Bioinformatics on Structure and Functions of ZmCOL3-encoded Protein
-
摘要:目的 分析ZmCOL3基因编码蛋白的结构及功能,预测ZmCOL3基因可能具备的功能,为该基因在玉米开花调控及其他功能的研究提供思路。方法 通过生物信息学的方法对ZmCOL3基因编码蛋白质的理化性质、保守结构域、二级结构、三级结构、信号肽、跨膜结构域、亚细胞定位及启动子顺式作用元件进行了预测,并对该基因在玉米不同组织的表达量进行了分析。结果 ZmCOL3基因所编码的蛋白包含335个氨基酸,相对分子质量为35.39 kD,理论等电点为5.04,属于酸性蛋白,具有亲水性和不稳定性,含有1个CCT结构域和1个B-box结构域,没有信号肽和跨膜结构域,主要定位在细胞核中,其二级结构主要是由无规则卷曲组成,其次是α螺旋,还含有少量的延伸链和β转角,同源建模相似度为64.15%,该基因的启动子不仅含有TATA-box、CAAT-box启动子基本的顺式作用元件,还含有Sp1等光响应作用元件,以及脱落酸、茉莉酸甲酯等激素响应元件。在玉米的种子、初生根、节间、叶、雌穗和雄穗等6个部位中,叶片中ZmCOL3基因的表达量最高,其次是雄穗,在种子中该基因表达量最低,总体上看ZmCOL3基因在叶片中的表达量显著高于其他部位。结论 ZmCOL3蛋白是一个亲水、不稳定的酸性蛋白,其含有CCT结构域和B-box结构域,符合CCT基因家族中COL亚家族的结构特征,属于该家族成员,可能参与生物钟的调控来影响玉米开花。启动子顺式作用元件分析发现ZmCOL3基因的启动子包含光响应及各种激素响应元件,推断该基因可能受到光周期调控和激素等非生物胁迫调控,暗示其可在多重反应调控网络中发挥作用。Abstract:Objective Functions of ZmCOL3 involving the flowering regulation and other mechanisms in maize were investigated by analyzing the structure and functions of the protein encoded by the gene.Method Based on bioinformatics, the physicochemical properties, conserved domain, secondary and tertiary structures, signal peptide, transmembrane domain, subcellular localization, and cis acting elements of ZmCOL3 protein were predicted. Expression of the gene in various organs of a maize plant were analyzed.Result The ZmCOL3-encoded protein contained 335 amino acids with a molecular weight of 35.39 KD and a theoretical isoelectric point of 5.04. It was an unstable acidic, hydrophilic protein located primarily in the nucleus and consisted of a CCT domain and a B-box domain but no signal peptide or transmembrane domain. Its secondary structure was mostly irregular coils with some α helixes and a small number of extended chains and β turns. The homology modeling similarity was 64.15%. The promoter of ZmCOL3 gene not only contained the basic cis acting elements, such as TATA and CAAT boxes, but also light response elements, such as SP1, as well as hormone response elements, such as abscisic acid and methyl jasmonate. In various tissues, the leaves, followed by the male ears, had the highest and significantly higher expression of ZmCOL3 than the primary roots, internodes, or tassels, while and the seeds the lowest.Conclusion The unstable acidic, hydrophilic ZmCOL3 protein contained CCT and B-box domains consistent with the structural characteristics of COL subfamily in the CCT gene family of which it belonged. It was postulated to participate in the regulation of biological clock that affects maize florescence. The promoter of ZmCOL3 gene contained the elements responding to light and various hormones that suggested a possible involvement on the multiple response network regulating the photoperiod and abiotic stress of a maize plant.
-
Keywords:
- Maize /
- ZmCOL3 /
- flowering /
- CCT gene family /
- bioinformatics analysis
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】开花时间是作物重要的农艺性状之一[1],对植物开花时间的调控是植物繁殖的核心问题[2]。在特定的时间开花是植物由营养生长转变为生殖生长的关键步骤,是植物生殖产生后代的重要节点[3]。玉米(Zea mays L.)起源于拉丁美洲,是世界主要粮食作物之一,在农业生产中有极其重要的地位[4]。玉米是短日照作物[5],一些热带、亚热带玉米品种(系)在非短日照条件下种植时常常出现花期不遇甚至无法进入生殖生长等现象,严重限制了玉米育种的进展[6-11]。因此了解玉米的开花调控机理对于玉米的研究和改良具有十分重要的意义。植物由营养生长到生殖生长的转变,与开花基因的表达息息相关[12]。要清晰玉米开花的分子机理,首先要研究开花调控基因的作用机制。本研究以与开花相关的ZmCOL3基因为分析对象,用生物信息学的方法分析其所编码蛋白的结构,预测该基因在玉米开花及其可能参与的调控网络,对ZmCOL3基因的潜在功能及其在玉米开花调控中作用机制的进一步研究具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】在众多已报道的开花调控基因中,有一类基因具有多效性,不仅能直接调控植物早花或晚花,还具有调控产量及抗逆等生物学功能[13]。由于这类基因都含有CCT结构域,故被称为CCT 结构域基因[14]。目前已有诸多研究证实CCT基因家族影响植物开花,拟南芥中的开花关键基因CO、TOC1等均属于CCT基因家族。CCT基因家族的成员较多,目前已知玉米中含有80多个CCT基因家族成员[13],功能也都不尽相同。根据所含结构域的不同CCT家族可以分为CMF、COL、PRR和TIFY四个亚家族[4],其中COL亚家族成员的结构特征为含有1个CCT结构域和1-2个B-box锌指结构域[15,16]。COL蛋白是一类植物特异的转录因子,通常情况下,植物感受光周期诱导的昼夜节律变化与开花调控都需要COL蛋白的参与[17,18]。不同COL基因的CCT结构域序列较为保守,B-box结构域的差异比较明显,CCT结构域约由43个保守的氨基酸组成,一般位于蛋白质的C端,是DNA结合域,具有核定位、核蛋白运输及调节基因转录的功能[19,20],B-box结构域在N端,是蛋白互作的区域,在COL蛋白与卷曲螺旋蛋白相互作用过程中发挥重要作用[21,22]。COL3是COL亚家族的一个重要成员,在拟南芥中AtCOL3是光形态发生的正向调节因子,在COP1酶的下游发挥作用[23]。水稻中的OsCO3基因含有1个B-box及1个CCT结构域,参与了水稻的光周期开花途径,是短日照条件下的开花抑制因子[24]。玉米中发现的ZmCOL3基因是水稻组成型开花抑制因子OsCOL4的同源基因,可以通过调控ZmCCT基因表达参与玉米光周期途径,进而调控玉米的开花期[15,25]。【本研究切入点】ZmCOL3基因的克隆虽然已经完成,但其作为转录因子应行使的多重功能还未被确定,在生物信息学方面仍有很多值得挖掘的地方,可为该基因的蛋白功能研究提供思路。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究用生物信息学方法对玉米ZmCOL3基因编码的蛋白质序列进行了深入分析,获得了其编码蛋白的理化性质、保守结构域、二级结构、信号肽、跨膜结构以及亚细胞定位的预测结果,通过同源建模的方法预测ZmCOL3基因编码蛋白的三级结构,对ZmCOL3基因的启动子区域所包含的顺式作用元件进行了分析,利用检索得到的表达数据进行该基因的组织表达分析。本研究预测ZmCOL3基因可能具备的功能,为该基因在玉米开花调控及其他潜在功能的研究奠定基础。
1. 材料和方法
在NCBI网站通过登录号NP_001147679查询并下载ZmCOL3基因的序列信息。使用ProtParam(http://web.expasy.org/protparam/)进行该基因编码蛋白序列的理化性质分析;使用NCBI的保守结构域数据库(CDD-search)(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/bwrpsb/bwrpsb.cgi)对ZmCOL3的蛋白序列进行保守结构域的查找;在NPS@:HNNsecondarystructureprediction(https://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=/NPSA/npsa_hnn.html)网站预测该基因编码蛋白质的二级结构;通过SSWISS MODEL(http://swissmodel.expasy.org/)中的同源建模预测ZmCOL3基因编码蛋白的三级结构;使用TMHMM(http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/)进行跨膜结构域预测;在SignalP(http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/)进行信号肽分析;利用Plant-mPLocserver(http://www.csbio.sjtu.edu.cn/cgi-bin/PlantmPLoc.cgi)进行亚细胞定位预测;使用PlantCARE(http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/)网站进行启动子的顺式作用元件分析;通过MaizeGDB数据库(https://www.maizegdb.org/)检索获得ZmCOL3基因在玉米的种子、初生根、节间、叶、雌穗、和雄穗中的表达数据,用Excel绘制基因在不同组织中的表达图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 ZmCOL3基因编码蛋白的理化性质分析
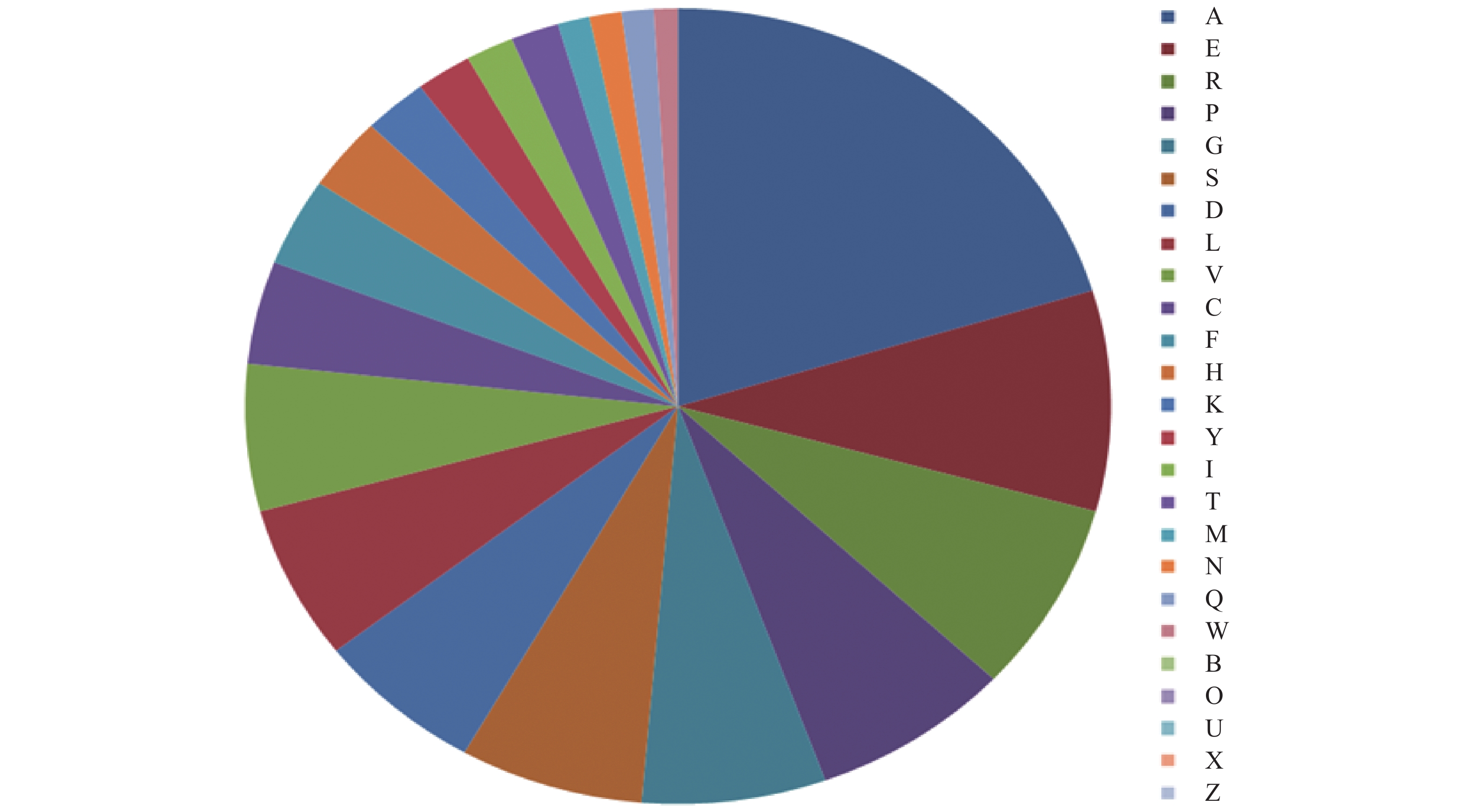
使用在线软件对ZmCOL3基因所编码蛋白序列进行分析,结果表明该基因所编码蛋白的分子式为C1530H2376N452O482S18,相对分子质量为35.39 kD,理论等电点为5.04,属于酸性蛋白;该基因共编码335个氨基酸,氨基酸组分如图1所示,含量最高的为A(丙氨酸),共68个,占总体的20.29%,在该蛋白中带负电荷的氨基酸(Asp+Glu)数量为51,带正电荷的氨基酸(Arg+Lys)数量为34,脂肪族氨基酸指数为69.04;平均亲水性系数为−0.241,属于亲水性蛋白,不稳定系数为53.72,该蛋白是不稳定蛋白。
![]() 图 1 玉米ZmCOL3基因的蛋白组分注:A:丙氨酸;E:谷氨酸;R:精氨酸;P:脯氨酸;G:甘氨酸;S:丝氨酸;D:天冬氨酸;L:亮氨酸;V:缬氨酸;C:半胱氨酸;F:苯丙氨酸;H:组氨酸;K:赖氨酸;Y:酪氨酸;I:异亮氨酸;T:苏氨酸;M:蛋氨酸;N:天冬酰胺;Q:谷氨酰胺;W:色氨酸;O:吡咯赖氨酸;U:硒半胱氨酸;B、X、Z:酸水解后不确定的氨基酸Figure 1. Composition of maize ZmCOL3Note: A: Alanine; E: Glutamic acid; R: Arginine; P: Proline; G: Glycine; S: Serine; D: Aspartic acid; L: Leucine; V: Valine; C: Cysteine; F: Phenylalanine; H: Histidine; K: Lysine; Y: Tyrosine; I: Isoleucine; T: Threonine; M: Methionine; N: Asparagine; Q: Glutamine; W: Tryptophan; O: Pyrrolysine; U: Selenocysteine; B, X, and Z: Uncertain amino acids after acid hydrolysis.
图 1 玉米ZmCOL3基因的蛋白组分注:A:丙氨酸;E:谷氨酸;R:精氨酸;P:脯氨酸;G:甘氨酸;S:丝氨酸;D:天冬氨酸;L:亮氨酸;V:缬氨酸;C:半胱氨酸;F:苯丙氨酸;H:组氨酸;K:赖氨酸;Y:酪氨酸;I:异亮氨酸;T:苏氨酸;M:蛋氨酸;N:天冬酰胺;Q:谷氨酰胺;W:色氨酸;O:吡咯赖氨酸;U:硒半胱氨酸;B、X、Z:酸水解后不确定的氨基酸Figure 1. Composition of maize ZmCOL3Note: A: Alanine; E: Glutamic acid; R: Arginine; P: Proline; G: Glycine; S: Serine; D: Aspartic acid; L: Leucine; V: Valine; C: Cysteine; F: Phenylalanine; H: Histidine; K: Lysine; Y: Tyrosine; I: Isoleucine; T: Threonine; M: Methionine; N: Asparagine; Q: Glutamine; W: Tryptophan; O: Pyrrolysine; U: Selenocysteine; B, X, and Z: Uncertain amino acids after acid hydrolysis.2.2 ZmCOL3基因编码蛋白的保守结构域分析
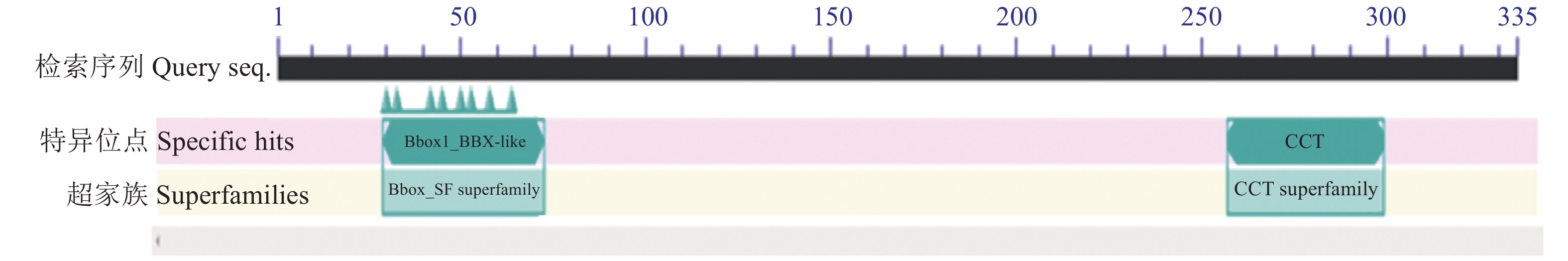
使用NCBI的保守结构域数据库(CDD-search)对ZmCOL3的氨基酸序列进行保守结构域的查找。如图2中的结果显示,ZmCOL3基因所编码蛋白含有1个CCT结构域和1个B-box锌指结构域,证明了其作为CCT基因家族中的COL亚族所含有的蛋白结构特征。
2.3 ZmCOL3基因编码蛋白的二级结构预测
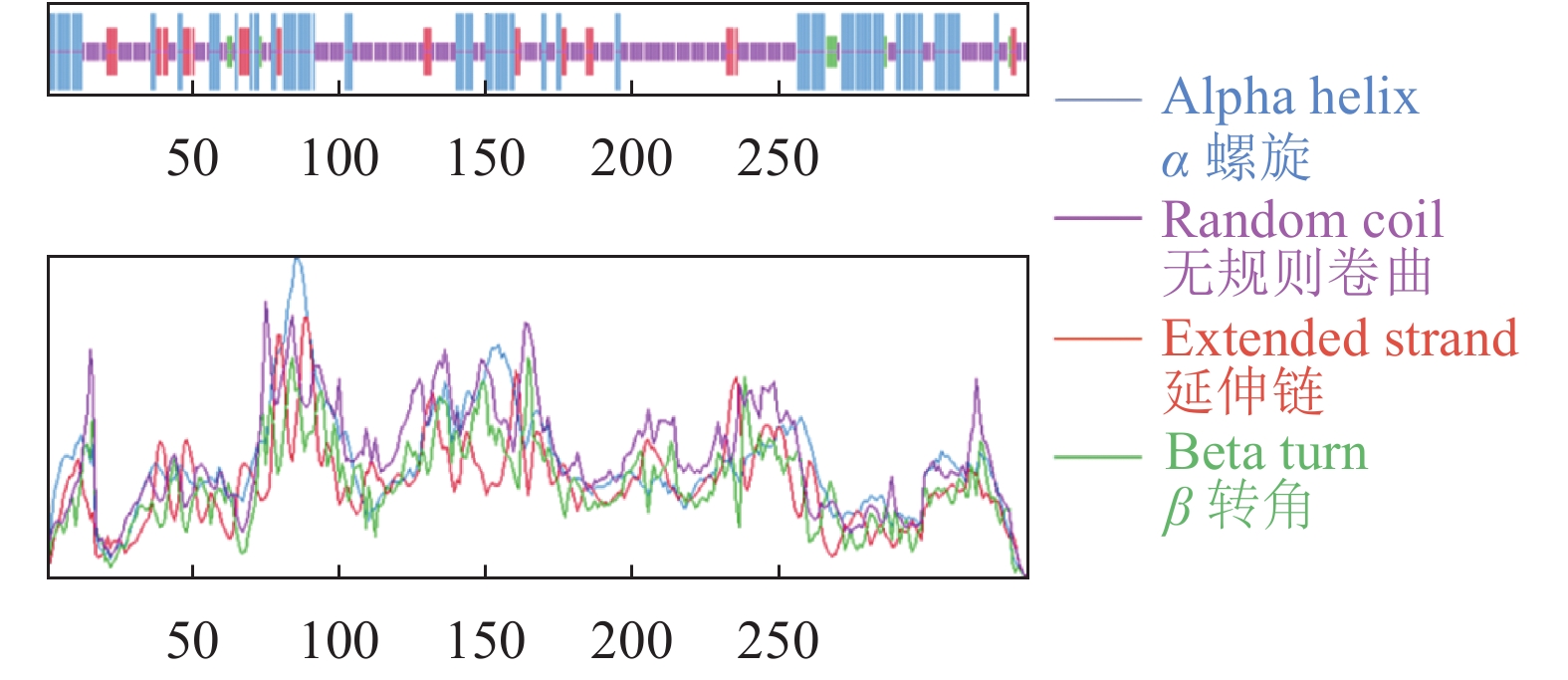
如图3所示ZmCOL3蛋白质的二级结构主要由α螺旋和无规则卷曲组成,含有少量的延伸链和β转角。其中占比最大的为无规则卷曲,有184个氨基酸,占54.93%;其次是α螺旋(108个氨基酸),占32.24%;占比最少的是β转角,仅有9个氨基酸,只在靠近N端和C端的位置有所分布,主要集中在60~70和235~240这2个区间内。
2.4 ZmCOL3
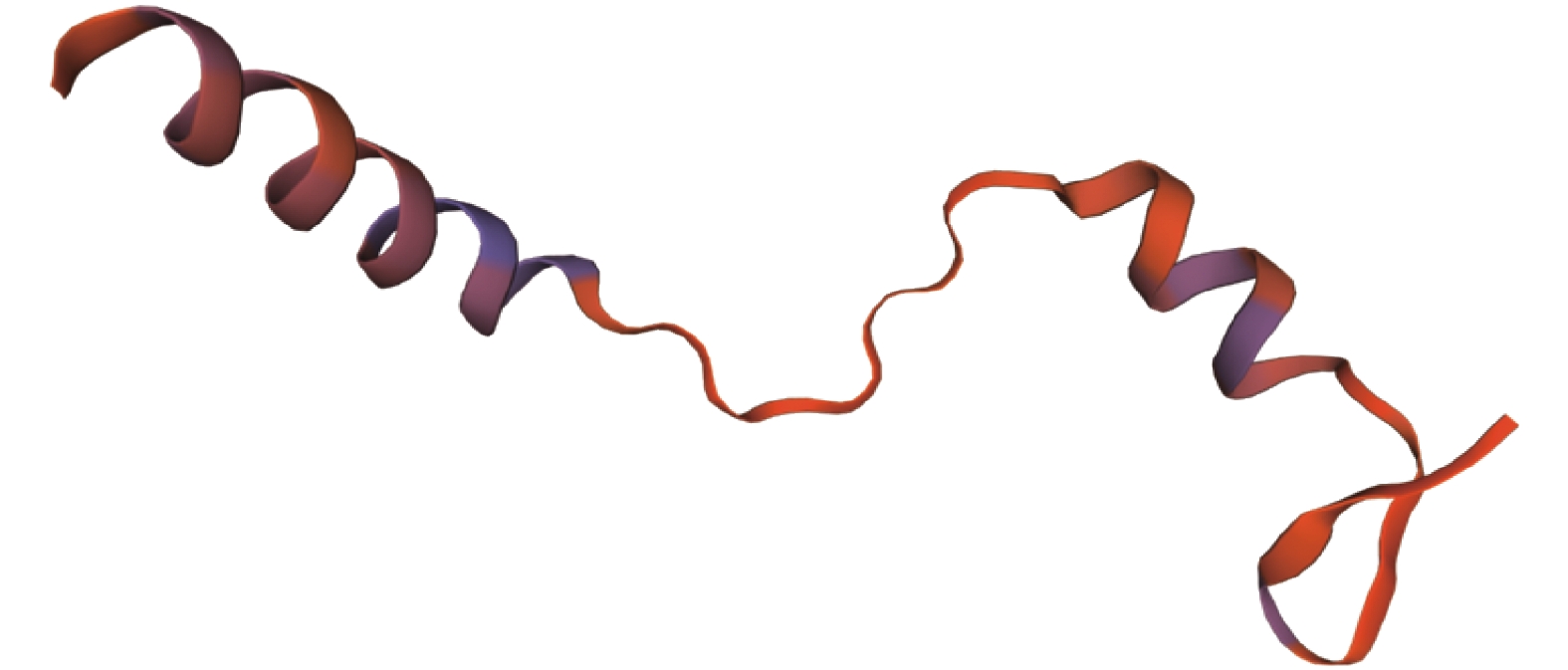
基因编码蛋白的三级结构预测 使用SWISS-MODEL同源建模的方法进行三级结构预测,结果如图4所示。QMEAN值为−0.33,相似度为64.15%,表明该模型与2020年报道的DNA结合CCT/NF-YB/YC复合物的晶体结构模型[26]相似性较高,并且与前文二级结构预测结果相符,以α螺旋和无规则卷曲为主体形成三级结构。
2.5 ZmCOL3
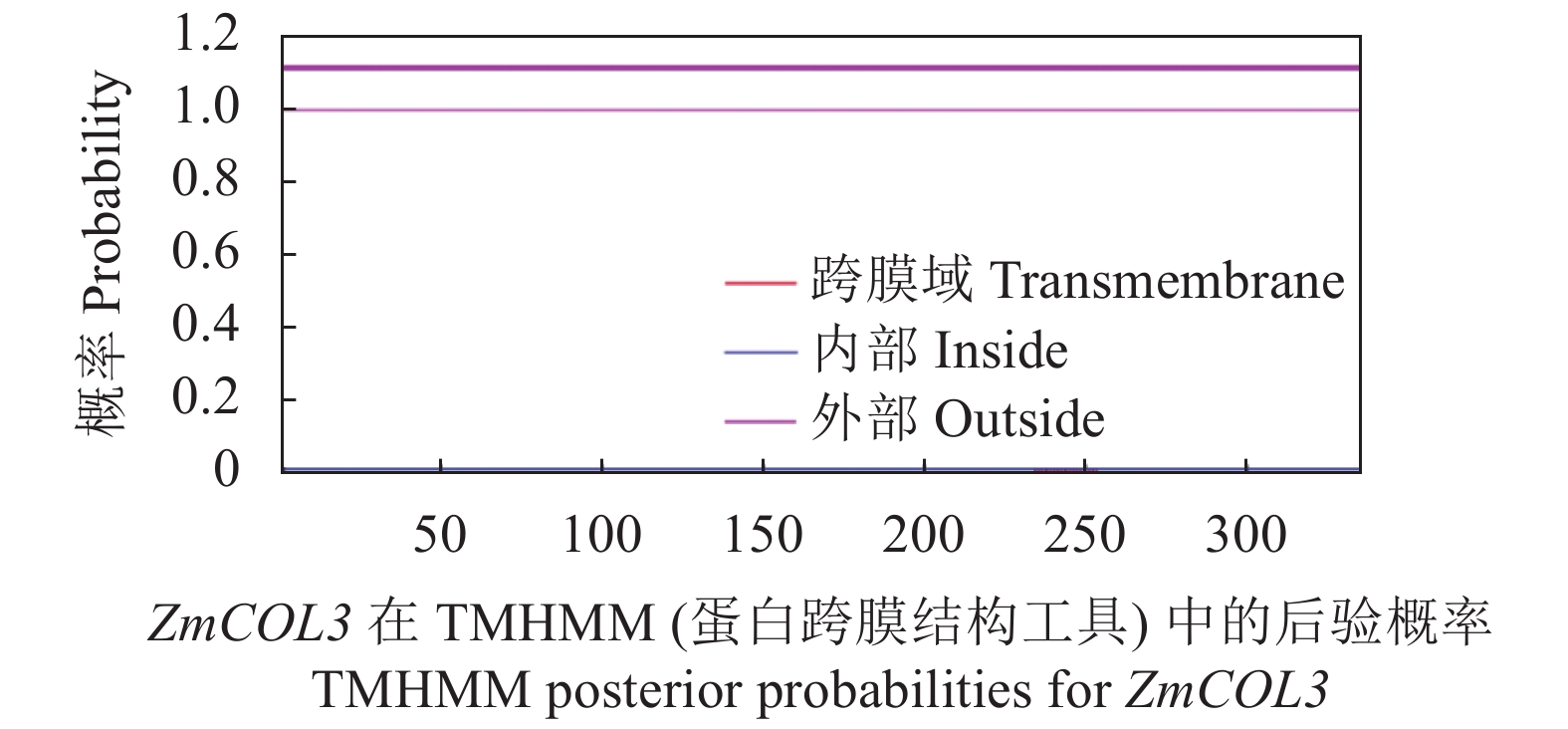
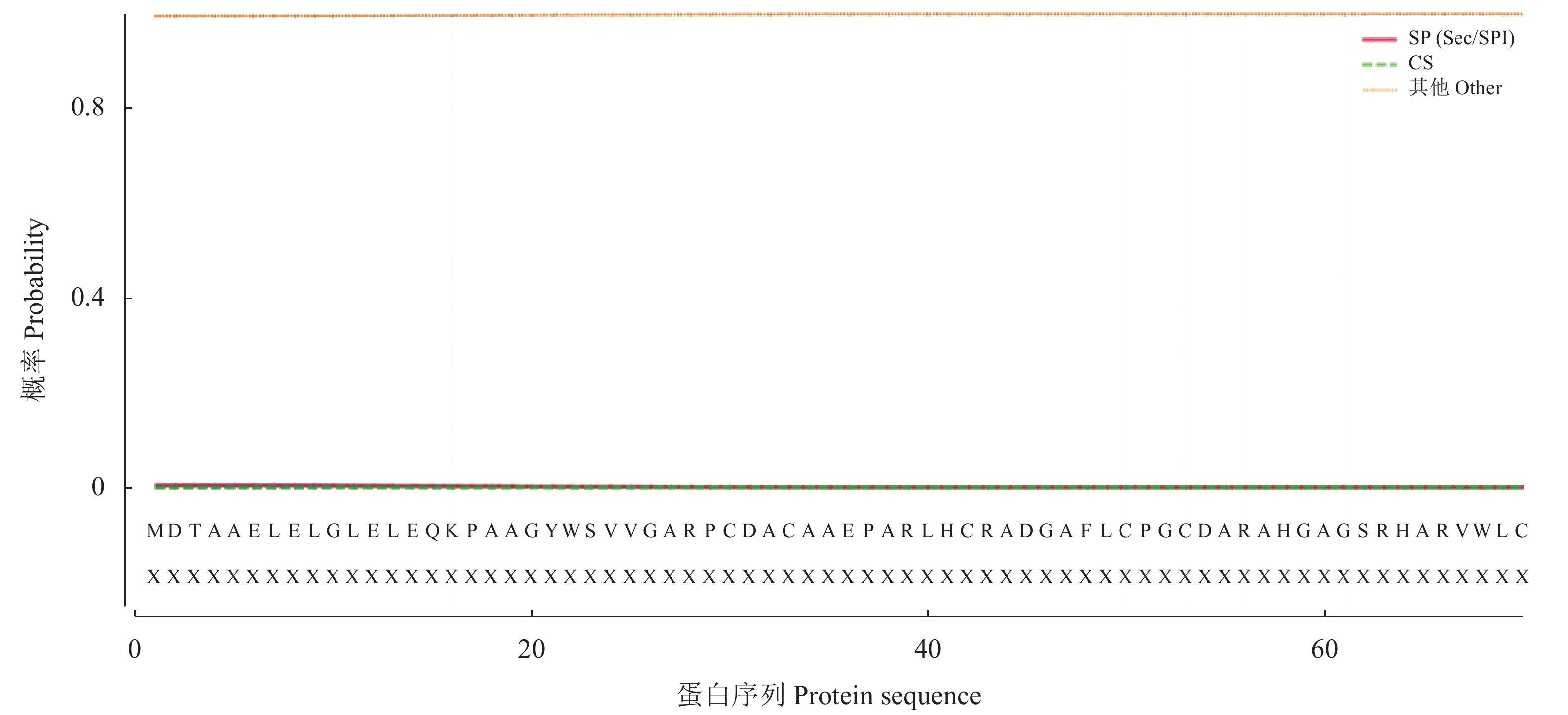
基因编码蛋白跨膜结构及信号肽分析 ZmCOL3基因编码蛋白跨膜结构预测结果如图5所示,该基因编码蛋白没有形成跨膜螺旋,即该蛋白不含有跨膜结构域,且主要分布于细胞膜外,表明该蛋白为非跨膜蛋白。如图6所示,玉米COL3基因编码蛋白前70个氨基酸中不存在典型的信号肽趋势,CS缺陷概率为0,SP(Sec/SPI)概率仅为0.004,相比之下,Other的概率为0.996,表明该基因所编码蛋白不含有信号肽。
2.6 ZmCOL3
基因编码蛋白的亚细胞定位分析 将获取的玉米ZmCOL3基因编码序列提交到Plant-mPLoc网站进行亚细胞定位预测,结果如图7所示,预测定位在细胞核内。而跨膜结构域预测该蛋白为膜外,推测该基因可能在合成后受到某些因子的作用,在细胞核内发挥作用。
2.7 ZmCOL3启动子顺式作用元件分析
从maize sequence网站获取ZmCOL3基因ATG上游2300 bp序列,提交到PlantCARE网站进行顺式作用元件分析,结果如表1所示。该基因启动子除了含有基本的顺式作用元件,如TATA-box、CAAT-box等,还含有脱落酸(ABA)响应元件、光响应元件、茉莉酸甲酯(MeJA)响应元件等,表明该基因可能在多重反应调控网络中发挥作用,受到光照和多种激素调控。
表 1 ZmCOL3启动子顺式作用元件分析Table 1. Analysis on cis acting elements of ZmCOL3 promoter元件名称
Element name位置
Site功能
FunctionAAGAA-motif −222 胁迫响应 stress response element A-box −718,−768,−789,+1230,+1251,−1773 顺式作用调控元件 cis-acting regulatory element ABRE +1223,+1702,−2059,+2060,+2158 脱落酸响应顺式作用元件
cis-acting element involved in the abscisic acid responsivenessACE +54 光响应顺式作用元件
cis-acting element involved in light responsivenessARE +686,+959 厌氧诱导必需的顺式作用元件
cis-acting regulatory element essential for the anaerobic inductionCAAT-box −6,−142,+283,+600,−946,+1018,−1031等 启动子和增强子区的共同顺式作用元件
common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regionsCAT-box −350 与分生组织表达相关的顺式作用元件
cis-acting regulatory element related to meristem expressionCGTCA-motif +860,+1215 茉莉酸甲酯响应的顺式作用元件
cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA-responsivenessDRE core −894 ABRE的耦合功能元件 funtions as a coupling element of ABRE ERE −1299 乙烯响应元件 ethylene-responsive element GATA-motif +1023 光响应元件的一部分 part of a light responsive element G-box −22,−316,−1701,−1222,−2059 光响应顺式作用元件
cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsivenessGC-motif −592 与缺氧特异性诱导相关的增强子类元件
enhancer-like element involved in anoxic specific inducibilityI-box +971 光响应元件的一部分 part of a light responsive element JERE +900 JA和诱导子响应 JA and elicitor responsive LTR −764 低温响应的顺式作用元件
cis-acting element involved in low-temperature responsivenessMYC −1279 茉莉酸甲酯响应的顺式作用元件
cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA-responsiveO2-site +546,−1824 玉米醇溶蛋白调控的顺式作用元件
cis-acting regulatory element involved in zein metabolismP-box −293 赤霉素响应元件 gibberellin-responsive element Sp1 +167,−583,−903,−2157 光响应元件 light responsive element STRE −235,−329,+865,−1080,+1242,−2053,−2076 热休克、渗透胁迫、低pH值、营养缺乏引起的活化
activation by heat shock, osmotic stress, low pH, nutrient starvationTATA-box −107,+110,−178,−181,+182,+802,+917等 转录起始点−30左右的核心启动子元件
core promoter element around −30 of transcription startTCA-element +195,−259 水杨酸响应的顺式作用元件
cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsivenessTC-rich repeats −1912 防御和应激响应的顺式作用元件
cis-acting element involved in defense and stress responsivenessTCT-motif +475 光响应元件的一部分 part of a light responsive element TGACG-motif −860,−1215 茉莉酸甲酯响应的顺式作用元件
cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA-responsivenessTGA-element −446 生长素响应元件 auxin-responsive element W box −772 植物特异性转录调节因子WRKY的结合位点
binding sites for the WRKY plant-specific transcriptional regulatorsWUN-motif +982 创伤响应元件 wound-responsive element 2.8 ZmCOL3
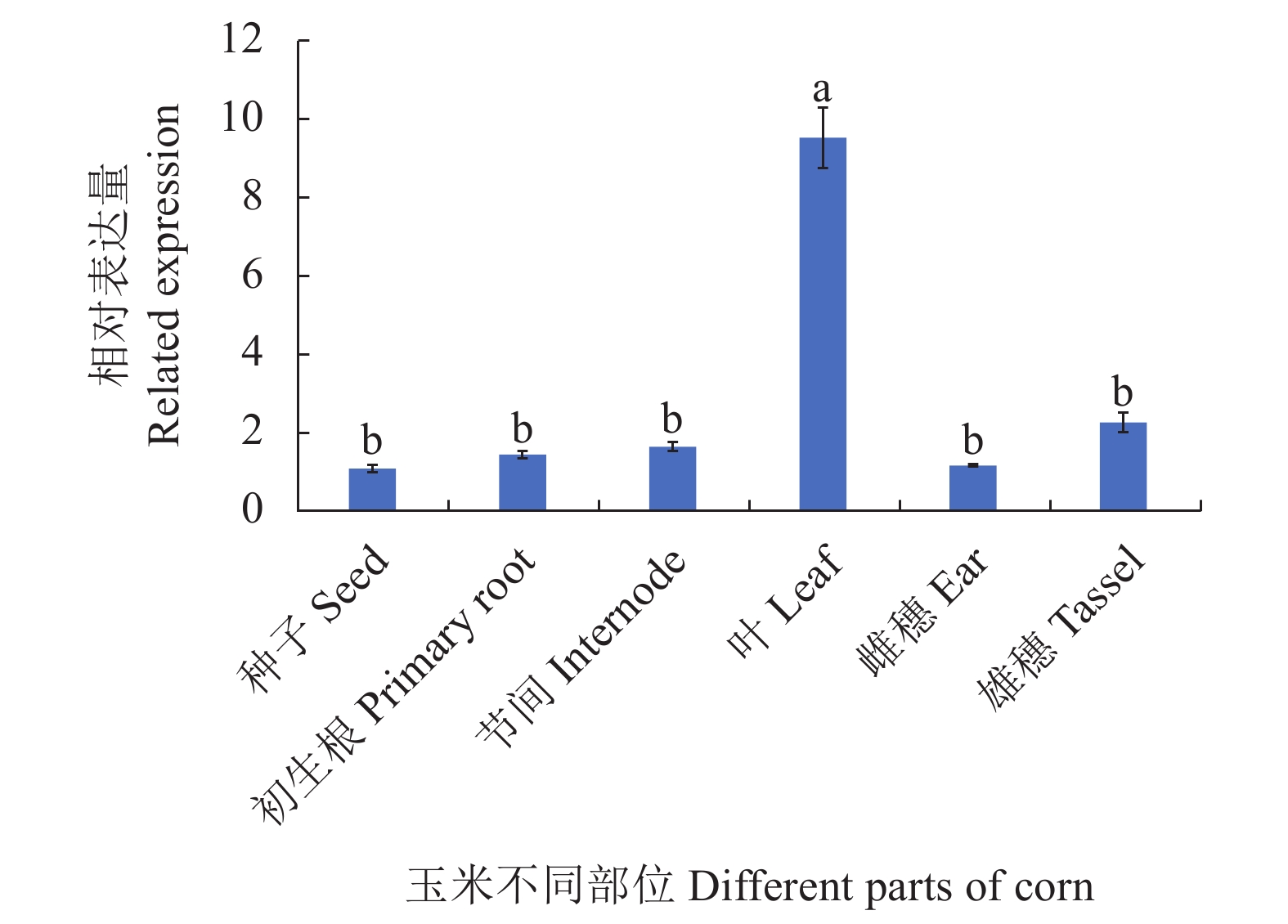
基因在玉米不同组织中的表达 下载获得了ZmCOL3基因在玉米的种子、初生根、节间、叶、雌穗和雄穗6个组织部位中的表达数据。分析结果如图8所示,ZmCOL3基因在玉米的叶片中表达量最高,雄穗中的表达量次之,在种子中该基因表达量最低,总体上看ZmCOL3基因在叶片中的表达量显著高于其他组织,其余5个不同组织中的表达量差异较小。
3. 讨论与结论
玉米起源于美洲大陆,在人类的长期驯化和自然选择下,现今广泛种植于世界各地,并集粮、饲、经三种用途于一体,具有很大的开发潜力[27]。但由于玉米的光周期敏感性导致热带、亚热带的玉米种质资源在长日照地区无法正常完成生命周期,限制了现代玉米育种的创新和进步。要改变这一现状,首先要清晰玉米的开花调控机制。有研究表明在玉米开花过程中,ZmCOL3的作用主要是通过反式激活调控玉米开花的关键基因之一ZmCCT的转录,或者通过干扰生物钟来抑制玉米开花[4],该基因是玉米开花调控网络中不可忽视的一环。本研究利用生物信息学方法对ZmCOL3基因所编码蛋白质的结构和功能进行预测和分析,能进一步挖掘和确认该基因的功能和特点,也为ZmCOL3基因功能的深入研究提供思路。
对ZmCOL3基因所编码的蛋白质序列进行分析发现ZmCOL3基因共编码335个氨基酸,理化性质分析结果显示ZmCOL3蛋白相对分子质量为35.39 kD,理论等电点为5.04,属于酸性蛋白,具有亲水性和不稳定性,没有信号肽和跨膜结构域。ZmCOL3蛋白包含2个保守结构域,分别是CCT结构域和B-box锌指结构域,证明ZmCOL3是CCT家族的成员,具备COL亚族的基本特征。CCT家族基因能影响植物开花,部分基因参与到生物钟的调控,ZmCOL3作为该家族成员之一,很可能具备玉米开花调控的相关功能,这与金敏亮[15]发现ZmCOL3是玉米开花抑制子的研究结果相吻合。亚细胞定位预测该蛋白在细胞核中,这可能是由于ZmCOL3蛋白所含有的CCT结构域具有核定位的功能[28]。该蛋白的二级结构主要由无规则卷曲组成,其次是α螺旋,还含有少量的延伸链和β转角。通过同源建模对其蛋白三级结构进行预测,QMEAN值为−0.33,同源性高达64.15%。对该基因的启动子顺式作用元件分析发现其含有光响应元件,这一特点与COL家族基因作为光周期途径主要调节因子的功能相符,同时含有脱落酸(ABA)响应元件、茉莉酸甲酯(MeJA)响应元件等多种激素响应元件,表明该基因可能受到多种激素调控,暗示其可在多重反应调控网络中发挥作用。ZmCOL3基因在玉米的不同组织中有明显的差异表达,在玉米的叶片中表达量最高,在种子中该基因表达量最低,该结果与果天宇等[25]对ZmCOL3启动子的组织特异性分析结果存在差异,推测为物种间启动子片段的置换所造成。
本文通过生物信息学方法对玉米ZmCOL3基因编码蛋白的性质、亚细胞定位、启动子顺式作用元件及在不同组织间的表达等方面进行分析,可以为后续研究该基因的功能及参与的调控通路提供参考。
-
图 1 玉米ZmCOL3基因的蛋白组分
注:A:丙氨酸;E:谷氨酸;R:精氨酸;P:脯氨酸;G:甘氨酸;S:丝氨酸;D:天冬氨酸;L:亮氨酸;V:缬氨酸;C:半胱氨酸;F:苯丙氨酸;H:组氨酸;K:赖氨酸;Y:酪氨酸;I:异亮氨酸;T:苏氨酸;M:蛋氨酸;N:天冬酰胺;Q:谷氨酰胺;W:色氨酸;O:吡咯赖氨酸;U:硒半胱氨酸;B、X、Z:酸水解后不确定的氨基酸
Figure 1. Composition of maize ZmCOL3
Note: A: Alanine; E: Glutamic acid; R: Arginine; P: Proline; G: Glycine; S: Serine; D: Aspartic acid; L: Leucine; V: Valine; C: Cysteine; F: Phenylalanine; H: Histidine; K: Lysine; Y: Tyrosine; I: Isoleucine; T: Threonine; M: Methionine; N: Asparagine; Q: Glutamine; W: Tryptophan; O: Pyrrolysine; U: Selenocysteine; B, X, and Z: Uncertain amino acids after acid hydrolysis.
表 1 ZmCOL3启动子顺式作用元件分析
Table 1 Analysis on cis acting elements of ZmCOL3 promoter
元件名称
Element name位置
Site功能
FunctionAAGAA-motif −222 胁迫响应 stress response element A-box −718,−768,−789,+1230,+1251,−1773 顺式作用调控元件 cis-acting regulatory element ABRE +1223,+1702,−2059,+2060,+2158 脱落酸响应顺式作用元件
cis-acting element involved in the abscisic acid responsivenessACE +54 光响应顺式作用元件
cis-acting element involved in light responsivenessARE +686,+959 厌氧诱导必需的顺式作用元件
cis-acting regulatory element essential for the anaerobic inductionCAAT-box −6,−142,+283,+600,−946,+1018,−1031等 启动子和增强子区的共同顺式作用元件
common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regionsCAT-box −350 与分生组织表达相关的顺式作用元件
cis-acting regulatory element related to meristem expressionCGTCA-motif +860,+1215 茉莉酸甲酯响应的顺式作用元件
cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA-responsivenessDRE core −894 ABRE的耦合功能元件 funtions as a coupling element of ABRE ERE −1299 乙烯响应元件 ethylene-responsive element GATA-motif +1023 光响应元件的一部分 part of a light responsive element G-box −22,−316,−1701,−1222,−2059 光响应顺式作用元件
cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsivenessGC-motif −592 与缺氧特异性诱导相关的增强子类元件
enhancer-like element involved in anoxic specific inducibilityI-box +971 光响应元件的一部分 part of a light responsive element JERE +900 JA和诱导子响应 JA and elicitor responsive LTR −764 低温响应的顺式作用元件
cis-acting element involved in low-temperature responsivenessMYC −1279 茉莉酸甲酯响应的顺式作用元件
cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA-responsiveO2-site +546,−1824 玉米醇溶蛋白调控的顺式作用元件
cis-acting regulatory element involved in zein metabolismP-box −293 赤霉素响应元件 gibberellin-responsive element Sp1 +167,−583,−903,−2157 光响应元件 light responsive element STRE −235,−329,+865,−1080,+1242,−2053,−2076 热休克、渗透胁迫、低pH值、营养缺乏引起的活化
activation by heat shock, osmotic stress, low pH, nutrient starvationTATA-box −107,+110,−178,−181,+182,+802,+917等 转录起始点−30左右的核心启动子元件
core promoter element around −30 of transcription startTCA-element +195,−259 水杨酸响应的顺式作用元件
cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsivenessTC-rich repeats −1912 防御和应激响应的顺式作用元件
cis-acting element involved in defense and stress responsivenessTCT-motif +475 光响应元件的一部分 part of a light responsive element TGACG-motif −860,−1215 茉莉酸甲酯响应的顺式作用元件
cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA-responsivenessTGA-element −446 生长素响应元件 auxin-responsive element W box −772 植物特异性转录调节因子WRKY的结合位点
binding sites for the WRKY plant-specific transcriptional regulatorsWUN-motif +982 创伤响应元件 wound-responsive element -
[1] 蔡云婷, 贾力, 拓昊苑. 玉米ZmTOC1a、ZmTOC1b基因的克隆、表达及亚细胞定位分析 [J]. 华北农学报, 2019, 34(4):24−31. DOI: 10.7668/hbnxb.201751601 CAI Y T, JIA L, TUO H Y. Cloning, expression and subcellular localization of ZmTOC1a andZmTOC1b genes in maize [J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2019, 34(4): 24−31.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7668/hbnxb.201751601
[2] POSTMA F M, LUNDEMO S, ÅGREN J. Seed dormancy cycling and mortality differ between two locally adapted populations of Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Annals of Botany, 2016, 117(2): 249−256.
[3] 许淑娟, 种康. “先驱”转录因子LEC1在早期胚胎重置春化状态的机制 [J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(1):1−4. DOI: 10.11983/CBB17234 XU S J, CHONG K. Mechanism of the “pioneer” transcription factor LEC1 in resetting vernalized state in early embryos [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(1): 1−4.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11983/CBB17234
[4] JIN M L, LIU X G, JIA W, et al. ZmCOL3, a CCT gene represses flowering in maize by interfering with the circadian clock and activating expression of ZmCCT [J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2018, 60(6): 465−480. DOI: 10.1111/jipb.12632
[5] 赵淑靓. 玉米伪应答调节基因ZmPRR73的克隆与表达分析[D]. 洛阳: 河南科技大学, 2018. ZHAO S L. Gene Cloning and Expression Analysis of Pseudo-Response Regulator 73 (ZmPRR73) in Maize[D]. Luoyang : Henan University of Science and Technology, 2018. (in Chinese).
[6] HUNG H Y, SHANNON L M, TIAN F, et al. ZmCCT and the genetic basis of day-length adaptation underlying the postdomestication spread of maize [J]. PNAS, 2012, 109(28): E1913−E1921. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1203189109
[7] HOLLAND J B. Plant genetics: Two steps on the path to maize adaptation [J]. Current Biology, 2018, 28(18): R1098−R1101. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.07.049
[8] GOODMAN M M, MORENO J, CASTILLO F, et al. Using tropical maize germplasm for temperate breeding [J]. Maydica, 2000, 45(3): 221−234.
[9] DAO A, SANOU J, MITCHELL S E, et al. Genetic diversity among INERA maize inbred lines with single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers and their relationship with CIMMYT, IITA, and temperate lines [J]. BMC Genetics, 2014, 15: 127.
[10] LIU T L, NEWTON L, LIU M J, et al. A G-box-like motif is necessary for transcriptional regulation by circadian pseudo-response regulators in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Physiology, 2015, 170(1): 528−539.
[11] BÖHM J, SCHIPPRACK W, UTZ H F, et al. Tapping the genetic diversity of landraces in allogamous crops with doubled haploid lines: A case study from European flint maize [J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2017, 130(5): 861−873. DOI: 10.1007/s00122-017-2856-x
[12] BLÜMEL M, DALLY N, JUNG C. Flowering time regulation in crops—what did we learn from Arabidopsis? [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2015, 32: 121−129. DOI: 10.1016/j.copbio.2014.11.023
[13] 贾伟, 尹悦佳, 柳青, 等. 抑制ZmCol3基因表达调控玉米开花期 [J]. 玉米科学, 2017, 25(6):28−33. JIA W, YIN Y J, LIU Q, et al. Regulation of maize flowering time by down-regulatedZmCol3 gene expression [J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2017, 25(6): 28−33.(in Chinese)
[14] MILLAR A J. The intracellular dynamics of circadian clocks reach for the light of ecology and evolution [J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2016, 67: 595−618. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-043014-115619
[15] 金敏亮. 玉米泛转录组的构建及玉米开花抑制因子ZmCOL3的功能解析[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2018. JIN M L. Maize Pan-transcriptome construction and functional analysis of maize flowering repressor ZmCOL3[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2018. (in Chinese).
[16] COCKRAM J, THIEL T, STEUERNAGEL B, et al. Genome dynamics explain the evolution of flowering time CCT domain gene families in the Poaceae [J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(9): e45307. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045307
[17] VALVERDE F. Constans and the evolutionary origin of photoperiodic timing of flowering [J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2011, 62(8): 2453−2463. DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erq449
[18] 胡冬秀, 刘浩, 鲁清, 等. 花生CONSTANS-like(COL)家族基因的克隆与表达分析 [J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2020, 42(5):778−786. HU D X, LIU H, LU Q, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of CONSTANS-Like(COL) family genes in peanut(Arachis hypogaea L.) [J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 2020, 42(5): 778−786.(in Chinese)
[19] CROCCO C D, BOTTO J F. BBX proteins in green plants: Insights into their evolution, structure, feature and functional diversification [J]. Gene, 2013, 531(1): 44−52. DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.08.037
[20] 付建新, 王翊, 戴思兰. 高等植物CO基因研究进展 [J]. 分子植物育种, 2010, 8(5):1008−1016. DOI: 10.3969/mpb.008.001008 FU J X, WANG Y, DAI S L. Advanced research on CO genes in higher plants [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2010, 8(5): 1008−1016.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/mpb.008.001008
[21] WU W X, ZHANG Y X, ZHANG M, et al. The rice CONSTANS-like protein OsCOL15 suppresses flowering by promoting Ghd7 and repressing RID1 [J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2018, 495(1): 1349−1355. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.11.095
[22] 张雅文, 梁山, 徐国云, 等. 烟草CONSTANS-like基因家族的鉴定与分析 [J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1):33−43. DOI: 10.11983/CBB20147 ZHANG Y W, LIANG S, XU G Y, et al. Genome-wide identification and analysis of CONSTANS-like gene family in Nicotiana tabacum [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(1): 33−43.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11983/CBB20147
[23] DATTA S, HETTIARACHCHI G H C M, DENG X W, et al. Arabidopsis CONSTANS-LIKE3 is a positive regulator of red light signaling and root growth [J]. The Plant Cell, 2006, 18(1): 70−84.
[24] KIM S K, YUN C H, LEE J H, et al. OsCO3, a CONSTANS-LIKE gene, controls flowering by negatively regulating the expression of FT-like genes under SD conditions in rice [J]. Planta, 2008, 228(2): 355−365. DOI: 10.1007/s00425-008-0742-0
[25] 果天宇, 尹悦佳, 贾伟, 等. 玉米ZmCOL3pro217启动子的克隆及功能分析 [J]. 玉米科学, 2020, 28(2):54−60. GUO T Y, YIN Y J, JIA W, et al. Cloning and functional analysis of ZmCOL3pro217 promoter in maize [J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2020, 28(2): 54−60.(in Chinese)
[26] SHEN C C, LIU H Y, GUAN Z Y, et al. Structural insight into DNA recognition by CCT/NF-YB/YC complexes in plant photoperiodic flowering [J]. The Plant Cell, 2020, 32(11): 3469−3484. DOI: 10.1105/tpc.20.00067
[27] WYLIE S J, ADAMS M, CHALAM C, et al. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Potyviridae [J]. Journal of General Virology, 2017, 98(3): 352−354. DOI: 10.1099/jgv.0.000740
[28] ROBSON F, COSTA M M, HEPWORTH S R, et al. Functional importance of conserved domains in the flowering-time gene CONSTANS demonstrated by analysis of mutant alleles and transgenic plants [J]. The Plant Journal, 2001, 28: 619−31.
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: