Identification and Characterization of Phosphate-solubilizing Endophytes in Coix lacryma-jobi L.
-
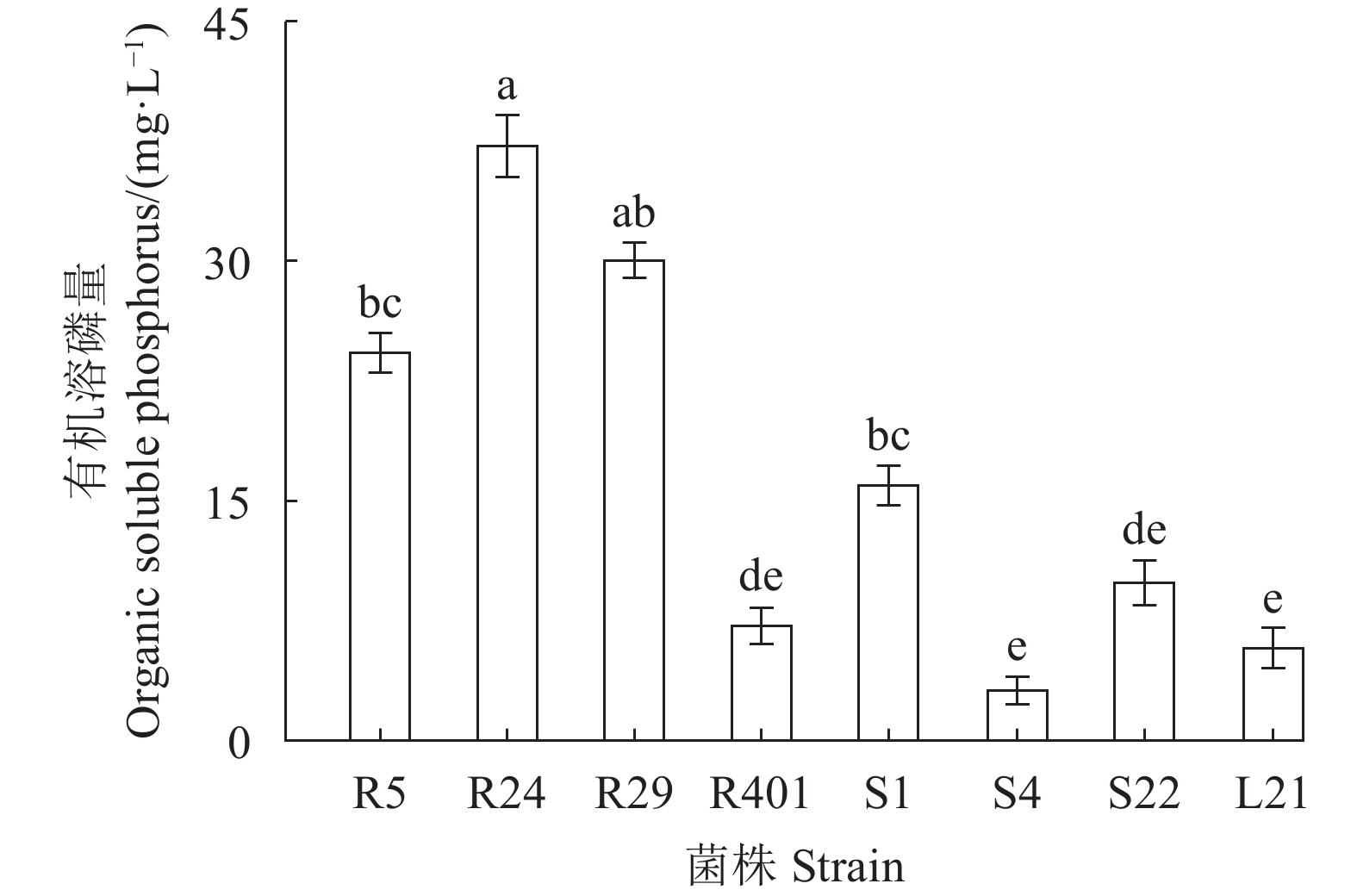
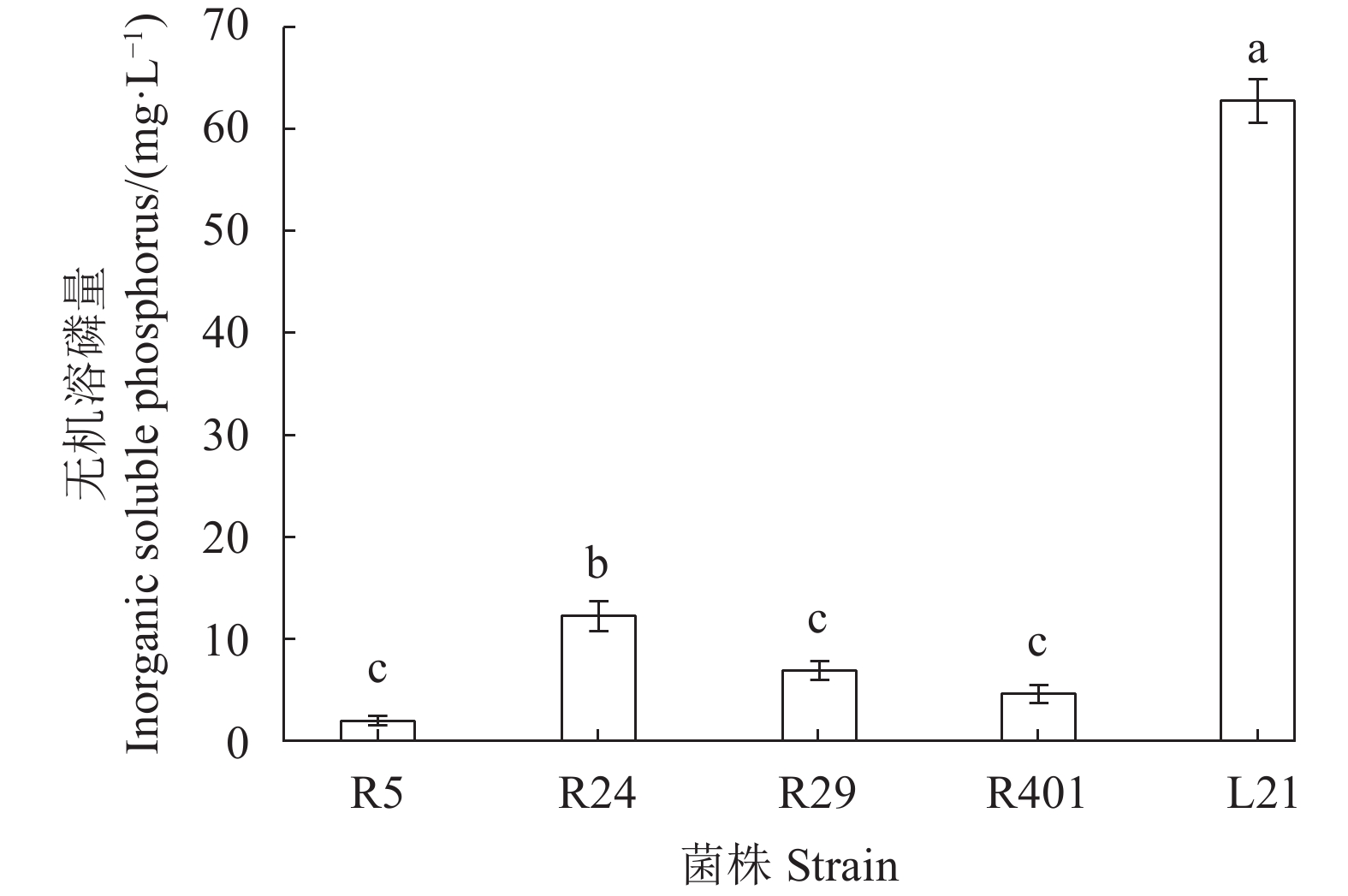
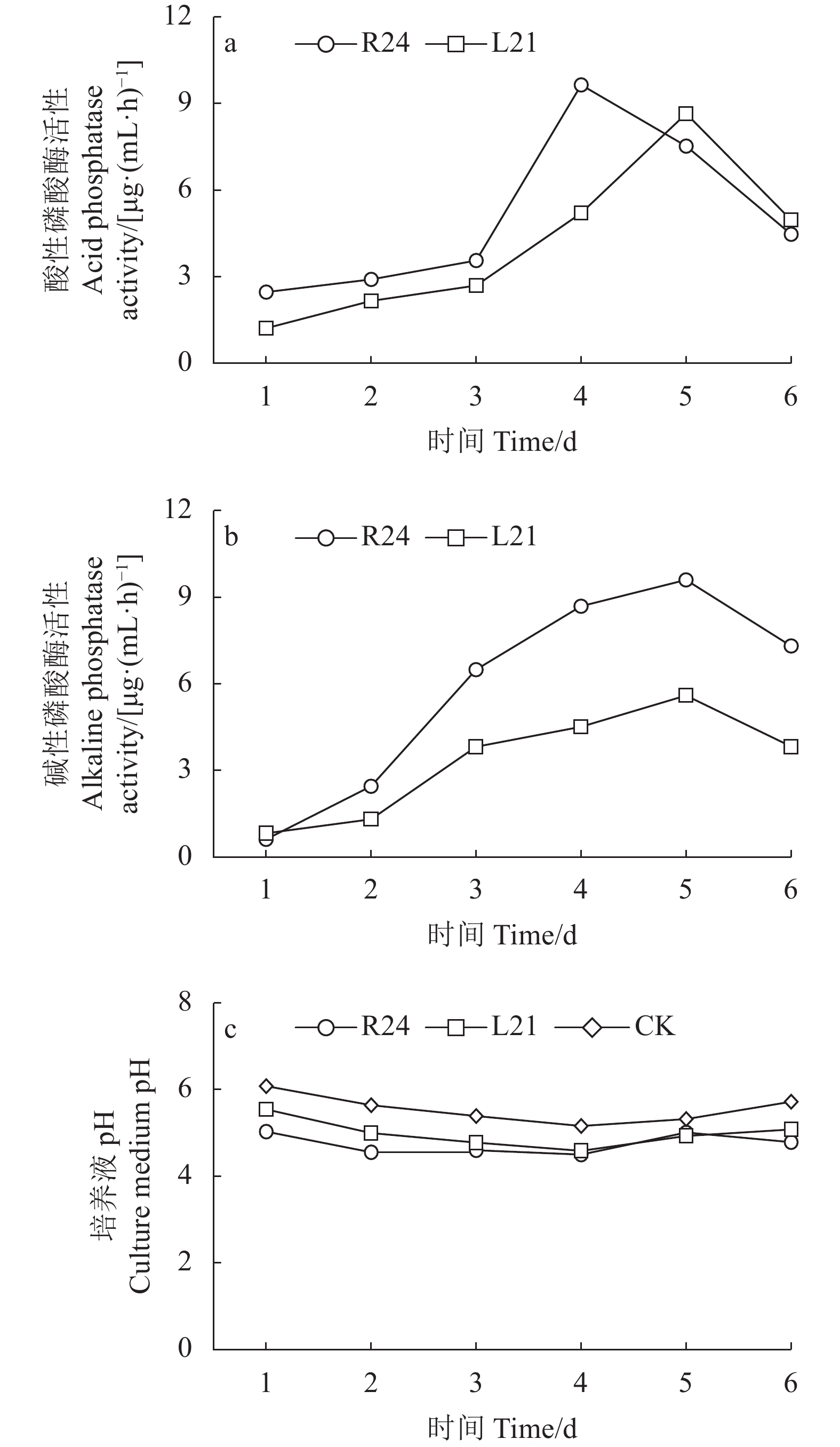
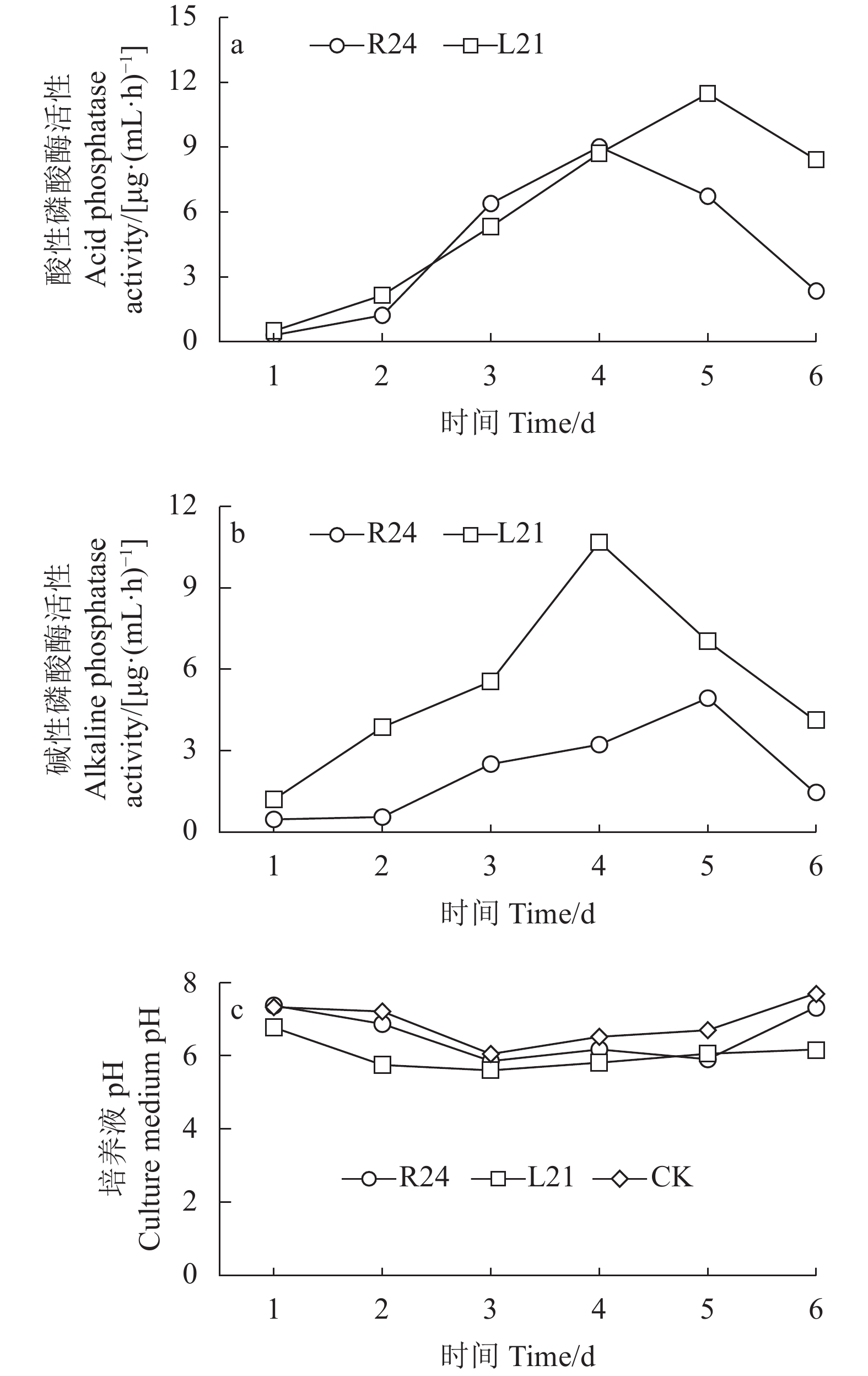
摘要:目的 筛选具有溶磷能力的薏苡内生细菌并明确其类型,为后续研制生物菌肥提供优良菌株资源。方法 以播种25 d的薏苡幼苗为试验材料,采用研磨稀释涂板法从薏苡的根、茎、叶中分离筛选具有溶磷能力的薏苡内生菌,探索该类菌溶解有机磷、无机磷、分泌磷酸酶的能力;通过盆栽试验探究溶磷内生菌对薏苡幼苗的促生长作用。结果 筛选到溶解有机磷细菌8株,溶解无机磷细菌5株。其中,编号为R24的菌株溶解有机磷能力最强,摇瓶5 d后,上清液可溶性磷含量为37.20 mg·L−1;编号为L21的菌株溶解无机磷能力最强,摇瓶5 d后,上清液可溶性磷含量为62.93 mg·L−1。2株溶磷菌及等比例混合菌液能够促进盆栽薏苡的株高、茎粗、分蘖数,促生长能力从大到小为:L21>R24>混合菌液[V(R24)∶V(L21)=1∶1]。通过16S rDNA序列鉴定,R24为短小芽孢杆菌,L21为贝莱斯芽孢杆菌。结论 溶磷菌L21和R24对薏苡生长有显著促进作用。Abstract:Objective Screening bacteria with phosphate-solubilizing ability in Coix were identified and provide excellent strain resource for bio-fertilization agent.Methods Endophytic bacteria were isolated and purified from specimens the roots, stems, and leaves of 25-d-old seedlings of Coix lacryma-jobi L. Abilities of the isolates in dissolving organophosphate and inorganic phosphate as well as in secreting phosphatase were determined. In a pot experiment, effects of two selected isolates on the growth of Coix seedlings were examined.Results Eight strains of bacteria capable of dissolving organophosphate and 5 of degrading inorganic phosphate were isolated. In the 5-d culture supernatants, the highest concentration of phosphorous converted from organophosphate at 37.20 mg·L−1 was reached by R24, and that from inorganic phosphate at 62.93 mg·L−1 by L21. The enhancing effects on plant height, stem girth, and tillering number of the potted Coix seedlings by each and mixture in equal proportion of the two supernatants ranked in the order of L21>R24>mixed bacterial liquid[ V (R24)∶ V (L21)=1∶1]. The 16S rDNA sequence phylogenetic analysis identified R24 as Bacillus pumilus and L21 as B. velezensis.Conclusion The phosphobacteria L21 and R24 displayed a significant effect in promoting the growth of Coix seedlings.
-
Keywords:
- Coix /
- endophytes /
- phosphobacteria /
- phosphate-solubilizing ability /
- identification
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】福建省是中国乌龙茶之乡,是名茶铁观音、武夷岩茶的发源地,位居中国重点产茶省份之首。土壤作为茶树生长赖以生存的营养来源,其酸化程度对茶树的生长及茶叶的品质有重要影响。然而,目前福建省土壤pH值适宜茶树生长的茶园比例还不足15%,pH值在4.5以下的茶园占比87%[1],茶园土壤酸化成为影响茶树生长、茶叶品质的关键因素。土壤酸化不仅造成钙离子、锰离子、钾离子等大量流失,大大降低土壤磷、钼和硼的有效性,致使土壤肥力显著下降[1-2],而且可导致重金属元素的活化[3],重金属在土壤中的不断积累,最终可通过茶叶危害人类健康,成为茶叶质量安全的主要限制因素[4-6]。除此之外,土壤酸化还会减少土壤中有益微生物的活性和数量,进而影响土壤中碳、氮、硫、磷等的循环[3],导致茶树根的发育受阻,阻止养分的吸收[7],最终影响茶树生长和茶叶品质。因此,有效缓解茶园土壤酸化进程,对提高茶叶品质和发展茶叶质量安全生产等具有重要的意义。【前人研究进展】茶树属于喜酸植物,但是由于长期施肥不合理以及茶树特性[2],导致我国茶园土壤酸化程度日益严重。土壤酸化可带来一系列问题,首先是土壤重金属的活化[8];茶园土壤酸度降低会导致土壤吸附重金属离子的能力降低,从而活化重金属,使重金属溶解性、移动性和有效性增加[9]。目前,我国农田重金属污染主要分为5种健康风险元素,包括Cd、As、Hg、Pb和Cr;以及3种生态风险元素,包括Ni、Cu和Zn[10]。鉴于茶园重金属污染主要暴露途径是通过茶叶对人体健康造成损害,因此茶园重金属污染主要检测上述5种健康风险元素,其中更以Cd为主[10]。钟晓兰等[11]的研究发现,土壤酸性增加能增强土壤活性态Cd的含量,且随着pH的降低,Cd活化能力增高,土壤Cd含量越高。其次,茶园土壤酸化可导致土壤有益微生物的活性降低和菌落组成减少[8, 12]。茶园微生物具有固氮、解磷、释钾、分解有机物和保持土壤保湿性等作用,可以有效调节茶园生态,促进茶的芽萌发,影响茶树次生代谢。除此之外,还可以帮助合成茶叶特殊的芳香物质,对茶树生长、茶叶品质提高具有积极的影响[12-13]。然而,随着近年来茶园集约化的高强度生产,福建省茶园土壤酸化呈加重趋势。因此,为了有效遏制土壤酸化、确保农产品的食品安全生产,需要找到快速、有效遏制的防治策略。西班牙河碳酸盐岩(Spanish river carbonatite, SRC)作为酸性土壤调理剂、草碳堆肥和矿物肥料,具有碱性强,微量元素高、有害元素低等优势,已在加拿大、俄罗斯等国家应用[14-15]。在我国,SRC已证明可以显著改良蔬菜种植土壤的酸性,例如,陈云峰等[15]采用大田和室内试验证明SRC对种植小白菜的土壤酸性具有明显的改良效果。【本研究切入点】然而,SRC对于茶园土壤酸化的改良效果还未可知,其在茶园的相关应用调查还未见报道。【拟解决的关键问题】为验证SRC在茶园土壤改良方面的应用潜力,采用盆栽和大田试验分别验证SRC对土壤酸性、土壤重金属及土壤微生物的影响,测定土壤pH值、重金属含量、并利用高通量测序技术检测微生物群落结构,评估SRC对茶园土壤理化性质改良和修复的情况,以有效减缓茶园土壤酸化进程,保障茶园可持续发展。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 室内试验设计
室内试验所用土壤为红壤,取自福建农林大学南区茶园温室土壤,pH 6.13。本研究在不施化肥条件下进行。新鲜土壤粉碎,去除枯枝落叶等杂质后,过3 cm筛子备用。取7份土壤,其中3份土壤(每份土壤重量不少于200 g)进行微生物多样性检测,并测定pH值及8种重金属(Cd、Pb、Cr、Cu和Zn、Ni、Hg、As)的含量[CK(2017)]。本研究所用的碳酸盐岩由博莱生态农业科技有限公司提供,主要成分 SiO2 24.6%、CaO 28.3%、N 0.30%、P2O5 3.13%、K2O 1.07%、pH 8.92,容重 1.52 g·cm−3,为颗粒状固体。剩余4份土壤分别按体积比土壤∶SRC=80∶20、90∶10、95∶5和99∶1进行混合(即分别对应为处理组20%SRC、10%SRC、5%SRC和1%SRC),同时留一组土壤不掺入SRC,作为对照。每个处理组或对照土壤分别装入3个花盆(45 cm×20 cm×15 cm,长×宽×高),每个花盆种植2年生毛蟹品种茶树苗10株。茶苗在室外恢复半月后移至室内条件,LED灯光照,光周期12 h∶12 h,温度(28±1)℃,相对湿度(70±5)%,生长至2018年6月12日[CK(2018)],每个花盆内取土约50 g进行微生物多样性检测分析以及pH值测定,并检测Cd、Pb、Cr、Cu和Zn、Ni、Hg、As等8种重金属的含量。
1.2 大田试验设计
试验地位于福建省泉州市安溪县西坪镇红星茶场内茶园(简称红星茶园,25°0′15.76″N,117°52′0.04″E; 海拔700~750 m)。茶园面积约40 000 m2,该茶园试验地为有机试验茶园,不施用化肥、农药等。该地区属于亚热带湿润季风气候,气温在16~19 ℃,年降水量在1 700~2 100 mm。茶园种植茶树品种为毛蟹,种植年限在50年以上,茶园土壤为红壤。2018年7月14日,在茶园内选择6块茶树地块,每块地面积约300 m2。在6块试验地利用5点取样法采取土样,采样部位选自茶树与施肥沟的中央位置,去除表面枯枝落叶层后0~20 cm的土层。利用工兵铲和锄头挖掘采样断面,用竹铲去除与工具接触的部分后,在整个断面层均衡取样,土壤样本混合均匀后分为3份,用于土壤微生物多样性检测、pH值测定,以及Cd、Pb、Cr、Cu、Zn、Ni、Hg和As等8种重金属的含量检测。随后,在6块试验地中随机选择3块,按1 120 kg·hm−2在茶树主干土壤附近撒施SRC。2019年10月14日,在6块试验地按上述方法取土壤进行微生物、pH值及重金属检测。
1.3 土壤pH、重金属含量分析
取土样10 g放入50 mL烧杯中,加入25 mL水,用玻璃棒剧烈搅动2 min,静置30 min,用台式pH计[型号:FF28,梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海)有限公司,METTLER TOLEDO]进行检测。
土样中Hg和As的含量使用原子荧光法进行测定,详细方法参照国家标准《土壤质量 总汞、总砷、总铅的测定 原子荧光法GB/T 22105.1—2008》;其他6种重金属采用原子吸收分光光度法进行检测,参考标准为《土壤质量 铅、镉的测定 石墨炉原子吸收分光光度法GB/T 17141—1997》、《土壤总铬的测定火焰原子吸收分光光度法HJ 491—2009》、《土壤质量锌、铜的测定 火焰原子吸收分光光度法GB/T 17138—1997》、《土壤质量镍的测定 火焰原子吸收分光光度法GB/T 17139—1997》。
1.4 土壤细菌DNA的提取和纯化
用DNeasy Power Soil Kit (QIAGEN, Inc., Netherlands)试剂盒进行微生物总DNA的提取,并将提取的DNA保存于−20 ℃冰箱内。分别用NanoDrop ND-1000核酸检测仪(Thermo Fisher Scientific,Waltham,MA,USA)和0.8%琼脂糖凝胶电泳对提取的DNA进行品质检测;同时采用紫外分光光度计对提取的DNA进行定量。
以细菌核糖体RNA等能够反映菌群组成和多样性的目标序列为靶点,以稀释后的DNA作为模板,应用带Barcode的特异引物515F(5′-GTGCCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA-3′)和907R (5′-CCGTCAATTCMTTTRAGTTT-3′)对细菌16S V4区进行PCR扩增,PCR采用25 μL反应体系:2×Phanta Max Buffer 12.5 μL,上下游引物各1 μL,DNA模板1 μL,Phanta Max Super-Fidelity DNA Polymerase 0.5 μL,dNTP Mix 0.5 μL, ddH2O 8.5 μL,使用PCR仪器是Bio-rad T100梯度PCR仪。程序设定为:98 ℃预变性2 min;25个循环(98 ℃变性15 s;55 ℃退火30 s;72 ℃延伸30 s);然后72 ℃延伸5 min。PCR产物使用1.2%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测。将PCR扩增产物用磁珠纯化回收。将纯化回收的PCR产物进行荧光定量,荧光试剂为Quant-iT PicoGreen dsDNA Assay Kit,定量仪器为Microplate reader(BioTek,FLx800)。根据荧光定量结果,按照每个样本的测序量需求,对各样本按相应比例进行混合。
1.5 土壤细菌DNA多样性分析
依照Illumina公司的TruSeq Nano DNA LT Library Prep Kit制备测序文库流程进行文库制备;通过2%琼脂糖凝胶电泳,对文库做最终的片段选择与纯化。上机测序前,需要先对文库在Agilent Bioanalyzer上进行质检,采用Agilent High Sensitivity DNA Kit。合格的文库有且只有单一的峰,且无接头,之后,采用Quant-iT PicoGreen dsDNA Assay Kit在Promega QuantiFluor荧光定量系统上对文库进行定量,合格的文库浓度应在2 nmol·L−1以上;将合格的各上机测序文库(Index序列不可重复)梯度稀释后,根据所需测序量按相应比例混合,并经NaOH变性为单链进行上机测序;使用MiSeq测序仪进行双端测序。
通过质量初筛的原始序列按照index和barcode信息,进行文库和样本划分,并去除barcode序列。利用FLASH(v 1.2.7)对每个样本的reads进行拼接。本研究主要利用QIIME 和R(v3.2.0)包对数据进行分析。利用QIIME对细菌进行OUT聚类,并计算细菌的多样性指数,包括丰富度指数(CHAO1、ACE)、辛普森多样性指数(Simpson index)、香农多样性指数(Shannon diversity index)。利用R包进行细菌群落间差异性分析(t test以及Monte Carlo permutation test)。同时,为了降低噪音,利用R包(v3.2.0),选取了丰度前5%的菌落进行属水平的主成分分析(PCA)。并对所选取的丰度前5%的菌落,利用聚类分析(Hierarchical clustering)的方法,基于非加权组平均法(Unweighted pair-group method with arithmetic means,UPGMA)评价不同土壤样本之间的相似度。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 SRC对室内盆栽茶树土壤pH及重金属的改良
与2017年处理前土样相比,2018年对照组土样pH值有降低,但是降低的并不显著(表1),说明较短时间(如一年内)种植茶树不能显著改变土壤pH。然而,种植茶树可显著影响土壤重金属的含量。如室内盆栽种植茶苗一年后,土壤中的重金属Cr、Pb、Ni、As、Zn的含量发生显著富集(表1)。为了探索SRC对土壤酸碱度、重金属的调节作用,分析了4种SRC浓度对土壤的改良效果,结果显示:与2018年对照组相比(5.93 ± 0.09),4组SRC处理对土壤的酸化均有调节作用,其中施入10% SRC对土壤酸碱度改良效果最为显著(6.60 ± 0.54)。从重金属上看,SRC效果显著,1% SRC的施入量就可显著降低土壤中Cd的含量。低浓度的SRC(1%~5%)施入对一些重金属含量的降低效果并不理想,甚至使有些重金属含量升高;说明必须要较高浓度的SRC施入量才可改良土壤的重金属含量,然而,高浓度的SRC施入(20%SRC)并不能有效降低Hg含量。同时,发现土壤的pH值并不能随着SRC浓度的升高而升高,例如,20% SRC施入量的土壤pH值低于10% SRC施入量的土壤pH值。这一结果与前人的研究相似,陈云峰等[15]在研究SRC对蔬菜种植土壤酸性改良中,发现土壤pH值提升效果与施用量并不存在正相关关系。因此,认为高浓度的SRC施入(>10%)对茶园土壤有一定的改良作用。
表 1 室内SRC处理对土壤pH值及重金属含量的影响Table 1. Effects of SRC on pH and heavy metals in pot soil指标 Index CK(2017) CK(2018) 1%SRC 5%SRC 10%SRC 20%SRC pH 6.13±0.09 b 5.93±0.09 b 6.23±0.19 ab 6.10±0.06 b 6.60±0.54 a 6.10±0.15 b Cd/(mg·kg−1) 0.29±0.02 b 0.35±0.034 ab 0.21±0.01 c 0.21±0.02 c 0.38±0.02 a 0.11±0.001 c Cr/(mg·kg−1) 40.30±1.55 b 54.20±4.84 a 51.70±1.24 a 55.40±2.66 a 50.70±0.29 a 39.90±3.89 b Pb/(mg·kg−1) 29.10±2.02 c 39.10±4.05 ab 33.00±0.75 b 45.60±1.12 a 34.70±3.07 b 25.50±1.70 c Cu/(mg·kg−1) 116.70±2.90 b 104.70±9.60 b 220.80±13.50 a 221.50±12.20 a 65.50±4.80 c 30.60±2.20 d Ni/(mg·kg−1) 18.70±0.88 b 36.80±3.77 a 32.20±1.09 a 34.40±2.03 a 32.80±3.13 a 17.60±2.50 b Zn/(mg·kg−1) 149.00±7.05 b 263.30±31.80 a 227.70±8.37 a 237.20±11.00 a 232.00±27.20 a 80.90±4.09 c Hg/(mg·kg−1) 0.05±0.01 c 0.04±0.001 c 0.09±0.01 b 0.09±0.01 b 0.04±0.00 c 0.13±0.00 a As/(mg·kg−1) 4.85±0.23 b 3.82±0.37 c 6.17±0.04 a 6.60±0.24 a 3.82±0.37 c 2.58±0.24 d 注:同行数据后不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。表3同。
Note: Data with different lowercase letters indicate significant difference among treatments at P<0.05. The same as Table 3.2.2 SRC对室内盆栽茶树土壤细菌多样性的影响
通过高通量测序数据,共得到802 020条有效序列,其中2017年室内种植茶树的土壤的平均有效数据为42 289,2018年室内种植茶树土壤的平均有效数据为44 959,4个处理组20%SRC、10%SRC、5%SRC和1%SRC的土壤样本平均有效数据分别是41 032、46 179、49 355以及43 525。经过数据库比对分析及注释后,基于QIIME软件,对物种进行了OUT聚类。结果显示,20%SRC处理组OTU数最大(1033.7),CK2017对照组最小(911.7),且两组OTU数目差异显著,表明SRC对于土壤细菌的物种数目具有显著影响。进一步对土壤细菌群落丰度指数(Chao1、ACE)以及多样性指数(Shannon、Simpson)进行调查,结果显示,施用SRC可一定程度上增加土壤细菌的种群丰度,但差异不显著(表2)。
表 2 室内SRC处理对土壤细菌多样性的影响Table 2. Effects of SRC on microbial diversity in pot soil样本 Samples Simpson Chao1 ACE Shannon CK(2017) 0.994 b 1 072.0 b 1 147.4 b 8.91 b CK(2018) 0.997 a 1 223.8 ab 1 339.8 ab 9.32 a 1%SRC 0.997 a 1 323.0 a 1 451.7 a 9.36 a 5%SRC 0.996 a 1 208.7 ab 1 333.1 ab 9.17 ab 10%SRC 0.997 a 1 264.1 a 1 404.5 a 9.28 a 20%SRC 0.997 a 1 334.3 a 1 464.7 a 9.38 a 注:同列数据后不同小写字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。表4同。
Note: Data with different lowercase letters indicate significant difference among treatments at P<0.05. The same as Table 4.2.3 SRC对室内茶树种植土壤细菌群落组成与结构的影响
在门水平上,对照组与SRC处理组中的优势菌群均为变形菌门(Proteobacteria)、绿弯菌门(Choroflexi)以及放线菌门(Actinobacteria)。然而,结果显示,茶树的种植可影响土壤细菌群落组成和结构。相较于2017年,种植一年茶树后,其土壤变形菌门和绿弯菌门的比例升高,但是放线菌门的比例却明显降低(图1-A)。SRC处理后,这些优势菌群的结构也发生了明显的改变。土壤中的变形菌门比例降低,绿弯菌门的比例升高,且放线菌门的比例也发生了波动(图1-A);此外,各SRC处理组土壤中蓝藻菌(Cyanobacteria)比例下降明显,5%SRC、10%SRC和20%SRC处理组尤为显著,比例均在1%以下(对照为3.3%)。对丰度前5%的细菌群落,在属水平对群落组成结构进行PCA分析(图1-B),结果表明,SRC处理组土壤细菌的群落组成与对照组的差异较大。
基于非加权组平均法(Unweighted pair-group method with arithmetic means,UPGMA)评价不同土壤样本之间的相似度。发现10%SRC处理组土壤细菌群落组成聚为一类(图2)。同时,聚类分析也发现了1%SRC处理的土壤重复之间差异较大,这一结果与上述PCA结果相同,说明1%SRC处理所取土壤样本细菌不均一,后续研究可通过增加重复数目来进行改良。
2.4 SRC对茶园土壤pH及重金属的改良
结果显示,一年内茶树种植对茶园土壤的影响并不显著,土壤酸化或者重金属的含量变化不明显(表3)。然而,SRC却可以在短时间内影响茶园土壤,例如,SRC可以在一年内明显改良土壤酸化,使土壤pH值显著上升(表3);对重金属的改良也作用明显,结果显示,施用SRC后,8种土壤重金属含量均显著下降(表3),显示了SRC对茶园土壤改良的潜力。
表 3 SRC处理对茶园土壤pH值和重金属含量的影响Table 3. Effects of SRC on pH and heavy metals in soils at tea plantations指标 Index CK 2018 CK 2019 SRC pH 5.40±0.12 b 5.49±0.25 b 6.23±0.14 a Cd/(mg·kg−1) 0.16±0.01 a 0.17±0.01 a 0.10±0.01 b Cr/(mg·kg−1) 74.60±4.73 ab 78.30±5.31 a 63.30±2.65 b Pb/(mg·kg−1) 88.00±4.57 ab 102.10±10.41 a 82.20±2.90 b Cu/(mg·kg−1) 126.40±4.30 a 149.40±11.26 a 97.30±5.19 b Ni/(mg·kg−1) 83.20±4.16 a 84.90±10.45 a 68.18±6.13 b Zn/(mg·kg−1) 320.80±8.64 a 307.30±24.91 a 159.60±14.20 b Hg/(mg·kg−1) 0.06±0.01 a 0.06±0.01 a 0.04±0.01 b As/(mg·kg−1) 8.15±0.30 a 9.46±0.48 a 5.89±0.95 b 2.5 SRC对茶园土壤细菌群落组成与结构的影响
SRC处理后的茶园土壤细菌丰富度上升显著(表4)。从土壤细菌种类在门水平的分布上看(图3),土壤细菌分布比例最高为变形菌(Proteobacteria),两组对照(2018和2019)土壤中变形菌比例均高于55%,分别为57.8%和55.5%,但在SRC处理组中,这一比例降为45.1%(图3-A)。相比两个不同时间段的对照土样CK2018和CK2019,SRC处理组中酸杆菌(Acidobacteria)和厚壁菌(Firmicutes)比例同样下降明显。相反,拟杆菌(Bacteroidetes)和绿弯菌(Chloroflexi)比例上升显著,分别达到9.6%和11.3%。属水平的PCA主成分分析结果表明,SRC处理组土壤细菌群落结果与对照组差异显著(图3-B)。
表 4 SRC处理对茶园土壤细菌多样性的影响Table 4. Effects of SRC on microbial diversity in soils at tea plantations样本 Sample Simpson Chao1 Shannon CK 2018 0.954 a 482.5 c 6.33 c CK 2019 0.972 a 1699.7 b 7.64 b SRC 0.997 a 3077.0 a 9.89 a 3. 讨论与结论
在不施肥的前提下,大田和盆栽试验均表明SRC能明显提升土壤pH,说明SRC对于提升茶树种植土壤pH的效果较稳定,对土壤pH的提升效果不随施用方式不同而波动。SRC是一种火成岩,有害元素较低、碱性较强,磷、硅、钙、钾及微量元素较高,能对土壤酸度起到一定的中和作用[14-16]。盆栽试验中的SRC与土壤混合均匀,而大田试验中,本研究采取的是常用的条施方法,施用深度在20 cm左右。此外,盆栽试验说明,SRC对土壤pH的提升效果不与SRC施用浓度呈正比,10%SRC对土壤pH提升效果最好,这与陈云峰等[15]、James等[17]的研究结果一致。且SRC对于土壤酸化的改良效果已在其他多种经济作物上被验证,如在芦笋、大麦等[15]。综上所述,对于茶园土壤逐年酸化严重的问题,可以通过补施SRC来快速缓解土壤酸化问题。
本研究结果表明,茶园土壤中富集最多的重金属为锌和铜。根据颜明娟等[18]的调查显示,福建地区锌含量有超标现象。此外,叶琛等[19]发现,土壤中的铜、铬、镉含量与茶叶重金属含量具有较强的相关性。盆栽与大田试验发现,添加SRC对重金属污染的改良有一定的效果,盆栽试验表明低浓度SRC的施入量就可显著降低土壤中Cd含量,然而,低浓度的SRC(<10%)对于其他重金属含量的降低效果并不显著。因此,可通过增加碳酸盐岩施用量来解决这一问题。因此,本研究用大剂量的SRC施用量来进行大田试验(1 120 kg·hm−2左右),结果表明大剂量SRC的施用可显著降低8大重金属的含量。
微生物生物群落数量和活性是影响土壤肥力的重要因素[20],而土壤酸化可严重影响土壤微生物群落、结构,导致有益微生物种群大量减少,不利于茶园土壤中养分的转化[21]。部分研究学者提出细菌可分为富营养菌和寡营养菌[22-23],例如,酸杆菌门多生长于营养贫瘠的土壤环境中,因此属于寡营养细菌[23]。本研究发现,相较于未施用SRC的茶园,施用SRC的处理土壤中的酸杆菌门的相对丰度显著下降,这也说明施用SRC可提高土壤养分。
综上所述,在茶园内施用碳酸盐岩(SRC)可以降低土壤酸性、改良土壤重金属污染,提高茶园土壤养分。
-
表 1 菌株降解有机磷能力的比较
Table 1 Organic phosphate degrading ability of strains
菌株
Strains菌株直径
Strain diameter/
cm透明圈直径
Diameter of transparent
ring/cmD/d R5 0.35±0.05 b 0.55±0.05 cd 1.58±0.09 b R24 0.29±0.06 b 0.63±0.09 bc 2.15±0.13 a R29 0.33±0.05 b 0.53±0.05 d 1.62±0.11 b R401 0.50±0.01 a 0.77±0.05 a 1.53±0.12 b S1 0.29±0.05 b 0.49±0.05 d 1.71±0.16 b S4 0.37±0.03 b 0.54±0.03 cd 1.46±0.19 b S22 0.39±0.03 b 0.66±0.06 b 1.69±0.09 b L21 0.49±0.11 a 0.79±0.02 a 1.66±0.32 b 不同小写字母表示不同材料间差异显著(P<0.05);下同。
Different small letters indicate significant 0.05 among different materials.The same as below.表 2 菌株降解无机磷的能力比较
Table 2 Inorganic phosphate degrading ability of strains
菌株编号
Strains菌株直径
Strain
diameter/cm透明圈直径
Diameter transparent
ring/cmD/d R5 0.70±0.10 a 1.32±0.18 a 1.89±0.15 bc R24 0.35±0.06 b 0.65±0.12 b 1.88±0.39 bc R29 0.29±0.04 b 0.52±0.09 b 1.82±0.16 bc R401 0.79±0.07 a 1.19±0.06 a 1.52±0.06 c L21 0.33±0.02 b 0.67±0.04 b 2.01±0.25 a 表 3 不同处理下盆栽薏苡农艺性状
Table 3 Agronomic traits of potted plants after treatments
时间
Time/d处理
Treatment株高
Plant height/cm茎粗
Stem diameter/mm分蘖
Tillers number/个叶片
Blades number/片叶面积
Leaf area/m2叶绿素相对含量
SPAD15 T1 38.80±3.49 a 5.34±0.09 a 0.00±0.00 4.40±0.55 a 0.29±0.03 a 19.45±0.85 ab T2 37.00±2.12 a 4.72±0.23 bc 0.00±0.00 4.00±0.00 a 0.28±0.05 a 21.14±1.37 a T3 39.40±2.07 a 5.05±0.20 ab 0.00±0.00 4.40±0.55 a 0.25±0.04 a 20.17±1.64 ab CK 36.80±3.96 a 4.66±0.45 c 0.00±0.00 4.20±0.45 a 0.25±0.06 a 18.12±1.83 b 30 T1 52.00±7.18 a 6.94±0.27 a 1.60±0.89 a 5.20±0.45 a 0.56±0.06 a 23.11±1.72 a T2 42.00±3.54 b 7.07±0.36 a 1.40±0.89 a 5.40±0.55 a 0.47±0.09 ab 21.78±1.69 ab T3 46.60±6.31 ab 6.82±0.54 a 1.40±0.55 a 5.40±0.55 a 0.54±0.09 a 20.84±1.62 bc CK 40.80±7.05 b 5.87±0.19 b 0.60±0.55 a 5.20±0.45 a 0.40±0.06 b 19.30±0.49 c 45 T1 55.80±4.21 a 8.91±0.42 a 2.20±0.45 a 6.00±0.00 a 0.79±0.06 a 22.79±0.78 a T2 51.00±4.30 a 8.56±0.3 a 2.20±0.45 a 5.60±0.55 a 0.70±0.09 b 20.38±0.91 b T3 52.80±9.73 a 7.21±0.36 b 1.80±1.10 ab 5.60±0.55 a 0.74±0.04 ab 18.90±0.48 c CK 54.40±2.88 a 6.76±0.35 b 1.00±0.71 b 5.40±0.55 a 0.61±0.02 c 16.90±1.16 d 60 T1 70.80±4.32 a 9.04±0.34 a 2.20±0.45 ab 6.20±0.45 a 0.92±0.04 a 18.42±0.92 a T2 67.20±4.44 a 8.68±0.19 a 2.40±0.55 a 6.00±0.00 a 0.77±0.06 b 18.70±1.01 a T3 66.00±4.30 a 7.70±0.12 b 1.80±1.10 ab 5.80±0.45 a 0.89±0.07 a 15.67±1.21 b CK 58.00±2.55 b 7.24±0.62 b 1.20±0.84 b 6.00±0.00 a 0.60±0.08 c 16.28±2.45 b 表 4 菌株的生理生化特性
Table 4 Physiological and biochemical characteristics of strains
试验指标 Test index 菌株 Strains R24 L21 革兰氏染色 Gram stain + + V-P试验 V-P test + + 甲基红试验 Methyl red test − + 淀粉水解试验 Starch hydrolysis test − + 吲哚试验 Indole test + + 柠檬酸试验 Citrate test + − 明胶液化 Gelatin liquefaction + + 硝酸盐试验 Nitrate reduction test − + +:阳性;−:阴性。
+: Positive; −: Negative. -
[1] 李晓凯, 顾坤, 梁慕文, 等. 薏苡仁化学成分及药理作用研究进展 [J]. 中草药, 2020, 51(21):5645−5657. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2020.21.031 LI X K, GU K, LIANG M W, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Coicis Semen [J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2020, 51(21): 5645−5657.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2020.21.031
[2] 王艳玲, 何园球, 吴洪生, 等. 长期施肥下红壤磷素积累的环境风险分析 [J]. 土壤学报, 2010, 47(5):880−887. DOI: 10.11766/trxb200901090016 WANG Y L, HE Y Q, WU H S, et al. Environmental risk analysis of accumulated phosphorus in red soil under long-term fertilization [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2010, 47(5): 880−887.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11766/trxb200901090016
[3] SANTOYO G, MORENO H G, OROZCO M M, et al. Plant growth-promoting bacterial endophytes [J]. Microbiological Research, 2016, 183: 92−99. DOI: 10.1016/j.micres.2015.11.008
[4] 潘复静, 陈英倩, 梁月明, 等. 种植密度对马尾松人工林土壤磷转化功能微生物与细菌群落结构的影响 [J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(5):1233−1243. PAN F J, CHEN Y Q, LIANG Y M, et al. Effects of stand density on community structure of soil phoD-harboring microorganisms and bacteria in Pinus massoniana plantations [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(5): 1233−1243.(in Chinese)
[5] WONIAK M, GAZKA A, TYKIEWICZ R, et al. Endophytic bacteria potentially promote plant growth by synthesizing different metabolites and their phenotypic/physiological profiles in the biolog GEN III MicroPlateTM Test [J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(21): 5283. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20215283
[6] 池景良, 郝敏, 王志学, 等. 解磷微生物研究及应用进展 [J]. 微生物学杂志, 2021, 41(1):1−7. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7021.2021.01.001 CHI J L, HAO M, WANG Z X, et al. Advances in research and application of phosphorus-solubilizing microorganism [J]. Journal of Microbiology, 2021, 41(1): 1−7.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7021.2021.01.001
[7] 陆蓝翔, 江明明, 王焱, 等. 两株樟树促生抗病内生细菌的分离、筛选及鉴定 [J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(6):128−136. LU L X, JIANG M M, WANG Y, et al. Isolation, screening and identification of endophytic bacteria from Cinnamomum camphora that promote growth and antagonistic pathogen [J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University(Natural Sciences Edition), 2018, 42(6): 128−136.(in Chinese)
[8] 卢志红, 倪国荣, 陈龙, 等. 鸭跖草抗铜内生菌株的筛选及其促生性质研究 [J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2019, 41(6):1167−1174. LU Z H, NI G R, CHEN L, et al. Isolation and growth-promoting properties of Anti-copper endophytes strains from Commelina communis [J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2019, 41(6): 1167−1174.(in Chinese)
[9] 蔡红丹, 王碧盈, 肖翠红, 等. 解磷、溶磷菌对水稻种子萌发的影响 [J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2019(7):42−45. DOI: 10.11942/j.issn1002-2767.2019.07.0042 CAI H D, WANG B Y, XIAO C H, et al. Effects of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria on seed germination of rice [J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019(7): 42−45.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11942/j.issn1002-2767.2019.07.0042
[10] 农明英, 张世鲍, 高海涛, 等. 薏苡品种文薏2号及主要栽培技术 [J]. 中国种业, 2018(10):94−97. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-895X.2018.10.036 NONG M Y, ZHANG S B, GAO H T, et al. Variety Wenyi No. 2 and its main cultivation techniques [J]. China Seed Industry, 2018(10): 94−97.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-895X.2018.10.036
[11] CARDOSO V M, CAMPOS F F, SANTOS A, et al. Biotechnological applications of the medicinal plant Pseudobrickellia brasiliensis and its isolated endophytic bacteria [J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2020, 129(4): 926−934. DOI: 10.1111/jam.14666
[12] 郭艺鹏, 王海儒, 孙林琦, 等. 枣根际解磷细菌的分离筛选及16S rDNA鉴定 [J]. 河南农业大学学报, 2015, 49(6):811−816,837. GUO Y P, WANG H R, SUN L Q, et al. Screening and 16S rDNA identification of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria in rhizosphere soils of jujube [J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 2015, 49(6): 811−816,837.(in Chinese)
[13] 张黎丽, 张阁, 王欣艺, 等. 土壤中降解有机磷微生物的筛选 [J]. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 50(5):774−777. ZHANG L M, ZHANG G, WANG X Y, et al. Screening of strains for Organophosphorus-degradation in soil [J]. Journal of Shandong Agricultural University(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 50(5): 774−777.(in Chinese)
[14] 赵为容. 小麦亲和性根际解磷菌解磷机理及促生效果研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2018. ZHAO W R. Study on phosphorus dissolving mechanisms and growth-promoting effects of affinity Phosphate-solubilizing rhizobacteria for wheat[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2018. (in Chinese)
[15] ADNAN M, FAHAD S, ZAMIN M, et al. Coupling phosphate-solubilizing bacteria with phosphorus supplements improve maize phosphorus acquisition and growth under lime induced salinity stress [J]. Plants, 2020, 9(7): 900. DOI: 10.3390/plants9070900
[16] 张云霞, 雷鹏, 许宗奇, 等. 一株高效解磷菌Bacillus subtilis JT-1的筛选及其对土壤微生态和小麦生长的影响 [J]. 江苏农业学报, 2016, 32(5):1073−1080. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2016.05.019 ZHANG Y X, LEI P, XU Z Q, et al. Screening of a high-efficiency phosphate solubilizing bacterium Bacillus subtilis JT-1 and its effects on soil microecology and wheat growth [J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 32(5): 1073−1080.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2016.05.019
[17] 马骢毓, 张英, 马文彬, 等. 黄芪根际促生菌(PGPR)筛选与特性研究 [J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(1):149−159. DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2016263 MA C Y, ZHANG Y, MA W B, et al. Identification of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria Astragalus membranaceus and their effectives [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(1): 149−159.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2016263
[18] 狄义宁, 刘鲁峰, 谢林艳, 等. 一株甘蔗内生菌鉴定及其溶磷能力的研究 [J]. 作物杂志, 2018, 34(6):68−75. DOI: 10.16035/j.issn.1001-7283.2018.06.011 DI Y N, LIU L F, XIE L Y, et al. Identification and characterization of a phosphate-solubilizing endophyte from sugarcane [J]. Crops, 2018, 34(6): 68−75.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.16035/j.issn.1001-7283.2018.06.011
[19] 庄馥璐, 柴小粉, 高蓓蓓, 等. 苹果根际解磷菌的分离筛选及解磷能力 [J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2020, 25(7):69−79. DOI: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2020.07.07 ZHUANG F L, CHAI X F, GAO B, et al. Isolation and screening of phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria in apple rhizosphere [J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2020, 25(7): 69−79.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2020.07.07
[20] XIE J, YAN Z, WANG G, et al. A bacterium isolated from soil in a Karst rocky desertification region has efficient Phosphate-solubilizing and plant growth-promoting ability [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2021(11): 625450.
[21] 刘胜亮, 朱舒亮, 祁先慧, 等. 四株解磷菌分泌有机酸与溶解磷酸三钙能力的研究 [J]. 新疆农业科学, 2017, 54(6):1114−1121. DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2017.06.019 LIU S L, ZHU S L, QI X H, et al. Study on organic acid secreted from 4 strains Phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria and calcium phosphate dissolving ability [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 54(6): 1114−1121.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2017.06.019
[22] LI Y, LIU X, HAO T, et al. Colonization and maize growth promotion induced by phosphate solubilizing bacterial isolates [J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2017, 18(7): 1253. DOI: 10.3390/ijms18071253
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 章明清,李娟,张立成,姚宝全,张华. 三元肥料效应模型的整合与优化建模策略. 土壤学报. 2021(03): 755-766 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 韦玲玲. 融水县中晚稻最佳施肥量研究. 现代农业科技. 2020(15): 3-4 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陈兴麟,刘洋,罗土炎,王昌毓,杨海宁,曾润颖. 海藻寡糖生物肥对水稻产量及土壤菌群的影响. 福建农业科技. 2020(09): 19-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: