Diversity of Culturable Endophytes and Rhizosphere Fungi of Volvariella brumalis
-
摘要:目的 明确冬小包脚菇菌基土壤真菌和可培养内生真菌组成情况,为冬小包脚菇子实体分离及栽培奠定基础。方法 以野生冬小包脚菇子实体及其菌基土壤为研究对象,采用传统组织分离法对子实体进行分离、纯化及ITS测序鉴定,并结合高通量测序法对菌基土壤真菌进行测序。结果 分离得到的冬小包脚菇纯菌株属于Volvopluteus类群,也可属于传统定义的Volvariella类群。共得到冬小包脚菇内生真菌菌株50个,分属为3门13科16属20种,另有未定义科2个菌株,分别属于2个属,其中镰刀菌属(Fusarium)和毛霉属(Mucor)为优势属,且冬小包脚菇子实体内生真菌Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(H)为2.45,Simpson指数(D)为0.88,均匀度指数Pielou(J)为0.88,Margalef丰富度指数(R)为3.83。而冬小包脚菇菌基土壤中共检测到平均样品序列数67 919个,鉴定出276种土壤真菌,归属于10门131科213属,优势属为被孢霉属(Mortierella)、瓶毛壳属(Lophotrichus)、假散囊菌属(Pseudeurotium)、Pseudaleuria和两个未定义属unclassified_o_Sordariales、unclassified_c_Sordariomycetes。3个土样平均Ace指数达298.7,Shannon指数达3.53,Simpson指数为0.08,Chao 指数为304.23。结论 冬小包脚菇可培养内生真菌和菌基土壤真菌都具有较为丰富的物种组成,该结论对冬小包脚菇菌种分离、培养、病虫害防治等栽培要点提供一定理论指导。Abstract:Objective To promote the cold climate, specialty mushrooms in Guizhou, Volvariella brumalis as an ideal fill-in of the popular straw mushroom, V. volvacea, for wintertime market, the culturable endophytes and rhizosphere fungi associated with it were isolated and investigated to aid the cultivation.Methods Specimens from the fruiting bodies and rhizosphere soil of V. brumalis in the wild were collected. Endophytes in the fruiting bodies were isolated, cultured, and identified by ITS sequencing using the traditional tissue separation method, and fungal community in the rhizosphere soil analyzed by high-throughput sequencing.Results The 50 isolated endophytic strains were Volvopluteus, or the traditionally defined Volvariella, genera. They belonged to 3 phyla, 13 families, 16 genera (two of undefined families), and 20 species. Among them, Fusarium and Mucor were the dominant genera. The fungal Shannon-Wiener diversity index was 2.45, the Simpson index 0.88, the evenness index Pielou 0.88, and the Margalef richness index 3.83. In the rhizosphere soil, 67 919 sequences were detected with 276 kinds of fungi that belonged to 10 phyla, 131 families, and 213 genera. The dominant genera included Mortierella, Lophotricus, Pseudeurotium, Pseudaleuria, unclassified_o_Sordariales, and unclassified_c_Sordariomycetes. The Ace indices of 3 soil samples averaged 298.7, the Shannon indices 3.53, the Simpson indices 0.08, and the Chao indices 304.23.Conclusion Both the culturable endophytes and the rhizosphere fungi of V. brumalis were relatively rich in diversity. The information obtained would facilitate further research on the isolation, cultivation, and pest control of the mushroom for potentially valuable marketing in winter.
-
Keywords:
- Volvariella brumalis /
- identification /
- endophytic fungi /
- rhizosphere soil /
- fungal diversity
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】冬小包脚菇(Volvariella brumalis He sp. nav.)是一种独具特色的低温型可食用大型真菌。最早由贵州生物研究所何绍昌研究员发现并于1987年正式予以命名,归属于担子菌门(Basidiomycota),蘑菇纲(Agaricomycetes),蘑菇目(Agaricales),光柄菇科(Pluteaceae),包脚菇属(Volvariella)[1]。该菇口感滑嫩,富含多种氨基酸及无机元素[2],在口感及外观上同包脚菇属著名栽培品种草菇(Volariella volvacea)较为相似。但该菌子实体形成温度在4~14 ℃,主要生长在冬季水稻收割后换茬种植小麦、油菜、蚕豆的农田里,明显区别于喜高温高湿环境的草菇[3-6],有“低温草菇”之称,具有重要的市场价值和研究价值。【前人研究进展】近年来,由于农药化肥的过度使用和冬季农田的闲置致使其小生境变化剧烈,其野外发生地激剧缩小,出菇频率也大不如从前。冬小包脚菇自被发现以来,研究学者对其营养成分[3]、野外生境[7-8]、形态特征[9]等方面进行了探讨。同时,冬小包脚菇子实体分离难度大,培养过程中获得杂菌概率高,驯化后产量不稳定;真菌是引起食用菌病害的最主要的病原,而聚焦冬小包脚菇内生真菌和菌基土壤真菌的研究目前较少。【本研究切入点】冬小包脚菇是贵州特有的珍稀食用菌,本课题组自2019年初开始在贵州省范围内采集、分离、纯化,直至2020年底才成功获得纯菌种10余株,其可培养内生真菌及菌基土壤真菌的关键微生物类群组成亟待深入探讨。【拟解决的关键问题】采用传统组织分离法对冬小包脚菇子实体进行分离培养及鉴定,得到了冬小包脚菇纯菌株及其可培养内生真菌菌株,并结合高通量测序法对冬小包脚菇菌基土壤真菌进行测序研究,旨在了解冬小包脚菇菌基土壤真菌和子实体可培养真菌组成情况,以突破冬小包脚菇分离难关,为冬小包脚菇驯化栽培及推广奠定理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 样品采集
子实体采集与分离:在贵州省遵义市汇川区、黔南州龙里县和六盘水市钟山区等地,共采集野生冬小包脚菇标本约200份;选择完整、无病虫害的120个子实体分别标号,装入采集袋,带回实验室,12 h内完成真菌分离。
菌基土壤采集:2020年12月于贵州省遵义市汇川区板桥镇(27°98′63.22′′ N,106°90′94.65′′ E,海拔879~1000 m,温度6.5 ℃)采集野生冬小包脚菇主要分布地区的菌基土壤;该区域地貌类型为河谷盆地,土壤类型为砂质壤土,生境为水稻收割翻耕后轮作种植油菜的农田。方法:根据野生冬小包脚菇的分布情况设置3个10 m×10 m的平行样方,戴无菌手套和口罩,挖取长势良好的冬小包脚菇子实体,用无菌镊子小心刮取其菌托表面的土壤,每个样方按照对角线型路线采集3个菌基土壤为1个混合样,共采集土壤样品9个,得到土壤混合样3个,分别编号为S1、S2、S3。置于灭菌的离心管中,放入车载冰箱−20 ℃保存备用。
1.2 菌基土壤真菌高通量测序
将采集到的冬小包脚菇菌基土壤送美吉生物有限公司进行高通量测序,得到的原始数据利用FLASH和fastp软件,根据PE reads之间的overlap关系,对各样本数据进行优化和质控过滤,得到有效数据。按照97%相似水平下的OTU进行生物信息统计分析,将OTU与NCBI数据库比对并对OTU进行物种注释。利用交互式微生物多样性云分析平台(www.majorbio.com,上海美吉生物医药科技有限公司)进行Alpha多样性Shannon指数(H)、Simpson指数(D)、ACE指数和Chaol指数分析,采用RDP classifier 贝叶斯算法对OTU代表序列进行分类学分析。
1.3 冬小包脚菇菌株及其内生真菌的分离与鉴定
1.3.1 分离与鉴定
培养基:马铃薯(去皮)200 g,稻草40 g(剪成2−3 cm段,沸水30 min),葡萄糖20 g,蛋白胨2 g,磷酸二氢钾0.5 g,磷酸氢二钾0.5 g,MgSO4·7H2O 0.5 g,维生素B1 10 mg,琼脂粉20 g,去离子水1000 mL,pH自然。
采用传统组织分离法对冬小包脚菇子实体进行分离,并置于18 ℃培养箱中培养,将培养得到的菌丝体进一步纯化后进行分子鉴定。用生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司Ezup柱式真菌基因组DNA抽提试剂盒提取分离纯化真菌基因组DNA,提取之后的DNA选用真菌通用引物(ITS1:TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG;ITS4:TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC)进行PCR扩增,得到的PCR产物经1.0%琼脂糖电泳检测扩增后,送生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司测序。
1.3.2 数据处理
利用Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(H)、Simpson指数(D)、均匀度指数Pielou(J)、Margalef丰富度指数(R)评价冬小包脚菇内生真菌多样性。并利用BioEdit软件对分离得到的冬小包脚菇菌株及其内生真菌菌株,下载相应序列进行排列匹配,用MEGA6分别构建冬小包脚菇系统发育树及冬小包脚菇内生真菌系统发育树。
H=−∑(PilnPi) (Pi 为第i种菌株数占全部菌株数的百分比)D=1−∑(Pi)2 (Pi 为第i种菌株数占全部菌株数的百分比)J=H/lnS (H为Shannon-Wiener指数,S为物种总数目)R=(S−1)/lnN (S为物种总数目,N为样本数)相对丰度/%=(分离得到的内生真菌某属的菌株数/分离得到的内生真菌总菌株数) ×100
2. 结果与分析
2.1 冬小包脚菇子实体分子鉴定
对采集到的冬小包脚菇子实体进行分离、纯化,得到冬小包脚菇菌株。经PCR扩增和序列测定,结果显示供试冬小包脚菇菌株rDNA ITS区段长度为640 bp,上传GenBank得到登录号为OM108495,且经Blast搜索,结果均为Volvopluteus gloiocephalus和Volvariella gloiocephala,下载相似序列20条,并结合Volvopluteus、Volvariella及Pluteus三大属常见种序列,共同构建冬小包脚菇系统发育树。由图1可知,该系统发育关系可分为三大类群,即Volvopluteus、Volvariella和Pluteus各为一个类群,而冬小包脚菇属于Volvopluteus类群;若分为两大类群,则Volvopluteus、Volvariella在同一类群,为传统定义的Volvariella类群,Pluteus单独为一个类群,即冬小包脚菇属于传统定义的Volvariella类群下。
2.2 冬小包脚菇可培养内生真菌菌群组成及其系统发育关系
通过对采集到的冬小包脚菇120个子实体内生真菌进行分离鉴定,共分离出50个杂菌菌株分属为3门,13科,16属,20种,另有未定义科2个菌株,分别属于2个属(表1)。在门水平上,冬小包脚菇子实体内生真菌主要有子囊菌门(Ascomycota)、担子菌门(Basidomycota)和接合菌门(Zygomycota),其中子囊菌门为优势菌门,共分离到菌株29个,相对丰度达58.00%;其次为担子菌门,共分离到菌株13个,相对丰度为26.00%;接合菌门共分离到菌株8个,相对丰度为16.00%。在科水平上,丛赤壳科(Nectriaceae)和毛霉菌科(Mucoraceae)为优势科,相对丰度分别为24.00%和16.00%;此外,球盖菇科(Strophariaceae)、曲霉科(Aspergillaceae)相对丰度均为8.00%;原毛平革菌科(Phanerochaetaceae)、裂褶菌科(Schizophyllaceae)、生赤壳科(Bionectriaceae)、山野壳菌科(Montagnulaceae)和梨孢假壳科(Apiosporaceae)相对丰度为6.00%;多孔菌科(Polyporales)相对丰度为4.00%;皱孔菌科(Meruliaceae)、瘤座孢科(Tubeculariaceae)和革菌科(Coriolaceae)相对丰度为2.00%;未定义科的相对丰度为4.00%。从属水平上,镰刀菌属(Fusarium)和毛霉属(Mucor)为优势属,相对丰度分别为24.00%和16.00%;球盖菇属(Stropharia)相对丰度为8.00%;烟管菌属(Bjerkandera)、裂褶菌属(Schizophyllum)、粘帚霉菌属(Clonostachys)、节菱孢属(Arthrinium)、曲霉属(Aspergillus)和小球壳孢属(Microsphaeropsis)相对丰度为6.00%;多孔菌属(Polyporus)相对丰度为4.00%;射脉菌属(Phlebia)、漆斑菌属(Myrothecium)、蜡孔菌属(Ceriporia)、青霉属(Penicillium)、Leiothecium和Parengyodontium相对丰度仅为2.00%。
表 1 冬小包脚菇可培养内生真菌菌群组成Table 1. Composition of culturable endophytes in V. brumalis门 Phylum 科 Family 属 Genus 菌株数
Number of strains相对丰度
Relative abundance/%相似种
Similar species菌株数
Number of strains担子菌门
Basidomycota原毛平革菌科
Phanerochaetaceae烟管菌属
Bjerkandera3 6.00 烟管菌
Bjerkandera adusta3 球盖菇科
Strophariaceae球盖菇属
Stropharia4 8.00 大球盖菇
Stropharia rugosoannulata4 皱孔菌科
Meruliaceae射脉菌属
Phlebia1 2.00 胶质射脉革菌
Phlebia tremellosa1 多孔菌科
Polyporales多孔菌属
Polyporus2 4.00 漏斗多孔菌
Polyporus arcularius2 裂褶菌科
Schizophyllaceae裂褶菌属
Schizophyllum3 6.00 裂褶菌
Schizophyllum commune3 接合菌门
Zygomycota毛霉菌科 Mucoraceae 毛霉属 Mucor 8 16.00 不规则毛霉
Mucor irregularis2 冻土毛霉
Mucor hiemalis6 子囊菌门
Ascomycota丛赤壳科
Nectriaceae镰刀菌属
Fusarium12 24.00 禾谷镰刀菌
Fusarium graminearum6 木贼镰刀菌
Fusarium equiseti3 尖孢镰刀菌
Fusarium oxysporum3 瘤座孢科
Tubeculariaceae漆斑菌属
Myrothecium1 2.00 Myrothecium sp. 1 生赤壳科
Bionectriaceae粘帚霉菌属
Clonostachys3 6.00 粉红粘帚菌
Clonostachys rosea3 梨孢假壳科
Apiosporaceae节菱孢属
Arthrinium3 6.00 暗孢节菱孢菌
Arthrinium phaeospermum3 革菌科
Coriolaceae蜡孔菌属
Ceriporia1 2.00 撕裂蜡孔菌
Ceriporia lacerata1 曲霉科
Aspergillaceae青霉属 Penicillium 1 2.00 Penicillium aquaticum 1 曲霉属 Aspergillus 3 6.00 烟曲霉 Aspergillus fumigatus 1 聚多曲霉 Aspergillus sydowii 2 山野壳菌科
Montagnulaceae小球壳孢属
Microsphaeropsis3 6.00 Microsphaeropsis amaranthi 3 未定义 Leiothecium 1 2.00 Leiothecium ellipsoideum 1 Parengyodontium 1 2.00 Parengyodontium album 1 从多样性指数上看,冬小包脚菇子实体内生真菌Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(H)为2.45,Simpson指数(D)为0.88,均匀度指数Pielou(J)为0.88,Margalef丰富度指数(R)为3.83。这表明冬小包脚菇子实体可培养内生真菌较为复杂,将增大该菇子实体分离难度。
2.3 冬小包脚菇菌基土壤真菌菌群组成及其系统发育关系
由表2可知,3个土壤样品的文库覆盖率均大于99%,表明注释结果能够反映样品中菌基土壤真菌群落的真实情况。通过比较3个土壤中的Shannon指数、Simpson指数、Chao指数以及Ace指数可知,冬小包脚菇不同菌基土壤真菌多样性有一定差异,但普遍较为复杂,且平均Ace指数达298.7,Shannon指数达3.53,Simpson指数为0.08,Chao指数为304.23。
表 2 Alpha多样性指数分析Table 2. Alpha diversity index analysis土壤样品
Soil sample序列数
NumberAce指数
Ace indexShannon指数
Shannon indexSimpson指数
Simpson indexChao指数
Chao index覆盖度
Coverage/%S1 60290.00 334.90 3.11 0.12 341.14 99.88 S2 71619.00 283.08 4.05 0.04 292.00 99.95 S3 71849.00 278.25 3.44 0.08 279.56 99.94 平均值 Mean 67919.33 298.74 3.53 0.08 304.23 — 由冬小包脚菇3个菌基土壤样品共检测出276种土壤真菌,归属于10门131科213属。如图2所示,在属水平上,冬小包脚菇3个菌基土壤真菌中被鉴定出来相对丰度大于1%的属有被孢霉属(Mortierella)、枝顶孢属(Acremonium)、尾孢菌属(Cercophora)、鬼伞属(coprinellus)、翅孢壳属(Emericellopsis)、镰刀菌属(Fusarium)、膝梗孢属(Gonytrichum)、烧瓶状霉属(Lecythophora)、瓶毛壳属(Lophotrichus)、绿僵菌属(Metarhizium)、油壶菌属(Olpidium)、小盘菌属(Pezizella)、癣囊腔菌属(Plestosphaerella)、假散囊菌属(Pseudeurotium)、木霉属(Trichoderma)、绿核菌属(Ustilaginoidea)、托光柄菇属(Volvopluteus)、韦斯特壳属(Westerdykella)、Eleutherascus、Pseudaleuria、Ticharina、Apiotrichum、Cistella及仅知道较大分类单元的未定义属11个,包括Unclassified_o_Sodariales、Unclassified_c_Sodariomycetes、Unclassified_p_Mortierellomycota、Unclassified_o_Hypocreales、Unclassified_o_Glomerellales、Unclassified_o_Rozellomycota、Unclassified_f_Pyronemataceae、Unclassified_f_Lasiosphaeriaceae、Unclassified_f_Nectriaceae、Unclassified_p_Chytridiomycota、Unclassified_f_Chaetomiaceae。所有属在3个土样中均有发现,但相对丰度差距很大。以相对丰度大于3%的属为优势属,土样S1的优势属有Mortierella(20.59%)、Unclassified_o_Sodariales(17.13%)、Westerdykella(6.67%)、Metarhizium(6.17%)、Unclassified_c_Sodariomycetes(3.69%)、Pseudaleuria(3.48%)、Lophotrichus(3.45%)、Unclassfied_f_Pyronemataceae(3.42%);土样S2的优势属有Pseudaleuria(28.28%)、Lophotrichus(16.72%)、Mortierella(14.81%)、Eleutherascus(6.50%)、Coprinellus(4.15%)、Unclassified_o_Hypocreales(3.05%);土样S3的优势属有Unclassified_c_Sodariomycetes(16.00%)、Mortierella(12.88%)、Cercophora(6.06%)、Unclassified_o_Sodariales(5.52%)、Pseudeurotium(5.38%)、Volvopluteus(4.62%)、Tricharina(3.76%)、Lecythophora(3.67%)、Unclassified_p_Mortierellomycota(3.66%);其中仅Mortierella为3个土样共有优势属。而综合3个土样真菌组成,冬小包脚菇菌基土壤优势属有Mortierella(16.10%)、Pseudaleuria(10.64%)、unclassified_o_Sordariales(7.74%)、Lophotrichus(6.91%)、unclassified_c_Sordariomycetes(6.86%)、Pseudeurotium(3.47%)。除Mortierella属于被孢霉门(Mortierellomycota)外,其余属均属于子囊菌门(Ascomycota)。
3. 讨论
潘高潮等提出冬小包脚菇子实体生长发育所需的温度约在6~12 ℃,生长基物水分含量33%~60%,相对湿度一般达60%以上[8],子实体多发生于雨后,这表明冬小包脚菇是一种喜低温高湿出菇的食用菌,子实体含水量高、菌丝体较弱和生长速度慢的特性制约了该菇的分离和培养。本研究采用传统组织分离法对冬小包脚菇子实体进行分离培养及鉴定,得到了冬小包脚菇纯菌株及其可培养内生真菌菌株50个。初步研究了冬小包脚菇系统发育关系,发现冬小包脚菇属于Volvopluteus类群,也可属于传统定义的Volvariella类群。因为Volvopluteus是2011年由Justo等从传统Volvariella类群中分出来的新类群,中文名为托光柄菇属,而冬小包脚菇早在1987年就已被命名[2,10-12]。在系统发育关系中,冬小包脚菇同粘盖包脚菇(Volvopluteus gloiocephalus)亲缘性较近,但二者在子实体菌盖颜色和发生季节等方面都存在明显差异[13]。在3个冬小包脚菇菌基土壤中也发现了一定量的Volvopluteus类群序列,这说明冬小包脚菇菌基土壤中含有大量自身菌丝或孢子,这也是冬小包脚菇出菇的前提。而除Volvopluteus属外,经高通量测序鉴定出来的土壤真菌相对丰度超过1%的属超过30属,其中相对丰度最大的优势属是被孢霉属,在本研究所用的分类系统上归属于被孢霉门被孢霉科,但很多时候也被分类学家归属于接合菌门被孢霉科[14-16],该属真菌主要腐生于土壤,属下有些物种可能与植物形成共生关系[17-18],这对改善土壤的结构性质、促进植物的生长起一定的作用。但被孢霉属有些物种也能引起动植物甚至其他微生物发生病变,例如贝勒被孢霉(Mortiereiia bainieri)能在双孢蘑菇(Agaricus bisporus)上寄生引起菌柄粗糙病,沃尔夫被抱霉(Mortiereiia wolfii)可以引起人和动物病害,比如牛霉菌性流产、全身性真菌病肺炎[19-21]。而被孢霉属下真菌大多数是嗜冷真菌[22-23],同冬小包脚菇一样嗜好低温,这可能是冬小包脚菇菌基土壤中检测出大量的被孢霉属真菌的原因之一。此外,冬小包脚菇常见发生地是水稻和油菜轮作农用地,不可避免的长期施肥也会致使农田土壤中被孢霉数量增加[24-25]。劳承英等通过高通量测序对不同耕作方式下水稻根际土壤真菌群落组成研究中也表明其土壤中被孢霉属相对丰度较高,为优势菌属,且鉴定到的其他优势类群同本研究中冬小包脚菇菌基土壤真菌相对丰度大于1%的类群相同的还有镰刀菌属、枝顶孢属、韦斯特壳属、绿僵菌属等[26],这表明冬小包脚菇菌基土壤真菌物种组成同水稻根际土壤真菌有一定相似之处。尽管冬小包脚菇菌基土壤中被孢霉属真菌占比最大,但其可培养内生真菌中尚未分离鉴定出被孢霉属真菌,但这并不能排除菌基土壤中的被孢霉具备侵染冬小包脚菇能力的可能性。土壤中的被孢霉在冬小包脚菇生长过程中起着什么样的作用尚无法定论,还需进一步针对性研究,但能明确知道的是被孢霉属下真菌对冬小包脚菇母种菌株分离造成的负面影响较小。
而在分离过程中对冬小包脚菇纯菌株获得影响最大的是其内生真菌镰刀菌属真菌,其次为毛霉属。镰刀菌属是冬小包脚菇可培养内生真菌最大优势菌群,且该属真菌在3个菌基土壤样品中均有发现,虽不是菌基土壤真菌优势属,但在所得属中相对丰度较高,这表明冬小包脚菇生长过程中容易被镰刀菌侵染,分离过程中受镰刀菌影响也较大。在多数植物内生真菌组成中均可发现镰刀菌,且往往被确定为优势菌群[27-29],这同本研究所得结果相似。水稻和油菜作为冬小包脚菇发生地的主要农作物,其根部内生真菌组成中镰刀菌属相对丰度也较大,通常也为优势菌群[30-31]。尽管某些学者提出镰刀菌在一定程度上能够降解环境中有毒物质[32],但目前研究较多的是其致病机理。作为一种土壤中广泛分布的致病菌,镰刀菌具有致病范围广和致病能力强等特点[33],其中大多数是导致多种农作物病害的病原真菌,如镰刀菌可引起马铃薯干腐病[34]、西葫芦根腐病[35-36]、西瓜枯萎病[37]等多种病害。但Le等从栽培水稻中分离到一株内生真菌Fusarium spp.
可用于根结线虫的生物防治[38],这表明对于宿主来说,镰刀菌也可为有益菌。而在冬小包脚菇可培养内生真菌中毛霉属是相对丰度仅次于镰刀菌属的优势属。且该属真菌并未在冬小包脚菇菌基土壤真菌中被明确鉴定,这很大可能是土壤中毛霉属菌丝或孢子相对占比较少,在高通量测序结果中不明显,也可能是所采土壤有限所致,还有就是该种内生真菌的传播途径并非仅来源于土壤,还可能受空气或枯枝落叶层等的影响[39]。 除此之外,冬小包脚菇可培养内生真菌中还含有相对丰度达26%的担子菌门类群,具体包括球盖菇属、烟管菌属、裂褶菌属、多孔菌属和射脉菌属,同其他内生真菌不同,这类菌群在适宜条件下均能发育形成子实体,这不仅在大型真菌子实体分离中较为少见,甚至在植物可培养内生真菌分离培养中也是不常见的。这类内生真菌传播来源是多途径的,并增大冬小包脚菇菌株的分离难度。
而冬小包脚菇菌基土壤已鉴定出的已知真菌除主要优势属被孢霉属和主要属镰刀菌属外,还有其他致病菌和竞争菌,同时也含有一定量的抗病菌。如尾孢菌属真菌能侵染寄主,可引致叶斑、疫病、果斑和果腐等[40-41]。黄瓜油壶菌(Olpidium bornovanus)可能是造成甜瓜藤蔓凋萎的病原体之一[42]。而绿僵菌能有效感染马尾松毛虫(Dendrolimus punctatus)和榕管蓟马(Gynaikothrips uzeli)成虫,起到生物防治作用[43-44]。这些土壤真菌是否将成为冬小包脚菇栽培过程中的主要致病菌或抑虫菌仍需进一步研究。木霉属真菌能够产生多种次级代谢产物抗植物病原真菌活性、促进植物生长活性、抗酵母活性、抗细菌活性、抗病毒活性等,广泛应用于植物病害防治,并在生物及其医药领域有一定的应用价值[45-47],但对于草菇来说,木霉属真菌却是难以根治的病害,且有研究表明鬼伞属也是草菇栽培种极为常见且难以控制的竞争性杂菌[48-49]。而素来有着“低温草菇”称号的冬小包脚菇,菌丝生长较普通草菇更慢,生长条件更苛刻,很大程度上也会受此类真菌的影响,在今后栽培试验中应多加防控。
4. 结论
本研究对冬小包脚菇系统发育关系、子实体可培养内生真菌和菌基土壤真菌菌群组成进行了研究,表明冬小包脚菇属于 Volvopluteus 类群,也可属于传统定义的 Volvariella 类群,冬小包脚菇内生真菌中的镰刀菌属和毛霉属为优势属,菌基土壤优势属为被孢霉属、瓶毛壳属、假散囊菌属、 Pseudaleuria 和两个未定义属 unclassified _ o _ Sordariales 、 unclassified _ c _ Sordariomycetes ,不同土壤样本间共有优势属为被孢霉属;并探讨了主要功能真菌的作用,为冬小包脚菇纯菌株的获得、人工驯化栽培及病虫害防控的研究奠定理论基础。但有关冬小包脚菇与菌基土壤真菌的相互作用及其调控机制,有待进一步深入研究。
-
表 1 冬小包脚菇可培养内生真菌菌群组成
Table 1 Composition of culturable endophytes in V. brumalis
门 Phylum 科 Family 属 Genus 菌株数
Number of strains相对丰度
Relative abundance/%相似种
Similar species菌株数
Number of strains担子菌门
Basidomycota原毛平革菌科
Phanerochaetaceae烟管菌属
Bjerkandera3 6.00 烟管菌
Bjerkandera adusta3 球盖菇科
Strophariaceae球盖菇属
Stropharia4 8.00 大球盖菇
Stropharia rugosoannulata4 皱孔菌科
Meruliaceae射脉菌属
Phlebia1 2.00 胶质射脉革菌
Phlebia tremellosa1 多孔菌科
Polyporales多孔菌属
Polyporus2 4.00 漏斗多孔菌
Polyporus arcularius2 裂褶菌科
Schizophyllaceae裂褶菌属
Schizophyllum3 6.00 裂褶菌
Schizophyllum commune3 接合菌门
Zygomycota毛霉菌科 Mucoraceae 毛霉属 Mucor 8 16.00 不规则毛霉
Mucor irregularis2 冻土毛霉
Mucor hiemalis6 子囊菌门
Ascomycota丛赤壳科
Nectriaceae镰刀菌属
Fusarium12 24.00 禾谷镰刀菌
Fusarium graminearum6 木贼镰刀菌
Fusarium equiseti3 尖孢镰刀菌
Fusarium oxysporum3 瘤座孢科
Tubeculariaceae漆斑菌属
Myrothecium1 2.00 Myrothecium sp. 1 生赤壳科
Bionectriaceae粘帚霉菌属
Clonostachys3 6.00 粉红粘帚菌
Clonostachys rosea3 梨孢假壳科
Apiosporaceae节菱孢属
Arthrinium3 6.00 暗孢节菱孢菌
Arthrinium phaeospermum3 革菌科
Coriolaceae蜡孔菌属
Ceriporia1 2.00 撕裂蜡孔菌
Ceriporia lacerata1 曲霉科
Aspergillaceae青霉属 Penicillium 1 2.00 Penicillium aquaticum 1 曲霉属 Aspergillus 3 6.00 烟曲霉 Aspergillus fumigatus 1 聚多曲霉 Aspergillus sydowii 2 山野壳菌科
Montagnulaceae小球壳孢属
Microsphaeropsis3 6.00 Microsphaeropsis amaranthi 3 未定义 Leiothecium 1 2.00 Leiothecium ellipsoideum 1 Parengyodontium 1 2.00 Parengyodontium album 1 表 2 Alpha多样性指数分析
Table 2 Alpha diversity index analysis
土壤样品
Soil sample序列数
NumberAce指数
Ace indexShannon指数
Shannon indexSimpson指数
Simpson indexChao指数
Chao index覆盖度
Coverage/%S1 60290.00 334.90 3.11 0.12 341.14 99.88 S2 71619.00 283.08 4.05 0.04 292.00 99.95 S3 71849.00 278.25 3.44 0.08 279.56 99.94 平均值 Mean 67919.33 298.74 3.53 0.08 304.23 — -
[1] 何绍昌, 冯丽. 小包脚菇属一新种 [J]. 真菌学报, 1987, 6(3):150−152. HE S C, FENG L. A new species of the genus volvariella from Guizhou Province of China [J]. Mycosystema, 1987, 6(3): 150−152.(in Chinese)
[2] 连宾, 何绍昌, 张林, 何应华. 新型食用真菌冬小包脚菇(Volvariella brumalis)的生物学特性及营养分析 [J]. 西南农业学报, 1998, 11(1):126−128. LIAN B, HE S C, ZHANG L, et al. Biological charaeters and nutrition analysis for A newly found edible fungus, Volvariella brumalis [J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 1998, 11(1): 126−128.(in Chinese)
[3] 李瑞容, 林俊芳, 郑倩望, 等. 草菇采后生物学特性变化及保鲜技术研究进展 [J]. 中国蔬菜, 2021(6):27−33. DOI: 10.19928/j.cnki.1000-6346.2021.2017 LI R R, LIN J F, ZHENG Q W, et al. Changes in biological characteristics of postharvest mushroom (Volvariella volvacea) and research progress in quality preservation technology [J]. China Vegetables, 2021(6): 27−33.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.19928/j.cnki.1000-6346.2021.2017
[4] 秦惠娟, 陈屏, 王琦, 等. 草菇的化学成分、生物活性及栽培现状 [J]. 食品工业, 2017, 38(3):203−206. QIN H J, CHEN P, WANG Q, et al. The chemical composition, biological activity and cultivation situation of straw mushroom [J]. The Food Industry, 2017, 38(3): 203−206.(in Chinese)
[5] CHEN B, WU G, LI L, et al. Effects of 1-methylcyclopropene on the quality attributes of harvested Chinese mushroom (Volvariella volvacea) fruiting bodies [J]. Food Science & Nutrition, 2019, 7(2): 747−754.
[6] 赵妍, 查磊, 陈明杰, 等. 草菇4℃贮藏期间的品质及生理生化研究 [J]. 分子植物育种, 2018, 16(21):7179−7186. DOI: 10.13271/j.mpb.016.007179 ZHAO Y, ZHA L, CHEN M J, et al. Morphological and physiological indexes of straw mushroom(Volvariella volvacea) during storage at 4℃ [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2018, 16(21): 7179−7186.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13271/j.mpb.016.007179
[7] 邹方伦. 贵州冬小包脚菇的生态及成分的初步研究 [J]. 贵州农业科学, 1997, 25(4):57−58. ZOU F L. Preliminary study on ecology and composition of Pleurotus eryngii in Guizhou [J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 1997, 25(4): 57−58.(in Chinese)
[8] 潘高潮, 龙汉武, 陈宵, 等. 贵州冬小包脚菇生境调查分析 [J]. 中国食用菌, 2013, 32(6):7−9. DOI: 10.13629/j.cnki.53-1054.2013.06.012 PAN G C, LONG H W, CHEN X, et al. Analysis on habitat of Volvariella brumalis in Guizhou Province [J]. Edible Fungi of China, 2013, 32(6): 7−9.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13629/j.cnki.53-1054.2013.06.012
[9] 孙燕, 龙汉武, 邹方伦, 等. 冬小包脚菇形态特征及显微结构观察 [J]. 贵州科学, 2016, 34(5):22−24. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6563.2016.05.006 SUN Y, LONG H W, ZOU F L, et al. Morphological characteristics and microscopic structure of Volvariella brumalis [J]. Guizhou Science, 2016, 34(5): 22−24.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6563.2016.05.006
[10] JUSTO A, MINNIS A M, GHIGNONE S, et al. Species recognition in Pluteus and Volvopluteus (Pluteaceae, Agaricales): Morphology, geography and phylogeny [J]. Mycological Progress, 2011, 10(4): 453−479. DOI: 10.1007/s11557-010-0716-z
[11] JUSTO A, CASTRO M L. An annotated checklist of Volvariella in the Iberian Peninsula and Balearic Islands [J]. Mycotaxon, 2010, 112: 271−273. DOI: 10.5248/112.271
[12] JUSTO A, CASTRO M L. The genus Volvariella in Spain: V. dunensis comb. & stat. nov. and observations on V. earlei [J]. Mycotaxon, 2010, 112: 261−270. DOI: 10.5248/112.261
[13] 徐江. 中国光柄菇属和小包脚菇属分类学研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2016: 117. XU J. Taxonomy of Pluteus and Volvariella from china[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2016: 117
[14] HIBBETT D S, BINDER M, BISCHOFF J F, et al. A higher-level phylogenetic classification of the Fungi [J]. Mycological Research., 2007, 111(5): 509−547. DOI: 10.1016/j.mycres.2007.03.004
[15] HOFFMANN K, PAWŁOWSKA J, WALTHER G, et al. The family structure of the Mucorales: A synoptic revision based on comprehensive multigene-genealogies [J]. Persoonia, 2013, 30: 57−76. DOI: 10.3767/003158513X666259
[16] SPATAFORA J W, CHANG Y, BENNY G L, et al. A Phylum-level phylogenetic classification of zygomycete fungi based on genome-scale data [J]. Mycologia, 2016, 108(5): 1028−1046. DOI: 10.3852/16-042
[17] WANI Z A, KUMAR A, SULTAN P, et al. Mortierella alpina CS10E4, an oleaginous fungal endophyte of Crocus sativus L. enhances apocarotenoid biosynthesis and stress tolerance in the host plant [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 8598. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-08974-z
[18] JOHNSON J M, LUDWIG A, FURCH A C U, et al. The beneficial root-colonizing fungus Mortierella hyalina promotes the aerial growth of Arabidopsis and activates calcium-dependent responses that restrict Alternaria brassicae-induced disease development in roots [J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2019, 32(3): 351−363. DOI: 10.1094/MPMI-05-18-0115-R
[19] HOOG G S D, GUARRO J , GENÉ J, et al. Atlas of Clinical Fungi[M]. 3rd Edition. Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures, Utrecht, The Netherlands/Universitat Rovira I Virgilli, Reus, Spain, 2009.
[20] MUNDAY J, WOLFE A, LAWRENCE K, et al. Disseminated Mortierella wolfii infection in a neonatal calf [J]. New Zealand Veterinary Journal, 2010, 58(1): 62−63. DOI: 10.1080/00480169.2010.65062
[21] 刘泽. 中国被孢霉属及近缘属的分类与分子系统发育研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2020: 1-2. LIU Z. Studies on the taxonomy and molecular phylogeny of Mortierella and allied Genera in china[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2020: 1-2.
[22] MARGESIN R, SCHINNER F. Properties of cold-adapted microorganisms and their potential role in biotechnology [J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 1994, 33(1): 1−14. DOI: 10.1016/0168-1656(94)90093-0
[23] FIEDUREK J, TRYTEK M, SKOWRONEK M. Strategies for improving the efficiency of bioprocesses involving toxic compounds [J]. Current Organic Chemistry, 2012, 16(24): 2946−2960. DOI: 10.2174/138527212804546732
[24] FRANCIOLI D, SCHULZ E, LENTENDU G, et al. Mineral vs. Organic amendments: Microbial community structure, activity and abundance of agriculturally relevant microbes are driven by long-term fertilization strategies. [J]. Frontiers in microbiology, 2016(7): 1446.
[25] NING Q, CHEN L, JIA Z J, et al. Multiple long-term observations reveal a strategy for soil pH-dependent fertilization and fungal communities in support of agricultural production [J]. Agriculture Ecosystems and Environment, 2019, 293(C): 106837.
[26] 劳承英, 申章佑, 李艳英, 等. 基于高通量测序技术分析不同耕作方式下水稻根际土壤真菌多样性 [J]. 热带作物学报, 2021, 42(9):2717−2726. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2021.09.038 LAO C Y, SHEN Z Y, LI Y Y, et al. Diversity analysis of fungal in rhizosphere soils of rice under different tillage methods based on high-throughput sequencing technique [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2021, 42(9): 2717−2726.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2021.09.038
[27] 陈梦, 陈敬忠, 刘济明, 等. 小蓬竹根际土壤微生物及内生真菌多样性分析 [J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(10):4120−4130. CHEN M, CHEN J Z, LIU J M, et al. Diversity analysis of rhizosphere soil fungi and endophytic fungi in Ampelocalamus luodianensis [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(10): 4120−4130.(in Chinese)
[28] 张青青, 董醇波, 梁宗琦, 等. 不同产地杜仲树皮可培养内生真菌群落组成和多样性 [J]. 菌物学报, 2021, 40(10):2685−2699. DOI: 10.13346/j.mycosystema.210120 ZHANG Q Q, DONG C B, LIANG Z Q, et al. Community composition and diversity of culturable endophytic fungi in bark of Eucommia ulmoides from different regions of China [J]. Mycosystema, 2021, 40(10): 2685−2699.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13346/j.mycosystema.210120
[29] 王世伟, 王卿惠, 李小鹏, 等. 镰刀菌分子鉴定与重要应用的研究进展 [J]. 微生物学通报, 2018, 45(4):907−919. DOI: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.170419 WANG S W, WANG Q H, LI X P, et al. Progress in molecular identification in the genus Fusarium and its important applications [J]. Microbiology China, 2018, 45(4): 907−919.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.170419
[30] 田新莉, 蔡爱群, 曹理想, 等. 水稻内生真菌类群分析及其颉抗病原菌活性研究 [J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 44(2):69−73. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0529-6579.2005.02.018 TIAN X L, CAI A Q, CAO L X, et al. Studies on communities of endophytic fungi from rice and their antipathogenic activities in vitro [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2005, 44(2): 69−73.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0529-6579.2005.02.018
[31] 张清华. 油菜内生真菌的多样性及生防潜力评估[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2014. ZHANG Q H. Evaluation of the diversity and biocontrol potential of the endophytic fungi in oilseed rape[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2014.
[32] 蔡伟建, 潘俊雅, 李济吾. 镰刀菌(Fusarium sp. )对2, 4, 6-三氯苯酚的降解特性及其机制 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(9):3187−3192. CAI W J, PAN J Y, LI J W. Biodegradation characteristics and mechanism of 2, 4, 6-trichlorophenol by Fusarium sp. in solution [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2016, 36(9): 3187−3192.(in Chinese)
[33] 谢安娜, 徐浩飞, 张志林, 等. 致病镰刀菌的研究进展 [J]. 湖北工程学院学报, 2020, 40(6):37−41. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4824.2020.06.009 XIE A N, XU H F, ZHANG Z L, et al. Research development of Fusarium [J]. Journal of Hubei Engineering University, 2020, 40(6): 37−41.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4824.2020.06.009
[34] 徐雪雪, 王东, 秦舒浩, 等. 沟垄覆膜连作马铃薯根际土壤真菌多样性分析 [J]. 水土保持学报, 2015, 29(6):301−306,310. DOI: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2015.06.053 XU X X, WANG D, QIN S H, et al. Diversity analysis of fungal communities in potato continuous cropping soil under different patterns of ridge-furrow film mulching [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2015, 29(6): 301−306,310.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2015.06.053
[35] AGNIESZKA J, KRZYSZTOF S. Biodiversity of fungi colonising aboveground parts of zucchini ( Cucurbita pepo L. var.giromontina ) [J]. Folia Horticulturae, 2011, 23(1): 29−35. DOI: 10.2478/v10245-011-0005-6
[36] 孙广正, 姚拓, 侯栋, 等. 西葫芦根腐病菌拮抗细菌的防病促生作用 [J]. 微生物学通报, 2017, 44(5):1121−1130. DOI: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.160543 SUN G Z, YAO T, HOU D, et al. Biocontrol potential of antagonistic bacteria strains against Fusarium oxysporum and their growth-promoting effects on zucchini [J]. Microbiology China, 2017, 44(5): 1121−1130.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.160543
[37] XUE C, SHEN Z, HAO Y, et al. Fumigation coupled with bio-organic fertilizer for the suppression of watermelon Fusarium wilt disease reshapes the soil microbiome [J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2019, 140: 49−56. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2019.04.007
[38] LE H T T, PADGHAM J L, SIKORA R A. Biological control of the rice root-knot nematode Meloidogyne graminicola on rice, using endophytic and rhizosphere fungi [J]. International Journal of Pest Management, 2009, 55(1): 31−36. DOI: 10.1080/09670870802450235
[39] CARROLL G. Fungal Endophytes in Stems and Leaves: From Latent Pathogen to Mutualistic Symbiont [J]. Ecology, 1988, 69(1): 2−9. DOI: 10.2307/1943154
[40] CHUPP C. A Monograph of the Fungus Genus Cercospora [M]. Ithaca, New York: 1954.
[41] PONS N, SUTON B C. Cercospora and similar fungi on yams (Dioscorea spp. ) [J]. Mycol Pap, 1988, 160: 1−78.
[42] 明德南. 黄瓜油壶菌和瓜类坏死斑点病毒与危地马拉甜瓜藤蔓凋萎的关系 [J]. 世界热带农业信息, 2009(2):28. MING D N. Relationship between Curcuma cucumeris and Melon Necrosis Spot Virus and the wilting of melon vines in Guatemala [J]. World Tropical Agriculture Information, 2009(2): 28.(in Chinese)
[43] 曾丽琼, 何学友, 蔡守平, 等. 白僵菌和绿僵菌感染榕管蓟马成虫试验 [J]. 防护林科技, 2019(2):8−10. DOI: 10.13601/j.issn.1005-5215.2019.02.004 ZENG L Q, HE X Y, CAI S P, et al. Infection experiment of Metarhizium anisopliae and Beauveria bassiana against adults of Gynaikothrips uzeli [J]. Protection Forest Science and Technology, 2019(2): 8−10.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13601/j.issn.1005-5215.2019.02.004
[44] 蔡守平, 何学友, 曾丽琼, 等. 白僵菌和绿僵菌不同菌株对马尾松毛虫的致病力 [J]. 福建林业科技, 2018, 45(4):1−4,10. DOI: 10.13428/j.cnki.fjlk.2018.04.001 CAI S P, HE X Y, ZENG L Q, et al. Comparison of pathogenicity of different Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae strains against Dendrolimus punctatus [J]. Journal of Fujian Forestry Science and Technology, 2018, 45(4): 1−4,10.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13428/j.cnki.fjlk.2018.04.001
[45] INBAR J, ABRAMSKY M, COHEN D, et al. Plant growth enhancement and disease control byTrichoderma harzianum in vegetable seedlings grown under commercial conditions [J]. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 1994, 100(5): 337−346. DOI: 10.1007/BF01876444
[46] DEGENKOLB T, DIECKMANN R, NIELSEN K F, et al. The Trichoderma brevicompactum clade: A separate lineage with new species, new peptaibiotics, and mycotoxins [J]. Mycological Progress, 2008, 7(3): 177−219. DOI: 10.1007/s11557-008-0563-3
[47] MUKHERJEE P K, HORWITZ B A, KENERLEY C M. Secondary metabolism in Trichoderma: A genomic perspective[J]. Microbiology (Reading, England), 2012, 158(pt 1): 35-45.
[48] 黄毅. 食用菌栽培全一册[M]. 3版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2008. [49] 黄李琳. 草菇常见病虫害及其无公害防治技术 [J]. 福建农业科技, 2017(3):38−39. DOI: 10.13651/j.cnki.fjnykj.2017.03.015 HUANG L L. Common pests and diseases occurring in straw mushroom and its harmless control [J]. Fujian Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017(3): 38−39.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13651/j.cnki.fjnykj.2017.03.015
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 熊雪,李鹏,向准,黄静. 一株我国特有低温草菇菌株液体菌种发酵条件优化. 广东农业科学. 2024(10): 42-52 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




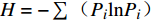
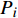
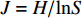
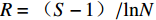

 下载:
下载:

