Effects of modified polyaspartic acid urea basal application in paddy field
-
摘要:目的 探究基施不同分子量改性聚天门冬氨酸(PASP)尿素对水稻产量、氮肥利用率及田面水氮素变化的影响。方法 以辽宁省水稻高产区辽河三角洲为试验区域,基于减量施氮情况下,将不同分子量改性PASP与尿素进行复配,通过大田试验研究基施不同分子量改性聚天尿素对稻田田面水氮素动态变化、水稻氮吸收利用及生长影响;利用灰色关联度法,综合评价基施不同分子量改性聚天尿素在稻田中的应用效果。结果 与大颗粒尿素处理相比,不同分子量改性聚天尿素处理降低了田面水氮素浓度,尤其在施基肥后第3天,分子量7500、10000和12500的改性聚天尿素处理田面水NH4+-N浓度较大颗粒尿素处理显著降低了24.54%~56.66%。其中分子量10000的改性聚天尿素处理的田面水NH4+-N浓度较分子量7500、12500和14700 的改性聚天尿素处理显著降低了36.84%~45.67%。施用分子量10000的改性聚天尿素能促进水稻生长,提高养分吸收,使水稻产量增加8.22%,籽粒、秸秆氮吸收量显著增加36.47%和62.39%,氮肥表观利用率提高38.31个百分点。结论 通过对以上各指标进行综合评价,表明基施改性聚天尿素效果优于大颗粒尿素,且尿素添加改性PASP的最佳分子量为10000。推荐辽河三角洲稻区应用分子量10000的改性聚天尿素。Abstract:Objective In order to evaluate the effects of modified polyaspartic acid (PASP) urea with different molecular weights on rice yield, nitrogen use efficiency and nitrogen(N)concentrations in the surface water of paddy fields.Method The Liaohe River delta, a rice-producing area in Liaoning Province, was selected as the experimental area, Modified PASP with different molecular weights was combined with urea. Then the effects of modified PASP urea with different molecular weights on N concentrations in the paddy field ponding water, rice growth, N uptake and utilization were studied under the condition of reduced nitrogen application. And the effects of basal modified PASP urea application with different molecular weights in paddy field were comprehensively evaluated by Grey Relational Analysis.Result The results showed that modified PASP urea treatment tests decreased the N concentrations in the surface water compared with the large particle urea treatment test. In particular, NH4+-N concentrations in the surface water in 7500mw, 10000mw and 12500mw modified PASP urea treatments test were significantly reduced by 20.23%~56.66% compared with large particle urea treatment test on the third day after basal fertilization. Among them, NH4+-N concentrations in the surface water in 10000 mw modified PASP urea treatment test was significantly lower (36.84%~45.67%) than 7500,12500 and 14700 mw modified PASP urea treatment tests. The application of 10000 mw modified PASP urea could significantly promote rice growth, nutrient absorption, and increase yield, with a 8.22% higher yield, a 36.47% higher N uptake in grain, a 62.39% higher N absorption in straw, a 38.31 percentage point higher of N use-efficiency, compared to the control.Conclusion Considering rice yield, nitrogen uptake, nitrogen use efficiency and N concentrations in the surface water, basal application of modified PASP urea treatment based on reduced nitrogen application was better than the treatment using large particle urea. Therefore, urea mixed with 10000 mw modified PASP urea is recommended to be used in Liaohe Delta rice region.
-
Keywords:
- rice /
- modified polyaspartic acid /
- urea /
- grey incidence analysis
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】化肥的有效投入是保障粮食增产最有效、最迅速的措施,对我国粮食单产增长的贡献率高达40%~50%[1]。但初步统计发现化学氮肥利用率仅为35.0%左右[2]。水稻作为我国重要的粮食作物,农民为追求高产往往投入过量氮肥,且习惯基肥用量较重,追肥用量较少,东北稻区尤为明显[3],而基肥期稻苗较小需氮量不高,加上大水漫灌泡田,这大大加剧了氮肥流失风险。基肥期氮肥的低利用率与高流失率易使数量庞大的化肥氮随地表径流、淋溶及挥发等损失掉,引起流域水环境富营养化,周围空气质量变差,对人类健康构成了威胁,已是不容忽视的事情。因此提高基肥期的氮肥利用率、减少氮素流失是亟待解决的问题。尿素是水稻生产中最主要的氮素来源,尿素转化与氮素利用和损失息息相关[4],因此开展缓控释型尿素的开发研究对于氮肥利用率的提高和氮肥流失的控制十分关键。【前人研究进展】聚天门冬氨酸(Polyaspartic acid,PASP)是一种新兴的可生物降解的环境友好材料,是一种人工仿生合成的水溶性高分子物质,是由天门冬氨酸单体的氨基和羧基进行分子间缩合脱水而成的缩聚产物[4],具有无毒、无磷、无公害和可完全生物降解的特性,在国际上被认为是“绿色化学品”[5]。分子中的羟基和羧基能螯合金属离子,富集N、P、K及微量元素供给作物,提高作物对氮、磷、钾的利用,具有极强的螯合、分散、吸附和缓慢释放养分等作用,常作为肥料增效剂和缓释剂应用于农业生产中[5-10]。改性PASP是通过化学改性在 PASP 分子链上引入官能团,使原来主链上无活性基团的聚合物功能化,或者改变PASP分子链的空间分布,延长分子链或形成三维网状结构,改性PASP效能显著增强[11-12]。PASP与尿素复配,将尿素包裹在内,缓控尿素在土壤中转化与释放,延长尿素养分持效期[13-14],改善土粒结构和提高土壤全氮含量[15],促进植株氮素吸收利用,提高作物产量与氮肥利用率[16-21],稳定粮食安全的同时降低了氮素流失风险。【本研究切入点】现有研究报道主要集中常规PASP对旱田作物增产效果和增产机制及氮肥利用率等方面,而研究改性PASP对水稻产量、氮肥利用率和田面水氮素变化等方面的应用效果相关报道较少,尤其未见关于基施不同分子量的改性聚天尿素应用效果综合评价的相关报道。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究以辽宁省水稻高产区辽河三角洲为试验区域,基于减量施氮情况下,将不同分子量改性PASP与尿素进行复配,通过大田试验研究基施不同分子量改性聚天尿素对稻田田面水氮素动态变化、水稻氮吸收利用及生长影响,采用灰色关联度法对改性聚天尿素的应用效果进行综合评价,以期获得改性PASP的最佳分子量,进而为水稻生产、稻田面源污染防控提供理论依据与技术支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验区概况
本试验于2018年5~9月在辽宁省盘锦市盘山县坝墙子镇烟李村(北纬41º10'29'',东经122º15'9'')进行。试验点所在区域位于辽河三角洲中心地带,是滨海盐土和盐渍化土壤分布区,年均降雨量612 mm,年平均温度8.4 ℃,全年无霜期约174 d。土壤为中等肥力水稻土。耕层土壤理化性质参见文献[22]。
1.2 试验材料
供试水稻品种为盐丰47。供试氮肥为大颗粒尿素(含N 46%)、改性聚天尿素(改性PASP选用聚天门冬氨酸钙盐,分子量分别为7500、10000、12500和14700,添加量按尿素质量的0.3%计算);磷肥和钾肥分别为磷酸二铵(P2O5 46%、N 18%)和氯化钾(K2O 60%)。
1.3 试验设计
试验共设置6个水稻氮肥基施处理:CK为不施肥,T1为大颗粒尿素,T2为7500改性聚天尿素,T3为10000改性聚天尿素,T4为12500改性聚天尿素,T5为14700改性聚天尿素。除对照外,T1~T5处理的基施氮占总氮的80%,剩余20%的氮在分蘖期施用,追肥均用常规尿素;氮肥(N)用量为210 kg·hm−2、磷肥(P2O5)和钾肥(K2O)全部作为基肥一次施入,用量均为90 kg·hm−2。每个处理3次重复,共18个小区,小区间田埂上覆塑料薄膜,防止串灌串排。施肥后旋耕泡田,其他田间管理按当地常规方法进行。
1.4 样品采集与测定
分别于施肥后第1、3、5、7、10、15 天的上午10:00采集田面水,采集后置于装有冻冰的保温箱带回,AA3 流动分析仪(Bran Luebbe,德国)测定全氮(TN)、硝态氮(NO3−-N)、氨态氮(NH4+-N)含量。水稻成熟时,3点取样法沿土表收割水稻地上部分,每点收割1 m2样方,测定籽粒和秸秆生物量及水稻株高、有效分蘖。采用凯氏定氮法测定籽粒和秸秆的全氮含量,然后根据公式计算水稻的氮素累积吸收量、氮肥表观利用率[23]。
1.5 数据整理与分析
采用Microsoft Excel 2013软件进行数据处理与作图,用SPSS 19.0软件检验数据显著性差异。应用灰色关联度法[24]对不同施肥处理的应用效果进行综合评价。效果评价方法参照文献[22]。
2. 结果与分析
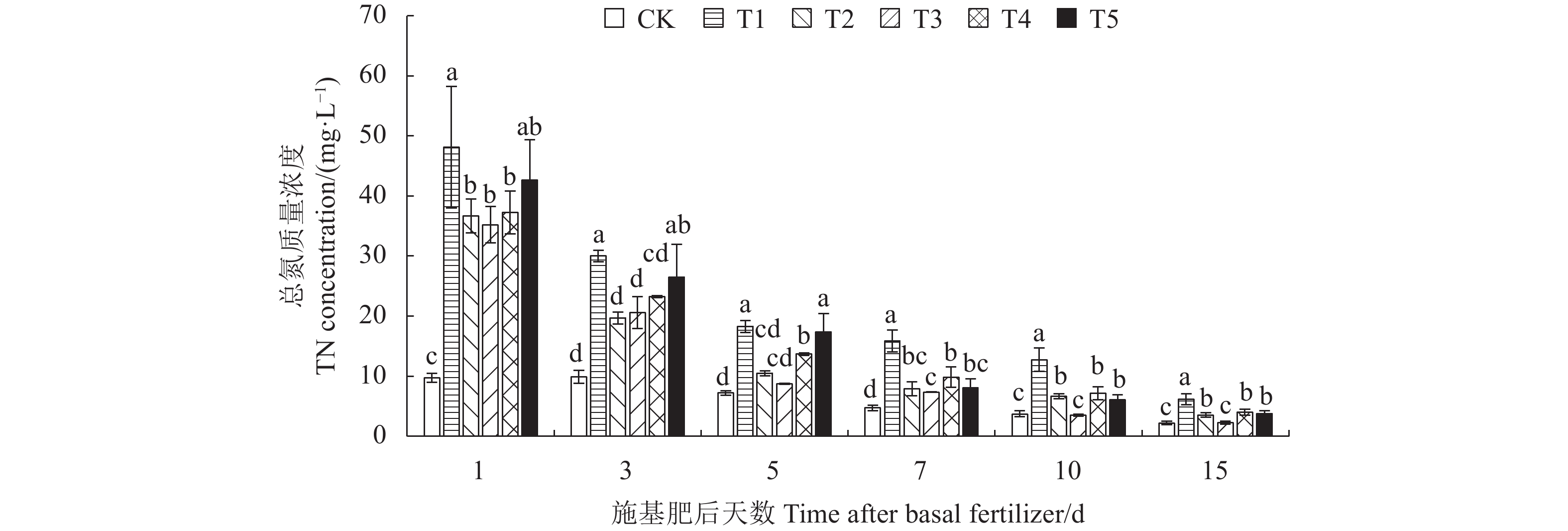
2.1 稻田田面水TN动态变化
通过对监测期稻田田面水TN分析发现(图1),CK处理的田面水TN含量整体处于较低水平;施基肥后,各施肥处理的田面水TN含量均高于CK处理,说明施用氮肥可增加田面水TN。施肥后第1天所有施肥处理的田面水TN含量即达到峰值,其中大颗粒尿素T1处理的田面水TN含量最大,为48.09 mg·L−1,高于所有改性聚天尿素处理(T2~T5),在第7~15 天差异显著;而在改性聚天尿素处理中,峰值期的T3处理田面水TN含量最小,较T1处理显著降低了26.81%,其次T2和T4处理分别显著降低了23.77%、22.53%,而T5处理与T1处理无显著差异。各施肥处理田面水TN含量随着时间推移呈降低趋势,于第10 天降至峰值的9.89%~26.44%,改性聚天尿素处理的田面水TN含量较T1处理显著降低了43.67%~72.61%,其中T3处理与CK处理差异不显著。
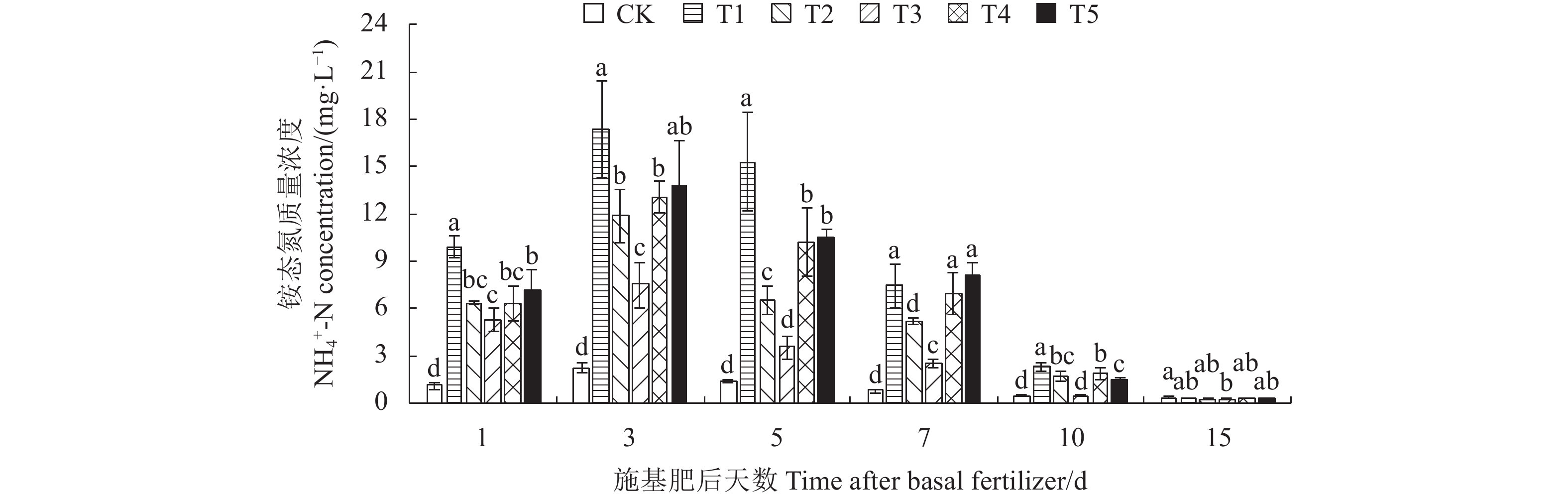
2.2 稻田田面水NH4+-N动态变化
通过对监测期稻田田面水NH4+-N含量分析发现(图2),CK处理的田面水NH4+-N含量整体处于较低水平。在施肥后第3 天,各施肥处理田面水NH4+-N含量均达到峰值,而后迅速下降,于第10 天降至峰值的4.75%~15.77%后逐渐趋于稳定。在施肥后第3天峰值期,与T1处理相比,改性聚天尿素处理(T2、T3、T4)田面水NH4+-N含量显著降低了24.54%~56.66%,与T5处理差异不显著。在改性聚天尿素处理中,峰值期的T3处理的田面水NH4+-N含量最低,较T2、T4和T5处理显著降低了36.84%~45.67%,其中T2处理的田面水NH4+-N含量低于T4和T5处理,差异不显著;在施肥后第5~10 天,T2、T3处理的田面水NH4+-N含量低于T4和T5处理,其中T3处理的田面水NH4+-N含量较其他改性聚天尿素处理(T2、T4、T5)显著降低了46.00%~81.17%,尤其在第10 天,与CK处理差异不显著。
2.3 稻田田面水NO3−-N动态变化
通过对监测期稻田田面水NO3−-N含量分析发现(图3),CK处理的田面水NO3−-N含量整体处于较低水平。在施基肥后第1 天,所有施肥处理的田面水NO3−-N含量到达最高,而后即呈迅速下降趋势,于第7 天降至峰值的7.14%~17.81%后趋于稳定。在施肥后1~7 d,改性聚天尿素处理(T2~T5)的田面水NO3−-N含量较T1处理降低了6.53%~66.64%,与T2、T3处理差异显著;而在施肥后3~7 d,T2、T3处理低于T4、T5处理,在第7 天差异显著。
2.4 不同处理对水稻产量及构成因素的影响
通过对水稻籽粒产量、秸秆产量、有效分蘖、株高的分析发现(表1),所有施肥处理(T1~T5)水稻有效分蘖数、秸秆产量和籽粒产量均显著高于不施肥处理(CK),T1、T3处理水稻株高显著高于CK处理。与T1处理相比,T2、T3的水稻有效分蘖数、秸秆产量和籽粒产量相对增加,并且T3处理籽粒产量显著高于T1处理,水稻增产8.22%。说明施用氮肥可促进水稻增产,且适宜分子量的改性聚天尿素可有效促进水稻生长,提高水稻产量。
表 1 水稻株高、有效分蘖数及产量Table 1. Rice height, effective tiller number and yield处理
Treatments有效分蘖数
Productive tillers/(穗·株−1)株高
Height/cm秸秆产量
Straw yield/(kg·hm−2)籽粒产量
Grain yield/(kg·hm−2)CK 15.67±2.08 b 79.17±1.44 c 5356.2 ± 430.2 c 6791.3 ±626.5 c T1 23.33±2.08 a 91.50±2.18 a 9287.5±841.5 b 11682.6±413.9 b T2 23.67±2.08 a 84.07±2.31 bc 9455.2±972.9 b 11822.1±697.4 b T3 24.67±2.52 a 86.47±3.68 ab 10929.2±907.0 a 12642.4±114.7 a T4 23.33±2.08 a 83.73±4.03 bc 9263.2b±303.8 b 11412.8±334.3 b T5 22.67±1.53 a 83.67±4.25 bc 9035.8±162.6 b 11353.2±137.5 b 同列数据后不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
The different lowercase letters after data in a column indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 levels.2.5 不同处理对水稻氮素吸收量和氮肥利用率的影响
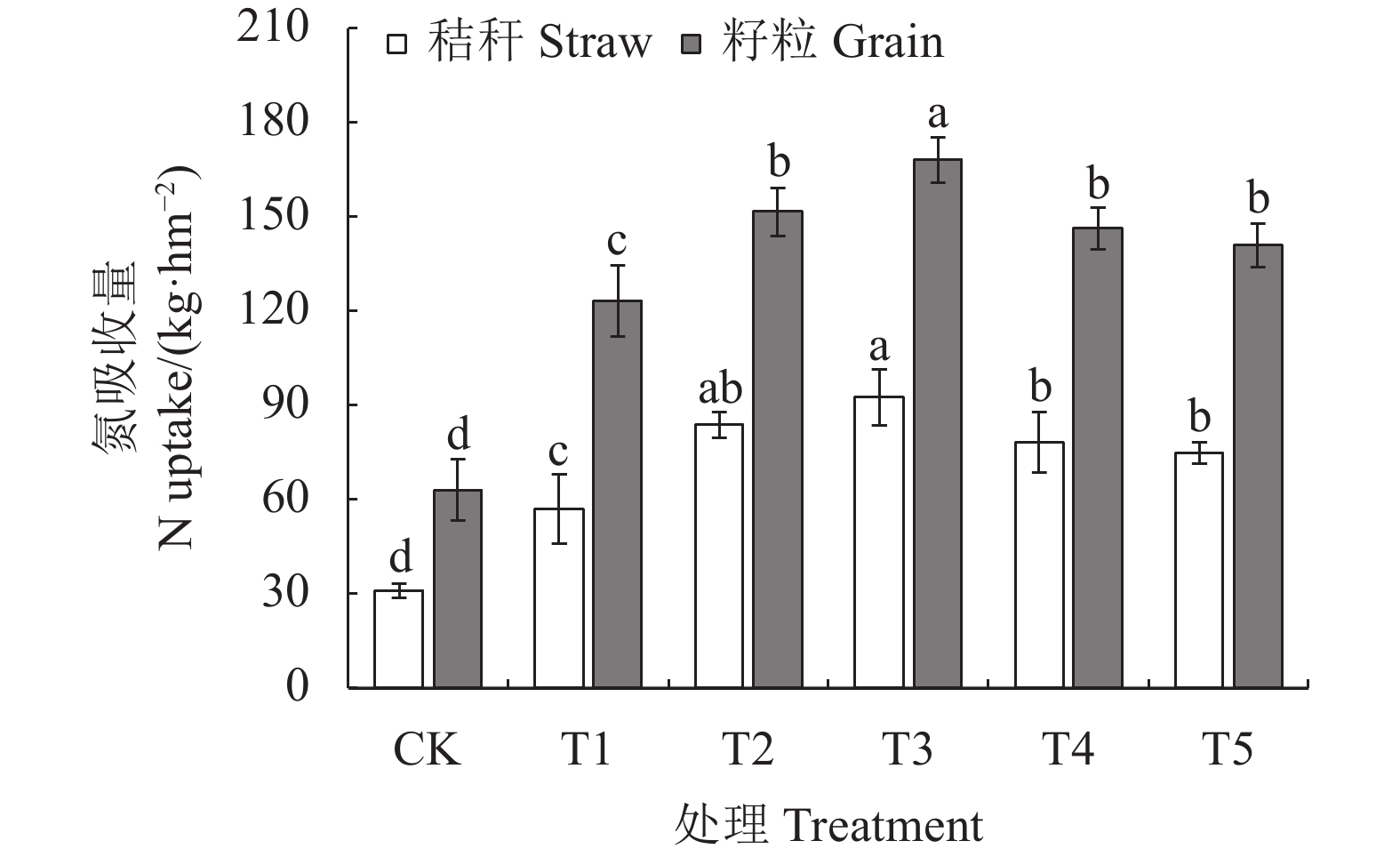
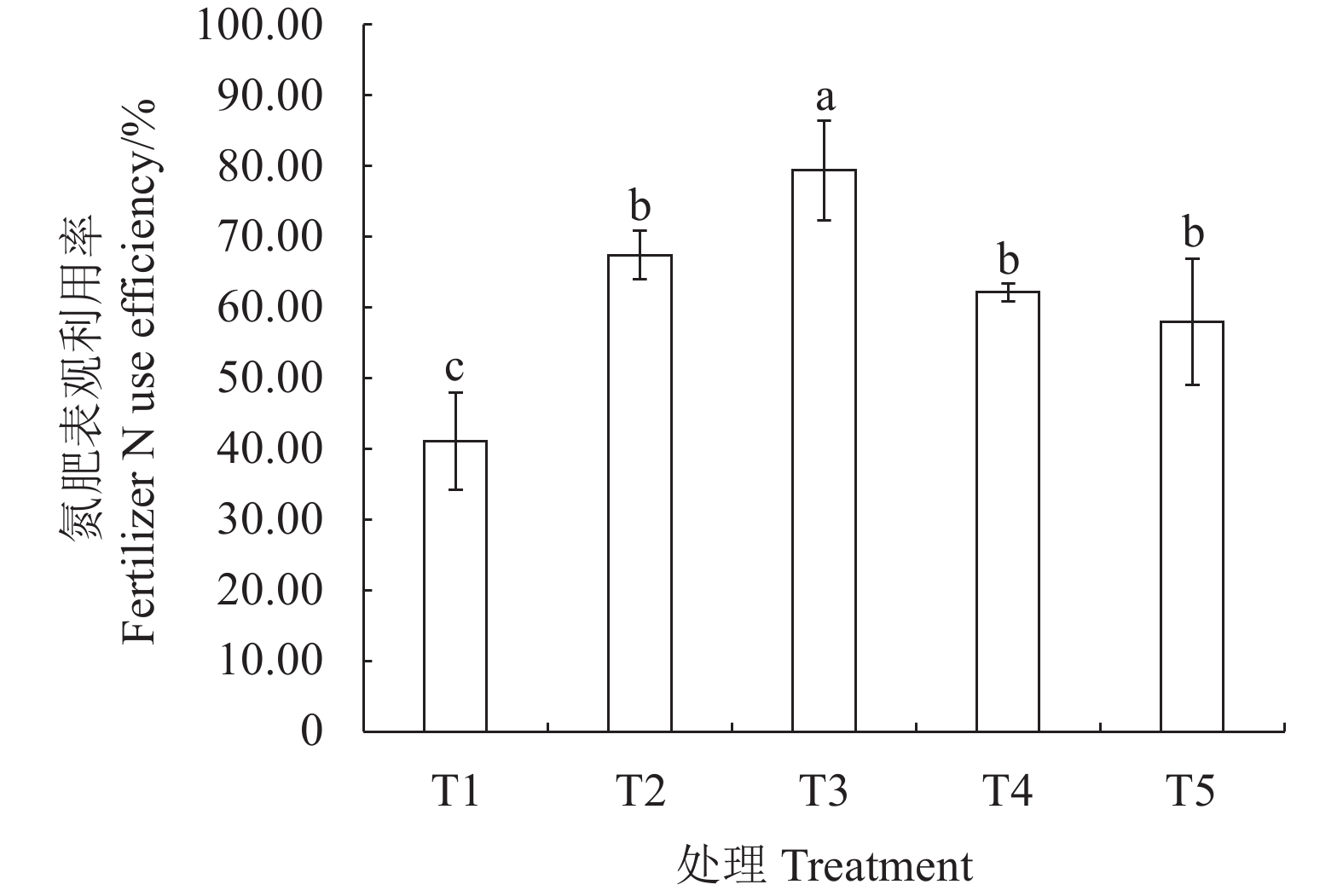
与CK处理相比,所有施肥处理水稻籽粒和秸秆氮吸收量均显著增高(图4)。在施肥处理组中,与T1处理相比,改性聚天尿素处理(T2~T5)水稻籽粒和秸秆氮吸收量均高于T1处理,氮累积吸收量增加了19.64%~44.66%,其中T3处理效果最好,籽粒、秸秆氮吸收量相对于T1处理显著增加了36.47%和62.39%。如图5所示,改性聚天尿素处理提高了氮肥表观利用率16.85~38.31个百分点,其中T3处理氮肥表观利用率达79.37%,与T1处理相比显著提高了38.31个百分点,说明添加改性PASP能促进水稻吸收氮素,增加水稻氮素累积,提高氮肥表观利用率,尤其T3处理。
2.6 不同施肥处理应用效果综合评价
灰色关联度分析显示,在单指标关联度中,基肥期田面水TN含量关联度、植株生物量关联度相对较大,分别为0.7696和0.7297,其次是植株氮累积吸收量为0.6639,表明不同施肥处理对稻田田面水TN含量、水稻氮吸收和生长的影响最大(表2)。从综合指标关联度与排序来看,T3处理关联度最高,其次依次为T2、T4和T5处理,T1处理关联度最低,表明改性聚天尿素好于大颗粒尿素,尤其添加分子量10000的改性PASP效果较明显。
表 2 应用效果综合评价排序Table 2. Comprehensive evaluation sorting of application effect处理
Treatments关联系数 Correlation coefficients 综合指标关联度
Correlation degree
of comprehensive
index排序
Sorting田面水
NH4+-N峰值
NH4+-N peak in
surface water田面水
TN峰值
TN peak in
surface water植株
生物量
Biomass of
plant植株氮
累积吸收量
N uptake of
plant氮肥
表观利用率
Fertilizer N use
efficiencyT1 0.3333 0.5138 0.7196 0.4785 0.3482 0.4787 5 T2 0.3651 0.8766 0.6852 0.6865 0.6765 0.6580 2 T3 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1 T4 0.3323 0.8370 0.6330 0.6039 0.5838 0.5980 3 T5 0.3169 0.6204 0.6108 0.5507 0.3964 0.4990 4 单指标关联度
Correlation degree
of single index0.4695 0.7696 0.7297 0.6639 0.6010 — — 3. 讨论
3.1 改性聚天尿素对田面水氮素含量的影响
本试验中,不同分子量改性聚天尿素对基肥时期田面水TN、NH4+-N、NO3−-N含量的影响存在一定差异。改性聚天尿素处理(T2~T5)的田面水TN、NH4+-N含量均低于等量大颗粒尿素处理,其中T3处理的田面水NH4+-N含量最低,其原因可能是,尿素外层包裹的10000改性聚天溶解速度相对较慢,因而抑制了尿素释放速度;其次是分子量10000的改性PASP分子结构更利于吸附较多的NH4+-N并将其转运到土壤里;再者是分子量10000的改性PASP分子结构有利于土壤中相应的酶与其活性位点相结合,分解改性PASP分子结构主链,使其断裂成片段[25],并裸露出大量的羧基与田面水中的NH4+-N螯合,形成作物易吸收的形态并促进作物吸收利用,使田面水NH4+-N含量降低。同时改性PASP抑制了铵态氮硝化作用[26],降低了田面水中NO3−-N含量,这可能是一方面改性聚天尿素降解相对缓慢,因而生成较少的NH4+-N,硝化作用减弱,生成较少的NO3−-N;一方面改性PASP与NH4+-N螯合,NH4+-N浓度不断降低,硝化形成的NO3−-N相对减少[12];另外由于长期处于淹水条件下,减弱的硝化作用及增强的反硝化作用,致使田面水NO3−-N浓度不断降低[27];再者水稻为喜铵作物,对于NH4+-N的需求高于NO3−-N[28-29],随着NH4+-N被水稻吸收利用,硝化形成的NO3−-N相对减少。另外随着NO3−-N向下移动,发生淋溶损失,也降低了田面水NO3−-N浓度。
3.2 改性聚天尿素对水稻产量、氮素累积量及氮肥利用率的影响
本试验中,与不施肥处理(CK)相比,所有施肥处理的水稻产量均有所提高,表明水稻生产过程中有必要人为补充氮肥。并且所有施肥处理相对于CK,水稻生长及产量指标均显著提高,说明氮肥的施用是水稻产量增加的关键因素。与T1处理相比,T3处理水稻增产8.22%,氮肥累积吸收量增加了44.66%,氮肥表观利用率提高了38.31个百分点,表明添加分子量10000的改性聚天尿素既可以提高水稻产量,又能实现氮肥高效利用。这可能是由于添加改性PASP后,氮素释放与水稻生长需氮规律实现了协调一致,有利于水稻养分吸收,促进水稻干物质积累,增加水稻产量,提高氮料利用率。而分子量12500和14700的改性聚天尿素处理水稻产量低于大颗粒尿素处理,但差异不显著,这可能受土壤性质、气候条件、施肥方式、施肥时期等因素的影响,需另行设计试验验证。
3.3 改性聚天尿素应用效果的综合评价
利用灰色关联度法对不同分子量改性聚天尿素应用效果相关的主要指标进行综合评价,筛选出改性PASP的最佳分子量,避免利用单一指标评价改性聚天尿素效果的片面性,评价更加客观全面,能真实地反映不同分子量改性聚天尿素的实际应用效果。本试验中,将田面水氮素含量、植株生物量和氮累积吸收量以及氮肥利用率等作为主要比较指标,单指标关联分析发现,关联度相对较大的为田面水TN含量和植株生物量,其次是植株氮累积吸收量,因此推荐水稻籽粒和秸秆产量以及田面水TN含量作为不同分子量改性聚天尿素应用效果的主要评价指标。从综合指标关联度排序来看,T3处理关联度最高,其次依次为T2、T4和T5处理,T1处理关联度最低,表明改性聚天尿素对于提高氮肥利用效率和防控氮素流失具有较好的作用效果,其中添加10000分子量的改性PASP效果最佳。
4. 结论
应用灰色关联度法对减量施肥下基施不同分子量改性聚天尿素应用效果进行综合评价,兼顾水稻产量、氮吸收和田面水氮素浓度等因素,推荐辽河三角洲稻区基肥应用分子量10000的改性聚天尿素,有助于保障粮食稳定和环境安全。本研究仅是一年大田试验结果,相关结论有待于进一步开展多年田间熟化验证,以保证改性聚天尿素规模化推广应用效果。
-
表 1 水稻株高、有效分蘖数及产量
Table 1 Rice height, effective tiller number and yield
处理
Treatments有效分蘖数
Productive tillers/(穗·株−1)株高
Height/cm秸秆产量
Straw yield/(kg·hm−2)籽粒产量
Grain yield/(kg·hm−2)CK 15.67±2.08 b 79.17±1.44 c 5356.2 ± 430.2 c 6791.3 ±626.5 c T1 23.33±2.08 a 91.50±2.18 a 9287.5±841.5 b 11682.6±413.9 b T2 23.67±2.08 a 84.07±2.31 bc 9455.2±972.9 b 11822.1±697.4 b T3 24.67±2.52 a 86.47±3.68 ab 10929.2±907.0 a 12642.4±114.7 a T4 23.33±2.08 a 83.73±4.03 bc 9263.2b±303.8 b 11412.8±334.3 b T5 22.67±1.53 a 83.67±4.25 bc 9035.8±162.6 b 11353.2±137.5 b 同列数据后不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
The different lowercase letters after data in a column indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 levels.表 2 应用效果综合评价排序
Table 2 Comprehensive evaluation sorting of application effect
处理
Treatments关联系数 Correlation coefficients 综合指标关联度
Correlation degree
of comprehensive
index排序
Sorting田面水
NH4+-N峰值
NH4+-N peak in
surface water田面水
TN峰值
TN peak in
surface water植株
生物量
Biomass of
plant植株氮
累积吸收量
N uptake of
plant氮肥
表观利用率
Fertilizer N use
efficiencyT1 0.3333 0.5138 0.7196 0.4785 0.3482 0.4787 5 T2 0.3651 0.8766 0.6852 0.6865 0.6765 0.6580 2 T3 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1 T4 0.3323 0.8370 0.6330 0.6039 0.5838 0.5980 3 T5 0.3169 0.6204 0.6108 0.5507 0.3964 0.4990 4 单指标关联度
Correlation degree
of single index0.4695 0.7696 0.7297 0.6639 0.6010 — — -
[1] 曾靖, 常春华, 王雅鹏. 基于粮食安全的我国化肥投入研究 [J]. 农业经济问题, 2010, 31(5):66−70,111. DOI: 10.13246/j.cnki.iae.2010.05.007 ZENG J, CHANG C H, WANG Y P. Study on the fertilizer inputs based on China’s food security [J]. Issues in Agricultural Economy, 2010, 31(5): 66−70,111.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13246/j.cnki.iae.2010.05.007
[2] 朱兆良, 金继运. 保障我国粮食安全的肥料问题 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2013, 19(2):259−273. DOI: 10.11674/zwyf.2013.0201 ZHU Z L, JIN J Y. Fertilizer use and food security in China [J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2013, 19(2): 259−273.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11674/zwyf.2013.0201
[3] 王激清, 马文奇, 江荣风, 等. 我国水稻、小麦、玉米基肥和追肥用量及比例分析 [J]. 土壤通报, 2008, 39(2):329−333. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2008.02.024 WANG J Q, MA W Q, JIANG R F, et al. Analysis about amount and ratio of basal fertilizer and topdressing fertilizer on rice, wheat, maize in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2008, 39(2): 329−333.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2008.02.024
[4] 程凤娴, 官利兰, 邓兰生, 等. 聚天门冬氨酸对玉米生长的影响 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2015, 43(4):105−106,139. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2015.04.036 CHENG F X, GUAN L L, DENG L S, et al. Effects of polyaspartic acid on maize growth [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(4): 105−106,139.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2015.04.036
[5] 杨晋辉, 刘泰, 陈艳雪, 等. 聚天门冬氨酸/盐的合成、改性及应用研究进展 [J]. 材料导报, 2018, 32(11):1852−1862. DOI: 10.11896/j.issn.1005-023X.2018.11.012 YANG J H, LIU T, CHEN Y X, et al. Synthesis, modification and application of polyaspartic acid/salt: The state-of-art technological advances [J]. Materials Review, 2018, 32(11): 1852−1862.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11896/j.issn.1005-023X.2018.11.012
[6] 柳建良, 崔英德, 尹国强, 等. 聚天门冬氨酸的合成及其在农业上的应用 [J]. 仲恺农业技术学院学报, 2008, 21(2):52−56. LIU J L, CUI Y D, YIN G Q, et al. Progress in the synthesis and agricultural application of polyaspartic acid [J]. Journal of Zhongkai University of Agriculture and Technology, 2008, 21(2): 52−56.(in Chinese)
[7] 黄启亮, 韩广泉, 侯红燕, 等. 土壤肥料增效剂—聚天门冬氨酸研究现状及应用前景 [J]. 农村经济与科技, 2015, 26(4):62−63. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7103.2015.04.025 HUANG Q L, HAN G Q, HOU H Y, et al. Research status and application prospect of soil fertilizer synergist-polyaspartic acid [J]. Rural Economy and Science-Technology, 2015, 26(4): 62−63.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7103.2015.04.025
[8] 杜中军, 杨浩, 王树昌, 等. 农用聚天门冬氨酸同源多肽研究进展 [J]. 热带作物学报, 2011, 32(12):2381−2384. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2011.12.037 DU Z J, YANG H, WANG S C, et al. Advance of homologous polypeptides polyaspartic acids for agriculture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2011, 32(12): 2381−2384.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2011.12.037
[9] 冷一欣, 韶晖, 蒋俊杰, 等. 肥料增效剂聚天冬氨酸的应用效果研究 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2002, 30(3):412−413. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2002.03.047 LENG Y X, SHAO H, JIANG J J, et al. Study on poly as fertilizer synergist [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2002, 30(3): 412−413.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2002.03.047
[10] KINNERSLEY A M, KOSKAN L P, STROM D J, et al. Method for more efficient uptake of plant growth nutrients: US5593947[P]. 1997-01-14.
[11] 胡志光, 王昕, 张玉玲, 等. 改性聚天冬氨酸研究最新进展 [J]. 应用化工, 2014, 43(2):360−362. DOI: 10.16581/j.cnki.issn1671-3206.2014.02.017 HU Z G, WANG X, ZHANG Y L, et al. Latest research development of modified polyaspartic acid [J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2014, 43(2): 360−362.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.16581/j.cnki.issn1671-3206.2014.02.017
[12] 徐嘉翼, 牛世伟, 隋世江, 等. 聚天门冬氨酸/盐对水稻田面水氮素变化及养分利用的影响 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(8):1696−1703. DOI: 10.11654/jaes.2019-0229 XU J Y, NIU S W, SUI S J, et al. Effects of polyaspartic-acid/salt on nitrogen loss from paddy surface water and nutrients utilization [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(8): 1696−1703.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11654/jaes.2019-0229
[13] 陈倩, 李洪娜, 门永阁, 等. 不同聚天冬氨酸水平对盆栽平邑甜茶幼苗生长及15N-尿素利用与损失的影响 [J]. 水土保持学报, 2013, 27(1):126−129,135. CHEN Q, LI H N, MEN Y G, et al. Effects on the growth of potted Malus hupehensis Rehd. seedlings, utilization and loss of 15N-urea under different supply levels of polyaspartic acid [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2013, 27(1): 126−129,135.(in Chinese)
[14] 谢方淼, 李东坡, 李健强, 等. 聚天冬氨酸尿素对土壤微生物量碳、氮的影响 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2011(4):8−12. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6257.2011.04.003 XIE F M, LI D P, LI J Q, et al. Effects of polyaspartic urea(PASP-Urea) on soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen under incubation and pot experiment [J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2011(4): 8−12.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6257.2011.04.003
[15] 雷全奎, 杨小兰, 马雯场, 等. 聚天门冬氨酸对土壤理化性状的影响 [J]. 陕西农业科学, 2007, 53(3):75−76. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0488-5368.2007.03.025 LEI Q K, YANG X L, MA W C, et al. Effect of polyaspartic acid on soil physical and chemical properties [J]. Shaanxi Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2007, 53(3): 75−76.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0488-5368.2007.03.025
[16] 杜中军, 杨浩, 王永造, 等. 聚天门冬氨酸同源多肽的水稻产量效应和磷素营养吸收效应研究 [J]. 现代农业科技, 2012(18):12−13,15. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2012.18.002 DU Z J, YANG H, WANG Y Z, et al. Effects on yield and Phosphorus nutrition absorbing for rice using homologous polypeptides of polyaspartic acids [J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2012(18): 12−13,15.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2012.18.002
[17] 侯晓娜. 黄腐酸和聚天冬氨酸对蔬菜氮素吸收及肥料氮转化的影响[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2013. HOU X N. Effects of fulvic acid and polyaspartic acid on nitrogen uptake of vegetables and transformation of fertilizer nitrogen[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2013. (in Chinese)
[18] 张琳, 左强, 邹国元. 施用不同水平聚天门冬氨酸对油菜生长的影响 [J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2013(12):27−29. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2767.2013.12.008 ZHANG L, ZUO Q, ZOU G Y. Effects of polyaspartic acid with different levels on growth of Brassica campestris L [J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2013(12): 27−29.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2767.2013.12.008
[19] 唐会会, 许艳丽, 王庆燕, 等. 聚天门冬氨酸螯合氮肥减量基施对东北春玉米的增效机制 [J]. 作物学报, 2019, 45(3):431−442. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2019.83056 TANG H H, XU Y L, WANG Q Y, et al. Increasing spring maize yield by basic application of PASP chelating nitrogen fertilizer in northeast China [J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2019, 45(3): 431−442.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2019.83056
[20] 郭明海. 尿素增效剂聚天门冬氨酸的分子量及其分布测定 [J]. 大氮肥, 2006, 29(1):29−31. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5782.2006.01.009 GUO M H. Measurement of absolute molecular weight and its distribution of polyaspartic acid as urea synergic agent [J]. Large Scale Nitrogenous Fertilizer Industry, 2006, 29(1): 29−31.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5782.2006.01.009
[21] 张弓长, 蔡虎铭, 钱程, 等. 不同配方增效尿素对玉米生长及产量的影响 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2016, 44(34):20−22. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2016.34.008 ZHANG G C, CAI H M, QIAN C, et al. Effects of different synergistic urea on the growth and yield of maize [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(34): 20−22.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2016.34.008
[22] 王娜, 徐嘉翼, 张鑫, 等. 聚天门冬氨酸尿素对水稻产量及田面水氮素变化的综合影响 [J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2021, 38(1):96−103. DOI: 10.13254/j.jare.2020.0072 WANG N, XU J Y, ZHANG X, et al. Effects of polyaspartic acid urea on rice yield and nitrogen concentrations in paddy field ponding water [J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2021, 38(1): 96−103.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13254/j.jare.2020.0072
[23] 巨晓棠. 氮肥有效率的概念及意义: 兼论对传统氮肥利用率的理解误区 [J]. 土壤学报, 2014, 51(5):921−933. JU X T. The concept and meanings of nitrogen fertilizer availability ratio-discussing misunderstanding of traditional nitrogen use efficiency [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2014, 51(5): 921−933.(in Chinese)
[24] 邓聚龙. 灰色系统基本方法[M]. 武汉: 华中工学院出版社, 1987. [25] 成大明, 陈强, 朱爱萍, 等. 聚天冬氨酸及其衍生物的研究进展 [J]. 材料导报, 2002, 16(7):60−63. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-023X.2002.07.019 CHENG D M, CHEN Q, ZHU A P, et al. Progress in research on poly(aspartic acid) and its derivatives [J]. Materials Review, 2002, 16(7): 60−63.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-023X.2002.07.019
[26] 张康宁. 氮素管理对稻田氮素迁移转化及水稻生长的影响研究[D]. 金华: 浙江师范大学, 2019. ZHANG K N. Study on the nitrogen transfermation and rice growth under different nitrogen management methods in the rice field[D]. Jinhua: Zhejiang Normal University, 2019. (in Chinese)
[27] 宫亮, 隽英华, 王建忠, 等. 盘锦地区稻田田面水氮素动态变化及化学氮肥投入阈值研究 [J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2013, 30(6):96−100. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4944.2013.06.020 GONG L, JUAN Y H, WANG J Z, et al. Variations of nitrogen in surface water body of a paddy field and input threshold of chemical N fertilizer in Panjin City, China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2013, 30(6): 96−100.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4944.2013.06.020
[28] OGAWA S, VALENCIA M O, ISHITANI M, et al. Root system architecture variation in response to different NH4 [J]. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2014, 36(9): 2361−2372. DOI: 10.1007/s11738-014-1609-6
[29] 王晓琪, 姚媛媛, 陈宝成, 等. 淹水条件硝态氮和铵态氮配施对水稻生长与土壤养分的影响 [J]. 土壤, 2020, 52(2):254−261. DOI: 10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2020.02.005 WANG X Q, YAO Y Y, CHEN B C, et al. Effects of combined application of nitrate and ammonium on rice growth and soil nutrients under flooding conditions [J]. Soils, 2020, 52(2): 254−261.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2020.02.005
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 戴惠新,吴金洋,张梦樵,张湘菊,吴丽娜. 喷涂机器人用改性聚天门冬氨酸酯腻子制备及性能测试. 粘接. 2024(12): 42-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: