Cloning and Analyzing of AP3-3 and Its Promoter from Dendrobium officinale
-
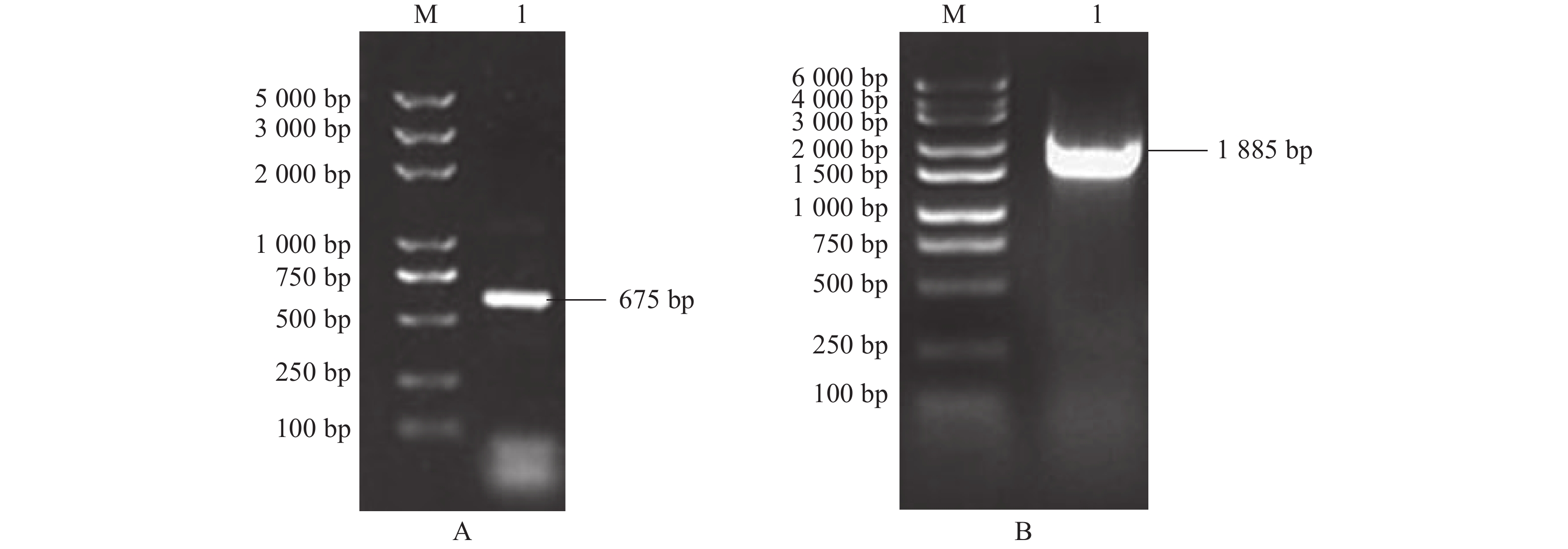
摘要:目的 AP3-3属于MADS-box基因家族B类基因,参与兰科植物花被和唇瓣的形成,克隆该基因并进行启动子分析可以进一步研究该基因的生物学功能及其启动子调控作用机制。方法 使用RT-PCR和常规PCR技术克隆铁皮石斛DoAP3-3基因及其启动子序列,进行生物信息学分析,构建启动子缺失片段与GUS基因融合表达载体,农杆菌介导转化铁皮石斛原球茎,进行瞬时表达。结果 DoAP3-3基因cDNA长度为675 bp,编码蛋白质的分子式为C1129H1803N333O347S12,分子量25.98 kDa,pI为 8.71,不稳定性指数40.14,GRAVY为−0.823,不存在跨膜区域,亚细胞定位预测得分为细胞核87.0%、线粒体8.7%、细胞质4.3%。启动子片段长度1885 bp,顺式作用元件含有大量的光响应元件等;3个启动子片段均可驱动GUS基因表达,表达强度为−1885~0 bp>−1604~0 bp>−750~0 bp。结论 DoAP3-3蛋白具有碱性、亲水性和不稳定性,无跨膜结构域,亚细胞定位于细胞核中。DoAP3-3启动子可能受光照、植物激素、MYB转录蛋白等多个因素调控,具备启动活性,且随启动子缺失长度减少呈现增加趋势。Abstract:Objective AP3-3 of class B gene of MADS box family that involves in the formation of perianth and labellum of Dendrobium officinale was cloned to study the biological function, and the promoter analyzed to decipher the regulation mechanism.Method Sequences of AP3-3 and promoter of D. officinale were cloned by RT-PCR and conventional PCR, and bioinformatics analyzed. A fusion expression vector of promoter-deleted fragments and GUS gene was constructed. Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation was used to transform protocorm of D. officinale for the transient expression.Result The cDNA length of DoAP3-3 was 675 bp with an encoded formula of C1129H1803N333O347S12, a molecular weight of 25.98 kDa, a PI of 8.71, an instability index of 40.14, and GRAVY of −0.823. There was no transmembrane region detected in the protein. The predicted score of subcellular localization was 87.0% in nucleus, 8.7% in mitochondria, and 4.3% in cytoplasm. The 1885 bp promoter fragment had a cis acting element containing a significant number of photo-responsive elements among others. The 3 promoter fragments could drive GUS with an order of expression intensity of −885–0 bp>−1 604–0 bp>−750–0 bp.Conclusion The predicted DoAP3-3 was an alkali, hydrophilic, and unstable protein with no transmembrane domain and a subcellular localization in the nucleus. The DoAP3-3 promoter might be regulated by light, plant hormones, MYB transcription protein, etc., and exhibited activities that increased with decreasing deletion length.
-
Keywords:
- Dendrobium officinale /
- AP3-3 /
- cDNA /
- promoter /
- cloning /
- sequence analysis
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】杜鹃花是杜鹃花科(Ericaceae)杜鹃花属(Rhododendron)多年生木本花卉,我国作为杜鹃花的原产地之一,有650多种杜鹃花属植物,物种资源丰富,杜鹃花因花色艳丽、极具观赏价值,在家庭观赏和园林造景的应用极大[1],同时杜鹃花体内富含槲皮素、黄酮等活性成分,有很高的药用价值[2]。杜鹃花在生产中通常采用播种、扦插、压条、嫁接等方式进行繁殖[3],这些繁殖方式受环境气候影响极大,为此国内外已对杜鹃花科植物建立了组织培养技术体系[4-6],虽然组织培养技术能使杜鹃花的生长发育突破季节与气候的限制,但该技术对无菌操作要求严格,极大限制了技术的推广、应用和发展,并且由于组织培养材料的变异率比常规育苗大,对材料进行遗传鉴别成为关键。崔刚等[7]提出的开放式组织培养,通过向培养基中添加抑菌剂限制微生物的生长,达到灭菌效果,培养基无需高压灭菌处理,对无菌操作要求不严格,具有很大的应用前景。【前人研究进展】目前甘蔗[8]、香蕉[9]、铁皮石斛[10]、葡萄[11]、马铃薯[12]、红豆杉[13]、菊花[14]等作物已成功建立开放式组织培养体系,主要对抑菌剂种类及添加浓度进行探索,使用抑菌剂大多为次氯酸钠、山梨酸钾、代森锰锌以及复合试剂。【本研究切入点】目前杜鹃花科植物的开放式组织培养还鲜有报道,开放式组织培养技术对杜鹃花试管苗的生长是否存在影响有待研究。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究以锦绣杜鹃(Rhododendron pulchrum Sweet.)当年生顶芽和带腋芽茎段为材料,探索杜鹃花开放式组织培养体系建立的条件与方法,并利用ISSR分子标记技术对所培养试管芽苗的遗传稳定性进行检测,以期为杜鹃花开放式组织培养的工厂化、规模化育苗提供参考和技术支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
供试材料为福建农林大学苗圃内种植的锦绣杜鹃;双氧水(H2O2)溶液(上海沃凯生物技术有限公司)、次氯酸钠(NaClO)溶液(上海麦克林生化科技有限公司)、代森锰锌(上海生工生物技术服务有限公司)、二氧化氯(ClO2)泡腾片(临朐华威生物科技有限公司),S106抑菌剂(江西万年创新植物组培技术应用研究所)。
遗传稳定性分析所用材料为相同培养条件下,不同处理培养30 d的试管芽苗叶片(表1),液氮速冻,−80 ℃保存备用,所用引物为加拿大哥伦比亚大学公布的ISSR引物序列,由福州白鲸生物科技有限公司合成。
表 1 遗传稳定性分析材料Table 1. Materials subjected to genetic stability analysis编号
Number样品标签
Sample
lable样品来源及处理方式
Source and treatment method of sample编号
Number样品标签
Sample
lable样品来源及处理方式
Source and treatment method of sample1 母本
Mother
plant锦绣杜鹃取样母株嫩芽,未处理
Buds of Rhododendron pulchrum Sweet., Untreated16 CL7 材料使用400 mg·L−1 ClO2 消毒10 min,初代培养基
Material disinfected by 400 mg·L−1ClO2 solution for 10 min, Incipience media2 SY1 材料使用10% H2O2消毒 5 min,初代培养基
Material disinfected by 10% H2O2 solution for 5 min, Incipience media17 CL8 材料使用400 mg·L−1 ClO2消毒 20 min,初代培养基
Material disinfected by 400 mg·L−1ClO2 solution for 20 min, Incipience media3 SY2 材料使用10% H2O2消毒 10 min,初代培养基
Material disinfected by 10% H2O2 solution for 10 min, Incipience media18 CL9 材料使用400 mg·L−1 ClO2消毒 30 min,初代培养基
Material disinfected by 400 mg·L−1ClO2 solution for 30 min, Incipience media4 SY3 材料使用10% H2O2消毒 15 min,初代培养基
Material disinfected by 10% H2O2 solution for 15 min, Incipience media19 OPC1 开放式初代培养,初代培养基 + 100 mg·L−1代森锰锌
Open primary culture, Incipience media + 100 mg·L−1 mancozeb5 SY4 材料使用12% H2O2消毒 5 min,初代培养基
Material disinfected by 12% H2O2 solution for 5 min, Incipience media20 OPC2 开放式初代培养,初代培养基 + 75 mg·L−1代森锰锌
Open primary culture, Incipience media + 75 mg·L−1mancozeb6 SY5 材料使用12% H2O2消毒 10 min,初代培养基
Material disinfected by 12% H2O2 solution for 10 min, Incipience media21 OPC3 开放式初代培养,初代培养基 + 50 mg·L−1代森锰锌
Open primary culture, Incipience media + 50 mg·L−1mancozeb7 SY6 材料使用12% H2O2消毒 15 min,初代培养基
Material disinfected by 12% H2O2 solution for 15 min, Incipience media22 OPC4 开放式初代培养,初代培养基 + 25 mg·L−1代森锰锌
Open primary culture, Incipience media + 25 mg·L−1 mancozeb8 CN1 材料使用2% NaClO消毒 20 min,初代培养基
Material disinfected by 2% NaClO solution for 20 min,23 OPC5 开放式初代培养,初代培养基 + 0.01% NaClO
Open primary culture, Incipience media + 0.01% NaClO9 CN2 材料使用2% NaClO消毒 30 min,初代培养基
Material disinfected by 2% NaClO solution for 30 min,24 OPC6 开放式初代培养,初代培养基 + 0.015% NaClO
Open primary culture, Incipience media + 0.015% NaClO10 CL1 材料使用200 mg·L−1 ClO2消毒 10 min,初代培养基
Material disinfected by 200 mg·L−1ClO2 solution for 10 min, Incipience media25 OPC7 开放式初代培养,初代培养基 + 0.02% NaClO
Open primary culture, Incipience media + 0.02% NaClO11 CL2 材料使用200 mg·L−1ClO2消毒 20 min,初代培养基
Material disinfected by 200 mg·L−1ClO2 solution for 20 min, Incipience media26 OZZ1 开放式增殖培养,增殖培养基 + 0.01% NaClO
Open proliferation culture, Proliferation medium + 0.01% NaClO12 CL3 材料使用200 mg·L−1 ClO2消毒 30 min,初代培养基
Material disinfected by 200 mg·L−1ClO2 solution for 30 min, Incipience media27 OZZ2 开放式增殖培养,增殖培养基 + 0.015% NaClO
Open proliferation culture, Proliferation medium + 0.015% NaClO13 CL4 材料使用300 mg·L−1 ClO2消毒 10 min,初代培养基
Material disinfected by 300 mg·L−1ClO2 solution for 10 min, Incipience media28 OZZ3 开放式增殖培养,增殖培养基 + 0.02% NaClO
Open proliferation culture, Proliferation medium + 0.02% NaClO14 CL5 材料使用300 mg·L−1 ClO2消毒 20 min,初代培养基
Material disinfected by 300 mg·L−1ClO2 solution for 20 min, Incipience media29 OZZ4 开放式增殖培养,增殖培养基 + 100 mg·L−1代森锰锌
Open proliferation culture, Proliferation medium + 100 mg·L−1 mancozeb15 CL6 材料使用300 mg·L−1 ClO2消毒 30 min,初代培养基
Material disinfected by 300 mg·L−1ClO2 solution for 30 min, Incipience media30 OZZ5 开放式增殖培养,增殖培养基 + 75 mg·L−1代森锰锌
Open proliferation culture, Proliferation medium + 75 mg·L−1 mancozeb1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 不同外植体消毒方式的筛选
当年生枝条剪去叶片,流水初步冲洗后,于洗衣粉溶液和纯水中分别浸泡30 min,将洗净的材料转移至紫外消毒的超净工作台内,70%酒精震荡消毒30 s,无菌水冲洗3次,采用不同含量H2O2(10%、12%)、ClO2(200、300、400 mg·L−1) 和常用消毒剂NaClO(含量为2%)对材料进行不同时间的消毒处理,无菌水冲洗5次后,用灭菌滤纸吸干材料表面水分;切去材料底部的褐化部分,并将顶芽与带腋芽茎段部分切开,分别接种在高压灭菌的初代培养基上,初代培养基配方为WPM + 0.5 mg·L−1 GA3 + 0.5 mg·L−1 ZT,每升培养基添加蔗糖30 g,琼脂粉6.8 g,pH 5.0~5.4;每组消毒处理接种20瓶,每瓶接1个外植体,重复试验3次;培养室温度(25 ± 2) ℃,光照2 000 lx,光照时间12 h·d−1,培养条件下同;接种28 d后统计外植体的存活率、死亡率和污染率。
1.2.2 开放式组织培养的初步建立
外植体材料经1.2.1的最佳消毒方式处理后,接种在添加不同含量NaClO(0.01%、0.015%、0.02%)、代森锰锌(25、50 、75 、100 mg·L−1)以及S106(含量为0.3%)抑菌剂的初代培养基中,培养基不高压,对照组为培养基高压且不添加抑菌剂的初代培养基。每组处理接种15瓶,每瓶接1个外植体,重复试验3次,接种28 d后观察统计外植体的存活率、死亡率、污染率及生长状况。
1.2.3 增殖培养基配方的优化
在前期研究基础上对增殖培养基配方中玉米素(ZT)的含量进行优化,设置1.5、2.0、2.5、3.0 mg·L−1等4个梯度,对照组培养基配方为:WPM + 0.1 mg·L−1 NAA。将长势大小基本一致的无菌材料,修剪成顶芽和带腋芽茎段,分别接种在高压灭菌的培养基上,每组处理接种15瓶,每瓶接3个材料,每10 d观察1次,30 d后统计存活材料的增殖系数。
1.2.4 开放式增殖培养
根据1.2.2、1.2.3配制开放式增殖培养基,将长势大小基本一致的无菌材料,与1.2.3做相同处理后,接种至开放式增殖培养基上,每组处理接种15瓶,每瓶接3个材料,每10 d观察1次,30 d后统计存活材料的增殖系数。
1.2.5 遗传稳定性分析
DNA提取:使用改良CTAB法[15]提取材料DNA,用CLARIOstar(BMGLRBTECH)酶标仪检测DNA纯度及浓度,1.0%琼脂糖凝胶检测质量,选取OD 260/OD 280为1.7~1.9,浓度大于100 ng·μL−1的DNA,将其稀释至40 ng·μL−1,于−20 ℃保存备用。
ISSR检测:对合成的38条ISSR引物进行分析筛选,根据电泳条带筛选出13条集中、整齐、清晰、无拖尾弥散的ISSR引物,并对这些引物进行PCR扩增反应。ISSR扩增反应体系的体积为20 μL,其中DNA模板1 μL(40 ng·μL−1),引物1 μL, ddH2O 8 μL, 2×PCR buffer 10 μL。ISSR-PCR反应程序为:94 ℃预变性5 min,94 ℃变性1 min,52 ℃退火40 s,72 ℃延伸90 s,38个循环后,72 ℃延伸7 min,4 ℃保存。PCR产物用2 %琼脂糖于4 V·cm−1电场下电泳50 min,使用Alphalmager EP通用型荧光/可见光数字成像分析系统进行拍照分析,获得各引物的DNA扩增图谱。
1.3 数据处理
存活率=(存活外植体数/外植体接种总数)×100%
死亡率=(死亡外植体数/外植体接总数)×100%
污染率=(污染外植体数/外植体接总数)×100%
增殖系数=外植体增殖芽总数/接种外植体总数
数据使用Excel软件进行统计,使用SPSS 24软件利用Duncan’s新复极差法进行方差分析,检验水平为P<0.05,使用Excel软件绘制柱形图,根据PCR扩增产物的电泳结果,制成0-1原始矩阵,使用NTSYSpc V2.10e软件计算遗传相似系数及遗传距离,并依据遗传相似系数利用UPGMA法进行聚类分析,绘制树状聚类图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同消毒处理对顶芽材料存活率的影响
顶芽材料经不同消毒方式处理后,结果如图1所示:使用H2O2消毒材料,当H2O2含量为10%时,随着消毒时间的延长,材料存活率总体呈上升趋势,消毒15 min时存活率最高,为61.67%,死亡率总体呈下降趋势,各组污染率无显著差异,当H2O2含量为12%时,随着消毒时间的延长,材料存活率显著降低,消毒5 min时存活率最高,为26.67%,死亡率呈上升趋势,各组污染率无显著差异;使用2% NaClO消毒时,材料存活率随消毒时间的延长显著提高,消毒30 min时存活率最高,为20.00%,死亡率随消毒时间的延长,呈上升趋势,同时污染率逐渐下降;使用不同质量浓度ClO2溶液消毒材料,消毒时间延长,各组存活率均逐渐降低,消毒10 min时,ClO2质量浓度为200 mg·L−1的材料存活率最高,为36.67%,各浓度材料的死亡率均随消毒时间延长而提高。综合比较所有消毒处理的材料存活率可发现,使用10% H2O2消毒15 min时,存活率最高,且该处理死亡率仅为5.00%,说明该处理对材料的损害较小,因此,顶芽材料的最适消毒方式为10% H2O2消毒15 min。
![]() 图 1 不同消毒处理对顶芽材料的影响注:柱形图上方的不同小写字母表示不同处理组内差异显著测验(P<0.05),小写字母的不同下标表示不同处理组。图2、3同。Figure 1. Effects of disinfection treatments on terminal budsNote: Different lower case letters above the column indicate the significant differences in Duncan’s new Multiple-Range test in different processing groups, p<0.05, different subscripts of lowercase letters indicate different processing groups. The same as Fig2-3.
图 1 不同消毒处理对顶芽材料的影响注:柱形图上方的不同小写字母表示不同处理组内差异显著测验(P<0.05),小写字母的不同下标表示不同处理组。图2、3同。Figure 1. Effects of disinfection treatments on terminal budsNote: Different lower case letters above the column indicate the significant differences in Duncan’s new Multiple-Range test in different processing groups, p<0.05, different subscripts of lowercase letters indicate different processing groups. The same as Fig2-3.2.2 不同消毒处理对带腋芽茎段材料存活率的影响
带腋芽茎段材料经不同消毒方式处理后,结果如图2所示:使用 H2O2 消毒材料,当 H2O2 含量为10%时,消毒10 min的材料存活率最高,为23.33%,其余消毒时间存活率均低于10%且彼此无显著差异,材料死亡率随消毒时间延长逐渐增加,当 H2O2 含量为12%时,存活率均低于10%,且各组间无显著差异,材料死亡率随消毒时间延长显著增加;使用2% NaClO 消毒材料,消毒10 min时,污染率100%,延长消毒时间至20 min及以上,存活率、死亡率均提高,且污染率随消毒时间延长,显著降低;使用不同质量浓度 ClO2 消毒材料,400 mg·L−1 ClO2消毒 10 min,材料存活率最高,为21.67%,其余消毒处理的存活率均低于10%,材料死亡率随消毒时间的延长,总体均呈上升趋势;比较所有消毒处理的材料存活率可发现,10% H2O2 消毒10 min与400 mg·L−1 ClO2 消毒 20 min的存活率较高,比较死亡率可发现, H2O2 消毒的材料死亡率更低,为8.33%,说明该处理对材料的损害较小,所以腋芽茎段的最适消毒方式为10% H2O2 消毒10 min。
2.3 开放式组织培养的初代培养
顶芽材料经消毒后,接种在开放式培养基中,探讨抑菌剂在开放式组织培养的初代培养阶段对材料的影响,由图3可知,添加S106的培养基中,存活率为80.00%,显著高于CK,新生叶片浅绿色,死亡率、污染率与CK无显著差异;使用NaClO作抑菌剂,培养基添加含量为0.01%时,存活率为62.22%,叶片浅绿色且茎间明显伸长,提高培养基中 NaClO含量,材料存活率逐渐降低,当添加含量为0.02%时,存活率仅为2.22%,死亡率与污染率极显著高于CK,叶片为黄绿色,生长受抑制;添加代森锰锌作抑菌剂,当质量浓度低于50 mg·L−1时,材料污染率高导致存活率极低且褐化现象严重,提高代森锰锌质量浓度至100 mg·L−1时,污染率降低,存活率显著提高至26.67%,但新生叶片明显变白,在添加代森锰锌的开放式培养基中,材料外观改变较明显。对各组间的存活材料进行比较,结果添加S106与0.01% NaClO的培养基中,存活率均高于对照组,但添加0.01% NaClO 的培养基中,死亡率仅为2.22%,且茎间明显伸长,叶片数更多(图4),说明该抑菌剂添加方式更适合材料生长。因此,开放式组织培养的初代培养阶段,抑菌剂的适宜添加方式为0.01% NaClO。
![]() 图 3 不同抑菌剂对材料生长的影响注:1:CK;2:0.3% S106;3:0.01% NaClO;4:0.015% NaClO;5:0.02% NaClO;6:25 mg·L−1 代森锰锌;7:50 mg·L−1 代森锰锌;8:75 mg·L−1 代森锰锌;9:100 mg·L−1 代森锰锌。Figure 3. Effect of antibacterial agents on growth of cut plant tissues1: CK; 2: 0.3% S106; 3: 0.01% NaClO; 4: 0.015% NaClO; 5: 0.02% NaClO; 6: 25 mg·L−1 mancozeb; 7: 50 mg·L−1 mancozeb; 8: 75 mg·L−1 mancozeb; 9: 100 mg·L−1 mancozeb。
图 3 不同抑菌剂对材料生长的影响注:1:CK;2:0.3% S106;3:0.01% NaClO;4:0.015% NaClO;5:0.02% NaClO;6:25 mg·L−1 代森锰锌;7:50 mg·L−1 代森锰锌;8:75 mg·L−1 代森锰锌;9:100 mg·L−1 代森锰锌。Figure 3. Effect of antibacterial agents on growth of cut plant tissues1: CK; 2: 0.3% S106; 3: 0.01% NaClO; 4: 0.015% NaClO; 5: 0.02% NaClO; 6: 25 mg·L−1 mancozeb; 7: 50 mg·L−1 mancozeb; 8: 75 mg·L−1 mancozeb; 9: 100 mg·L−1 mancozeb。2.4 增殖培养基配方的优化
将无菌顶芽和带腋芽茎段分别接种在增殖培养基中,探讨不同浓度ZT对材料增殖系数的影响,结果如表2所示,由于顶芽材料的顶端优势较强,接种顶芽的各组均未出现增殖现象;带腋芽茎段材料的增殖系数随着ZT浓度的提高而增加,当ZT添加量为3.0 mg·L−1时,增殖系数最高,为2.994。因此增殖阶段培养基的最适配方为:WPM+0.1 mg·L−1 NAA +3.0 mg·L−1 ZT。
表 2 不同ZT含量对材料增殖系数的影响Table 2. Effects of ZT content on proliferation coefficient of materials材料
MaterialsZT含量
Content of
ZT/(mg·L−1)增殖系数
Multiplication coefficient10 d 20 d 30 d 带腋芽茎段
Stem segment with
axillary bud0 1.250 1.750 1.750 1.5 1.400 1.643 2.000 2.0 1.000 2.222 2.389 2.5 1.000 2.313 2.500 3.0 1.385 2.333 2.944 顶芽
Terminal bud
material0 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.5 1.000 1.000 1.000 2.0 1.000 1.000 1.000 2.5 1.000 1.000 1.000 3.0 1.000 1.000 1.000 2.5 开放式组织培养的增殖培养
向优化后的增殖培养基内添加抑菌剂,探索开放式组织培养增殖阶段抑菌剂的适宜添加方式,由于开放式组织培养初代阶段添加代森锰锌的质量浓度在50 mg·L−1及以下时,材料存活率过低,因此后续将不再对该浓度及以下进行试验。结果如表3所示,顶芽材料在开放式组织培养时,依然未出现增殖现象;向培养基中添加NaClO,当添加浓度为0.01%时,带腋芽茎段材料的增殖系数最高,为3.067,当添加量提高至0.015%和0.02%时,增殖材料先后出现伤亡;向培养基中添加代森锰锌,添加质量浓度为100 mg·L−1时,茎段材料的增殖系数为2.667,添加质量浓度为75 mg·L−1时,带腋芽茎段材料的增殖系数2.526,但新生叶片均为黄白色。因此在开放式组织培养的增殖阶段,抑菌剂添加的最适方式为0.01% NaClO。
表 3 开放式增殖培养对材料的影响Table 3. Effect of open tissue culture on materials材料
Materials抑菌剂含量
Content of
bacteriostatic agent增殖系数
Multiplication
coefficient10 d 20 d 30 d 带腋芽茎段
Stem segment with
axillary bud0.01% NaClO 1.667 1.815 3.067 0.015% NaClO 1.364 1.636 1.333 0.02% NaClO 1.333 1.333 1.000 100 mg·L−1代森锰锌
100 m·L−1 mancozeb1.667 1.815 2.667 75 mg·L−1代森锰锌
75 mg·L−1 mancozeb1.167 2.000 2.526 顶芽
Terminal bud
material0.01% NaClO 1.000 1.000 1.000 0.015% NaClO 1.000 1.000 1.000 0.02% NaClO 1.000 1.000 1.000 100 mg·L−1代森锰锌
100 mg·L−1 mancozeb1.000 1.000 1.000 75 mg·L−1代森锰锌
75 mg·L−1 mancozeb1.000 1.000 1.000 2.6 试管芽苗遗传稳定性分析
2.6.1 试管芽苗ISSR-PCR产物的多态性分析
以母本材料为模板,对合成的38条ISSR引物进行PCR扩增,根据扩增条带的清晰度、重复性及稳定性,筛选出13条引物,利用筛选的引物,对表1中30份材料进行ISSR-PCR扩增,结果如表4所示,13条引物共扩增出110条谱带,其中多态性条带29条,平均多态性位点为26.36%,扩增谱带最多的引物是UBC 811、UBC 816、和UBC 845,均为10条谱带,扩增谱带最少的引物是UBC 827,为6条,多态性最高的引物为UBC 845(图5),多态位点百分率为80.00%,多态性最低的引物为UBC 811和UBC 816,不存在特异性条带。
表 4 13条ISSR引物的碱基序列扩增Table 4. Base sequence amplification of 13 ISSR primers编号
Serial name引物序列
Primer
sequence扩增总带数
Amplified
bands/条多态性带数
Polymorphic
bands/条多态性位点百分率
Percentage of
polymoephic/%UBC 810 (GA)8T 7 2 28.57 UBC 811 (GA)8C 10 0 0.00 UBC 815 (CT)8G 8 1 12.50 UBC 816 (CA)8T 10 4 40.00 UBC 823 (TC)8C 8 1 12.50 UBC 826 (AC)8C 9 0 0.00 UBC 827 (AC)8G 6 2 33.33 UBC 834 (AG)8YT 9 2 22.22 UBC 835 (AG)8YC 9 3 33.33 UBC 840 (GA)8YT 8 3 37.50 UBC 845 (CT)8RG 10 8 80.00 UBC 847 (CA)8RC 7 1 14.29 UBC 857 (AC)8YG 9 2 22.22 总计 Total − 110 29 − 平均 Average − 8.46 2.23 26.36 ![]() 图 5 引物UBC 845电泳结果注:1~30:锦绣杜鹃样品(顺序同表1);M:2 000 bp markerFigure 5. Electrophoretic map of UBC primer 845Note:1~30: sample of R. pulchrum (in same order as shown in Table 1);M:2 000 bp marker.
图 5 引物UBC 845电泳结果注:1~30:锦绣杜鹃样品(顺序同表1);M:2 000 bp markerFigure 5. Electrophoretic map of UBC primer 845Note:1~30: sample of R. pulchrum (in same order as shown in Table 1);M:2 000 bp marker.2.6.2 外植体消毒对材料遗传稳定性的影响
锦绣杜鹃外植体进行不同消毒处理后,存活材料的外观上无显著差异,由图6可知,18份材料的遗传相似系数为0.952~0.995,表明材料间的变异率小。当遗传相似系数0.955左右时,可将18份材料分成3组,母本材料为第一组,SY1、SY2、SY3材料为第二组,其他材料为第三组,母本与第二组间的遗传距离比第三组近;总体来看,使用H2O2消毒的材料,与母本的遗传距离小于NaClO和ClO2消毒的材料,其中,ClO2消毒的材料与母本遗传距离最远,说明ClO2对材料影响最大。外植体的不同消毒处理会对遗传稳定性造成一定影响,但H2O2与其他试剂相比,对材料的影响最小。
2.6.3 开放式组织培养对材料遗传稳定性的影响
在开放式组织培养体系中,13份材料的遗传相似系数为0.919~0.995,遗传稳定性较好。当遗传相似系数为0.945左右时,可以将材料分成3组,母本材料为第一组,开放式组织培养的初代培养材料为第二组,开放式组织培养的增殖培养材料为第三组。其中,OPC1和OPC7、OZZ1和OZZ2、OZZ3和OZZ4之间均没有差异,根据图7还可发现,当遗传相似系数在0.977左右时,OPC1、OPC2、OPC5、OPC6、OPC7等5个样本可聚为一组,当遗传相似系数在0.991左右时,OZZ5与开放式增殖的其他材料分成两组,由此可见,随着继代次数的增加,开放式初代阶段聚为一组的材料,在开放式增殖阶段出现差别。
3. 讨论与结论
杜鹃花属植物全株被毛、新生部位带粘液的特性,使其外植体材料消毒困难,刘艳红等[16]大都使用升汞消毒材料,但升汞作为一种对生物与环境伤害巨大强性毒药[17],我国已明确限制含汞制品的生产及使用。国内外研究者使用NaClO、H2O2、ClO2等强氧化剂均能对不同植物的外植体[18-20]进行成功消毒。本研究使用强氧化剂对锦绣杜鹃外植体材料进行消毒,相同消毒处理的顶芽材料存活率均高于带腋芽茎段材料,这是因为材料的顶端生长点被鳞片包围[21],消毒时材料受损较轻且生长点分生能力强,因此顶芽更适合作为外植体的消毒材料。使用10% H2O2消毒10~15 min时,材料存活率最高,并且此时的存活率与升汞消毒8 min[22]差距较小,说明该处理适合作为替代升汞的有效消毒方式;使用ClO2进行消毒,虽然在低浓度、短时间处理的方式中,材料存活率更高,但经一周期的培养后可发现,材料的死亡率大于存活率,这可能与杜鹃是多酚类植物有关,ClO2适合对非多酚类植物消毒[23],因此消毒过程中对材料损伤较大。培养基配方中植物生长调节剂种类和配比对杜鹃花组织培养有较大影响,在初代培养基中添加GA3有利于茎段材料腋芽萌发,并促使试管芽苗的伸长生长;对增殖培养基配方进行优化,细胞分裂素与生长素比例的提高,能明显促进茎段不定芽的分化,但增殖系数还比较低,后期可对配方进一步优化。
开放式组织培养的初代培养阶段中,添加0.01% NaClO后,除材料的存活率高于常规培养组,死亡率也略有降低,由此可见,抑菌剂的适当添加,除了能替代培养基的高温高压灭菌,还能降低组织培养过程中的污染率。开放式组织培养的增殖阶段,材料增殖系数普遍比对照组低,但添加0.01% NaClO时,增殖系数高于对照组,推测该浓度NaClO能促进不定芽的分化,添加0.02% NaClO时,材料的生长明显受抑制甚至死亡,说明该浓度及以上已不适合作为增殖阶段的抑菌剂;添加代森锰锌的增殖培养基中,新生芽苗的叶片颜色发生改变,可能是代森锰锌的添加,造成材料体内锌离子过量[24],叶绿体明显减少而造成的叶片黄化现象。
本研究使用ISSR分子标记技术对开放式体系的试管芽苗进行遗传稳定性分析,发现使用H2O2作为外植体消毒剂,对杜鹃花试管芽苗遗传变异的影响小于使用NaClO和ClO2;开放式组织培养体系中,试管芽苗的遗传关系聚类与试管芽苗培养的阶段相对应,说明杜鹃花试管芽苗遗传稳定性与培养周期有关;在开放式培养中,抑菌剂的添加会对试管芽苗的遗传稳定性造成一定影响,并且随着继代次数的增加,影响越来越明显,但具体培养到第几周期时材料遗传发生明显变化至与母本材料分为两个物种,还需要进一步的研究探索。
本研究成功建立了锦绣杜鹃的开放式组织培养体系,可为杜鹃的实际生产实践提供依据与技术支持,锦绣杜鹃试管芽苗在整个开放式培养阶段的生长依然存在一定程度的受抑制现象,因此在不影响材料存活率和增殖系数的基础上,如何减少抑菌剂对材料的影响,依然值得继续深入探究。
-
图 6 启动子融合GUS重组载体构建
A:启动子扩增电泳图(M:DNA marker DL6000;1:DoAP3-3-1885;2:DoAP3-3-1604;3:DoAP3-3-750);B:菌落PCR电泳(M:DNA marker DL6000;1:pB-DoAP3-3-A;2:pB-DoAP3-3-B;3:pB-DoAP3-3-C)。
Figure 6. Construction of fusion recombinant vector of promoter and GUS
A: promoter amplification electrophoresis (M: DNA marker DL6000; 1: DoAP3-3-1885; 2: DoAP3-3-1604; 3: DoAP3-3-750); B: colony PCR electrophoresis (M: DNA marker DL6000; 1: pB-DoAP3-3-A; 2: pB-DoAP3-3-B; 3: pB-DoAP3-3-C).
表 1 PCR引物信息
Table 1 PCR Primer information
引物名称
Primer name引物序列(5′→3′)
Primer sequence用途
Usage产物大小
Amplicon size/bpDoAP3-3 (F) TATCTTCCCCCTCCCCAT 基因克隆Gene cloning 675 DoAP3-3 (R) ATCTTCGTCTCGCTTGA DoAP3-3-promoter (F) CGCCGTTACCTGCGTCGTTC 启动子克隆Promoter cloning 1885 DoAP3-3-promoter (R) CCTGATCACTTCTTCTCCTC DoAP3-3-promoter-A (F) CAGTGGTCTCATAGACGCCGTTACCTGCGTCGTTC 启动子表达载体构建Construction of expression vector driven by DoAP 3-3 promoter 1885 DoAP3-3-promoter-B (F) CAGTGGTCTCATAGAGTTGGACAAAACTTTGAGAT 1604 DoAP3-3-promoter-C (F) CAGTGGTCTCATAGACAGTGATTTAAGGGGAATGG 750 DoAP3-3-promoter (R) CAGTGGTCTCAGTTGCCTGATCACTTCTTCTCCTC GUS-promoter-A (F) GAAGTTGAAGACCAATAAACT 检测启动子是否与GUS连接Detection of whether the DoAP3-3 promoter is connected to GUS 630 GUS-promoter-B (F) GCTGATGAATTTTTAAAATTCT 568 GUS-promoter-C (F) GATATTATGAAGCGTGAATG 374 GUS-promoter (R) ATAAAAAGAGAAAAGGGTCCTAACC 下划线为Eco31 I酶识别位点。
Recognition site of Eco31 I enzyme is underlined.表 2 DoAP3-3启动子顺式作用元件预测分析
Table 2 Predicted DoAP3-3 promoter cis-acting element
顺式作用元件
Cis-acting
elements位置(+/−链)
Position from
ATG/bp核心序列
Core sequence功能
FunctionAAGAA-motif 33 GAAAGAA 涉及脱落酸反应的顺式作用元件 Cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid reaction ACE 1479 CTAACGTATT 参与光响应的顺式作用元件 Cis-acting element involved in light responsiveness Box 4 1519, 898, 1331,
450, 1406, 708ATTAAT 参与光响应的保守DNA模块的一部分 Part of a conserved DNA module involved in light responsiveness CAT-box 674 GCCACT 与分生组织表达相关的顺式作用调控元件 Cis-acting regulatory element related to meristem expression GATA-motif 270 AAGGATAAGG 光响应元件的一部分 Part of a light responsive element GT1-motif 1115, 1652 GGTTAA 光响应元件 Light responsive element GTGGC-motif 1636 CATCGTGTGGC 光响应元件的一部分 Part of a light responsive element I-box 268 GATAAGGCG 光响应元件的一部分 Part of a light responsive element MBS 19 CAACTG MYB结合位点参与干旱诱导 MYB binding site involved in drought-inducibility MRE 1655 AACCTAA MYB结合位点参与光响应 MYB binding site involved in light responsiveness P-box 1708 CCTTTTG 赤霉素反应元件 Gibberellin-responsive element TATA-box 1360, 1003, 1728,
1001, 977, 917, 336TATATA 转录起始核心元件 Core promoter element of transcription start TGA-element 1866 AACGAC 生长素反应元件 Auxin-responsive element W box 1797 TTGACC 水杨酸响应元件 Salicylic acid-responsive element -
[1] LITT A, KRAMER E M. The ABC model and the diversification of floral organ identity [J]. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology, 2010, 21(1): 129−137.
[2] 王莹, 穆艳霞, 王锦. MADS-box基因家族调控植物花器官发育研究进展 [J]. 浙江农业学报, 2021, 33(6):1149−1158. WANG Y, MU Y X, WANG J. Research progress of floral development regulation by MADS-box gene family [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2021, 33(6): 1149−1158.(in Chinese)
[3] HUANG F Y, ZHANG Y H, HOU X L. BcAP3, a MADS box gene, controls stamen development and male sterility in Pak-choi (Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis) [J]. Gene, 2020, 747: 144698. DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144698
[4] IRISH V. The ABC model of floral development [J]. Current Biology, 2017, 27(17): R887−R890. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.03.045
[5] PAN Z J, CHENG C C, TSAI W C, et al. The duplicated B-class MADS-box genes display dualistic characters in orchid floral organ identity and growth [J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2011, 52(9): 1515−1531. DOI: 10.1093/pcp/pcr092
[6] DENG M H, LV J H, WANG Z R, et al. Two promoter regions confer heat-induced activation of SlDREBA4 in Solanum lycopersicum [J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2020, 524(3): 689−695. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.01.153
[7] 王树军, 刘保华, 孙进华, 等. 荔枝多酚氧化酶基因启动子克隆与功能分析 [J]. 果树学报, 2015, 32(3):427−433,524. WANG S J, LIU B H, SUN J H, et al. Cloning and function analysis of the promoter of PPO gene from Litchi(Litchi chinensis Sonn.) [J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2015, 32(3): 427−433,524.(in Chinese)
[8] HOU J J, JIANG P P, QI S M, et al. Isolation and functional validation of salinity and osmotic stress inducible promoter from the maize type-II H+-pyrophosphatase gene by deletion analysis in transgenic tobacco plants [J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(4): e0154041. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154041
[9] XIN S, TAO C C, LI H B. Cloning and functional analysis of the promoter of an ascorbate oxidase gene from Gossypium hirsutum [J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(9): e0161695. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161695
[10] 李泽卿. 二球悬铃木花发育基因PaAP3、PaPI和PaSTK启动子的克隆、功能分析及其在不育中的应用[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2017. LI Z Q. Cloning and functional analysis of the promoters of flower development genes PaAP3, PaPI and PaSTK in London plane tree and their application in sterility[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese)
[11] ROMBAUTS S, DÉHAIS P, VAN MONTAGU M, et al. PlantCARE, a plant Cis-acting regulatory element database [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1999, 27(1): 295−296. DOI: 10.1093/nar/27.1.295
[12] 张婷, 邢妮, 王超, 等. 小花草玉梅正常和自然变异植株的AP3-3基因研究 [J]. 西北植物学报, 2016, 36(2):231−240. ZHANG T, XING N, WANG C, et al. Cloning and sequence analysis of AP3-3 gene in normal plant and natural variant from Anemone rivularis var. flore-minore [J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2016, 36(2): 231−240.(in Chinese)
[13] JING D L, CHEN W W, SHI M, et al. Ectopic expression of an Eriobotrya japonica APETALA3 ortholog rescues the petal and stamen identities in Arabidopsis ap3-3 mutant [J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2020, 523(1): 33−38. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.11.177
[14] 李淑娴. 墨兰成花机理及花期调控技术研究[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2016. LI S X. Mechanism of flower development and early flowering technique of Cymbidium sinense[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2016. (in Chinese)
[15] 龚湉. 寒兰成花机理及花期调控研究[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2015. GONG T. Mechanism of floral formation of Cymbidium kanran and flowering regulation[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2015. (in Chinese)
[16] MUNDY J, YAMAGUCHI-SHINOZAKI K, CHUA N H. Nuclear proteins bind conserved elements in the abscisic acid-responsive promoter of a rice rab gene [J]. PNAS, 1990, 87(4): 1406−1410. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1406
[17] 李艳林, SHAHID IQBAL, 侍婷, 等. 梅PmARF17克隆及其在花发育中与内源激素的调控模式 [J]. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(13):2843−2857. DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2021.13.013 LI Y L, IQBAL S, SHI T, et al. Isolation of PmARF17 and its regulation pattern of endogenous hormones during flower development in Prunus mume [J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(13): 2843−2857.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2021.13.013
[18] POBORILOVA Z, PLCHOVA H, CEROVSKA N, et al. Transient protein expression in tobacco BY-2 plant cell packs using single and multi-cassette replicating vectors [J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2020, 39(9): 1115−1127. DOI: 10.1007/s00299-020-02544-w
-
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 孙文秀,邵晨阳,陈妍妍,聂明皓,李震,曹毅,刘应保. 干旱胁迫下2种内生真菌对烟草生理生化指标及NAC基因表达的影响. 华北农学报. 2024(01): 113-119 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 周英,谢科,蔡汉,黄长兵. 盐胁迫下外源褪黑素和丛枝菌根真菌对月季幼苗生长生理特性的影响. 西北植物学报. 2024(03): 370-380 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 余泽岑,晏梅静,补春兰,沈谦,刘刚,董廷发,胥晓. 不同AMF菌肥对桑树“嘉陵30”生长和叶品质的影响. 西华师范大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(03): 246-253 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 陈婷,张国龙,李春玲,马国江,李泽山. 不同AMF对番茄幼苗响应旱盐双重胁迫的影响. 农业科技通讯. 2024(07): 27-32 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 宗建伟,黄小迪,靳永安,杨雨华. NaCl胁迫下摩西斗管囊霉对文冠果生长及叶片解剖结构和叶绿素荧光参数的影响. 植物资源与环境学报. 2023(02): 73-81 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 张思华,弥春霞,虞轶俊,刘国群,朱春权,田文昊,朱练峰,曹小闯,张均华,孔亚丽. 丛枝菌根真菌缓解水稻盐碱胁迫的生理特性研究. 中国稻米. 2023(03): 56-61 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 齐玉玺,张琇,杨国平,季鸿飞,沈婷婷,吴凯华. 耐盐碱促生菌S4的鉴定及其提高水稻耐盐碱作用研究. 山东农业科学. 2023(04): 147-154 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 王海鸥,麦格皮热提古丽·达吾提,高文礼,陈晓楠,伊力努尔·艾力,马晓东. 盐胁迫对AMF介导下两种荒漠植物生长和生理特性的影响. 草地学报. 2023(09): 2712-2721 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 周楠,穆丹,梁英辉,李青楠. 丛枝菌根真菌在湿地修复中的应用研究进展. 中国野生植物资源. 2023(10): 75-78 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)




 下载:
下载: