Phenotypic Diversity of 62 Handroanthus impetiginosus Plants
-
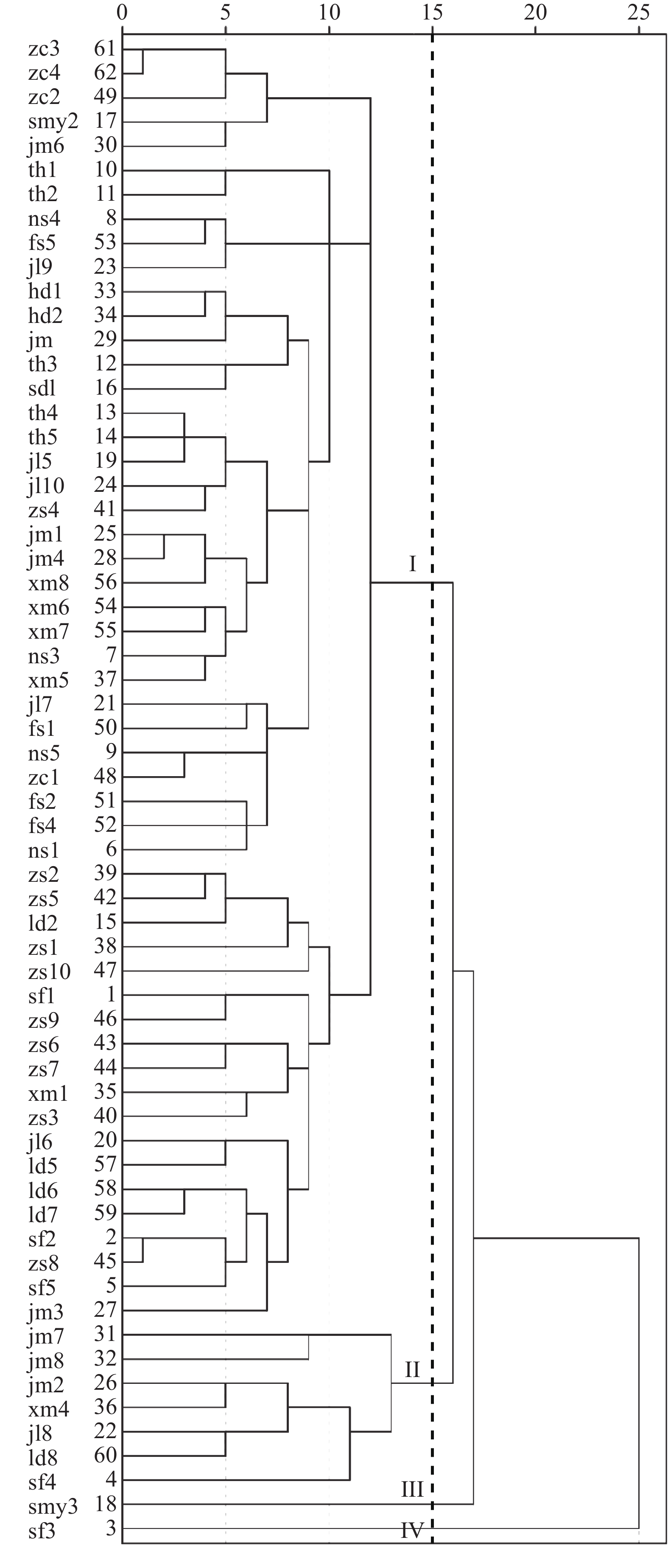
摘要:目的 紫花风铃木(Handroanthus impetiginosus)是我国南方广泛应用的一种园林观赏乔木,其表型性状存在较大的个体差异。通过对紫花风铃木表型多样性进行分析,了解其表型性状差异,可为紫花风铃木优质种质资源发掘和科学育种提供重要理论基础。方法 以广东省内6个城市12个群体62份紫花风铃木样本为材料,选取20个表型形状对样本进行变异度、Shannon多样性指数、相关性及主成分分析,并基于表型性状进行聚类分析。结果 紫花风铃木20个表型性状的变异系数为13.53%~59.13%,Shannon指数为0.79~4.08,表型性状变异性和多样性较高,具有丰富的表型性状多样性。相关性分析显示,叶性状相关的数量指标之间相互关联。主成分分析显示,从20个表型性状中提取6个主成分,其中叶宽、叶面积、小叶柄长、叶长、叶柄长等叶性状指标和胸径、枝下高等枝条与树干指标贡献较大。采用Hierarchical法进行表型性状聚类分析可将62份紫花风铃木材料划分为4大类群。结论 紫花风铃木具有较为丰富的表型变异性和多样性,其中与枝条和树干有关的指标变异系数最高,而叶性状相关指标的多样性较高。主成分分析显示贡献较大的为叶表型性状指标和枝条与树干指标。通过聚类分析可知第II类群中包含的个体花量较大,花色较深;而第I类群中存在开白花的个体,花色比较独特,均具有较好的观赏效果,可从中进一步筛选和繁殖优良品种。Abstract:Objective A popular ornamental tree for landscaping, Handroanthus impetiginosus tends to differ in phenotypic traits between individual plants. This study aimed to collect information on the resources for selection and cultivation.Method Twenty different phenotypic traits of 62 H. impetiginosus plants collected from 12 population groups in 6 cities of Guangdong Province were used to calculate coefficient of variation (CV) and Shannon diversity index as well as conduct correlation, principal component, and clustering analysis.Result The CVs of these phenotypic traits varied between 13.53%–59.13%, while the Shannon diversity index between 0.79–4.08. High CV and diversity index connotated richness in phenotype diversity of the species. Their qualitative indices differentiated more greatly than quantitative ones, and the qualitative indices correlated with one another. Among the 6 principal components in the 20 traits, the indices associated with leaf, including width, area, length, petiolule length, and petiole length, were the major contributors which were followed by those related to the branch and trunk diameters at breast height and under branch height. A hierarchical clustering analysis divided the 62 H. impetiginosus plants into 4 population groups based on their phenotypic characteristics.Conclusion H. impetiginosus was richly diverse phenotypically. The indices related to branch and trunk ranked highest on CV, while those associated with leaf greatest on diversity index. The principal components of the traits, such as leaf-, branch-, and trunk-related indices, largely determined the phenotype of H. impetiginosus plants. The population Group II plants as classified by the cluster analysis had more dark color flowers, whereas Group I carried distinctive, attractive white blossoms that were valued generally for landscaping, cultivation, and breeding purposes.
-
0. 引 言
【研究意义】沙门氏菌是最主要的病原微生物之一,由其引起的食物中毒占食物中毒病例的第1或第2位[1]。仅在2005—2011年,国外发生的19起蔬菜因病原微生物污染而引起的食源性疾病案例中,有11起是由沙门氏菌污染引起的,占比高达58%[2]。沙门氏菌也是我国食源性疾病的主要病原体,我国发生的细菌性食源性中毒事件中有80%左右由沙门氏菌引起[3]。国内已有多篇研究文献发现胡萝卜、香菜、香葱、生菜等新鲜蔬菜中存在沙门氏菌污染风险[4-6]。蔬菜的沙门氏菌污染可能发生在从农田到餐桌的每个环节[7-8],近年来,随着对蔬菜供应链主要环节中沙门氏菌污染风险和来源的深入研究,发现沙门氏菌污染风险虽然贯穿供应链的每个主要环节,但仍以栽培环节,特别是蔬菜栽培土壤中沙门氏菌污染风险最大,也是沙门氏菌检测和风险控制的重点[8-11]。【前人研究进展】目前环介导等温扩增技术(loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification,LAMP)已经运用到多种食品中沙门氏菌的快速检测中,因其具有快速、灵敏的优点备受关注。Hara-Kudo等[12]采用环介导等温扩增技术,可以检出沙门氏菌最低含量为2.2 CFU·管−1,并在1 h以内获得检测结果;张宏伟等[13]采用环介导等温扩增技术检测食品样品中沙门氏菌最低检出限为1.5 CFU·hg−1;王瑾等[14]采用实时荧光环介导等温扩增技术,可检测沙门氏菌最低含量为6 CFU·管−1,人工污染鸡肉的检出限为450 CFU·g−1,全程用时约7 h;Wu等[15]利用实时荧光定量环介导等温扩增技术对生菜中沙门氏菌进行检测,灵敏度达到了4 CFU.g−1,而检测过程仅需3 h左右;庞心怡等[16]采用环介导等温扩增技术快速检测肉类中沙门氏菌,对人工污染的沙门氏菌肉样检测灵敏度达98 CFU·mL−1,而全程仅用时15 h。【本研究切入点】目前对沙门氏菌检测多采用国标《食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 沙门氏菌检验》(GB 4789.4—2016)方法,但该方法需要对待检样品进行预增菌、选择性分离和生化试验鉴定,操作繁琐,耗时费力,仅筛选出沙门氏菌可疑菌落就需要3~4 d,后续的生化试验还需2~3 d[17],满足不了沙门氏菌快速检测的要求。而环介导等温扩增技术(loop-mediated isothermal amplification,LAMP)最早在2000年由日本科学家Notomi[18]发明,该技术可在恒温条件下(60~65 ℃)1h内完成核酸的高倍扩增,灵敏度比PCR技术高2~7个数量级,反应产物不仅可以通过琼脂糖电泳、浊度仪和定量PCR进行检测,也可以通过钙黄绿素、羟基萘酚蓝、SYBR Green I显色后观察[19, 20],目前已成功应用于沙门氏菌、蜡样芽孢杆菌、副溶血弧菌、志贺氏菌等多种病原微生物的检测[14, 21-23],但国内尚未见有关蔬菜栽培土壤中沙门氏菌LAMP检测方法的研究报道。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究以沙门氏菌特有侵袭蛋白A (invA)基因序列设计可视化LAMP检测引物,建立基于钙黄绿素显色的蔬菜栽培土壤中沙门氏菌可视化快速检测方法,以期为蔬菜栽培土壤中沙门氏菌的防控提供技术支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
1.1.1 蔬菜栽培土壤
供试蔬菜栽培土壤样品集自闽清县东桥镇绿辉蔬菜种植农场,样品按S型多点采集土壤表层(0~20 cm)的混合样,采样后立即用冰袋包装新鲜样品带回实验室,人工除去植物残体、根系和石头,过2 mm筛后测定土壤理化指标。供试蔬菜栽培土壤具体理化指标如下:土壤类型为黄红壤,0~20 cm土层pH值5.31,有机质含量16.61 g·kg−1,碱解氮含量126.54 mg·kg−1,速效磷含量18.25 mg·kg−1,速效钾含量113.79 mg·kg−1。
1.1.2 材料与试剂
胰蛋白胨大豆肉汤(TSB)、胰蛋白胨大豆琼脂(TSA)(北京陆桥技术有限责任公司),DL2000 Marker、dNTP(Takara公司),Bst 2.0 DNA polymerase(美国NEB公司),琼脂糖(西班牙Biowest),Betaine、Tween-20(上海生工),MnCl2、NaCl、Calcein(阿拉丁公司),FastDNA® Spin Kit for Soil试剂盒(美国MP Bio公司),无菌均质袋(北京陆桥)。
1.1.3 仪器与设备
PCR仪(BIO-RADTM S1000),凝胶成像系统(BIO-RADTM Gel Doc XR+),FastPrepTM FP120核酸提取仪(美国MP Bio公司),easyMixTM拍击式均质器(法国AES Chemunex公司),电泳仪及电源(北京六一仪器厂),恒温水浴锅(上海一恒),恒温培养箱(上海一恒)。
1.1.4 菌株
表1为供试7种微生物菌株,分别来自中国工业微生物菌种保藏管理中心(CICC)、中国普通微生物菌种保藏管理中心(CGMCC)和美国典型培养物保存中心(ATCC)。
表 1 供试菌株Table 1. Bacteria used for testing菌株名称 Strains name 拉丁学名 Scientific name of strains 菌株编号 Strains number 菌株来源 Source of strains 鼠伤寒沙门氏菌 Salmonella typhimurium 1.1174 CGMCC 金黄色葡萄球菌 Staphylococcus aureus 25923 ATCC 大肠埃希氏菌 Escherichia coli 25922 ATCC 产气肠杆菌 Enterobacter aerogenes 1.0876 CGMCC 大肠埃希氏菌O157:H7 Escherichia coli O157:H7 10907 CICC 单核细胞增生李斯特氏菌 Listeria monocytogenes 1.9136 CGMCC 英诺克李斯特氏菌 Listeria innocua 1.7730 CGMCC 1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 引物设计
根据Genbank登录的沙门氏菌特有侵袭蛋白A (invasion protein A,invA)基因序列(Accession: M90846.1),在网站(http://primerexplorer.jp/e/)上使用Primer Explorer 5.0在线软件设计3对LAMP引物用于沙门氏菌检测,包括1对外引物(F3/B3)、1对内引物(FIP/BIP)和1对环引物(Loop F/Loop B)。检测引物交由上海生工合成。具体检测引物序列见表2。
表 2 环介导等温扩增引物Table 2. Primers of LAMP引物
Primer序列
SequenceFIP 5′-GCGCGGCATCCGCATCAATATGCCCGGTAAACA
GATGAGT-3′BIP 5′-GAACGGCGAAGCGTACTGGACATCGCACCGTC
AAAGGAA-3′F3 5′-CGGCCCGATTTTCTCTGG-3′ B3 5′-CGGCAATAGCGTCACCTT-3′ Loop F 5′-GGCCTTCAAATCGGCATCAAT-3′ Loop B 5′-AAGGGAAAGCCAGCTTTACG-3′ 1.2.2 沙门氏菌培养、计数及基因组DNA提取
将TSA平板内活化的沙门氏菌,挑取单个菌落接种于5 mL TSB液体培养基中,37 ℃、180 r·min−1过夜培养15~18 h,以1∶100比例转接于100 mL TSB液体培养基,37 ℃、180 r·min−1培养3 h左右至细菌对数生长期(OD600≈0.55)。菌液使用生理盐水按10倍梯度依次稀释后,分别取100 μL不同浓度稀释液涂于TSA平板上,37 ℃倒置培养18~24 h计数。
沙门氏菌DNA模板采用热裂解法提取,取1 mL沙门氏菌菌液在台式离心机上10 000 r·min−1离心5 min,弃上清液,沉淀重悬于0.5 mL生理盐水,加入等体积2×TZ裂解液,于99.5 ℃加热10 min,冰上冷却2 min后,在10 000 r·min−1离心5 min,取上清液即为沙门氏菌DNA模板,−20 ℃保存备用。
1.2.3 LAMP反应体系和反应条件优化
分别对LAMP反应体系中dNTPs浓度、MgSO4浓度以及Betaine浓度,反应条件中反应温度和反应时间进行优化,其中dNTPs终浓度分别为0.8、1.2、1.6、2.0、2.4 mmol·L−1,MgSO4终浓度分别为2、4、6、8、10、12 mmol·L−1,Betaine终浓度分别为0.6、0.8、1.2、1.4、1.6 mol·L−1;反应温度分别设置58、59、60、61、62、63、64、65 ℃,反应时间分别为30、40、50、60、70、80、90 min。选用50 μmol·L−1 Calcein-500 μmol·L−1 MnCl2作为指示剂[24],阳性反应显绿色,阴性反应显橘黄色,每个因子设置3个重复,以确定最佳反应体系和反应条件。
1.2.4 LAMP反应特异性检测
分别以鼠伤寒沙门氏菌、金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠埃希氏菌、产气肠杆菌、大肠埃希氏菌O157:H7、单核细胞增生李斯特氏菌和英诺克李斯特氏菌菌株为材料,以热裂解法制备各菌株DNA,验证所建立LAMP检测方法的特异性。取1 μL各菌株的DNA作为模板,采取已优化的反应体系和条件进行特异性分析,反应结束后,以管内颜色变化来判断阴阳性,阳性为绿色,阴性为橘黄色;或将扩增产物在1.5%琼脂糖电泳上检测,阳性反应可观察到特征性梯形带,阴性反应则没有出现扩增条带。
1.2.5 LAMP反应灵敏度检测
以10倍递减将沙门氏菌浓度稀释为7×108~7×102 CFU·mL−1 7个梯度,以热裂解法提取沙门氏菌DNA,然后取1 μL不同含量的沙门氏菌DNA作为模板,对LAMP反应灵敏度进行检测。结果直接肉眼观察,阳性反应显绿色,阴性反应显橘黄色,同时在2%琼脂糖凝胶电泳上检测。
1.2.6 人工污染沙门氏菌的栽培土壤样品检测
取10 g经国标方法检测沙门氏菌阴性的蔬菜栽培土壤样品,置于装有90 mL蛋白胨缓冲水(BPW)的无菌均质袋中,分别加入灭菌生理盐水稀释至适宜含量的沙门氏菌0.5 mL,以制备含沙门氏菌含量为0、5×101、4×102、1×103、4×103、1×104、4×104、1×105 CFU·g−1的人工污染样品,将均质袋放置在拍击式均质器中拍打1 min,置37 ℃的恒温培养箱中预增菌4 h。预增菌后重新混匀土壤样品,吸取1 mL混匀土壤样品至FastDNA® Spin Kit for Soil试剂盒中的土壤裂解管中,12 000 r·min−1离心3 min,吸弃上清,然后在FastPrepTM FP120核酸提取仪上提取土壤微生物总DNA,100 μL溶解土壤微生物总DNA,取1 μL作为LAMP反应扩增模板。
1.2.7 蔬菜栽培土壤中沙门氏菌污染的检测
利用所建立的蔬菜栽培土壤中沙门氏菌LAMP检测方法对采自全省不同蔬菜产区的41份土壤样品进行沙门氏菌检测,同时采用国标方法(GB 4789.4—2016《食品微生物学检验 沙门氏菌检验》)进行检测分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 LAMP检测方法的建立
通过反应温度和时间进行优化,确定LAMP最适反应温度为65 ℃,反应时间为1 h。优化后蔬菜栽培土壤中沙门氏菌LAMP检测最佳反应体系25 μL包括:2.5 μL 10×Isothermal Amplification Buffer,1.4 mmol·L−1 dNTPs,0.2 μmol·L−1 F3-B3,1.6 μmol·L−1 FIP-BIP,0.4 μmol·L−1 Loop F~Loop B,0.8 mol·L−1 Betaine,6.0 mmol·L−1 MgSO4,8 U Bst 2.0 DNA polymerase,50 μmol·L−1 Calcein和500 μmol·L−1 MnCl2,DNA模板1 μl,灭菌超纯水补足25 μL体积。优化的LAMP反应效果如图1所示。
![]() 图 1 LAMP体系检测沙门氏菌注:A: LAMP产物琼脂糖电泳检测结果; B: LAMP产物钙黄绿素显色结果M: DL2 000 DNA Marker, 1: 鼠伤寒沙门氏菌, 2: 阴性对照Figure 1. Detection of Salmonella using optimized LAMP assayNote: A: LAMP products shown on 2.0% agarose gel electrophoresis; B: LAMP products after calcein staining; M: DL2 000 DNA marker; 1: S. typhimurium; 2: Negative control.
图 1 LAMP体系检测沙门氏菌注:A: LAMP产物琼脂糖电泳检测结果; B: LAMP产物钙黄绿素显色结果M: DL2 000 DNA Marker, 1: 鼠伤寒沙门氏菌, 2: 阴性对照Figure 1. Detection of Salmonella using optimized LAMP assayNote: A: LAMP products shown on 2.0% agarose gel electrophoresis; B: LAMP products after calcein staining; M: DL2 000 DNA marker; 1: S. typhimurium; 2: Negative control.2.2 特异性检测结果
分别以鼠伤寒沙门氏菌菌株和非沙门氏菌菌株的DNA为模板进行LAMP反应特异性分析,结果表明,在Calcein-MnCl2指示剂的作用下,65 ℃温育1 h后,鼠伤寒沙门氏菌LAMP反应产物显绿色,而供试6个非沙门氏菌菌株的LAMP反应产物均显橘黄色(图2-A)。进一步取2 μL扩增产物用2%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,结果除鼠伤寒沙门氏菌LAMP扩增产物出现梯形条带外,其他6个菌株均未出现任何条带(图2-B)。结果表明,本研究所建立的可视化LAMP检测方法对沙门氏菌具有良好的特异性。
![]() 图 2 LAMP方法检测沙门氏菌的特异性注:A:LAMP产物琼脂糖电泳检测结果,B:LAMP产物钙黄绿素显色结果;M:DL2 000 DNA Marker,1:阴性对照,2:鼠伤寒沙门氏菌,3:金黄色葡萄球菌,4:大肠埃希氏菌,5:产气肠杆菌,6:大肠埃希氏菌O157:H7,7:单核细胞增生李斯特氏菌,8:英诺克李斯特氏菌Figure 2. Specificity of LAMP assay in detecting SalmonellaNote: A: LAMP products shown on 2% agarose gel electrophoresis; B: LAMP products after calcein staining; M: DL2 000 DNA marker; 1: Negative control; 2: S. typhimurium; 3: Staphylococcus aureus; 4: Escherichia coli; 5: Enterobacter aerogenes; 6: E. coli O157:H7; 7: Listeria monocytogenes; 8: Listeria innocua.
图 2 LAMP方法检测沙门氏菌的特异性注:A:LAMP产物琼脂糖电泳检测结果,B:LAMP产物钙黄绿素显色结果;M:DL2 000 DNA Marker,1:阴性对照,2:鼠伤寒沙门氏菌,3:金黄色葡萄球菌,4:大肠埃希氏菌,5:产气肠杆菌,6:大肠埃希氏菌O157:H7,7:单核细胞增生李斯特氏菌,8:英诺克李斯特氏菌Figure 2. Specificity of LAMP assay in detecting SalmonellaNote: A: LAMP products shown on 2% agarose gel electrophoresis; B: LAMP products after calcein staining; M: DL2 000 DNA marker; 1: Negative control; 2: S. typhimurium; 3: Staphylococcus aureus; 4: Escherichia coli; 5: Enterobacter aerogenes; 6: E. coli O157:H7; 7: Listeria monocytogenes; 8: Listeria innocua.2.3 灵敏度检测结果
分别以7个不同含量沙门氏菌DNA为模板进行扩增来验证LAMP体系的灵敏度,琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测结果显示,在每管25 μL LAMP反应体系中沙门氏菌DNA含量为7×105~7 CFU时均可以出现LAMP产物特有的梯形条带(图3-A),而当沙门氏菌DNA含量为7 ×10−1 CFU时没有出现任何条带。可视化显色结果与琼脂糖凝胶电泳结果一致(图3-B),说明LAMP反应体系可以检测到7 CFU沙门氏菌DNA。
![]() 图 3 LAMP方法检测沙门氏菌的灵敏度注:A:LAMP产物琼脂糖电泳检测结果,B:LAMP产物钙黄绿素显色结果;M:DL2 000 DNA Marker,1:阴性对照,2~8:每管反应体系中分别含有7×105 CFU、7×104 CFU、7×103 CFU、7×102 CFU、7×101 CFU、7 CFU、7 ×10−1 CFUFigure 3. Sensitivity of LAMP assay in detecting SalmonellaNote: A: LAMP products shown on 2% agarose gel electrophoresis; B: LAMP products after calcein staining; M: DL2 000 DNA marker; 1: Negative control; 2-8: Amplified products using DNA at concentration of 7×105 CFU, 7×104 CFU, 7×103 CFU, 7×102 CFU, 7×101 CFU, 7 CFU, and 0.7 CFU, respectively, in LAMP reaction tube.
图 3 LAMP方法检测沙门氏菌的灵敏度注:A:LAMP产物琼脂糖电泳检测结果,B:LAMP产物钙黄绿素显色结果;M:DL2 000 DNA Marker,1:阴性对照,2~8:每管反应体系中分别含有7×105 CFU、7×104 CFU、7×103 CFU、7×102 CFU、7×101 CFU、7 CFU、7 ×10−1 CFUFigure 3. Sensitivity of LAMP assay in detecting SalmonellaNote: A: LAMP products shown on 2% agarose gel electrophoresis; B: LAMP products after calcein staining; M: DL2 000 DNA marker; 1: Negative control; 2-8: Amplified products using DNA at concentration of 7×105 CFU, 7×104 CFU, 7×103 CFU, 7×102 CFU, 7×101 CFU, 7 CFU, and 0.7 CFU, respectively, in LAMP reaction tube.2.4 人工污染沙门氏菌的栽培土壤样品检测结果
人工污染沙门氏菌的栽培土壤样品经37 ℃预增菌4 h后,提取土壤微生物总DNA进行扩增检测。分别设置0、5×101、4×102、1×103、4×103、1×104、4×104、1×105 CFU·g−1共7组不同梯度进行LAMP扩增检测。琼脂糖电泳结果显示,当LAMP反应体系中沙门氏菌含量为4×102~1×105 CFU·g−1时均可以出现LAMP产物特有的梯形条带(图4-A),而当沙门氏菌含量为5×101 CFU·g−1时没有出现任何条带。可视化显色结果与琼脂糖凝胶电泳结果一致(图4-B),说明本LAMP反应体系检测蔬菜栽培土壤样品灵敏度为4×102 CFU·g−1。
![]() 图 4 LAMP方法检测人工污染沙门氏菌的栽培土壤样品注:A:LAMP产物琼脂糖电泳检测结果;B:LAMP产物钙黄绿素显色结果;M:DL2 000 DNA Marker,1:阴性对照,2~8:不同含量人工污染沙门氏菌的栽培土壤样品扩增产物(0~1×105 CFU·g−1)Figure 4. LAMP assay for detecting artificially inoculated Salmonella in soil samplesNote: a: LAMP products shown on 2% agarose gel electrophoresis; B: LAMP products after calcein staining; M: DL2 000 DNA marker; 1: Negative control; 2-8: Amplified products on different concentrations of Salmonella in artificially inoculated soil samples (0-1×105 CFU·g−1).
图 4 LAMP方法检测人工污染沙门氏菌的栽培土壤样品注:A:LAMP产物琼脂糖电泳检测结果;B:LAMP产物钙黄绿素显色结果;M:DL2 000 DNA Marker,1:阴性对照,2~8:不同含量人工污染沙门氏菌的栽培土壤样品扩增产物(0~1×105 CFU·g−1)Figure 4. LAMP assay for detecting artificially inoculated Salmonella in soil samplesNote: a: LAMP products shown on 2% agarose gel electrophoresis; B: LAMP products after calcein staining; M: DL2 000 DNA marker; 1: Negative control; 2-8: Amplified products on different concentrations of Salmonella in artificially inoculated soil samples (0-1×105 CFU·g−1).2.5 蔬菜栽培土壤中沙门氏菌污染的检测结果
应用上述LAMP检测方法和国标检测法,同时对全省不同蔬菜产区的41份土壤样品进行沙门氏菌检测,结果见表3。2种方法都检测到2份沙门氏菌阳性样品和39份沙门氏菌阴性样品,LAMP检测方法与国标方法(GB 4789.4—2016《食品微生物学检验 沙门氏菌检验》)检测结果一致,而LAMP检测将国标方法检测时间由5~7 d缩短至8 h内,大幅减轻了检测强度,提高了检测效率。
表 3 2种方法对比检测蔬菜栽培土壤沙门氏菌污染结果Table 3. Salmonella detection in soil by two different methods方法
Method土壤样品
Soil samples阳性
Positive阴性
Negative国标方法 National standard method 41 2 39 LAMP方法 LAMP method 41 2 39 3. 讨论与结论
快速检测技术是监测和防控沙门氏菌等食源性疾病最重要的环节之一,而衡量快速检测技术性能最关键指标是检测用时与灵敏度。目前采用的国标检测方法《食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 沙门氏菌检验》(GB 4789.4—2016),需要对待检样品进行预增菌、选择性分离和生化试验鉴定等步骤,操作繁琐;最终拿到鉴定结果需要5~7d,耗时费力,难以满足沙门氏菌快速检测的要求。PCR方法虽然具有检测时间短、灵敏度高的特点,但需要专门的检测仪器(普通PCR仪或荧光定量PCR仪),而环介导等温扩增技术(loop-mediated isothermal amplification,LAMP)由于具有更高的灵敏度和视觉判断性的优点,且检测过程不需要专门的检测仪器,弥补了国标检测方法和PCR方法检测沙门氏菌的不足。
沙门氏菌侵袭蛋白(invasion protein)基因簇是沙门氏菌编码吸附和侵袭上皮细胞表面蛋白的基因,与沙门氏菌对肠道上皮细胞的侵袭有关,包括invA、invB、invC、invD、invE等基因,其中以invA基因应用最为广泛,目前根据invA基因序列设计特异性引物已成功应用于乳品、肉类、蔬菜等食品中沙门氏菌的检测[14, 15, 21]。本研究根据沙门氏菌侵袭蛋白A (invA)基因序列设计特异性LAMP引物,建立了一种基于颜色判定的简单、快速和灵敏的蔬菜栽培土壤中沙门氏菌的快速检测方法,对沙门氏菌纯菌检测灵敏度可达7 CFU/25 μL,人工污染的栽培土壤样品检测灵敏度为4×102 CFU·g−1。采用该LAMP方法与国标检测方法对比检测蔬菜栽培土壤中沙门氏菌污染,结果表明LAMP检测结果与国标方法检测结果一致,说明该方法能成功应用于蔬菜栽培土壤中沙门氏菌的快速检测,可为蔬菜栽培土壤中沙门氏菌污染的及时防控提供技术支撑。
-
表 1 62份紫花风铃木材料编号及来源
Table 1 Codes and origins of sampled 62 H. impetiginosus plants
来源
Origin地理坐标
Geographic coordinate城市
City样品名称
Name样品数量
Amounts of samples树龄
Ages/年花色
Color顺德区顺峰山
Mountain Shunfeng ,
Shunde District22°49′357″N
113°17′509″E佛山
Foshansf1,sf2,sf3,sf4,sf5 5 12−14 深粉红、粉红
Dark pink,pink三水区
Sanshui District23°19′181″N
112°59′137″E佛山
Foshanfs1,fs2,fs4,fs5 4 12−16 深粉红、紫红
Dark pink,fuchsia增城区
Zengcheng District23°24′375″N
113°34′393″E广州
Guangzhouzc1,zc2,zc3,zc4 4 6−8 白、紫红
White,fuchsia南沙区
Nansha District22°46′312″N
113°26′489″E广州
Guangzhouns1,ns3,ns4,ns5 4 5−12 深粉红、紫红
Dark pink,fuchsia天河区天河公园
Tianhe Park,Tianhe District23°07′768″N
113°21′810″E广州
Guangzhouth1,th2,th3,th4,th5 5 10 粉白、粉红、深粉红、紫红
Pinkish white,pink,dark
pink,fuchsia天河区龙洞
Longdong,Tianhe District23°12′356″N
113°22′440″E广州
Guangzhould2,ld5,ld6,ld7,ld8 5 10−12 深粉红
Dark pink天河区华南农业大学
SCAU,Tianhe District23°09′168″N
113°21′215″E广州
Guangzhousd1,smy2 2 5−10 粉红
Pink23°09′271″N
113°21′566″Esmy3 1 5 紫红
Fuchsia龙岗区金龙路
Jinlong Road,Longgang District22°35′838″N
114°02′594″E深圳
Shenzhenjl5,jl6, jl7,jl8,jl9,jl10 6 11 粉红、深粉红、紫红
Pink,dark pink,fuchsia福田区香蜜湖路
Xiangmihu Road, Futian District22°32′468″N
114°01′643″E深圳
Shenzhenxm1,xm4,xm5,xm6,xm7, xm8 6 13−15 深粉红、紫红
Dark pink,fuchsia共和镇
Gonghe Town22°34′406″N
112°50′863″E江门
Jiangmenjm1,jm2 2 10−14 紫红
Fuchsia新会镇
Xinhui Town22°32′128″N
112°58′853″E江门
Jiangmenjm3,jm4 2 8−12 深粉红
Dark pink22°31′593″N
112°59′533″Ejm5,jm6,jm7,jm8 4 6 深粉红
Dark pink惠东县
Huidong County22°56' 210"N
114°32' 380"E惠州
Huizhouhd1,hd2 2 5 粉红
Pink翠沙路
Cuisha Road
22°32′295″N
113°20′710″E中山
Zhongshanzs1,zs2,zs3,zs4,zs5,zs6,
zs7, zs8,zs9,zs1010 12−20 粉红、深粉红
Pink,dark pink总计 Total 62 表 2 紫花风铃木表型性状数量指标测定标准
Table 2 Scoring criteria on quantitative indices for phenotype traits of H. impetiginosus
性状 Phenotypic trait 评价标准 Evaluation criterion 叶面积 Leaf area/cm2 一片完整的复叶叶片所占的面积 The area of a fully expanded compound leaf 叶长 Leaf length/cm 一片完整复叶叶片的最长小叶叶尖到叶柄基部的距离
The length between leaf apex of the longest leaflet and the base of petiole in a fully expanded compound leaf叶宽 Leaf width/cm 一片完整复叶叶片中宽度最大的位置 The largest stage of width in a fully expanded compound leaf 叶宽长比 Leaf width/leaf length 叶宽与叶长之比 Ratio of leaf width to leaf length 形状系数 Leaf shape coefficient 参照文中所述的公式进行计算 Follow the formula in the passage for calculating 叶柄长 Petiole length/cm 复叶叶轴基部到叶片基部的距离 The length between rachis base of a compound leaf and leaf base
小叶柄长 Petiolule length/cm 组成复叶的小叶基部的柄长
The footstalks length of the base of leaflet on a fully expanded compound leaf
小叶柄长/叶长 Petiolule length/leaf length 小叶柄长与叶长之比 Ratio of petiolule length and leaf length 枝下高 Under branch height/cm 从地表面到树冠第一层分枝点的高度 The height between the floor and first layer of branch node 胸径 Diameter at breast height/cm 主干离地表面胸高处(1.3 m)的直径;断面畸形时,测取最大值和最小值的平均值
Diameter around the trunk at 1.3 meters above the floor. If the testing section is deformed,the average of maximum and minimum results is used花长 Flower length/cm 在一朵完整的单花上,长度为花瓣边缘到花基部的距离
The length between the margin of petal and the base of the flower within a full single flower花量 Amounts of flowers 测定时在一个完整的花序上单花的数量
Amounts of every single flower in a full inflorescence when observed表 3 紫花风铃木表型性状质量指标赋值标准
Table 3 Scoring criteria on qualitative indices for phenotype traits of H. impetiginosus
性状
Phenotypic trait赋值标准 Scoring criterion 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 叶尖
Leaf apex急尖
Acute渐尖
Acuminate长渐尖
Long acuminate骤尖
Cuspidate细尖
Apiculate尾尖
Caudate具芒
Aristate叶形
Leaf shape卵形
Oval卵圆
Ovoid椭圆
Ellipsoidal长椭圆
Oblong oval叶缘
Leaf margin光滑
Entire细锯齿
Serrulate锯齿
Serrate叶基
Leaf base偏斜
Oblique平滑
Glabrate楔形
Cuneate圆滑
Smooth花色
Flower color白色
White粉白
Pinkish white粉红
Pink深粉红
Dark pink紫红
Fuchsia开花时间/
(月−日)
Time of blossom11-15前
Before
November 15th11-15至
11-30
November 15th to
November 30th12-01至
12-15
December 1st to
December 15th12-16至
12-31
December 16th to
December 31st次年01-01
至01-15
January 1st to
January 15th in
next year次年01-16
至01-31
January 16th to
January 31st in
next year次年02-01
至02-15
February 1st to
February 15th in
next year次年02-16
至02-28
February 16th to
February 28th in
next year次年03-01
以后
After March 1st in
next year树皮颜色
Color of tree bark灰白
Greyish white灰棕
Greyish brown浅灰褐
Putty灰褐
Taupe灰黑
Ash black树皮状态
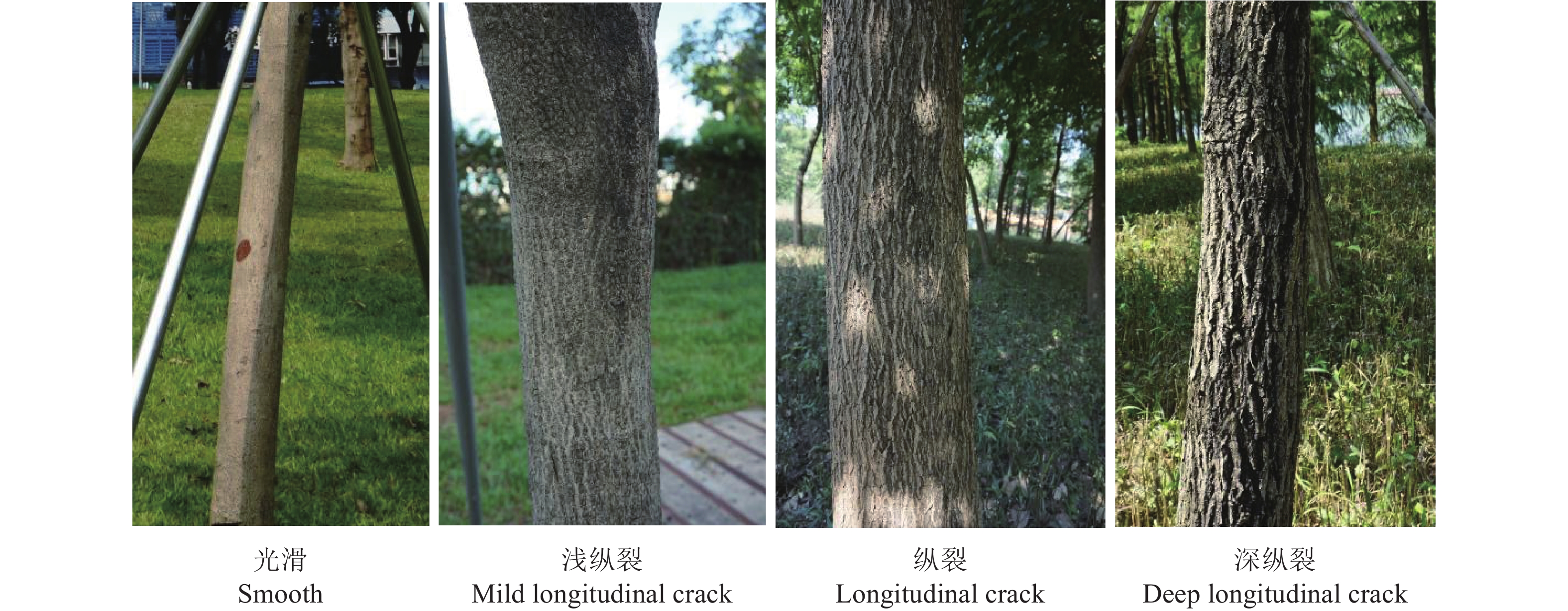
Condition of tree bark光滑
Smooth浅纵裂
Mild longitudinal crack纵裂
Longitudinal crack深纵裂
Deep longitudinal crack表 4 紫花风铃木表型性状的变异系数和Shannon多样性指数
Table 4 CVs and Shannon diversity indices of phenotype traits of H. impetiginosus
性状
Phenotypic trait极小值
Minimum极大值
Maximum平均值
Average标准差
SD变异系数
CVShannon 多样性指数
Shannon diversity index数量指标 Qualitative indices 叶面积 Leaf area/cm2 9.550 78.020 31.942 16.887 52.87% 4.08 叶长 Leaf length /cm 4.740 16.770 9.450 2.582 27.33% 4.06 叶宽 Leaf width /cm 2.420 7.620 4.515 1.310 29.02% 4.08 叶宽长比 Leaf width/leaf length 0.350 0.650 0.492 0.073 14.91% 3.17 形状系数 Leaf shape coefficient 0.400 0.710 0.535 0.072 13.53% 2.96 叶柄长 Petiole length/cm 3.100 20.000 9.155 3.085 33.70% 3.70 小叶柄长 Petiolule length/cm 0.820 6.560 2.467 0.869 35.23% 3.76 小叶柄长/叶长 Petiolule length/leaf length 0.140 0.470 0.266 0.073 27.46% 3.07 枝下高 Under branch height/cm 25.000 400.000 189.194 103.457 54.68% 3.10 胸径 Diameter at breast height/cm 2.000 40.000 14.806 7.368 49.76% 2.78 花长 Flower length/cm 7.000 18.000 12.548 2.386 19.02% 1.98 花量 Amounts of flowers 8.000 40.000 16.581 6.911 41.68% 2.48 质量指标 Quantitative indices 叶尖 Leaf apex 1.000 6.000 3.226 1.562 48.42% 1.26 叶缘 Leaf margin 1.000 5.000 3.419 1.542 45.10% 1.10 叶形 Leaf shape 1.000 7.000 4.452 2.086 46.85% 1.06 叶基 Leaf base 1.000 7.000 4.613 1.692 36.69% 0.79 树皮颜色 Color of tree bark 1.000 9.000 4.645 2.747 59.13% 1.21 树皮状态 Condition of tree bark 1.000 7.000 3.903 2.252 57.70% 1.58 花色 Flower color 1.000 9.000 6.419 1.860 28.98% 1.41 开花时间 Time of blossom 1.000 9.000 5.806 1.809 31.16% 1.36 表 5 紫花风铃木表型质量性状的频率分布
Table 5 Frequency distribution of qualitative phenotype traits of H. impetiginosus
性状 Phenotypic trait 频率分布 Frequency distribution 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 叶尖 Leaf apex 0.016 0.419 0.323 0.016 0.016 0.210 0.000 叶形 Leaf shape 0.210 0.080 0.484 0.226 叶缘 Leaf margin 0.210 0.371 — 0.419 叶基 Leaf base 0.145 0.016 0.742 0.097 花色 Flower color 0.048 0.016 0.274 0.500 0.162 开花时间
Time of blossom0.032 0.082 0.000 0.016 0.258 0.129 0.419 0.032 0.032 树皮颜色
Color of tree bark0.178 0.371 0.032 0.290 0.129 树皮状态
Condition of tree bark0.290 0.177 0.323 0.210 表 6 紫花风铃木表型性状相关性分析
Table 6 Correlation of phenotype traits of H. impetiginosus
指标
Indices叶面积
Leaf area叶长
Leaf length叶宽
Leaf width叶宽长比
Leaf width/leaf length形状系数
Leaf shape coefficient叶柄长
Petiole length小叶柄长
Petiolule length小叶柄长/叶长
Petiolule length/leaf length枝下高
Under branch height胸径
Diameter at breast height花长
Flower length花量
Amounts of flowers叶尖
Leaf apex叶缘
Leaf margin叶形
Leaf
shape叶基
Leaf base树皮颜色
Color of tree bark树皮状态
Condition of tree bark花色
Flower color开花时间
Time of blossom叶面积
Leaf area1.000 0.923 * * 0.951 * * 0.091 −0.103 0.452 * * 0.594 * * −0.116 0.070 −0.051 0.209 0.081 0.138 0.024 −0.291 * −0.313 * 0.049 −0.073 0.004 0.357 * * 叶长
Leaf length1.000 0.837 * * −0.197 −0.247 0.480 * * 0.554 * * −0.229 0.112 0.099 0.266 * 0.104 0.128 −0.037 −0.162 −0.199 0.046 −0.049 0.047 0.205 叶宽
Leaf width1.000 0.322 * −0.059 0.409 * * 0.596 * * −0.048 0.055 0.089 0.170 −0.020 0.202 0.086 −0.384 * * −0.368 * * 0.121 −0.035 −0.016 0.410 * * 叶宽长比
Leaf width/leaf length1.000 0.443 * * −0.126 0.074 0.237 −0.097 −0.007 −0.144 −0.178 0.065 0.193 −0.355 * * −0.316 * 0.210 0.003 −0.013 0.343 * * 形状系数
Leaf shape coefficient1.000 −0.066 −0.027 0.175 −0.062 0.014 −0.026 0.105 −0.200 0.049 0.166 −0.153 0.133 −0.019 0.111 0.002 叶柄长
Petiole length1.000 0.784 * * 0.474 * * −0.002 0.059 0.250 0.037 −0.016 0.109 0.054 0.024 −0.003 0.014 −0.062 0.192 小叶柄长
Petiolule length1.000 0.651 * * 0.137 0.230 0.310 * 0.065 0.014 0.001 −0.143 −0.129 0.179 0.148 0.022 0.291 * 小叶柄长/叶长
Petiolule length/leaf length1.000 0.046 0.177 0.136 0.025 −0.071 0.095 −0.048 −0.013 0.161 0.223 −0.047 0.117 枝下高
Under branch height1.000 0.592 * * 0.220 −0.089 −0.031 −0.034 −0.011 −0.016 0.378 * * 0.458 * * 0.067 0.076 胸径
Diameter at breast height1.000 0.181 −0.094 0.178 −0.128 −0.086 −0.040 0.589 * * 0.558 * * 0.159 0.082 花长
Flower length1.000 0.436 * * −0.249 −0.072 0.246 −0.052 −0.020 0.199 0.139 −0.059 花量
Amounts of flowers1.000 −0.190 −0.146 0.091 −0.177 −0.129 0.063 0.363 * * −0.104 叶尖
Leaf apex1.000 0.205 −0.122 0.071 0.157 0.053 0.068 0.184 叶缘
Leaf margin1.000 −0.254 * −0.213 0.113 −0.054 −0.302 * 0.171 叶形
Leaf shape1.000 0.422 * * −0.298 * −0.018 0.153 −0.341 * * 叶基
Leaf base1.000 −0.072 0.248 −0.010 −0.185 树皮颜色
Color of tree bark1.000 0.498 * * 0.100 −0.047 树皮状态
Condition of tree bark1.000 0.127 0.060 花色
Flower color1.000 −0.122 开花时间
Time of blossom1.000 “*”表示在P<0.05水平上显著相关,“**”表示在P<0.01水平上显著相关。
* denotes significant correlation at P<0.05. ** denotes significant correlation at P<0.01.表 7 紫花风铃木表型性状的主成分分析
Table 7 Principal components of phenotype traits of H. impetiginosus
性状 Phenotypic trait 主成分1 PC1 主成分2 PC2 主成分3 PC3 主成分4 PC4 主成分5 PC5 主成分6 PC6 叶面积 Leaf area 0.880 −0.284 0.174 −0.183 0.130 0.060 叶长 Leaf length 0.803 −0.202 0.370 −0.340 0.057 0.004 叶宽 Leaf width 0.900 −0.272 −0.019 −0.128 0.144 0.096 叶宽长比 Leaf width/leaf length 0.199 −0.116 −0.668 0.389 0.287 0.212 形状系数 Leaf shape coefficient −0.089 0.092 −0.235 0.576 0.391 0.211 叶柄长 Petiole length 0.624 0.031 0.323 0.336 −0.468 0.066 小叶柄长 Petiolule length 0.815 0.168 0.175 0.352 −0.278 0.099 小叶柄长/叶长 Petiolule length/leaf length 0.240 0.364 −0.129 0.716 −0.373 0.062 枝下高 Under branch height 0.222 0.645 −0.077 −0.280 0.053 −0.318 胸径 Diameter at breast height 0.306 0.756 −0.191 −0.240 0.071 −0.004 花长 Flower length 0.290 0.311 0.537 0.207 0.197 −0.319 花量 Flowers 0.046 0.073 0.498 0.261 0.517 −0.078 叶尖 Leaf apex 0.176 −0.043 −0.302 −0.427 −0.194 0.496 叶缘 Leaf margin 0.134 −0.213 −0.444 0.119 −0.210 −0.351 叶形 Leaf shape −0.402 0.195 0.568 0.133 −0.137 0.224 叶基 Leaf base −0.367 0.270 0.259 −0.169 −0.527 0.340 树皮颜色 Color of tree bark 0.271 0.595 −0.447 −0.143 0.124 −0.001 树皮状态 Condition of tree bark 0.142 0.779 −0.120 −0.116 −0.032 −0.008 花色 Flower color 0.001 0.289 0.265 −0.015 0.521 0.528 开花时间 Time of blossom 0.480 −0.170 −0.337 0.051 −0.073 0.085 贡献率 Contribution rate/% 21.429 13.496 12.374 9.617 8.485 5.755 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate/% 21.429 34.925 47.299 56.916 65.401 71.156 -
[1] JUSTINIANO M J, NASH D, FREDERICKSEN T. Ecología y silvicultura de e species menos conocidas. tajibos o lapachos Tabebuia spp [M]. Santa Cruz: Editora El País, 2000, 8.
[2] LARRABURU E E, LLORENTE B E. Azospirillum brasilense enhances in vitro rhizogenesis of Handroanthus impetiginosus (pink lapacho) in different culture media [J]. Annals of Forest Science, 2015, 72(2): 219−229. DOI: 10.1007/s13595-014-0418-9
[3] 蔡德才, 方良, 尚秀华, 等. 风铃木研究现状及开发利用前景 [J]. 桉树科技, 2016, 33(3):46−50. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3172.2016.03.009 CAI D C, FANG L, SHANG X H, et al. Research status and development prospects of Tabebuia [J]. Eucalypt Science & Technology, 2016, 33(3): 46−50.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3172.2016.03.009
[4] 张捷, 李蓉蓉, 孟景祥, 等. 我国风铃木类植物叶性状表型变异与遗传多样性研究 [J]. 植物研究, 2021, 41(6):851−861. DOI: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2021.06.002 ZHANG J, LI R R, MENG J X, et al. Phenotypic variation and genetic diversity of leaves traits of Tabebuia and Handroanthus (Bignoniaceace) in China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(6): 851−861.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2021.06.002
[5] 尹婷婷, 谷丽丽, 闫锋, 等. 59份老芒麦种质资源的表型多样性分析 [J]. 西南农业学报, 2021, 34(11):2307−2317. DOI: 10.16213/j.cnki.scjas.2021.11.001 YIN T T, GU L L, YAN F, et al. Phenotypic diversity analysis of 59 Elymus sibiricus germplasm resources [J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 34(11): 2307−2317.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.16213/j.cnki.scjas.2021.11.001
[6] 李红莉, 李雪, 逄宏扬. 黑龙江野生毛榛果实表型性状的多样性研究 [J]. 西部林业科学, 2022, 51(2):20−26. LI H L, LI X, PANG H Y. Phenotypic trait diversity of wild Corylusmandshurica fruit in Heilongjiang Province [J]. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 2022, 51(2): 20−26.(in Chinese)
[7] 张静. 风铃木类植物开花性状与观赏价值研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2016. ZHANG J. Study on flowering traits and ornamental value of Handroanthus and Tabebuia species[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2016. (in Chinese)
[8] 金海湘, 戴金宏, 黄桂莲, 等. 华南风铃木类植物种质资源的形态与分子鉴定 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(7):36−41. DOI: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb18100035 JIN H X, DAI J H, HUANG G L, et al. Germplasm resources of Tabebuia and Handroanthus in South China: Morphology and molecular identification [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2019, 35(7): 36−41.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb18100035
[9] LOZANO E C, ZAPATER M A. Delimitación y estatus de Handroanthus heptaphyllus y H. impetiginosus. (Bignoniaceae, tecomeae) [J]. Darwiniana, 2008, 46: 304−317.
[10] FELIX F C, Medeiros J, PACHECO M V. Morphology of seeds and seedlings of Handroanthus impetiginosus (Mart. ex DC.) Mattos [J]. Revista de Ciencias Agrarias, 2018, 41: 161−170.
[11] 周元刚, 姚宁, 冯浩, 等. 冬小麦叶片形状系数的变异性 [J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2017, 35(5):1−7,34. DOI: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2017.05.01 ZHOU Y G, YAO N, FENG H, et al. Variations of leaf shape coefficients of winter wheat [J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2017, 35(5): 1−7,34.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2017.05.01
[12] 张强强, 梁赛, 王艳, 等. 基于表型性状和SSR标记的57份辣椒种质遗传多样性分析 [J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 2020, 28(4):356−366. DOI: 10.11926/jtsb.4185 ZHANG Q Q, LIANG S, WANG Y, et al. Genetic diversity analysis of 57 germplasms of Capsicum annuum based on phenotypic traits and SSR markers [J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 2020, 28(4): 356−366.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11926/jtsb.4185
[13] 张斌斌, 蔡志翔, 沈志军, 等. 观赏桃种质资源表型性状多样性评价 [J]. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(11):2406−2420. DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2021.11.013 ZHANG B B, CAI Z X, SHEN Z J, et al. Diversity analysis of phenotypic characters in germplasm resources of ornamental peaches [J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(11): 2406−2420.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2021.11.013
[14] 苏群, 杨亚涵, 田敏, 等. 49份睡莲资源表型多样性分析及综合评价 [J]. 西南农业学报, 2019, 32(11):2670−2681. DOI: 10.16213/j.cnki.scjas.2019.11.027 SU Q, YANG Y H, TIAN M, et al. Phenotypic diversity analysis and comprehensive evaluation of 49 waterlily resources [J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 32(11): 2670−2681.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.16213/j.cnki.scjas.2019.11.027
[15] 魏晓羽, 刘红, 瞿辉, 等. 158份春兰种质资源的表型多样性分析 [J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2022, 23(2):398−411. WEI X Y, LIU H, QU H, et al. Phenotypic diversity analysis of 158 Cymbidium goeringii germplasm resources [J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2022, 23(2): 398−411.(in Chinese)
[16] 陆彭城, 郑燕, 周小琴, 等. 45个莲瓣兰品种的表型多样性研究 [J]. 热带作物学报, 2021, 42(9):2518−2525. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2021.09.011 LU P C, ZHENG Y, ZHOU X Q, et al. Phenotypic diversity of 45 cultivars of Cymbidium tortisepalum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2021, 42(9): 2518−2525.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2021.09.011
[17] 李雁瓷, 付乃峰, 孙加芝, 等. 秋海棠(Begonia grandis)的种内表型多样性 [J]. 植物研究, 2021, 41(5):775−788. DOI: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2021.05.016 LI Y C, FU N F, SUN J Z, et al. Intraspecific phenotypic diversity in Begonia grandis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(5): 775−788.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2021.05.016
[18] 尹世华, 王康, 黄晓霞, 等. 47份月季品种表型多样性分析及综合评价 [J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2021, 43(1):94−105. DOI: 10.13836/j.jjau.2021011 YIN S H, WANG K, HUANG X X, et al. Phenotypic diversity analysis and comprehensive evaluation of 47 rose resources [J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2021, 43(1): 94−105.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13836/j.jjau.2021011
[19] 刘洁. 锦带花表型、花粉形态及ISSR分子标记比较研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2012. LIU J. Comparative study of the morphological phenotype, pollen morphology and ISSR molecular markers between the white and pink Weigela florida[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2012. (in Chinese)
[20] 火艳, 招雪晴, 黄厚毅, 等. 观赏石榴表型遗传多样性分析 [J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2020, 37(5):939−949. DOI: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190619 HUO Y, ZHAO X Q, HUANG H Y, et al. Phenotypic genetic diversity of ornamental pomegranate cultivars [J]. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 2020, 37(5): 939−949.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190619
[21] 王业社, 侯伯鑫, 索志立, 等. 紫薇品种表型多样性分析 [J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2015, 16(1):71−79. DOI: 10.13430/j.cnki.jpgr.2015.01.011 WANG Y S, HOU B X, SUO Z L, et al. Phenotypic diversity of Lagerstroemia indica cultivars [J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2015, 16(1): 71−79.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13430/j.cnki.jpgr.2015.01.011
[22] 武丽琼. 红花风铃木的引种栽培及应用 [J]. 广东农业科学, 2010, 37(7):77−79. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2010.07.037 WU L Q. Introduction, cultivation and application of Tabebuia impetiginosus [J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 37(7): 77−79.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2010.07.037
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 高洁,陈伟,洪婷,姚帮本,姚丽,徐建国. 亚甲基蓝介导的电化学传感界面PCR鼠伤寒沙门氏菌检测方法. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(12): 1706-1710 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: