Structure and Genome Sequence of Papilio polytes Mitochondria
-
摘要:目的 对玉带凤蝶Papilio polytes的成虫形态特征和幼虫各龄期的特征进行描述,分析玉带凤蝶Papilio polytes完整的线粒体基因组结构特征,丰富蝶类基因组学数据。方法 根据翅面斑纹描述形态特征,利用高通量第二代测序技术,构建玉带凤蝶线粒体基因组全序列,分析线粒体基因组结构。结果 玉带凤蝶指名亚种和西藏亚种蝶翅面斑纹有较大区别。玉带凤蝶线粒体基因组序列全长15 267 bp(GenBank登录号为MZ188895),包括13个蛋白质编码基因、22个tRNAs基因、2个rRNAs基因和一段控制区。全序列的A+T的平均含量为80.6%,表现明显的A+T偏斜,有11处表现基因间隔,12处表现基因重叠。37个基因中除cox1基因是以TTG为起始密码子,其余蛋白质编码基因均以ATN起始,cox2基因以不完整终止密码子T结尾,核苷酸组成表现明显的AT偏斜,UUA的相对密码子使用频率最高。除trnS1基因,其余21个tRNAs的二级结构均为典型的三叶草结构,二级结构中有U-U或U-G碱基错配现象,其中有9个tRNAs没有出现碱基错配现象。控制区有最高的A+T平均含量,为94.5%。结论 玉带凤蝶指名亚种和西藏亚种外部形态的区别主要是由于地位分布位置的不同。玉带凤蝶线粒体基因组结构和基因排列顺序与鳞翅目昆虫线粒体基因组结构和排列一致。Abstract:Objective Adults and larvae of Papilio Polytes were studied with the complete mitochondrial genome sequenced for the butterfly genomics library collection.Method According to the morphological characteristics of wing markings, sequences of the mitochondrial genomes of P. Polytes were determined using the second-generation Illumina Hiseq 4 000 high-throughput sequencing technology.Result The wing markings of P. polytes polytes was found significantly different from those of P. polytes tibetanus’s. The length of complete mitochondrial genome was 15 267 bp (GenBank accession no. MZ188895) consisting of 13 protein-coding genes, 22 transfer RNAs, 2 ribosomal RNAs, and a control region. The average contents of A+T was 80.6% of the entire sequence representing a significant A+T deflection that had 11 gene intervals and 12 gene overlaps. Except Cox1, all protein coding genes started with ATN, whereas Cox2 ended with codon T. The nucleotide composition showed a significant AT skew. The relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) of UUA was the highest one. Other than trnS1, the transfer RNAs had the typical clover-leaf-like structure with U-U or U-G base mismatched in the secondary structure and 9 transfer RNAs without mismatch. The A+T average content was the highest in control region at 94.5%.Conclusion Morphologically, P. polytes polytes and P. polytes tibetanus mainly differed in location and distribution of the elements. The structures and sequences of the genomes of P. Polytes mitochondria as determined were in line with those of Lepidoptera insects.
-
Keywords:
- Papilio polytes /
- characteristics /
- mitochondrial genome /
- sequencing
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】玉带凤蝶(Papilio polytes)隶属于鳞翅目Lepidopetera凤蝶科Papilionoidea凤蝶属Papilio,幼虫主要以柑橘属、花椒等芸香科植物为食,是柑橘和花椒的重要害虫之一;国内分布于秦岭以南各省区,是蝶类里面为数不多的西藏和河南的共有种。国外主要分布在印度、日本、美国等地[1-2]。线粒体基因组具有进化速率较快、母系遗传、分子较小等特点,在昆虫鉴定、物种进化、系统发育树构建等方面应用广泛[3]。【前人研究进展】目前对玉带凤蝶的研究主要集中在玉带凤蝶人工养殖与生物学特性、特异性化合物对求偶行为的调节、玉带凤蝶产卵偏好性、铁蛋白功能表达、系统发育关系等方面[4-6]。【本研究切入点】关于玉带凤蝶线粒体基因组结构的研究相对较少[7-8],描述玉带凤蝶成虫翅面特征和幼虫龄期特征,分析构成玉带凤蝶指名亚种Papilio polytes polytes和西藏亚种Papilio polytes tibetanus翅面特征不同的影响因素。【拟解决的关键问题】对玉带凤蝶(P. polytes)线粒体基因组测序、组装,基因注释,分析线粒体基因组序列结构特征,以期丰富其基因组学的基础数据。此外,本研究还描述了玉带凤蝶指名亚种Papilio polytes polytes和西藏亚种Papilio polytes tibetanus的翅面特征。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 标本采集与保存
用于DNA提取与基因组测序的玉带凤蝶标本,2019年8月采集于宝天曼自然保护区(111°46′55″~112°03′32″E;33°20′12″~33°35′43″N),无水乙醇浸泡后保存于−20 ℃冰箱保存。
1.2 形态鉴定
形态鉴定主要根据翅面斑纹鉴定。
1.3 DNA提取与基因组测序
取玉带凤蝶成虫胸部肌肉约30 mg,根据天根公司基因组DNA提取试剂盒(TIANamp Genomic DNA Kit)步骤提取总DNA,利用全波长微量扫描分光光度计进行DNA浓度检测,检测合格后(DNA含量超过100 ng ·μL−1)送往北京贝瑞和康公司进行高通量测序。
1.4 序列拼接与注释分析
测序得到的原始序列通过GetOrganelle v1.7.3.5软件进行修剪、组装拼接,自动删去质量低的序列,得到的序列上传至MITOS Web Sever(http://mitos.bioinf.uni-leipzig.de/index.py)进行基因注释,获得线粒体基因组初注释结果,再将13个蛋白质编码基因和2个rRNA基因进行手动矫正,将再根据矫正注释的结果编制tbl文件,和fas文件一起提交至GenBank(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/WebSub/?form=history&tool=genbank)获得GenBank登录号,为MZ188895,使用cox1基因在GenBank数据库进行对比找近缘种,结果与形态鉴定一致。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 形态特征
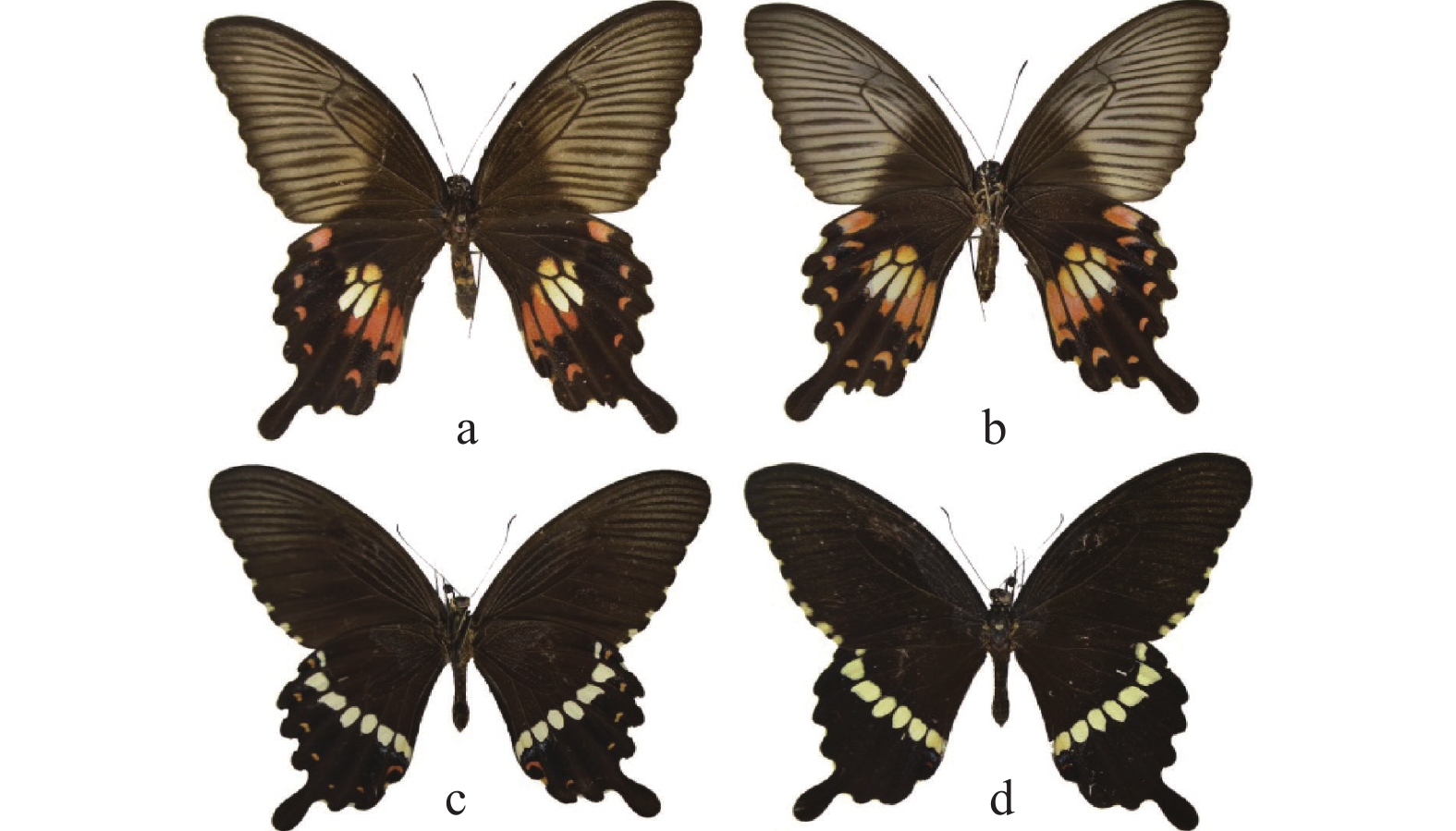
玉带凤蝶指名亚种Papilio polytes polytes成虫如图1所示,中型蝶,翅展77-95 mm,雄蝶体黑色,尾突短。前翅外缘平滑,背面外缘区有7~9个黄色斑点,且从臀角到顶角斑点依次变小;后翅外缘波浪状,背面外中区有6个乳白色斑块和1个乳黄色斑块,乳黄色斑被翅脉分隔成两部分;前翅腹面斑纹同背面,颜色较淡;后翅腹面中带斑纹同背面,外缘区有1列白斑,亚外缘区有7个月牙形白斑。雌蝶尾突较雄蝶长,雌蝶前翅颜色较雄蝶淡;后翅背面外中区有2~6个斑,其中靠近后缘的1~2个长斑呈红色,亚外缘区有7个月牙形红斑,其中近尾突处红斑最小,臀区外缘有近似三角形的红斑;前翅腹面颜色同背面,后翅腹面斑纹同背面,亚缘区有7个红斑,比背面大且清晰。
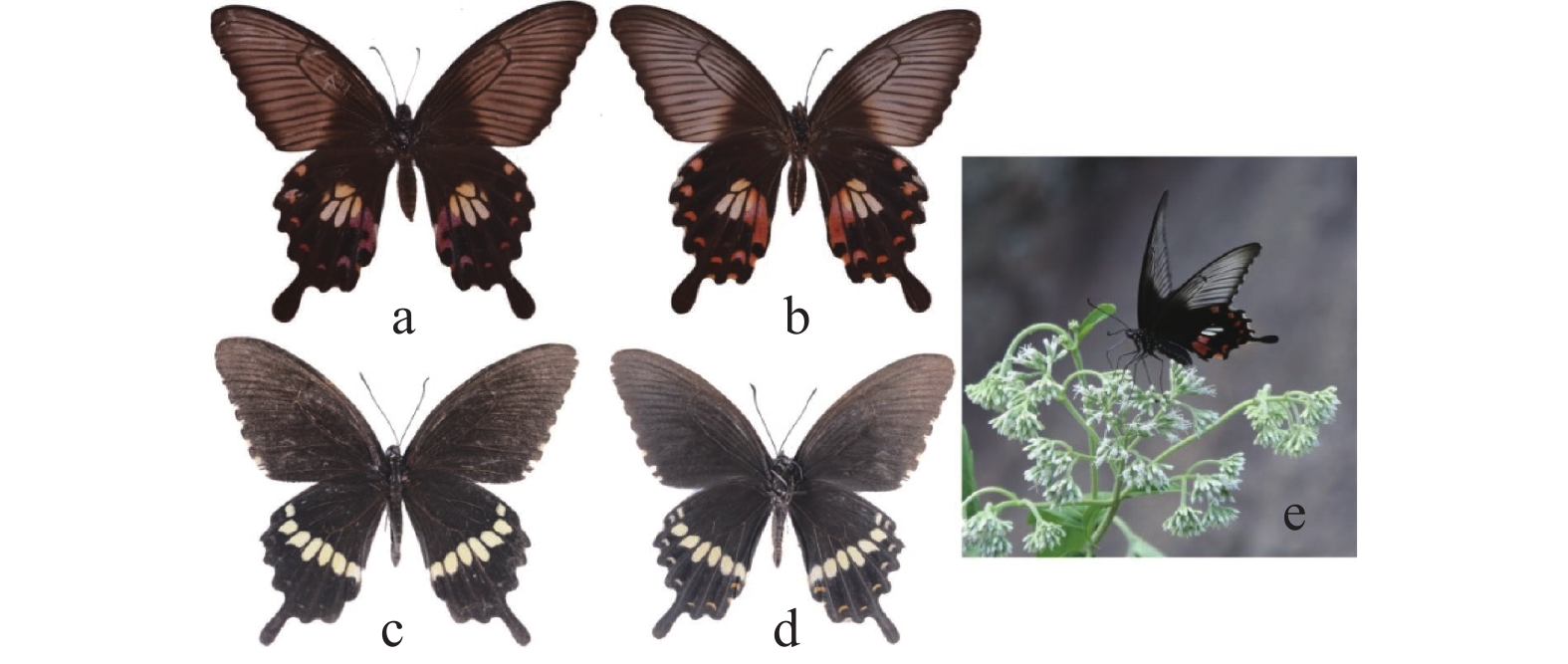
玉带凤蝶西藏亚种Papilio polytes tibetanus成虫如图2所示,雄蝶前翅背面外缘区有7个黄色斑点,后翅背面外中区有6个白斑点和1个黄斑点,臀角处有红色和蓝色2团鳞片;后翅腹面亚外缘区有6个月牙形黄斑。雌蝶后翅背面外中区有6个斑,其中后缘的2个长斑呈红色,第3个长斑靠近基部为白色,靠近端部为红色,2个小斑呈黄色,亚外缘区有6个月牙形红斑,其中近顶角处的1个红斑比其余红斑大;腹面后翅斑纹比背面复杂,外中区2个黄色小斑靠近外缘处比背面多1个红色斑点,与相近的小黄斑几乎连接,亚外缘区有7个斑点。
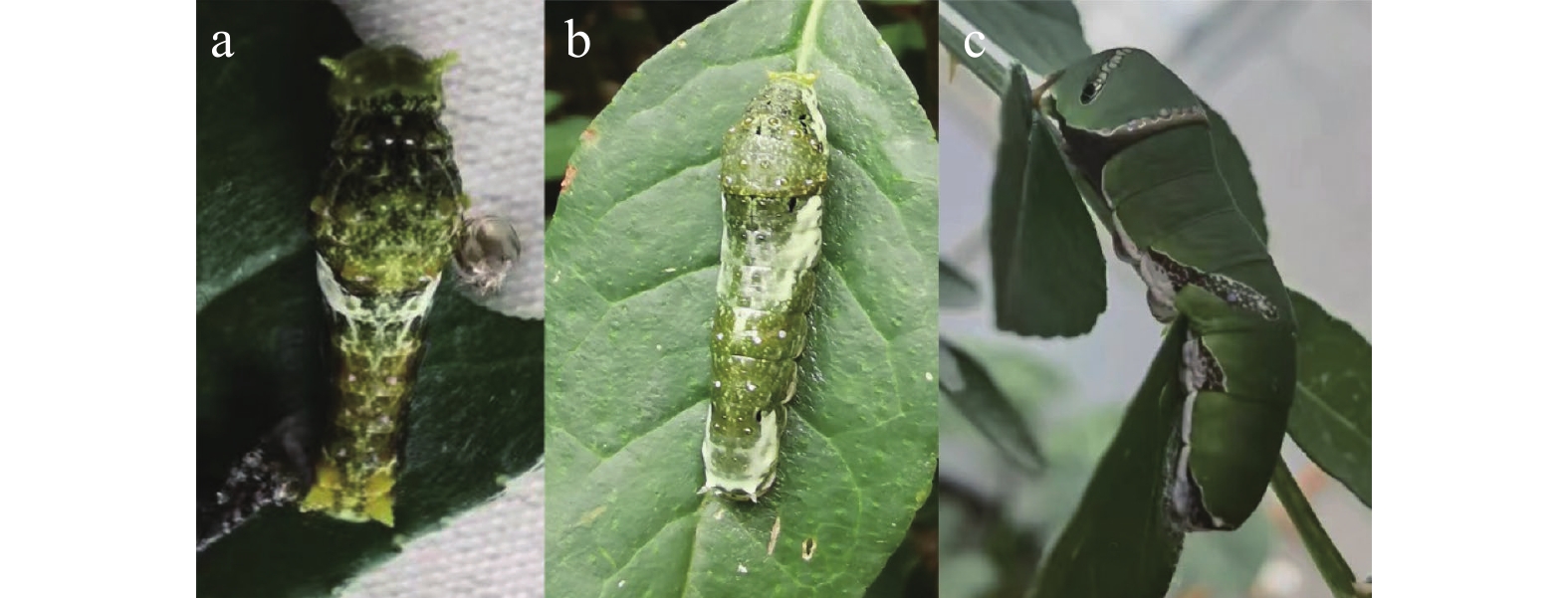
幼虫如图3所示,不同龄期幼虫体色和形状差异较大。1龄幼虫黄白色,头为暗黑色,各体节都生有1对刺状突,后胸膨大;2龄幼虫淡黄褐色,胸部、第8~9腹节背面和腹部末端有大块白斑;3龄幼虫深黄褐色,刺状突变短,腹部末端枝刺黄色,头部白斑变小,第8~9腹节背面和腹部末端的白斑破碎,不连成片;4龄幼虫体型明显变大,体色鲜绿,腹部背面有“X”形白斑、末端的黄色枝刺比3龄幼虫细;5龄幼虫深草绿色,后胸背面有齿状纹,斑纹两侧各有1个椭圆形黑色眼斑,第4~6腹节背面两侧各有1斜纹,腹部末端白色。
2.2 线粒体基因组结构
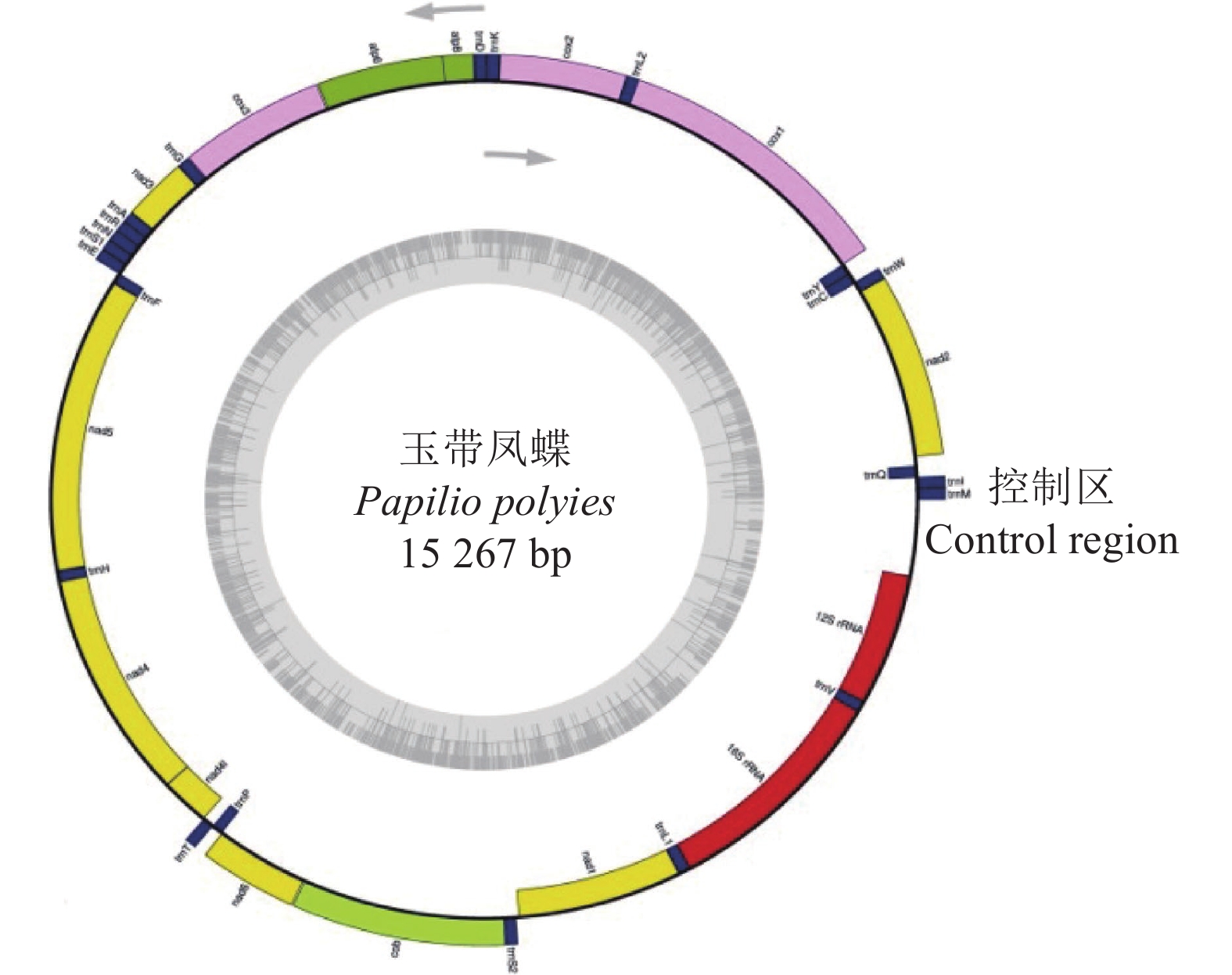
玉带凤蝶P. polytes线粒体基因组总长度为15 267 bp,碱基含量表现明显的AT偏好性,A+T平均含量为80.6%,详见表1。线粒体基因组包括37个基因和一段非编码区,GenBank登录号为MZ188895,共有 11处基因间隔区,最长的53 bp,在trnQ基因和nad2基因之间,有12处基因重叠区,最长的为8 bp,在trnW基因和trnC基因之间,详见表2。37个基因中,有23个基因在重链(Heavy strand)上,其中包括14个tRNAs、9个蛋白质编码基因;14个基因在轻链(Light strand)上,其中包括2个rRNAs、8个tRNAs、4个蛋白质编码基因。线粒体基因组结构如图4所示。
表 1 玉带凤蝶线粒体基因组核苷酸组成Table 1. Nucleotide composition of P. polytes mitochondrial genome区域 Regions T/% C/% A/% G/% A+T/% AT偏好性 AT skew GC偏好性 GC skew 全序列 Complete sequence 41.1 11.8 39.5 7.5 80.6 −0.019 −0.223 转运 RNAs tRNAs 39.3 7.9 42.4 10.5 81.6 0.038 0.144 核糖体 RNAs rRNAs 40.5 4.9 43.9 10.7 84.4 0.040 0.376 控制区 Control region 45.8 4.2 48.7 1.3 94.5 0.030 −0.524 atp6 46.5 12.3 33.3 7.9 79.8 −0.165 −0.215 atp8 45.5 5.5 47.3 1.8 92.7 0.020 −0.500 cytb 42.9 14.9 32.3 10.0 75.1 −0.141 −0.199 cox1 41.0 15.0 30.8 13.2 71.7 −0.143 −0.065 cox2 42.6 12.5 35.1 9.8 77.8 −0.097 −0.122 cox3 42.1 14.0 31.8 12.2 73.8 −0.139 −0.069 nad1 46.6 8.1 30.2 15.1 76.8 −0.214 0.302 nad2 48.7 10.2 34.5 6.6 83.2 −0.171 −0.211 nad3 46.2 12.3 35.1 6.4 81.3 −0.137 −0.313 nad4 47.1 6.7 34.5 11.8 81.5 −0.155 0.276 nad4l 51.0 4.6 31.8 12.6 82.8 −0.231 0.467 nad5 47.5 6.0 34.6 11.9 82.0 −0.157 0.327 nad6 51.6 7.0 35.5 5.8 87.1 −0.184 −0.094 注:AT偏斜 =(A−T)/(A+T), GC 偏斜 = (G-C)/(G+C)。
Note: AT skew =(A−T)/(A+T), GC skew = (G−C)/(G+C).表 2 玉带凤蝶线粒体基因组结构组成Table 2. Composition of P. polytes mitochondrial genome structure基因
Gene起始位置
Start position/bp终止位置
Stop position/bp基因长度
Gene length/bp基因间隔
Intergenic length/bp起始密码子
Start codon终止密码子
Stop codon反密码子
AnticodontrnM 1 68 68 0 ATG trnI 69 132 64 −3 ATC trnQ 130 197 68 53 CAA nad2 251 1 264 1 014 −2 ATT TAA trnW 1 263 1 327 65 −8 TGA trnC 1 320 1 384 65 1 TGC trnY 1 386 1 450 65 −1 TAC cox1 1 450 2 988 1 539 −5 TTG TAA trnL2 2 984 3 051 68 0 TTA cox2 3 052 3 733 682 0 ATG T trnK 3 734 3 803 70 0 AAG trnD 3 804 3 871 68 0 GAC atp8 3 872 4 039 168 −4 ATT TAA atp6 4 036 4 713 678 6 ATA TAA cox3 4 720 5 508 789 3 ATG TAA trnG 5 512 5 577 66 0 GGA nad3 5 578 5 931 354 −2 ATT TAG trnA 5 930 5 993 64 −1 GCA trnR 5 993 6 056 64 −1 CGA trnN 6 056 6 121 66 0 AAC trnS1 6 122 6 182 61 1 AGA trnE 6 184 6 249 66 −2 GAA trnF 6 248 6 311 64 0 TTC nad5 6 312 8 048 1 737 0 ATA TAA trnH 8 049 8 113 65 −1 CAC nad4 8 113 9 453 1 341 −1 ATG TAA nad4l 9 453 9 737 285 2 ATG TAA trnT 9 740 9 804 65 0 ACA trnP 9 805 9 868 64 2 CCA nad6 9 871 10 404 534 7 ATA TAA cytb 10 412 11 560 1 149 2 ATG TAA trnS2 11 563 11 628 66 16 TCA nad1 11 645 12 583 939 1 ATG TAG trnL1 12 585 12 653 69 0 CTA rrnL 12 654 13 980 1 327 0 trnV 13 981 14 043 63 0 GTA rrnS 14 044 14 823 780 0 控制区
Cortrol region14 824 15 267 444 2.3 蛋白质编码基因
13个蛋白质编码基因总长度为11 209 bp,其中最长的是nad5基因,长度为1 737 bp,最短的是atp8基因,为168 bp。12个基因均是以典型的ATN为起始密码子,仅有cox1基因是以特殊的TTG为起始密码子;只有cox2终止密码子不是TAA或TAG,而是以单独的T结尾。相对密码子使用频率最高是UUA,为4.93,如表3,平均使用频率最高的氨基酸是Leu(亮氨酸)。有8种氨基酸在13个蛋白质编码基因里均有出现,分别是Phe(苯丙氨酸)、Ile(异亮氨酸)、Lys(赖氨酸)、Leu(亮氨酸)、Met(蛋氨酸)、Gln(谷氨酰胺)、Ser(丝氨酸)、Tyr(酪氨酸)。Atp8基因里所含氨基酸种类最少,仅占总氨基酸种类的一半(10种)。
表 3 玉带凤蝶线粒体基因组相对密码子使用频率Table 3. Relative synonymous codon usage of P. polytes mitochondrial genome密码子
Codon数量
Count相对密
码子使
用频率
RSCU密码子
Codon数量
Count相对密
码子使
用频率
RSCU密码子
Codon数量
Count相对密
码子使
用频率
RSCU密码子
Codon数量
Count相对密
码子使
用频率
RSCUUUU(F) 23.9 1.81 UCU(S) 8.5 2.82 UAU(Y) 13.8 1.92 UGU(C) 2.2 1.75 UUC(F) 2.5 0.19 UCC(S) 1.2 0.38 UAC(Y) 0.5 0.08 UGC(C) 0.3 0.25 UUA(L) 33.8 4.93 UCA(S) 5.8 1.9 UAA(*) 0 0 UGA(W) 6.8 1.93 UUG(L) 1.1 0.16 UCG(S) 0.2 0.05 UAG(*) 0 0 UGG(W) 0.2 0.07 CUU(L) 3.8 0.56 CCU(P) 5.9 2.59 CAU(H) 4.8 1.85 CGU(R) 1.4 1.36 CUC(L) 0.2 0.03 CCC(P) 0.9 0.4 CAC(H) 0.4 0.15 CGC(R) 0.1 0.08 CUA(L) 2.1 0.3 CCA(P) 2.1 0.91 CAA(Q) 4.8 1.94 CGA(R) 2.5 2.42 CUG(L) 0.1 0.01 CCG(P) 0.2 0.1 CAG(Q) 0.2 0.06 CGG(R) 0.2 0.15 AUU(I) 31.7 1.9 ACU(T) 7.2 2.58 AAU(N) 18.2 1.88 AGU(S) 1.8 0.61 AUC(I) 1.7 0.1 ACC(T) 0.2 0.08 AAC(N) 1.2 0.12 AGC(S) 0 0 AUA(M) 20.1 1.88 ACA(T) 3.5 1.28 AAA(K) 6.2 1.74 AGA(S) 6.5 2.13 AUG(M) 1.2 0.12 ACG(T) 0.2 0.06 AAG(K) 0.9 0.26 AGG(S) 0.3 0.1 GUU(V) 6 2.24 GCU(A) 6.2 2.62 GAU(D) 3.9 1.65 GGU(G) 4.8 1.29 GUC(V) 0.1 0.03 GCC(A) 0.9 0.39 GAC(D) 0.8 0.35 GGC(G) 0.2 0.04 GUA(V) 4.5 1.7 GCA(A) 2 0.85 GAA(E) 5.4 1.84 GGA(G) 8.4 2.27 GUG(V) 0.1 0.03 GCG(A) 0.3 0.13 GAG(E) 0.5 0.16 GGG(G) 1.5 0.4 注:RSCU:相对密码子使用频率。 *:终止密码子Stop codon。
Note: RSCU: Relative synonymous codon usage. *: Stop codon.2.4 RNA基因与控制区
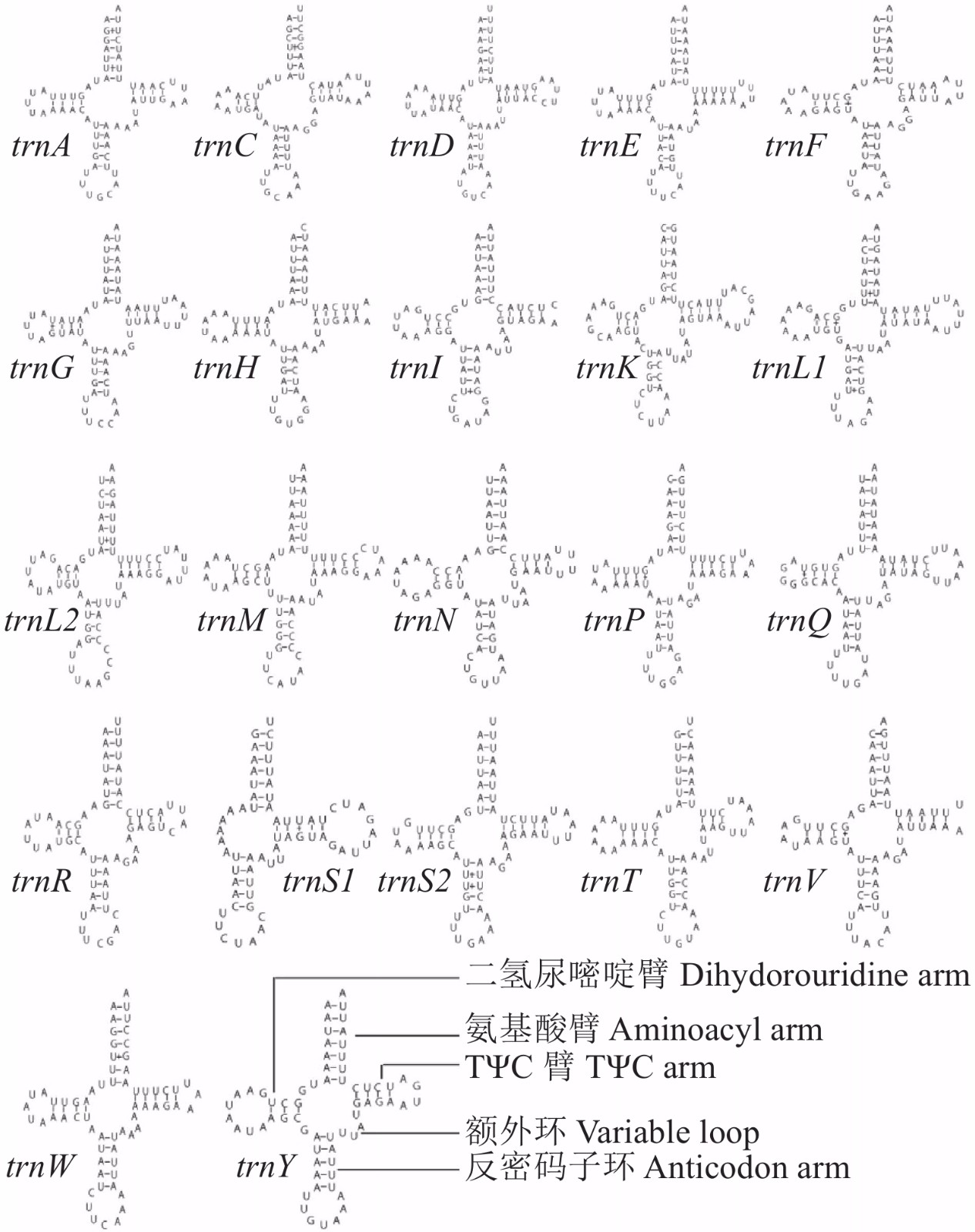
22个tRNAs总长度为1 444 bp,基因长度介于61 bp(trnS1基因)和70 bp(trnK基因)之间,除trnS1基因缺少DHU臂构不成三叶草结构外,其他21个二级结构均是典型的三叶草结构,如图5所示。碱基配对大多都是遵循Waston-Crick配对规律, G-U配对和U-U配对共有17处,其中G-U配对12处,U-U配对5处,有9个tRNAs基因未出现碱基错配。
2个rRNAs均位于轻链,rrnL基因位于trnL1基因和trnV基因之间,长度为1 327 bp,rrnS基因位于trnV基因和控制区之间,长度为780 bp。
控制区位于rrnS基因和trnM基因之间,长度为444 bp,A+T的平均含量最高,为94.5%。
3. 讨论与结论
玉带凤蝶指名亚种和西藏亚种蝶翅面斑纹有较大区别:指名亚种雄蝶前翅背面外缘区黄斑有7~9个不等,而西藏亚种有7个且后翅背面臀角处有红色和蓝色2团鳞片,指名亚种没有;指名亚种后翅腹面亚缘区有7个白色斑,西藏亚种有6个黄色斑。指名亚种雌蝶后翅背面外中区有斑2~6个不等,其中靠近后缘的1~2个斑红色,而西藏亚种有6个,其中后缘的2个斑红色,第3个斑近基部白色、近端部为红色,2个小斑黄色;指名亚种亚外缘区有月牙斑7个,西藏亚种6个;指名亚种后翅腹面亚缘区红斑有6个,西藏亚种7个,指名亚种后翅腹面斑纹同背面,西藏亚种斑纹比背面复杂,外中区2个黄色小斑,近外缘处比背面多1个红斑,与相近的小黄斑几乎连接。指名亚种分布于陕西、河北、河南、湖南、湖北、山东、山西、江西、浙江、江苏、广西、广东、福建等地,而西藏亚种仅分布在西藏,玉带凤蝶指名亚种和西藏亚种翅面斑纹的不同,与西藏特殊的地理位置、海拔和气候条件气候等有重要关系。
线粒体是细胞质中为细胞生命活动提供能量的细胞器。玉带凤蝶线粒体基因组中,37个基因的排列顺序和方向与小红珠绢蝶Parnassius nomion[9]、扬眉线蛱蝶Limenitis helmanni [10]一致,基因trnM-trnI-trnQ的排列顺序与研究较多的鞘翅目Coleoptera、直翅目Orthoptera等昆虫线粒体基因组的trnI-trnQ-trnM的排列顺序不一样[11-12],没有出现基因重排与缺失的现象。2个rRNA的排列位置,说明了蝶类线粒体基因组进化上比较保守。通过核苷酸组成分析,37个基因的A+T的平均含量明显高于G+C的平均含量,表明玉带凤蝶线粒体基因组有明显的AT偏向性,验证了昆虫线粒体基因组有AT偏向性的特征。关于基因重叠现象,累计重叠序列31 bp,验证了线粒体基因组结构紧密,编码效率高的观点[13]。13个蛋白质编码基因中的cox1基因是以特殊的TTG作为起始密码子,这种非正常的起始密码子可以经过转换完成翻译功能,研究表明,这种现象普遍存在于包括鳞翅目在内的节肢动物中[14-15]。cox2基因是以T作为终止密码子,这种不完整的终止密码子可以在RNA加工中经过添加Poly A尾巴转变为完整的终止密码子。22个tRNAs除trnS1基因外均为典型的三叶草结构,碱基配对出现的非典型配对或错配可以通过编辑矫正,不影响转运功能[16]。与其他大多数种类的昆虫相比,鳞翅目昆虫的控制区与更为保守,有最高的A+T含量,证明了控制区又叫A+T富含区的科学性。
本研究玉带凤蝶指名亚种和西藏亚种外部形态的区别主要是由于地位分布位置的不同,玉带凤蝶线粒体基因组结构和基因排列顺序与鳞翅目昆虫线粒体基因组结构和排列一致,线粒体基因组总长度为15 267 bp,有明显的AT偏向性。
-
表 1 玉带凤蝶线粒体基因组核苷酸组成
Table 1 Nucleotide composition of P. polytes mitochondrial genome
区域 Regions T/% C/% A/% G/% A+T/% AT偏好性 AT skew GC偏好性 GC skew 全序列 Complete sequence 41.1 11.8 39.5 7.5 80.6 −0.019 −0.223 转运 RNAs tRNAs 39.3 7.9 42.4 10.5 81.6 0.038 0.144 核糖体 RNAs rRNAs 40.5 4.9 43.9 10.7 84.4 0.040 0.376 控制区 Control region 45.8 4.2 48.7 1.3 94.5 0.030 −0.524 atp6 46.5 12.3 33.3 7.9 79.8 −0.165 −0.215 atp8 45.5 5.5 47.3 1.8 92.7 0.020 −0.500 cytb 42.9 14.9 32.3 10.0 75.1 −0.141 −0.199 cox1 41.0 15.0 30.8 13.2 71.7 −0.143 −0.065 cox2 42.6 12.5 35.1 9.8 77.8 −0.097 −0.122 cox3 42.1 14.0 31.8 12.2 73.8 −0.139 −0.069 nad1 46.6 8.1 30.2 15.1 76.8 −0.214 0.302 nad2 48.7 10.2 34.5 6.6 83.2 −0.171 −0.211 nad3 46.2 12.3 35.1 6.4 81.3 −0.137 −0.313 nad4 47.1 6.7 34.5 11.8 81.5 −0.155 0.276 nad4l 51.0 4.6 31.8 12.6 82.8 −0.231 0.467 nad5 47.5 6.0 34.6 11.9 82.0 −0.157 0.327 nad6 51.6 7.0 35.5 5.8 87.1 −0.184 −0.094 注:AT偏斜 =(A−T)/(A+T), GC 偏斜 = (G-C)/(G+C)。
Note: AT skew =(A−T)/(A+T), GC skew = (G−C)/(G+C).表 2 玉带凤蝶线粒体基因组结构组成
Table 2 Composition of P. polytes mitochondrial genome structure
基因
Gene起始位置
Start position/bp终止位置
Stop position/bp基因长度
Gene length/bp基因间隔
Intergenic length/bp起始密码子
Start codon终止密码子
Stop codon反密码子
AnticodontrnM 1 68 68 0 ATG trnI 69 132 64 −3 ATC trnQ 130 197 68 53 CAA nad2 251 1 264 1 014 −2 ATT TAA trnW 1 263 1 327 65 −8 TGA trnC 1 320 1 384 65 1 TGC trnY 1 386 1 450 65 −1 TAC cox1 1 450 2 988 1 539 −5 TTG TAA trnL2 2 984 3 051 68 0 TTA cox2 3 052 3 733 682 0 ATG T trnK 3 734 3 803 70 0 AAG trnD 3 804 3 871 68 0 GAC atp8 3 872 4 039 168 −4 ATT TAA atp6 4 036 4 713 678 6 ATA TAA cox3 4 720 5 508 789 3 ATG TAA trnG 5 512 5 577 66 0 GGA nad3 5 578 5 931 354 −2 ATT TAG trnA 5 930 5 993 64 −1 GCA trnR 5 993 6 056 64 −1 CGA trnN 6 056 6 121 66 0 AAC trnS1 6 122 6 182 61 1 AGA trnE 6 184 6 249 66 −2 GAA trnF 6 248 6 311 64 0 TTC nad5 6 312 8 048 1 737 0 ATA TAA trnH 8 049 8 113 65 −1 CAC nad4 8 113 9 453 1 341 −1 ATG TAA nad4l 9 453 9 737 285 2 ATG TAA trnT 9 740 9 804 65 0 ACA trnP 9 805 9 868 64 2 CCA nad6 9 871 10 404 534 7 ATA TAA cytb 10 412 11 560 1 149 2 ATG TAA trnS2 11 563 11 628 66 16 TCA nad1 11 645 12 583 939 1 ATG TAG trnL1 12 585 12 653 69 0 CTA rrnL 12 654 13 980 1 327 0 trnV 13 981 14 043 63 0 GTA rrnS 14 044 14 823 780 0 控制区
Cortrol region14 824 15 267 444 表 3 玉带凤蝶线粒体基因组相对密码子使用频率
Table 3 Relative synonymous codon usage of P. polytes mitochondrial genome
密码子
Codon数量
Count相对密
码子使
用频率
RSCU密码子
Codon数量
Count相对密
码子使
用频率
RSCU密码子
Codon数量
Count相对密
码子使
用频率
RSCU密码子
Codon数量
Count相对密
码子使
用频率
RSCUUUU(F) 23.9 1.81 UCU(S) 8.5 2.82 UAU(Y) 13.8 1.92 UGU(C) 2.2 1.75 UUC(F) 2.5 0.19 UCC(S) 1.2 0.38 UAC(Y) 0.5 0.08 UGC(C) 0.3 0.25 UUA(L) 33.8 4.93 UCA(S) 5.8 1.9 UAA(*) 0 0 UGA(W) 6.8 1.93 UUG(L) 1.1 0.16 UCG(S) 0.2 0.05 UAG(*) 0 0 UGG(W) 0.2 0.07 CUU(L) 3.8 0.56 CCU(P) 5.9 2.59 CAU(H) 4.8 1.85 CGU(R) 1.4 1.36 CUC(L) 0.2 0.03 CCC(P) 0.9 0.4 CAC(H) 0.4 0.15 CGC(R) 0.1 0.08 CUA(L) 2.1 0.3 CCA(P) 2.1 0.91 CAA(Q) 4.8 1.94 CGA(R) 2.5 2.42 CUG(L) 0.1 0.01 CCG(P) 0.2 0.1 CAG(Q) 0.2 0.06 CGG(R) 0.2 0.15 AUU(I) 31.7 1.9 ACU(T) 7.2 2.58 AAU(N) 18.2 1.88 AGU(S) 1.8 0.61 AUC(I) 1.7 0.1 ACC(T) 0.2 0.08 AAC(N) 1.2 0.12 AGC(S) 0 0 AUA(M) 20.1 1.88 ACA(T) 3.5 1.28 AAA(K) 6.2 1.74 AGA(S) 6.5 2.13 AUG(M) 1.2 0.12 ACG(T) 0.2 0.06 AAG(K) 0.9 0.26 AGG(S) 0.3 0.1 GUU(V) 6 2.24 GCU(A) 6.2 2.62 GAU(D) 3.9 1.65 GGU(G) 4.8 1.29 GUC(V) 0.1 0.03 GCC(A) 0.9 0.39 GAC(D) 0.8 0.35 GGC(G) 0.2 0.04 GUA(V) 4.5 1.7 GCA(A) 2 0.85 GAA(E) 5.4 1.84 GGA(G) 8.4 2.27 GUG(V) 0.1 0.03 GCG(A) 0.3 0.13 GAG(E) 0.5 0.16 GGG(G) 1.5 0.4 注:RSCU:相对密码子使用频率。 *:终止密码子Stop codon。
Note: RSCU: Relative synonymous codon usage. *: Stop codon. -
[1] SHOBANA K, MURUGAN K, NARESH K A. Influence of host plants on feeding, growth and reproduction of Papilio polytes (The common Mormon) [J]. Journal of Insect Physiology, 2010, 56(9): 1065−1070. DOI: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2010.02.018
[2] HONDA K, TAKASE H, ÔMURA H, et al. Procurement of exogenous ammonia by the swallowtail butterfly, Papilio polytes, for protein biosynthesis and sperm production [J]. Naturwissenschaften, 2012, 99(9): 695−703. DOI: 10.1007/s00114-012-0951-z
[3] CAMERON S L. Insect mitochondrial genomics: Implications for evolution and phylogeny [J]. Annual Review of Entomology, 2014, 59: 95−117. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-ento-011613-162007
[4] GAIKWAD S M, KOLI Y J, BHAWANE G P. Histomorphology of the female reproductive system in Papilio polytes polytes Linnaeus, 1758 (Lepidoptera: Papilionidae) [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, India Section B:Biological Sciences, 2014, 84(4): 901−908. DOI: 10.1007/s40011-014-0322-y
[5] SUWARNO M R, SALMAH C, ALI A, et al. Oviposition preference of swallowtail butterfly, Papilio polytes (Lepidoptera: Papilionidae) on four Rutaceae ( Sapindales ) host plant species [J]. Insect Science, 2010, 17(4): 369−378.
[6] ÔMURA H, HONDA K. Chemical composition of volatile substances from adults of the swallowtail, Papilio polytes (Lepidoptera: Papilionidae) [J]. Applied Entomology and Zoology, 2005, 40(3): 421−427. DOI: 10.1303/aez.2005.421
[7] YANG X W, HOU L X, ZHANG Y, et al. The complete mitochondrial genome of Papilio polytes (Lepidoptera Papilionidae) [J]. Mitochondrial DNA Part A, DNA Mapping, Sequencing, and Analysis, 2016, 27(2): 1537−1538.
[8] WANG L, DU X J, LI X F. The complete mitogenome of the common Mormon Papilio polytes (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Papilionoidea) [J]. Mitochondrial DNA Part A, DNA Mapping, Sequencing, and Analysis, 2016, 27(2): 1269−1270.
[9] 张敏, 赵盼, 尹洁, 等. 小红珠绢蝶线粒体基因组特征及基于线粒体基因组的蝶类高级阶元系统发育关系分析 [J]. 昆虫学报, 2017, 60(11):1324−1338. ZHANG M, ZHAO P, YIN J, et al. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Parnassius nomion(Lepidoptera: Parnassiidae) and analysis of the higher-level phylogenetic relationships of butterflies based on mitochondrial genome [J]. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 2017, 60(11): 1324−1338.(in Chinese)
[10] 王菊平, 曹天文, 张越, 等. 扬眉线蛱蝶线粒体基因组全序列测定和分析 [J]. 昆虫学报, 2017, 60(8):950−961. WANG J P, CAO T W, ZHANG Y, et al. Sequencing and analysis of the complete mitochondrial genome of Limenitis helmanni (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae) [J]. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 2017, 60(8): 950−961.(in Chinese)
[11] 党江鹏, 刘念, 叶伟, 等. 云斑车蝗线粒体基因组全序列测定与分析 [J]. 昆虫学报, 2008, 51(7):671−680. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0454-6296.2008.07.001 DANG J P, LIU N, YE W, et al. Complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Gastrimargus marmoratus (Thunberg) (Orthoptera: Acridoidea) [J]. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 2008, 51(7): 671−680.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0454-6296.2008.07.001
[12] 田天, 袁缓, 陈斌. 基于线粒体基因组序列的鞘翅目肉食亚目水生类群系统发育分析 [J]. 昆虫学报, 2020, 63(8):1016−1027. TIAN T, YUAN H, CHEN B. Phylogeny of hydradephagan water beetles (Coleoptera: Adephaga) inferred with mitochondrial genome sequences [J]. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 2020, 63(8): 1016−1027.(in Chinese)
[13] 张立. 隆线溞线粒体基因组序列的测定与分析[D]. 淮北: 淮北师范大学, 2014. ZHANG L. The analysis of the mitochondrial genome of Daphnia carinata (Clasocera: Daphniidae)[D]. Huaibei: Huaibei Normal University, 2014. (in Chinese)
[14] WOO H J, LEE Y S, PARK S J, et al. Complete mitochondrial genome of a troglobite millipede Antrokoreana gracilipes (Diplopoda, juliformia, julida), and juliformian phylogeny [J]. Molecules and Cells, 2007, 23(2): 182−191.
[15] KIM M I, BAEK J Y, KIM M J, et al. Complete nucleotide sequence and organization of the mitogenome of the red-spotted Apollo butterfly, Parnassius bremeri (Lepidoptera: Papilionidae) and comparison with other lepidopteran insects [J]. Molecules and Cells, 2009, 28(4): 347−363. DOI: 10.1007/s10059-009-0129-5
[16] VARANI G, MCCLAIN W H. The G x U wobble base pair. A fundamental building block of RNA structure crucial to RNA function in diverse biological systems [J]. EMBO Reports, 2000, 1(1): 18−23. DOI: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvd001
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 赵卓,刘晨阳,瓮青芬,王保海,翟卿. 茶六斑褐锦斑蛾Sorita pulchella线粒体基因组特征与系统发育分析. 河南农业大学学报. 2023(02): 277-287 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 韦春梦,陈亚珍,刘静,邓维安,李晓东. 云南瘤蚱线粒体基因组特征与蚱总科系统发育分析. 南方农业学报. 2023(05): 1303-1316 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载: