Effects of Dietary Rutin on Rumen Microbial Community Diversity and Composition of Hu Sheep
-
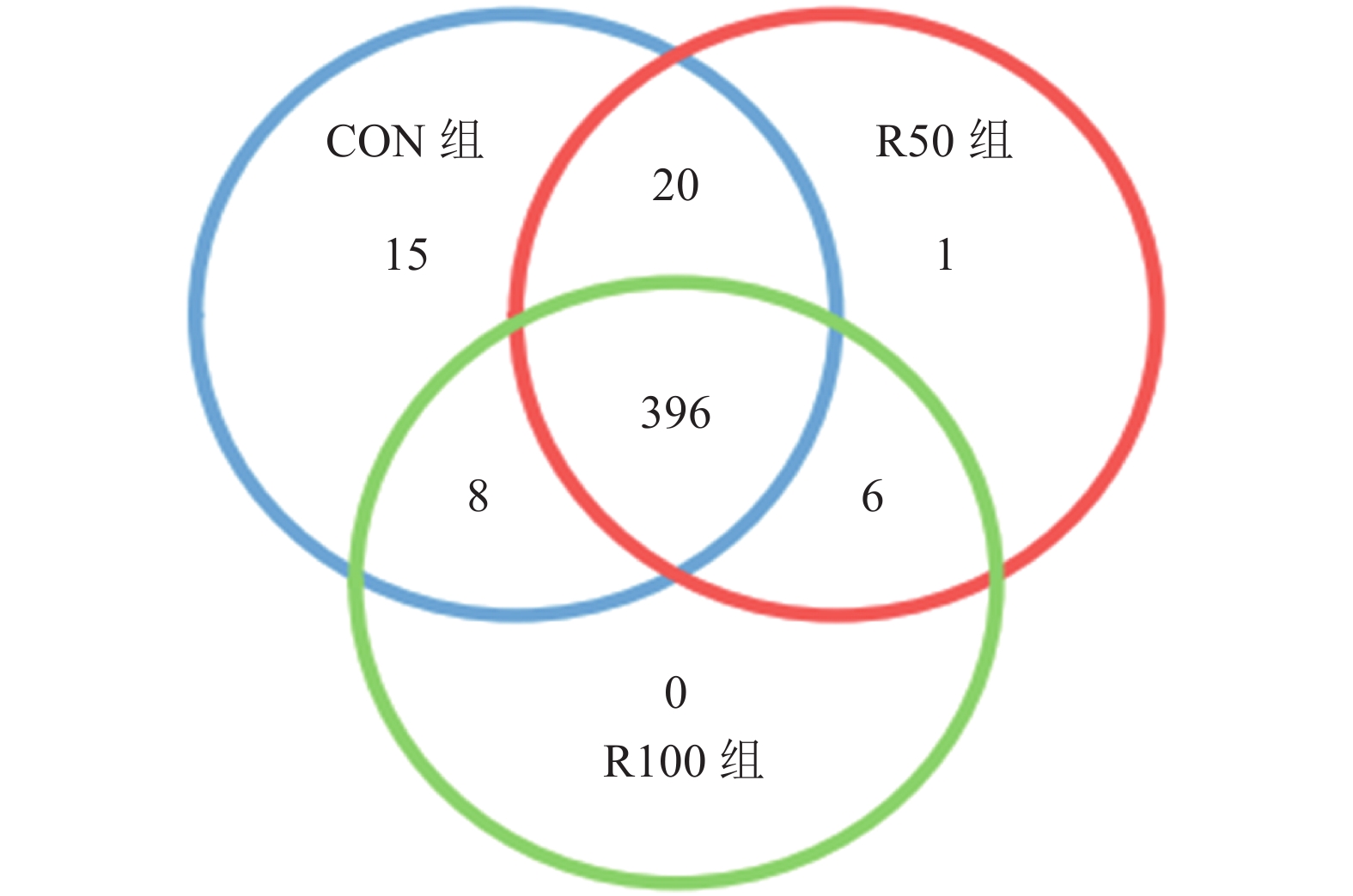
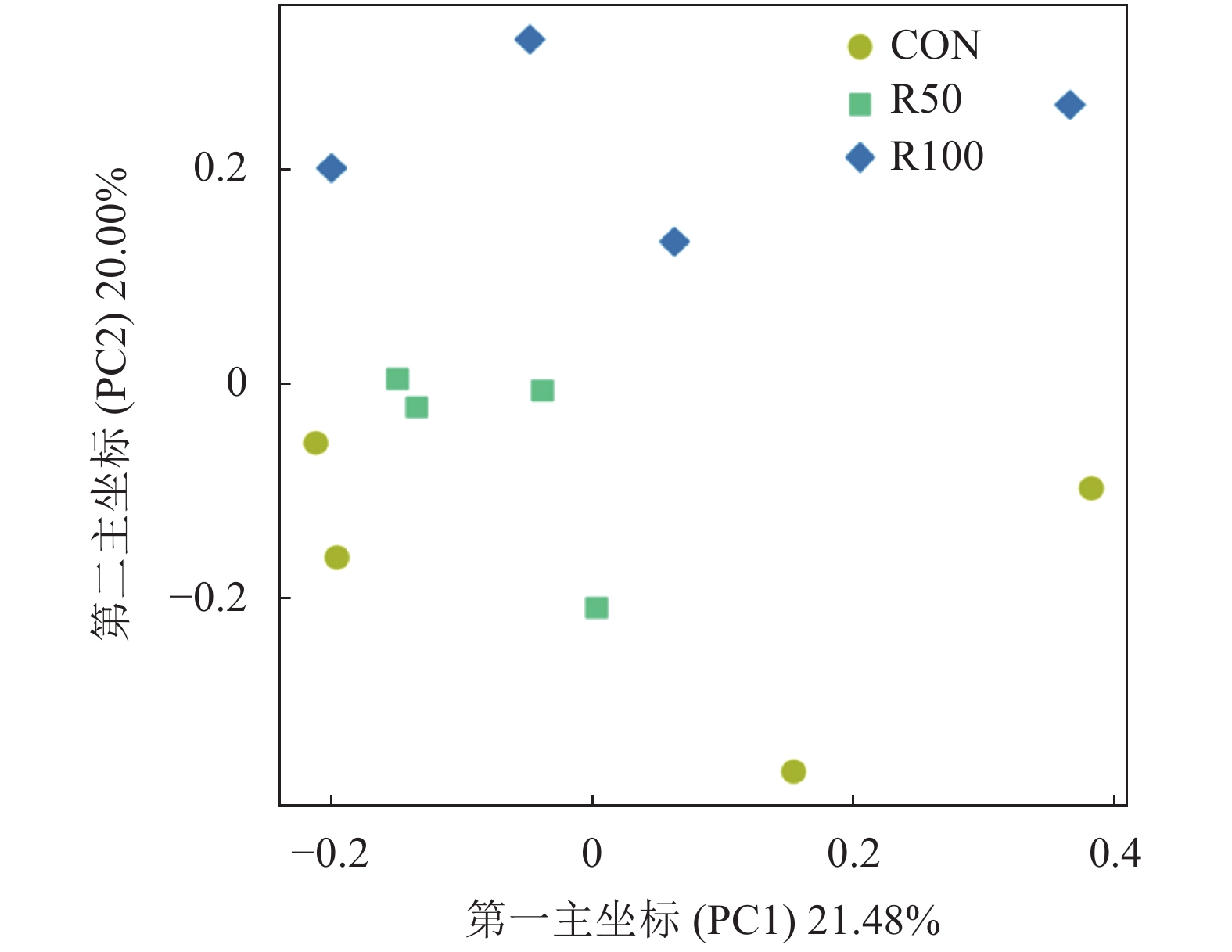
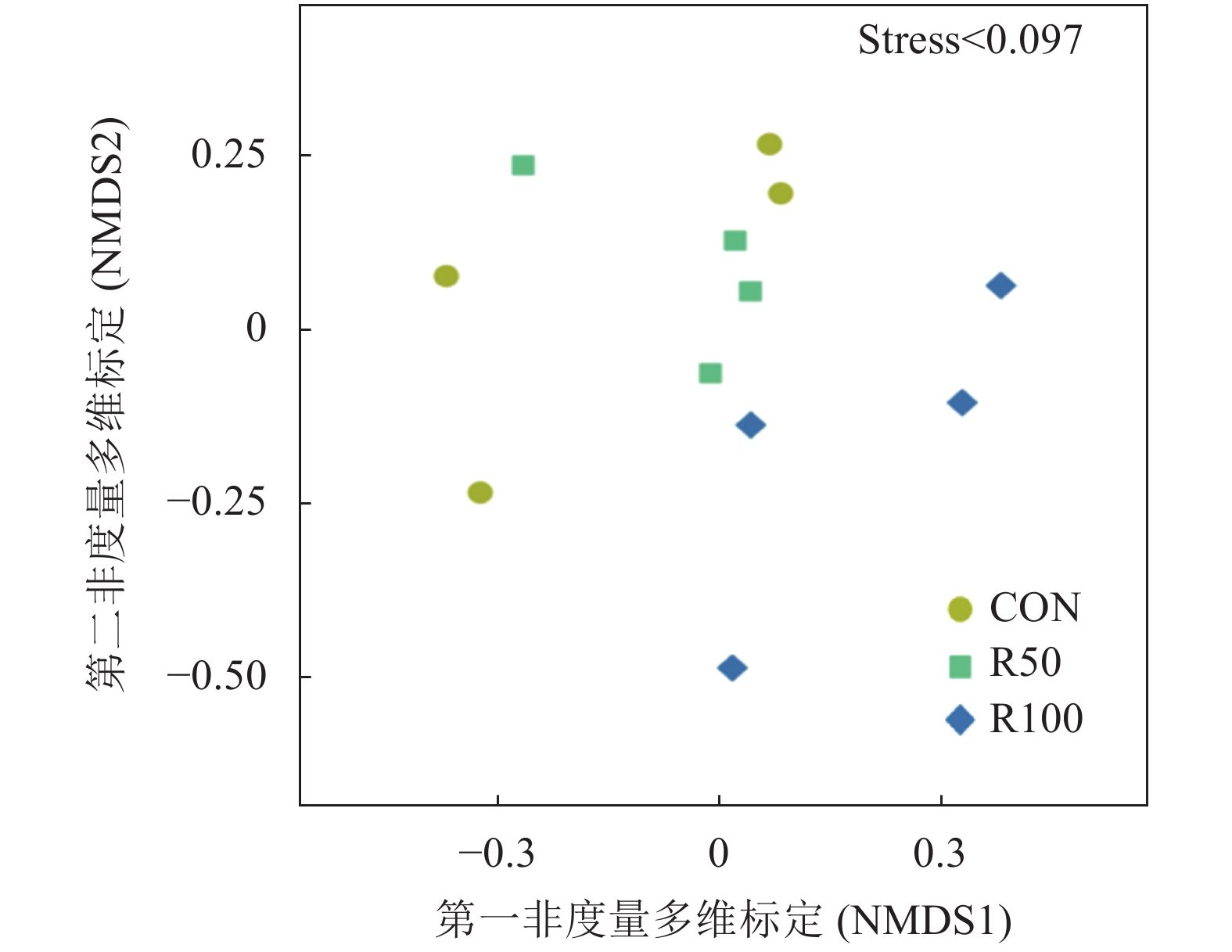
摘要:目的 研究日粮中添加芦丁对湖羊瘤胃细菌菌群多样性及组成的影响。方法 选择3月龄左右、健康且体重相近的湖羊36只,随机分为3个处理,每个处理12只(公母各半,分栏饲养)。对照组(CON组)饲喂基础日粮,试验组R50和R100分别在基础日粮中添加50、100 mg·kg−1(湖羊体重基础)的芦丁。试验期为70 d,预试期14 d,正试期56 d。结果 1)3组共产生446个OTUs(Operational taxonomic units),其中共有OTU为396个,占总OTU的88.79%,所有样品共注释了14个门(Phylum)、18个纲(Class)、21个目(Order)、34个科(Family)和99个属(Genus)。2)相对于CON组,R100组的ACE指数、Shannon指数、Chao1指数显著降低(P<0.05)。但CON和R50组中Alpha多样性均无显著差异(P>0.05)。3)通过PCoA分析(Principal co-ordinates analysis)、NMDS分析(Non-metric multi-dimensional scaling analysis)、UPGMA聚类方法(Unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean clustering analysis)和Anosim分析可知,R100组显著影响微生物群落结构。4)在门水平,拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)和厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)为两大优势菌门。相比CON组,R100组髌骨细菌门(Patescibacteria)的相对丰度显著提高,迷踪菌门(Elusimicrobia)的相对丰度显著降低(P<0.05),但R50组Elusimicrobia的相对丰度显著高于CON组和R100组(P<0.05)。5)在属水平,优势菌属均为普雷沃菌属_1(Prevotella_1)。在已鉴定丰度排名前30的属水平上,R100组新月形单胞菌属_1(Selenomonas_1)和琥珀酸菌属(Succiniclasticum)的相对丰度显著低于CON组(P<0.05),但与R50组差异不显著(P>0.05)。结论 添加100 mg·kg−1的芦丁能够影响湖羊瘤胃微生物多样性。Abstract:Objective Effects of rutin supplementation in forage on the rumen microbial community diversity and composition of Hu sheep were studied.Method Thirty-six healthy 3-month-old Hu sheep of similar body weight were randomly divided into 3 groups of 12 animals (half male and female) each for the treatments. The sheep in the control group (CON) were fed a basal diet, while those in two treatment groups on a daily diet supplemented with rutin at a rate of 50 mg (R50) or 100 mg (R100) per kg of animal body weight. The feeding test lasted for 70 d that included 14 d of pre-test and 56 d of actual test.Result (1) Of the 446 OTUs collected in the sheep rumens, 396 (constituted 88.79% of total) were commonly shared by the sheep in the 3 groups that annotated into 14 phyla, 18 classes, 21 orders, 34 families, and 99 genera. (2) The ACE, Shannon, and Chao1 indices of the sheep in the R100 group were significantly lower than those of CON (P
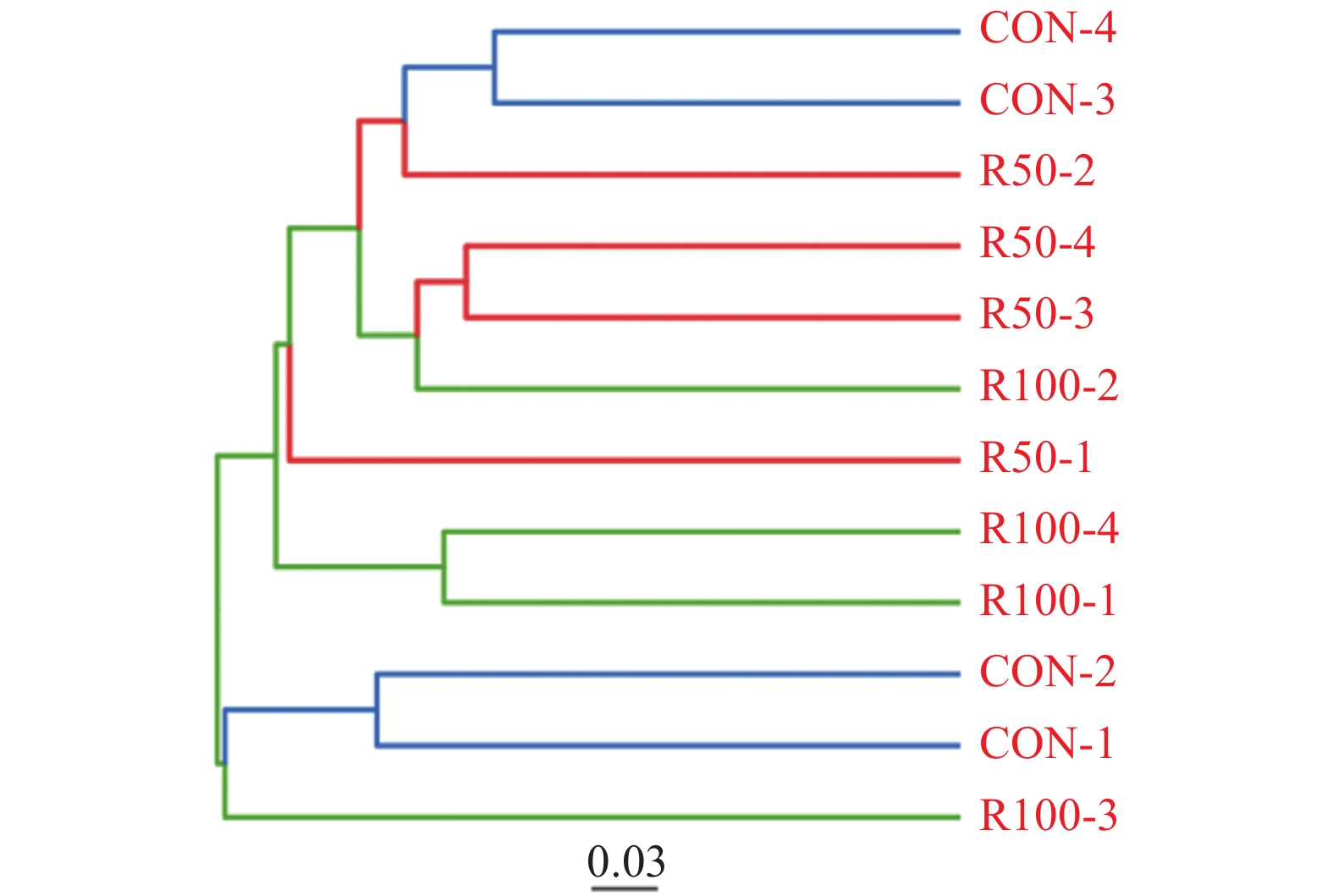
<0.05), while the alpha diversity not significantly different between CON and R50 groups (P>0.05). (3) The results of the principal co-ordinates analysis (PCoA), the non-metric multi-dimensional scaling analysis (NMDS), the unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean clustering analysis (UPGMA), and the anosim analysis showed that the microbial community was significantly altered by the R100 treatment (P<0.05). (4) Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes were two dominant phyla. R100 significantly increased the relative abundance of Patescibacteria but decreased that of Elusimicrobia (P <0.05). On the other hand, R50 significantly raised the relative abundance of Elusimicrobia over CON or R100 (P<0.05). (5) At genus level, the dominant microbes were Prevotella_1 . The relative abundance of Selenomonas_1 and Succiniclasticum in the sheep fed with R100 were significantly lower than CON (P<0.05) but not significantly different from R50 (P>0.05). Conclusion Addition of rutin to forage at a rate of 100 mg·kg−1 of sheep body weight significantly affected the rumen microbial diversity in Hu sheep .-
Keywords:
- Hu sheep /
- rutin /
- rumen /
- microorganism
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】茶树[Camellia sinensis(L.)O.Kuntze]作为我国南方的重要经济作物之一,喜温喜湿,最适宜生长pH为4.5~5.5。茶叶产量高低和品质优劣受茶树生长环境的影响,茶园土壤作为茶树赖以生存和发展的环境基础,土壤养分的丰缺和肥力水平的高低将直接影响茶树的生长[1-2]。了解茶园土壤肥力水平和养分缺失分布状况,可以为改良茶园土壤和测土配方施肥提供科学依据,有利于改良茶园土壤肥力状况,改善茶树种植技术,对提升茶叶产量和品质、增加茶园收益具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】姜彬等[3]通过对黄河中游渭北卤泊滩地区的盐碱地进行土壤肥力评价,提出使用有机肥以及因地制宜采用暗管排盐技术:李政昊等[4]通过对铁岭植烟区土壤进行肥力评价,提出要因地制宜地采取深松与旋耕联合作业加厚耕层并增施有机肥、微量元素肥料来均衡养分;李文昭等[5]通过采用Fuzzy综合评价法对贵州遵义茶园进行等级评价;温继良等[6]通过数值化综合评价,新平县8个茶园土壤肥力水平达到I级标准,但仍有部分含量低于标准,因此需要进一步加强土壤肥力管理,以保证茶园的可持续发展。并提出相应的施肥措施。【本研究切入点】安溪县作为“中国乌龙茶之乡”,茶叶产量连续多年位居我国重点产茶县第一位,茶产业是安溪县重要的经济支柱产业[7]。前人调查发现,在安溪县的茶园里,37.67%的土壤酸化严重,仅有10.03%的土壤能够满足茶树的生长需求。此外,随着茶树的生长,这些土壤的酸化程度会越来越严重,从而导致茶叶的产量和品质下降[8]。但关于安溪茶园土壤肥力及分布情况研究较少,养分结构和肥力等级尚不明确。【拟解决的关键问题】选择pH、有机质、速效钾、有效磷、碱解氮、全氮、全磷、全钾8个养分指标,并采用Fuzzy综合评判法,对安溪县22个主要产茶乡镇的茶园土壤肥力进行评估,得出其肥力评价指数值(IFI),并对茶园土壤肥力等级进行评价,明确安溪县茶园土壤养分结构及空间分布规律,并因地制宜提出施肥建议措施,为精准改良安溪县茶园土壤养分缺失状况提供技术支持。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 研究区概况
安溪县(25.05627 N,118.18719 E)位于福建省泉州市东南部,总面积3057.28 km2,属戴云山脉的延伸部分,地势从西北向东南倾斜,境内山峦起伏,景色宜人,气候宜人,地形地势复杂,多山地丘陵。安溪县属亚热带季风气候区,年均气温16~20 ℃,年降雨量1700 mm左右,无霜期约260 d。生态环境优越,气候温度适宜,雨水充沛,十分适合茶树生长[9]。
1.2 样品采集与指标测定
于2021年11月在安溪县22个主要产茶乡镇茶园进行随机取样,合计243个,土壤以红壤、黄壤、红黄壤为主。茶树以铁观音、本山、黄金桂、毛蟹为主,种植年限为5~20年。于取样区采用“S”形5点取样法采集0~30 cm土壤,混合均匀,剔除碎石、动植物残体后自然风干,过10目筛混匀备用。
根据鲍士旦《土壤农化分析》(第3版)的方法[10]:使用水浸提—电位法测定土壤pH;重铬酸钾氧化—外加热法测定有机质(OM);碱解扩散法测定碱解氮(AN);氟化铵—盐酸溶液浸提法测定速效磷(AP);醋酸铵—火焰光度计法测定速效钾(AK);自动定氮仪法(NY/T 1121.24—2012)测定土壤全氮(TN);碱熔-钼锑抗分光光度法(HJ 632-2011)测定土壤全磷(TP);NaOH熔融—火焰光度法测定土壤全钾(TK)。
1.3 土壤肥力质量等级评定标准
依据国家有关绿色食品产地质量标准(NY/T 391—2000)、国家茶叶产地环境技术条件(NY/T 853—2004)中的优质茶园的土壤营养诊断指标[11-12],提出茶园土壤养分含量分级标准(表1)。
表 1 茶园土壤养分分级标准Table 1. Standards for classifying nutrient contents in tea plantation soil指标
IndicatorsⅠ级
Grade ⅠⅡ级
Grade ⅡⅢ级
Grade Ⅲ优质茶园标准
High quality tea plantation standardpH 4.5~5.5 4.0~4.5或5.5~6.5 >6.5或<4.0 4.5~5.5 有机质 Organic matter/(g·kg−1) >20.00 15.00~20.00 <15.00 ≥20.00 全氮 Total nitrogen/(g·kg−1) >1.00 0.80~1.00 <0.80 ≥1.50 全磷 Total phosphorus/(g·kg−1) >1.00 0.40~1.00 <0.40 ≥1.00 全钾 Total potassium/(g·kg−1) >10.00 5.00~10.00 <5.00 ≥10.00 碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen/(mg·kg−1) >100.00 80.00~100.00 <80.00 ≥100.00 有效磷 Available phosphorus/(mg·kg−1) >20.00 5.00~20.00 <5.00 ≥20.00 速效钾 Available potassium/(mg·kg−1) >100.00 60.00~100.00 <60.00 ≥100.00 土壤肥力综合指数值(Integrated Fertility Index,IFI)是一种衡量茶园土壤肥力的重要指标,它反映了不同肥力指标的权重系数以及它们之间的隶属关系,并且可以用来衡量土壤的肥力水平。IFI的数值越大,说明该地区的土壤肥力水平越好。通过结合前人研究[13],将土壤肥力综合指数值测算结果划分为4个等级(表2)。
表 2 土壤肥力综合指数分级标准Table 2. Standards of comprehensive fertility index on tea plantation soil土壤肥力综合指标 IFI IFI≥0.7 0.6≤IFI<0.7 0.5≤IFI<0.6 IFI<0.5 肥力等级 Soil fertility grade Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ 肥力水平 Fertility level 高 High 较高 Higher 中等 Medium 低 Low 1.4 土壤肥力综合质量评价方法
根据Fuzzy综合评判法,可以将评估结果与各种养分指标之间的隶属度函数相联系,将它们划分为抛物线型和S型[14]。在本研究中,除了土壤pH,其他指标都属于S型。根据隶属度(Ei)的计算方法,可以通过观察x来确定每个指标的隶属度函数曲线的拐点,具体见表3[13,15]。
表 3 各项养分指标隶属度函数曲线转折点取值表Table 3. Threshold nutrient index on membership function curves转折点取值
Turning point
valuepH 有机质
Organic matter/
(g·kg−1)全氮
Total nitrogen/
(g·kg−1)全磷
Total phosphorus/
(g·kg−1)全钾
Total potassium/
(g·kg−1)碱解氮
Alkaline nitrogen/
(mg·kg−1)有效磷
Available phosphorus/
(mg·kg−1)速效钾
Available potassium/
(mg·kg−1)x1 4.0 20 0.75 0.30 5.00 30.00 3.00 30.00 x2 4.5 60 2.00 1.00 25.00 150.00 40.00 200.00 x3 5.5 — — — — — — — x4 7.0 — — — — — — — —表示无该取值
— Indicates that the value does not existEi=f(x)={0.1x≤x1 或 x≥x40.9(x−x1)x2−x1+0.1x1<x<x21.0x2≤x≤x31.0−0.9(x−x3)x4−x3x3<x<x4 (1) Ei=f(x)={1.0x≥x20.9(x−x1)x2−x1+0.1x1<x<x20.1x≤x1 (2) 变异系数(Vi)计算公式如下[13],其中αi是指第i项指标的标准差,
ˉxi 是指第i项指标的平均数。Vi=αixi 权重系数(Wi)计算公式如下[13],权重系数可以准确地反映各项土壤肥力评价指标在土壤肥力评价过程中所起的作用大小。
Wi=Vin∑i=1Vi IFI计算公式如下[13],Ei和Wi分别为单项肥力指标的隶属度值和权重系数。
IFI=n∑k=iiEi∗Wi 1.5 数据处理与方法
采用Excel_2010进行数据整理,采用SPSS_26.0单因素分析(one-way ANOVA)进行数据分析,使用Duncan法进行差异显著性分析(P<0.05),采用ArcMap_10.8.1绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 安溪县茶园土壤肥力指标权重系数
土壤肥力指标的权重系数主要是通过变异系数法计算所得,我们可以计算出各项土壤肥力评价指标的权重系数(表4)。
表 4 各项土壤肥力指标权重系数取值表Table 4. Weighted factors of soil fertility index指标
IndicatorspH 有机质
Organic Matter/
(g·kg−1)全氮
Total nitrogen/
(g·kg−1)全磷
Total phosphorus/
(g·kg−1)全钾
Total potassium/
(g·kg−1)碱解氮
Alkaline nitrogen/
(mg·kg−1)有效磷
Available phosphorus/
(mg·kg−1)速效钾
Available potassium/
(mg·kg−1)权重系数
Weighting factor/%2.75 11.34 10.19 14.12 12.44 5.72 26.41 17.04 2.2 安溪县茶园土壤养分总体分布情况
2.2.1 茶园土壤pH、有机质情况
试验结果表明(图1、表5),安溪县茶园土壤pH范围在3.79~4.97,pH平均值为4.36,变异系数为11.51%,表明各乡镇的茶园土壤pH变异呈现不显著,各乡镇土壤pH之间呈显著差异水平(P<0.05),其中41%茶园土壤pH低于安溪县茶园土壤pH平均值水平,长卿镇pH最低为3.79,pH最高的是城厢镇为4.97。此外,27.27%茶园土壤pH符合Ⅰ级茶园标准和优质高产肥力标准,59.09%茶园土壤pH符合Ⅱ级茶园土壤标准,13.64%茶园土壤符合Ⅲ级茶园土壤标准,说明安溪县大部分茶园土壤酸化问题很严重。
表 5 安溪县茶园土壤养分状况Table 5. Soil fertility of tea plantations in Anxi County乡镇
TownpH 有机质
Organic matter/
(g·kg−1)全氮
Total nitrogen/
(g·kg−1)全磷
Total phosphorus/
(g·kg−1)全钾
Total potassium/
(g·kg−1)碱解氮
Alkaline nitrogen/
(mg·kg−1)有效磷
Available phosphorus/
(mg·kg−1)速效钾
Available potassium/
(mg·kg−1)蓬莱 Penglai 4.39±0.06gⅡ 62.6±3.44dⅠ 1.05±0.07fⅠ 0.83±0.00dⅡ 13.4±0hⅠ 123.27±18.48lⅠ 153.04±16.99bⅠ 78.18±5.83jⅡ 祥华 Xianghua 4.34±0.35gⅡ 62.68±21.46dⅠ 1.35±0.42cⅠ 0.43±0.32jⅡ 15.21±9.6fⅠ 145.63±32.47hⅠ 31.56±34.76hⅠ 102.54±54.77hⅠ 福田 Futian 4.26±0.11iⅡ 61.47±28.23eⅠ 1.12±0.17fⅠ 0.89±0.42cⅡ 11.08±3.96iⅠ 126.72±16.29kⅠ 20.22±24.87jⅠ 90.64±57.92iⅡ 感德 Gande 4.54±0.47eⅠ 52.56±25.38gⅠ 1.07±0.45fⅠ 0.55±0.26hⅡ 15.27±6.92fⅠ 123.9±22.99lⅠ 83.25±72.5eⅠ 101.68±58.07iⅠ 虎邱 Huqiu 4.88±0.6bⅠ 55.2±20.7gⅠ 1.14±0.25fⅠ 0.81±0.28eⅡ 15.43±5.41fⅠ 142.49±29.12iⅠ 111.42±64.06cⅠ 238.66±86.28bⅠ 剑斗 Jiandou 4.07±0.19jⅡ 38.39±19.58mⅠ 1.11±0.36fⅠ 0.92±0.20cⅡ 13.84±2.26gⅠ 127.53±20.49kⅠ 84.46±66.7eⅠ 134.88±41.07gⅠ 桃舟 Taozhou 4.53±0.35eⅠ 58.04±14.12gⅠ 1.22±0.17eⅠ 0.67±0.30fⅡ 14.54±8.69fⅠ 136.12±24.22jⅠ 51.88±58.28hⅠ 162.69±52.44fⅠ 金谷 Jingu 4.59±0.13dⅠ 7.35±1.66oⅢ 0.38±0.05iⅢ 0.14±0.02oⅢ 12.35±1.21hⅠ 109.7±3.93mⅠ 5.34±3.83kⅡ 113.45±31.83hⅠ 湖上 Hushang 4.44±0.33fⅡ 42.62±18.8jⅠ 1.11±0.39fⅠ 0.87±0.22cⅡ 8.15±4.33kⅡ 184.7±34.66aⅠ 17.56±23.82jⅡ 114.78±72.6hⅠ 官桥 Guanqiao 3.99±0.26kⅢ 59.85±31.8fⅠ 1.17±0.35eⅠ 0.31±0.17lⅢ 4.83±0.62mⅢ 160.36±29.29eⅠ 63.65±70.91fⅠ 106.68±54.34hⅠ 蓝田 Lantian 3.92±0.2lⅢ 55.46±16.25gⅠ 1.32±0.46cⅠ 1.764±0.00aⅠ 18.1±0eⅠ 137.54±25.75jⅠ 257.21±36.28aⅠ 179.33±28.11eⅠ 大坪 Daping 4.01±0.44kⅡ 72.35±29.57aⅠ 1.58±0.3bⅠ 0.38±11.33kⅢ 24.06±3.71aⅠ 137.93±22.48jⅠ 46.37±49.44hⅠ 104.98±39.91hⅠ 长卿 Changqing 3.79±0.17mⅢ 65.06±18.86bⅠ 1.19±0.27eⅠ 0.89±0.25cⅡ 10.08±7.1jⅠ 170.3±70.71dⅠ 73.66±38.6fⅠ 189.85±106.37dⅠ 龙门 Longmen 4.73±0.44cⅠ 40.42±27.23kⅠ 1.3±0.59dⅠ 0.52±0.14hⅡ 20.45±7.15cⅠ 133.94±25.19jⅠ 87.71±108.6dⅠ 160.16±133.66fⅠ 参内 Cannei 4.32±0.27hⅡ 39.64±21.97lⅠ 0.88±0.25gⅡ 0.27±0.00mⅢ 5.8±0lⅡ 141.09±21.4iⅠ 24.03±25.18jⅠ 119.83±17.06hⅠ 芦田 Lutian 4.35±0.76gⅡ 44.31±23.47hⅠ 1.09±0.51fⅠ 0.89±0.15cⅡ 20.28±13.06cⅠ 157.5±46.55fⅠ 59.75±73.52gⅠ 239.98±171.94bⅠ 白濑 Bailai 4.27±0.3iⅡ 28.06±16.41nⅠ 0.98±0.33fⅠ 0.46±0.16iⅡ 19.6±8.2dⅠ 142.57±32.74iⅠ 28.59±26.73iⅠ 251.19±216.24bⅠ 龙涓 Longjuan 4.26±0.41iⅡ 54.69±22.5gⅠ 1.18±0.6eⅠ 0.64±0.19gⅡ 14.71±5.13fⅠ 149.28±26.95gⅠ 58.36±58.45gⅠ 167.1±61.63fⅠ 城厢 Chengxiang 4.97±0.4aⅠ 42.14±18.1jⅠ 1.26±0.62dⅠ 0.19±0.00nⅢ 9.7±0jⅡ 164.05±30.2eⅠ 31.38±26.62hⅠ 173.38±100.28eⅠ 湖头 Hutou 4.35±0.47gⅡ 43.56±19.61iⅠ 1.2±0.27eⅠ 0.49±0.11iⅡ 9.84±1.18jⅡ 175.87±22.8bⅠ 58.81±50.09gⅠ 272.2±201.37aⅠ 尚卿 Shangqing 4.62±0.17dⅠ 64.67±18.65cⅠ 2.05±0.96aⅠ 1.42±0.00bⅡ 22.8±0bⅠ 174.02±20.31cⅠ 36.71±36.68hⅠ 229.8±114.37cⅠ 西坪 Xiping 4.27±0.36iⅡ 40.85±20.06kⅠ 0.81±0.4hⅢ 0.23±0.06nⅢ 11.35±1.3iⅠ 147.24±26.63gⅠ 37.12±62.15hⅠ 177.99±150.92eⅠ 平均值 Average 4.36 50.96 1.14 0.62 14.53 145.82 60.66 165.50 变异系数(%)
Coefficient of variation11.51 47.54 71.4 110.68 23.96 52.14 42.72 59.16 表中数据显示为均值±标准差,同列不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ为茶园土壤养分分级标准。
Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation; those with different lowercase letters on same column indicate significant differences at P<0.05. Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, and Ⅳ are grades on soil nutrients of tea plantations.安溪县茶园土壤有机质变化范围为7.35~72.35,变异系数为47.54%。各乡镇土壤pH之间呈显著差异水平(P<0.05),其中,金谷镇有机质含量最低,有机质含量仅为7.35 g·kg−1,茶园土壤符合Ⅲ级茶园土壤有机质含量标准,金谷镇近年来大力发展第二产业,造成环境污染;其余乡镇有机质含量较为丰富,平均值为50.96 g·kg−1,95.45%茶园土壤有机质含量符合Ⅰ级茶园有机质标准和优质高产茶园有机质标准,说明安溪县大部分茶园有机质含量较为丰富。
2.2.2 茶园土壤氮素养分含量情况
试验结果表明(图2、表5),安溪县全氮的含量在0.38~2.05 g·kg−1,平均值为1.14 g·kg−1,各乡镇全氮含量变异系数为71.4%(P<0.05),呈显著变异水平,而碱解氮变异系数相对性较小,为52.14%,变化范围在109.70~184.70 mg·kg−1,碱解氮平均值为145.82 mg·kg−1,从茶园全氮含量分布情况来看,安溪县茶园全氮含量大于等于1.5 g·kg−1的优质高产茶园占比9.09%,白濑乡、参内镇、西坪镇、金谷镇全氮含量均低于Ⅰ级茶园养分含量标准(1.00 g·kg−1)。说明安溪县茶园全氮含量分布不均,普遍偏低。而金谷镇茶园土壤氮素养分含量最低,全氮含量仅为0.38 g·kg−1,碱解氮含量为109.70 mg·kg−1,尚卿乡氮素含量在安溪县各个乡镇中相对较高,全氮含量为2.05 g·kg−1,碱解氮含量为174.02 mg·kg−1,虎邱镇氮素含量则保持相对稳定。
2.2.3 茶园土壤磷素养分含量情况
试验结果表明(图3、表5),安溪县全磷含量分布范围在0.14~1.76 g·kg−1,全磷含量平均值为0.62 g·kg−1,有效磷含量范围为5.34~257.21 mg·kg−1,变异系数为42.72%,安溪县只有蓝田乡全磷含量达到优质茶园(Ⅰ级茶园)标准,安溪县有68.18%茶园全磷含量符合Ⅱ级茶园标准(0.40~1.00 g·kg−1),安溪县除湖上乡、金谷镇外,茶园土壤有效磷含量均大于20 mg·kg−1,可见安溪县磷素含量分布不均匀,金谷镇磷素含量最低,全磷含量仅为0.14 g·kg−1,有效磷含量为5.34 mg·kg−1,而全县的全磷储备含量相对较为缺乏,有效磷等速效养分含量丰富,但分布不均匀。
2.2.4 茶园土壤钾素养分含量情况
试验结果表明(图4、表5),安溪县全钾含量分布范围在4.83~24.06 g·kg−1,全钾平均值为14.53 g·kg−1,速效钾含量在78.18~272.20 mg·kg−1,速效钾平均值为165.50 g·kg−1,全县有72.27%茶园全钾含量达到高产优质茶园标准以及Ⅰ级茶园肥力标准,18.18%茶园均处于Ⅱ级茶园标准,官桥镇茶园土壤全钾含量则处于Ⅲ级茶园水平,全钾含量仅为4.83 g·kg−1。此外,蓬莱镇速效钾含量最低仅为78.18 mg·kg−1,福田乡速效钾含量也相对较低为90.64 mg·kg−1,全县除福田乡、蓬莱镇速效钾含量符合Ⅱ级茶园标准外,其他茶园速效钾含量均处于高产优质茶园标准以及Ⅰ级茶园肥力标准,说明安溪县土壤中钾素含量丰富,但地区分布不均匀。
2.3 安溪县茶园土壤肥力等级评定
通过数据计算可知安溪县茶园土壤肥力指数情况(表6):安溪县茶园土壤肥力综合指数值在0.419~0.983,平均指数为0.760,等均等级为Ⅰ级茶园土壤肥力标准,整体肥力处于高水平状态。其中,土壤肥力综合指数值最高的乡镇是尚卿镇,IFI指数值为0.983,最低的是金谷镇,IFI指数值为0.419,且土壤肥力等级为Ⅳ级,此外,处于Ⅲ级土壤肥力标准的乡镇还有湖上乡、参内镇,福田乡IFI指数值为0.615,处于Ⅱ级土壤肥力标准,其余乡镇均达到Ⅰ级土壤肥力等级标准。可见,安溪县茶园土壤肥力质量虽然差异较大,但整体处于高水平。
表 6 安溪县茶园土壤肥力指数情况Table 6. IFI of tea plantations in Anxi County乡镇
Town土壤肥力
综合指数值
IFI等级
Grade分布频率
Distribution frequency /%Ⅰ级
Grade ⅠⅡ级
Grade ⅡⅢ级
Grade ⅢⅣ级
Grade Ⅳ蓬莱
Penglai0.743 Ⅰ级 100.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 祥华
Xianghua0.754 Ⅰ级 44.1 5.9 14.7 35.3 福田
Futian0.615 Ⅱ级 25.0 5.0 15.0 55.0 感德
Gande0.765 Ⅰ级 54.2 8.3 8.3 29.2 虎邱
Huqiu0.875 Ⅰ级 85.7 9.5 4.8 0.0 剑斗
Jiandou0.733 Ⅰ级 58.3 16.7 8.3 16.7 桃舟
Taozhou0.847 Ⅰ级 75.0 25.0 0.0 0.0 金谷
Jingu0.419 Ⅳ级 0.0 0.0 0.0 100.0 湖上
Hushang0.578 Ⅲ级 16.7 16.7 16.7 50.0 官桥
Guanqiao0.724 Ⅰ级 25.0 25.0 25.0 25.0 蓝田
Lantian0.861 Ⅰ级 100.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 大坪
Daping0.860 Ⅰ级 61.1 27.8 0.0 11.1 长卿
Changqing0.829 Ⅰ级 79.2 12.5 8.3 0.0 龙门
Longmen0.838 Ⅰ级 50.0 16.7 0.0 33.3 参内
Cannei0.574 Ⅲ级 33.3 0.0 0.0 66.7 芦田
Lutian0.864 Ⅰ级 55.0 5.0 5.0 35.0 白濑
Bailai0.729 Ⅰ级 28.6 42.9 28.6 0.0 龙涓
Longjuan0.835 Ⅰ级 66.7 18.8 10.4 4.2 城厢
Chengxiang0.744 Ⅰ级 33.3 50.0 16.7 0.0 湖头
Hutou0.814 Ⅰ级 60.0 0.0 40.0 0.0 尚卿
Shangqing0.983 Ⅰ级 54.5 27.3 18.2 0.0 西坪
Xiping0.740 Ⅰ级 24.1 15.5 15.5 44.8 3. 讨论
3.1 安溪县茶园土壤酸化严重
安溪县茶园土壤pH大部分茶园均未达到高产优质茶园土壤标准,茶园土壤酸化严重且分布不均匀。茶树适宜在酸性土壤(pH值4.5~5.5)中生长,土壤pH过高或过低都不适宜茶树生长。安溪县茶园土壤pH范围在3.79~4.97,土壤多为酸性土壤,大部分茶园土壤酸化问题很严重,只有27.27%茶园土壤pH符合4.5~5.5这一茶树适宜生长范围,呈现由西北向东南“高-低-高”的变化趋势,可能是由于当地茶农施肥习惯影响以及西北部地区地势较高,植被生长较少,植物根系分泌的盐类物质和有机酸较少,对土壤pH影响较小,东南地区则反之;这与杨文俪等[16]研究的关于福建省安溪县的茶园土壤正在经历酸化,并且已经采取了相应的改良措施一致。户杉杉等[17]于2017年研究发现套种大豆可以增加土壤酶活性,改善茶园排灌系统,通过提升茶树对土壤营养的吸收能力,大大改善了茶叶的品质,并且可以有效地降低茶园施用30%的化肥量,有效缓解茶园土壤酸化。
3.2 安溪县茶园土壤养分结构不均衡
本研究调查范围广泛,可能是各地所施肥料种类和用量差异较大,养分测定数据波动较大,考虑到指标评价的统一性和公正性,权重系数的计算将采用变异系数法取得。研究结果表明,安溪县茶园土壤主要养分含量丰富,总体肥力较好,但结构分布不均衡[18]。氮素是茶树生长必不可少的营养元素之一,安溪县全氮含量分布不均匀,除蓝田乡外,其他乡镇全氮含量均低于Ⅰ级茶园养分含量标准(1.00 g·kg−1)。说明安溪县全氮含量储备不足,可能与安溪县近年来的土地利用方式的改变有关,大范围开垦茶园,改稻种茶使得土壤有机质和全氮等营养元素流失,土壤全氮储备下降[19]。而全县碱解氮含量均高于74.69 mg·kg−1,符合Ⅰ级茶园标准,这与安溪县茶园偏施氮肥以及土壤土质有一定关系,这与吴志丹等[20]关于安溪茶园氮素营养分布情况和影响因素的研究相一致。安溪县茶园土壤磷素养分结构不合理,其中以金谷镇、白濑乡、湖上乡、参内镇等磷素含量相对较少,主要分布在老茶园,可能由于老茶园使用年限长,且近年来翻耕较少,土壤板结较严重,不利于有机质和有效磷的转化,当pH低于6.0时,磷酸的活性会大大减弱,从而使得土壤中的磷元素和其他营养物质更容易被淋失,从而影响土壤的肥力和生物活力[21-22],而安溪大部分土壤酸化较严重,因此虽然部分地区有效磷测定含量较高,但茶树生长负面影响较小,茶树大量开花结果现象不普遍。安溪县茶园土壤钾素含量结构分布不合理,主要集中在官桥镇、蓬莱镇、城厢镇和参内镇等地区,集中在安溪县东南方位,海拔较低,降水量多,雨期绵长,茶园土壤中的钾离子容易被雨水淋溶到土壤的下层,导致茶园土壤中的钾离子数量偏少。这与吴志丹等[23]关于安溪县钾素营养状况和影响因素的研究相一致。相较于其他成分,只有土壤有机质含量分布较为均匀,可能与茶农多施有机肥有关[24]。
3.3 安溪县茶园土壤肥力空间分布差异大
安溪县属于南方丘陵地区,地形复杂,多山地丘陵,安溪县茶园土壤肥力呈现南高北低,西高东低的分布态势。安溪县受地理位置的影响,南北安溪气候特点差异较大,安溪县西北部多山地丘陵,受北方气流影响较大,四季分明,雨量较大,而安溪县东南部靠近海洋,受海洋气流影响较大,夏季漫长且炎热,冬季短暂且不寒冷,雨量充沛。安溪县土壤肥力综合指数较低的几个乡镇为金谷镇、参内镇、湖上乡,多集中在安溪县东部地区[25]。安溪县茶园土壤各项养分含量结构分布不均衡,受茶园管理方式、耕作方式等影响导致茶园土壤养分空间分布差异大,改善茶园土壤养分分布不均匀要因地制宜,根据不同的乡镇的地理环境和管理背景,要采取不同的管理方式改善土壤养分空间分布[26]。同时,IFI是由各项土壤养分指标加权形成,指标数值大,IFI的结果就高,而对于以营养生长为主的茶树,所需养分有一定区间合理性,尤其是对磷的需求量相对果实作物较小,因此,IFI在茶园土壤肥力评判上有一定局限性,茶园配方施肥时还应结合茶树养分需求规律做适当调整。
4. 结论
4.1 研究结论
综合以上研究结果可知,安溪县茶园土壤酸化严重,pH平均值为4.36,仅有27.27%的茶园pH达到优质茶园标准,且土壤pH空间差异较大;茶园土壤肥力总体较好,但养分结构不均衡,81.82%的茶园土壤肥力等级达到Ⅰ级标准,其中有机质和有效养分丰富,全氮和全钾含量尚可、全磷普遍不足;茶园土壤肥力空间分布差异大,土壤肥力综合指数值(IFI)为0.419~0.983,安溪东部的茶园土壤肥力综合指数较低。
4.2 施肥建议
(1)通过增施有机肥改良茶园土壤酸化。通常来说,有机肥是中性或微碱性的,它可以中和土壤游离酸,改善土壤物理化学性质,增加孔隙率,提升土壤的抗逆性,从而阻止和减少盐分的流失。
(2)适当增施用含氮磷钾全量养分的矿物质,以增加全量养分储备。通过施用有机肥或矿物质,可以提供丰富的钙、镁、钠、钾、磷等元素,从而增加土壤的养分储备,减轻土壤酸化的程度。此外,有机肥经过微生物分解后形成的腐殖质,可以与土壤中的矿物质结合,形成一种有机-无机复合胶体,有效地增强土壤的缓冲能力。
(3)推广测土配方技术,促进精准施肥和减肥增效。测土配方是科学有效的平衡施肥技术,增加测土配方密度,可以有效扩大科学施肥面积,精准施肥,提升肥料的科学利用率以及茶园土壤肥力水平。
-
表 1 瘤胃液细菌群Alpha多样性分析
Table 1 Alpha diversity analysis on microbial community in rumen fluid
项目
ItemsCON组
CON GroupR50组
R50 groupR100组
R100 groupACE 指数
ACE index405.40±7.47 a 395.08±3.34 a 372.51±9.07 b 赵氏指数
Chao1 index409.07±7.63 a 398.95±4.10 ab 377.80±12.46 b 香农指数
Shannon index6.52±0.17 a 6.69±0.14 a 5.92±0.23 b 辛普森指数
Simpson index0.97±0.01 ab 0.98±0.00 a 0.95±0.01 b 注:同行数据后的大写字母不同表示差异极显著(P<0.01),小写字母不同表示差异显著(P<0.05),相同或无字母表示差异不显著(P>0.05)。下表同。
Note:Different uppercase letters on the same line indicate extremely significant differences (P<0.01), lowercase letters indicate significant differences
(P<0.05), while the same or no letters mean no significant difference (P>0.05). The same as below.表 2 芦丁对湖羊瘤胃微生物相对丰度的影响(门水平)
Table 2 Effect of rutin on microbial relative abundance in rumen of Hu sheep (at phylum level) (单位:%)
项目
ItemsCON组
CON groupR50组
R50 groupR100组
R100 group拟杆菌门 Bacteroidetes 52.84±3.03 59.18±3.02 62.76±6.39 厚壁菌门 Firmicutes 35.47±1.87 31.56±1.39 29.67±5.23 变形菌门 Proteobacteria 5.80±2.10 1.97±1.22 1.67±0.75 互养菌门 Synergistetes 1.68±0.97 2.70±1.53 0.77±0.53 广古菌门 Euryarchaeota 1.43±1.15 0.67±0.13 2.12±1.52 螺旋体门 Spirochaetes 0.54±0.21 1.65±0.70 1.08±0.41 放线菌门 Actinobacteria 1.33±1.32 0.61±0.29 0.85±0.42 纤维杆菌门 Fibrobacteres 0.36±0.09 0.31±0.06 0.37±0.14 髌骨细菌门 Patescibacteria 0.17±0.06 b 0.30±0.06 ab 0.56±0.18 a 迷踪菌门 Elusimicrobia 0.06±0.04 b 0.80±0.40 a 0.00±0.00 c 软壁菌门 Tenericutes 0.27±0.14 0.22±0.11 0.07±0.03 Kiritimatiellaeota 0.05±0.01 0.03±0.01 0.03±0.01 蓝藻菌门 Cyanobacteria 0.00±0.00 0.01±0.00 0.05±0.04 k__Bacteria_Unclassified 0.02±0.02 0.01±0.01 0.02±0.02 表 3 芦丁对湖羊瘤胃微生物相对丰度的影响(属水平)
Table 3 Effect of rutin on microbial relative abundance in rumen of Hu sheep (at genus level)
(单位:%) 项目
ItemsCON组
CON groupR50组
R50 groupR100组
R100 group普雷沃菌属_1 Prevotella_1 20.28±5.92 26.34±3.35 26.79±7.98 理研菌科_RC9_gut_group
Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group12.16±2.99 11.05±2.13 18.60±4.48 f__F082_Unclassified 3.47±0.41 5.83±1.64 5.09±1.07 f__Muribaculaceae_Unclassified 4.83±1.60 5.55±1.93 1.98±1.35 新月形单胞菌属 Selenomonas_1 5.10±1.40 a 2.56±0.40 ab 1.51±0.52 b f__Prevotellaceae_Unclassified 2.67±0.53 2.61±0.52 3.65±1.55 瘤胃球菌属_2 Ruminococcus_2 0.80±0.19 2.11±1.31 5.11±3.26 f__Veillonellaceae_Unclassified 2.53±0.81 3.14±0.98 2.10±0.77 Ruminococcaceae_NK4A214_group 2.73±0.73 2.14±0.42 2.26±0.63 Christensenellaceae_R-7_group 1.95±0.11 1.66±0.31 2.89±1.99 Quinella 1.86±0.78 2.17±0.86 2.46±1.05 [Eubacterium]_coprostanoligenes_group 3.99±3.71 0.56±0.16 1.94±1.02 琥珀酸弧菌属 Succinivibrio 3.46±1.52 0.81±0.52 1.21±1.02 f__Bacteroidales_RF16_group_Unclassified 3.11±0.87 a 0.89±0.27 b 1.32±0.29 b Prevotellaceae_UCG-003 2.29±0.97 1.48±0.39 1.45±0.21 Fretibacterium 1.54±0.97 2.55±1.52 0.72±0.52 Prevotellaceae_UCG-001 1.30±0.43 1.91±0.79 1.49±0.46 Lachnospiraceae_ND3007_group 0.94±0.54 1.37±0.49 2.15±0.95 甲烷短杆菌属
Methanobrevibacter1.38±1.16 0.61±0.13 2.11±1.52 f__Lachnospiraceae_Unclassified 1.21±0.15 AB 1.87±0.42 A 0.52±0.14 B 瘤胃球菌属_1 Ruminococcus_1 1.15±0.37 1.41±0.28 0.78±0.14 密螺旋体属_2 Treponema_2 0.53±0.21 1.65±0.70 1.08±0.41 Veillonellaceae_UCG-001 1.43±0.52 1.04±0.24 0.49±0.15 f__Bifidobacteriaceae_Unclassified 1.32±1.32 0.61±0.30 0.85±0.42 琥珀酸菌属 Succiniclasticum 1.67±0.61 a 0.73±0.25 ab 0.26±0.12 b f__Bacteroidales_BS11_gut_group_Unclassified 0.50±0.21 1.00±0.39 0.78±0.54 Succinivibrionaceae_UCG-002 1.58±0.71 0.61±0.52 0.00±0.00 厌氧弧菌属 Anaerovibrio 0.98±0.27 0.73±0.23 0.48±0.28 Ruminococcaceae_UCG- 0020.42±0.19 0.66±0.13 0.65±0.17 Lachnospiraceae_NK3A20_group 0.58±0.18 0.61±0.06 0.55±0.09 -
[1] MORGAVI D P, RATHAHAO-PARIS E, POPOVA M, et al. Rumen microbial communities influence metabolic phenotypes in lambs [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2015, 6: 1060.
[2] YU J K, CAI L Y, ZHANG J C, et al. Effects of thymol supplementation on goat rumen fermentation and rumen microbiota in vitro [J]. Microorganisms, 2020, 8(8): 1160. DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms8081160
[3] 白齐昌, 郝小燕, 项斌伟, 等. 沙棘黄酮对绵羊体外产气量、瘤胃发酵参数和微生物菌群的影响 [J]. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(3):1405−1414. BAI Q C, HAO X Y, XIANG B W, et al. Effects of sea buckthorn flavone on gas production, rumen fermentation parameters and microflora population of sheep in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(3): 1405−1414.(in Chinese)
[4] 王霞, 刘莹莹, 曾青华, 等. 桑叶黄酮对动物氧化应激的作用 [J]. 中兽医医药杂志, 2020, 39(1):98−101. WANG X, LIU Y Y, ZENG Q H, et al. Reviewed on flavonoids in Folium Mori on animal oxidative stress [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine, 2020, 39(1): 98−101.(in Chinese)
[5] HEIM K E, TAGLIAFERRO A R, BOBILYA D J. Flavonoid antioxidants: Chemistry, metabolism and structure-activity relationships [J]. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 2002, 13(10): 572−584. DOI: 10.1016/S0955-2863(02)00208-5
[6] GANESHPURKAR A, SALUJA A K. The pharmacological potential of rutin [J]. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal, 2017, 25(2): 149−164. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2016.04.025
[7] CUSHNIE T P T, LAMB A J. Antimicrobial activity of flavonoids [J]. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, 2005, 26(5): 343−356. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2005.09.002
[8] OSKOUEIAN E, ABDULLAH N, OSKOUEIAN A. Effects of flavonoids on rumen fermentation activity, methane production, and microbial population [J]. BioMed Research International, 2013: 349129.
[9] BODAS R, PRIETO N, GARCÍA-GONZÁLEZ R, et al. Manipulation of rumen fermentation and methane production with plant secondary metabolites [J]. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2012, 176(1/2/3/4): 78−93.
[10] CUI K, GUO X D, TU Y, et al. Effect of dietary supplementation of rutin on lactation performance, ruminal fermentation and metabolism in dairy cows [J]. Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition, 2015, 99(6): 1065−1073. DOI: 10.1111/jpn.12334
[11] 占今舜, 钟小军, 杨群, 等. 芦丁的生物活性功能及其在反刍动物生产中的应用 [J]. 动物营养学报, 2019, 31(7):2952−2957. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2019.07.002 ZHAN J S, ZHONG X J, YANG Q, et al. Bio-active functions of rutin and its application in ruminant production [J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2019, 31(7): 2952−2957.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2019.07.002
[12] GHORBANI A. Mechanisms of antidiabetic effects of flavonoid rutin [J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 2017, 96: 305−312.
[13] 郭旭东. 芦丁对奶牛泌乳性能、瘤胃消化代谢和对大鼠乳腺发育的影响[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2011. GUO X D. Studies of rutin's role on lactation performance, the rumen digestion and metabolism in dairy cows, and the development of mammary glands in rats[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2011. (in Chinese)
[14] 占今舜, 霍俊宏, 钟小军, 等. 饲粮中添加芦丁对湖羊生长性能、血清生化指标和激素水平及瘤胃发酵的影响 [J]. 动物营养学报, 2021, 33(5):2717−2726. ZHAN J S, HUO J H, ZHONG X J, et al. Effects of diet added with rutin on growth performance, serum biochemical indexes and hormone levels, and rumen fermentation of Hu sheep [J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2021, 33(5): 2717−2726.(in Chinese)
[15] LV F, WANG X J, PANG X, et al. Effects of supplementary feeding on the rumen morphology and bacterial diversity in lambs [J]. PeerJ, 2020, 8: e9353. DOI: 10.7717/peerj.9353
[16] MA Y B, WANG W W, ZHANG H J, et al. Supplemental Bacillus subtilis DSM 32315 manipulates intestinal structure and microbial composition in broiler chickens [J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 15358. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-33762-8
[17] WANG W M, LI C, LI F, et al. Effects of early feeding on the host rumen transcriptome and bacterial diversity in lambs [J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 32479. DOI: 10.1038/srep32479
[18] AUFFRET M D, DEWHURST R J, DUTHIE C A, et al. The rumen microbiome as a reservoir of antimicrobial resistance and pathogenicity genes is directly affected by diet in beef cattle [J]. Microbiome, 2017, 5(1): 159. DOI: 10.1186/s40168-017-0378-z
[19] REQUENA T, COTTER P, SHAHAR D R, et al. Interactions between gut microbiota, food and the obese host [J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2013, 34(1): 44−53.
[20] XUE D, CHEN H, LUO X L, et al. Microbial diversity in the rumen, reticulum, omasum, and abomasum of yak on a rapid fattening regime in an agro-pastoral transition zone [J]. Journal of Microbiology (Seoul, Korea), 2018, 56(10): 734−743.
[21] SINGH K M, AHIR V B, TRIPATHI A K, et al. Metagenomic analysis of Surti buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) rumen: A preliminary study [J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2012, 39(4): 4841−4848. DOI: 10.1007/s11033-011-1278-0
[22] ZENG Y, ZENG D, NI X Q, et al. Microbial community compositions in the gastrointestinal tract of Chinese Mongolian sheep using Illumina MiSeq sequencing revealed high microbial diversity [J]. AMB Express, 2017, 7(1): 75. DOI: 10.1186/s13568-017-0378-1
[23] 孙美杰, 姜君, 徐诣轩, 等. 不同尿素添加水平对育肥湖羊瘤胃发酵及微生物菌群结构的影响 [J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2022, 45(2):323−332. SUN M J, JIANG J, XU Y X, et al. Effects of incremental urea supplementation in diet on rumen fermentation and microbial communities in fattening Hu lambs [J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2022, 45(2): 323−332.(in Chinese)
[24] MICHAUD L, LO GIUDICE A, TROUSSELLIER M, et al. Phylogenetic characterization of the heterotrophic bacterial communities inhabiting a marine recirculating aquaculture system [J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2009, 107(6): 1935−1946. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04378.x
[25] STEVENSON D M, WEIMER P J. Dominance of Prevotella and low abundance of classical ruminal bacterial species in the bovine rumen revealed by relative quantification real-time PCR [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2007, 75(1): 165−174. DOI: 10.1007/s00253-006-0802-y
[26] SHIN N R, WHON T W, BAE J W. Proteobacteria: microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota [J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2015, 33(9): 496−503. DOI: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2015.06.011
[27] 曲湘勇, 陈继发, 匡佑华, 等. 饲粮添加蒙脱石和枯草芽孢杆菌对产蛋鸡盲肠菌群和肠道通透性的影响 [J]. 动物营养学报, 2019, 31(4):1887−1896. QU X Y, CHEN J F, KUANG Y H, et al. Effects of dietary montmorillonite and Bacillus subtilis on cecal microflora and intestinal permeability of laying hens [J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2019, 31(4): 1887−1896.(in Chinese)
[28] PITTA D W, PINCHAK E, DOWD S E, et al. Rumen bacterial diversity dynamics associated with changing from bermudagrass hay to grazed winter wheat diets [J]. Microbial Ecology, 2010, 59(3): 511−522. DOI: 10.1007/s00248-009-9609-6
[29] HENDERSON G, YILMAZ P, KUMAR S, et al. Improved taxonomic assignment of rumen bacterial 16S rRNA sequences using a revised SILVA taxonomic framework [J]. PeerJ, 2019, 7: e6496. DOI: 10.7717/peerj.6496
[30] STROBEL H J. Vitamin B12-dependent propionate production by the ruminal bacterium Prevotella ruminicola 23 [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1992, 58(7): 2331−2333. DOI: 10.1128/aem.58.7.2331-2333.1992
[31] MCCANN J C, LUAN S Y, CARDOSO F C, et al. Induction of subacute ruminal acidosis affects the ruminal microbiome and epithelium [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2016, 7: 701.
[32] MOUFIDA A, AMINA B, RABAH A, et al. Effect of natural bioflavonoid on in vitro ruminal microbiota activity in sheep rumen liquor [J]. Journal of BioScience and Biotechnology, 2017, 6(1): 31−35.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 胡明勇,冯秋分,朱坚,任正伟,刘苏,易展平,吴宇辉. 基于主成分和聚类分析对长沙市不同土地利用方式下耕地土壤肥力的评价. 中国农学通报. 2024(36): 87-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王育平. 安溪县北部茶园土壤钾素含量分布状况研究. 茶叶学报. 2024(06): 48-54 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: