Expressions of Defense Signal Pathway Genes in Tomato Plant Induced by Ralstonia solanacearum of Different Virulence
-
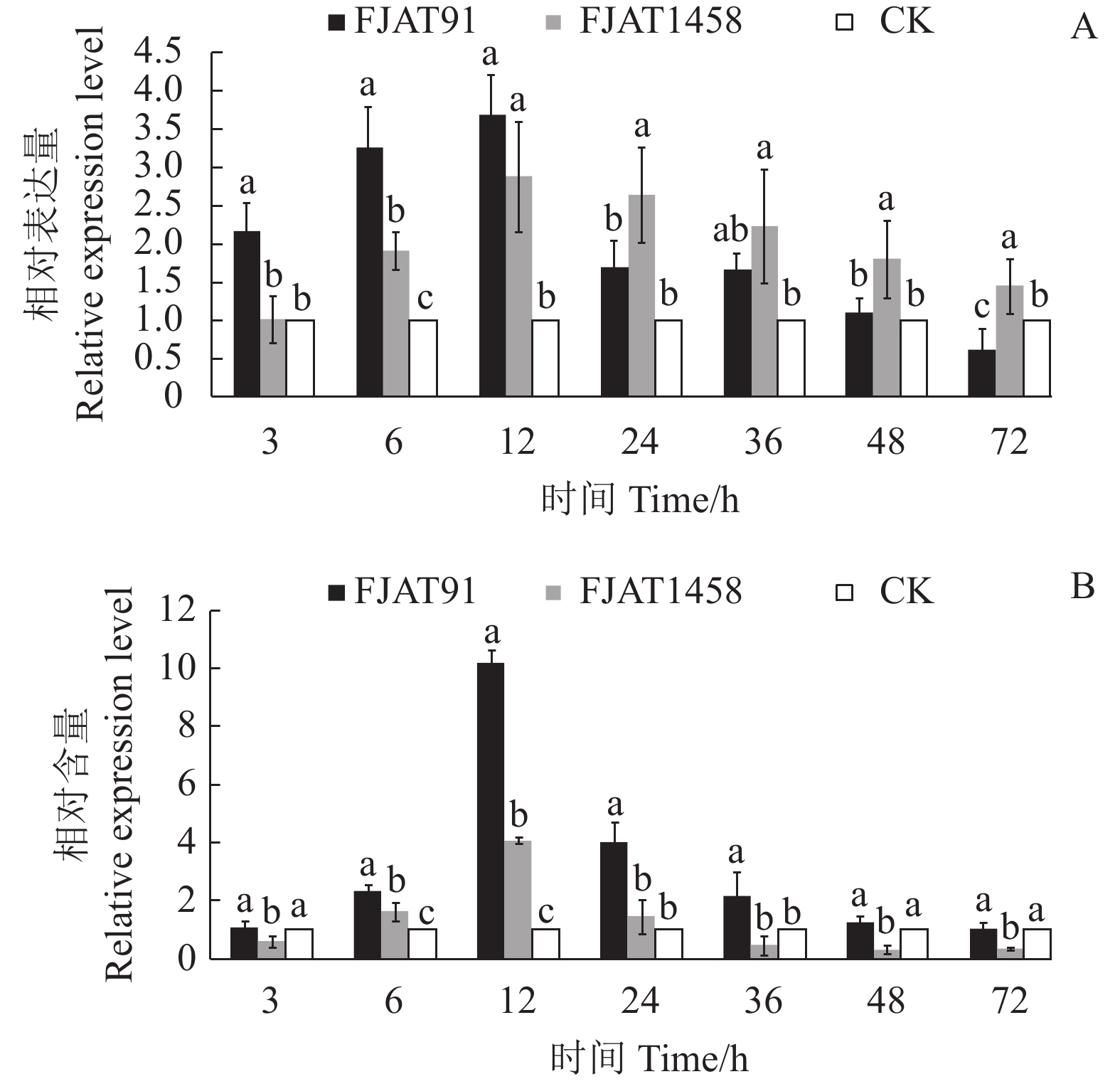
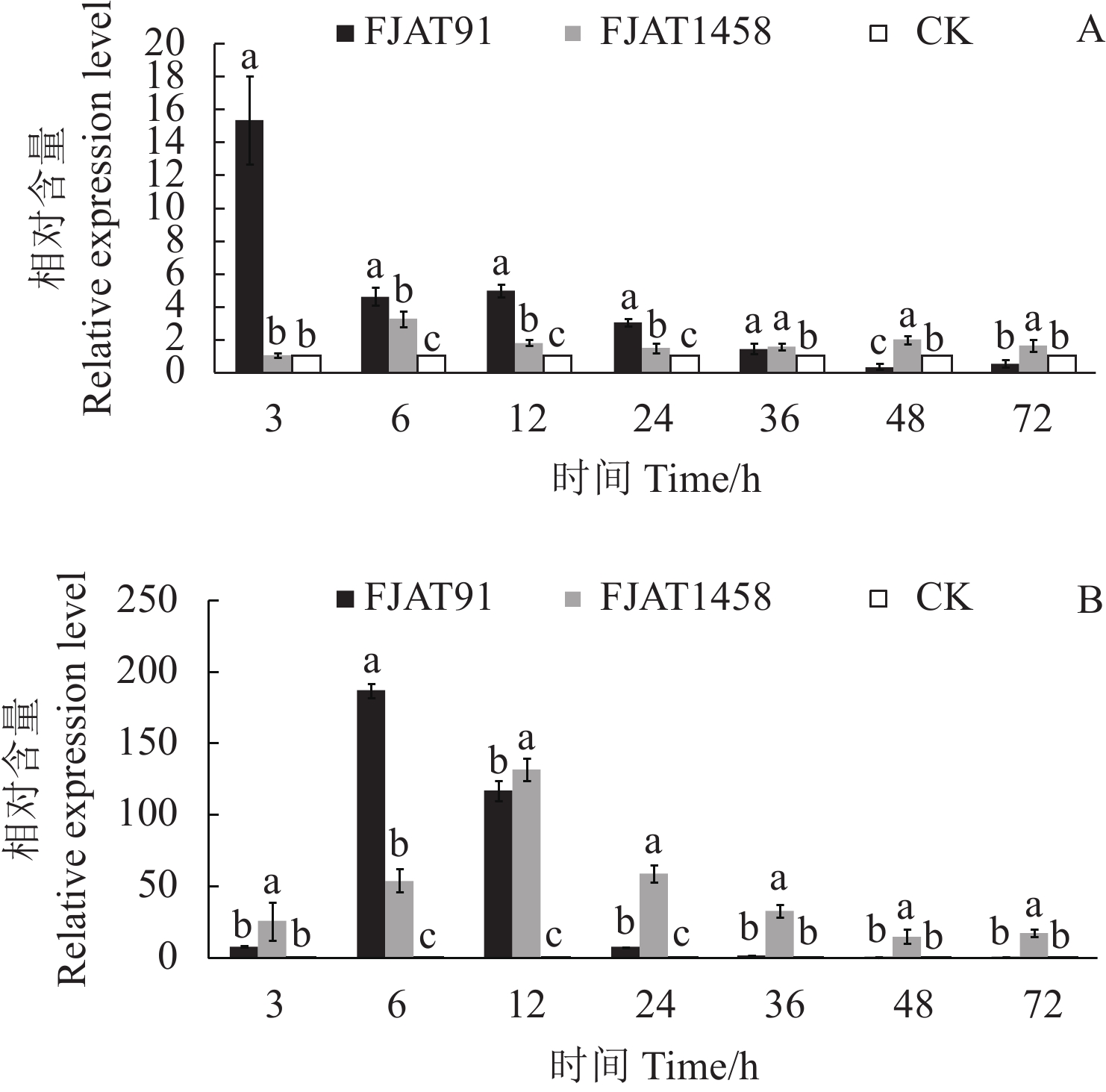
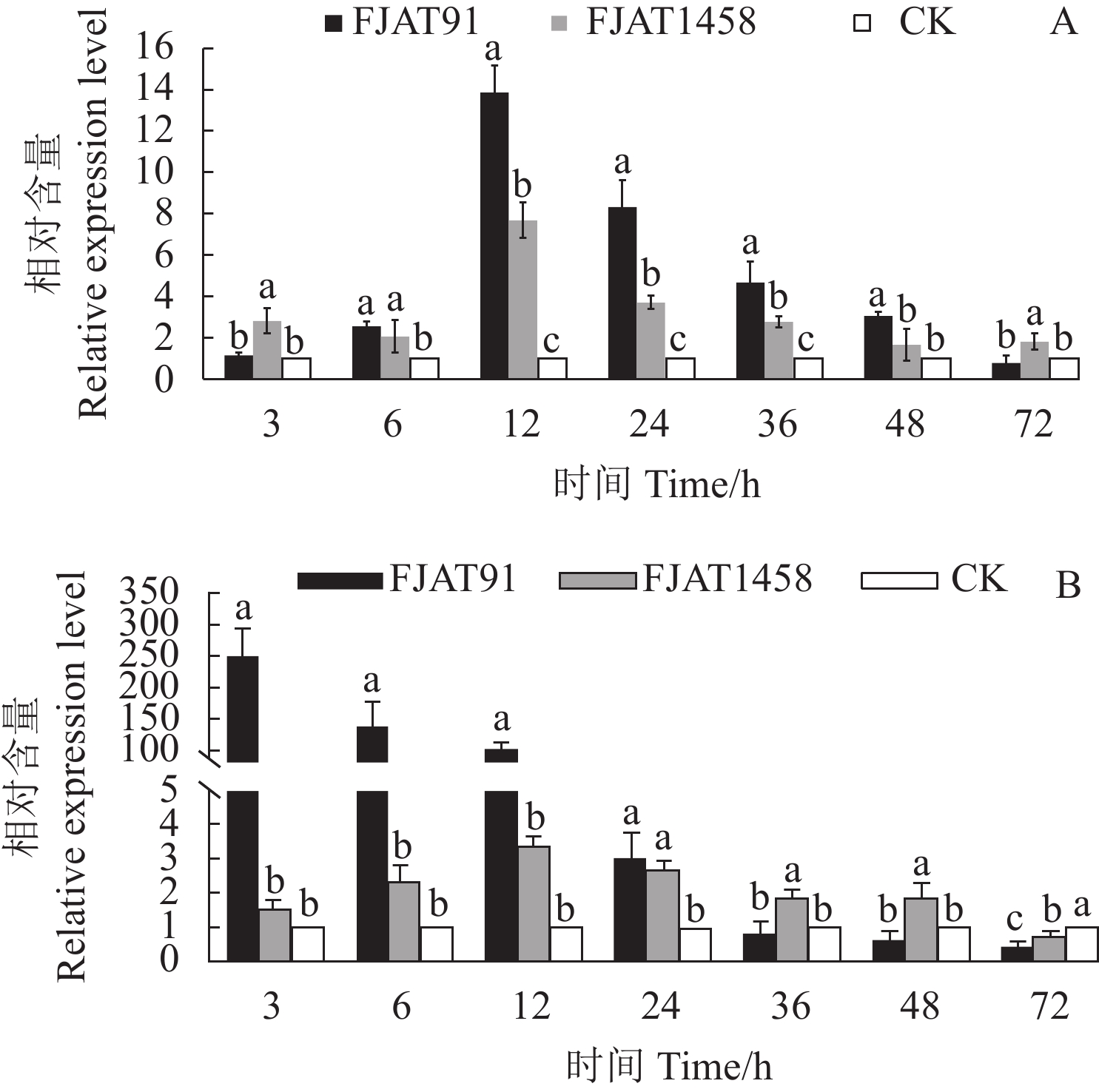
摘要:目的 探究不同致病力青枯雷尔氏菌诱导番茄防御相关基因的表达水平,为探明无致病力青枯雷尔氏菌的生防机制奠定基础。方法 以无菌水为对照(CK),分别接种青枯雷尔氏菌强致病力菌株FJAT91和无致病力菌株FJAT1458,接种后不同时间(0 ,3,6 ,12 ,24 ,36 ,48 ,72 h)取样,利用荧光定量PCR技术,检测接种不同致病力青枯雷尔氏菌后番茄植株中水杨酸(SA)信号转导途径的gluA和PR-1a基因、茉莉酸(JA)信号转导途径的loxA和pin2基因及乙烯(ET)信号转导途径的Osm和PR-1a基因相对表达量的变化。结果 菌株FJAT1458和FJAT91均能诱导番茄gluA、PR-1a、loxA、pin2、Osm和PR-1a基因的表达,接种后期(36 h之后),这些基因(PR-1a和Osm除外)在FJAT1458处理组的表达量均比FJAT91处理组高;FJAT1458和FJAT91诱导gluA和PR-1A基因表达量呈“先上升后下降”的趋势,接种12 h表达量最大;FJAT1458诱导番茄植株loxA和pin2基因表达量均显著高于CK,FJAT91诱导番茄植株loxA基因和pin2基因表达量在接种初期显著高于CK和FJAT1458处理组,后期迅速降低;FJAT-91诱导番茄植株Osm基因显著高于FJAT1458和对照处理(72 h除外),该菌株诱导番茄植株PR-1b基因表达量变化较为强烈,接种3 h,其诱导的PR-1b基因表达量为CK的251.33倍。结论 不同致病力青枯雷尔氏菌诱导番茄防御相关基因表达量不同,可以进一步通过转录组法挖掘更多差异表达的基因。Abstract:Objective Expressions of the defense-related genes in tomato plant induced by Ralstonia solanacearum of varied pathogenicity were studied to understand the biocontrol mechanisms of the avirulent FJAT1458.Method Real-time PCR was used to determine the expressions of gluA and PR-1a in the salicylic acid signal pathway, loxA and pin2 in the jasmonic acid signal pathway, and Osm and PR-1a in the ethylene signal pathway in tomato plants inoculated with the virulent strain FJAT91, the avirulent strain FJAT1458, or sterile water (CK) for 0, 3, 6, 12, 24, 36, 48, and 72 h.Result Both avirulent and virulent strains could induce expressions of gluA, PR-1a, loxA, pin2, Osm, and PR-1a. However, except for PR-1a and Osm, the gene expressions induced by FJAT1458 were significantly higher than those by FJAT91. Both FJAT1458 and FJAT91 inoculations raised the expressions of gluA and PR-1a to a peak followed by a decline in 12 h. The expressions of loxA and pin2 induced by FJAT1458 induction were significantly higher than CK, but FJAT91 did only initially. On the other hand, FJAT91 produced a significantly higher Osm expression than either FJAT1458 or CK, excluding the 72 h inoculation. And in the 3 h inoculation it rendered a PR-1b expression significantly stronger than FJAT1458 at 260.46 times higher than CK.Conclusion Both avirulent and virulent R. solanacearum could induce expressions of the defense-related genes in tomato plants in varied degrees. The transcriptomic method applied in this study could conceivably be used to unveil additional differently expressed genes associated with the pathways in tomato plants in the future.
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】黑木耳Auricularia auricula (L. ex Hook) Underw.又称木耳、云耳、木蛾、黑菜、榆耳,是一种药食兼用胶质菌,在我国已有1 000多年的栽培史[1-2]。国内外大量体外试验[3-4]、动物试验[5-8]、人体观察试验[9-10]研究表明黑木耳多糖具有明显的降血脂[11-12]和抗血栓形成的作用,是良好的膳食补充资源。黑木耳多糖的化学组成中含有葡萄糖醛酸(GlcUA)[13],糖醛酸不以游离单糖存在,而是以苷或多糖的形态存在,成为胶质或黏液物质的主要成分[14],糖醛酸可通过促进胆固醇代谢达到降低总胆固醇、甘油三酯和低密度脂蛋白胆固醇的作用;同时糖醛酸含量与其抗氧化活性呈正相关[15-16]。【前人研究进展】黑木耳细胞壁厚且坚韧,质地致密的结构特性阻碍糖醛酸成分溶出,破碎黑木耳细胞壁,对提高消化吸收率、提高活性具有十分重要的意义。目前常用物理破壁方法有超微粉碎[6, 17]、超声波[18-19]和微波[20-21]辅助提取技术等,而化学方法包括生物酶法[18, 20, 22]提取等。杨春瑜等[23]研究发现黑木耳超微粉碎可以使黑木耳多糖提取率提高3.6%。徐思绮等[24]研究热水发现浸提法、碱提取法和纤维素酶提取法等得到的非淀粉多糖中糖醛酸的含量、抗氧化和降血糖能力存在较大的差异,糖醛酸含量以碱提法最高,达0.24%,抗氧化能力最强。超微粉碎使物料粒径达到微米级别,可促进黑木耳糖醛酸的溶出。超声波是一种机械波,在弹性介质中传播,振动频率高于20 000 Hz。利用超声波的机械作用、热效应、空化效应使细胞组织变形、蛋白质变性,细胞壁破裂,加速有效成分进入溶剂进而增加黑木耳糖醛酸提取效率[25]。果胶酶能够催化果胶质分解,破坏黑木耳细胞壁结构,使糖醛酸能更好地溶出[26]。【本研究切入点】目前的研究集中在黑木耳多糖提取工艺、分离纯化和药理活性的研究,关于纯化的黑木耳多糖的单糖组成以及糖醛酸含量研究已有少量报道,但未见黑木耳糖醛酸的提取工艺的研究。因此,本研究针对黑木耳细胞壁结构特性,结合物理、化学、生物酶等破壁方法,最大限度破坏黑木耳的细胞壁,促进糖醛酸的溶出。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究利用超微粉碎技术降低黑木耳粉的粒径,接着采用超声波协同果胶酶技术提取黑木耳,最大限度破坏黑木耳的细胞壁,筛选适合糖醛酸提取的方法;其次以糖醛酸提取率为优化指标,筛选超声波协同果胶酶法主要影响因素进行响应面优化,最终获得响应面最佳工艺参数,为黑木耳糖醛酸纯化制备、活性分析提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
1.1.1 材料与试剂
黑木耳:市售优质黑龙江黑木耳,粉碎过18、28、50、70、100、150、200、250目筛;纤维素酶(酶活力50 000 U·g-1)、中性蛋白酶(酶活力10 000 U·g-1)、果胶酶(酶活力50 000 U·g-1),购自宁夏和氏璧生物技术有限公司;95%乙醇、苯酚、浓硫酸、四硼酸钠、D-葡萄糖醛酸、间羟基联苯等化学试剂均为分析纯。
1.1.2 仪器与设备
BL60S电子天平,德国Sartrius;GL10MD高速冷冻离心机,湖南湘仪试验仪器开发有限公司;R205B旋转蒸发器,上海申生科技有限公司;CLARIO Star多功能酶标仪,德国BMG LABTECH公司;KQ-600DV数控超声波清洗器,昆山市超声仪器有限公司;SCIENTZ冷冻干燥机,宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 黑木耳糖醛酸提取方法筛选
以传统热水提取为对照,比较超声波、微波、光波等3种辅助提取方法,以及果胶酶、纤维素酶、中性蛋白酶等3种酶提取方式的黑木耳糖醛酸提取率,筛选适宜的提取方法。具体参数见表 1。
表 1 黑木耳糖醛酸提取条件Table 1. Various methods to extract uronic acid from A. auricula方法
Method提取条件
Extraction conditions热水Hot water 液料比50 mL·g-1, 温度80℃, 时间2.5 h 超声波Ultrasonic 液料比50 mL·g-1, 超声功率480 W, 超声时间20 min, 温度60℃ 微波Microwave 液料比50 mL·g-1, 微波功率600 W, 提取时间1.5 min/次,共提取3次(<40℃) 光波Light wave 液料比50 mL·g-1, 提取功率400 W, 提取时间1.0 min/次,共提取3次(<40℃) 中性蛋白酶Neutral protease 液料比50 mL·g-1, 酶用量120 U·g-1木耳(1.25%), 提取温度45℃, pH 7.0, 时间2.5 h 纤维素酶Cellulase 液料比50 mL·g-1, 酶用量100 U·g-1木耳(0.2%), 提取温度50℃, pH5.0, 时间2.5 h 果胶酶Pectinase 液料比50 mL·g-1, 酶用量100 U·g-1木耳(0.2%), 提取温度55℃, pH5.0, 时间2.5 h 1.2.2 黑木耳糖醛酸提取单因素试验
经上述试验筛选,选取超声波辅助果胶酶法进行黑木耳糖醛酸提取。过250目筛(粒径58 μm)黑木耳粉(除粒径单因素实验外)先用480 W超声波处理20 min,然后用0.25%的果胶酶提取(除果胶酶单因素试验外),酶解结束升温至80℃水浴0.5 h灭酶。按表 2的试验设计进行单因素试验。每处理重复3次。
表 2 黑木耳糖醛酸的单因素提取条件Table 2. Conditions for uronic acid extraction from A. auricula by single-factor experiment提取因素
Extraction factors因素水平
Factor level其他提取条件
Other extraction conditions粒径Particle size /μm 880, 600, 270, 212, 150, 150, 106, 75, 58 液料比50 mL·g-1, 超声功率480 W, 超声时间20 min, 酶用量0.25%, 提取温度55℃, pH 5.0, 提取时间2 h 果胶酶Pectinase /% 0.25, 0.50, 0.75, 1.00, 1.25, 1.50, 1.75, 2.00 粒径58 μm, 液料比50 mL·g-1, 超声功率480 W, 超声时间20 min, 提取温度55℃, pH 5.0, 提取时间2 h 液料比Liquid material ratio/(mL·g-1) 20, 40, 50, 60, 80, 100, 110, 120 粒径58 μm, 超声功率480 W, 超声时间20 min, 酶用量0.25%, 提取温度55℃, pH 5.0, 提取时间2 h 温度Temperature /℃ 40, 45, 50, 55, 60, 65 粒径58 μm, 液料比60 mL·g-1, 超声功率480 W, 超声时间20 min, 酶用量0.25%, pH 5.0, 提取时间2 h 提取时间Extraction time/h 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0 粒径58 μm, 液料比60 mL·g-1, 超声功率480 W, 超声时间20 min, 酶用量0.25%, 提取温度50℃, pH 5.0 pH值pH value 3.5, 4.0, 4.5, 5.0, 5.5, 6.0, 6.5, 7.0 粒径58 μm, 液料比60 mL·g-1, 超声功率480 W, 超声时间20 min, 酶用量0.25%, 提取温度50℃, 提取时间2 h 超声功率Ultrasound power/W 240, 360, 420, 480, 540, 600 粒径58μm, 液料比60 mL·g-1, 超声时间20 min, 酶用量0.25%, 提取温度50℃, pH 5.0, 提取时间2 h 超声时间Ultrasound time/min 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60 粒径58 μm, 液料比60 mL·g-1, 超声功率480 W, 酶用量0.25%, 提取温度50℃, pH 5.0, 提取时间2 h 1.2.3 黑木耳糖醛酸提取工艺响应面优化
根据Box-Benhnken中心组合试验设计原理,在单因素试验基础上,选取液料比、pH、超声功率、提取温度等4个因素,采用4因素3水平的响应面设计(表 3),建立木耳糖醛酸含量与4个影响因子的回归方程。其他单因素最佳条件分别为:果胶酶添加量0.25%,提取时间2 h,超声时间30 min。
表 3 试验因素水平Table 3. Codes for factors and levels of experiment水平
Level液料比
Liquid material ratio/(mL·g-1)提取温度
Extract temperature/℃超声功率
Ultrasonic power/WpH值
pH value-1 90 45 480 5.0 0 100 50 540 5.5 1 110 55 600 6.0 1.2.4 糖醛酸提取率的测定
(1) D-葡萄糖醛酸标准曲线绘制精密吸取0.5 mg·mL-1 D-葡萄糖醛酸储备液0.1、0.2、0.4、0.6、0.8、1.0、1.2、1.4、2.0 mL于10 mL容量瓶中,加水稀释,得质量浓度分别为5、10、20、30、40、50、60、70、100 μg·mL-1的D-葡萄糖醛酸标准溶液。分别取D-葡萄糖醛酸标准溶液0.25 mL加入10 mL试管,置冰水浴中,再分别加入2.25 mL四硼酸钠-硫酸溶液继续冷却,在充分振荡后,将试管置于100℃水浴加热10 min,立即放入冰水浴至冷;之后加入0.025 mL 0.15%间羟基联苯溶液,充分振荡,显色,超声去除气泡,静置20 min,以0.25 mL蒸馏水同上制得空白液对照,于525 nm处测定吸光度。以D-葡萄糖醛酸浓度对吸光度制作标准曲线,得回归方程为y=0.0049x-0.0021,R2=0.9998,葡萄糖醛酸浓度在5~100 μg·mL-1范围内,与吸光度呈良好的线性关系。
(2) 糖醛酸含量的测定称取5 g黑木耳粉,加水提取,7 500 r·min -1离心10 min,上清液备用,记录体积并测定糖醛酸含量,糖醛酸含量的测定方法与标准曲线相同,用等量样液替代D-葡萄糖醛酸标准溶液。按以下公式计算糖醛酸提取率:黑木耳糖醛酸提取率(‰)=[(C·V)/W]×1000。式中,C为供试液中糖醛酸质量浓度(μg·mL-1);V为提取液体积(mL);W为供试黑木耳的质量(g)。
1.3 数据处理
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同提取方法的黑木耳糖醛酸提取率
不同提取方法对黑木耳糖醛酸提取率影响(表 4)结果表明,以传统热水法的糖醛酸提取率为对照,超声波、微波、光波3种辅助提取技术的糖醛酸提取率显著提高,超声波的糖醛酸提取率显著高于微波和光波;中性蛋白酶、纤维素酶、果胶酶对提取糖醛酸有利,其糖醛酸提取率比单一热水法显著提高,果胶酶的糖醛酸提取效果显著优于纤维素酶和中性蛋白酶。综合考虑提取效率、操作成本和后续的工业生产,采用超声波协同果胶酶法提取黑木耳糖醛酸。
表 4 不同提取方法对黑木耳糖醛酸提取率影响Table 4. Effect of method on uronic acid extraction rate项目
Items热水
Hot water超声波
Ultrasonic微波
Microwave光波
Light wave中性蛋白酶
Neutral protease纤维素酶
Cellulase果胶酶
Pectinase糖醛酸
uronic acid/‰2.64±0.03e 3.94±0.12ab 3.44±0.06d 3.44±0.25cd 3.72±0.16bc 3.79±0.14b 3.96±0.02a 注:同行数据后不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Note:Different lowercase letters means significant differences in the same line (P<0.05).2.2 超声波协同果胶酶提取黑木耳糖醛酸单因素试验
2.2.1 不同粒径对糖醛酸提取率的影响
从图 1可以看出,58 μm黑木耳粉的糖醛酸提取效果明显优于880 μm的黑木耳粉,糖醛酸提取率提高2倍,说明黑木耳粉越细越有利于黑木耳糖醛酸的溶出。粒径在58~880 μm的范围内糖醛酸提取率变化巨大,随粉末粒径减小呈现平台式不断上升的趋势,当粒径为270~880 μm时提取率基本稳定,但是粒径介于150~212 μm提取率迅速提高,当粒径为75~150 μm时提取率基本稳定、但当粒径为58 μm时糖醛酸提取率迅速提高,达最大值4.30‰。受限于试验室条件能做到最小粒径58 μm,因此木耳粒径采用250目超细粉进行后续试验。
2.2.2 不同果胶酶添加量对糖醛酸提取率的影响
图 2的结果表明,不同果胶酶(酶活50 000 U·g-1)添加量对糖醛酸提取率影响不明显,糖醛酸含量平均值为4.31‰,从提取成本、减少外源添加方面考虑,认为添加0.25%果胶酶,即果胶酶100 U·g-1木耳进行后续的提取试验为宜。
2.2.3 不同液料比对糖醛酸提取率的影响
液料比对糖醛酸提取率的影响见图 3,糖醛酸提取率随着液料比增加迅速提高,当液料比为20 mL·g-1,黑木耳子实体提取液少而黏稠,热水提取后成糊状,提取液无法分离,不利于提取,当液料比为40、50、60 mL·g-1,糖醛酸提取率基本稳定,糖醛酸提取率平均值为4.89‰,当液料比为80、100 mL·g-1,糖醛酸提取率迅速提高,达最大值7.65‰,提高了56%,当液料比增加到110、120 mL·g-1,糖醛酸提取率下降。由于液料比越大,后续浓缩和干燥所需要的能耗越大,成本越高,所以选择最佳液料比为100 mL·g-1。
2.2.4 不同提取温度对糖醛酸提取率的影响
从图 4可以看出,糖醛酸提取率随着温度升高呈现先升后降的变化趋势,原因是果胶酶的活力受温度影响,当温度为50℃,果胶酶的酶活最强,糖醛酸提取率最高达5.24‰。温度高于55℃,或者低于50℃,果胶酶的酶活降低,糖醛酸提取率反而下降,所以选择最佳提取温度为50℃。
2.2.5 不同提取时间对糖醛酸提取率的影响
图 5可见,随着提取时间的延长,糖醛酸提取率先升高后趋于平稳;当提取时间为0.5~1.5 h时,糖醛酸提取率逐渐增加,提取时间达到2.0~3.0 h,糖醛酸提取率基本维持稳定,当提取时间2.0 h时,黑木耳糖醛酸提取率达到最大值,4.51 ‰,所以认为最佳提取时间为2.0 h。
2.2.6 不同pH值对糖醛酸提取率的影响
从图 6中可以看出,在pH值为3.5~7.0,随着酸碱度增加,糖醛酸提取率呈现先升后降的变化,当pH5.5时,糖醛酸提取率最大达4.71‰。
2.2.7 不同超声功率对糖醛酸提取率的影响
不同超声功率对糖醛酸提取率的影响见图 7,随着超声功率增加,糖醛酸提取率平稳上升,当超声功率600 W时,糖醛酸提取率最大达4.85‰。由于受实验室超声提取设备的超声功率限制,当超声功率大于600 W对糖醛酸提取率的影响需要进一步研究。
2.2.8 不同超声时间对糖醛酸提取率的影响
不同超声时间对糖醛酸提取率的影响见图 8,随着超声时间延长,糖醛酸提取率先上升后趋于稳定,当超声时间30~60 min时,糖醛酸提取率基本稳定,与超声时间10、20 min相比,糖醛酸得率明显提高;当超声时间60 min时,提取率最高5.00‰,但是超声时间30 min与60 min的糖醛酸提取率差异不明显,综合考虑提取效率和成本,选择最佳超声时间30 min。
2.3 响应面法优化酶法提取工艺
2.3.1 响应面试验结果
根据表 3的试验因素水平,进行4因素3水平响应面设计,试验结果见表 5。利用Design-Expert 11.0软件对糖醛酸提取率结果进行回归分析,拟合得到回归模型为:Y=-237.95+1.73A-0.24B+0.30C+25.20D+0.06AD+0.14BD-0.01A2-0.01B2-3.43D2,二次多项式回归模型方差分析结果见表 6。
表 5 响应面法试验方案及结果Table 5. Response surface design and results on uronic acid extraction序号
No.液料比
Liquid-material ratio/(mL·g-1)提取温度
Extract temperature/℃超声功率
Ultrasonic power/WpH值
pH value糖醛酸提取率
Uronic acid extraction rate/‰1 90 45 540 5.5 6.38±0.28 2 110 45 540 5.5 7.36±0.07 3 90 55 540 5.5 5.81±0.60 4 110 55 540 5.5 6.78±0.41 5 100 50 480 5.0 5.58±0.10 6 100 50 600 5.0 5.96±0.49 7 100 50 480 6.0 6.02±0.10 8 100 50 600 6.0 6.38±0.28 9 90 50 540 5.0 5.83±0.13 10 110 50 540 5.0 5.84±0.10 11 90 50 540 6.0 5.37±0.22 12 110 50 540 6.0 6.60±0.21 13 100 45 480 5.5 6.69±0.42 14 100 55 480 5.5 5.74±0.34 15 100 45 600 5.5 6.51±0.08 16 100 55 600 5.5 6.37±0.09 17 90 50 480 5.5 5.16±0.27 18 110 50 480 5.5 6.65±0.14 19 90 50 600 5.5 5.27±0.35 20 110 50 600 5.5 6.10±0.52 21 100 45 540 5.0 6.92±0.23 22 100 55 540 5.0 5.91±0.23 23 100 45 540 6.0 6.49±0.42 24 100 55 540 6.0 6.85±0.46 25 100 50 540 5.5 7.70±0.19 26 100 50 540 5.5 7.65±0.23 27 100 50 540 5.5 7.75±0.48 28 100 50 540 5.5 7.93±0.53 29 100 50 540 5.5 7.84±0.28 表 6 回归模型方程方差分析Table 6. Variance analysis of regression equation方差来源
Source平方和
Sum of squares自由度
Degrees of freedom均方
Mean squareF值
F valueP值
Pvalue显著性
Significance模型Model 17.18 14 1.23 29.53 <0.0001 ** A 2.53 1 2.53 60.90 <0.0001 ** B 0.6960 1 0.6960 16.75 0.0011 ** C 0.0469 1 0.0469 1.13 0.3061 D 0.2324 1 0.2324 5.59 0.0330 * AB 0.0000 1 0.0000 0.0006 0.9808 AC 0.1089 1 0.1089 2.62 0.1277 AD 0.3721 1 0.3721 8.96 0.0097 ** BC 0.1640 1 0.1640 3.95 0.0668 BD 0.4692 1 0.4692 11.29 0.0047 ** CD 0.0001 1 0.0001 0.0024 0.9616 A2 5.65 1 5.65 136.11 <0.0001 ** B2 0.7999 1 0.7999 19.25 0.0006 ** C2 6.80 1 6.80 163.62 <0.0001 ** D2 4.78 1 4.78 115.12 <0.0001 ** 残差Residual 0.5816 14 0.0415 - - - 失拟项Lack of fit 0.5315 10 0.0531 4.24 0.0882 - 纯误差Pure error 0.0501 4 0.0125 - - - 总误差Cor total 17.76 28 - - - - 标准偏差Standard deviation 0.2038 - R2 0.9672 - - 平均值Average value 6.46 - RAdj2 0.9345 - - 变异系数Coefficient of variation/% 3.15 - RPred2 0.8232 - - 注:“-”表示无。*、**分别表示在0.05、0.01水平差异显著。
Note:‘-’means no. *,** means significant difference at 0. 05 and 0. 01 level,respectively.回归方差方差分析结果显示,数据模型的P<0.001说明该模型极显著。失拟项P=0.008,不显著。决定系数R2=0.9672,说明模型拟合程度良好,回归方程很好地描述各因素与响应值之间的真实关系。矫正决定系数RAdj2=0.9345,说明仅有总变异不到7%不能由该模型解释。变异系数CV=3.15%,说明试验结果可靠。
A、B、AD、BD、A2、B2、C2、D2对响应值糖醛酸提取率的影响极显著(P<0.01),D对响应值糖醛酸提取率的影响显著(P<0.05),而C、AB、AC、BC、CD对响应值糖醛酸提取率的影响均不显著(P>0.05)。在所取的各因素水平范围内,根据F值和P值可以判断各工艺条件对糖醛酸提取率的影响强弱,F值越大,说明作用影响越强(或P值越小,作用越强),影响因子的主效应的主次顺序为:液料比>提取温度>pH值>超声功率。
2.3.2 响应面分析
根据回归方程绘出的等高线图(图 9)能比较直观地解释各变量之间对响应值的影响。等高线的形状可以反映因素间交互作用的强弱。在试验设计范围内,各个因素中液料比对糖醛酸提取率的影响最大,提取温度的影响次之,pH值的影响第三,超声功率的影响最小;交互作用中,提取温度和pH值的交互作用对糖醛酸提取率的影响最大,液料比和pH值交互作用的影响次之,两者之间交互作用明显(P<0.01)。其他因素之间无明显交互作用。从图 9-E可以看出,其等高线图为椭圆形,说明提取温度和pH值交互作用极明显;响应面坡度较为陡峭,响应值随pH值的变化率大于提取温度的变化率,说明二者交互作用中pH值对糖醛酸提取率的影响大于提取温度。从图 9-C可以看出,其等高线图为椭圆形,说明料液比和pH值交互作用极明显;响应面坡度较为陡峭,响应值随pH值的变化率大于料液比的变化率,说明二者交互作用中料液比对糖醛酸提取率的影响大于pH值。
2.3.3 黑木耳糖醛酸的最佳工艺及验证试验
通过Design-Expert 11对二次多项式模型进行求导,可得到该模型的极值点,预测糖醛酸的最大值为7.77‰,参数的最佳水平分别为:液料比109.26 mL·g-1、pH5.60、超声功率535.69 W、提取温度48.63℃,对最佳点调整为液料比110 mL·g-1、pH5.60、超声功率540 W、提取温度49℃,进行5次重复试验进行优化结果验证,取5次试验结果的平均值,得到优化后的糖醛酸提取率最大值为7.95‰,接近模型预测值7.77‰,该响应面模型可以较好地预测黑木耳糖醛酸提取情况。
3. 讨论
黑木耳糖醛酸是黑木耳多糖的成分之一,糖醛酸的提取与其子实体内部结构密切相关,黑木耳子实体横切面中分为绒毛层、致密层、亚致密上层、中间层、下致密层和子实体层,细胞粗大、壁厚以及质地坚韧致密使得黑木耳活性成分难以透过细胞壁溶于水中[27]。由于黑木耳糖醛酸含量较低,直接进行黑木耳糖醛酸提取工艺的研究较少,一般先提取多糖;黑木耳多糖的单糖组成中含有葡萄糖醛酸,糖醛酸提取率与多糖提取率呈正相关。黑木耳多糖中糖醛酸含量的研究报道显示:传统热水浸提法黑木耳的多糖提取率仅为4%~8%[28-29],通过超微粉碎、超声波、微波、生物酶法等提取技术破壁处理黑木耳的多糖提取率可达8%~25%[20-21, 30]。许海林[31]优化黑木耳水溶性多糖提取工艺,多糖得率8%,进一步纯化获得多糖组分AAP-10、AAP-80,其糖醛酸的含量分别为23.76%和30.14%。樊黎生[32]纯化黑木耳多糖AAP-Ⅱa组分中葡萄糖糖醛酸的含量为33.82%。本文研究结果显示,传统热水浸提法的糖醛酸含量2.64‰,采用超微粉碎法、超声波联合生物酶法的现代提取技术,在液料比110 mL·g-1、pH5.60、超声功率540 W、提取温度49℃的最佳工艺条件下,糖醛酸的提取率提高2倍,最高达7.95‰。本文首次研究黑木耳糖醛酸提取工艺,尽管糖醛酸和多糖的提取方法密切相关,提取因素水平存在差异,如有报道多糖提取最佳的液料比为80 mL·g-1[18],综合考虑多糖制备成本,甚至更低液料比,但是提取糖醛酸的最佳液料比是110 mL·g-1;另外,酶法的提取结果局限于所选用酶的种类和厂家,细胞壁由果胶、纤维素、半纤维素、蛋白质等构成,将果胶酶、纤维素酶、蛋白酶等复合酶作用于细胞壁的结构,理论上可以提升破壁效果,后续可进一步研究其他商业单一酶和复合酶的提取效果,提高多糖中糖醛酸含量,为糖醛酸的进一步纯化制备、活性分析提供基础。
4. 结论
本研究通过单因素试验筛选出液料比、pH、超声功率和提取温度4个因素,再通过响应面进行优化,当液料比为110 mL·g-1、pH值5.60、超声功率540 W、提取温度49℃时,超声波辅助提取黑木耳糖醛酸的得率达到7.95‰。研究以提高糖醛酸提取率为目标,采用超声波协同果胶酶法进行提取,为黑木耳糖醛酸纯化、活性分析的功能食品深加工提供有益的参考。
-
表 1 RT-PCR检测基因的特异引物序列
Table 1 Specific primer sequences used for RT-PCR
检测基因
Tested
gene信号通路
Signal pathways基因库
登记号
GenBank accession no.引物序列
Primer sequencegIuA SA M80604 F: TCAGCAGGGTTGCAAAATCA R: CTCTAGGTGGGTAGGTGTTGGTTAA PR-1a SA M69247 F: TCT TGT GAG GCC CAA AAT TC R: ATA GTC TGG CCT CTC GGA CA loxA JA U09026 F: TGGTAGACCACCAACACGAA R: GACCAAAACGCTCGTCTCTC pin2 JA AY129402 F: TGATGCCAAGGCTTGTACTAGAGA R: AGCGGACTTCCTTCTGAACGT PR-1b ET X14065 F: CCA AGA CTA TCT TGC GGT TC R: GAA CCT AAG CCA CGA TAC CA Osmotin-like ET M21346 F: TGTACCACGTTTGGAGGACA R: ACCAGGGCAAGTAAATGTGC -
[1] HAYWARD A C. Biology and epidemiology of bacterial wilt caused by Pseudomonas solanacearum [J]. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 1991, 29: 65−87. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.py.29.090191.000433
[2] PRIOR P, AILLOUD F, DALSING B L, et al. Genomic and proteomic evidence supporting the division of the plant pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum into three species [J]. BMC Genomics, 2016, 17: 90. DOI: 10.1186/s12864-016-2413-z
[3] SUGA Y, HORITA M, UMEKITA M, et al. Pathogenic characters of Japanese potato strains of Ralstonia solanacearum [J]. Journal of General Plant Pathology, 2013, 79(2): 110−114. DOI: 10.1007/s10327-013-0429-7
[4] CELLIER G, PRIOR P. Deciphering phenotypic diversity of Ralstonia solanacearum strains pathogenic to potato [J]. Phytopathology, 2010, 100(11): 1250−1261. DOI: 10.1094/PHYTO-02-10-0059
[5] BALABEL N M, EWED W E, MOSTAPHA M I, et al. Some epidemiological aspects of Ralstonia solanacearum [J]. Egypt Journal of Agriculture Research, 2005, 83(4): 1547−1563.
[6] FREY P, PRIOR P, MARIE C, et al. Hrp mutants of Pseudomonas solanacearum as potential biocontrol agents of tomato bacterial wilt [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1994, 60(9): 3175−3181. DOI: 10.1128/aem.60.9.3175-3181.1994
[7] 杨宇红, 刘俊平, 杨翠荣, 等. 无致病力hrp-突变体防治茄科蔬菜青枯病 [J]. 植物保护学报, 2008, 35(5):433−437. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-7518.2008.05.010 YANG Y H, LIU J P, YANG C R, et al. Control of Solanacearum vegetable bacterial wilt with avirulent hrp- mutants [J]. Acta Phytophylacica Sinica, 2008, 35(5): 433−437.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-7518.2008.05.010
[8] 刘波, 蓝江林, 朱育菁, 等. 植物免疫系统的研究与应用 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2007, 23(S):163−172. LIU B, LAN J L, ZHU Y J, et al. Study and application of Plant immune system [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2007, 23(S): 163−172.(in Chinese)
[9] FENG D X, TASSET C, HANEMIAN M, et al. Biological control of bacterial wilt in Arabidopsis thaliana involves abscissic acid signalling [J]. The New Phytologist, 2012, 194(4): 1035−1045. DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04113.x
[10] PARROTT D L, HUANG L, FISCHER A M. Downregulation of a barley (Hordeum vulgare) leucine-rich repeat, non-arginine-aspartate receptor-like protein kinase reduces expression of numerous genes involved in plant pathogen defense [J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2016, 100: 130−140. DOI: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.01.005
[11] BLOCK A, SCHMELZ E, O'DONNELL P J, et al. Systemic acquired tolerance to virulent bacterial pathogens in tomato [J]. Plant Physiology, 2005, 138(3): 1481−1490. DOI: 10.1104/pp.105.059246
[12] THALER J S, OWEN B, HIGGINS V J. The role of the jasmonate response in plant susceptibility to diverse pathogens with a range of lifestyles [J]. Plant Physiology, 2004, 135(1): 530−538. DOI: 10.1104/pp.104.041566
[13] ISHIHARA T, MITSUHARA I, TAKAHASHI H, et al. Transcriptome analysis of quantitative resistance-specific response upon Ralstonia solanacearum infection in tomato [J]. Plos One, 2012, 7(10): e46763. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046763
[14] CHEN Y N, REN X P, ZHOU X J, et al. Dynamics in the resistant and susceptible peanut (Arachis hypogaea L. ) root transcriptome on infection with the Ralstonia solanacearum [J]. BMC Genomics, 2014, 15: 1078. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-1078
[15] ZULUAGA A P, SOLÉ M, LU H B, et al. Transcriptome responses to Ralstonia solanacearum infection in the roots of the wild potato Solanum commersonii [J]. BMC Genomics, 2015, 16: 246. DOI: 10.1186/s12864-015-1460-1
[16] 郑雪芳, 刘波, 林乃铨, 等. 青枯雷尔氏菌无致病力突变菌株的构建及其防效评价模型分析 [J]. 植物病理学报, 2013, 43(5):518−531. ZHENG X F, LIU B, LIN N Q, et al. Construction of Ralstonia solanacearum avirulent mutants and evaluation model of their control efficacy against tomato bacterial wilt disease [J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 2013, 43(5): 518−531.(in Chinese)
[17] 郑雪芳, 朱育菁, 刘波, 等. 番茄青枯病植物疫苗胶悬菌剂的制备及其对病害的防治效果 [J]. 植物保护, 2017, 43(2):208−211. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.2017.02.037 ZHENG X F, ZHU Y J, LIU B, et al. Preparation of colloidal suspension agent used as plant vaccine against tomato bacterial wilt disease and its control efficacy [J]. Plant Protection, 2017, 43(2): 208−211.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.2017.02.037
[18] KELMAN A. The relationship of pathogenicity in Pseudomonas solanacearum to colony appearance on a tetrazolium medium [J]. Phytopathology, 1954, 44: 693−695.
[19] SCHMITTGEN T D, LIVAK K J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method [J]. Nature Protocols, 2008, 3(6): 1101−1108. DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2008.73
[20] 陈达. 拮抗菌和青枯菌无致病力突变株防控茄科作物青枯病的效应和机理研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2014. CHEN D. The control efficacy of bacterial wilt in solanaceae crops by antagaonistic bacterium and avirulent mutants of Ralstonia solanacearum and mechanisms [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing agricultural university, 2014. (in Chinese)
[21] 刘俊平. 无致病力hrp-突变体防治番茄青枯病作用研究 [D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2006. LIU J P. Study on the control effect against tomato bacterial wilt with avirulent hrp- mutants [D]. Beijing: Chinese academy of agricultural sciences, 2006. (in Chinese)
[22] MILLING A, BABUJEE L, ALLEN C. Ralstonia solanacearum extracellular polysaccharide is a specific elicitor of defense responses in wilt-resistant tomato plants [J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(1): e15853. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015853
[23] CHEN D, LI C, WU K, et al. A PhcA- marker-free mutant of Ralstonia Solanacearum as potential biocontrol agent of tomato bacterial wilt [J]. Biological Control, 2015, 80: 96−102. DOI: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2014.09.005
[24] CIARDI J A, TIEMAN D M, LUND S T, et al. Response to Xanthomonas campestris pv. Vesicatoria in tomato involves regulation of ethylene receptor gene expression [J]. Plant Physiology, 2000, 123(1): 81−92. DOI: 10.1104/pp.123.1.81
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: