Efficiency Improvement of Low-grade Phosphorus Fertilizer by Phosphate-solubilizing Fungus JL-7
-
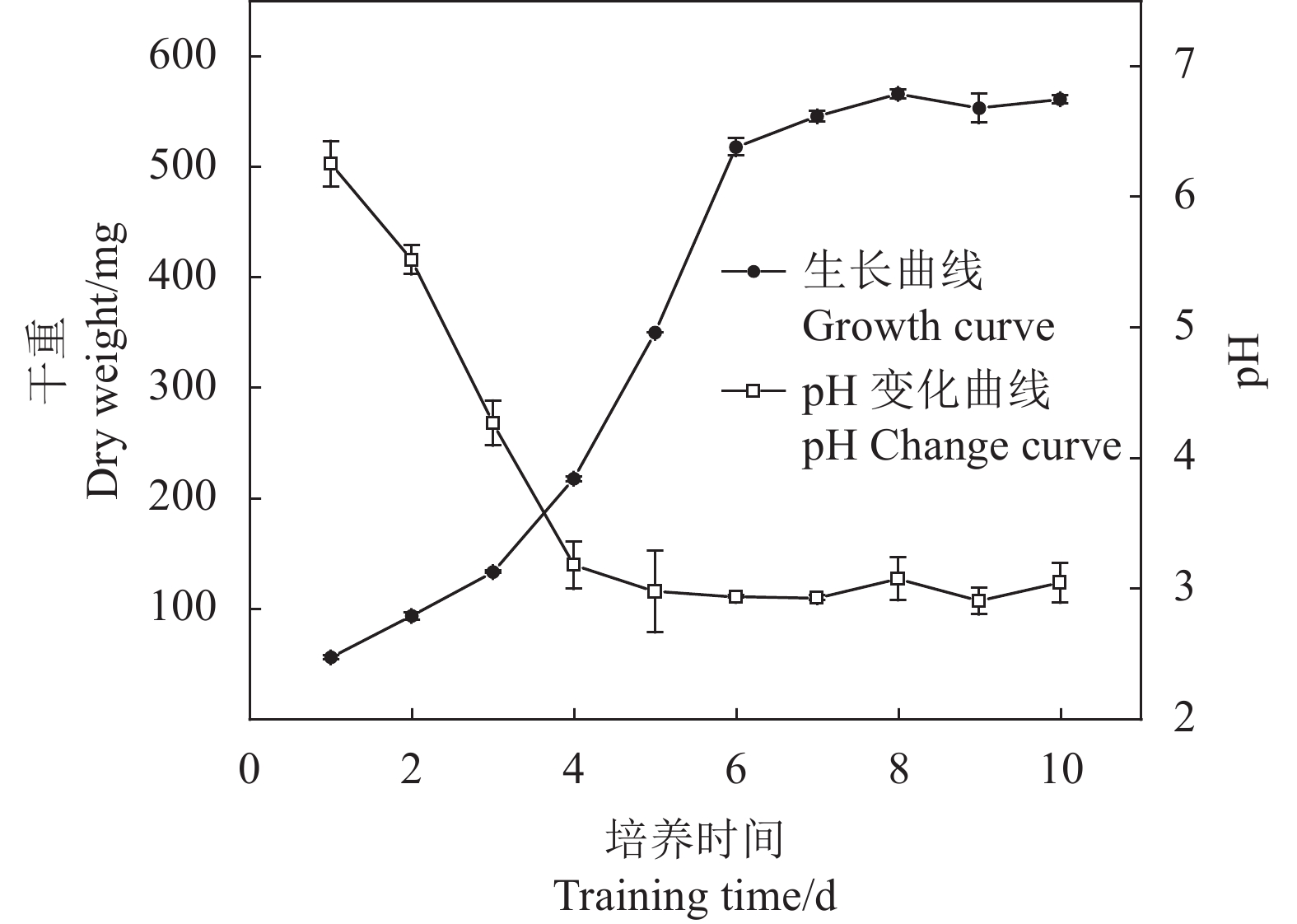
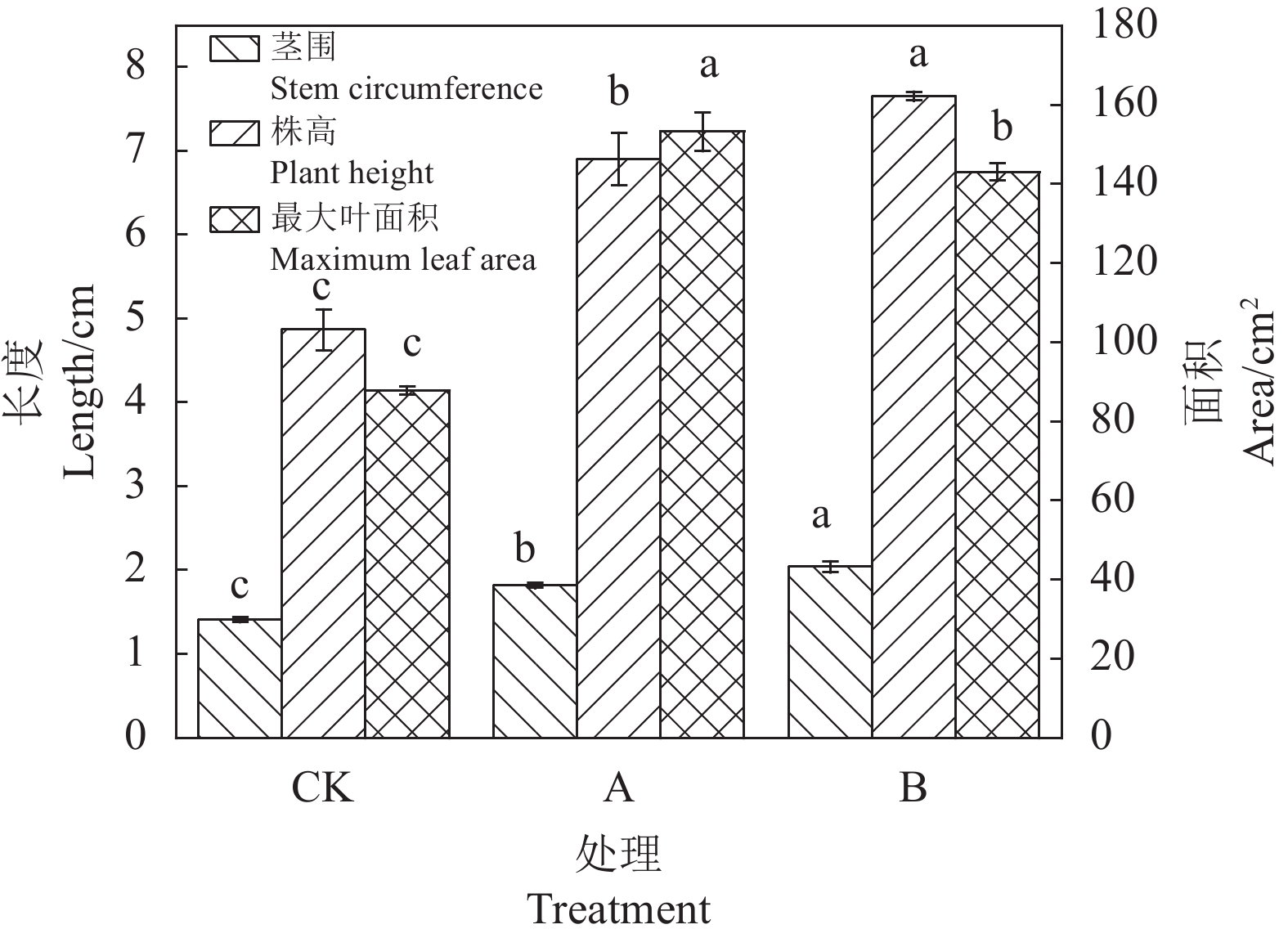
摘要:目的 针对我国低品位磷矿资源利用率低、耕地土壤有效磷含量低以及传统化肥的大量使用造成的土壤易固化等一系列问题,筛选可解离低品位磷矿的高效菌株,为低品位磷矿的资源利用提供途径。方法 以砂培法从贵州铜仁烟草种植基地土壤中筛选出一株新型解磷真菌,将其命名为JL-7,经过生理生化试验和分子生物学鉴定该菌为烟曲霉菌(Aspergillus fumigatiaffinis)。采用单因素和正交试验对该菌的解磷性能进行优化,在最佳优化条件下制备微生物菌肥并通过烟草盆栽试验进行肥效验证。结果 从烟草根际土壤中筛选的真菌JL-7在优化条件(接菌量1×105 cfu·mL−1、初始pH 6、解离时间8 d、解离温度26 ℃)下对低品位磷矿的最高解磷量达到967.4 mg·kg−1,真菌解离液中pH可降低至2.9左右。以高效解磷菌株JL-7制备菌肥,通过烟草盆栽种植试验,该菌肥对烟草(云烟87)的茎围、株高、最大叶面积分别提升44.60%、57.29%、62.90%。种植后对土壤进行分析,结果表明,该菌肥对土壤中的有效磷、速效钾、碱解氮含量分别提升48.5%、3.7%、9.1%。结论 菌株JL-7解磷效果优异且性能稳定,具有制备新型微生物肥料的潜力,具备一定的推广及应用价值。Abstract:Objective A fungal strain highly efficient in dissociating low-grade phosphorus ore for fertilization was isolated to determine the applicability.Method Soil samples at Guizhou Tongren Tobacco Planting Base were screened using the sand culture method for fungi that exhibited capability to solubilize phosphate. The selected isolate was identified by physiological, biochemical, and molecular biological tests. Conditions for optimal phosphate solubilization were determined by single factor and orthogonal experiments. Effect of the fungal addition on fertilization was verified by a pot test conducted on tobacco seedlings.Result The selected isolate was code-named JL-7 and, subsequently, identified to be a strain of Aspergillus fumigatiaffinis. The optimized conditions to maximize the phosphate-solubilization of JL-7 applied an inoculation at the rate of 1×105 cfu·mL−1 with an initial pH of 6 to incubate at 26 ℃ for 8 d. The process dissolved a low-grade phosphorus ore material up to 967.4 mg·kg−1 with the resulting solution reduced to approximately pH 2.9. In the pot experiment, the Yunyan 87 tobacco seedlings grown on a medium with the addition of a JL-7-inoculated phosphorus fertilizer had the stem girth, plant height, and maximum leaf area increased by 44.60%, 57.29%, and 62.90%, respectively, over control. Meanwhile, the pot soil increased 48.5% on available phosphorus, 3.7% on available potassium, and 9.1% on alkali-hydrolysable nitrogen after the planting as well.Conclusion The identified strongly phosphate-solubilizing Fungus JL-7 displayed a significant and consistent ability of dissolving phosphate. It was considered a potential candidate to be widely promoted as a microbial fertilization enhancer.
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】由炭疽菌属(Colletotrichum spp.)真菌侵染引起的大豆炭疽病(soybean anthracnose),普遍存在于全球大豆主产区,包括中国、美国南部、巴西、印度、东南亚及南亚,已成为大豆十大重要病害之一[1]。影响炭疽病发生的主要环境因子为温度和降雨量,南方高温多雨的气候环境适宜该病的发生和流行,大豆炭疽病对南方鲜食大豆的生产造成严重影响,近年有明显加重的趋势[2−4]。目前,大豆炭疽病的防治除了采用抗病品种外,主要依靠化学药剂种子处理和喷施杀菌剂[5]。但随着药剂的常年使用和剂量的提高,导致病原菌对防治药剂的敏感性降低,产生抗药性[6]。因此,监测大豆炭疽病菌对防治药剂的敏感性具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】大豆炭疽病是一种种传病害,可侵染大豆的任何生长发育阶段,造成死苗、植株早衰、豆荚坏死,严重影响大豆的产量和外观品质,造成的产量损失达16%~50%,部分地块甚至绝收。1996—2007年,大豆炭疽病造成我国大豆产量损失累计达
1660 万t[7−8]。大豆炭疽病的病原菌种类繁多,包括平头炭疽菌、毁灭炭疽菌、胶胞炭疽菌以及禾谷炭疽菌等,福建省大豆炭疽病的病原菌主要为胶孢炭疽菌和平头炭疽菌2种[9−10]。我国登记注册用于防治炭疽病登记的杀菌剂主要有三唑类、咪唑类、甲氧基丙烯酸酯类和取代苯类等[11]。吡唑醚菌酯(德国巴斯夫公司)是一种甲氧基丙烯酸酯类杀菌剂,其通过阻断真菌线粒体中的电子传递链,有效抑制ATP合成,从而干扰真菌呼吸,抑制线粒体内能量产生,导致细胞死亡。吡唑醚菌酯不仅具有高活性、广谱杀菌、长效保护、低毒性和对环境生物安全的特点,还具有作物保健功能,诱导作物生理变化,增强作物的光合作用,促进蛋白质和干物质的积累,降低乙烯的生物合成,延缓衰老,增强作物抗逆性,提高作物产量和品质[12]。吡唑醚菌酯因其良好的防效和保健增产作用,被广泛用于不同作物的炭疽病防治。田间试验表明,吡唑醚菌酯对大豆炭疽病的防效达85.7%,且显著提高了大豆的产量和品质[13]。然而,甲氧基丙烯酸酯类杀菌剂由于其作用位点单一,抗药性问题也频繁出现。1996年,德国报道小麦白粉病对其产生了抗性,此后,陆续发现了葡萄霜霉病菌(Plasmopara viticola)、梨黑斑病菌(Alternaria alternata)、玉米大斑病菌(Exserohilum turcicum)、桃炭疽病菌(Colletotrichum siamense)的抗性菌株[14−15]。【本研究切入点】吡唑醚菌酯在用于防治大豆胶孢炭疽病中,长期大量使用是否引起病菌抗药性的产生有待深入研究。【拟解决的关键问题】测定分离自福建省不同地区大豆胶孢炭疽菌对吡唑醚菌酯的敏感性,建立其敏感基线,采用药剂驯化法筛选抗性突变体,测定抗性突变体的生物学特性及对其他杀菌剂的交互抗性情况,旨在为吡唑醚菌酯在防治大豆胶孢炭疽病中的科学用药策略制订、预防抗性产生等提供理论依据。1. 材料和方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 供试菌株和品种
2022—2023年从福建省闽东(福州市、宁德市)、闽西(龙岩市)、闽南(漳州市)、闽北(南平市)、闽中(莆田市、三明市)等大豆主产区采集大豆炭疽病标本,分离并纯化获得单孢菌株,经鉴定和致病性测定,获得112株大豆胶孢炭疽菌,其中闽东地区24株、闽南地区31株、闽西地区27株、闽北地区15株、闽中地区15株。菌株保存在4 ℃的PDA斜面中,备用。供试大豆品种为毛豆3号,由福建省农业科学院作物研究所提供。
1.1.2 供试培养基
马铃薯葡萄糖培养基(PDA):马铃薯200 g、葡萄糖20 g、琼脂粉15 g、蒸馏水
1000 mL。1.1.3 供试药剂
供试药剂:98%吡唑醚菌酯和96%多菌灵(江苏辉丰生物农业股份有限公司),96.1%苯醚甲环唑(江苏耕耘化学有限公司),97%咪鲜胺(江苏辉丰农化股份有限公司),98%啶氧菌酯(山东潍坊润丰化工股份有限公司),99%水杨羟肟酸(Salicylohydroxamic, SHAM)[西格玛奥德里奇(上海)贸易有限公司]。母液配置:多菌灵用0.1 mol·L−1盐酸溶液配置,其他药剂用二甲基亚砜(dimethyl sulfoxide, DMSO)配置,SHAM配成质量浓度为1×105 µg·mL−1母液,非特定原药的其他药剂配制成1×104 µg·mL−1母液,置于4 ℃冰箱中备用。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 大豆胶孢炭疽菌对吡唑醚菌酯的敏感性测定
采用菌丝生长速率法[16],测定112株大豆胶孢炭疽菌对吡唑醚菌酯的敏感性。供试菌株在PDA平板上活化培养后,使用直径为5 mm的打孔器,从菌落边缘截取菌饼,将其菌丝面朝下接种至含有不同质量浓度吡唑醚菌酯(0.03~0.48 µg·mL−1)的PDA平板上。为减少旁路氧化途径的干扰,在含药平板中额外添加了质量浓度为50 µg·mL−1的SHAM。以加入等体积二甲基亚砜和SHAM的PDA平板作为对照。接种后的平板置于28 ℃黑暗培养7 d后,采用十字交叉法测量菌落直径,每处理3次重复。
参照周明国等[17] 的方法,计算各浓度处理下药剂对菌丝生长的抑制率,并进行回归分析,求出吡唑醚菌酯对各供试菌株的抑制中浓度EC50值、相关系数r、回归方程以及95%置信限。比较分析福建省5个地区大豆胶孢炭疽菌群体对吡唑醚菌酯的敏感性差异,计算不同地区菌株个体间的变异系数[18−19]。变异系数=EC50最大值/EC50最小值。对菌株的EC50值进行排序,并划分为7个不同的区间,然后统计每个区间内菌株的数量和频率。利用Shapiro-Wilk检验确认数据正态性后,绘制112株胶孢炭疽菌对吡唑醚菌酯的敏感性分布图。若呈正态分布,则以EC50均值作为福建省大豆胶孢炭疽菌的敏感基准[20]。随后,根据FRAC标准,进一步将菌株的EC50值与敏感基线进行比较,从而判断菌株的敏感性水平。当EC50值与基线的比值≤5时为敏感菌株;当比值在5~10时,为低抗菌株;在10~40时,为中抗菌株;而当比值>40时,则视为高抗菌株[21]。
1.2.2 室内抗性突变体诱导及筛选
参考乐默怡等[22] 的方法,药剂驯化诱导获得大豆胶孢炭疽菌抗吡唑醚菌酯突变体。选取大豆胶孢炭疽菌敏感菌株CG23017和CG23052作为野生敏感菌株,在PDA平板上活化培养5 d后,打取直径5 mm菌饼,转移至含1 µg·mL−1吡唑醚菌酯的PDA平板上,于28 ℃黑暗培养,待长出扇形突变后,转接至下个浓度含吡唑醚菌的PDA平板上,质量浓度梯度分别为2、5、10 µg·mL−1,PDA含药平板中加入质量浓度为50 µg·mL−1的SHAM。选取在含10 µg·mL−1吡唑醚菌酯的PDA平板上生长良好的菌株,转至无药平板复壮培养,标记为F1代。为评估菌株的抗性水平,进行抗性突变体EC50值的测定,并据此计算得到抗性倍数。同时,通过统计接种的菌饼中抗性菌株的数量,进一步得出抗性突变频率。根据计算所得的抗性倍数,菌株被划分为不同的抗性等级[23]:敏感(抗性倍数≤3)、低度抗性(抗性倍数在3~10)、中度抗性(抗性倍数在10~100)以及高度抗性(抗性倍数>100)。
1.2.3 抗药突变体的生物学性状研究
(1)抗性突变体抗药稳定性。参考范昆等[24] 的方法,将抗性突变体在无药PDA平板上连续转接至F7代,28 ℃黑暗培养7 d,每处理3次重复,利用菌丝生长速率法分别测定F1、F3、F5、F7代的EC50值。为分析抗性突变体在连续转接过程中的抗药稳定性,采用以下公式计算抗性倍数(RM):RM = 突变体的EC50 / 亲本菌株的EC50。
(2)抗性突变体对温度的敏感性。根据孙东晗等[25] 的方法,测定抗性突变体及其亲本菌株对不同温度(16 ℃、20 ℃、25 ℃、28 ℃、35 ℃)的敏感性。接种PDA平板后,菌饼在黑暗中培养7 d,每处理3次重复,以评估其在不同温度下的生长情况。
(3)抗性突变体的菌丝生长速率测定。按照乐默怡等[22] 的方法,将直径5 mm的菌饼接种在PDA平板上,于28 ℃黑暗条件下培养7 d。之后,用十字交叉法测量菌落直径,每处理3次重复,以计算并得出菌丝生长速率,菌丝生长速率/%=(菌落直径/菌丝生长天数)×100。
(4)抗性突变体的产孢能力测定。参考乐默怡等[22] 的方法,将活化的抗性突变体和亲本菌株制成直径5 mm的菌饼,接种在直径90 mm的PDA平板中央,28 ℃黑暗培养,10 d后用50 mL ddH2O,分数次加入培养皿中,用涂布棒将所有菌丝刮下,配置成分生孢子悬浮液,用血球计数板计算孢子浓度,计算单位面积内菌株产孢量,每处理3次重复。菌株产孢量=孢子浓度×50 mL/(3.14×菌落半径2)。
(5)抗性突变体的致病力测定。将活化的抗性突变体及其亲本菌株直径5 mm的菌饼接种于PDA平板中央(平板直径90 mm),28 ℃黑暗培养,10 d后用含0.1%吐温80 ddH2O,洗下分生孢子,配置成1×105 个·mL−1的孢子悬浮液,备用。毛豆3号,种植于埔垱基地,行距30 cm,株距15 cm,每处理种植4株,于大豆始荚期,傍晚喷施孢子悬浮液于大豆豆荚上,每处理100 mL,3次重复,以只喷施含0.1%吐温80 ddH2O为空白对照。14 d后,每个处理调查100个豆荚,依据以下分级标准计算病情指数。
大豆炭疽病病情分级标准如下[26]。0级:无病斑;1级:豆荚上有褐点型小病斑,病斑面积占整个豆荚面积的5%以下;3级:豆荚上出现典型病斑,病斑面积占整个豆荚面积的6%~10%;5级:豆荚上出现典型病斑,病斑面积占整个豆荚面积的11%~25%;7级:豆荚上出现典型病斑,病斑面积占整个豆荚面积的26%~50%;9级:豆荚上出现典型病斑,病斑面积占整个豆荚面积的50%以上。
病情指数=100×∑(各级病荚数×各级代表值)/(调查总荚数×9)
1.2.4 吡唑醚菌酯与不同杀菌剂间的交互抗性
采用1.2.1所述菌丝生长速率法,分别测定2个亲本菌和5个抗性突变体对多菌灵、苯醚甲环唑、咪鲜胺和啶氧菌酯的敏感性。多菌灵的质量浓度为0.01~0.16 µg·mL−1,苯醚甲环唑的质量浓度为0.1~0.8 µg·mL−1,咪鲜胺的质量浓度为0.01~0.08 µg·mL−1,啶氧菌酯的质量浓度为3~48 µg·mL−1。为减少旁路氧化途径的干扰,在啶氧菌酯的含药平板中额外添加质量浓度为50 µg·mL−1的SHAM。啶氧菌酯处理组以加入等体积二甲基亚砜和SHAM的PDA平板作为对照,苯醚甲环唑和咪鲜胺处理组以加入等体积二甲基亚砜的PDA平板作为对照,多菌灵处理组以加入等体积0.1 mol·L−1盐酸的PDA平板作为对照,每处理3次重复。根据亲本菌株和抗性突变体对多菌灵及其他药剂敏感性变化情况,判断交互抗性关系[19]。
1.3 数据分析
使用 Excel软件计算大豆炭疽病菌对杀菌剂的敏感性,包括毒力回归方程和有效中浓度的确定,并绘制敏感性频率分布图。采用Duncan氏新复极差法进行差异显著性检验;采用SPSS26.0软件进行Shapiro-Wilk正态性检验和相关性分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 大豆胶孢炭疽菌对吡唑醚菌酯的敏感性测定
供试菌株对吡唑醚菌酯的敏感性测定结果表明(表1),吡唑醚菌酯对112株大豆胶孢炭疽菌的毒力(EC50)值分布在
0.0682 ~1.0309 µg·mL−1,平均值为(0.2036 ±0.1215) µg·mL−1,菌株间变异系数为15.12;从地区上看,闽东、闽南、闽西、闽北和闽中5个地域内的大豆胶孢炭疽菌菌株对吡唑醚菌酯的毒力响应(EC50平均值)分别为0.1662 、0.1845 、0.2451 、0.2387 、0.1933 µg·mL−1,5个地区菌株群体间敏感性差异不显著;5个地区区域内菌株间变异系数分别为5.54、4.60、8.02、8.03和4.15。表 1 福建不同地区大豆胶孢炭疽菌对吡唑醚菌酯的敏感性Table 1. Sensitivity to pyraclostrobin of C. gloeosporioides isolated from regions in Fujian采集地区
Sampling region菌株数
Number of isolates吡唑醚菌酯EC50值
EC50 of Pyraclostrobin/(µg·mL−1)菌株间变异系数
Variation factor范围 Range 平均值 Mean 闽东地区 Eastern Fujian 24 0.0682 ~0.3777 0.1662 ±0.0633 a5.54 闽南地区 Southern Fujian 31 0.0763 ~0.3506 0.1845 ±0.0751 a4.60 闽西地区 Western Fujian 27 0.0801 ~0.6428 0.2451 ±0.1359 a8.02 闽北地区 Northern Fujian 15 0.1284 ~1.0309 0.2387 ±0.2269 a8.03 闽中地区 Central Fujian 15 0.0725 ~0.3007 0.1933 ±0.0670 a4.15 总计 Total 112 0.0682 ~1.0309 0.2036 ±0.1215 a15.12 表中数据为平均数±标准差。同列数据后不同小写字母分别表示经Duncan氏新复极差法检验差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。
Data are mean±SD; those with different lowercase letters on same column indicate significant difference at P<0.05 in Duncan's new multiple range test. Same for below.2.2 大豆胶孢炭疽菌对吡唑醚菌酯的敏感性分析
大豆胶孢炭疽菌对吡唑醚菌酯的敏感性分析表明(图1),112株测试菌株的敏感性频率分布呈连续性单峰曲线,且符合偏正态分布特征(skew=3.592, kurt=20.271, W=0.712, P<0.05)。在95%的显著性水平下,未观察到敏感性下降的亚群体。因此,确定EC50平均值为(
0.2036 ±0.1215) µg·mL−1作为福建省大豆胶孢炭疽菌对吡唑醚菌酯的敏感基线。比较各菌株的EC50值与敏感基线,发现1株为低抗菌株,抗性比值为5.06;111株为敏感菌株,抗性比值低于5。2.3 抗性突变体的获得及抗性水平测定
经过药剂驯化,成功筛选出5株抗性突变体(表2),这些突变体的突变频率为8.3×10−4,其中4株突变体的抗性倍数分别为13.10、14.29、18.71、16.84,表现为中抗水平,1株突变体抗性倍数为4.95,表现为低抗水平。
表 2 吡唑醚菌酯抗性突变体连续转代培养后EC50和抗性倍数的变化Table 2. Changes on EC50 and resistance multiple of pyraclostrobin-resistant C. gloeosporioides mutants after continuous generational transference菌株
Strain第一代
1st generation第三代
3rd generation第五代
5th generation第七代
7th generationEC50 /(µg·mL−1) RM EC50/(µg·mL−1) RM EC50/(µg·mL−1) RM EC50/(µg·mL−1) RM CG23017 0.1349 / 0.1396 / 0.1369 / 0.1344 / CG23017-1 1.7673 13.10 1.7823 12.77 1.7121 12.5 1.6661 12.39 CG23017-2 0.6674 4.95 0.5275 3.78 0.4891 3.57 0.4376 3.26 CG23017-3 1.9268 14.29 1.9084 13.67 1.8966 13.85 1.8612 13.85 CG23052 0.1611 / 0.1647 / 0.1623 / 0.1580 / CG23052-1 3.0151 18.71 3.0198 18.34 2.9742 18.33 2.9574 18.72 CG23052-2 2.7140 16.84 2.7191 16.51 2.7200 16.76 2.6425 16.73 RM为抗性倍数。
RM: resistance multiple.2.4 抗性突变体生物学性状
2.4.1 抗药稳定性
连续培养7代后,抗药突变体CG23017-1、CG23017-2、CG23017-3、CG23052-1和CG23052-2的EC50值分别为
1.6661 、0.4376 、1.8612 、2.9574 、2.6425 µg·mL−1(表2),抗性水平分别为12.39、3.26、13.85、18.72和16.73,抗性倍数保持在中抗和低抗水平,大豆胶孢炭疽菌对吡唑醚菌酯的抗性水平能稳定遗传。2.4.2 对温度的敏感性
对抗性突变体及其亲本菌株在不同温度条件下的生长特性测定结果发现,两者在温度敏感性上存在显著差异(表3)。抗性突变体与其亲本菌株的菌落直径均在28 ℃时达最大值,35 ℃时达最小值;在16 ℃时,突变体CG23017-3和CG23052-1与亲本菌株在菌落直径上未见显著差异,而突变体CG23017-1、CG23017-2和CG23052-2则表现出显著的差异;在20 ℃条件下,突变体CG23017-1和CG23052-2与亲本菌株的菌落直径相近,但突变体CG23017-2、CG23017-3和CG23052-1则呈现出显著差异;在25 ℃时,突变体CG23017-1、CG23017-2和CG23017-3与亲本菌株的菌落直径差异不明显,而突变体CG23052-1和CG23052-2则显示出显著差异。然而,值得注意的是,在28 ℃和35 ℃条件下,所有抗性突变体与其亲本菌株的菌落直径均未见显著差异。
表 3 抗性突变体及其亲本菌株对温度的敏感性测定Table 3. Mycelial growth of resistant mutants and parents under different temperatures菌株 Strain 菌落直径 Colony diameter/mm 16 ℃ 20 ℃ 25 ℃ 28 ℃ 35 ℃ CG23017 31.33±0.58 cd 43.33±1.53 c 59.33±2.31 c 63.67±1.53 b 20.67±1.53 a CG23017-1 28.67±0.58 e 41.33±1.15 cd 58.33±1.15 c 60.67±1.53 b 18.67±3.06 ab CG23017-2 25.33±1.15 f 37.67±1.15 e 56.67±1.53 c 60.33±2.31 b 19.33±1.53 ab CG23017-3 29.67±1.53 de 39.33±1.53 de 57.33±1.53 c 60.67±2.31 b 19.67±1.15 ab CG23052 35.67±2.08 a 48.33±1.15 a 72.67±0.58 a 74.67±1.53 a 17.67±1.53 ab CG23052-1 34.33±1.53 ab 45.67±1.15 b 69.67±1.15 b 71.67±1.53 a 18.33±0.58 ab CG23052-2 32.33±1.53 bc 46.33±0.58 ab 68.33±1.53 b 71.33±2.52 a 16.67±2.52 b 2.4.3 抗性突变体的适生性
经对抗性突变体的适生性测定发现(表4),5个抗性突变体的菌丝生长速率和产孢能力均略低于其亲本菌株;CG23017-1、CG23017-3和CG23052-2 3个抗性突变体接种后大豆的病情指数与其亲本菌株相比,无显著性差异;CG23017-2和CG23052-1抗性突变体接种后大豆的病情指数显著低于其亲本菌株。
表 4 抗性突变体及其亲本菌株菌丝生长速率、产孢能力、致病力测定Table 4. Mycelial growth rate, sporulation per area, and disease index of resistant mutants and parents菌株
Strain菌丝生长速率
Mycelium growth rate/(mm·d−1)单位面积产孢量
Sporulation per area/(×103个·mm−2)病情指数
Disease indexCG23017 9.1±0.22 b 4.58±0.27 ab 47.52±2.34 a CG23017-1 8.67±0.22 b 4.55±0.19 ab 40.37±4.56 a CG23017-2 8.62±0.33 b 4.32±0.08 b 27.08±4.83 b CG23017-3 8.67±0.33 b 4.50±0.26 ab 42.48±10.06 a CG23052 10.67±0.22 a 4.77±0.25 a 41.48±8.82 a CG23052-1 10.24±0.22 a 4.74±0.23 a 26.63±6.32 b CG23052-2 10.19±0.36 a 4.61±0.2 ab 37.43±0.89 ab 5株抗性突变体在整体的生存适应度方面略低于亲本菌株。其中3株中抗突变体的菌丝生长速度、产孢能力、致病力等生存适合度与其亲本菌株无显著性差异;1株中抗突变体、1株低抗突变体菌丝生长速度、产孢能力与其亲本菌株无显著性差异,致病力显著低于其亲本菌株。
2.5 抗性突变体交互抗性
交互抗性分析结果表明,吡唑醚菌酯与多菌灵、苯醚甲环唑、咪鲜胺和啶氧菌酯的相关性方程分别为y=−
1.3197 +0.0119 x(ρ=0.393,P=0.682,图2A)、y=−0.3668 +0.0033 x(ρ=0.273,P=0.913,图2B)、y=−1.3465 −0.0071 x(ρ=0.396,P=0.164,图2C)和y=1.2159 +0.6111 x(ρ=0.821,P=0.000,图2D),说明吡唑醚菌酯与不同类杀菌剂多菌灵、苯醚甲环唑、咪鲜胺之间不存在交互抗性,与同类杀菌剂啶氧菌酯存在交互抗性。3. 讨论与结论
大豆炭疽病是南方大豆生产中的重要病害。吡唑醚菌酯作为一种甲氧基丙烯酸酯类杀菌剂,已被广泛用于作物炭疽病的防治。研究表明,吡唑醚菌酯对大豆、辣椒、草莓等作物炭疽病菌均具有较好的防治效果[13,14,21],25%吡唑醚菌酯26.67 g·hm−2对大豆炭疽病的田间防效达75.8%,草莓炭疽病菌的敏感基线为(0.36±0.162) µg·mL−1,辣椒炭疽病菌的敏感基线为(
0.2272 ±0.2027) µg·mL−1。吡唑醚菌酯对大豆炭疽病具有较好的防治效果,且其保健增产作用还能显著提高大豆的产量和品质[13]。本研究分析了福建省大豆胶孢炭疽菌对吡唑醚菌酯的敏感性特征。结果显示,其EC50值分布于0.0682 ~1.0309 µg·mL−1,敏感性频率分布呈现为连续的单峰曲线,符合连续的偏正态分布。据此,确立的敏感性基线值为(0.2036 ±0.1215 ) µg·mL−1,经比对发现,低抗菌株仅1株,而敏感菌株高达111株,这一数据有力验证了福建省大豆胶孢炭疽菌对吡唑醚菌酯的显著敏感性,吡唑醚菌酯用于大豆胶孢炭疽病菌的防治潜力较大。通过药剂驯化,从2株大豆胶孢炭疽菌野生菌株中诱导获得4株中抗吡唑醚菌酯的突变体,1株低抗吡唑醚菌酯的突变体。抗性突变体生物学性状测定发现,抗性突变体继代培养能稳定遗传;抗性突变体相较于亲本菌株,在温度敏感性上表现出差异性,并且在生长速率、产孢能力和致病性方面存在轻微的适应度劣势,但抗性突变体具有一定的自然竞争优势,在特定条件下,也可能形成优势菌群,此结果与孙东晗等[25]研究的西瓜蔓枯病菌抗吡唑醚菌酯突变体的结论一致,因此,大豆胶孢炭疽菌对吡唑醚菌酯存在中等抗性风险。交互抗性研究发现,吡唑醚菌酯与常用不同类杀菌剂多菌灵、苯醚甲环唑、咪鲜胺之间不存在交互抗性,与同类杀菌剂啶氧菌酯存在交互抗性,这与姚锦爱[21]、孙东晗[25]、董国然[27]等研究报道结果一致。因此,混合或交替使用吡唑醚菌酯与不同类别的杀菌剂,如多菌灵、苯醚甲环唑、咪鲜胺,不仅可以提高大豆胶孢炭疽病防控效果,还有助于延缓大豆胶孢炭疽菌抗药性的产生。吡唑醚菌酯对大豆炭疽病菌具有较好的抑制效果,在田间的防治中,应对吡唑醚菌酯的合理使用进行指导,应与多菌灵、苯醚甲环唑、咪鲜胺混合或交替使用,以延缓大豆胶孢炭疽菌抗药性的产生,同时要加强田间抗药性监测。
-
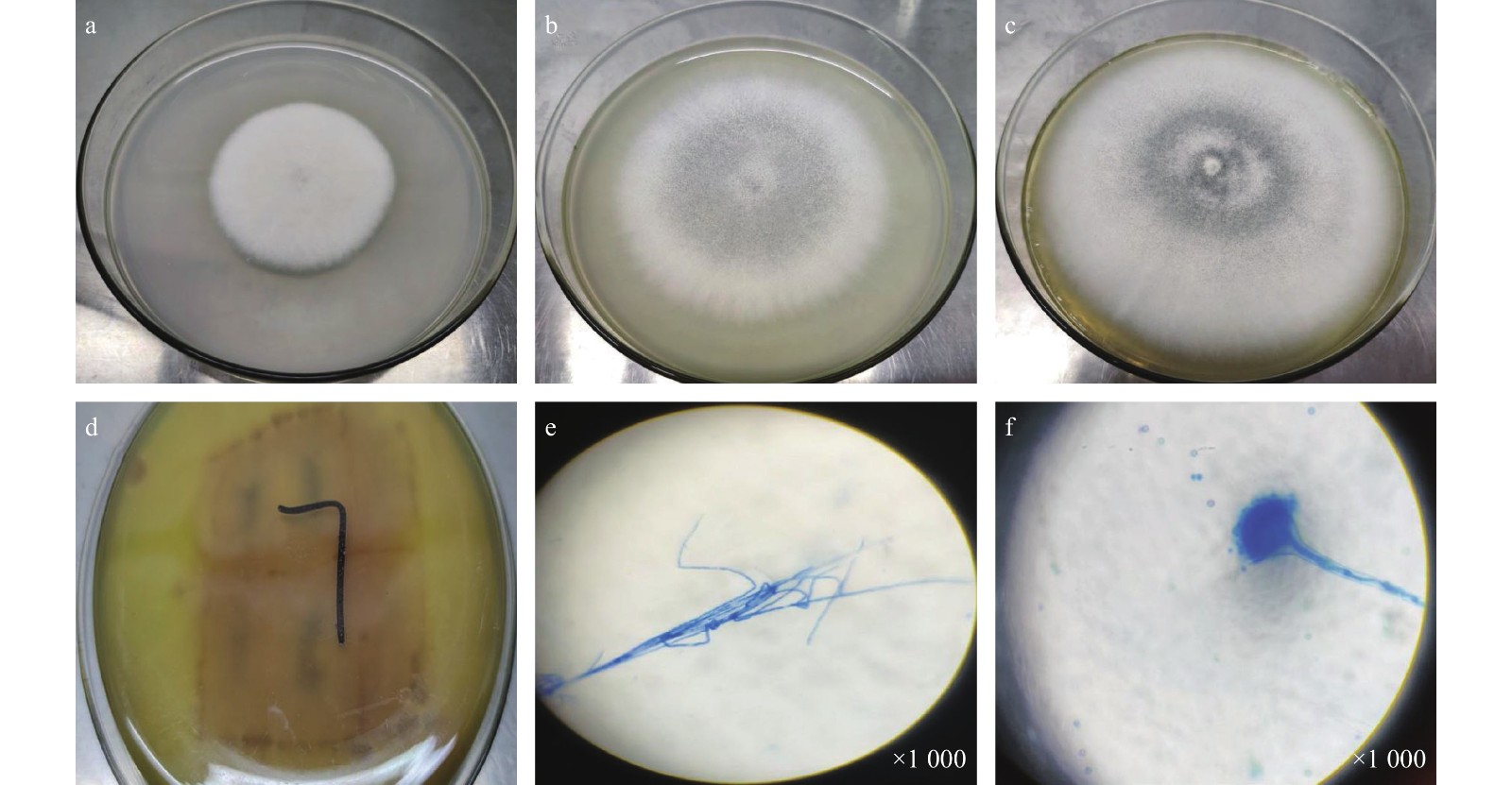
图 1 JL-7的生长变化过程及显微图
a:初生菌丝生长情况;b:5天后菌落生长情况;c、d:9天后菌落生长情况和平板背面观察到的菌落外观;e、f:光学显微镜下放大1 000倍观察到的真菌菌丝和分生孢子梗。
Figure 1. Growth and change process and micrograph of JL-7
a: Growth of primary mycelium; b: growth of colony after 5 d; c and d: growth of colony after 9 d and rear view of colony on plate; e and f: fungal mycelium and conidiophore under optical microscope (1 000×).
表 1 JL-7的生理生化试验结果
Table 1 Physiological and biochemical test results on JL-7
项目
Item结果
Result项目
Item结果
Result项目
Item结果
ResultD-阿拉伯糖 − D-核糖 + 麦芽三糖 + L-阿拉伯糖 + D-棉子糖 + N-乙酰-半乳糖胺 + D-纤维二糖 + L-鼠李糖 + N-乙酰-葡萄糖胺 + L-山梨糖 − D-甘露糖 + N-乙酰-甘露糖胺 + D-果糖 + D-松三糖 + D-葡萄糖胺 + L-岩藻糖 + D-蜜二糖 + 葡糖醛酰胺 − D-半乳糖 − D-塔格糖 + 丙酸胺 + +表示阳性反应;−表示阴性反应。
+ means positive reaction; − means negative reaction.表 2 单因素设计的L9(3)4正交试验表
Table 2 L9(3)4 orthogonal experiment design with single factor experiment
因素
Level接菌量
Inoculation
amount/(cfu·mL−1)初始pH
Initial pH解离时间
Dissociation
time/d解离温度
Dissociation
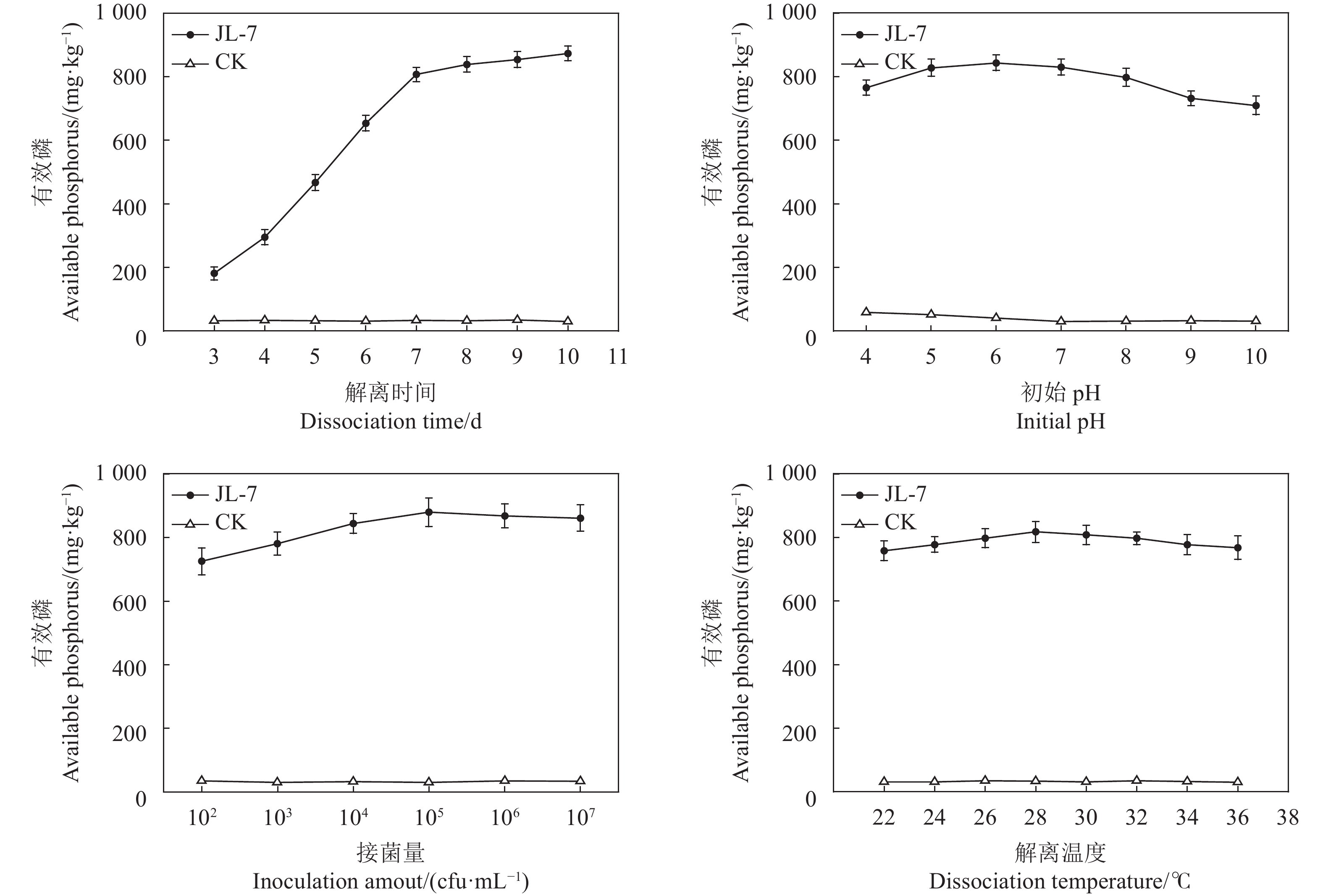
temperature/ ℃1 1×104 5 6 26 2 1×105 6 7 28 3 1×106 7 8 30 表 3 正交试验对菌株JL-7解磷条件的优化结果
Table 3 Orthogonal optimized conditions for JL-7 phosphate solubilization
因素
Level接菌量
Inoculation amount/(cfu·mL−1)初始pH
Initial pH解离时间
Dissociation time/d解离温度
Dissociation temperature/ ℃有效磷含量
Available phosphorus/(mg·kg−1)1 1×104 5 6 26 779. 8 2 1×104 6 7 28 811.3 3 1×104 7 8 30 793.1 4 1×105 5 7 30 852.5 5 1×105 6 8 26 872.9 6 1×105 7 6 28 828.8 7 1×106 5 8 28 837.6 8 1×106 6 6 30 812.1 9 1×106 7 7 26 803.6 K1 794.733 823.300 806.900 818.767 K2 851.400 832.100 822.467 825.900 K3 817.767 805.500 834.533 819.233 极差 R 56.667 23.600 27.633 7.133 表 4 菌肥对土壤肥力的影响
Table 4 Effect of fungal fertilization enhancer on soil fertility
(mg·kg−1) 处理方式
Processing method碱解氮
Alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen有效磷
Available phosphorus速效钾
Available potassiumCK(对照) 107.47±2.09 c 58.87±2.56 c 139.20±1.06 b A(施用A菌肥) 124.43±1.94 a 73.10±2.59 b 144.45±2.17 a B(施用B菌肥) 117.17±2.65 b 87.41±0.97 a 144.42±1.88 a 同列数据后不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Data with different letters on the same column indicate significant differences (P<0.05). -
[1] SHAHZAD S M, ARIF M S, RIAZ M, et al. Interaction of compost additives with phosphate solubilizing rhizobacteria improved maize production and soil biochemical properties under dryland agriculture [J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2017, 174(12): 70−80.
[2] VENEKLAAS E J, LAMBERS H, BRAGG J, et al. Opportunities for improving phosphorus-use efficiency in crop plants [J]. The New Phytologist, 2012, 195(2): 306−320. DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04190.x
[3] TALLAPRAGADA P, SESHACHALA U. Phosphate-solubilizing microbes and their occurrence in the rhizospheres of Piper betel in Karnataka, India [J]. Turkish Journal of Biology, 2012, 36(1): 25−35.
[4] ZHANG J, FENG L, OUYANG Y, et al. 2020. Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and fungi in relation to phosphorus availability under different land uses for some latosols from Guangdong, China [J]. Catena, 2020, 195(5): 41−62.
[5] 池景良, 郝敏, 王志学, 等. 解磷微生物研究及应用进展 [J]. 微生物学杂志, 2021, 41(1):1−7. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7021.2021.01.001 CHI J L, HAO M, WANG Z X, et al. Advances in research and application of phosphorus-solubilizing microorganism [J]. Journal of Microbiology, 2021, 41(1): 1−7.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7021.2021.01.001
[6] 王向英, 武欣, 张杰, 等. 解磷菌在复垦土壤中的定殖及促生效果研究 [J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2021, 52(7):40−47. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9369.2021.07.005 WANG X Y, WU X, ZHANG J, et al. Colonization of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria in reclaimed soil and the growth-promoting effects on maize [J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2021, 52(7): 40−47.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9369.2021.07.005
[7] 张云霞, 雷鹏, 许宗奇, 等. 一株高效解磷菌Bacillus subtilis JT-1的筛选及其对土壤微生态和小麦生长的影响 [J]. 江苏农业学报, 2016, 32(5):1073−1080. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2016.05.019 ZHANG Y X, LEI P, XU Z Q, et al. Screening of a high-efficiency phosphate solubilizing bacterium Bacillus subtilis JT-1 and its effects on soil microecology and wheat growth [J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 32(5): 1073−1080.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2016.05.019
[8] 林志伟, 肖翠红, 白鑫雨, 等. 解磷菌DQ-N对大豆种子萌发及苗期生长的影响 [J]. 大豆科学, 2021(5):676−681. LIN Z W, XIAO C H, BAI X Y, et al. Effects of DQ-N strain on seed germination and seedling growth of soybean [J]. Soybean Science, 2021(5): 676−681.(in Chinese)
[9] AHMAD A, ZAFAR U, KHAN A, et al. Effectiveness of compost inoculated with phosphate solubilizing bacteria [J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2022, 133(2): 1115−1129. DOI: 10.1111/jam.15633
[10] 鲁如坤. 土壤磷素水平和水体环境保护 [J]. 磷肥与复肥, 2003, 18(1):4−8. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6220.2003.01.002 LU R K. The phosphorus level of soil and environmental protection of water body [J]. Phosphate & Compound Fertilizer, 2003, 18(1): 4−8.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6220.2003.01.002
[11] ANZUAY M S, CIANCIO M G R, LUDUEÑA L M, et al. Growth promotion of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L. ) and maize (Zea mays L. ) plants by single and mixed cultures of efficient phosphate solubilizing bacteria that are tolerant to abiotic stress and pesticides [J]. Microbiological Research, 2017, 199: 98−109. DOI: 10.1016/j.micres.2017.03.006
[12] 唐哲, 杨洪一, 李丽丽. 解磷真菌的研究进展与应用前景 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2014(32):11287−11288,11296. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2014.32.022 TANG Z, YANG H Y, LI L L. Advance and application prospect of phosphate-solubilizing fungi [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2014(32): 11287−11288,11296.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2014.32.022
[13] 赵小蓉, 林启美, 李保国. 溶磷菌对4种难溶性磷酸盐溶解能力的初步研究 [J]. 微生物学报, 2002, 42(2):236−241. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-6209.2002.02.017 ZHAO X R, LIN Q M, LI B G. The solubilization of four insoluble phosphates by some microorganisms [J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2002, 42(2): 236−241.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-6209.2002.02.017
[14] SHIRMOHAMMADI E, ALIKHANI H A, POURBABAEI A A, et al. Improved phosphorus (P) uptake and yield of rainfed wheat fed with P fertilizer by drought-tolerant phosphate-solubilizing fluorescent pseudomonads strains: A field study in drylands [J]. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2020, 20(4): 2195−2211. DOI: 10.1007/s42729-020-00287-x
[15] 刘洋, 洪坚平, 卫迎. 接种AM真菌与解磷细菌对矿区复垦土壤磷形态及油菜产量的影响 [J]. 山西农业科学, 2018(5):785−790,861. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2481.2018.05.27 LIU Y, HONG J P, WEI Y. Effects of inoculation of AM fungi and phosphate solubilizing bacteria on phosphorus morphology and rape yield in reclaimed soil in mining area [J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 2018(5): 785−790,861.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2481.2018.05.27
[16] IWASAKI S, FUKUDA M, IKAZAKI K, et al. Optimal P fertilization using low-grade phosphate rock-derived fertilizer for rice cultivation under different ground-water conditions in the Central Plateau of Burkina Faso [J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2021, 67(4): 460−470. DOI: 10.1080/00380768.2021.1932584
[17] CALLE-CASTANEDA S M, MARQUEZ-GODOY M A, HERNANDEZ-ORTIZ J P. Phosphorus recovery from high concentrations of low-grade phosphate rocks using the biogenic acid produced by the acidophilic bacteria Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2018, 115(1): 97−105.
[18] 李豆豆, 尚双华, 韩巍, 等. 一株高效解磷真菌新菌株的筛选鉴定及解磷特性 [J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(7):2384−2392. DOI: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201907.033 LI D D, SHANG S H, HAN W, et al. Screening, identification, and phosphate solubilizing characteristics of a new efficient phosphate solubilizing fungus [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(7): 2384−2392.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201907.033
[19] 杨锦发. 多目标生态地球化学土壤样品高精度测试与质量监控 [J]. 岩矿测试, 2007, 26(1):36−39. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2007.01.010 YANG J F. High precision measurements and quantity monitoring and control for soil sample analysis in eco-geochemistry survey [J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2007, 26(1): 36−39.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2007.01.010
[20] 马卫, 刘诚, 邵闯, 等. 一株高效溶磷真菌MEM07的筛选鉴定及其溶磷条件优化 [J]. 绿色科技, 2017(20):193−195. DOI: 10.16663/j.cnki.lskj.2017.20.068 MA W, LIU C, SHAO C, et al. Screening and identification of a high-efficiency phosphate-dissolving fungus MEM07 and optimization of its phosphate-dissolving conditions [J]. Journal of Green Science and Technology, 2017(20): 193−195.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.16663/j.cnki.lskj.2017.20.068
[21] 全国农业技术推广服务中心. 土壤分析技术规范[M]. 第2版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2006. [22] 魏景超. 真菌鉴定手册[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1979. [23] 柴文亚, 李红丽, 王勇, 等. 生物有机肥防治烟草黑胫病效果及对烟株生长发育的影响 [J]. 天津农业科学, 2014, 20(4):24−27. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6500.2014.04.008 CHAI W Y, LI H L, WANG Y, et al. Effect of bio-organic fertilizer on prevention and control of tobacco black shank disease and its influence on tobacco growth [J]. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 20(4): 24−27.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6500.2014.04.008
[24] 汤宏, 李向阳, 曾掌权, 等. 不同施磷量对烟草生长及产量的影响 [J]. 华北农学报, 2018(S1):201−207. DOI: 10.7668/hbnxb.2018.S1.033 TANG H, LI X Y, ZENG Z Q, et al. Effects of different phosphorus application rate on growth and yield of tobacco [J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2018(S1): 201−207.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7668/hbnxb.2018.S1.033
[25] 李玥, 赖勇林, 王军, 等. 不同养分缺乏对烤烟根系形态及营养生长的影响 [J]. 中国烟草科学, 2015, 36(2):60−65. DOI: 10.13496/j.issn.1007-5119.2015.02.011 LI Y, LAI Y L, WANG J, et al. Effect of different nutrient deficiencies on root morphology and vegetative growth in flue-cured tobacco [J]. Chinese Tobacco Science, 2015, 36(2): 60−65.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13496/j.issn.1007-5119.2015.02.011
[26] 李静, 艾加敏, 余天飞, 等. 一株溶磷真菌的鉴定及其促生特性研究 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2021(10):1224−1230. DOI: 10.19303/j.issn.1008-0384.2021.10.015 LI J, AI J M, YU T F, et al. Identification and growth-promoting effect of a phosphate-solubilizing fungus on wheat seedlings [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021(10): 1224−1230.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.19303/j.issn.1008-0384.2021.10.015
[27] ALIYAT F Z, MALDANI M, EL GUILLI M, et al. Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria isolated from phosphate solid sludge and their ability to solubilize three inorganic phosphate forms: Calcium, iron, and aluminum phosphates [J]. Microorganisms, 2022, 10(5): 980. DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms10050980
[28] MONROY MIGUEL R, CARRILLO GONZÁLEZ R, RIOS LEAL E, et al. Screening bacterial phosphate solubilization with bulk-tricalcium phosphate and hydroxyapatite nanoparticles [J]. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 2020, 113(7): 1033−1047. DOI: 10.1007/s10482-020-01409-2
[29] 刘娟, 张乃明, 何云. 黑曲霉素J4对中低品位磷矿粉的溶磷效果及重金属释放的影响 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(6):1260−1267. DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2020.06.023 LIU J, ZHANG N M, HE Y. Effect of Niger Aspergillus J4 on phosphate dissolution and release of heavy metals in medium and low grade phosphate powder [J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 2020, 29(6): 1260−1267.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2020.06.023
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 刘勉,肖玉辉,勾朝金,古旭,芦俊佳. 大花海棠炭疽病病原菌鉴定、生物学特性测定及防治药剂室内毒力测定. 南方农业学报. 2025(02): 508-519 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: