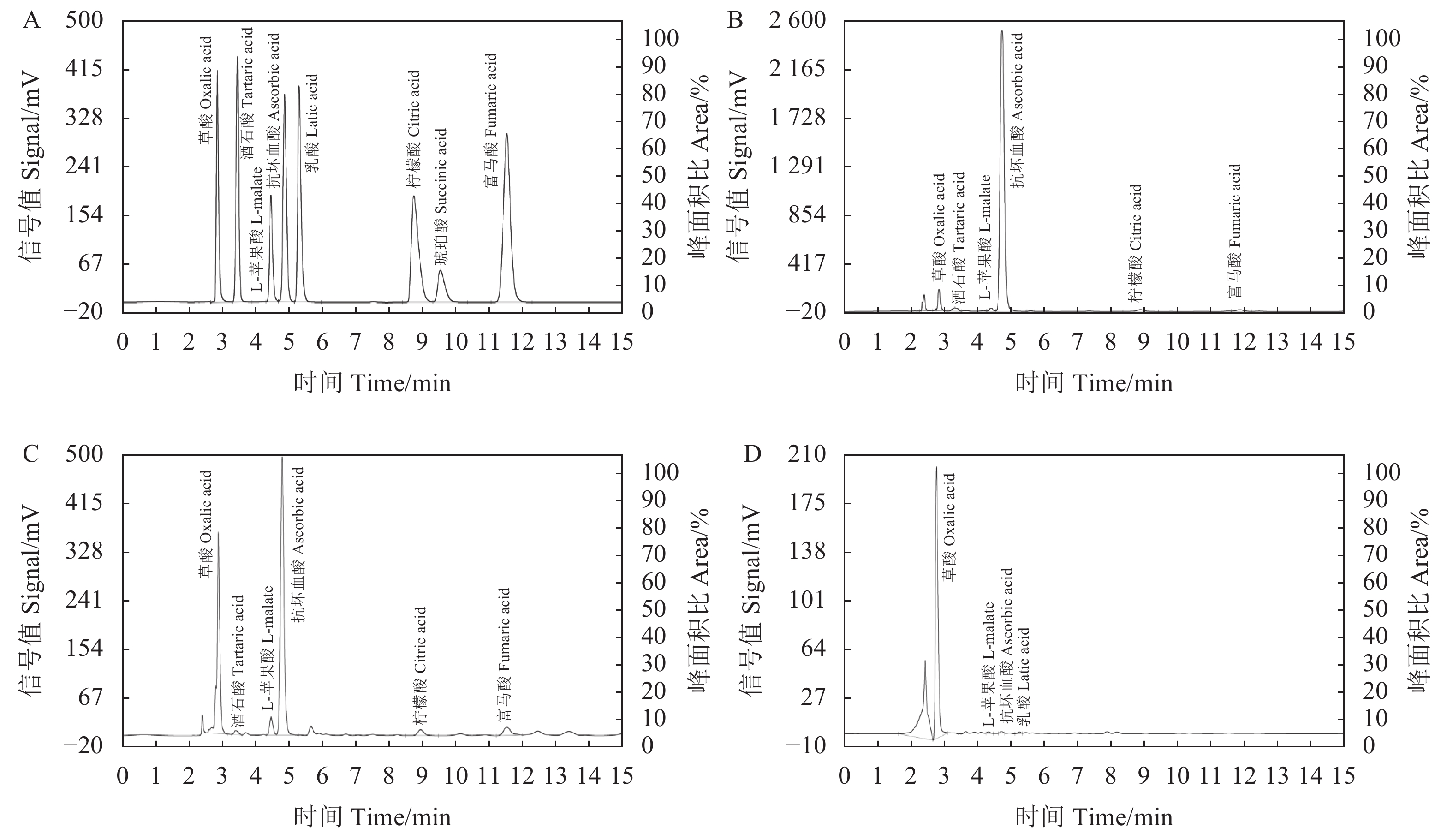
表 1 各有机酸的线性范围、回归方程及相关系数
Table 1 Linear ranges, regression equations, and correlation coefficients on 6 organic acids
有机酸
Organic acids线性范围
Linear range/
(mg·L−1)线性回归方程
Regression
equation相关系数
R2
Correlation草酸 Oxalic acid 19.76~197.60 y=1963.12x+15.23 0.99994 酒石酸 Tartaric acid 99.80~998.00 y=2505.44x−5.58 0.99995 L-苹果酸 L-malate 99.80~998.00 y=1195.33x−3.26 0.99994 抗坏血酸 Ascorbic acid 19.96~199.60 y=2612.34x−8.32 0.99991 乳酸 Latic acid 2.00~19.96 y=2810.59x−3.90 0.99995 柠檬酸 Citric acid 199.60~1996.00 y=2892.76x−2.65 0.99996 琥珀酸 Succinic acid 99.80~998.00 y=855.67x−2.66 0.99994 富马酸 Fumaric acid 2.00~19.96 y=4446.75x−4.36 0.99996 表 2 铝胁迫下杉木针叶中有机酸含量的变化
Table 2 Changes on organic acids in needles of Chinese fir under Al-stress
(单位:g·kg−1) 有机酸
Organic acidCK 1 mmol·L−1 铝胁迫
1 mmol·L−1 Al concentration3 mmol·L−1 铝胁迫
3 mmol·L−1 Al concentration5 mmol·L−1 铝胁迫
5 mmol·L−1 Al concentration草酸 Oxalic acid 0.71±0.03 a 0.89±0.13 a 0.75±0.08 a 0.90±0.17 a 酒石酸 Tartaric acid 1.17±0.12 a 1.27±0.14 a 1.15±0.09 a 1.04±0.08 a L-苹果酸 L-malate 1.21±0.09 c 1.77±0.14 a 1.46±0.07 b 1.23±0.10 c 抗坏血酸 Ascorbic acid 16.23±0.69 ab 17.44±0.90 a 16.35±0.32 ab 15.37±0.69 b 柠檬酸 Citric acid 0.89±0.05 a 1.32±0.39 a 0.79±0.27 a 0.85±0.33 a 富马酸 Fumaric acid 5.84±0.32 c 9.90±1.11 a 10.51±0.76 a 7.59±0.30 b 注:同行数据后同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。
Note: Different lowercase letters in the same line mean significant differences (P<0.05). The same below.表 3 铝胁迫下杉木根中有机酸含量的变化
Table 3 Changes on organic acids in roots of Chinese fir under Al-stress
(单位:g·kg−1) 有机酸
Organic acidCK 1 mmol·L−1 铝胁迫
1 mmol·L−1 Al concentration3 mmol·L−1 铝胁迫
3 mmol·L−1 Al concentration5 mmol·L−1 铝胁迫
5 mmol·L−1 Al concentration草酸 Oxalic acid 1.88±0.21 a 1.11±0.44 b 0.89±0.13 b 0.61±0.11 b 酒石酸 Tartaric acid 0.29±0.02 a 0.16±0.01 b 0.14±0.01b 0.13±0.03 b L-苹果酸 L-malate 1.82±0.01 a 1.19±0.13 b 0.91±0.41 bc 0.64±0.07 c 抗坏血酸 Ascorbic acid 3.49±0.75 a 1.91±0.19 b 1.57±0.17 b 1.49±0.25 b 柠檬酸 Citric acid 0.82±0.18 a 0.30±0.13 b 0.22±0.01 b 0.12±0.03 b 富马酸 Fumaric acid 9.51±2.36 a 0.88±0.05 b 0.57±0.02 b 0.50±0.02 b 表 4 铝胁迫对杉木根尖有机酸分泌的影响
Table 4 Effects of Al-stress on organic acids secreted from root-tips of Chinese fir
(单位:mg·L−1) 有机酸
Organic acidCK 1 mmol·L−1 铝胁迫
1 mmol·L−1 Al concentration3 mmol·L−1 铝胁迫
3 mmol·L−1 Al concentration5 mmol·L−1 铝胁迫
5 mmol·L−1 Al concentration草酸 Oxalic acid 126.57±18.69 a 67.79±18.43 b 85.85±23.15 b 71.81±4.01 b L-苹果酸 L-malate 7.42±3.21 a 4.62±1.41 ab 3.54±0.26 b 5.67±0.60 ab 抗坏血酸 Ascorbic acid 0.52±0.05 b 1.22±0.48 a 0.65±0.22 ab 0.85±0.18 ab 乳酸 Latic acid 0.05±0.02 a 0.03±0.02 a 0.03±0.01 a 0.05±0.02 a 表 5 杉木中有机酸、铝含量相关分析结果
Table 5 Correlations between organic acids and Al content in Chinese fir
有机酸
Organic acid针叶铝
Needle Al根铝
Root Al针叶/根有机酸
Needle organic acid/
root organic acid草酸 Oxalic acid 0.528 −0.666* −0.304 酒石酸 Tartaric acid −0.019 −0.927** 0.021 L-苹果酸 L-malate 0.491 −0.653* −0.145 抗坏血酸 Ascorbic acid 0.091 −0.917** −0.175 柠檬酸 Citric acid 0.238 −0.893** −0.104 富马酸 Fumaric acid 0.818** −0.995** −0.799** 注:*表示显著相关(P<0.05),**表示极显著相关(P<0.01)。
Note: * represented significant correlation(P<0.05),** represented extremely significant correlation (P<0.01). -
[1] 夏丽丹, 于姣妲, 邓玲玲, 等. 杉木人工林地力衰退研究进展 [J]. 世界林业研究, 2018, 31(2):37−42. XIA L D, YU J D, DENG L L, et al. Researches on soil decline of Chinese fir plantation [J]. World Forestry Research, 2018, 31(2): 37−42.(in Chinese)
[2] 任继鹏, 张逸, 钱诚, 等. 南方酸性森林土壤中铝的形态分布与活化机理 [J]. 环境化学, 2011, 30(6):1131−1135. REN J P, ZHANG Y, QIAN C, et al. Fraction distribution and release mechanism of aluminum in acidic forest soils of southern China [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2011, 30(6): 1131−1135.(in Chinese)
[3] SIECIŃSKA J, NOSALEWICZ A. Aluminium toxicity to plants as influenced by the properties of the root growth environment affected by other co-stressors: A Review [J]. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2017, 243: 1−26. DOI: 10.1007/398_2016_15
[4] RIAZ M, YAN L, WU X W, et al. Boron increases root elongation by reducing aluminum induced disorganized distribution of HG epitopes and alterations in subcellular cell wall structure of trifoliate orange roots [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 165: 202−210. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.09.004
[5] 滕建晒, 陈健, 彭亮, 等. 水杨酸调控内源H2S缓解黑大豆铝胁迫的作用机理研究 [J]. 西北植物学报, 2019, 39(1):121−130. TENG J S, CHEN J, PENG L, et al. Mechanism of salicylic acid regulating endogenous H2S alleviating aluminum stress in the root of black soybean [J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2019, 39(1): 121−130.(in Chinese)
[6] 闫磊. 硼对柑橘枳砧根系铝毒缓解效应及机理研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2020. YAN L. Ameliorative role and mechanism of boron on aluminum toxicity in trifoliate orange roots[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2020. (in Chinese).
[7] 梅映学. 碱蓬内生菌高Y1-1对镉和/或铝胁迫下水稻幼苗内源激素及有机酸含量的影响[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳师范大学, 2017. MEI Y X. Effect of endophyte Gao Y1-1 infection on endogenous hormones and organic acids of rice seedlings under Cd and/or Al stress[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Normal University, 2017. (in Chinese).
[8] YANG J L, FAN W, ZHENG S J. Mechanisms and regulation of aluminum-induced secretion of organic acid anions from plant roots [J]. Journal of Zhejiang University-Science B, 2019, 20(6): 513−527. DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B1900188
[9] MA J F, RYAN P R, DELHAIZE E. Aluminium tolerance in plants and the complexing role of organic acids [J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2001, 6(6): 273−278. DOI: 10.1016/S1360-1385(01)01961-6
[10] RANGEL A F, RAO I M, BRAUN H P, et al. Aluminum resistance in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) involves induction and maintenance of citrate exudation from root apices [J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2010, 138(2): 176−190. DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2009.01303.x
[11] 庞叔薇, 康德梦, 王玉保, 等. 化学浸提法研究土壤中活性铝的溶出及形态分布 [J]. 环境化学, 1986, 5(3):68−76. PANG S W, KANG D M, WANG Y B, et al. Studies on the leaching of active aluminum from soil and the distribution of aluminum species by chemical extraction [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 1986, 5(3): 68−76.(in Chinese)
[12] 孙宝利, 赤杰, 范中南, 等. 土壤及植物复合体系中有机酸的测定 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2010, 33(9):130−134. SUN B L, CHI J, FAN Z N, et al. Determination of organic acids from integrated system of soil and plant [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 33(9): 130−134.(in Chinese)
[13] 戴勤. 铝诱导不同耐铝型速生桉无性系有机酸分泌及其代谢调控[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2014. DAI Q. The correspond regulation on Al-induced exudation and metabolism of organic acids of Al-resistance of Fast-growing in different Aluminum-resistant types of Eucalyptus Clones[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2014. (in Chinese).
[14] 刘玉民. 酸铝环境马尾松根系分泌物特性及其缓解铝毒的根际效应[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2018. LIU Y M. The characteristics and rhizosphere effects in alleviating Al-toxicity of Pinus massoniana root exudation in acid-aluminum environment[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2018. (in Chinese).
[15] 汪建飞, 沈其荣. 有机酸代谢在植物适应养分和铝毒胁迫中的作用 [J]. 应用生态学报, 2006, 17(11):2210−2216. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2006.11.041 WANG J F, SHEN Q R. Roles of organic acid metabolism in plant adaptation to nutrient deficiency and aluminum toxicity stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2006, 17(11): 2210−2216.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2006.11.041
[16] 宋松泉. 植物线粒体的物质运输 [J]. 长沙水电师院(自然科学学报), 1988, 3(4):95−102. SONG S Q. Material transport in plant mitochondria [J]. Journal of Changsha Normal University of Water Resources and Electric Power(Natural Science Edition), 1988, 3(4): 95−102.(in Chinese)
[17] 娄成后, 张蜀秋. 高等植物生长发育中同化物的转移 [J]. 科学通报, 2011, 56(30):2446−2460. DOI: 10.1360/csb2011-56-30-2446 LOU C H, ZHANG S Q. Transfer of assimilates during growth and development of higher plants [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(30): 2446−2460.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.1360/csb2011-56-30-2446
[18] MA J F. Role of organic acids in detoxification of aluminum in higher plants [J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2000, 41(4): 383−390. DOI: 10.1093/pcp/41.4.383
[19] 马士成. 铝对茶树氟吸收、累积、分布特性的影响及其机理研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2012. MA S C. Effects of aluminum on uptake, distribution and accumulation of fluorine in tea plants and its mechanism[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2012. (in Chinese).
[20] 钱莲文, 李清彪, 孙境蔚, 等. 铝胁迫下常绿杨根系有机酸和氨基酸的分泌 [J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 57(2):221−227. QIAN L W, LI Q B, SUN J W, et al. Root secretion of organic acids and amino acids of evergreen poplar under aluminum stress [J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 57(2): 221−227.(in Chinese)
[21] 李东芹. 铝通过有机酸途径缓解氟对茶树的影响[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2017. LI D Q. Research on aluminum relieves the effect of fluorine by organic acid in tea plant[Camellia sinensis(L.) kuntze][D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese).
[22] 田聪, 张烁, 粟畅, 等. 铝胁迫下大豆根系有机酸积累的特性 [J]. 大豆科学, 2017, 36(2):256−261. TIAN C, ZHANG S, SU C, et al. Effects of aluminum (Al) on organic acid accumulation in soybean roots [J]. Soybean Science, 2017, 36(2): 256−261.(in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载: