Effects of Seed-coating Bacillus subtilis Suspension on Growth and Physiology of Chili Pepper Seedlings
-
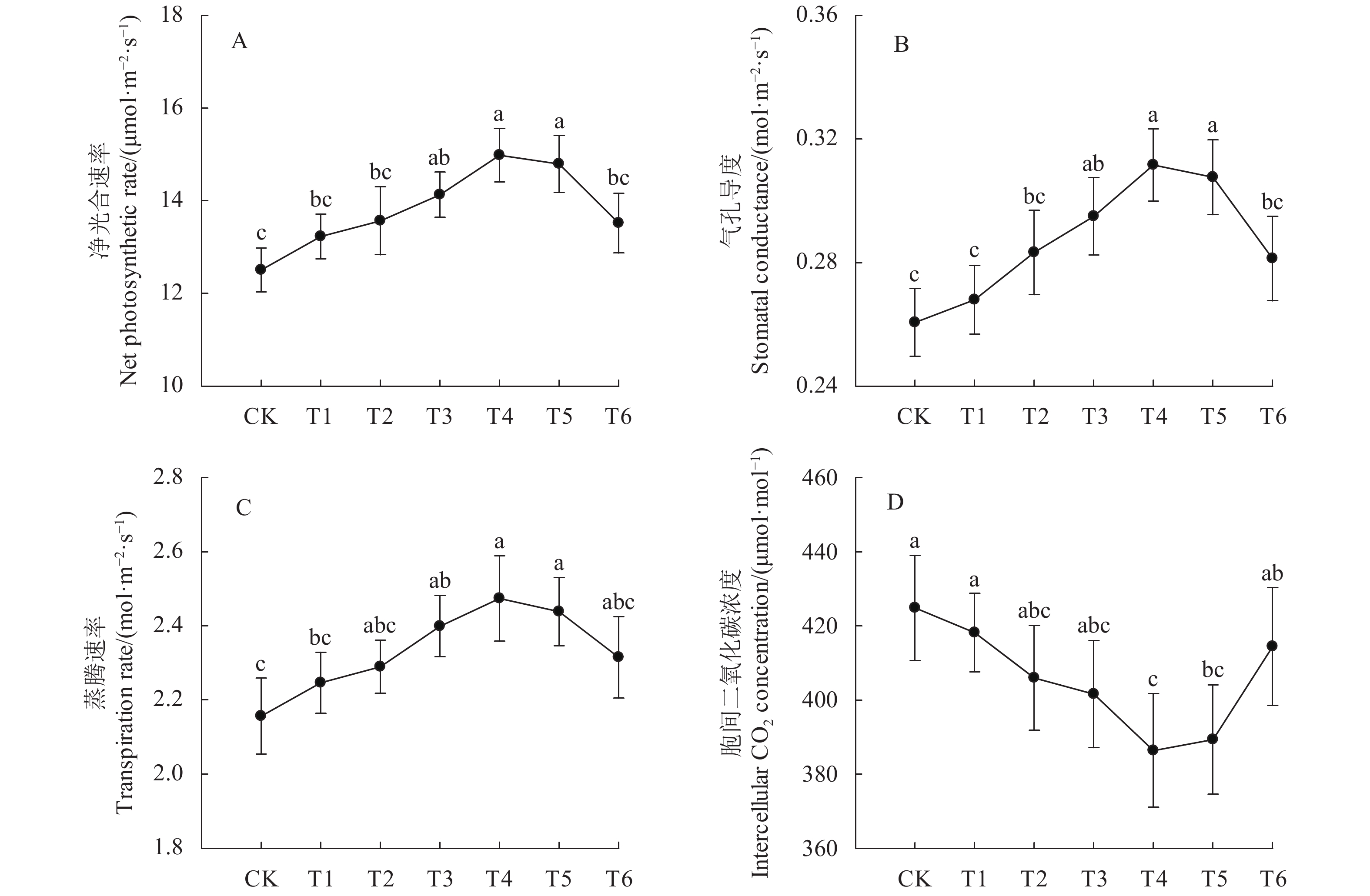
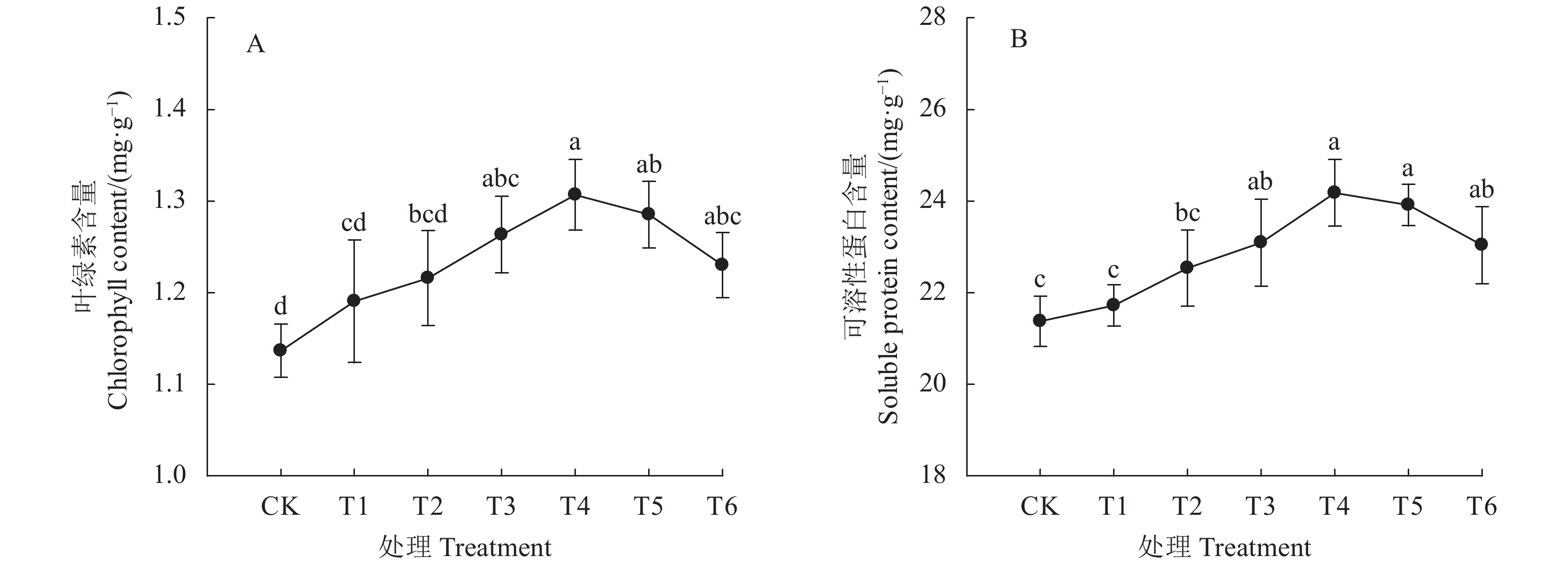
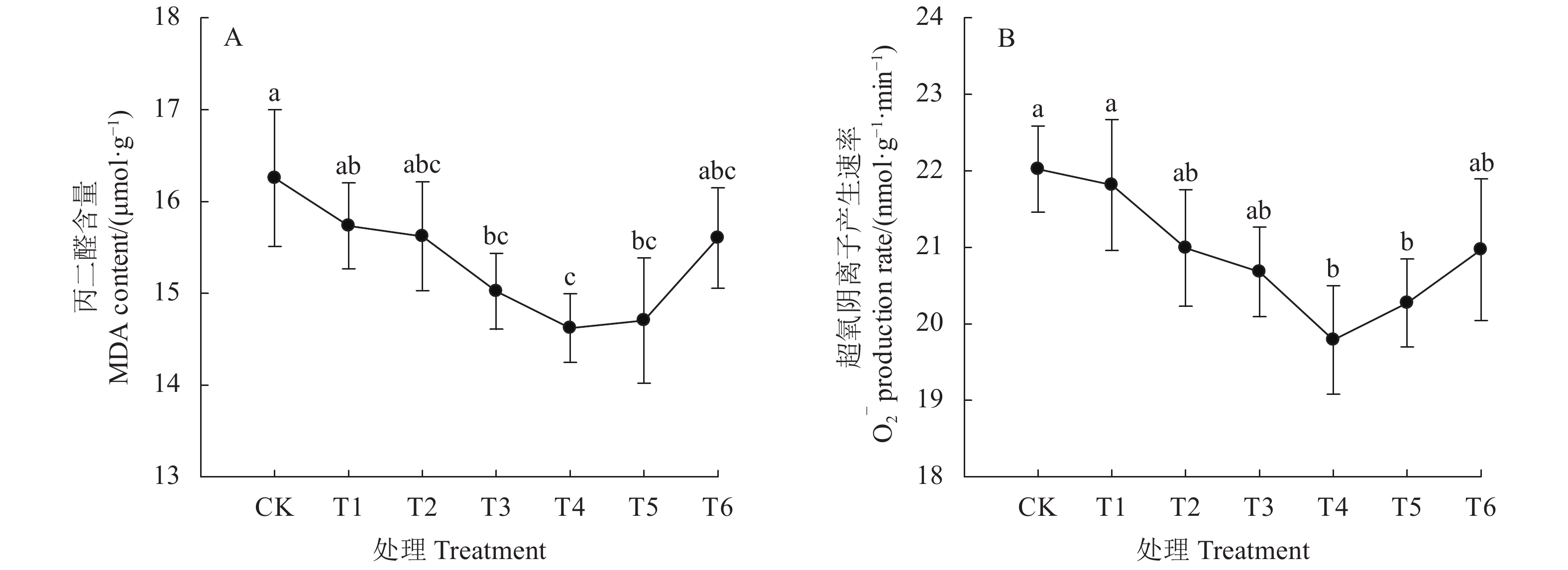
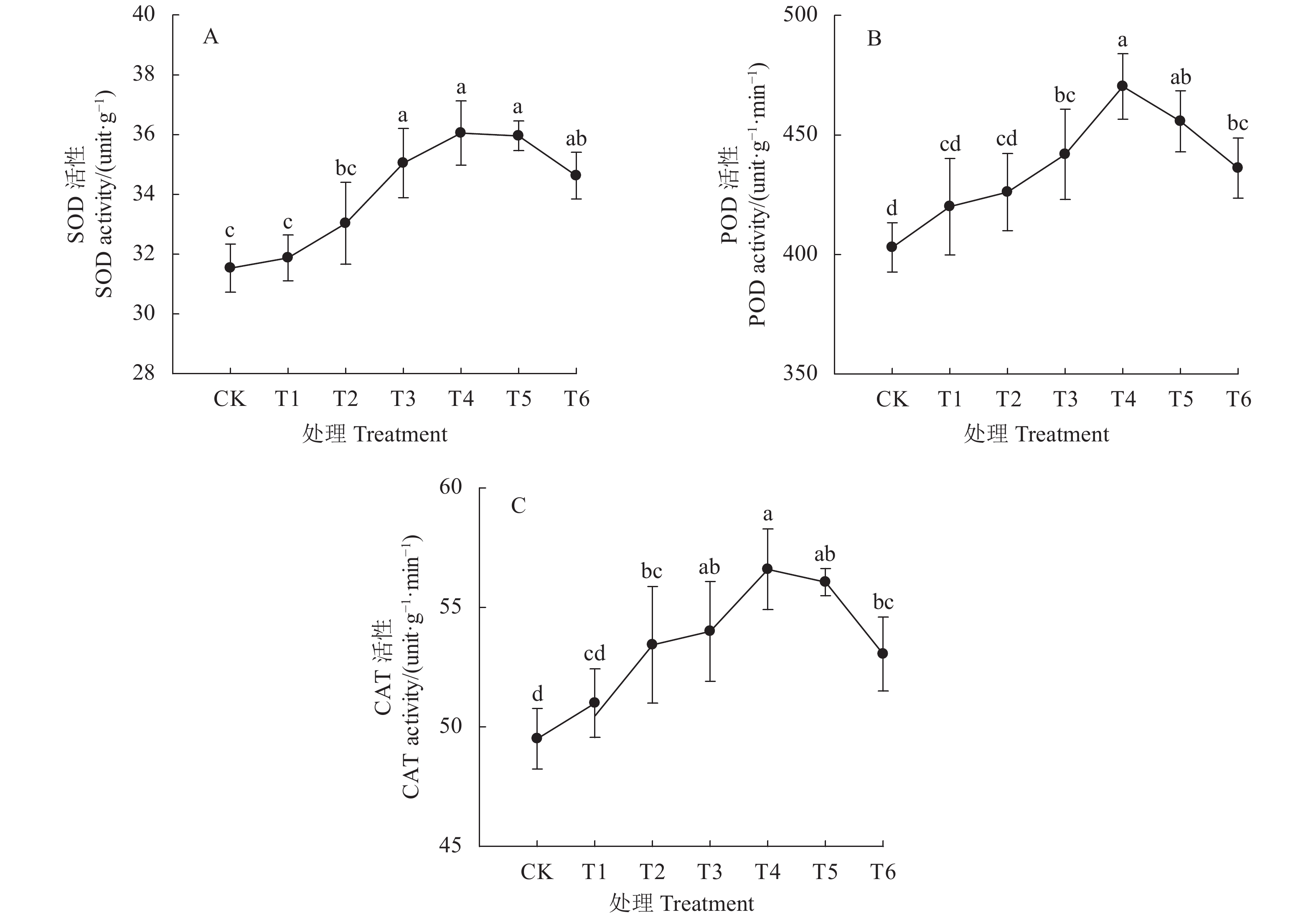
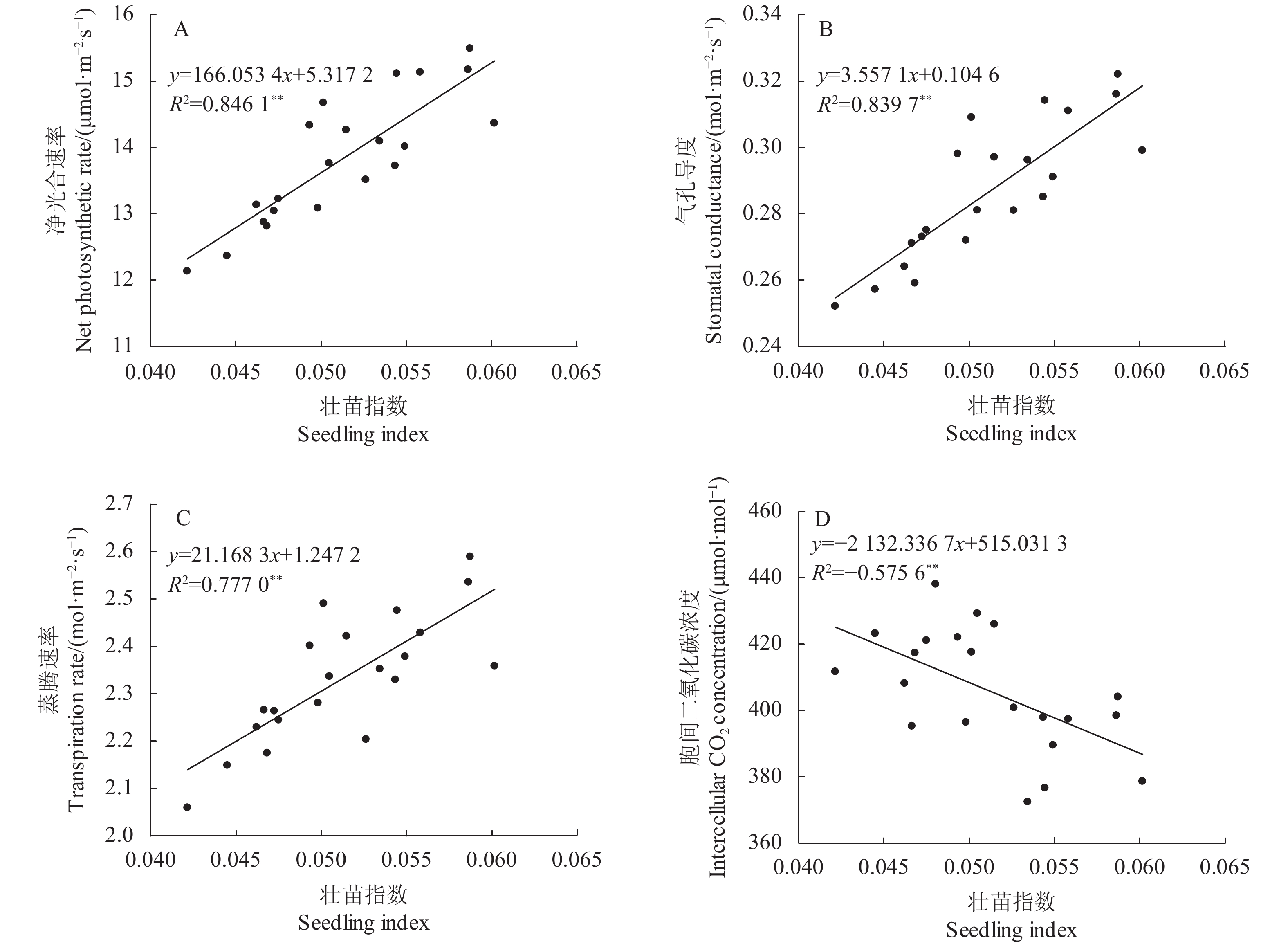
摘要:目的 为在辣椒生产中合理利用枯草芽孢杆菌悬浮种衣剂提供理论依据。方法 以扬椒2号为材料,研究了枯草芽孢杆菌悬浮种衣剂母液与种子不同药种比[1∶2、1∶4、1∶6、1∶8、1∶10和1∶12 (mL∶g)]对辣椒幼苗生长和生理特性的影响。结果 与对照(不包衣)相比,种衣剂处理提高了辣椒幼苗出苗率、株高、茎粗、叶面积、植株干重和壮苗指数,且提高幅度随药种比的降低呈先上升后下降的趋势,以药种比1∶8的提高幅度最大。种衣剂处理提高了叶片净光合速率(Pn)、蒸腾速率(Tr)和气孔导度(Gs),降低了胞间CO2浓度(Ci),增强了植株的光合能力。同时,种衣剂处理降低了叶片丙二醛(MDA)含量和超氧阴离子(O2−)产生速率,提高了超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)和过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性,有利于维持叶片较高的叶绿素含量和可溶性蛋白含量。此外,相关分析表明,辣椒幼苗壮苗指数与叶片净光合速率、蒸腾速率和气孔导度呈显著正相关,与胞间CO2浓度呈显著负相关。结论 枯草芽孢杆菌悬浮种衣剂通过降低膜脂过氧化程度和提高抗氧化物酶活性来维持叶片较强的光合能力,从而有利于辣椒壮苗的形成,且以药种比1∶8的效果最佳。Abstract:Objective Applicability of a seed-coating Bacillus subtilis suspension for promoting chili pepper seedling growth was investigated.Method The chili pepper, Yangjiao No. 2, was used in the study by applying a B. subtilis agent on the seeds at the pharmacopoeia ratios of suspension to seeds at 1∶2, 1∶4, 1∶6, 1∶8, 1∶10, or 1∶12 (ml∶g). Subsequently, the seed germination as well as the seedling growth and physiological characteristics were monitored to determine the effects brought about by the coating treatments.Result Compared with control, the coating increased the seed germination rate and the plant height, stem diameter, leaf area, plant dry weight, and growth index of the seedlings. The effects peaked at the suspension to seeds ratio at 1∶8. The coating treatments enhanced the net photosynthetic rate (Pn), transpiration rate (Tr), and stomatal conductance (Gs) but reduced the intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci) on the leaves resulting in an uplifted photosynthetic capacity of the plants. Moreover, the treatments decreased the MDA content and O2−production rate, while increased the SOD, POD and CAT activities, of the leaves that were conducive to sustaining high contents of chlorophyll and soluble protein for the plants. The seedling growth index was found positively correlated with the net photosynthetic rate, transpiration rate, and stomatal conductance but inversely correlated with the intercellular CO2 concentration.Conclusion The seed-coating B. subtilis suspension alleviated the peroxidation of membrane lipids and increased antioxidant enzyme activities with a sustained high photosynthetic capacity in the leaves benefiting a vigorous subsequent growth of the seedlings. The pharmacopoeia ratio at 1ml of suspension to 8g of seeds provided the most desirable results.
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】金线莲(Anoectochilus roxburghii),又名金草、金蚕,天门冬目兰科,单子叶植物,主要分布于我国东南部福建、台湾、浙江、江西等地[1]。其味道甘甜、药性平和,具有降火、祛湿气、祛毒、镇痛止咳、降低血压血糖、抑制肿瘤等功效,具有极高的药用价值,在民间被誉为“药王” “鸟人参”等[2-3]。金线莲对外界环境要求极高,多生长在环境阴凉、土质良好、水气充足、有良好团粒结构且有充足肥力的土壤[4]。近年来由于人类过度开垦、灌溉、施肥等活动,导致土壤板结、水土流失、土壤质量不断恶化,极大地限制了金线莲产量和品质的提升[5],因此急需寻找一种合适的种植方式。有研究发现通过调控土壤紧实度能改变土壤物理机械结构,进而影响作物产量[6]。土壤紧实度是指土壤抵抗外力的压实和破碎的能力,可通过土壤容重、孔隙度和机械阻力等指标来评价,其中土壤容重是反映土壤紧实度最直接、最常用的指标[7]。土壤容重和土壤紧实度直接相关,土壤容重提高,土壤紧实度也增大[7]。土壤紧实度的大小影响作物根系的穿透能力和矿质元素的转移,进而影响植物生长进程,因此栽培金线莲不仅需要适宜的水肥,还必须有适宜的土壤紧实度[8]。【前人研究进展】多项研究表明,土壤过度疏松或紧实,会影响作物生长,造成作物减产,品质下降。土壤过于松弛,土壤保水持肥能力下降,更容易加快土壤水分和养分的流失。吴晓莲等[9]研究发现,土壤容重过低会影响甘蔗苗期生长,最终导致减产。邹俊等[10]对活血丹设置不同容重处理后发现,土壤容重0.8 g·cm−3处理,活血丹各项生长指标和生物量,以及光合色素、可溶性糖、游离氨基酸含量均显著低于土壤容重1.0 g·cm−3处理。土壤过于紧实,通气性变差,影响根系生长发育及生理代谢。刘永晨等[11]研究发现,土壤紧实胁迫处理抑制甘薯生长,降低块根中干物质分配率和块根产量。Tracy等[12]研究发现,土壤过于紧实,抑制番茄根系生长,降低根系活性,导致番茄产量和品质下降。【本研究切入点】目前,对金线莲生长的研究绝大多数集中在栽培基质材料与配方,而缺乏从栽培基质物理性质-土壤紧实度角度出发,对金线莲生长和品质影响的研究。【拟解决的关键问题】本试验通过改变土壤和珍珠岩用量,设置不同容重处理,研究不同土壤紧实度对金线莲生长和品质的影响,筛选出金线莲生长所需的适宜紧实度,以期为金线莲高产栽培、产量品质提升提供有力的理论支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
供试植物为小叶品种金线莲组培苗,取自福建农林大学自然生物资源保育利用福建省高校工程研究中心。
供试土壤为红壤,0~20 cm土壤pH值5.82、有机质25.40 g·kg−1,碱解氮63.54 mg·kg−1,有效磷35.41 mg·kg−1,速效钾109.28 mg·kg−1。
供试珍珠岩购自市场,粒径大小3~6 mm,容重为100~150 kg·cm−3。
试验于2019年1月13日~6月13日在福建农林大学田间实验室(阳光房)内进行,试验地地理坐标为(25°15′~26°39′N,118°08′~120°31′E),属典型亚热带海洋性季风气候区,年平均气温约20.1 ℃,气温适宜,温暖湿润,光照充沛,适宜金线莲生长。
1.2 试验设计
试验采用盆栽试验,花盆为口径20 cm,底径16 cm,高15 cm的PVC盆,花盆底部放置有塑料网,防止土壤冲刷。试验设置5个土壤容重处理,分别为0.7(T1)、0.8(T2)、0.9(T3)、1.0(T4)、1.1 g·cm−3(T5),每个处理设置5个重复。各处理所需土壤与珍珠岩见表1,选用m(N)∶m(P2O5)∶m(K2O)=15∶15∶15的复合肥,每盆施用量为1.2 g,折合大田施用量为444 kg·hm−2。将土壤、肥料与珍珠岩混合均匀后装入花盆,并压至相应的刻度(距盆顶3 cm),缓慢浇水,放置2 d后,选取长势良好、大小一致的金线莲幼苗,用5 %的多菌灵溶液浸泡10 min进行消毒杀菌,晾干后均匀移栽至PVC花盆中,每盆移栽10株,试验期间水肥、光照、病虫害管理按常规进行。
表 1 各处理土壤和珍珠岩质量Table 1. The quality of soil and perlite for each treatment处理
Treatment红壤
Red soil/g珍珠岩
Perlite/g容重
Bulk density/(g·cm−3)T1 1200 120 0.7 T2 1400 80 0.8 T3 1600 40 0.9 T4 1800 20 1.0 T5 2000 0 1.1 1.3 试验方法
1.3.1 样品采集与处理
金线莲栽培管理150 d后,采收所有地上部金线莲样品,将采收金线莲样品分为两部分,一部分植株样品位于4 ℃冰箱进行冷藏处理,用于植物生长、生理指标测定,另一部分植株样品置于105 ℃鼓风干燥箱杀青2 h,65 ℃烘干至恒重,粉碎至粉末状,过0.149 mm筛,装袋编号,用于植物品质指标测定。
1.3.2 生长指标测定
金线莲采收时对植物生长指标进行测定,每个处理选取5株金线莲,用卷尺测定植株株高、叶长、叶宽和根长(株高以地面到植株最高处为准;叶长、叶宽测定选取金线莲中最大的叶片,以长宽最大处为准;根长测定选取金线莲主根系,以地面到根最底端为准),用电子游标卡尺测定植株地径(距离地面1 cm处),用电子天平称量植株鲜重,计算折干率,折干率(%)=(植株干重/植株鲜重)×100%。
1.3.3 生理指标测定
选用整个植株鲜样进行金线莲生理指标测定,叶绿素a、叶绿素b、类胡萝卜素含量均采用乙醇浸提-分光光度法测定,吸收光波长分别为663、645、470 nm[13]。
1.3.4 品质指标测定
全碳、全氮含量采用全自动微量碳氮元素分析仪(德国ELEMENTAR)测定,全磷含量采用钒钼黄比色法测定,全钾含量采用火焰光度法测定。多糖含量采用苯酚-硫酸法测定,游离氨基酸含量采用茚三酮柱后衍生法测定,Vc含量采用2,6-二氯酚靛酚滴定法测定,总酚含量采用酒石酸亚铁比色法测定,黄酮含量以芦丁为标准品对照,分光光度法测定[13]。
1.4 数据处理与分析
采用Microsoft Excel 2016整理数据与绘图,用SPSS 20.0软件对试验数据进行单因素方差分析和SNK法进行显著性检验(P<0.05)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲生长的影响
由表2可以看出,土壤紧实度对于金线莲的生长影响显著。金线莲株高和地径都随土壤容重的增加呈先增加后减少的趋势,株高在土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3达到最大值12.40 cm,分别是其他处理的1.25、1.10、1.11、1.15倍,与其他处理均达显著性差异(P<0.05);地径在土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3达到最大值2.75 mm,分别是其他处理的1.12、1.01、1.12、1.10倍;表明过高或过低的容重都不利于金线莲株高和地径的增长。金线莲叶片数、叶长、叶宽也受土壤紧实度的影响,叶片数以土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3处理为最大,以土壤容重0.7 g·cm−3处理为最小,两者间相差0.49片;叶长除容重0.7 g·cm−3处理外,其余处理间无显著性差异,都显著大于容重0.7 g·cm−3的处理;各处理叶宽位于1.68~1.77 cm,处理间无显著差异;表明过高过低的容重都不利于金线莲叶片的生长。金线莲根长在土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3达到最大值4.53 cm,分别是其他处理的1.50、1.42、1.06、1.01倍,与土壤容重0.7、0.8 g·cm−3处理间差异较大,表明土壤容重过低会显著影响根系的生长发育。
表 2 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲生长指标的影响Table 2. The effect of different soil compaction on the growth index of Anoectochilus处理
Treatment株高
Plant height/cm地径
Ground path/mm叶数
Number of leaves叶长
Leaf length/cm叶宽
Leaf width/cm根长
Root length/cmT1 9.92±0.32 c 2.46±0.22 b 3.87±0.33 b 2.03±0.19 b 1.74±0.14 a 3.02±0.31 c T2 11.28±0.44 b 2.71±0.20 a 4.34±0.22 a 2.51±0.08 a 1.75±0.07 a 3.20±0.27 c T3 12.40±0.73 a 2.75±0.15 a 4.36±0.37 a 2.63±0.13 a 1.77±0.07 a 4.53±0.34 a T4 11.14±0.51 b 2.45±0.26 b 4.00±0.35 b 2.41±0.13 a 1.71±0.16 a 4.26±0.28 b T5 10.80±0.65 bc 2.50±0.23 b 4.12±0.18 ab 2.41±0.14 a 1.68±0.10 a 4.49±0.45 a 注:表中标注不同小写字母表示在(P<0.05)水平差异显著,下同。
Note: Different lowercase letters in the table indicate significant differences at(P<0.05), the same below.由图1可知,土壤紧实度对金线莲产量有着显著的影响。金线莲鲜重和折干率均随土壤容重的增加呈现先增加后减少的趋势。鲜重在土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3达到最大值1.35 g,相比其他处理显著增加68.51%、18.04%、16.61%、24.13%(P<0.05),在土壤容重0.7 g·cm−3达到最小值0.80 g,与其他各处理间均达显著性差异。折干率在土壤容重0.8 g·cm−3达到最大值14.18%,相比其他处理显著增加47.71%、26.72%、57.73%、51.17%,在土壤容重1.0 g·cm−3达到最小值8.99%,而土壤容重0.7、1.0、1.1 g·cm−3处理下折干率之间无显著差异。表明过高或过低的土壤紧实度均不利于金线莲产量提升和体内干物质的合成与积累。
2.2 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲生理的影响
由表3可知,土壤紧实度对金线莲叶绿素和类胡萝卜素合成有着显著的影响。金线莲叶片中叶绿素及类胡萝卜素随土壤容重总体上均呈现先增加后减少的趋势,叶绿素a含量在土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3达到最大值1.99 mg·g−1,分别是其他处理的1.08、1.02、1.07、1.09倍,土壤容重0.8、0.9 g·cm−3处理间无明显差异。各处理叶绿素b含量平均为0.45 mg·g−1,各处理间差异不显著。各处理类胡萝卜素含量平均为0.56 mg·g−1,在土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3达到最大值0.63 mg·g−1,分别是其他处理的1.24、1.15、1.07、1.19倍,在土壤容重0.7 g·cm−3达到最小值0.51 mg·g−1,与最大值间存在显著性差异(P<0.05),但与其他处理间无显著差异。表明适宜的土壤紧实度会促进金线莲叶绿素和类胡萝卜素的合成,影响植物光合作用。
表 3 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲叶绿素与类胡萝卜素的影响Table 3. The effect of different soil compaction on physiological index of Anoectochilus处理
Treatment叶绿素a
Chlorophyll a/
(mg·g−1)叶绿素b
Chlorophyll b/
(mg·g−1)类胡萝卜素
Carotenoids/
(mg·g−1)T1 1.84±0.12 b 0.43±0.05 a 0.51±0.09 b T2 1.96±0.15 a 0.43±0.02 a 0.55±0.04 b T3 1.99±0.08 a 0.46±0.06 a 0.63±0.05 a T4 1.86±0.17 b 0.47±0.03 a 0.59±0.03 ab T5 1.83±0.13 b 0.46±0.07 a 0.53±0.08 b 2.3 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲养分、品质的影响
各处理间金线莲植株碳、氮、磷、钾养分含量变化趋势相同(见表4),均随土壤容重的增加呈先增加后减少的趋势。金线莲中碳素的含量最多,平均达到348.59 mg·g−1,其次是氮元素,磷元素含量最少,平均为1.15 mg·g−1。碳素含量在土壤容重1.0 g·cm−3达到最大值357.92 mg·g−1,相比其他处理分别增加了18.34、16.37、2.59、9.34 mg·g−1,在土壤容重0.7 g·cm−3达到最小值339.58 mg·g−1,高土壤容重(大于0.9 g·cm−3)处理的金线莲碳素积累量显著大于低土壤容重。氮素含量位于25.79~28.71 mg·g−1,除土壤容重1.1 g·cm−3处理金线莲氮素积累量最低外,其余处理间无显著性差异。磷素含量在土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3达到最大值1.27 mg·g−1,分别是其他处理的1.23、1.10、1.09、1.13倍,与其他处理均达显著差异(P<0.05)。钾素含量也以土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3处理为最大,以土壤容重1.1 g·cm−3处理为最小,两处理间钾素含量差距达到1.80 mg·g−1,达到显著差异。表明适宜的土壤容重可以促进金线莲植株养分积累,对碳、磷、钾素促进作用较为明显,而对氮素促进作用不明显。
表 4 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲养分含量的影响Table 4. The effect of different soil compaction on nutrient content of Anoectochilus处理
Treatment养分含量 Nutrient content/(mg·g−1) C N P K T1 339.58±10.47 b 28.15±1.27 a 1.03±0.04 c 19.27±1.05 b T2 341.55±12.54 b 28.35±1.31 a 1.15±0.08 b 20.62±1.30 a T3 355.33±9.92 a 28.71±0.52 a 1.27±0.07 a 20.77±1.52 a T4 357.92±17.43 a 28.21±1.39 a 1.16±0.12 b 19.13±0.99 b T5 348.58±8.04 a 25.79±0.93 b 1.12±0.09 b 18.97±1.41 b 由表5可知,土壤紧实度显著影响金线莲的品质。多糖含量在土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3达到最大值143.07 mg·g−1,相比其他处理显著增加了30.65%、70.81%、24.83%、29.00%(P<0.05),而在土壤容重0.8 g·cm−3时含量最低。氨基酸含量位于1.44~2.57 mg·g−1,在土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3达到最大值,相比其他处理显著增加了25.37%、29.80%、44.38%、78.47%,在高容重下氨基酸含量下降明显。黄酮含量位于8.65~13.98 mg·g−1,以土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3处理为最大,以土壤容重0.8 g·cm−3处理为最小。总酚和Vc含量均随土壤容重的增加呈先增加后减少的趋势,总酚在土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3达到最大值34.37 mg·g−1,相比其他处理显著增加了27.39%、24.80%、14.68%、26.92%,除土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3处理外,其余处理间无显著差异。Vc含量位于21.77~27.57 mg·g−1,以土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3处理为最大,以土壤容重1.1 g·cm−3处理为最小,两处理间Vc含量差距为5.80 mg·g−1,达到显著性差异。表明中等土壤紧实度的土壤最适于金线莲多糖、氨基酸、Vc等的合成和积累,促进品质提升。
表 5 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲品质指标的影响Table 5. The effect of different soil compaction on the quality index of Anoectochilus处理
Treatment多糖
Polysaccharide/(mg·g−1)氨基酸
Amino acid/(mg·g−1)总酚
Total phenols/(mg·g−1)黄酮
Flavonoids/(mg·g−1)Vc
Vitamin C/(mg·g−1)T1 109.51±3.55 b 2.05±0.13 b 26.98±1.64 b 12.01±0.84 ab 23.36±1.23 b T2 83.76±1.29 c 1.98±0.15 b 27.54±1.47 b 8.65±0.52 c 27.28±2.04 a T3 143.07±4.97 a 2.57±0.21 a 34.37±2.06 a 13.98±1.11 a 27.57±1.84 a T4 114.61±4.25 b 1.78±0.08 bc 29.97±2.34 b 13.74±0.95 a 24.67±1.81 b T5 110.91±3.88 b 1.44±0.17 c 27.08±1.82 b 10.66±0.69 b 21.77±2.45 c 3. 讨论
3.1 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲生长的影响
土壤紧实度作为反映土壤松紧状况的指标,通过影响土壤水分、养分、通气状况、热量以及微生物,进而影响植物的生长[14]。本试验结果表明,通过珍珠岩调控,土壤物理性质发生变化,金线莲株高、地径、叶片数、根长、鲜重等随着土壤容重增加,都呈先增加后减少的趋势。在红壤与珍珠岩配比为40∶1,即土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3时达到最大。表明适宜的土壤容重会促进金线莲的生长,提高作物产量,而过高或过低的土壤容重会影响金线莲生长发育进程。这些与前人的研究结果相似。
刘宪辉[15]研究发现珍珠岩施入蔬菜大棚土壤中能有效改良土壤,增加作物产量。这是因为一方面珍珠岩具有较高的吸附容量和离子交换能力,可有效起到保水保肥、抗渗漏、提高养分生物有效性作用,另一方面它自身含有一定量的钾、磷、钛、锰、硅、铁、钙等植物不可缺少的中微量元素,为农作物提高了良好的生长条件。徐海等[16]研究发现,玉米地上部生长受土壤容重影响显著,土壤过松或过紧均不利于作物的生长。刘兆娜等[17]对花生设置不同容重处理,发现适宜土壤容重在整个生育期都有利于花生各器官干物质积累,有利于增加结果数和荚果饱满度,提高荚果和籽仁产量。土壤紧实度过高,土壤孔隙度降低,土壤板结程度增加,土壤通气透水能力变差,土壤内空气缺乏,进而抑制微生物活动和养分转化进程,根系对水和养分的吸收能力降低;而土壤紧实度过低,土壤孔隙度大,土壤内部空气浓度变高,土壤热量扩散速度加快,植物根系与土壤接触面积变小,土壤对植物根系的支持能力减弱,土壤保水持肥能力下降,养分易随降水或灌溉水流失。因此,只有适宜的土壤紧密度,才能保证土壤水分、养分供应充足、通气状况良好,有助于金线莲的正常生长[18]。
3.2 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲生理的影响
叶绿素和类胡萝卜素作为表征植物光合作用能力的指标,其含量的高低会影响植物光合作用,进而影响植物物质的合成与转运[19]。本试验结果表明,在红壤与珍珠岩配比为40∶1,即土壤容重0.9 g·cm−3时金线莲叶绿素a和类胡萝卜素含量最高,叶绿素b含量无显著差异,表明土壤紧实度会影响金线莲的生理,影响叶绿素和类胡萝卜素的合成,过高或者过低的土壤紧实度均不利于金线莲叶绿素和类胡萝卜素的合成与积累。尚庆文等[20]研究表明,土壤紧实度增加,生姜叶片活性降低,叶绿素含量下降,光合速率下降,光合作用减弱。田树飞等[21]研究表明适宜的土壤紧实度有利于花生叶片光合色素的合成与积累。这些都与本研究结果一致。适宜的土壤紧实度会提高植株中叶绿素和类胡萝卜素含量,促进光合作用。这可能与土壤环境改善、水肥气热环境适宜、植株生长发育良好、植株各项生理活性提高有关[22]。
3.3 不同土壤紧实度对金线莲养分和品质的影响
C、N、P、K含量是间接反映植物生长及物质合成的指标,通过影响植物体内物质转化进程,进而影响物质的合成与积累[23]。多糖、总酚、氨基酸、黄酮、Vc等物质,是反映金线莲营养及药用价值的重要指标,其含量高低能够反映金线莲活性物质含量的高低[24]。
本试验结果表明,金线莲N、P、K含量均在0.9 g·cm−3处理达到最大值,C含量在1.0 g·cm−3处理达到最大值,在0.9 g·cm−3处理与1.0 g·cm−3处理间两者仅相差2.59 mg·g−1,可以得知金线莲生长在红壤与珍珠岩配比为40∶1,即容重为0.9 g·cm−3的土壤中,其养分含量最高。金线莲多糖、氨基酸、总酚、黄酮、Vc含量随土壤容重的增加总体呈先增加后减少的趋势,也均在0.9 g·cm−3处理达到最大值,多糖、氨基酸、总酚含量与其他处理均达显著差异,表明过高过低的土壤紧实度均不利于金线莲品质的提升。张亚如等[25]研究发现,土壤过高或者过低的紧实度都会抑制花生结荚期氮、磷、钾等元素的吸收,影响植株品质。张向东等[26]对桔梗设置不同紧实度处理,发现土壤紧实胁迫下,桔梗根系活力下降,叶绿素含量降低,可溶性蛋白含量减少,植株品质降低。综合分析原因,过高过低的土壤紧实度,会导致金线莲根系对于土壤中营养元素的供给和吸收能力降低,从而使体内物质循环和转化途径效率降低[27]。过高的土壤紧实度,其土壤结构紧实黏重,土层氧气浓度低,土壤胶体对养分和水分的吸附作用强烈,土壤酶活性低,微生物活动弱,根系难以下扎,从而根系难以吸收水分和养分;过低的土壤紧实度,土壤结构松碎易散,土壤保水保肥能力低,土壤水分易通过土面蒸腾而损失,土壤养分易流失,土壤养分和水分供应不足,进而导致金线莲养分积累量降低、品质下降等[28]。
4. 结论
适宜的土壤紧实度会促进金线莲生长和产量提升,对金线莲根、茎、叶生长及物质合成与积累有显著影响,在红壤与珍珠岩配比达到40∶1,土壤容重为0.9 g·cm−3时效果最佳,而土壤紧实度对金线莲叶长和叶宽的增长没有显著影响。
土壤紧实度的高低会影响金线莲的生理,适宜的土壤紧实度促进金线莲叶片中叶绿素a和类胡萝卜素的合成,但对叶绿素b含量没有显著影响。
适宜的土壤紧实度增加金线莲体内C、N、P、K养分含量,提高植株中多糖、氨基酸、总酚、黄酮和Vc含量,在红壤与珍珠岩配比达到40∶1,土壤容重为0.9 g·cm−3时效果最佳,土壤容重过高或者过低均不利于金线莲养分合成积累和品质提升。
综上,土壤紧实度对于金线莲的生长和品质有显著影响。在红壤与珍珠岩配比达到40∶1,即土壤容重为0.9 g·cm−3时金线莲各项生长、品质指标优于其他处理,总体效果最佳,对金线莲科学种植具有一定的指导意义。
-
表 1 枯草芽孢杆菌悬浮种衣剂不同药种比对辣椒幼苗生长的影响
Table 1 Effect of seed-coating applications on growth of chili pepper seedlings
处理
Treatment出苗率
Germination rate/
%株高
Plant height/
cm茎粗
Stem diameter/
mm叶面积
Leaf area/
cm2植株干重
Plant dry weight/
mg地上部干重
Aboveground dry weight/
mg地下部干重
Underground dry weight/
mg根冠比
Root shoot ratio壮苗指数
Seedling indexCK 82.67 b 6.80 b 1.27 c 5.75 c 283.65 d 249.11 c 34.54 d 0.138 b 0.0446 d T1 85.33 ab 6.92 b 1.30 bc 5.99 bc 291.90 cd 254.94 bc 36.95 cd 0.145 ab 0.0478 cd T2 86.67 ab 7.19 ab 1.31 bc 6.26 abc 295.46 cd 257.08 bc 38.37 bc 0.149 ab 0.0490 bc T3 87.33 a 7.31 ab 1.34 abc 6.36 ab 309.44 bc 268.30 ab 41.13 ab 0.153 a 0.0531 ab T4 90.00 a 7.60 a 1.42 a 6.61 a 328.65 a 284.04 a 44.60 a 0.157 a 0.0577 a T5 89.33 a 7.52 a 1.40 ab 6.54 a 323.11 ab 279.87 a 43.23 a 0.154 a 0.0559 a T6 88.00 a 7.16 ab 1.32 abc 6.22 abc 294.86 cd 256.45 bc 38.40 bc 0.150 ab 0.0496 bc 注:同列数据后不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Note: Data with different lowercase letters on same column indicate significant differences at P<0.05. -
[1] 旷碧峰, 余席茂, 肖昌华, 等. 辣椒早春设施栽培技术 [J]. 上海蔬菜, 2012(5):21−23. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1469.2012.05.015 KUANG B F, YU X M, XIAO C H, et al. Facility cultivation techniques of pepper in early spring [J]. Shanghai Vegetables, 2012(5): 21−23.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1469.2012.05.015
[2] 郑井元, 李雪峰, 周书栋, 等. 2017年度辣椒科学研究进展 [J]. 中国蔬菜, 2018(5):9−15. ZHENG J Y, LI X F, ZHOU S D, et al. Research progress of pepper in 2017 [J]. China Vegetables, 2018(5): 9−15.(in Chinese)
[3] 弭宝彬, 周火强, 谢玲玲, 等. 育苗基质配比及育苗方式对辣椒成苗的影响 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(28):63−69. DOI: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb18110049 MI B B, ZHOU H Q, XIE L L, et al. Proportions of seedling substrate and seedling culture mode affect pepper seedling formation [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2019, 35(28): 63−69.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb18110049
[4] 崔文艳, 何鹏飞, 何朋杰, 等. 微生物复合种衣剂对玉米发芽、苗期生理特性及产量的影响 [J]. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学), 2016, 31(4):630−636. CUI W Y, HE P F, HE P J, et al. Effect of mirobial complex seed-coating agent on germination, seedling biological traits and yield of maize [J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science), 2016, 31(4): 630−636.(in Chinese)
[5] 沈奇, 杨森, 徐静, 等. 种衣剂对紫苏发芽率及产量品质性状的影响 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2018, 34(28):21−25. DOI: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb17120078 SHEN Q, YANG S, XU J, et al. Seed coating affects the germination rate, yield and quality of Perilla [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2018, 34(28): 21−25.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb17120078
[6] 李星星, 王燕提, 严青青, 等. 种衣剂对低温下棉花幼苗光合特性的影响 [J]. 西北植物学报, 2018, 38(3):525−534. DOI: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2018.03.0525 LI X X, WANG Y T, YAN Q Q, et al. Effect of seed coating agent on photosynthetic characteristics of cotton seedlings under low temperature [J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2018, 38(3): 525−534.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2018.03.0525
[7] 李进, 李杰, 丁媛, 等. 不同种衣剂对辣椒幼苗生长及立枯病防效的影响 [J]. 北方园艺, 2017(16):55−60. LI J, LI J, DING Y, et al. Effect of different seed coating agents on control of Rhizoctonia solani kühn and growth of pepper [J]. Northern Horticulture, 2017(16): 55−60.(in Chinese)
[8] CHANDA M, DE GROOTE H, KINOTI L, et al. Farmer evaluation of pesticide seed-coating to control fall armyworm in maize [J]. Crop Protection, 2021, 148: 105691. DOI: 10.1016/j.cropro.2021.105691
[9] WIATRAK. Infuence of seed coating with micronutrients on growth and yield of winter wheat in Southeastern Coastal Plains [J]. American Journal of Agricultural and Biological Sciences, 2013, 8(3): 230−238. DOI: 10.3844/ajabssp.2013.230.238
[10] 杜玉宁, 邢敏, 陈杭, 等. 不同种衣剂对黄瓜种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响 [J]. 种子, 2018, 37(10):75−78. DU Y N, XING M, CHEN H, et al. Effects of different seed coating agents on seed germination and seedling growth of cucumber [J]. Seed, 2018, 37(10): 75−78.(in Chinese)
[11] 张政兵, 刘勇, 郭海明, 等. 15%蔬菜种衣剂处理对辣椒的促生作用研究 [J]. 广西农业科学, 2007, 38(1):55−57. ZHANG Z B, LIU Y, GUO H M, et al. Effects of 15% vegetable seed coating agent on growth-promoting of pepper [J]. Guangxi Agricultural Sciences, 2007, 38(1): 55−57.(in Chinese)
[12] 陈丽华, 高秋雨, 张家恒, 等. 生物复合种衣剂对水稻苗期生长的影响 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(12):105−110. DOI: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.2014-2614 CHEN L H, GAO Q Y, ZHANG J H, et al. Effect of a biological complex seed-coating agent on rice seedling growth [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2015, 31(12): 105−110.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.2014-2614
[13] MA Y. Seed coating with beneficial microorganisms for precision agriculture [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2019, 37(7): 107423. DOI: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.107423
[14] ROCHA I, MA Y, CARVALHO M F, et al. Seed coating with inocula of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for nutritional enhancement of maize under different fertilisation regimes [J]. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 2019, 65(1): 31−43. DOI: 10.1080/03650340.2018.1479061
[15] 杨洪凤, 薛雅蓉, 余向阳, 等. 内生解淀粉芽孢杆菌CC09菌株在小麦叶部的定殖能力及其防治白粉病效果研究 [J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2014, 30(4):481−488. YANG H F, XUE Y R, YU X Y, et al. Colonization of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens CC09 in wheat leaf and its biocontrol effect on powdery mildew disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2014, 30(4): 481−488.(in Chinese)
[16] TU L, HE Y H, SHAN C H, et al. Preparation of microencapsulated Bacillus subtilis SL-13 seed coating agents and their effects on the growth of cotton seedlings [J]. BioMed Research International, 2016: 3251357.
[17] 罗振亚, 徐淑, 林开春. 枯草芽孢杆菌Yz菌株丸化种衣剂配方筛选试验 [J]. 广东农业科学, 2019, 46(7):100−106. LUO Z Y, XU S, LIN K C. Screening of formula for seed pelleting agent of Bacillus subtilis yz strain [J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 46(7): 100−106.(in Chinese)
[18] SABERI-RISE R, DE MORADI-POUR M. The effect of Bacillus subtilis Vru1 encapsulated in alginate - bentonite coating enriched with titanium nanoparticles against Rhizoctonia solani on bean [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2020, 152: 1089−1097. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.10.197
[19] 柴文臣, 马蓉丽, 焦彦生, 等. 低温胁迫对不同辣椒品种生长及生理指标的影响 [J]. 华北农学报, 2010, 25(2):168−171. DOI: 10.7668/hbnxb.2010.02.034 CHAI W C, MA R L, JIAO Y S, et al. Influences of low temperature stress on pepper's growth index and physiological index [J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2010, 25(2): 168−171.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7668/hbnxb.2010.02.034
[20] 颉建明, 郁继华, 颉敏华, 等. 低温弱光下辣椒3种渗透调节物质含量变化及其与品种耐性的关系 [J]. 西北植物学报, 2009, 29(1):105−110. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4025.2009.01.016 XIE J M, YU J H, XIE M H, et al. Changes of three osmotic regulatory metabolites in leaves of pepper under low temperature and poor light stress and relations between its and varietal tolerance [J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2009, 29(1): 105−110.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4025.2009.01.016
[21] 王水霞, 崔世茂, 付崇毅, 等. 高温逆境下嫁接辣椒耐热性的研究 [J]. 华北农学报, 2012, 27(1):155−158. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7091.2012.01.029 WANG S X, CUI S M, FU C Y, et al. Studies on the heat tolerance of grafted pepper under high temperature stress [J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2012, 27(1): 155−158.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7091.2012.01.029
[22] 周静, 徐强, 张婷. NaCl胁迫对不同品种辣椒幼苗生理生化特性的影响 [J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 43(2):120−125. ZHOU J, XU Q, ZHANG T. Effect of NaCl stress on physiological characteristics of seedlings of different pepper varieties [J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(2): 120−125.(in Chinese)
[23] 张志军, 李会珍, 乔绍俊, 等. 生物保水种衣剂对蔬菜种子发芽及幼苗生理特性的影响 [J]. 种子, 2010, 29(3):36−38. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4705.2010.03.011 ZHANG Z J, LI H Z, QIAO S J, et al. Effect of bioactive water retaining agent on seed germination and physiological features of seedling in vegetable [J]. Seed, 2010, 29(3): 36−38.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4705.2010.03.011
[24] 杨万基, 蒋欣梅, 高欢, 等. 28-高芸苔素内酯对低温弱光胁迫辣椒幼苗光合和荧光特性的影响 [J]. 南方农业学报, 2018, 49(4):741−747. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2018.04.19 YANG W J, JIANG X M, GAO H, et al. Effects of 28-homobrassinolide on photosynthetic and fluorescence characteristics of pepper seedlings under low temperature with dim light [J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2018, 49(4): 741−747.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2018.04.19
[25] 孙小玉, 刘金娜, 周蒙, 等. LA浸种对小麦种子萌发和幼苗生理特性的影响 [J]. 麦类作物学报, 2018, 38(6):742−747. DOI: 10.7606/j.issn.1009-1041.2018.06.15 SUN X Y, LIU J N, ZHOU M, et al. Effect of laxogenin on seed germination and physiological properties of wheat seedling [J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2018, 38(6): 742−747.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7606/j.issn.1009-1041.2018.06.15
[26] 王洪皓, 乔辉, 何伟锋, 等. 密度对小豆叶片发育和光合特性以及产量的影响 [J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2020, 43(1):30−38. WANG H H, QIAO H, HE W F, et al. Effect of density on leaf growth, photosynthetic character and yield of adzuki bean [J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural University, 2020, 43(1): 30−38.(in Chinese)
[27] 班兆军, 关军锋, 李莉, 等. 非生物胁迫下植物体内活性氧产生和抗氧化机制的研究概述 [J]. 中国果菜, 2012, 32(5):40−47. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1038.2012.05.023 BAN Z J, GUAN J F, LI L, et al. Overview of studies on reactive oxygen generation and antioxidant mechanism in plants under abiotic stress [J]. China Fruit Vegetable, 2012, 32(5): 40−47.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1038.2012.05.023
[28] 韦峰, 祁娟霞, 李佳梅, 等. 不同光质对辣椒种子萌发、幼苗生长及抗寒性的影响 [J]. 浙江农业学报, 2015, 27(11):1932−1938. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2015.11.12 WEI F, QI J X, LI J M, et al. Effect of different light qualities on the seed germination, seedling growth and cold resistance of pepper [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2015, 27(11): 1932−1938.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2015.11.12
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 朱兴龙,张佳旭,陈晓妍,黄旭龙,周涛,吴清华,裴瑾. 遂宁川白芷产地变迁过程中土壤质地对药材质量的影响. 世界中医药. 2024(18): 2725-2733 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 潘可可,王克磊,李斌奇,张曦文,陈发兴. 不同比例红蓝光及光照强度对金线莲生理及叶绿素荧光特性的影响. 热带作物学报. 2022(08): 1628-1635 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(9)




 下载:
下载: