Effects of Allicin and Bacillus natto Supplements on Production, Antioxidant Enzymes, Intestinal Morphology, and Cecal Microbiota of Fujian White Rabbits
-
摘要:目的 研究大蒜素、纳豆菌及其复合物对福建白兔生产性能、抗氧化活性、肠道形态和菌群的影响,筛选合适的添加剂替代饲料抗生素。方法 选取48只体重相近的40日龄福建白兔,随机分成4组,每组12只(公母各半),试验期50 d。对照组饲喂基础饲粮(A组,CK),试验在基础饲粮上分别添加200 mg·kg−1大蒜素、0.5%纳豆菌、200 mg·kg−1大蒜素+0.5%纳豆菌,设置大蒜素处理组(B组)、纳豆菌处理组(C组)和大蒜素+纳豆菌处理组(D组)。试验期间测定生产性能,试验结束测定屠宰性能、血清抗氧化酶、肠道形态和盲肠菌群结构。结果 (1)试验组的腹泻率和死亡率都低于对照组;平均日增重大蒜素+纳豆菌处理(D组)极显著高于基础饲粮处理组(A组)和大蒜素处理组(B组)(P<0.01),显著高于纳豆菌处理组(C组)(P<0.05);D组料重比最低,半净膛重极显著高于A组和B组(P<0.01);全净膛率和半净膛率各组之间差异不显著。(2)血清中GSH-Px含量,对照组均显著低于试验组,且A组和B组差异显著(P<0.05), A组和C、D组差异极显著(P<0.01)。(3)回肠隐窝深度B组显著高于C组(P<0.05);空肠隐窝深度,对照组低于试验组,且与B组差异极显著(P<0.01),与D组差异显著(P<0.05)。(4)菌群结构分析,科水平和属水平盲肠unclassified_o__Clostridiales菌科、菌属在组间差异均显著 (P<0.05),且A组显著高于D 组;属水平Ruminococcaceae_UCG-010在组间差异显著 (P<0.05),A组显著高于C 组。结论 大蒜素和纳豆菌联合使用可提高福建白兔平均日增重、半净膛重,降低料重比,增加空肠隐窝深度,减少有害菌,调整肠道菌群平衡,降低腹泻和死亡,促进生长发育。Abstract:Objective Effects of addition of allicin and/or Bacillus natto in feed on the production performance, antioxidant enzymes, intestinal morphology, and cecal microbiota of Fujian white rabbits were studied for forage supplement as an antibiotic replacement.Method Forty-eight healthy 40-day-old Fujian white rabbits with similar body weight were randomly divided into 4 groups of 12 rabbits each, half male and half female, for a 50 d feeding trial. The rabbits in the control group were fed a basal diet (Group A), while those in the treatment groups the basal diet supplemented with 200 mg·kg−1 allicin (Group B), 0.5% B. natto (Group C), and 200 mg·kg−1 allicin+0.5% B. natto (Group D). Growth of the rabbits was monitored during the trial, and at the end, the animals were slaughtered to determine the meat production, serum antioxidant enzymes, intestinal morphology, and cecum microbiota.Results (1) The rates of diarrhea occurrence and mortality of the rabbits in Group B, C, and D were lower than those of Group A. The average daily weight gain of Group D was significantly higher than that of Group A and B at P<0.01 and Group C at P<0.05. Group D had the lowest F/G among all, and significantly higher half-eviscerated weight than that of Group A or Group B (P<0.01). No significant differences were observed in the eviscerated and half-eviscerated rates among the groups. (2) On serum GSH-Px, Group A was significantly lower than Group B, C and D. The difference between group A and Group B was significant (P<0.05), while those between Group A and Group C and between Group A and Group D extremely significant (P<0.01). (3) The ileal crypt depth of Group B was significantly higher than Group C(P <0.05). Group A had a lower depth of jejunum crypt than the treatment groups and significantly different from Group B (P<0.01) and Group D (P<0.05). (4) The unclassified_o__Clostridiales significantly differed at both family and genus levels among the groups (P<0.05) with Group A being significantly higher than Group D. Whereas, at genus level, Ruminococcaceae_UCG-010 significantly differed among the groups (P<0.05), but Group A was significantly higher than Group C.Conclusion The combined use of allicin and B. natto in feed significantly increased the average daily weight gain and half-eviscerated weight, decreased the F/G, increased the depth of jejunum crypt, reduced the harmful bacteria population, balanced the cecum microbiota, mitigated diarrhea and deaths, promoted the growth and development of Fujian white rabbits.
-
Keywords:
- Fujian white rabbit /
- allicin /
- Bacillus natto /
- production performance /
- intestinal morphology /
- cecal microbiota
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】近年来,兔肉作为“三高三低”的保健肉,越来越受到人们的青睐,其消费市场逐渐拓展,市场潜力大。福建白兔属小型肉用地方兔,2014年通过了国家畜禽遗传资源专家委员会认定[1],2015年列入福建省畜禽遗传资源保护名录和中国畜禽遗传资源志,其全身披白色毛,具有适应性广、繁殖性能好、肉质优异等优点[2],是中国地方优良兔品种。与大种肉兔相比,其肌肉营养成分高(肌肉粗蛋白含量高),肉质鲜嫩(肌纤维面积小,肌内脂肪含量高)[3-4]。福建白兔耐粗饲、易饲养、价格高,近年来该品种受到农业农村部和福建省农业部门的重视,福建白兔的养殖户和养殖企业逐渐增多,养殖量不断增多,但其饲养方式主要是采取限制饲养。自由采食,幼兔消化道疾病发生率和死亡率高,适宜的家兔饲料添加剂可以让家兔自由采食的同时保证较高的成活率。【前人研究进展】大蒜素(Allicin)是以大蒜鳞茎为原料提取的产品,也可化工合成。动物饲料中使用的大蒜素一般是由合成的大蒜油为原料制成的预混料,具有清除自由基和抗氧化[5]、增强机体免疫力[6]等功能,可改善饲料的适口性、提高采食量、促进动物生长发育、提高生产性能[7]、减少动物患病率[8],倍受养殖行业的青睐。纳豆芽孢杆菌(Bacillus natto,BN),属枯草芽孢杆菌纳豆菌亚种,革兰阳性菌,只具有单层细胞外膜,是一类好氧型、内生抗逆孢子的杆状细菌,具有广谱抗菌活性[9]和极强的抗逆能力[10];可以调节肠道菌群,增强动物细胞免疫反应[11],并能生成多种蛋白酶、糖化酶、脂肪酶等,降解植物性饲料中的碳水化合物,提高饲料的转化率。陈兵等[12]研究发现日粮中添加200 mg·kg−1的纳豆芽孢杆菌可以提高肉鸡的平均日增重、日采食量。在推行无抗饲养的大环境下,纳豆菌作为益生菌既能提高动物免疫力,又不会出现耐药性等不利影响,是环境友好型饲料添加剂。纳豆菌在猪[13]、羊[14]、牛[15]上作为饲料添加剂使用的案例均有研究报道。大蒜素能抑制有害菌,且对益生菌如干酪乳杆菌有促进作用,这是大蒜既能防病治病,又能够促进食欲、帮助消化的重要原因[16]。丁酸梭菌与大蒜素同用,对青脚麻鸡具有显著的生长促进作用[17]。【本研究切入点】大蒜素和纳豆菌作为动物饲料添加剂,两者均可提高采食量、降低发病率、促进生长和改善饲养环境,目前关于二者联合使用在肉兔中的饲养效果未见报道。大蒜素既可提高食欲,又可抑制有害菌、促进有益菌(如纳豆菌)的生长,两者联合使用,可能有协同作用。【拟解决的关键问题】本试验通过研究大蒜素、纳豆菌及其复合物对福建白兔生长性能、抗氧化活性、肠道形态和菌群的影响,旨在为肉兔生产中合理开发利用无抗饲料添加剂,且为开发适用于肉兔自由采食饲喂方式的饲料提供理论参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
试验动物为健康的福建白兔(40日龄,公母各半),35日龄时购自武平县武东乡袁田村福建白兔生态养殖场,暂养5 d后开始试验。大蒜素购自潍坊加易加生物科技有限公司,大蒜素含量25%;纳豆芽孢杆菌冻干粉购自福建盛德实业有限公司,含量为3.5×108 CFU·g−1。
1.2 试验方法
试验在福建省农业科学院畜牧兽医研究所兔场基地进行。选择平均体重为(657.25±102.21)g的健康福建白兔48只,随机分为4个处理组,对照组饲喂基础饲粮(A组,CK),试验组在基础饲粮上分别添加200 mg·kg−1大蒜素、0.5%纳豆菌、200 mg·kg−1大蒜素+0.5%纳豆菌,设置大蒜素处理组(B组)、纳豆菌处理组(C组)和大蒜素+纳豆菌处理组(D组)。每组12只,饲养于仔兔代谢笼(规格60 cm×40 cm×40 cm),每笼1只。试验期为50 d。全价颗粒料饲喂,每天早晚饲喂2次,乳头式饮水器自由饮水。饲养管理与免疫程序按常规进行。全价饲粮参照NRC(1977) [18]家兔营养标准和De Blas等[19]的生长兔营养需求进行配制,基础饲粮组成及营养水平见表1。
表 1 基础饲粮组成及营养水平(干物质基础)Table 1. Composition and nutrient levels of basic diets (DM basis)项目
Items含量
Content原料 Ingredients 玉米 Corn/% 30.0 豆粕 Soybean meal/% 15.0 麸皮 Wheat bran/% 25.0 花生壳粉 Peanut shell powder/% 5.0 草粉 Grass meal/% 20.0 预混料 Premix1)/% 5.0 合计 Total/% 100.0 营养水平 Nutrient levels2) 粗蛋白质 Crude protein/% 17.0 消化能 Digestible energy/(MJ·kg−1) 10.6 粗纤维 Crude fiber/% 13.0 钙 Ca/% 1.0 磷 P/% 0.5 注:1)预混料为每千克饲粮提供:赖氨酸1 500 mg,蛋氨酸 1 500 mg,CaHPO4 15 000 mg,NaCl 5 000 mg,VA 10 000 IU,VD3 2 000 IU,VE 50 mg,VK3 2.5 mg,硫胺素5 mg,VB12 1 mg,核黄素10 mg,泛酸50 mg,烟酸20 mg,叶酸2.5 mg,氯化胆碱400 mg,Fe 100 mg,Zn 50 mg,Cu 40 mg,Mn 30 mg,I 0.5 mg,Se 0.05 mg,其余为载体补足。2)营养水平为计算值。
Note: 1) Premix provided the following per kg of diets: Lys 1 500 mg, Met 1 500 mg, CaHPO415 000 mg, NaCl 5 000 mg, VA 10 000 IU, VD3 2 000 IU, VE 50 mg, VK3 2.5 mg, thiamine 5 mg, VB12 1 mg, riboflavin 10 mg, pantothenic acid 50 mg, nicotinic acid 20 mg, folic acid 2.5 mg, choline chloride 400 mg, Fe 100 mg, Zn 50 mg, Cu 40 mg, Mn 30 mg, I 0.5 mg, Se 0.05 mg, the rest was meal carrier complement. 2) Nutrient levels were calculated.1.3 指标测定
1.3.1 生长性能测定
试验于40日龄正式开始,于90日龄结束,试验始末对试验兔空腹称重,试验期每日记录每只兔采食情况,包括每日喂料量、剩余料量及浪费料量,并观察试验期间的腹泻和死亡情况。计算仔兔的平均日增重(Average daily gain,ADG)、平均日采食量(Average daily feed intake,ADFI)及料重比(Feed/gain,F/G),计算公式为料重比=消耗饲料总量(kg)/增重总量(kg)。试验结束时,采集每只兔血样后屠宰,进行屠宰测定,测定全净膛重、半净膛重等。无菌采集盲肠内容物进行菌群测定,采集肠道组织样品用于形态学观察。
1.3.2 血清抗氧化酶的测定
丙二醛(Malondialdehyde,MDA)含量、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(Glutathion peroxidase,GSH-Px)活性和总抗氧化能力(Total antioxidant capacity, T-AOC),均采用南京建成生物工程研究所提供的试剂盒测定。
1.3.3 肠绒毛高度和隐窝深度
家兔屠宰后迅速剖开腹腔,每只家兔十二指肠、空肠和回肠的相同部位各取下一段肠管1 cm(回肠取最上端),生理盐水冲洗干净,放入10%中性甲醛中固定。石蜡包埋,连续横断切片,厚6 µm,进行常规HE染色。光镜下详细观察和比较各组肠绒毛形态结构的变化情况。每张切片挑选3个100倍视野进行拍照。拍照时尽量让组织充满整个视野,保证每张照片的背景光一致。应用Image-Pro Plus 6.0软件,每张切片选取5根完整的绒毛,分别测量绒毛高度(mm)、隐窝深度(mm);计数每个视野内绒毛和隐窝的数量,计算视野面积(mm2),求出单位面积内绒毛和隐窝的数量。
1.3.4 盲肠微生物多样性
取各组家兔盲肠食糜,迅速放置液氮中,备用。
(1) DNA 抽提和 PCR 扩增。根据 E.Z.N.A.® soil DNA kit(Omega Bio-tek, Norcross, GA, U.S.)说明书进行微生物群落总 DNA 抽提,使用1%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测DNA的提取质量,使用NanoDrop2000测定DNA 浓度和纯度;使用338F(5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3′)和806R(5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′)对16S rRNA基因V3~V4 可变区进行 PCR 扩增,扩增程序如下:95 ℃ 预变性 3 min,27 个循环(95 ℃ 变性 30 s,55 ℃ 退火 30 s,72 ℃ 延伸 30 s),然后 72 ℃ 稳定延伸 10 min,最后在4 ℃进行保存(PCR 仪:ABI GeneAmp® 9700型)。PCR反应体系为:5×TransStart FastPfu 缓冲液4 μL,2.5 mmol·L−1 dNTPs 2 μL,上游引物(5 μmol·L−1)0.8 μL,下游引物(5 μmol·L−1)0.8 μL,TransStart FastPfu DNA聚合酶0.4 μL,模板DNA 10 ng,补足至20 μL。每个样本3个重复。
(2)Illumina Miseq 测序。将同一样本的PCR产物混合后使用2%琼脂糖凝胶回收PCR产物,利用AxyPrep DNA Gel Extraction Kit(Axygen biosciences,union city,CA,USA)进行回收产物纯化,2%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,并用Quantus™ Fluorometer (Promega,USA)对回收产物进行检测定量。使用NEXTFLEX® Rapid DNA-Seq Kit进行建库:接头链接;使用磁珠筛选去除接头自连片段;利用PCR扩增进行文库模板的富集;磁珠回收PCR产物得到最终的文库。利用Illumina公司的Miseq PE300平台进行测序(上海美吉生物医药科技有限公司)[20]。
1.4 数据统计分析
采用Excel 2010 和SPSS 20.0 统计软件对数据进行处理分析,采用单因素方差分析(Oneway ANOVA)检验组间差异显著性,试验结果以平均值±标准差表示。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同添加剂对福建白兔生产性能的影响
2.1.1 对腹泻率和死亡率的影响
由表2可知,试验全期,对照A组的腹泻率明显高于试验组, B组与C组腹泻率相当, D组的腹泻率最低;且40~60日龄A组的试验兔腹泻率和死亡率最高, D组死亡率和腹泻率最低。
表 2 不同添加剂对福建白兔腹泻率和死亡率的影响Table 2. Effects of supplements on rates of diarrhea incident and mortality of Fujian white rabbits组别
Groups腹泻率 Number of diarrhea/% 死亡率 Mortality/% 平均
Average40~60 d 60~90 d 平均
Average40~60 d 60~90 d 对照A组 CK 50.00 33.33 25.00 33.33 33.33 0.00 处理B组 Treatment B 25.00 25.00 0.00 33.33 33.33 0.00 处理C组 Treatment C 25.00 25.00 0.00 25.00 16.67 8.33 处理D组 Treatment D 8.33 8.33 0.00 16.67 8.33 8.33 2.1.2 对生长性能的影响
由表3可知,各组的初始体重差异不显著,试验结束的终末体重,处理D组显著高于处理A组(P<0.05),极显著高于处理B组(P<0.01);平均日采食量处理C和D组都极显著高于处理B组(P<0.01);平均日增重处理D组均极显著高于处理A组、处理B组(P<0.01),显著高于处理C组(P<0.05);与其他组比较,料重比D组最低,但各组差异不显著。
表 3 不同添加剂对福建白兔生长性能的影响Table 3. Effect of supplements on growth performance of Fujian white rabbits组别
Groups初始体重
Original weight/g终末体重
Final weight/g平均日采食量
Average feed intake/(g·d−1)平均日增重
Average weight gain/(g·d−1)料重比
F/G处理A组 CK 667.25±78.68 1635.31±131.67 ABb 110.26±8.70 ABab 19.36±2.16 Bb 5.74±0.54 处理B组 Treatment B 659.13±86.17 1622.25±98.21 Bb 105.87±9.75 Bb 19.43±2.07 Bb 5.81±0.86 处理C组 Treatment C 690.33±83.40 1697.61±108.44 ABab 118.20±7.68 Aa 20.27±1.94 ABb 5.92±0.70 处理D组 Treatment D 618.9±112.43 1772.00±90.22 Aa 119.92±8.23 Aa 23.06±3.10 Aa 5.35±0.68 注:同列数据后字母相同或不标者表示差异不显著(P>0. 05);小写字母不同表示差异显著(P<0.05); 大写字母不同表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。表4~8同。
Note: The datas with the same or no letters in a line mean no significance (P>0. 05), the datas with different small letters indicate significance difference (P<0.05), the datas with different capital letters indicate extremely significances difference (P<0.01). Same for Table 4–8.2.1.3 对福建白兔屠宰性能的影响
由表4可知,全净膛重,处理D组均显著高于处理A组(P<0.05)和处理B组(P<0.01);半净膛重处理D组极显著高于处理A和处理B组(P<0.01),处理C组显著高于处理B组(P<0.05)。全净膛率和半净膛率各组之间差异不显著。
表 4 不同添加剂对福建白兔屠宰性能的影响Table 4. Effect of supplements on slaughter performance of Fujian white rabbits组别
Groups全净膛重
Carcass net weight/g半净膛重
Half eviscerated weight/g全净膛率
Whole net carcass rate/%半净膛率
Half-complete ratio/%对照A组 CK 799.06±65.05 ABb 880.31±68.27 Bb 0.49±0.02 0.54±0.02 处理B组Treatment B 790.63±44.17 Bb 870.56±49.53 Bb 0.49±0.02 0.54±0.02 处理C组Treatment C 835.39±47.79 ABab 928.78±52.59 ABa 0.49±0.03 0.55±0.03 处理D组Treatment D 861.65±56.93 Aa 957.8±56.53 Aa 0.49±0.02 0.54±0.02 2.2 对福建白兔血清抗氧化酶的影响
由表5可知,血清中GSH-Px含量,处理B、C、D三组都显著高于处理A组,且 B组和A组之间差异显著(P<0.05),C、D组和A组之间差异均为极显著(P<0.01)。
表 5 不同添加剂对福建白兔血清抗氧化酶的影响Table 5. Effect of supplements on serum antioxidant enzymes of Fujian white rabbits组别
Groups总抗氧化能力
T-AOC/(mmol·L−1)谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶
GSH-Px/(U·mL−1)丙二醛
MDA/(nmol·mL−1)对照A组 CK 0.59±0.08 202.03±37.00 Bb 5.23±1.14 处理B组 Treatment B 0.61±0.08 275.63±53.97 ABa 5.38±1.51 处理C组 Treatment C 0.58±0.12 311.51±49.82 Aa 4.59±2.52 处理D组 Treatment D 0.56±0.06 318.22±69.78 Aa 4.43±1.29 2.3 对福建白兔肠道形态的影响
由表6~7可知,不同组别的肠道绒毛长度和数量差异不显著;回肠隐窝深度处理B组显著高于处理C组(P<0.05);空肠隐窝深度,处理B、C、D组高于处理A组,且B组与A组差异极显著(P<0.01),D组与A组差异显著(P<0.05),B组显著高于C组(P<0.05)。十二指肠隐窝深度不同组别之间差异不显著。回肠隐窝数量A组显著高于组C和D组(P<0.05),其他差异不显著。不同组织切片见图1。
表 6 不同添加剂对福建白兔肠道绒毛长度和隐窝深度的影响Table 6. Effects of supplements on intestinal villus length and crypt depth of Fujian white rabbits(单位:mm) 组别
Groups绒毛长度 Villus length 隐窝深度 Crypt depth 十二指肠
Duodenum回肠
Ileal空肠
Jejunum十二指肠
Duodenum回肠
Ileal空肠
Jejunum对照A组 CK 0.68±0.07 0.54±0.13 0.51±0.08 0.13±0.02 0.10±0.02 Aab 0.10±0.01 Bc 处理B组 Treatment B 0.62±0.13 0.49±0.09 0.49±0.05 0.13±0.05 0.12±0.04 Aa 0.13±0.03 Aa 处理C组 Treatment C 0.65±0.07 0.57±0.07 0.53±0.05 0.10±0.02 0.09±0.01 Ab 0.11±0.02 ABb 处理D组 Treatment D 0.62±0.13 0.52±0.06 0.52±0.07 0.12±0.03 0.10±0.02 Aab 0.12±0.03 ABab 表 7 不同添加剂对福建白兔肠道绒毛数量和隐窝数量的影响Table 7. Effects of supplements on intestinal villi population and crypts of Fujian white rabbits(单位:根·mm−2) 组别
Groups绒毛数量 Villus number 隐窝数量 Crypt number 十二指肠
Duodenum回肠
Ileal空肠
Jejunum十二指肠
Duodenum回肠
Ileal空肠
Jejunum对照A组 CK 4.15±0.88 7.62±1.74 7.44±2.68 13.08±4.03 18.01±7.88Aa 23.5±17.38 处理B组 Treatment B 4.75±1.17 7.70±0.96 6.73±1.02 18.01±6.76 17.34±4.75Aab 28.94±27.38 处理C组 Treatment C 4.58±1.05 7.61±1.05 6.28±0.60 14.68±6.50 12.19±3.48Ab 16.54±6.34 处理D组 Treatment D 4.75±0.95 7.41±1.87 6.16±0.76 14.29±4.78 13.75±2.62Ab 14.32±4.48 2.4 对福建白兔盲肠微生物区系的影响
2.4.1 不同添加剂对福建白兔盲肠菌群 Alpha 多样性分析
肠道微生物测序,对不同组别肠道内容物进行测序,共获得有效序列数为1 702 885 条,每条序列平均长度为408.64 bp,以97%的序列一致性。由表8可知,处理A组的群落多样性Shannon指数显著高于C组(P<0.05),其他差异不显著。
表 8 试验各组测序结果及Alpha多样性分析Table 8. Sequence and alpha diversity of treatment groups项目
Item对照A组
CK处理B组
Treatment B处理C组
Treatment C处理D组
Treatment D分类单元数量 OUT/个 648.00±49.88 571.25±90.6 578.56±144.44 575.20±147.72 覆盖率 Coverage/% 99.58±0.03 99.63±0.05 99.60±0.11 99.62±0.09 Shannon指数 Shannon index 4.82±0.18 Aa 4.59±0.36 Aab 4.53±0.33 Ab 4.54±0.52 Aab Simpson指数 Simpson index 0.02±0.01 0.03±0.02 0.04±0.02 0.03±0.02 ACE指数 ACE index 742.16±54.21 657.55±98.67 673.62±165.4 668.17±150.36 Chaol指数 Chaol index 751.06±49.72 668.86±98.81 689.77±171.52 673.87±169.42 注:同行数据后字母相同或不标者表示差异不显著(P>0. 05);小写字母不同表示差异显著(P<0.05);大写字母不同表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。
Note: The datas with the same or no letters indicate no significance in a row(P>0.05), the datas with different small letters indicate significance difference(P<0.05), the datas with different capital letters indicate extremely significances difference(P<0.01).2.4.2 不同组别福建白兔盲肠菌群结构分析
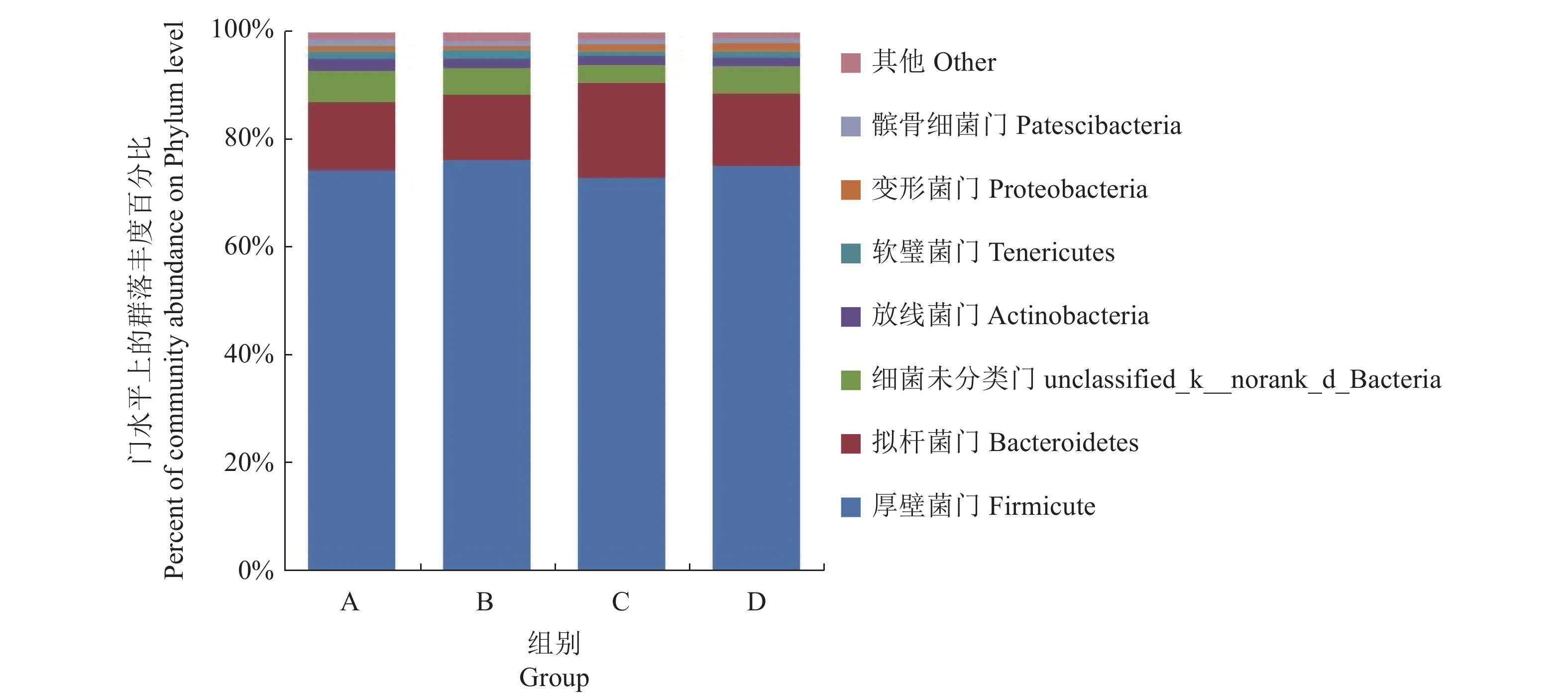
(1)不同组别福建白兔盲肠菌群门水平的结构分析。不同组别福建白兔盲肠菌群由厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)、拟杆菌门 (Bacteroidetes)、细菌未分类门(Unclassified_k__norank_d__Bacteria)、放线菌门(Actinobacteria);软壁菌门(Tenericutes);变形菌门(Proteobacteria);髌骨细菌门(Patescibacteria)等组成,其中前 3 种菌门是不同组别中菌群的主要组成部分,分别占73.02%、12.03%、2.06%以上(图2)。
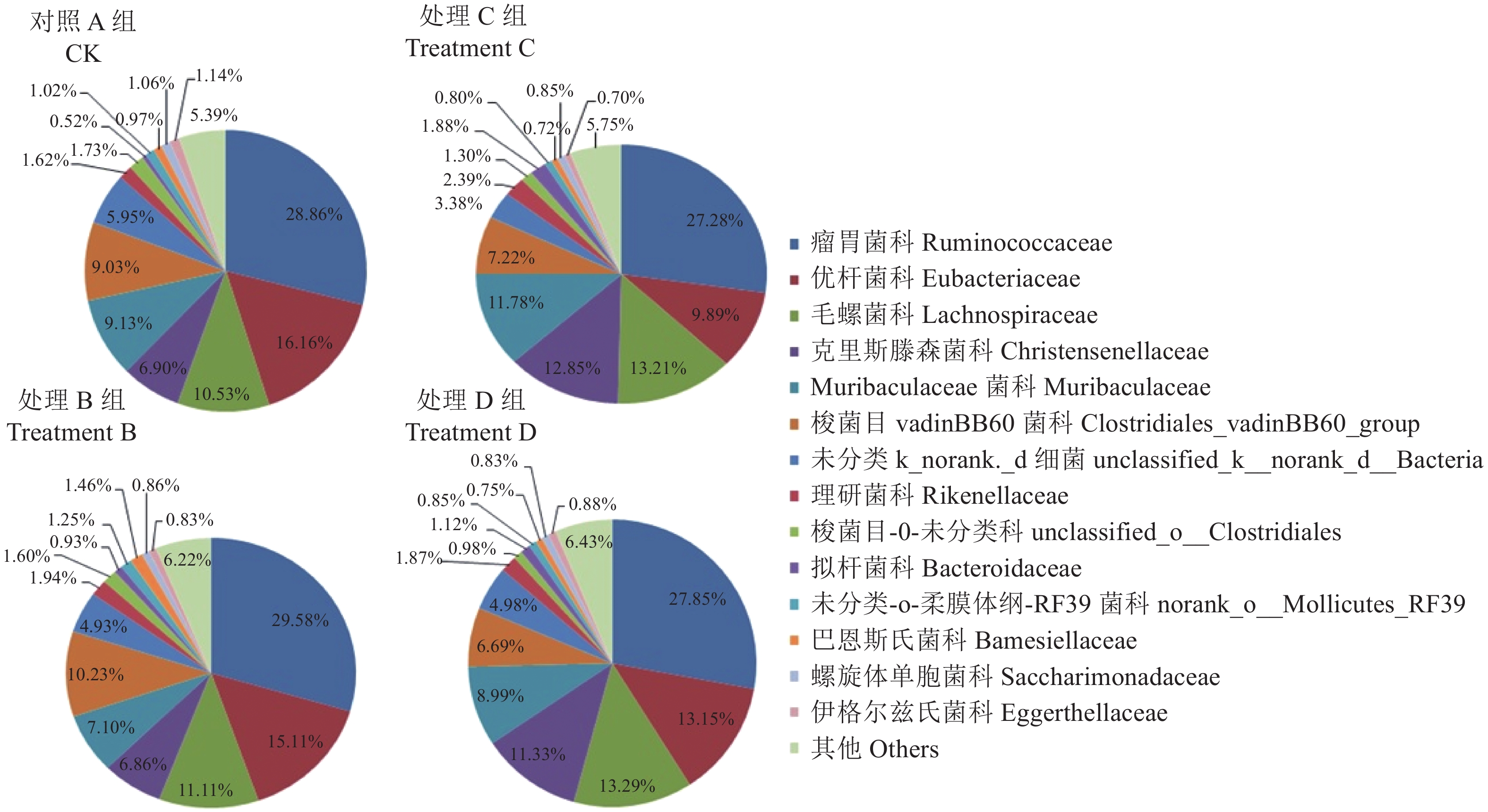
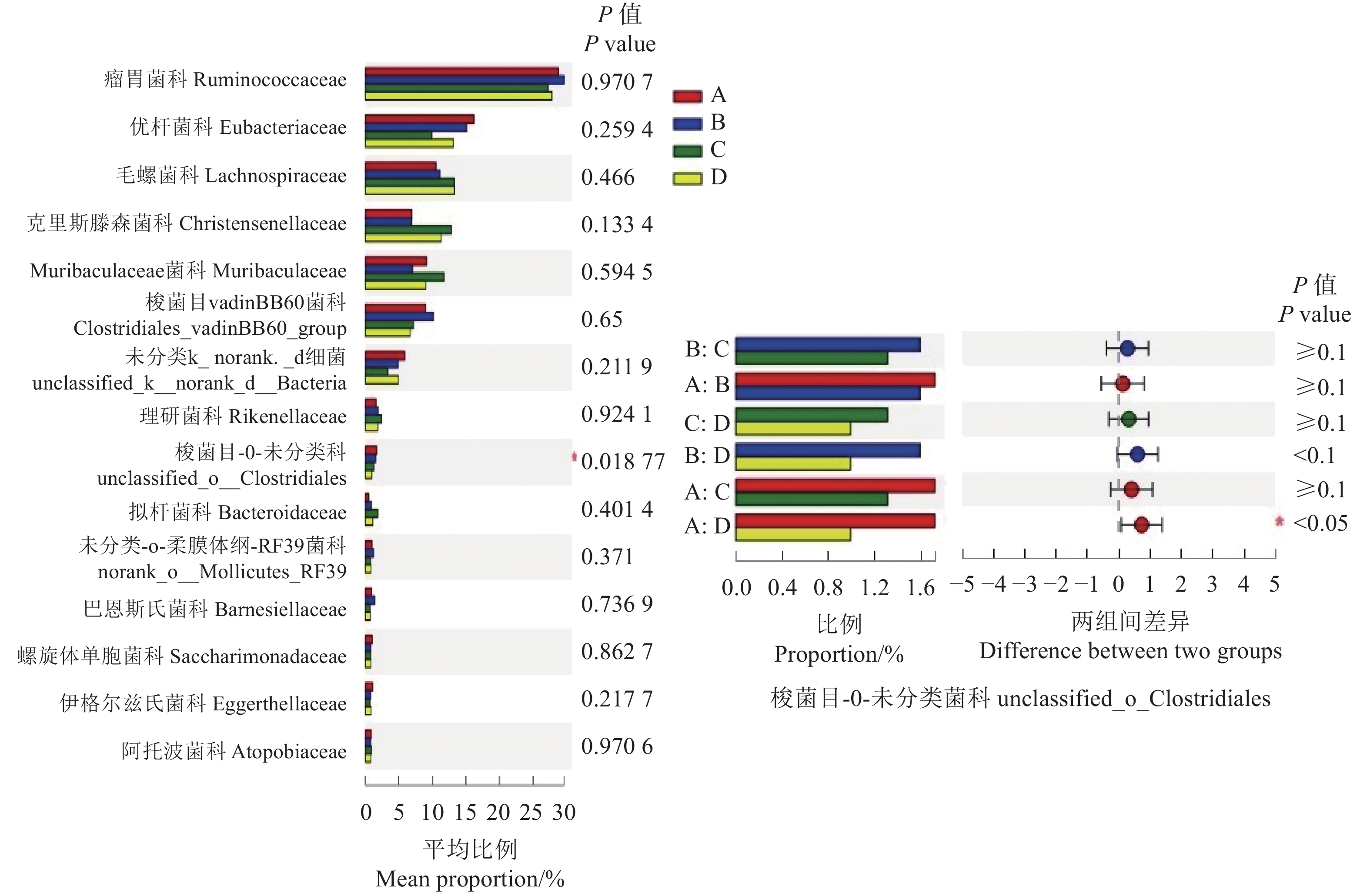
(2)不同组别福建白兔盲肠菌群科水平的结构分析。不同组别福建白兔盲肠菌群在科水平以瘤胃菌科Ruminococcaceae、优杆菌科Eubacteriaceae、毛螺菌科Lachnospiraceae、克里斯滕森菌科 Christensenellaceae等为主,分别占27.28%、13.15%、10.53%、6.86%以上(图3)。肠道菌梭菌目-0-未分类(Unclassified_ o_ Clostridiales)在组间差异显著(P<0.05),A组显著高于D 组,其他差异不显著(图4)。
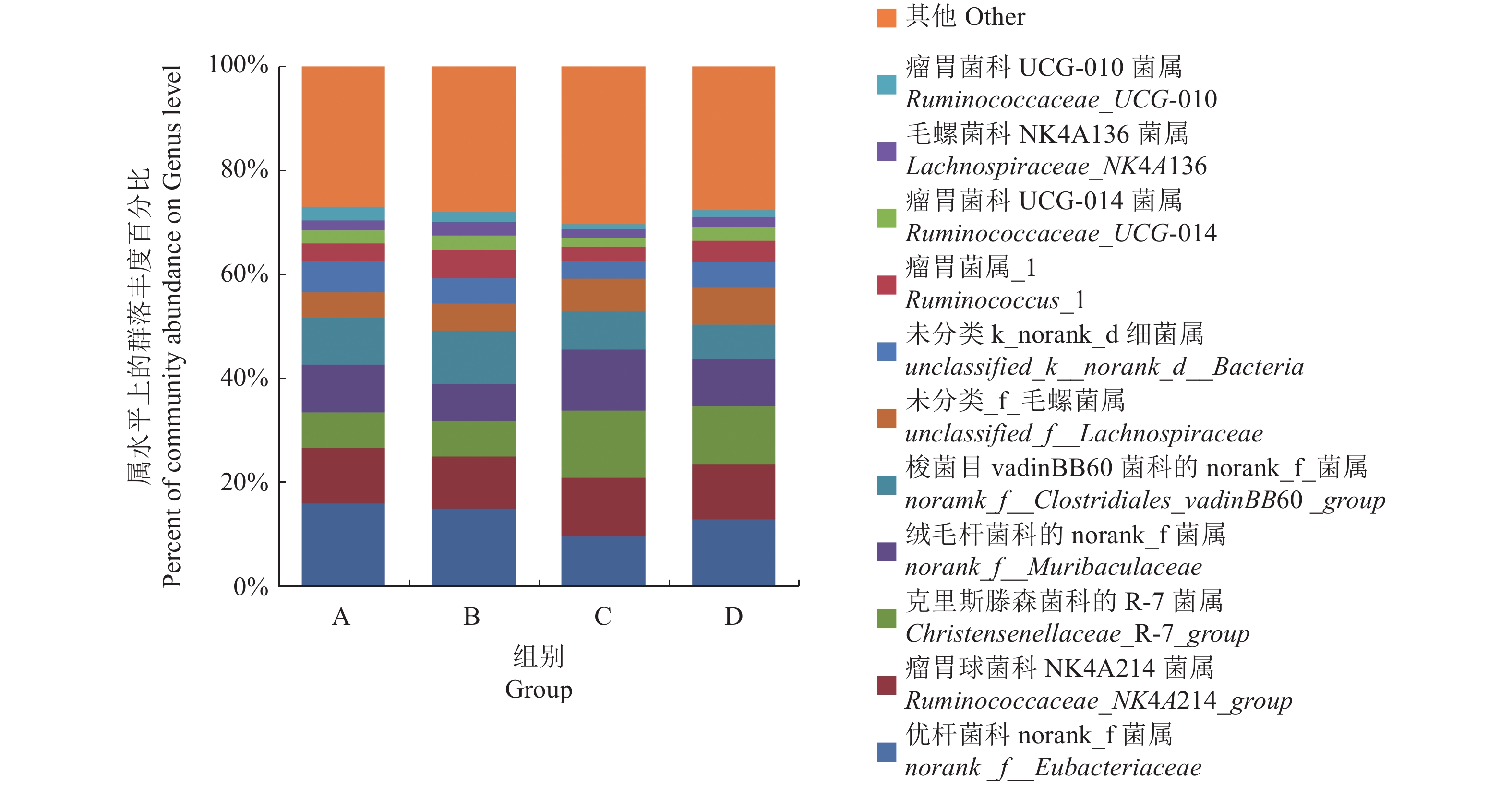
(3)不同组别福建白兔盲肠菌群属水平的结构分析。不同组别福建白兔盲肠菌群在属水平以优杆菌科的norank_f(norank_f__Eubacteriaceae)、瘤胃球菌科的NK4A214菌属(Ruminococcaceae_NK4A214_group)、克里斯滕森菌科的R-7菌属(Christensenellaceae_R-7_group)、绒毛杆菌科的norank_f__菌属 (norank_f__Muribaculaceae)和梭菌目vadinBB60菌科的norank_f__菌属(norank_f__Clostridiales_vadinBB60_group)为主,分别占9.86%、10.05%、6.83%、7.10%、6.69%以上(图5)。Ruminococcaceae_UCG-010在组间差异显著 (P<0.05) ,A组显著高于C 组;unclassified_o__Clostridiales在组间差异显著 (P<0.05) ,A组显著高于D 组(图6)。
3. 讨论
兔是单胃草食动物,断奶仔兔自由采食,容易发生消化道紊乱,造成腹泻甚至死亡[21]。本试验各组的腹泻率和死亡率较高,这是由于采用自由采食的饲喂方式。处理B组与对照A组相比,腹泻率和死亡率明显降低,这与Marchese等[8]研究表明大蒜素可以减少发病率以及降低死亡率的结果一致。何晓政等[17]研究显示大蒜素和丁酸梭菌联用可以促进青脚麻鸡的生长。大蒜素可提高免疫力[6],纳豆芽孢杆菌具有调节肠道和提高机体免疫力[11]的功效。本试验全期,对照组的腹泻率明显高于试验组,大蒜素或纳豆菌处理组腹泻情况相当,大蒜素和纳豆菌复合处理组(D组)的腹泻率最低;且40~60日龄阶段对照A组腹泻和死亡数最高,D组最低,说明大蒜素和纳豆芽孢杆菌有降低死亡和腹泻的作用,而且两者一起使用效果更佳,其原因可能是处理D组肠道有害菌unclassified_ o_ Clostridial显著低于对照A组,这也验证了处理D组试验兔的平均日增重和料重比均高于其他组别。
谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-Px)是体内重要的自由基捕获酶之一,不仅具有清除自由基和衍生物的作用,还可减少脂质过氧化物的形成,增强机体抗氧化损伤的能力[22]。肠绒毛长短直接影响着动物的生长发育,绒毛长度增加可以增大小肠吸收营养物质的面积。肠隐窝是绒毛根部上皮陷入固有层形成的管状腺,隐窝深度反映上皮细胞的生产率,上皮细胞从隐窝基部向绒毛端迁移、分化,形成具有吸收功能的绒毛细胞[23]。肠道微生物对宿主的营养代谢、生长、免疫等起着不可忽视的重要作用。而肠道微生物的变化又受到宿主的品种、日粮、所处环境,特别是胃肠道环境的影响,因此宿主与其肠道菌群之间建立了一种共生关系[24]。本试验发现,处理组血清中的GSH-Px含量显著高于对照A组,这与大蒜素具有清除自由基和抗氧化[5]的功效有关。空肠隐窝深度对照A组低于处理组,这可能是由大蒜素可促进食欲且纳豆菌有促进益生菌生长的作用所致。
16S rRNA 的高通量测序,多样性分析得出对照组与试验组肠道菌群菌落丰富度无明显差异。菌群结构分析,以厚壁菌门、拟杆菌门为主,两者占85.05%以上,门水平差异不显著;不同组别福建白兔盲肠菌群在科水平以瘤胃菌科、优杆菌科、毛螺菌科、克里斯滕森菌科等为主,分别占27.28%、13.15%、10.53%、6.86%以上;不同组别福建白兔盲肠菌群在属水平以优杆菌科的norank_f属、瘤胃球菌科的NK4A214菌属、克里斯滕森菌科的R-7菌属、绒毛杆菌科的norank_f菌属为主,分别占9.86%、10.05%、6.83%、7.10%以上,对照组Ruminococcaceae_UCG-010显著高于纳豆菌处理(P<0.05)。有报道显示菌属Ruminococcaceae_UCG-010可能影响血糖的升高[25] ;He等[26]的研究表明番茄籽油可以降低小鼠肠道unclassified_o__Clostridiales菌属,进而改善小鼠的高血脂症。对照组unclassified_o__Clostridiales相对丰度显著高于大蒜素和纳豆菌复合处理组(P<0.05),说明大蒜素和纳豆菌联合使用可调节肠道菌群,改善血脂。
-
表 1 基础饲粮组成及营养水平(干物质基础)
Table 1 Composition and nutrient levels of basic diets (DM basis)
项目
Items含量
Content原料 Ingredients 玉米 Corn/% 30.0 豆粕 Soybean meal/% 15.0 麸皮 Wheat bran/% 25.0 花生壳粉 Peanut shell powder/% 5.0 草粉 Grass meal/% 20.0 预混料 Premix1)/% 5.0 合计 Total/% 100.0 营养水平 Nutrient levels2) 粗蛋白质 Crude protein/% 17.0 消化能 Digestible energy/(MJ·kg−1) 10.6 粗纤维 Crude fiber/% 13.0 钙 Ca/% 1.0 磷 P/% 0.5 注:1)预混料为每千克饲粮提供:赖氨酸1 500 mg,蛋氨酸 1 500 mg,CaHPO4 15 000 mg,NaCl 5 000 mg,VA 10 000 IU,VD3 2 000 IU,VE 50 mg,VK3 2.5 mg,硫胺素5 mg,VB12 1 mg,核黄素10 mg,泛酸50 mg,烟酸20 mg,叶酸2.5 mg,氯化胆碱400 mg,Fe 100 mg,Zn 50 mg,Cu 40 mg,Mn 30 mg,I 0.5 mg,Se 0.05 mg,其余为载体补足。2)营养水平为计算值。
Note: 1) Premix provided the following per kg of diets: Lys 1 500 mg, Met 1 500 mg, CaHPO415 000 mg, NaCl 5 000 mg, VA 10 000 IU, VD3 2 000 IU, VE 50 mg, VK3 2.5 mg, thiamine 5 mg, VB12 1 mg, riboflavin 10 mg, pantothenic acid 50 mg, nicotinic acid 20 mg, folic acid 2.5 mg, choline chloride 400 mg, Fe 100 mg, Zn 50 mg, Cu 40 mg, Mn 30 mg, I 0.5 mg, Se 0.05 mg, the rest was meal carrier complement. 2) Nutrient levels were calculated.表 2 不同添加剂对福建白兔腹泻率和死亡率的影响
Table 2 Effects of supplements on rates of diarrhea incident and mortality of Fujian white rabbits
组别
Groups腹泻率 Number of diarrhea/% 死亡率 Mortality/% 平均
Average40~60 d 60~90 d 平均
Average40~60 d 60~90 d 对照A组 CK 50.00 33.33 25.00 33.33 33.33 0.00 处理B组 Treatment B 25.00 25.00 0.00 33.33 33.33 0.00 处理C组 Treatment C 25.00 25.00 0.00 25.00 16.67 8.33 处理D组 Treatment D 8.33 8.33 0.00 16.67 8.33 8.33 表 3 不同添加剂对福建白兔生长性能的影响
Table 3 Effect of supplements on growth performance of Fujian white rabbits
组别
Groups初始体重
Original weight/g终末体重
Final weight/g平均日采食量
Average feed intake/(g·d−1)平均日增重
Average weight gain/(g·d−1)料重比
F/G处理A组 CK 667.25±78.68 1635.31±131.67 ABb 110.26±8.70 ABab 19.36±2.16 Bb 5.74±0.54 处理B组 Treatment B 659.13±86.17 1622.25±98.21 Bb 105.87±9.75 Bb 19.43±2.07 Bb 5.81±0.86 处理C组 Treatment C 690.33±83.40 1697.61±108.44 ABab 118.20±7.68 Aa 20.27±1.94 ABb 5.92±0.70 处理D组 Treatment D 618.9±112.43 1772.00±90.22 Aa 119.92±8.23 Aa 23.06±3.10 Aa 5.35±0.68 注:同列数据后字母相同或不标者表示差异不显著(P>0. 05);小写字母不同表示差异显著(P<0.05); 大写字母不同表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。表4~8同。
Note: The datas with the same or no letters in a line mean no significance (P>0. 05), the datas with different small letters indicate significance difference (P<0.05), the datas with different capital letters indicate extremely significances difference (P<0.01). Same for Table 4–8.表 4 不同添加剂对福建白兔屠宰性能的影响
Table 4 Effect of supplements on slaughter performance of Fujian white rabbits
组别
Groups全净膛重
Carcass net weight/g半净膛重
Half eviscerated weight/g全净膛率
Whole net carcass rate/%半净膛率
Half-complete ratio/%对照A组 CK 799.06±65.05 ABb 880.31±68.27 Bb 0.49±0.02 0.54±0.02 处理B组Treatment B 790.63±44.17 Bb 870.56±49.53 Bb 0.49±0.02 0.54±0.02 处理C组Treatment C 835.39±47.79 ABab 928.78±52.59 ABa 0.49±0.03 0.55±0.03 处理D组Treatment D 861.65±56.93 Aa 957.8±56.53 Aa 0.49±0.02 0.54±0.02 表 5 不同添加剂对福建白兔血清抗氧化酶的影响
Table 5 Effect of supplements on serum antioxidant enzymes of Fujian white rabbits
组别
Groups总抗氧化能力
T-AOC/(mmol·L−1)谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶
GSH-Px/(U·mL−1)丙二醛
MDA/(nmol·mL−1)对照A组 CK 0.59±0.08 202.03±37.00 Bb 5.23±1.14 处理B组 Treatment B 0.61±0.08 275.63±53.97 ABa 5.38±1.51 处理C组 Treatment C 0.58±0.12 311.51±49.82 Aa 4.59±2.52 处理D组 Treatment D 0.56±0.06 318.22±69.78 Aa 4.43±1.29 表 6 不同添加剂对福建白兔肠道绒毛长度和隐窝深度的影响
Table 6 Effects of supplements on intestinal villus length and crypt depth of Fujian white rabbits
(单位:mm) 组别
Groups绒毛长度 Villus length 隐窝深度 Crypt depth 十二指肠
Duodenum回肠
Ileal空肠
Jejunum十二指肠
Duodenum回肠
Ileal空肠
Jejunum对照A组 CK 0.68±0.07 0.54±0.13 0.51±0.08 0.13±0.02 0.10±0.02 Aab 0.10±0.01 Bc 处理B组 Treatment B 0.62±0.13 0.49±0.09 0.49±0.05 0.13±0.05 0.12±0.04 Aa 0.13±0.03 Aa 处理C组 Treatment C 0.65±0.07 0.57±0.07 0.53±0.05 0.10±0.02 0.09±0.01 Ab 0.11±0.02 ABb 处理D组 Treatment D 0.62±0.13 0.52±0.06 0.52±0.07 0.12±0.03 0.10±0.02 Aab 0.12±0.03 ABab 表 7 不同添加剂对福建白兔肠道绒毛数量和隐窝数量的影响
Table 7 Effects of supplements on intestinal villi population and crypts of Fujian white rabbits
(单位:根·mm−2) 组别
Groups绒毛数量 Villus number 隐窝数量 Crypt number 十二指肠
Duodenum回肠
Ileal空肠
Jejunum十二指肠
Duodenum回肠
Ileal空肠
Jejunum对照A组 CK 4.15±0.88 7.62±1.74 7.44±2.68 13.08±4.03 18.01±7.88Aa 23.5±17.38 处理B组 Treatment B 4.75±1.17 7.70±0.96 6.73±1.02 18.01±6.76 17.34±4.75Aab 28.94±27.38 处理C组 Treatment C 4.58±1.05 7.61±1.05 6.28±0.60 14.68±6.50 12.19±3.48Ab 16.54±6.34 处理D组 Treatment D 4.75±0.95 7.41±1.87 6.16±0.76 14.29±4.78 13.75±2.62Ab 14.32±4.48 表 8 试验各组测序结果及Alpha多样性分析
Table 8 Sequence and alpha diversity of treatment groups
项目
Item对照A组
CK处理B组
Treatment B处理C组
Treatment C处理D组
Treatment D分类单元数量 OUT/个 648.00±49.88 571.25±90.6 578.56±144.44 575.20±147.72 覆盖率 Coverage/% 99.58±0.03 99.63±0.05 99.60±0.11 99.62±0.09 Shannon指数 Shannon index 4.82±0.18 Aa 4.59±0.36 Aab 4.53±0.33 Ab 4.54±0.52 Aab Simpson指数 Simpson index 0.02±0.01 0.03±0.02 0.04±0.02 0.03±0.02 ACE指数 ACE index 742.16±54.21 657.55±98.67 673.62±165.4 668.17±150.36 Chaol指数 Chaol index 751.06±49.72 668.86±98.81 689.77±171.52 673.87±169.42 注:同行数据后字母相同或不标者表示差异不显著(P>0. 05);小写字母不同表示差异显著(P<0.05);大写字母不同表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。
Note: The datas with the same or no letters indicate no significance in a row(P>0.05), the datas with different small letters indicate significance difference(P<0.05), the datas with different capital letters indicate extremely significances difference(P<0.01). -
[1] 陈冬金, 陈岩锋, 孙世坤, 等. 福建白兔非特异性抗病特性研究 [J]. 中国草食动物科学, 2015, 35(6):34−37. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-3887.2015.06.011 CHEN D J, CHEN Y F, SUN S K, et al. Study on general resistance characteristics on Fujian white rabbits [J]. China Herbivore Science, 2015, 35(6): 34−37.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-3887.2015.06.011
[2] 陈冬金, 桑雷, 孙世坤, 等. 福建白兔与新西兰白兔生长和生化指标比较 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2019, 34(4):433−437. CHEN D J, SANG L, SUN S K, et al. Growth and biochemistry of white rabbits from Fujian and new Zealand [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 34(4): 433−437.(in Chinese)
[3] 陈岩锋, 陈冬金, 孙世坤, 等. 福建白兔肌肉营养成分分析与评价 [J]. 家畜生态学报, 2013, 34(5):75−79. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1182.2013.05.016 CHEN Y F, CHEN D J, SUN S K, et al. Analysis and evaluation of nutritional components of Fujian white rabbit muscle [J]. Acta Ecologiae Animalis Domastici, 2013, 34(5): 75−79.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1182.2013.05.016
[4] 桑雷, 王锦祥, 孙世坤, 等. 闽西地方肉兔与新西兰兔屠宰和肉质性状研究 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2018, 33(9):888−892. SANG L, WANG J X, SUN S K, et al. Carcass characteristics and meat quality of local breeds and new Zealand white rabbits [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 33(9): 888−892.(in Chinese)
[5] ICHIKAWA M, YOSHIDA J, IDE N, et al. Tetrahydro-beta-carboline derivatives in aged garlic extract show antioxidant properties [J]. The Journal of Nutrition, 2006, 136(3): 726S−731S. DOI: 10.1093/jn/136.3.726S
[6] 王飞, 章生根, 李勇. 大蒜素对肉鸡生产性能和免疫机能的影响 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2013, 40(36):17608−17610. WANG F, ZHANG S G, LI Y. Effects of allicin on performance and immune function of broilers [J]. Journal of Anhui Agriculture Science, 2013, 40(36): 17608−17610.(in Chinese)
[7] 黄瑞华, 王建辉, 陈雯, 等. 大蒜素对断奶仔猪生长发育及其周围环境的影响 [J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2002, 34(8):1−3. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-5130.2002.08.001 HUANG R H, WANG J H, CHEN W, et al. Effects of garlicin on the growth performance of weaned piglets and on the surroundings [J]. Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2002, 34(8): 1−3.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-5130.2002.08.001
[8] MARCHESE A, BARBIERI R, SANCHES-SILVA A, et al. Antifungal and antibacterial activities of allicin: A review [J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2016, 52: 49−56.
[9] 吉美萍, 肖志婷, 那日, 等. 纳豆芽孢杆菌的相关研究进展 [J]. 河南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 44(5):83−93. JI M P, XIAO Z T, NA R, et al. Related progress of research of Bacillus natto [J]. Journal of Henan Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(5): 83−93.(in Chinese)
[10] 董尚智, 陈远凤, 黄燕华, 等. 纳豆芽孢杆菌的饲料学特性研究 [J]. 动物营养学报, 2009, 21(3):371−378. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2009.03.015 DONG S Z, CHEN Y F, HUANG Y H, et al. Research on feed characteristics of Bacillus natto [J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2009, 21(3): 371−378.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2009.03.015
[11] 周国勤, 杜宣, 吴伟. 纳豆芽孢杆菌对鱼类非特异性免疫功能的影响 [J]. 水利渔业, 2006, 27(1):101−103. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1278.2006.01.044 ZHOU G Q, DU X, WU W. Effects of Bacillus natto on non-specific immune function in fish [J]. Reservoir Fisheries, 2006, 27(1): 101−103.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1278.2006.01.044
[12] 陈兵, 何世山, 朱凤香, 等. 纳豆芽孢杆菌剂对AA鸡生产性能和十二指肠消化酶的影响 [J]. 浙江农业学报, 2003, 15(5):289−292. CHEN B, HE S S, ZHU F X, et al. Effects of Bacillus natto sawamura preparation on growth capability and duodenum digestive enzyme of AA broilers [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2003, 15(5): 289−292.(in Chinese)
[13] 盛清凯, 姜殿文, 刘艳艳, 等. 日粮中纳豆芽孢杆菌对体外猪粪发酵液中臭气及微生物的影响 [J]. 家畜生态学报, 2014, 35(10):36−40. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1182.2014.10.007 SHENG Q K, JIANG D W, LIU Y Y, et al. Effect of Bacillus natto in diet on odors and microbes in pig manure fermentation broths in vitro [J]. Acta Ecologiae Animalis Domastici, 2014, 35(10): 36−40.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1182.2014.10.007
[14] 张俊瑜, 王连群, 王承敏, 等. 纳豆芽孢杆菌对绵羊生长性能、消化性能和血清生化指标的影响 [J]. 动物营养学报, 2019, 31(6):2666−2671. ZHANG J Y, WANG L Q, WANG C M, et al. Effects of Bacillus subtilis natto on growth performance, digestive performance and serum biochemical indexes of sheep [J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2019, 31(6): 2666−2671.(in Chinese)
[15] 赵会利, 曹玉凤, 高艳霞, 等. 纳豆芽孢杆菌对断奶犊牛生长性能和血液生化指标的影响 [J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2013, 49(17):66−69. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7033.2013.17.016 ZHAO H L, CAO Y F, GAO Y X, et al. Effects of Bacillus natto on growth performance and blood biochemical indices of weaned calves [J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2013, 49(17): 66−69.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7033.2013.17.016
[16] 杨佳栋, 魏凤菊. 大蒜素的功能与处理方法 [J]. 动物科学与动物医学, 2004, 21(5):50−51. YANG J D, WEI F J. Function and treatment of allicin [J]. Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2004, 21(5): 50−51.(in Chinese)
[17] 何晓政, 王晓丽. 大蒜素与丁酸梭菌联用对青脚麻鸡生长性能的影响 [J]. 养禽与禽病防治, 2021(1):14−16. HE X Z, WANG X L. Effects of allicin combined with Clostridium butyricum on growth performance of Qingojiao chicken [J]. Poultry Husbandry and Disease Control, 2021(1): 14−16.(in Chinese)
[18] NRC. Nutrient requirements of rabbits[M]. Washington, D. C. : National Academies Press, 1977.
[19] DE BLAS C, WISEMAN J. Nutrition of the rabbit[M]. Wallingford: CABI, 2010.
[20] ZHENG P, WU J, ZHANG H P, et al. The gut microbiome modulates gut–brain axis glycerophospholipid metabolism in a region-specific manner in a nonhuman primate model of depression [J]. Molecular Psychiatry, 2021, 26(6): 2380−2392. DOI: 10.1038/s41380-020-0744-2
[21] DE BLAS J C. Nutritional impact on health and performance in intensively reared rabbits [J]. Animal, 2013, 7: 102−111. DOI: 10.1017/S1751731112000213
[22] 吴玉臣, 郭爽, 阴正兴, 等. 复方中药对肉鸡免疫功能和抗氧化功能的影响研究 [J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2011, 38(1):206−209. WU Y C, GUO S, YIN Z X, et al. Effect of one dose Chinese traditional medicine on immunity and antioxidant activity in broile [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2011, 38(1): 206−209.(in Chinese)
[23] 刘秋东, 张中文, 刘凤华, 等. 复方白头翁胶囊对腹泻犬小肠绒毛长度和隐窝深度的影响 [J]. 北京农学院学报, 2011, 26(3):38−40. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3186.2011.03.011 LIU Q D, ZHANG Z W, LIU F H, et al. Effects of herbal medicine on villus height and crypt depth in small intestine of canine [J]. Journal of Beijing University of Agriculture, 2011, 26(3): 38−40.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3186.2011.03.011
[24] WANG Y, YI L, ZHAO M L, et al. Effects of zinc-methionine on growth performance, intestinal flora and immune function in pigeon squabs [J]. British Poultry Science, 2014, 55(3): 403−408. DOI: 10.1080/00071668.2014.919375
[25] ZHANG Q, XIAO X H, LI M, et al. Vildagliptin increases butyrate-producing bacteria in the gut of diabetic rats [J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(10): e0184735. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184735
[26] HE W S, LI L L, RUI J X, et al. Tomato seed oil attenuates hyperlipidemia and modulates gut microbiota in C57BL/6J mice [J]. Food & Function, 2020, 11(5): 4275−4290.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 付红蕾,张朋朋,于新海. 大蒜素对奶牛泌乳性能、乳品质及抗氧化功能的影响. 饲料研究. 2024(03): 14-18 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 何玉琴,陈冬金,姚浪群,许卫华,曹翀,林标声. 乳化植物甾醇对福建白兔生长性能、肠道形态及盲肠菌群与代谢物的影响. 动物营养学报. 2024(05): 3231-3246 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张超帅,李绍钰. 纳豆芽孢杆菌的生物学功能和在畜禽生产中的应用. 饲料研究. 2024(20): 151-155 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王丁,徐彬,席燕燕,王改利,付趁,孙全友,李绍钰. 纳豆芽孢杆菌对肉仔鸡生长性能、免疫功能及肠道健康的影响. 饲料研究. 2023(10): 34-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 陈冬金,孙世坤,王锦祥,桑雷,陈岩锋,高承芳,谢喜平. 限饲对福建白兔生长性能、屠宰性能、肉品质、血清免疫和脂类指标、肠道形态及盲肠菌群的影响. 动物营养学报. 2022(09): 6043-6055 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 韩松林,安才让吉. 大蒜素生物学功能及其在畜禽养殖中的应用研究进展. 饲料研究. 2022(20): 157-159 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(6)




 下载:
下载: