Cloning and Expression of Nitrite Reductase Gene HcNiR in Kenaf
-
摘要:目的 了解红麻亚硝酸还原酶基因HcNiR生物信息学特性及组织表达特异性,为培育红麻氮高效利用品种提供理论依据。方法 以红麻材料349叶片的cDNA为模板,利用PCR扩增HcNiR基因的CDS序列,采用生物信息学方法分析HcNiR的氨基酸组成、蛋白质跨膜结构、信号肽、高级结构以及蛋白的同源进化树;采用实时荧光定量PCR检测HcNiR基因在红麻不同组织的表达情况。结果 HcNiR基因cDNA全长1395 bp,编码蛋白含有464个氨基酸,包含2个保守的亚硝酸和亚硫酸还原酶4Fe-4S结构域及铁氧蛋白部分结构域。HcNiR蛋白是一个不含跨膜转运结构与信号肽的亲水稳定性蛋白质,该蛋白质等电点是5.49,分子量51.68 kDa;具有26处潜在磷酸化位点。在其蛋白二级结构中,α-螺旋和无规则卷曲所占比例超过70%。通过氨基酸序列同源性分析发现,红麻HcNiR氨基酸序列与木槿HsNiR氨基酸序列相似性较高,达到97.37%,都含有铁-硫/铁血红素结合位点。进化树分析结果表明,红麻HcNiR基因与木槿HsNiR基因亲缘关系较近。组织特异性表达结果显示,红麻HcNiR基因在叶中的表达量高于根。结论 HcNiR基因编码蛋白含亚硝酸和亚硫酸还原酶4Fe-4S结构域及铁氧蛋白部分结构域;HcNiR基因具有组织表达特异性,在红麻叶片中表达较高,推测其主要在初级氮的同化过程中发挥重要调控作用。Abstract:Objective Bioinformatics and expressions of the nitrate reductase gene of kenaf(Hibiscus cannabinus) were studied for breeding varieties highly efficient in nitrogen utilization.Method From the leaf of kenaf 349, the coding sequences (CDS) of HcNiR was amplified by PCR. Bioinformatics method was applied to analyze the amino acid sequences, protein transmembrane structure, protein signal peptide, high-level structures, and homologous evolutionary tree associated with the gene, while the expression in various tissues detected by qRT-PCR.Result The full length of HcNiR cDNA was 1395 bp encoded 464 amino acids. The amino acid sequence contained two conserved nitrite and sulfite reductase 4Fe-4S domains and two conserved nitrite/sulfite reductase ferredoxin-like half domains. The predicted stable, hydrophilic HcNiR protein with an isoelectric point of 5.49 and molecular weight of 51.68 kDa had no transmembrane domain or signal peptide. It contained 26 potential phosphorylation sites in a secondary structure that consisted of more than 70% in the forms of alpha helix and irregular coils. The amino acid sequence of HcNiR was 97.37% homologous with that of H. syriacus, and both included nitrite and sulfite reductases iron-sulfur/siroheme-binding sites. The phylogenetic tree on HcNiR showed it closely related to HsNiR. The HcNiR expression was higher in the leaves than in the roots of a kenaf plant.Conclusion HcNiR contained two conserved nitrite and sulfite reductase 4Fe-4S domains and two conserved nitrite/sulfite reductase ferredoxin-like half domains. The gene was abundantly expressed in the kenaf leaves and speculated to be mainly involved in the process of primary nitrogen assimilation.
-
Keywords:
- kenaf /
- nitrate reductase /
- HcNiR /
- gene cloning /
- expression analysis
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】红麻(Hibiscus cannabinus L.)为锦葵科木槿属一年生韧皮纤维作物,其经济价值不仅仅体现于纤维利用,在材料、生物能源、医用、饲料、造纸及碳汇交易等多方面都具有重要的研究前景[1-3];在生产实践中发现红麻具有生长速度快、生物量大等特点,作为畜禽饲料的价值也尤为突出:红麻生长速度快,叶片中含黄酮和多酚,抗虫能力强,无需施药,属于天然绿色蛋白饲料[4]。近年来国内畜牧业飞速进步,饲料产业一跃而起,如何提高饲料的品质成为关键问题[5]。亚硝酸还原酶NiR(Nitrite reductase)是植物硝态氮同化过程中重要的酶。植物从土壤里摄取氮素一般可以分为两种形式,一种是以硝态氮形式进入植物体中,该形式必须首先经历一个还原过程方可被同化为有机含氮化合物;而另一种是以氨态氮形式进入植物体后,直接被结合成含氮的有机物。亚硝酸还原酶NiR与硝酸还原酶(Nitrate reductase,NR)偶联完成NO3−无机同化[6],继而NO2−进一步被NiR还原酶还原成NH4+,该酶在硝酸盐降解并生成铵的过程中起承前启后的作用。硝酸还原酶是NO3−无机同化步骤中的第一个酶,也是整个过程的限速酶,而亚硝酸还原酶是NO3−无机同化的控制酶,两个酶偶联完成NO3−的无机同化[7,8]。本研究通过克隆红麻亚硝酸还原酶基因HcNiR,研究其编码蛋白的生物信息学与表达特性,对了解红麻氮代谢调控机制及生物学功能具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】相对于硝酸还原酶NR,亚硝酸还原酶NiR相关的研究并不多见,其生物学功能也未明确。Lahners等[9]对ZmNiR基因结构进行研究,并获得该基因的分子结构,其氨基酸序列与菠菜序列相比有86%的相似性,该基因参与对氮吸收的调节。Wang等[10]通过研究拟南芥根中硝酸盐诱导的结果,发现在氮饥饿的条件下,由于硝酸盐量的增加,亚硝酸还原酶mRNA也具有了较高的表达量。Takahashi等[11]将菠菜亚硝酸还原酶NiR基因导入拟南芥中得出,NiR-mRNA与NiR的总蛋白含量(r=0.74)、NiR总蛋白与NiRA(r=0.71)、NiRA与通过分析NO2产生的还原氮同化NO2(r=0.65)均呈显著正相关,结果证实NiR为植物无机氮循环中NO2–同化部分的控制酶;Kato等[12]等研究发现烟草中含有4个不同的NiR基因,且在叶片和根系中均有表达,且与氮吸收相关。Ozawa等[13]克隆一个水稻的NiR基因,将该基因在水稻品种越光中超量表达,提高了其愈伤组织的生长及再生能力,可作为农业转基因水稻高产的选择系统。夏磊等[14]克隆了黄瓜亚硝酸还原酶基因CsNiR,研究发现其活性与外植体分化率表现出负相关关系。【本研究切入点】本课题组前期研究中利用不同蛋白含量饲用红麻叶片转录组与蛋白组测序联合分析得到红麻亚硝酸还原酶关键基因HcNiR,根据其基因序列设计引物克隆该基因。但其作为亚硝酸还原酶基因功能还未被确定,在生物信息学方面仍有较多值得挖掘的地方。【拟解决的关键问题】克隆红麻HcNiR基因并对该基因进行生物信息学分析和组织特异性表达分析,为更进一步研究该基因在红麻氮代谢调控机制及培育红麻氮高效利用品种提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试剂与材料
供试红麻材料349由中国农业科学院麻类研究所一年生麻类作物育种团队提供,该材料在70多个具有代表性的红麻材料中经多年试验得出,其叶片具有较高的粗蛋白含量(27.36%)[15];主要试剂:KOD-FX高保真酶[东洋纺(上海)生物科技有限公司],GoldenstarTM RT6 cDNA Synthesis Kit (北京擎科新业生物技术有限公司),零背景pTOPO-TA/Blunt Simple克隆试剂盒(北京艾德莱生物科技有限公司),PC33-2xSybr Green qPCR Mix(北京艾德莱生物科技有限公司)。
1.2 红麻叶片总RNA提取
取萌发后培养45 d长势良好的红麻叶片约100 mg,液氮中快速研磨成微小粉末状,红麻叶片RNA提取步骤按照EASY spinPlus多糖多酚复杂植物总RNA快速提取试剂盒说明书操作,13 μL预处理DEPC水溶解,1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测提取RNA是否完整。
1.3 HcNiR基因引物设计
根据HcNiR基因序列设计引物(表1),内参基因beta-actin选择参考文献[16]。
表 1 引物序列Table 1. Primer sequence引物名称
Primer names引物序列(5′-3′)
Primer sequence(5′-3′)HcNiR-F ATGACAGATGGGAGATTTATGATG HcNiR-R GCATTTTCCACTTCTTCTTCCC HcNiR-qPCR-F TCTTGGTTACAGGGGCAATAGAC HcNiR-qPCR-R TGGACACCAAGATAGTCTCTCCT beta-actin-F ATCCTCCGTCTTGACCTTG beta-actin-R TGTCCGTCAGGCAACTCAT 1.4 目的基因PCR扩增
以红麻叶片总RNA反转录成cDNA,扩增红麻HcNiR基因cDNA全长序列,PCR反应体系为25 μL:cDNA 1 μL,2×PCR Buffer 12.5 µL,dNTPs(2 mmol·L−1)5 μL,KOD FX (1 U·μL−1) 1 μL,上游引物HcNiR-F 1 μL,下游引物HcNiR-R 1 μL,ddH2O补至25 μL。扩增程序:94 ℃预变性5 min,32个循环反应(94 ℃ 30 s变性,58 ℃ 30 s复性,72 ℃ 1.5 min延伸),72 ℃终延伸10 min,4 ℃保存PCR产物。引物合成及测序工作由北京擎科生物有限公司完成。
1.5 目的片段与载体的连接与转化
PCR产物经琼脂糖凝胶电泳后回收目的DNA片段,加入溶胶液彻底溶解后进行胶回收,连接到T载体,利用冻融法转化大肠杆菌DH5α感受态细胞,并均匀涂布于含氨苄青霉素抗性的LB固体培养基上,37 ℃恒温培养14 h左右。挑取白色单菌落,摇菌待菌液完全浑浊后作菌液PCR鉴定并测序。
1.6 生物信息学分析
利用SMART (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/)预测蛋白结构域,利用TMHM Server v.2.0 (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/)预测蛋白跨膜结构;利用Signal IP工具(http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/)预测信号肽;Protscale模体数据库(https://web.expasy.org/protscale/)分析蛋白质产物疏水性和亲水性;利用NetPhos 2.0 Server (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetPhos/)预测磷酸化位点;利用ExPASy软件ProtParam程序(http://web.expasy.org/protparam/)分析氨基酸序列特性;ProtComp v. 9.0数据库(http://linux1.softberry.com/berry.phtml)预测蛋白亚细胞定位;SOPMA和Phyre (http://www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk/phyre/)软件依次预测蛋白质二级及三级结构;且从NCBI中收集已知各物种NiR基因序列,利用ClustalX比对蛋白质序列,MEGA7.0软件设置以邻接法用于构建HcNiR基因与其他物种NiR基因系统进化树[17]。
1.7 组织特异性分析
将低温保存的红麻种子用75%酒精清洗并擦干,种子放置于发芽盒中, 25 ℃萌发7 d 转入温室水培。生长条件设定:昼夜温度25/20 ℃,光周期16/8 h(光/暗),相对湿度60%,光强度700 µmol·m−2,1/4 Hoagland营养液,两天更换一次。培养45 d后取红麻叶片、根部分组织。提取红麻总 RNA,使用金牌逆转录试剂盒(北京擎科生物有限公司,北京)反转录合成 cDNA,选取beta-actin作为内参基因;以各样品的cDNA为模板,根据PC33-2xSybr Green qPCR Mix说明书在实时定量PCR仪(BIO-RAD CFX96)上进行实时荧光定量PCR,检测不同组织HcNiR基因在转录水平上的相对表达水平,采用2−ΔΔCT算法计算相对表达量。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 HcNiR基因克隆和序列特征
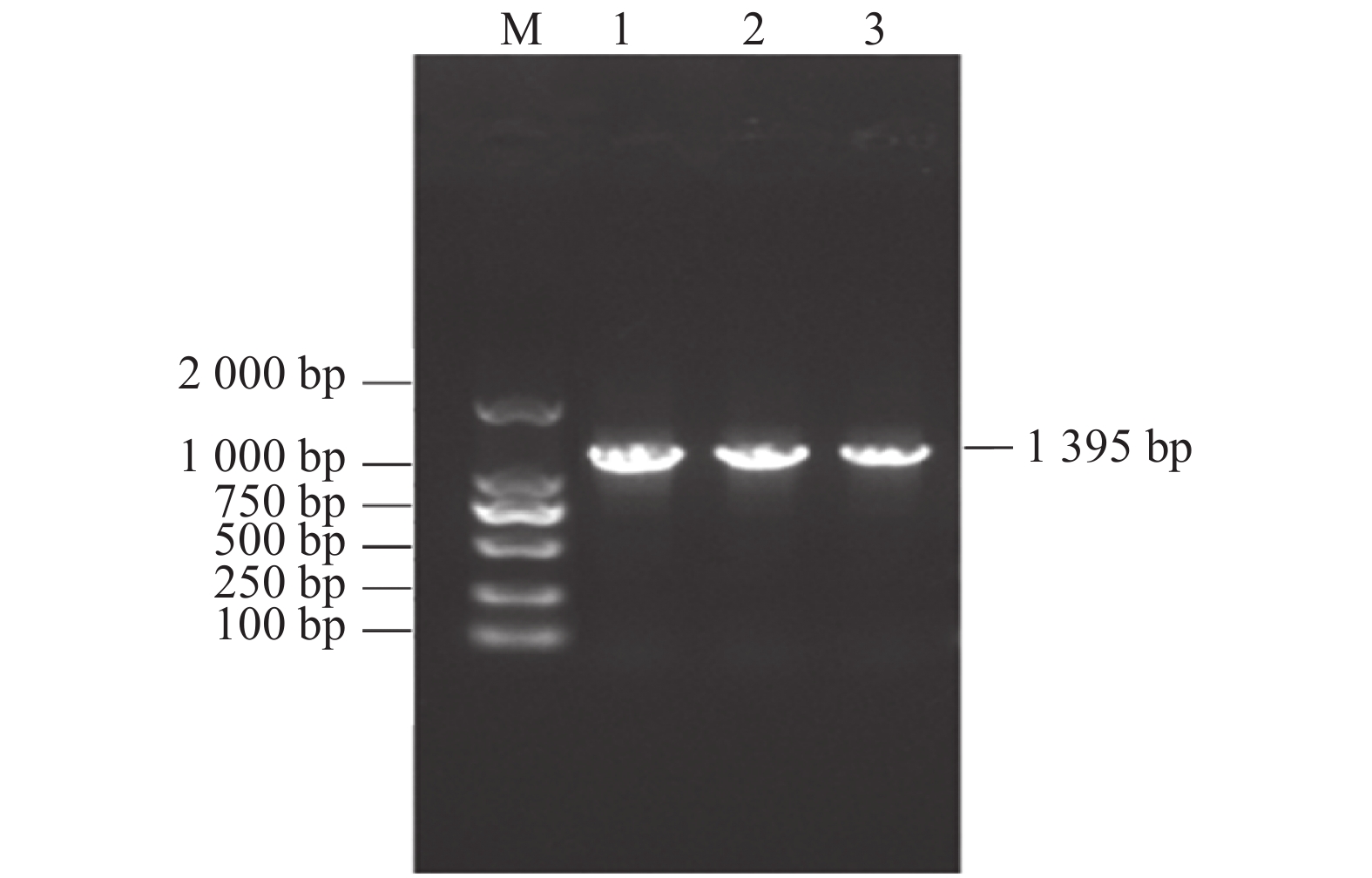
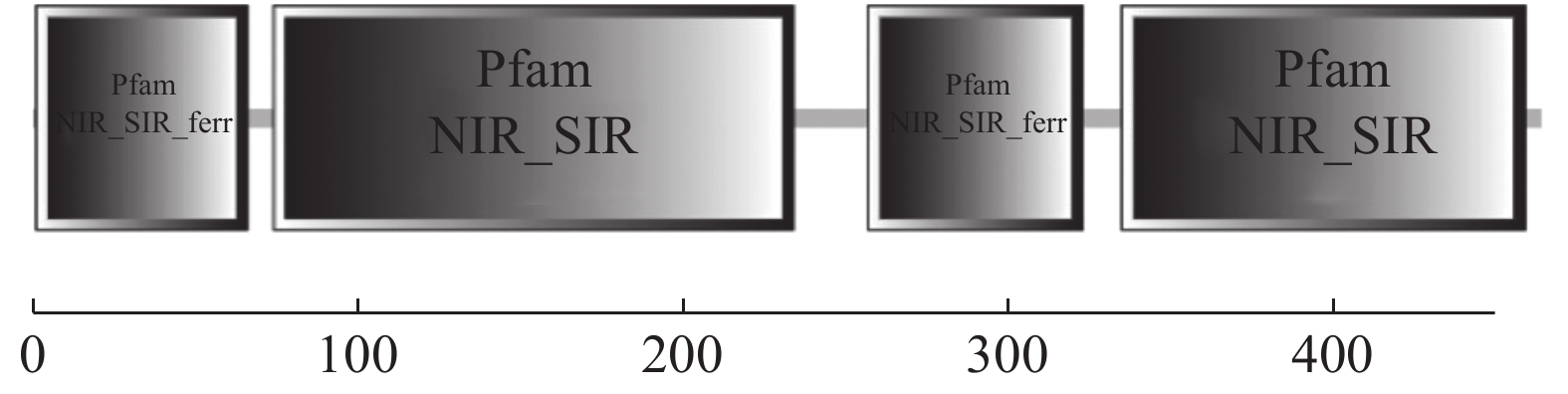
基于红麻叶片转录组与蛋白组联合分析数据,设计特异性引物扩增红麻HcNiR基因的cDNA 序列,结果获得一条大小约1500 bp的扩增产物,与预期大小一致(图1)。测序结果显示,该基因含有一个1395 bp 的开放阅读框(ORF),编码464 个氨基酸。用SMART 软件对红麻 HcNiR蛋白进行序列分析,分析结果如图2,HcNiR氨基酸序列中包含2个保守的亚硝酸和亚硫酸还原酶4Fe-4S结合域(Nitrite and sulphite reductase 4Fe-4S domain)分别位于74~234 aa和335~459 aa,同时还具有2个亚硝酸/亚硫酸还原酶铁氧蛋白结构域蛋白部分结构域(Nitrite/Sulfite reductase ferredoxin-like half domain),分别位于1~66 aa和257~323 aa。
2.2 红麻HcNiR基因编码蛋白的亲/疏水性分析
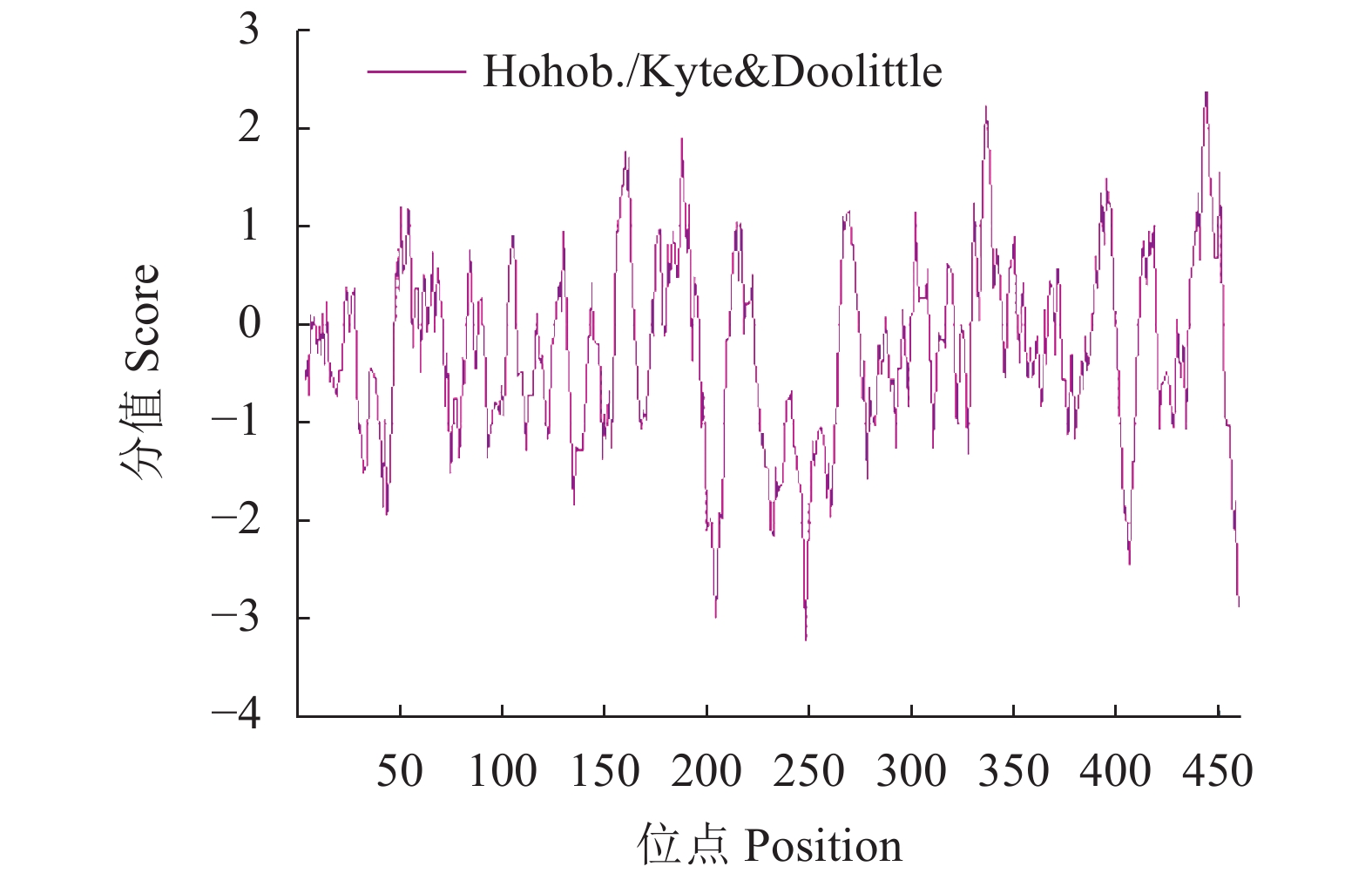
运用ProtScale工具分析红麻HcNiR基因编码的蛋白质产物亲水性和疏水性,从分析结果可见,亲水性分析中,在多肽链第249位的谷氨酸处产生最大峰值,对应峰数值−3.200;疏水性分析中,在多肽链第444位的丙氨酸处产生最大峰值,对应峰数值2.456。根据氨基酸分值越高疏水性越强和分值越低亲水性越强的规律,亲水性最强的氨基酸是该基因序列第249位的谷氨酸,疏水性最强的氨基酸是该基因序列第444位的丙氨酸。从整体上看,亲水性氨基酸多于疏水性氨基酸,且均匀分布在肽链中;推测HcNiR基因编码的蛋白质是亲水性蛋白(图3)。
2.3 HcNiR蛋白质磷酸化位点预测分析
以神经网络算法为基础预测蛋白质磷酸化位点,HcNiR基因编码蛋白质的可能磷酸化位点如图4-A所示;结果可知,HcNiR蛋白存在12个丝氨酸磷酸化位点(分别是27、73、105、112、132、166、239、265、312、370、422和424)、12个苏氨酸磷酸化位点(分别是2、18、22、41、69、150,208、240、354、362、372和380)以及2个潜在的酪氨酸磷酸化位点(分别是136和266),相对应的磷酸化势见图4-B,表明HcNiR蛋白可能被这3种氨基酸激酶磷酸化且激活,最终调控基因表达。
2.4 红麻HcNiR基因编码蛋白质产物一级结构分析
红麻HcNiR基因编码蛋白质产物一级结构分析预测结果见表2,由结果可知,该蛋白质不稳定系数37.930,低过阈值40。HcNiR蛋白是稳定酸性亲水蛋白质。利用ProtComp预测HcNiR蛋白的亚细胞定位,该蛋白定位于叶绿体上。
表 2 HcNiR基因编码蛋白质产物一级结构预测分析Table 2. Primary structure of HcNiR encoded protein一级结构特征
Characteristics of
primary structure氨基酸数量
Number of
amino acids等电点
pI相对分子质量
Relative molecular
mass/Da分子式
Molecular
formula正电荷
残基
Arg+Lys负电荷
残基
Asp+Glu平均疏水性
Average
hydrophobicity脂肪系数(AI)
Fatty
coefficient不稳定系数(Ⅱ)
Instability
coefficient (Ⅱ)半衰期
Estimated
half-life/h预测结果
Prediction result464 5.490 51683.220 C2276H3632N644O681S24 54 64 −0.289 89.480 37.930 30 2.5 红麻HcNiR基因编码蛋白质产物二级结构及高级结构预测
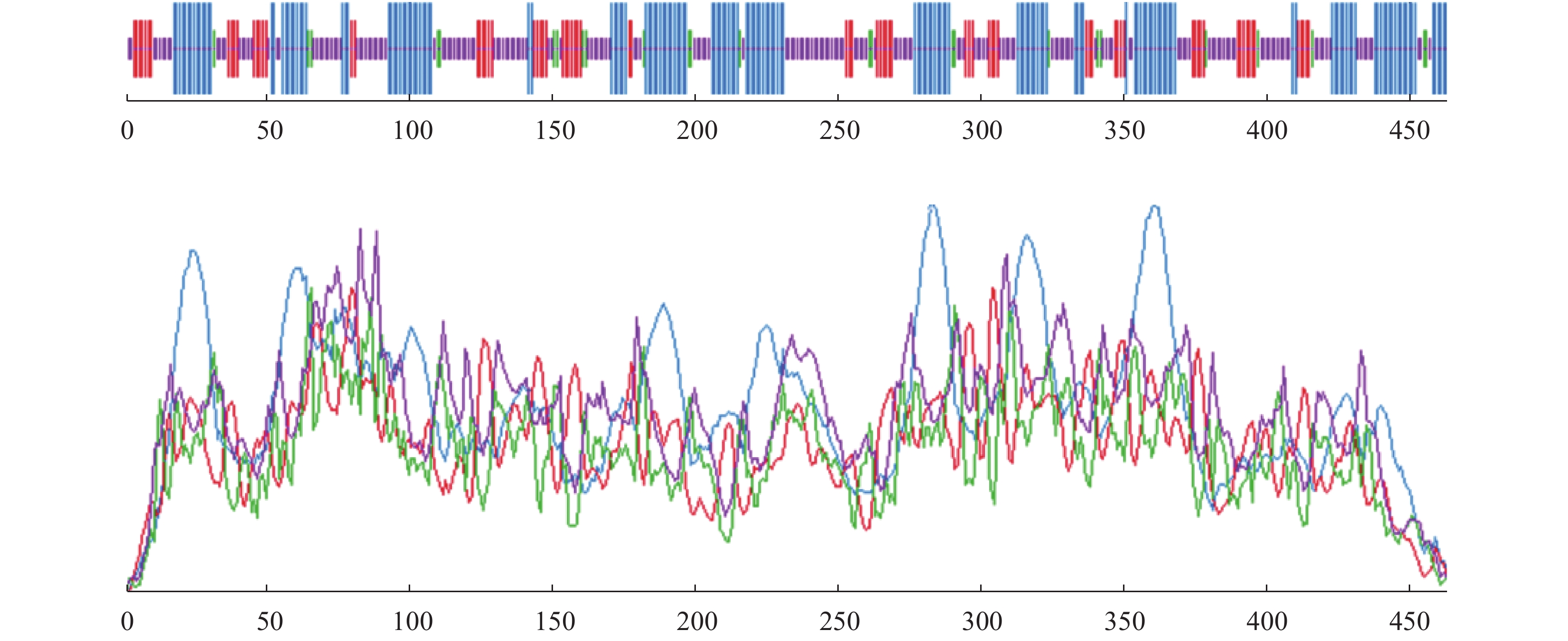
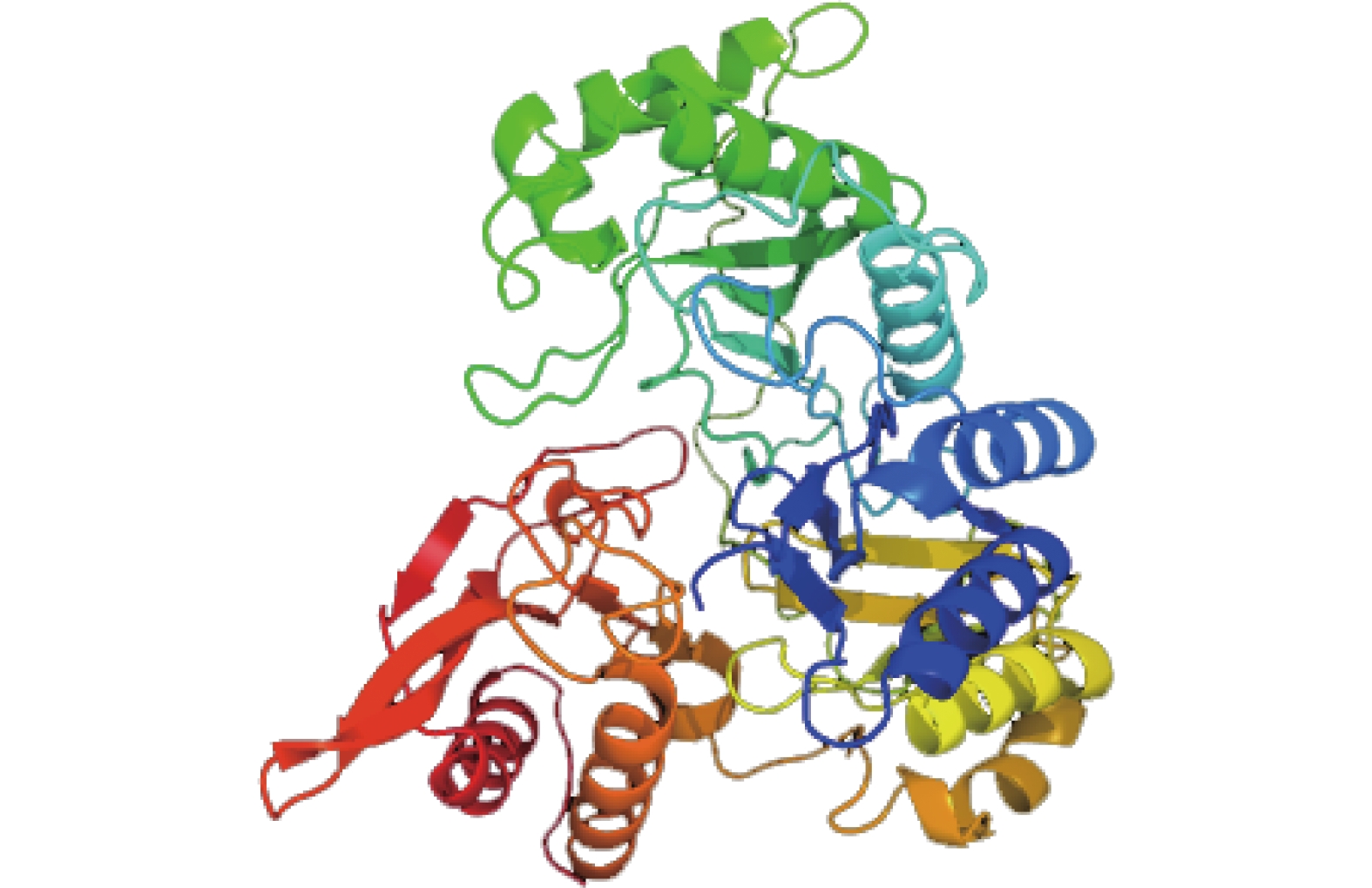
运用SOPMA软件分析红麻 HcNiR基因编码的蛋白质产物二级结构,从分析结果可知(图5),HcNiR蛋白二级结构由α螺旋、不规则卷曲、β折叠及β转角组成。其中,α螺旋占35.99%,不规则卷曲占41.81%,β折叠占16.81%,β转角占5.39%。利用跨膜预测服务运用Phyre2数据库在线分析 HcNiR基因编码的蛋白质产物并预测分析蛋白质三级结构,运用Rasmol软件分析红麻HcNiR基因编码的蛋白质产物三级结构,并以图形化分析。从分析数据中可得到,HcNiR基因编码的蛋白质产物三级结构中含α螺旋25个,氢键286个,β折叠36个,转角43个(图6)。
2.6 HcNiR编码蛋白质的跨膜结构及信号肽分析
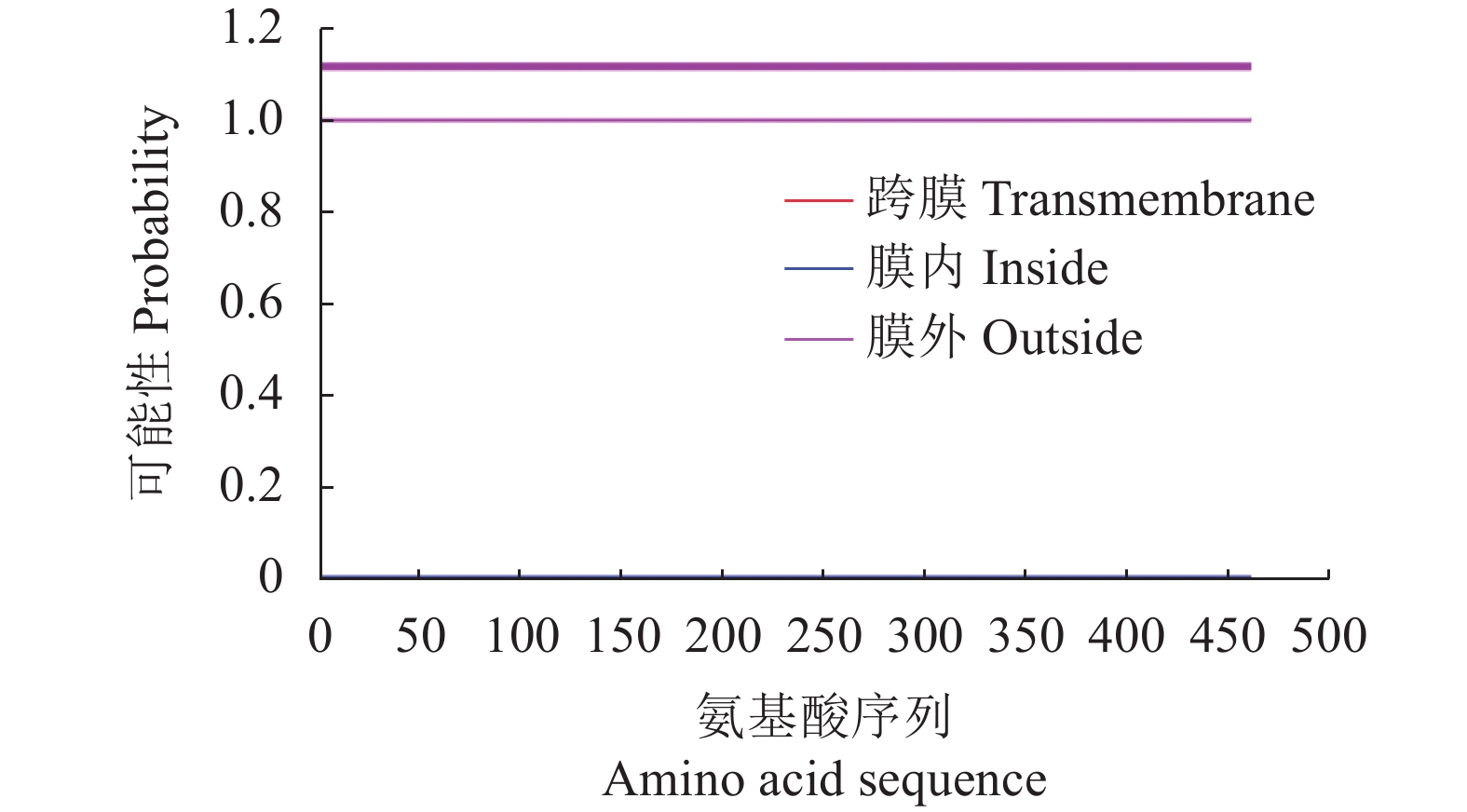
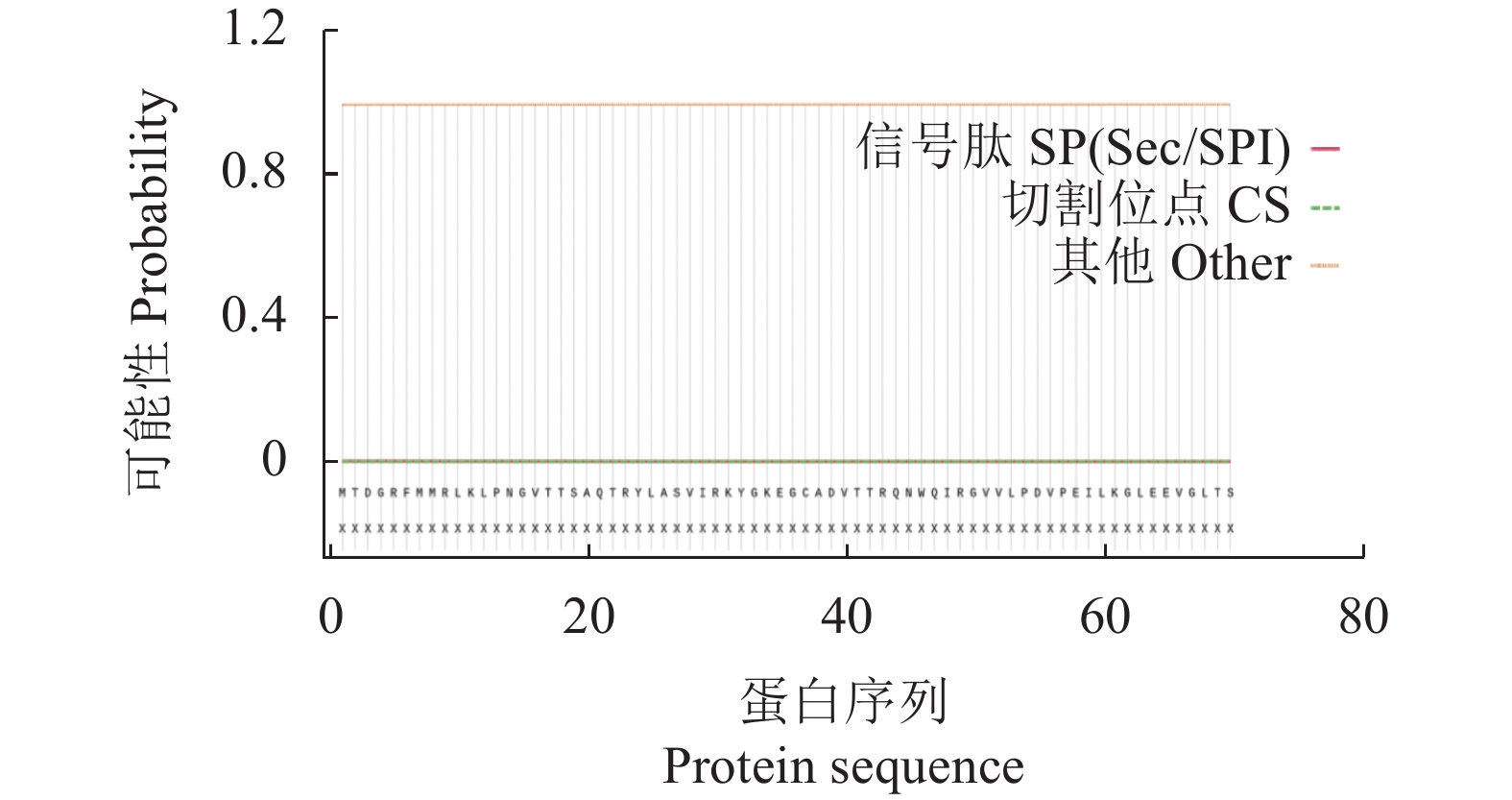
利用跨膜预测服务器TMHMM Server 2.0分析HcNiR基因编码蛋白质的跨膜结构(图7),分析结果表明其氨基酸在膜外区域几率比较接近于1,而在膜内区域几率非常低,存在跨膜区域的几率也比较低。所以推测HcNiR蛋白464个氨基酸残基几乎完全在膜外且无明显跨膜区域。因而可知HcNiR蛋白并无跨膜转运信号,同样也不是膜上受体。通常由5~30个氨基酸残基组成的一个蛋白质片段称为信号肽。HcNiR蛋白质信号肽预测结果可知(图8),其氨基酸序列中并不含有信号肽。
2.7 红麻HcNiR的同源性与系统进化树分析
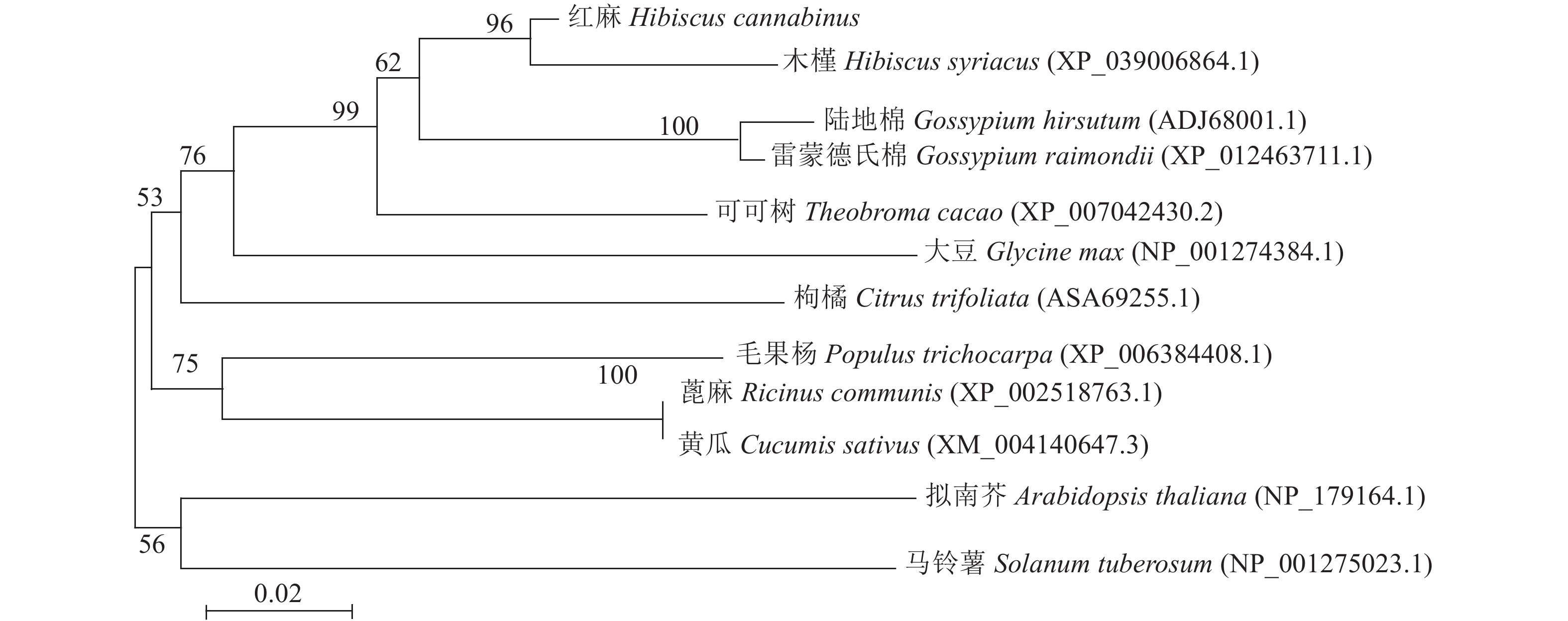
BlastP程序对HcNiR 464个氨基酸与其他物种中NiR氨基酸序列进行同源性比对,由结果(图9)可知,红麻HcNiR与木槿(XP_039006864.1)、雷蒙德氏棉(XP_012463711.1)、陆地棉(ADJ68001.1)和可可树(XP_007042430.2)的相似度分别为97.37%、93.65%、93.00%和92.12%。对红麻HcNiR蛋白序列分析发现,其存在由17个氨基酸组成的铁-硫/铁血红素结合位点“TGCPNSCGQVQVADIGF” 。使用MEGA7.0 对来自12种植物的HcNiR氨基酸序列绘制NJ(Neighbor-joining 法)系统进化树(图10),结果表明,红麻HcNiR与木槿HsNiR (Hibiscus syriacus)聚在同一分枝,亲缘关系较近;雷蒙德氏棉GrNiR (XP_012463711.1)、陆地棉GhNiR (ADJ68001.1)与HcNiR距离也相对较近。红麻HcNiR蛋白与可可树TcNiR(XP_007042430.2)蛋白聚成一支。
![]() 图 9 HcNiR的氨基酸序列对比HcNiR:红麻;HsNiR:木槿(XP_039006864.1);TcNiR:可可树(XP_007042430.2);GhNiR:陆地棉(ADJ68001.1);GrNiR:雷蒙德氏棉(XP_012463711.1)。Figure 9. Amino acid sequences of HcNiRHcNiR: H. cannabinus; HsNiR: H. syriacus (XP_039006864.1); TcNiR: Theobroma cacao (XP_007042430.2); GhNiR: Gossypium hirsutum (ADJ68001.1); GrNiR: Gossypium raimondii (XP_012463711.1).
图 9 HcNiR的氨基酸序列对比HcNiR:红麻;HsNiR:木槿(XP_039006864.1);TcNiR:可可树(XP_007042430.2);GhNiR:陆地棉(ADJ68001.1);GrNiR:雷蒙德氏棉(XP_012463711.1)。Figure 9. Amino acid sequences of HcNiRHcNiR: H. cannabinus; HsNiR: H. syriacus (XP_039006864.1); TcNiR: Theobroma cacao (XP_007042430.2); GhNiR: Gossypium hirsutum (ADJ68001.1); GrNiR: Gossypium raimondii (XP_012463711.1).2.8 HcNiR基因在红麻不同组织中的表达分析
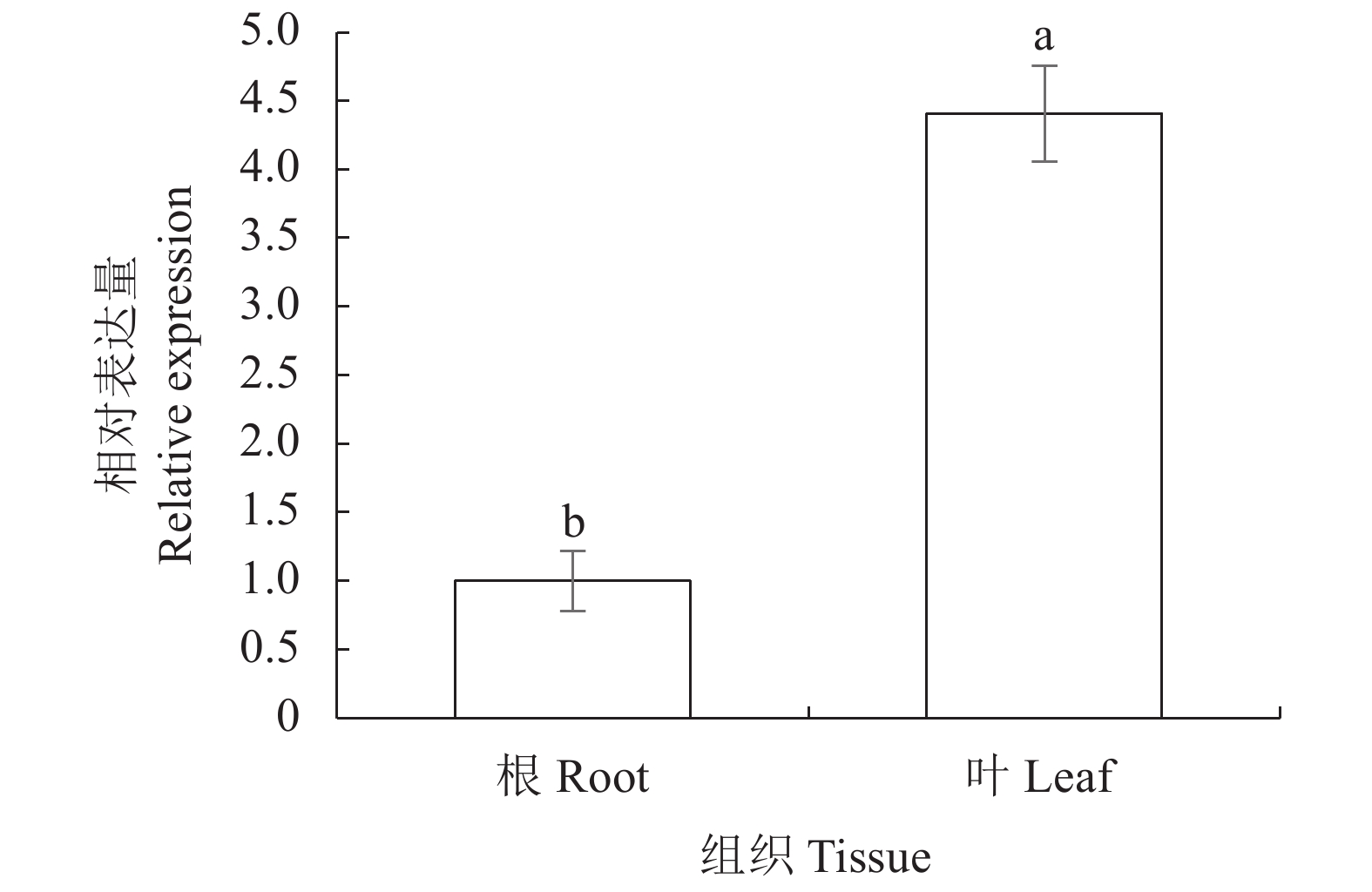
以红麻叶、根cDNA 为模板,以HcNiR-qPCR-F和HcNiR-qPCR-R 为引物,beta-actin 为内参引物进行实时荧光定量PCR 反应,检测不同组织中HcNiR基因的相对表达量。Real time PCR 结果表明其在红麻不同器官中(叶、根)中均有表达,在叶中的相对表达量显著高于根(P<0.05)(图11)。
3. 讨论
植物体中氮同化需要在不同氮代谢酶的参与下进行,由NO3−还原成NH4+这一代谢过程需要由硝酸还原酶和亚硝酸还原酶联合完成;NR和NiR都与光合作用有着极为密切的联系,其中NR是光诱导酶,并且NADH 提供还原力是保证硝酸还原反应顺利完成的必要条件[18],而NADH正是由光反应产生的NADPH转换得来;NiR需要光反应中产生的铁氧还蛋白(Fd)才能够完成还原反应[19],并将 NO2−还原成NH4+。本研究中克隆到红麻NiR基因,其目的条带长度为1395 bp,共编码464个氨基酸,同时包含保守的亚硝酸和亚硫酸还原酶4Fe-4S结构域及亚硝酸/亚硫酸还原酶铁氧蛋白部分结构域。小麦TaNiR基因也含有4个保守的参与铁硫蛋白簇(4Fe-4S)结构域及铁氧还蛋白结合位点[20]。NiR基因在拟南芥、水稻、菠菜、烟草等植物中克隆得到[21]的氨基酸序列中也都含有铁氧还蛋白亚硝酸盐还原酶结构域。
提取红麻总RNA进行HcNiR基因组织特异表达定量分析时,选择45 d的叶片和根组织,此时麻苗正处在旺长期,各组织基因表达量均衡且较高。铁氧化还原蛋白(Fd)依赖的亚硝酸还原酶不仅存在于叶绿体中,根等非光合组织中也有发现[22]。本试验中对红麻HcNiR基因亚细胞定位的结果发现该基因主要存在于叶绿体中;从组织表达分析得到,HcNiR基因在叶中表达量较高,明显高于根。张芬等[23]研究了茶树亚硝酸还原酶基因及其表达特性,发现该基因在成熟叶片中表达量高于一芽二叶和根;孙菲菲等[24]研究发现白菜亚硝酸还原酶基因叶片中的表达量远高于根表达量,证明叶与根中的确存在NiR基因的表达,且在叶中的表达量高于根,本研究结果与二者的研究结果相符。
植物中亚硝酸还原酶基因表达规律与各类内在、外在因素有关。张芬等[23]研究了不同供氮水平茶树叶片中亚硝酸还原酶基因NiR表达特性,石晓艳等[25]研究了甜菜亚硝酸还原酶基因NiR在不同NO3--N 和NH4+-N浓度对甜菜叶片NiR基因表达的影响,孙菲菲等[24]研究了不同NO3–-N和NH4+-N浓度对白菜根和叶片BpNiR基因表达的影响。陈何等[26]研究苋菜亚硝酸还原酶基因NiR对不同硝酸铵含量配比与红蓝复合光配比的共同调控氮代谢。本研究结果有助于深入研究HcNiR基因在红麻硝态氮同化过程中的关键作用,提高氮的转化效率,能够为种质资源鉴定、培育氮红麻高蛋白品种提供分子生物学理论依据;但还需通过亚细胞定位、诱导蛋白及红麻遗传转化等技术进一步对基因结构与功能进行验证。
综上,HcNiR基因编码蛋白含有2个保守的亚硝酸和亚硫酸还原酶4Fe-4S结构域及2个保守亚硝酸/亚硫酸还原酶铁氧蛋白部分结构域,与其他植物NiR在生物学功能上具有一致性;HcNiR基因具有组织表达特异性,在红麻叶片中高效表达,推测其主要在初级氮的同化过程中发挥重要调控作用。
-
图 9 HcNiR的氨基酸序列对比
HcNiR:红麻;HsNiR:木槿(XP_039006864.1);TcNiR:可可树(XP_007042430.2);GhNiR:陆地棉(ADJ68001.1);GrNiR:雷蒙德氏棉(XP_012463711.1)。
Figure 9. Amino acid sequences of HcNiR
HcNiR: H. cannabinus; HsNiR: H. syriacus (XP_039006864.1); TcNiR: Theobroma cacao (XP_007042430.2); GhNiR: Gossypium hirsutum (ADJ68001.1); GrNiR: Gossypium raimondii (XP_012463711.1).
表 1 引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequence
引物名称
Primer names引物序列(5′-3′)
Primer sequence(5′-3′)HcNiR-F ATGACAGATGGGAGATTTATGATG HcNiR-R GCATTTTCCACTTCTTCTTCCC HcNiR-qPCR-F TCTTGGTTACAGGGGCAATAGAC HcNiR-qPCR-R TGGACACCAAGATAGTCTCTCCT beta-actin-F ATCCTCCGTCTTGACCTTG beta-actin-R TGTCCGTCAGGCAACTCAT 表 2 HcNiR基因编码蛋白质产物一级结构预测分析
Table 2 Primary structure of HcNiR encoded protein
一级结构特征
Characteristics of
primary structure氨基酸数量
Number of
amino acids等电点
pI相对分子质量
Relative molecular
mass/Da分子式
Molecular
formula正电荷
残基
Arg+Lys负电荷
残基
Asp+Glu平均疏水性
Average
hydrophobicity脂肪系数(AI)
Fatty
coefficient不稳定系数(Ⅱ)
Instability
coefficient (Ⅱ)半衰期
Estimated
half-life/h预测结果
Prediction result464 5.490 51683.220 C2276H3632N644O681S24 54 64 −0.289 89.480 37.930 30 -
[1] ZHANG L W, XU Y, ZHANG X T, et al. The genome of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L. ) provides insights into bast fibre and leaf shape biogenesis [J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 18(8): 1796−1809. DOI: 10.1111/pbi.13341
[2] AYADI R, HANANA M, MZID R, et al. Hibiscus cannabinus L.- kenaf: A review paper [J]. Journal of Natural Fibers, 2017, 14(4): 466−484.
[3] 陶爱芬, 张晓琛, 祁建民. 红麻综合利用研究进展与产业化前景 [J]. 中国麻业科学, 2007, 29(1):1−5. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3532.2007.01.001 TAO A F, ZHANG X C, QI J M. Research progress and industrialization prospect of comprehensive utilization on kenaf [J]. Plant Fiber Sciences in China, 2007, 29(1): 1−5.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3532.2007.01.001
[4] SWINGLE R S, URIAS A R, DOYLE J C, et al. Chemical composition of kenaf forage and its digestibility by lambs and in vitro [J]. Journal of Animal Science, 1978, 46(5): 1346−1350. DOI: 10.2527/jas1978.4651346x
[5] 李超显. 饲料产业的环保问题及解决对策 [J]. 中国饲料, 2019(18):114−117. LI C X. Environmental protection problems and solutions in feed industry [J]. China Feed, 2019(18): 114−117.(in Chinese)
[6] SEITH B, SCHUSTER C, MOHR H. Coaction of light, nitrate and a plastidic factor in controlling nitrite-reductase gene expression in spinach [J]. Planta, 1991, 184(1): 74−80.
[7] ZHANG J, LV J, XIE J M, et al. Nitrogen source affects the composition of metabolites in pepper (Capsicum annuum L. ) and regulates the synthesis of capsaicinoids through the GOGAT-GS pathway [J]. Foods (Basel, Switzerland), 2020, 9(2): 150.
[8] KYAING M, 顾立江, 程红梅. 植物中硝酸还原酶和亚硝酸还原酶的作用 [J]. 生物技术进展, 2011, 1(3):159−164. KYAING M, GU L J, CHENG H M. The role of nitrate reductase and nitrite reductase in plant [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2011, 1(3): 159−164.(in Chinese)
[9] LAHNERS K, KRAMER V, BACK E, et al. Molecular cloning of complementary DNA encoding maize nitrite Reductase: Molecular analysis and nitrate induction [J]. Plant Physiology, 1988, 88(3): 741−746. DOI: 10.1104/pp.88.3.741
[10] WANG R C, XING X J, CRAWFORD N. Nitrite acts as a transcriptome signal at micromolar concentrations in Arabidopsis roots [J]. Plant Physiology, 2007, 145(4): 1735−1745. DOI: 10.1104/pp.107.108944
[11] TAKAHASHI M, SASAKI Y, IDA S, et al. Nitrite reductase gene enrichment improves assimilation of NO2 in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Physiology, 2001, 126(2): 731−741. DOI: 10.1104/pp.126.2.731
[12] KATO C, TAKAHASHI M, SAKAMOTO A, et al. Differential expression of the nitrite reductase gene family in tobacco as revealed by quantitative competitive RT-PCR [J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2004, 55(403): 1761−1763. DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erh182
[13] OZAWA K, KAWAHIGASHI H. Positional cloning of the nitrite reductase gene associated with good growth and regeneration ability of calli and establishment of a new selection system for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation in rice (Oryza sativa L. ) [J]. Plant Science, 2006, 170(2): 384−393. DOI: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2005.09.015
[14] 夏磊, 王团团, 段莉莉, 等. 黄瓜亚硝酸还原酶基因(CsNiR)的克隆及对外植体分化的影响 [J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2020, 43(2):231−237. DOI: 10.7685/jnau.201906021 XIA L, WANG T T, DUAN L L, et al. Cloning of nitrite reductase gene(CsNiR)in cucumber and its effect on explant differentiation [J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2020, 43(2): 231−237.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7685/jnau.201906021
[15] 张超, 黄思齐, 邓勇, 等. 高蛋白饲用红麻品种筛选及饲用品质研究 [J]. 中国麻业科学, 2021, 43(6):287−293. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3532.2021.06.002 ZHANG C, HUANG S Q, DENG Y, et al. Selection of high protein forage kenaf varieties and study on their feed quality [J]. Plant Fiber Sciences in China, 2021, 43(6): 287−293.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3532.2021.06.002
[16] 邓勇. 硫化氢缓解红麻重金属镉胁迫功能分析[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2019. DENG Y. Function analysis of hydrogen sulfide-mediated alleviation of cadmium stress in kenaf(Hibiscus cannabinus L.) seedlings[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2019. (in Chinese)
[17] 张超, 张勇, 满百膺, 等. 大豆GmPID基因生物信息学分析及克隆 [J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2020, 51(1):13−22. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9369.2020.01.002 ZHANG C, ZHANG Y, MAN B Y, et al. Bioinformatic analysis and cloning of gene GmPID in soybean [J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2020, 51(1): 13−22.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9369.2020.01.002
[18] 田华, 段美洋, 王兰. 植物硝酸还原酶功能的研究进展 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2009, 25(10):96−99. TIAN H, DUAN M Y, WANG L. Research progress on nitrate reductase functions in plants [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2009, 25(10): 96−99.(in Chinese)
[19] NAVARRO F J, PERDOMO G, TEJERA P, et al. The role of nitrate reductase in the regulation of the nitrate assimilation pathway in the yeast Hansenula polymorpha [J]. FEMS Yeast Research, 2003, 4(2): 149−155. DOI: 10.1016/S1567-1356(03)00163-6
[20] 佘茂云, 陈朵朵, 冯晨, 等. 小麦亚硝酸还原酶基因及调控序列克隆、定位和表达分析 [J]. 作物学报, 2011, 37(1):28−39. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2011.00028 SHE M Y, CHEN D D, FENG C, et al. Isolation, chromosome assignment, and expression assay of nitrite reductase gene and regulatory sequence in wheat [J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2011, 37(1): 28−39.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2011.00028
[21] 曾彦达, 石晓艳, 马凤鸣. 甜菜亚硝酸还原酶(NiR)基因的克隆与分析 [J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2012, 43(1):77−82. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9369.2012.01.013 ZENG Y D, SHI X Y, MA F M. Cloning and analysis of NiR gene in sugar beet [J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2012, 43(1): 77−82.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9369.2012.01.013
[22] HIRASAWA M, FUKUSHIMA K, TAMURA G, et al. Immunochemical characterization of nitrite reductases from spinach leaves, spinach roots and other higher plants [J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology, 1984, 791(2): 145−154. DOI: 10.1016/0167-4838(84)90004-9
[23] 张芬, 王丽鸳, 成浩, 等. 茶树亚硝酸还原酶基因CsNiR的克隆及表达分析 [J]. 园艺学报, 2016, 43(7):1348−1356. ZHANG F, WANG L Y, CHENG H, et al. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of nitrite reductase gene CsNiR in tea plant [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2016, 43(7): 1348−1356.(in Chinese)
[24] 孙菲菲, 蒋芳玲, 侯喜林, 等. 白菜亚硝酸还原酶基因BcNiR的克隆及表达分析 [J]. 园艺学报, 2009, 36(10):1511−1518. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0513-353X.2009.10.017 SUN F F, JIANG F L, HOU X L, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of nitrite reductase gene BcNiR from non-heading Chinese cabbage [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2009, 36(10): 1511−1518.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0513-353X.2009.10.017
[25] 石晓艳, 曾彦达, 李世龙, 等. 甜菜亚硝酸还原酶(NiR)基因的克隆与表达分析 [J]. 作物学报, 2011, 37(8):1406−1414. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2011.01406 SHI X Y, ZENG Y D, LI S L, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of nitrite reductase gene from sugarbeet [J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2011, 37(8): 1406−1414.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2011.01406
[26] 陈何, 王乐, 赵春丽, 等. 氮素和红蓝复合光配比对苋菜幼苗亚硝酸还原酶活性及其基因表达的影响 [J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2021, 26(8):61−71. DOI: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2021.08.07 CHEN H, WANG L, ZHAO C L, et al. Effects of nitrogen and red and blue light on NiR enzyme activity and gene expression in Amaranthus tricolor L. seedlings [J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2021, 26(8): 61−71.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2021.08.07
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 罗德香,朱奕璟,单蕖,李鑫磊,赵正雄,杨志娟,欧阳铖人. 前期干旱寡雨条件下移栽期后移对烤烟碳氮代谢和产质量的影响. 核农学报. 2025(01): 182-190 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 牛苏燕,张珍华,蒋素华,梁芳,袁秀云,张燕,赵慧园,崔波. 马铃薯StNiR基因的克隆及其在低氮肥胁迫下的表达分析. 江苏农业科学. 2024(14): 40-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: