Pathogen Identification and Fungicide Selection for Leaf Spot Disease on Plectranthus scutellarioides in Fujian
-
摘要:目的 明确福建省彩叶草(Plectranthus scutellarioides)叶部病害的病原种类,筛选可用于病害防控的化学药剂。方法 采用常规组织分离法获得病原菌株并进行柯赫氏法则验证,结合形态学与分子生物学(ITS与LSU序列)对分离菌株进行鉴定,采用生长速率法测定6种杀菌剂对该病原菌的室内毒力。结果 用分离菌株ZZCYC1706分生孢子接种彩叶草,侵染叶片症状与田间症状相似;形态特征及ITS和LSU多基因序列分析表明,该病原菌为链格孢(Alternaria alternata)。供试6种药剂室内毒力测定结果显示,96%啶菌恶唑抑菌效果最好,其EC50为0.621 μg·mL−1,其次为98%异菌脲和95%嘧霉胺,EC50分别为1.155 、5.258 μg·mL−1;而96.4%克菌丹效果较差,EC50值最高,为89.010 μg·mL−1。结论 福建漳州彩叶草叶斑病病原菌鉴定为链格孢(A. alternata),该发现为国内首次报道。啶菌恶唑、异菌脲和嘧霉胺对该病原菌的毒力较高,并分属不同药剂类型,可用于链格孢引起叶斑病的防治。Abstract:Objective Identification of the leaf spot pathogen on Plectranthus scutellarioides in Fujian and screening fungicides for effective disease prevention and control were conducted.Method A causative pathogen was isolated from the diseased tissues, and the species verified by Koch’s rule, morphological observations under a microscope, and molecular ITS and LSU sequence analyses. An in vitro toxicity test on 6 commercially available fungicides was performed on the pathogen to determine their efficacy.Result The coleus leaves inoculated with the conidia of the isolated ZZCYC1706 produced same symptoms as those observed on the diseased plants in the field. The ITS and LSU sequences of ZZCYC1706 suggested it be Alternaria alternata. The toxicity test showed, among the 6 fungicides, 96% pyrisoxazole to be most effective in inhibiting the pathogenic growth with the lowest EC50 of 0.621 μg·mL−1. It was followed by 98% iprodione with an EC50 at 1.155 μg·mL−1 , 95% pyrimethanil at 5.258 μg·mL−1, and 96.4% captan, which was the least effective, at 89.010 μg·mL−1.Conclusion The pathogen of the leaf spot disease on P. scutellarioides in Fujian province was identified as A. alternata, which was the first reported in China. The fungicides, pyrisoxazole, iprodione, and pyrimethanil, were shown in the laboratory effective in inhibiting the growth of A. alternata. And, being of different types, these fungicides could potentially be applicable for the coleus leaf spot disease control with a reduced concern of the development of drug resistance by the pathogen.
-
Keywords:
- Plectranthus scutellarioides /
- leaf spot /
- Alternaria alternata /
- toxicity test /
- EC50
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】澳洲茶树[Melaleuca alternifolia(Maiden & Betche)Cheel],又名互叶白千层、澳洲白千层,属桃金娘科(Myrtaceae)白千层属(Melaleuca)植物,原产于新南威尔士北部和东部的昆士兰州,是澳大利亚著名的芳香油料树种[1],1993年起,我国广东、广西、云南等地先后成功地引种澳洲茶树[2-3]。澳洲茶树为速生树种,萌芽能力强,定植后可多次收割枝叶,其枝叶可提取精油,称为茶树精油,茶树精油是优良的天然芳香剂、防腐剂和抗菌剂,在制药、日化、食品、香料等行业得到广泛应用[4],经济价值和经济效益极高[5]。然而,澳洲茶树不同部位精油成分和含量不尽相同[6-8],对澳洲茶树不同部位精油含量及成分进行比较分析,选取合适的部位进行提取精油可以保证精油的品质。同时,采用主成分分析(principal component analysis, PCA)可以通过降维的方式提取茶树精油的代表性主成分,能够为茶树精油的组分分析做简化指导。【前人研究进展】目前,对于茶树精油化学成分的研究已有多篇报道,包含不同生化类型[9]、不同季节[10]、不同收获时间[11]、不同枝叶储藏时间[12]和不同工艺[13]等对茶树精油得油率和化学成分的影响,有关不同部位精油得油率和化学成分的研究仅见3篇报道[6-8],其分析了不同部位叶片、花和果的精油成分。【本研究切入点】在澳洲茶树收割加工利用过程中,一般不会选取花和果作为原材料,也不会只选取叶片作为原材料,通常会同时包含叶片、枝条甚至茎干,但枝条、茎干的精油成分和含量与叶片是否存在显著差异而影响茶树精油的品质尚未见报道。而对茶树精油化学成分分析时,多数学者选取的成分较为随机,没有理论支撑其选择代表性的主要成分。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究选取澳洲茶树嫩叶、老叶、枝条和茎干作为试验材料,采用气相色谱-质谱联用技术,分析比较不同部位精油的得油率和化学成分的差异,同时对不同部位精油化学成分的含量进行主成分分析,提取茶树精油的代表性主成分,为澳洲茶树精油的开发利用提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
试验材料来源于广西壮族自治区林业科学研究院苗圃(N22°55′13.85″,E108°21′4.39″)内长势良好的5年生澳洲茶树。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 样品采集
2018年11月,在5年生澳洲茶树上分别采集嫩叶(叶绿素SPAD含量≤4.5 )、老叶(叶绿素SPAD含量>8.1 )、枝条(直径≤0.5 cm)和茎干(直径>3.0 cm)各100 g,每一样株采集10个样本,提取精油后测定精油成分及含量。
1.2.2 精油提取与成分测定
参照《中华人民共和国药典》[14]中水蒸气蒸馏法测定得油率。参照气相色谱-质谱联用技术[13]的定性分析结果,并按照国家标准GB/T 26514-2011[15]确定澳洲茶树精油主要的化学成分;用气相色谱法进行定量分析,面积归一化法确定各组分的含量,其定性和定量条件参照梁忠云等[9]的研究结果。
1.3 数据处理
采用Microsoft Excel 2007软件对数据进行常规统计和作图。采用IBM SPSS 19.0软件对澳洲茶树不同部位得油率及精油化学成分含量进行单因素方差分析和多重比较(采用邓肯氏新复极差法),并对澳洲茶树不同部位精油化学成分进行主成分分析和作图。所有分析显著性水平均设定为α=0.05。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同部位得油率
不同部位得油率见图1,澳洲茶树不同部位精油的得油率差异显著(P<0.05),其中老叶中精油得油率最高,可达1.89%,其次是嫩叶和枝条,得油率分别为1.42%和1.50%,嫩叶和枝条中精油得油率差别不显著,茎干中精油得油率最低,为0.39%,仅为老叶中得油率的约1/4,显著低于嫩叶、老叶和枝条。
2.2 不同部位精油的化学成分及含量
由表1可知,澳洲茶树不同部位提取的精油主要化学成分相似,但具体成分和含量有所差别,4个部位共检测出26种化学成分,其中有20个共有成分,主要为萜烯烃类和烯醇类化合物,在嫩叶精油中为未检测到驱回素、喇叭烯和榄香素,老叶精油中未检测到胡萝卜醇、喇叭茶醇和α-荜澄茄油萜,枝条中未检测到驱回素,茎干精油中未检测到喇叭茶醇和榄香素。在嫩叶、老叶、枝条和茎干精油的差别化学成分中,除茎干精油中的喇叭烯含量较高外,其他成分(胡萝卜醇、α-荜澄茄油萜、喇叭茶醇和榄香素)均含量较低,不是精油的主要成分。在不同部位精油检测出的化学成分中,4-松油醇含量最高,在嫩叶、老叶、枝条和茎干精油中分别占33.71%、40.13%、31.28%和15.59%,嫩叶、老叶、枝条精油中4-松油醇含量约为茎干精油的2倍,符合国家标准[15],茎干精油中4-松油醇含量不符合茶树精油(4-松油醇型)国家标准。1,8桉叶素含量在嫩叶、老叶和枝条精油中差别不显著,分别为1.07%、1.04%和1.06%,在茎干精油中含量为1.36%,显著高于嫩叶、老叶和枝条,但都符合茶树精油(4-松油醇型)国家标准。嫩叶、老叶和枝条精油中含量排名前三的成分均是4-松油醇、γ-松油烯和α-松油烯,而茎干精油中含量排名前三的成分是4-松油醇、α-松油烯和α-松油醇,α-松油醇在嫩叶、老叶和枝条精油中分别为2.62%、2.71%和2.46%,差别不显著,但均显著低于茎干精油的含量(4.17%)。
表 1 澳洲茶树不同部位的精油化学成分及含量Table 1. Essential oils from various parts of M. alternifolia plant精油化学成分
chemical composition of essential oil精油含量 content of essential oil/% 嫩叶
young leaves老叶
old leaves枝条
branches茎干
stems4-松油醇 terpinen-4-ol 33.71±0.74 b 40.13±1.16 a 31.28±0.86 c 15.59±1.15 d γ-松油烯γ-terpinene 18.02±0.47 b 20.02±0.73 a 10.56±0.78 c 1.09±0.14 d α-松油烯 α-terpinene 10.61±0.51 a 9.11±1.53 b 10.76±1.03 a 8.56±0.89 b 异松油烯 terpinolene 3.01±0.32 a 2.65±0.31 b 0.12±0.02 c 2.59±0.35 b 桧烯 sabinene 3.12±0.20 a 0.15±0.03 d 2.16±0.08 c 2.77±0.02 b α-松油醇 α-terpineol 2.62±0.11 b 2.71±0.24 b 2.46±0.59 b 4.17±0.46 a δ-杜松烯 δ-cadinene 2.11±0.15 a 0.45±0.03 d 1.52±0.16 b 1.37±0.03 c α-蒎烯 α-pinene 1.99±0.04 b 2.22±0.20 b 1.02±0.06 c 3.45±0.52 a 白千层烯 viridiflorene 1.05±0.19 b 0.69±0.02 c 1.76±0.10 a 1.85±0.13 a 香橙烯 aromadendrene 1.21±0.01 b 0.45±0.03 d 1.14±0.08 c 1.32±0.03 a 1,8-桉叶素 1,8-cineole 1.07±0.04 b 1.04±0.04 b 1.06±0.08 b 1.36±0.09 a α-侧柏烯 α-thujene 0.86±0.03 d 2.49±0.03 a 1.13±0.06 c 2.34±0.05 b 蓝桉醇 globulol 0.85±0.01 c 2.00±0.08 a 1.13±0.07 b 1.96±0.10 a β-月桂烯 β-myrcene 0.78±0.02 c 0.80±0.02 c 1.74±0.02 a 0.91±0.05 b β-水芹烯 β-phellanderene 0.78±0.01 c 0.44±0.03 d 1.10±0.08 b 1.40±0.07 a β-蒎烯 β-pinene 0.51±0.09 a 0.45±0.03 b 0.48±0.06 ab 0.45±0.01 b 柠檬烯 limonene 0.60±0.01 c 0.70±0.01 b 1.48±0.02 a 0.56±0.07 d α-水芹烯 α-phellanderene 0.40±0.02 a 0.25±0.00 c 0.41±0.06 a 0.38±0.04 a 对伞花烃 p-cymene 0.37±0.03 b 0.72±0.11 b 3.25±0.60 a 3.52±0.96 a 白千层醇 viridiflorol 0.35±0.03 b 0.16±0.07 b 1.45±0.10 a 1.52±0.46 a 胡萝卜醇(+)-Carotol 0.18±0.01 a 0.00±0.02 c 0.18±0.01 a 0.15±0.01 b 喇叭茶醇 Ledol 0.17±0.00 b 0.00±0.00 c 1.00±0.01 a 0.00±0.00 c α-荜澄茄油萜 α-Cubebene 0.14±0.00 b 0.00±0.02 d 0.08±0.03 c 0.24±0.02 a 驱蛔素 Ascaridole 0.00±0.00 c 0.11±0.01 b 0.00±0.00 c 0.63±0.02 a 喇叭烯(+)-Ledene 0.00±0.00 c 1.37±0.14 b 1.30±0.06 b 4.06±0.14 a 榄香素 Elemicin 0.00±0.00 c 0.12±0.04 b 0.31±0.03 a 0.00±0.00 c 注:同行数值后不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Note: Data with different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at P<0.05.2.3 不同部位精油化学成分含量的主成分分析
采用SPSS 19.0软件对不同部位20种共有精油化学成分含量进行主成分分析,提取特征值大于1的主成分,得到主成分的特征值和贡献率(表2)。由表2可知,前4个主成分的特征值8.30、6.12、3.37、1.03,第1主成分的贡献率为41.49%,第2主成分的贡献率为30.61%,第3主成分的贡献率为16.85%,第4主成分的贡献率为5.13%。前4个主成分的累计贡献率达94.09%(>85%),因此,选取前4个主成分作为精油化学成分分析的主要成分,能够代表20个精油化学成分变量94.09%的信息量,具有很好的代表性,基本可以代表其样品化学成分含量的差别。
表 2 主成分的特征值及其贡献率Table 2. Eigenvalues, contribution, and cumulative contribution of principal components主成分
Principal component初始特征值 Initial Eigenvalues 提取的主成分 The extracted principal component 合计
Total方差的贡献率
The contributionrate of
variance/%累积贡献率%
Cumulative contribution
rate/%合计
Total方差的贡献率
The contributionrate of
variance/%累积贡献率
Cumulative contribution
rate/%1 8.30 41.49 41.49 8.30 41.49 41.49 2 6.12 30.61 72.11 6.12 30.61 72.11 3 3.37 16.85 88.96 3.37 16.85 88.96 4 1.03 5.13 94.09 1.03 5.13 94.09 5 0.53 2.63 96.71 6 0.28 1.39 98.10 7 0.15 0.77 98.87 8 0.06 0.32 99.19 9 0.04 0.22 99.42 10 0.04 0.19 99.61 11 0.02 0.10 99.70 12 0.02 0.09 99.79 13 0.01 0.07 99.86 14 0.01 0.04 99.91 15 0.01 0.03 99.94 16 0.00 0.02 99.96 17 0.00 0.01 99.97 18 0.00 0.01 99.99 19 0.00 0.01 99.99 20 0.00 0.01 100.00 由表3主成分载荷矩阵可知各主成分各变量的载荷值。在第1主成分中载荷较高的正影响成分有β-水芹烯、白千层烯、白千层醇、香橙烯、对花伞烃,载荷值分别为 0.99、0.96、0.91、0.88、0.83;负向影响较大的为γ-松油烯和4-松油醇,载荷值分别为−0.91和−0.89。第2主成分中载荷较高的正影响成分依次为α-侧柏烯、α-蒎烯、蓝桉醇、α-松油醇、1,8-桉叶素和异松油烯,载荷值分别为0.90、0.89、0.88、0.73、0.62;负向影响最大的为柠檬烯,载荷值为−0.72。第3主成分中载荷较高的正影响成分依次为异松油烯、δ-杜松烯、桧烯,载荷值分别为0.69、0.66、0.62;负向影响最大的为柠檬烯,载荷值为−0.66。第4主成分中载荷较高的正影响成分为β-蒎烯,载荷值为0.78;负向影响最大的为α-松油烯,载荷值为−0.52。主成分载荷矩阵反映了该指标在该主成分上的载荷程度,载荷值小的挥发性成分对精油化学成分的贡献小,同时也表明它的含量较低。其中第1主成分和第2主成分的累计贡献率为72.11%,说明这2个主成分对精油的化学成分的贡献超过一半。做20种化学成分的主成分散点图(图2),2D图(图2-a)分别以PCA1、PCA2为X、Y轴,3D图(2-b)分别以PCA1、PCA2、PCA3为X、Y、Z轴,可以直观地看出各化学成分在前3个主成分的分布状况,图2-a可知,大部分化学成分处于一、四象限,由图2-b可知,不同化学成分在前3个主成分上的分布存在显著差异。综合表3和图2,可选择在第1、第2主成分综合表现突出的化学成分作为代表进行精油分析。因此,β-水芹烯、白千层烯、白千层醇、香橙烯、对花伞烃、γ-松油烯和4-松油醇、α-侧柏烯、α-蒎烯、蓝桉醇、α-松油醇、1,8-桉叶素和柠檬烯,这13种化学成分可作为精油的代表性化学成分。
![]() 图 2 20种化学成分的主成分散点图注:TL:4-松油醇;TER:γ-松油烯;TEP:α-松油烯;TE:异松油烯;SA:桧烯;TEL:α-松油醇;CE:δ-杜松烯;PIN:α-蒎烯;VE:白千层烯;AR:香橙烯;CI:1,8-桉叶素;TH:α-侧柏烯;GL:蓝桉醇;MY:β-月桂烯;PH:β-水芹烯;PI:β-蒎烯;LI:柠檬烯;PHE:α-水芹烯;PC:对伞花烃;VL:白千层醇。Figure 2. PCA biplot for 20 chemical components in essential oil of M. alternifolia plantNote: TL: terpinen-4-ol; TER:γ-terpinene; TEP:α-terpinene; TE: terpinolene; SA: sabinene; TEL: α-terpineol; CE:δ-cadinene; PIN: α-pinene; VE: viridiflorene; AR: aromadendrene; CI: 1,8-cineole; TH: α-thujene; GL: globulol MY: β-myrcene; PH:β-phellanderene; PI: β-pinene; LI: limonene; PHE: α-phellanderene; PC: p-cymene; VL: viridiflorol.表 3 主成分载荷矩阵Table 3. Loading matrix of principal components
图 2 20种化学成分的主成分散点图注:TL:4-松油醇;TER:γ-松油烯;TEP:α-松油烯;TE:异松油烯;SA:桧烯;TEL:α-松油醇;CE:δ-杜松烯;PIN:α-蒎烯;VE:白千层烯;AR:香橙烯;CI:1,8-桉叶素;TH:α-侧柏烯;GL:蓝桉醇;MY:β-月桂烯;PH:β-水芹烯;PI:β-蒎烯;LI:柠檬烯;PHE:α-水芹烯;PC:对伞花烃;VL:白千层醇。Figure 2. PCA biplot for 20 chemical components in essential oil of M. alternifolia plantNote: TL: terpinen-4-ol; TER:γ-terpinene; TEP:α-terpinene; TE: terpinolene; SA: sabinene; TEL: α-terpineol; CE:δ-cadinene; PIN: α-pinene; VE: viridiflorene; AR: aromadendrene; CI: 1,8-cineole; TH: α-thujene; GL: globulol MY: β-myrcene; PH:β-phellanderene; PI: β-pinene; LI: limonene; PHE: α-phellanderene; PC: p-cymene; VL: viridiflorol.表 3 主成分载荷矩阵Table 3. Loading matrix of principal components精油化学成分
chemical composition of essential oil成分 Component 1 2 3 4 4-松油醇 terpinen-4-ol −0.89 −0.40 −0.10 −0.04 γ-松油烯 γ-terpinene −0.91 −0.32 0.16 −0.10 α-松油烯 α-terpinene 0.02 −0.67 0.10 −0.52 异松油烯 terpinolene −0.31 0.62 0.69 0.02 桧烯 sabinene 0.73 −0.28 0.62 −0.02 α-松油醇 α-terpineol 0.58 0.73 0.10 −0.22 δ-杜松烯 δ-cadinene 0.50 −0.54 0.66 −0.08 α-蒎烯 α-pinene 0.29 0.89 0.28 −0.01 白千层烯 viridiflorene 0.96 −0.08 −0.22 −0.01 香橙烯 aromadendrene 0.88 −0.21 0.42 −0.06 1,8-桉叶素 1,8-cineole 0.72 0.62 0.11 −0.11 α-侧柏烯 α-thujene −0.15 0.90 −0.39 0.07 蓝桉醇 globulol −0.08 0.88 −0.44 0.09 β-月桂烯 β-myrcene 0.41 −0.65 −0.63 −0.01 β-水芹烯 β-phellanderene 0.99 0.09 −0.03 −0.02 β-蒎烯 β-pinene 0.01 −0.39 0.31 0.78 柠檬烯 limonene 0.20 −0.72 −0.66 −0.02 α-水芹烯 α-phellanderene 0.69 −0.51 0.26 0.18 对伞花烃 p-cymene 0.83 0.07 −0.49 0.12 白千层醇 viridiflorol 0.91 −0.02 −0.35 0.04 3. 讨论与结论
澳洲茶树含有多种化学成分,根据成分及含量的不同,澳洲茶树可分为多种生化类型。Laura[16]共发现了6种澳洲茶树的生化类型。引种中国后,不同研究者对不同单株进行测定,结果大不相同,分别发现了桉叶素型、桉叶素-异松油烯型[17]、4-松油醇型[18]、桉叶素-松油醇型和γ-松油烯型 [19]。本研究通过比较澳洲茶树不同部位化学成分差异发现,尽管各部位精油的化学成分含量差别较大,但不同部位的茶树精油化学成分均以4-松油醇含量最高,均≥30%,且显著高于其他物质,而且1,8-桉叶素含量极低,均≤10%,依据茶树精油(4-松油醇型)的国家标准[20],本研究的澳洲茶树属于4-松油醇型。
4-松油醇、1,8-桉叶素和α-松油烯是茶树精油的主要抑菌成分[21-22]。但1,8-桉叶素容易引起皮肤过敏,还具有致癌和生殖毒性[23],α-松油烯对空气和光等较为敏感,暴露于空气中易氧化分解,形成致敏物对异丙基甲苯和1,4-过氧对孟烯,刺激皮肤导致不适[24],为避免茶树精油使用出现上述问题,我国通常以1,8-桉油素和4-松油醇作为评价茶树精油品质的指标(1,8-桉油素的含量应在10%以下,而4-松油醇应不少于30%),其中4-松油醇含量越高,精油品质越好[25]。本研究中澳洲茶树4个不同部位中1,8-桉叶素含量极低(1.04%~1.36%),均符合国家标准,但茎干精油中4-松油醇含量仅为15.59%,不符合高品质茶树精油的标准,而且茎干的提油率也显著低于其他3个部位,因此,为保证精油的品质,选择嫩叶、老叶和枝条作为原材料提油更佳。
在分析澳洲茶树精油含量变化规律时,对所有成分均进行分析,数据量较大,故学者一般仅选择几种成分进行分析[10],但随机选择的成分可能会由于不具代表性而影响实际结果的准确性。主成分分析法是通过降维处理,将多个变量整合成少数几个综合变量,尽可能多地反映原有变量信息的统计分析方法,该方法能够化繁为简,避免主观随意性,已得到广泛应用[26-27]。本研究通过主成分分析,提取了13种化学成分,基本可以代表所有化学成分的信息。
综上所述,供试澳洲茶树属于4-松油醇型,为提高得油率和精油品质,在采收澳洲茶树时最好选择嫩叶、老叶和枝条作为材料进行提油,在进行澳洲茶树精油成分含量差异分析时,为简化分析内容,可选取β-水芹烯、白千层烯、白千层醇、香橙烯、对花伞烃、γ-松油烯和4-松油醇、α-侧柏烯、α-蒎烯、蓝桉醇、α-松油醇、1,8-桉叶素和柠檬烯这13种化学成分作为代表性特征化学成分,基本可以代表精油化学成分的信息。
-
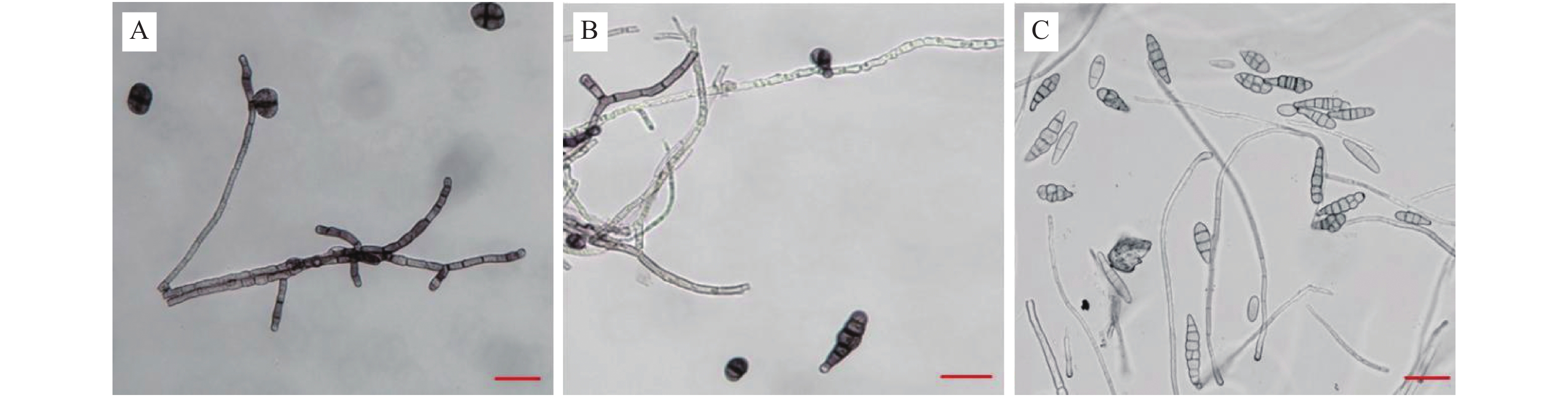
图 2 菌落形态和致病性鉴定
注:A,生长3 d的菌落形态;B,生长10 d的正面菌落形态;C,生长10 d的反面菌落形态;D,接种对照叶片(3 d);E,分生孢子接种叶片(3 d)
Figure 2. Colony morphology and pathogenic assay
Note: A: Colony on PDA after 3 d incubation; B: Colony top-view after 10 d incubation; C: Colony bottom-view after 10 d incubation; D: Control leaf after 3 d incubation; E: Artificially inoculated leaf after 3 d incubation.
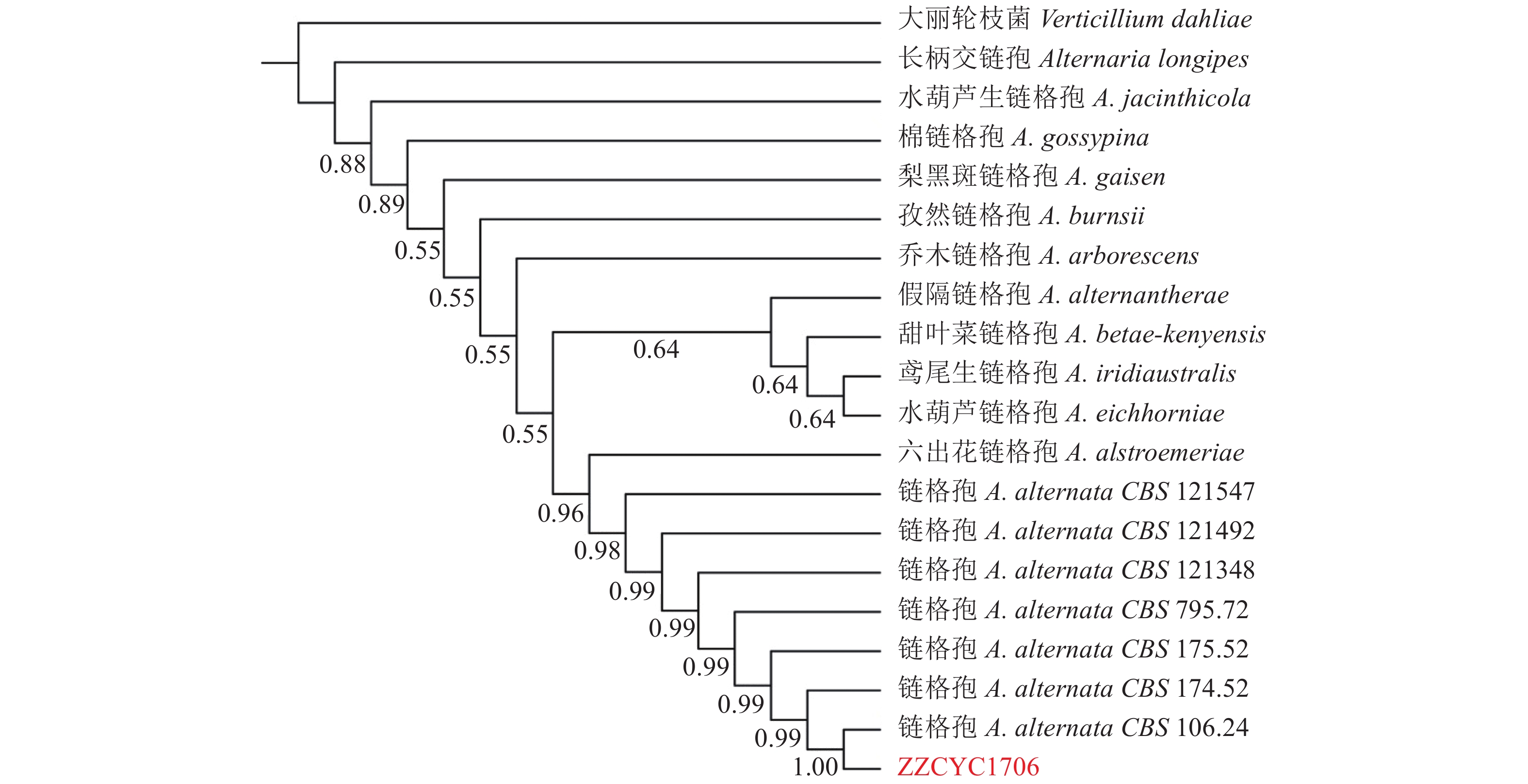
图 4 基于ITS和LSU序列构建链格孢属系统发育树
注:分支上的数字标示Bootstrap 检验的支持率,大丽轮枝菌(V. dahliae)作为外群,ZZCYC1706为分离菌株
Figure 4. Phylogenetic tree of Alternaria spp. based on ITS and LSU sequences
Note: Data shown at each node are confidence values from 1 000 replicate bootstrap samplings; Verticillium dahliae was out group, while ZZCYC1706, isolate.
表 1 6种药剂对彩叶草叶斑病病原菌的毒力测定
Table 1 Toxicities of 6 fungicides on A. alternata
药剂
Fungicide回归方程
Regression
equation相关系数r
Correlation
coefficient, rEC50值
EC 50 Value/
(µg·mL−1)95%嘧霉胺
95%Pyrimethanily=0.994x+3.647 0.985 5.258 98%异菌脲
98% Iprodioney=0.827x+4.962 0.984 1.155 96.4%克菌丹
96.4% Captany=0.427x+3.085 0.917 89.010 96%啶菌恶唑
96% Pyrisoxazoley=0.386x+5.184 0.999 0.621 99%腐霉利
99% Procymidoney=0.535x+2.929 0.995 48.120 96%啶酰菌胺
96% Boscalidy=0.566x+2.884 0.998 42.210 -
[1] SUVA M A, A M PATEL, N SHARMA. Coleus species: Solenostemon scutellarioides [J]. J Inventi Rapid:Planta Activa, 2015(2): 1−5.
[2] 李东霞, 宋妍, 王彩凤, 等. 药用植物彩叶草的研究进展 [J]. 生命的化学, 2021, 41(4):680−685. LI D X, SONG Y, WANG C F, et al. Research progress on the medicinal plant Plectranthus scutellarioides [J]. Chemistry of Life, 2021, 41(4): 680−685.(in Chinese)
[3] ROOSITA K, KUSHARTO C M, SEKIYAMA M, et al. Medicinal plants used by the villagers of a Sundanese community in West Java, Indonesia [J]. Journal of ethnopharmacology, 2008, 115(1): 72−81. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2007.09.010
[4] LEVITA J, SUMIWI S A, PRATIWI T I, et al. Pharmacological activities of Plectranthus scutellarioides (L. ) R. Br. leaves extract on cyclooxygenase and xanthine oxidase enzymes [J]. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research, 2016, 10(20): 261−269.
[5] CRETTON S, SARAUX N, MONTEILLIER A, et al. Anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative diterpenoids from Plectranthus scutellarioides [J]. Phytochemistry, 2018, 154: 39−46. DOI: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2018.06.012
[6] SWAMY M K, U R SINNIAH, A GHASEMZADEH. Anticancer potential of rosmarinic acid and its improved production through biotechnological interventions and functional genomics [J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2018, 102(18): 7775−7793. DOI: 10.1007/s00253-018-9223-y
[7] 方梅玉. 漳州市花卉、苗木产业现状及发展方向 [J]. 福建热作科技, 2019, 44(4):60−64. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2327.2019.04.020 FANG M Y. Current status and development direction of flower and seedling industry in Zhangzhou [J]. Fujian Science & Technology of Tropical Crops, 2019, 44(4): 60−64.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2327.2019.04.020
[8] DENTON G J, BEAL E, DENTON J O, et al. First record of downy mildew, caused by Peronospora belbahrii, on Solenostemon scutellarioides in the UK [J]. New Disease Reports, 2015, 31(1): 14−14. DOI: 10.5197/j.2044-0588.2015.031.014
[9] ITO Y, TAKEUCHI T, MATSUSHITA Y, et al. Downy mildew of coleus caused by Peronospora belbahrii in Japan [J]. Journal of general plant pathology, 2015, 81(4): 328−330. DOI: 10.1007/s10327-015-0601-3
[10] GORAYEB E S, PIERONI L P, CRUCIOL G C D, et al. First report of downy mildew on coleus (Plectranthus spp. ) caused by Peronospora belbahrii sensu lato in Brazil [J]. Plant Disease, 2020, 104(1): 294.
[11] GARIBALDI A, BERTETTI D, POLI A, et al. First report of Verticillium wilt caused by Verticillium dahliae on Coleus verschaffeltii in Italy [J]. Plant disease, 2011, 95(7): 878−878.
[12] GARIBALDI A, BERTETTI D, MATIĆ S, et al. First report of leaf necrosis caused by Alternaria alternata on Plectranthus scutellarioides in Italy [J]. Plant Disease, 2020, 104(2): 590−590.
[13] 王文. 彩叶草的栽培与病虫防治 [J]. 中国林副特产, 2012(4):77. WANG W. Cultivation and Control of Diseases and Pests on Plectranthus scutellarioides [J]. Forest By-Product and Speciality in China, 2012(4): 77.(in Chinese)
[14] 陈丹, 张纯, 阮煜. 观叶花卉彩叶草的繁殖方法及栽培技术 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2015(16):30−31,62. CHEN D, ZHANG C, RUAN Y. Colored Grass Breeding Methods and Cultivation Techniques [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2015(16): 30−31,62.(in Chinese)
[15] 陈少萍. 彩叶草栽培管理 [J]. 中国花卉园艺, 2020(3):64−65. CHEN S P. Cultivation and management on Plectranthus scutellarioides [J]. China Flowers & Horticulture, 2020(3): 64−65.(in Chinese)
[16] 田忠锋, 荣梅, 王秀玲. 彩叶草栽培及管理技术浅析 [J]. 农村实用技术, 2020(5):49. TIAN Z F, RONG M, WANG X L. Analysis on cultivation and management techniques of Plectranthus scutellarioides [J]. Nongcun Shiyong Jishu, 2020(5): 49.(in Chinese)
[17] 李本金, 陈庆河, 兰成忠, 等. 福建省大豆根腐病病原菌的鉴定 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2011, 26(5):798−803. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2011.05.024 LI B J, CHEN Q H, LAN C Z, et al. A identification and pathogenicity test of the pathogens causing soybean root rot in Fujian [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 26(5): 798−803.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2011.05.024
[18] 席中刚, 游景茂, 郑露, 等. 湖北省黄连叶斑病病原鉴定及其生物学特性 [J]. 植物保护学报, 2018, 45(2):315−321. XI Z G, YOU J M, ZHENG L, et al. Identification and biological characteristics of the pathogen causing leaf spot on Coptis chinensis in Hubei Province [J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2018, 45(2): 315−321.(in Chinese)
[19] LAWRENCE D P, F ROTONDO, P B GANNIBAL. Biodiversity and taxonomy of the pleomorphic genus Alternaria [J]. Mycological Progress, 2016, 15(1): 1−22. DOI: 10.1007/s11557-015-1147-7
[20] DOYLE J J, DOYLE J L. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue [J]. Phytochem Bull, 1987, 19: 11−15.
[21] WOUDENBERG J H C, SEIDL M F, GROENEWALD J Z, et al. Alternaria section Alternaria: Species, formae speciales or pathotypes? [J]. Studies in mycology, 2015, 82: 1−21. DOI: 10.1016/j.simyco.2015.07.001
[22] 王荣波, 陈姝樽, 刘裴清, 等. 荔枝霜疫霉中双组分信号转导系统的鉴定与表达分析 [J]. 植物病理学报, 2020, 50(1):49−59. WANG R B, CHEN S Z, LIU P Q, et al. Identification and expression analysis of two-component signaling system-related genes in Peronophythora litchi [J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 2020, 50(1): 49−59.(in Chinese)
[23] 常红洋, 王荣波, 李本金, 等. 防治荔枝霜疫霉病的药剂筛选及田间应用 [J]. 农药, 2018, 57(2):137−138,142. CHANG H Y, WANG R B, LI B J, et al. Effective fungicides screening and field application for litchi downy blight [J]. Agrochemicals, 2018, 57(2): 137−138,142.(in Chinese)
[24] 李永, 岳志强, 朴春根, 等. 链格孢属真菌的分子复核鉴定及系统发育研究 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2013(27):165−169. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2013.27.029 LI Y, YUE Z Q, PU C G, et al. Molecular identification and phylogeny of genus Alternaria [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2013(27): 165−169.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2013.27.029
[25] PINTO V E F, PATRIARCA A. Alternaria species and their associated mycotoxins [M]. New York: Humana Press, 2017: 13-32.
[26] 张丹华, 张红楠, 吴頔, 等. 重庆地区枇杷叶斑病病原初步鉴定及防治药剂室内筛选 [J]. 中国南方果树, 2017, 46(4):102−106, 111. ZHANG D H, ZHANG H N, WU D, et al. Identification of The Pathogen Causing Loquat Leaf-spot Disease and The Screening of Fungicides [J]. South China Fruits, 2017, 46(4): 102−106, 111.(in Chinese)
[27] 王彩霞, 李兴红, 魏艳敏, 等. 引起葡萄叶斑病的链格孢种类的初步鉴定 [J]. 植物保护学报, 2019, 46(1):175−183. WANG C X, LI X H, WEI Y M, et al. Identification of Alternaria species causing leaf spots in grapes [J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2019, 46(1): 175−183.(in Chinese)
[28] SUN, H F, WEI M Y, LI N, et al. First report of Alternaria alternata causing leaf spot on Menispermum dauricum DC. in China[J]. Plant Disease, 2021. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-07-21-1447-PDN.
[29] LI S, SHEN Q, WANG H, et al. First report of Alternaria alternata causing leaf spot of Tartary Buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum) in China[J]. Plant Disease, 2021. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-01-21-0191-PDN.
[30] ZHANG Q, ZHANG Y, SHI H, et al. First report of leaf spot caused by Alternaria alternata on Yucca gloriosa in China[J]. Plant Disease, 2021. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-04-21-0857-PDN
[31] ZHONG F T, LIU Y L, ZHENG D, et al. First report of Alternaria alternata causing brown leaf spot on wild rice (Oryza rufipogon) in China[J]. Plant Disease, 2021. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-05-21-1024-PDN.
[32] 赵炽娜, 胡津瑜, 王云萍, 等. 申嗪霉素对4种链格孢属植物病原真菌的室内毒力测定 [J]. 长江大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 17(1):74−77. ZHAO Z N, HU J Y, WANG Y P, et al. Indoor toxicity test of phenazine-1-carboxylic acid to 4 species of Alternaria plant pathogenic fungi [J]. Journal of Yangtze University(Natural Science Edition), 2020, 17(1): 74−77.(in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 王秀芬,黄添舆,罗冬兰,张雨,曹森. 天麻褐腐病病原真菌的分离鉴定及柠檬醛对其抑制效果. 食品工业科技. 2025(08): 148-155 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 朱玲,付钰铭,陈兰兰,舒梦霜,张潇月,郑兴汶,崔汝强. 白莲缘枯病病原菌的分离鉴定与防治药剂筛选. 生物灾害科学. 2024(01): 21-27 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王鹏,夏乐乐,别赵薇,张晓峰,张敏. 陆生路易斯安那鸢尾叶部病害病原分离与鉴定. 分子植物育种. 2024(10): 3253-3263 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 白建波,张晋,杨伟,孔琼,周银丽. 蓝莓叶斑病病原菌分离鉴定及室内药剂筛选. 江苏农业科学. 2024(07): 118-123 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李嘉妮,周义蒙,刘杰,曾慧兰,李润根. 龙牙百合褐斑病菌梨黑斑链格孢生物学特性及室内药剂筛选. 中药材. 2024(03): 559-562 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 卞晓春,王凡,刘陈玮,徐仁超,陆红臣,吴春芳. 江苏省蚕豆叶斑病病原菌的分离鉴定、生物学特性与防控药剂筛选. 福建农业学报. 2024(11): 1298-1305 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 瞿光凡,王瑞,马超,雷霁卿,巴良杰,曹森,芈婷婷,龙芳. ‘东红’猕猴桃软腐病病原菌的分离鉴定及褪黑素对其控制效果. 食品工业科技. 2023(02): 170-177 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 王鹏,别赵薇,夏乐乐. 路易斯安那鸢尾叶部病害病原鉴定和防治药剂筛选. 河南农业科学. 2023(12): 107-115 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)





 下载:
下载: