Isolation, Identification, and S1 Gene Sequencing of Two Strains of Avian Infectious Bronchitis Virus
-
摘要:目的 了解福建地区鸡传染性支气管炎病毒(Infectious bronchitis virus,IBV)的流行及其S1基因变异情况。方法 对2021年在福建地区鸡群中分离的2株病毒,通过鸡胚致病性试验、电子显微镜观察及RT-PCR方法进行鉴定。对2株分离株的S1基因进行克隆、测序并利用生物学软件进行分析。结果 分离到的2株病毒均为IBV,分别命名为FJ-NP01和FJ-FZ01;FJ-NP01株和FJ-FZ01株的S1基因全长分别为1629 nt和1620 nt,编码543 aa和540 aa。FJ-FZ01株的 S1基因裂解位点为HRRRR,与基因型I分支所有参考毒株裂解位点一致;分离株FJ-NP01的 S1基因裂解位点为HRRKR,与已报道的基因型ⅣIBV分离毒株的裂解位点不同,与基因型Ⅵ参考毒株TC07-2的裂解位点一致。FJ-NP01株和FJ-FZ01株之间的核苷酸和氨基酸同源性较低,分别为83.2%和79.6%;与中国使用的Mass型常规疫苗H120和H52核苷酸和氨基酸序列同源性仅为75.7%~76.3%和77.1%~83.5%。FJ-NP01株是由基因型Ⅳ毒株CK CH GD LZ12-4与基因型I毒株L-1148在S1基因处发生重组而产生的新毒株,其核苷酸序列1438~1506 nt与推测的亲本毒株CK CH GD LZ12-4同源性达97%,其他S1基因核苷酸序列与推测的亲本毒株L-1148同源性达95.9%。结论 以上结果表明福建地区IBV流行较为复杂,现有Mass型疫苗在福建省可能起不到良好的免疫保护作用。
-
关键词:
- 鸡传染性支气管炎病毒 /
- 分离 /
- 鉴定 /
- S1基因 /
- 序列分析
Abstract:Objective Epidemiology and genetic variations of the infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) in Fujian province were studied.Method Two strains of virus isolated from the diseased chickens in Fujian in 2021 were identified by chicken embryo pathogenicity test, electron microscope observation, and RT-PCR. S1 genes of the isolates were cloned, sequenced, and analyzed using biological software.Result The two IBV strains were code named FJ-NP01 and FJ-FZ01. The full length of S1 of FJ-NP01 was 1629 nt encoding 543 amino acids, and that of FJ-FZ01, 1620 nt encoding 540 amino acids. The S1 gene cleavage site of FJ-FZ01 was HRRRR, same as all reference strains of genotype I branch; while that of FJ-NP01 HRRKR differed from the reported site of IBV isolated from genotype Ⅳ but same as that of TC07-2 reference strain of genotype Ⅵ. The homology of nucleotide and amino acid between the two isolates was 83.2% and 79.6%, respectively, but merely 75.7%–76.3% and 77.1%–83.5% with the Mass-type conventional vaccines H120 and H52, respectively. Further analysis showed that FJ-NP01 was from a recombination event between CK CH GD LZ12-4 and L-1148, the homology of nucleotide acid between 1438–1506 nt of FJ-NP01 with CK CH GD LZ12-4 was 97%, and 95.9% between the other nucleotide acid of S1 gene with L-1148 .Conclusion It appeared that the IBV epidemic experienced in the province was complex in nature and that the existing Mass vaccines would not provide sufficient immune protection to deter the spread.-
Keywords:
- Infectious bronchitis virus /
- isolation /
- identification /
- S1 genes /
- sequence analysis
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】鸡传染性支气管炎(Infectious bronchitis,IB)是由鸡传染性支气管炎病毒(Infectious bronchitis virus,IBV)感染引起的一种急性、接触性传染性病,被世界兽医局列为禽病B类传染病[1]。根据IBV对宿主组织的亲嗜性及引起的主要症状,可将其划分为呼吸系型、肾型和肠型等。IBV基因型较多且不同类型毒株之间交叉免疫保护的能力弱,导致该病的防控难度较大,至今IB仍是妨碍世界养鸡业健康发展的主要疫病之一[2-3]。【前人研究进展】IBV基因组为不分节的单股正链RNA,全长约27.6 kb,囊括6种亚基因组 mRNA(1~6),其中mRNA2、mRNA3、mRNA4和mRNA6分别编码4个结构蛋白:纤突蛋白(S)、小膜蛋白(E)、膜蛋白(M)和核蛋白(N)[4-7]。S蛋白与宿主细胞膜上的病毒受体结合后被宿主细胞的蛋白酶裂解为N端的S1蛋白和C端的S2蛋白[4]。S1蛋白是IBV产生感染性、致病性及组织嗜性的主要蛋白。不同IBV毒株间S1基因变异较大,其编码的氨基酸差异在2%~25%[8-9]。由于IBV复制依赖的RNA聚合酶缺乏校正能力,以及疫苗的频繁使用,致使病毒在复制过程中容易发生变异或重组[10-13]。S1基因核苷酸序列的点突变、插入、缺失或重组是导致IBV基因型较多的主要原因,国内外学者开展了许多基于S1 基因的序列差异分析研究工作[14-17]。国内外学者在IBV的病原学、流行与分布、分子遗传变异机制、IBV诱导的天然免疫应答、体外培养、诊断技术和防控措施等方面都有深入研究。然而,由于IBV自身变异频率高以及频繁地使用疫苗加剧了野毒株的变异压力,导致病毒进化加快。因此,对IBV的流行病学和分子遗传变异情况进行监测,已成为有效防控IBV的重要组成部分。【本研究切入点】近年来,福建省IBV流行发生频繁,2021年福建地区IBV的流行及变异情况亟需开展相关研究。【拟解决的关键问题】在福建地区疑似发生IB的临床样品中分离到2株病毒,通过对鸡胚致病性试验、电镜观察以及RT-PCR进行鉴定确认分离到的2株病毒均为IBV,并进一步对2株IBV分离株的 S1基因进行克隆、测序及序列分析,以期为福建省有效防控IB提供科学依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 病料来源、SPF鸡胚及主要试剂
2021年在福州市、南平市鸡场采集疑似IB病死鸡脏器组织样品。10日龄SPF鸡胚购自广东大华农动物保健品股份有限公司SPF实验动物中心;IBV毒株由本研究室分离、鉴定及保存。核酸提取试剂盒(EasyPure® viral DNA/RNA kit)、反转录试剂盒(TransScript® One-Step gDNA Removal and cDNA Synthesis Super Mix)、克隆试剂盒(pEASY®-Blunt Zero Cloning kit)均购自北京全式金生物技术有限公司;DNA纯化回收试剂盒(TianGen·Universal DNA Purification kit)购自天根生物技术有限公司;高保真酶(2 ×CataAmp High Fidelity PCR Mix)购自爱博泰克生物技术有限公司;DL2000 DNA Marker购自大连宝生物有限公司。
1.2 引物设计
下载GenBank中收录的IBV S1全基因序列,利用Oligo7.0软件设计1对特异性引物,上游引物S1F:5′-ACTGAACAAAAGACCGACT-3′;下游引物S1R: 5′-GGCACTATCATCTTTAACGAAC-3′,扩增片段大小为1 770 bp;IBV鉴定引物参照参考文献[17]设计,由福州尚亚生物技术有限公司合成。
1.3 样品处理
在生物安全柜中将组织剪碎,每克组织加入4 mL无菌PBS溶液研磨;加入2000 UI·mL−1青霉素和2000 μg·mL−1链霉素,4 ℃作用4 h,−70 ℃冰箱反复冻融3次,6000 r·min−1,4 ℃离心10 min,取上清,分装保存;取部分上清,平板划线,37 ℃过夜培养,确定有无细菌污染,并将无细菌生长的样品冻存。
1.4 病毒分离与电镜鉴定
将1.3中上清经0.22 µm过滤器过滤后取200 µL接种于10日龄SFP 鸡胚尿囊腔中,置于37 ℃恒温培养箱中孵育。剔除24 h内死亡的鸡胚。收取48~120 h内死亡的鸡胚, 4 ℃冰箱静置12 h以上;无菌收取尿囊液,将收取的尿囊液在SPF鸡胚中盲传4代后进行PCR鉴定。取第4代 PCR 鉴定为阳性的鸡胚尿囊液2 mL,参照参考文献[18]处理,电镜下观察病毒形态。
1.5 核酸提取和RT-PCR鉴定
按EasyPure® viral DNA/RNA kit说明书提取尿囊液中的核酸。按照TransScript® One-Step gDNA Removal and cDNA Synthesis Super Mix试剂盒的操作说明书对提取的RNA进行反转录,反转录后的cDNA取3 µL、2×CataAmp High Fidelity PCR Mix 10 µL,上/下游引物(10 µmol·L−1) 各1 µL,无菌去离子水补足至20 µL。反应条件:95 ℃ 预变性5 min;95 ℃热变性 30 s,55 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃ 延伸15 s,35个循环;72 ℃ 终延伸7 min。反应结束后取7 µL扩增产物于1%琼脂糖凝胶上进行电泳,电泳条件为125 V、25 min。
1.6 IBV分离株S1基因克隆测序
提取盲传后第4代鸡胚尿囊液中的病毒总RNA。参照TransScript® One-Step gDNA Removal and cDNA Synthesis Super Mix试剂盒的操作说明对1.5中提取的RNA进行反转录,反转录后的cDNA取3 µL、2×CataAmp High Fidelity PCR Mix 10 µL,S1F/S1R引物(10 µmol·L−1) 各1 µL,无菌去离子水补足至20 µL。反应条件为:95 ℃预变性5 min;95 ℃ 30 s,57 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 2 min,35个循环;72 ℃ 延伸10 min,4 ℃保存。反应结束后取7 µL扩增产物于1%琼脂糖凝胶上进行电泳,电泳条件为125 V、25 min。PCR产物回收纯化后连接于pEASY®-Blunt Zero 克隆载体上并转化至Trans1-T1感受态细胞中,经菌落PCR检测阳性的单个菌落进行扩繁并提取质粒,阳性质粒送往福州尚亚生物技术有限公司进行测序。
1.7 IBV分离株S1基因序列分析
利用DNAStar Lasergene 7软件对2株IBV分离株的S1基因测序结果进行拼接并上传至GenBank数据库。采用MEGA7.0软件对2株分离株的S1基因与GenBank数据库收录的有代表性的37株IBV参考株(表1)的S1基因序列进行比对分析,构建S1基因的遗传进化树。使用SimPlot3.5.1和 RDP4.101软件进行分离株S1基因遗传重组分析。
表 1 IBV参考毒株Table 1. IBV reference strains毒株 Virus 登录号 Locus 毒株 Virus 登录号 Locus Ma5
H120
LDT3
4/91
H52
28/86
M41
G13-1
Holte
UK/7/93
Italy-02
TW2575/98
3468/07
JP9758
TA03
GX-NN-6
TC07-2
PSH050513
QXIBVAY561713
FJ888351
AY702975
KF377577
EU817497
AY846750
DQ834384
L14069
L18988
Z83979
AJ457137
DQ646405
EU822336
AY296746
AY837465
JX291985
GQ265948
DQ160004
AF193423ZJ971
L-1148
A2
LX4
HB08
HN08
CK/CH/GD/HY09
CK/CH/HN/HN09
CKCHJSLYG1911-8
CKCHJSLYG1911-10
CKCHJSLYG1911-11
CK/CH/LGX/091109
CK/CH/LDL/07II
X
CK/CH/LCQ/08II
ck/CH/LGX/091110
CKCHJSLYG1912-1
CK CH GD LZ12-4AF352313
DQ431199
AY043312
AY338732
GQ265934
GQ265940
HQ018887
HQ018886
MW044574
MW044575
MW044583
KF411041
EU563940
FJ8298882
GQ258305
HM194643
MW044590
KC6922772. 结果与分析
2.1 病毒分离鉴定结果
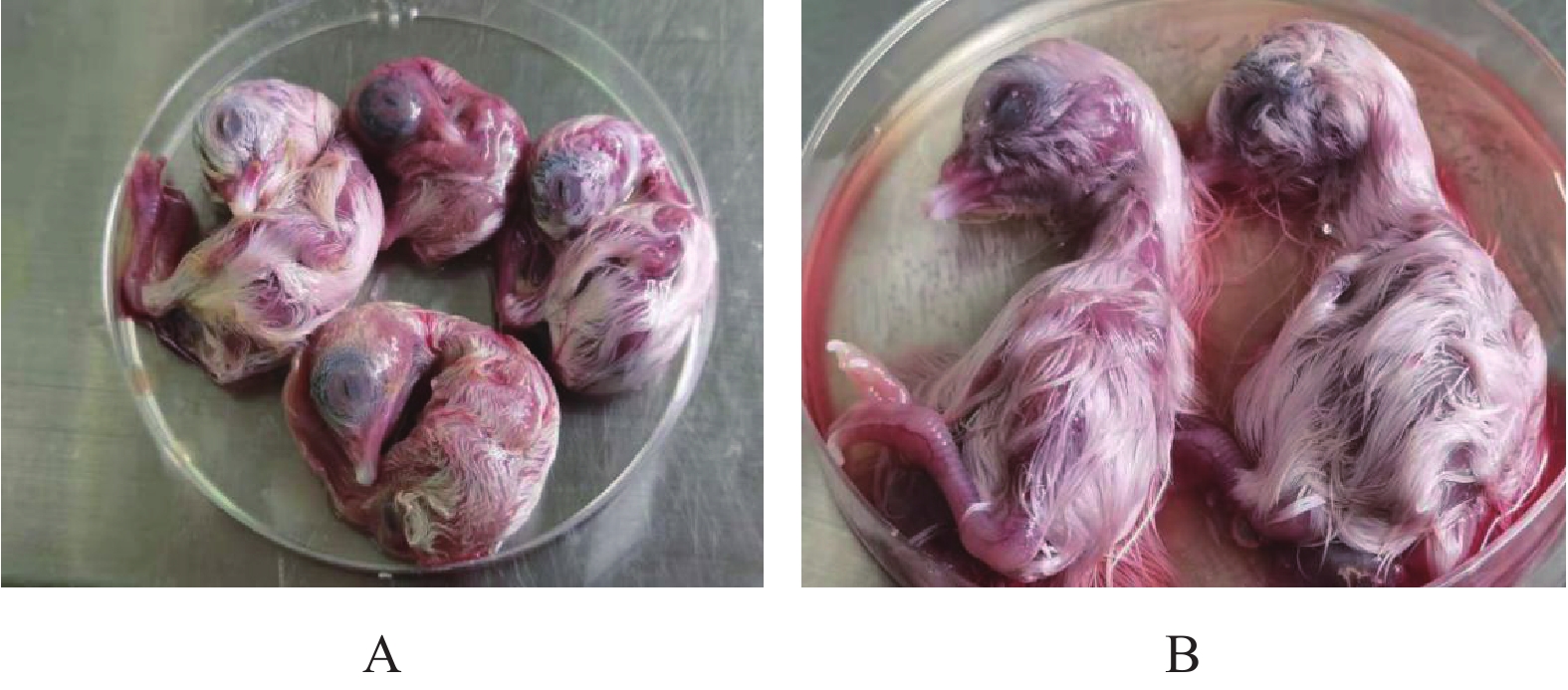
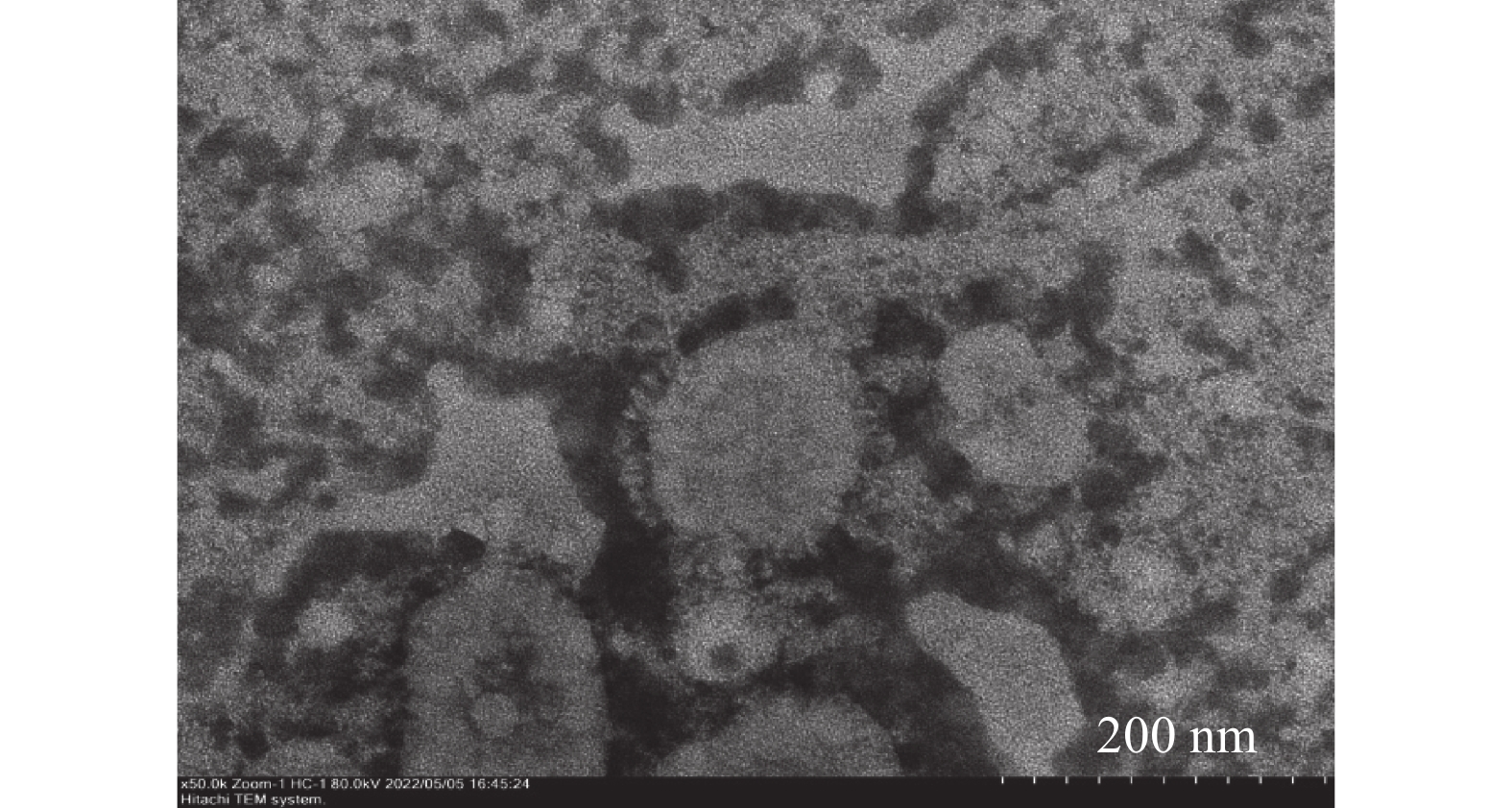
10日龄SPF鸡胚接种2种病料研磨液后,鸡胚陆续出现死亡。与对照组相比,接毒组表现发育不良、胚体蜷曲、弥漫性出血(图1)。分离株4代SPF鸡胚尿囊液经1%磷钨酸负染后电镜下可见直径约80~120 nm、略呈圆形的病毒粒子,表面有松散的冠状突起,与冠状病毒特有的形态学特征相一致(图2)。通过RT-PCR对4代鸡胚尿囊液进行检测,结果扩增出大小约800 bp的目的片段,而阴性对照无特异性扩增片段(图3)。将2株分离株分别命名为FJ-NP01(南平)和FJ-FZ01(福州)。
2.2 IBV分离株S1基因克隆测序
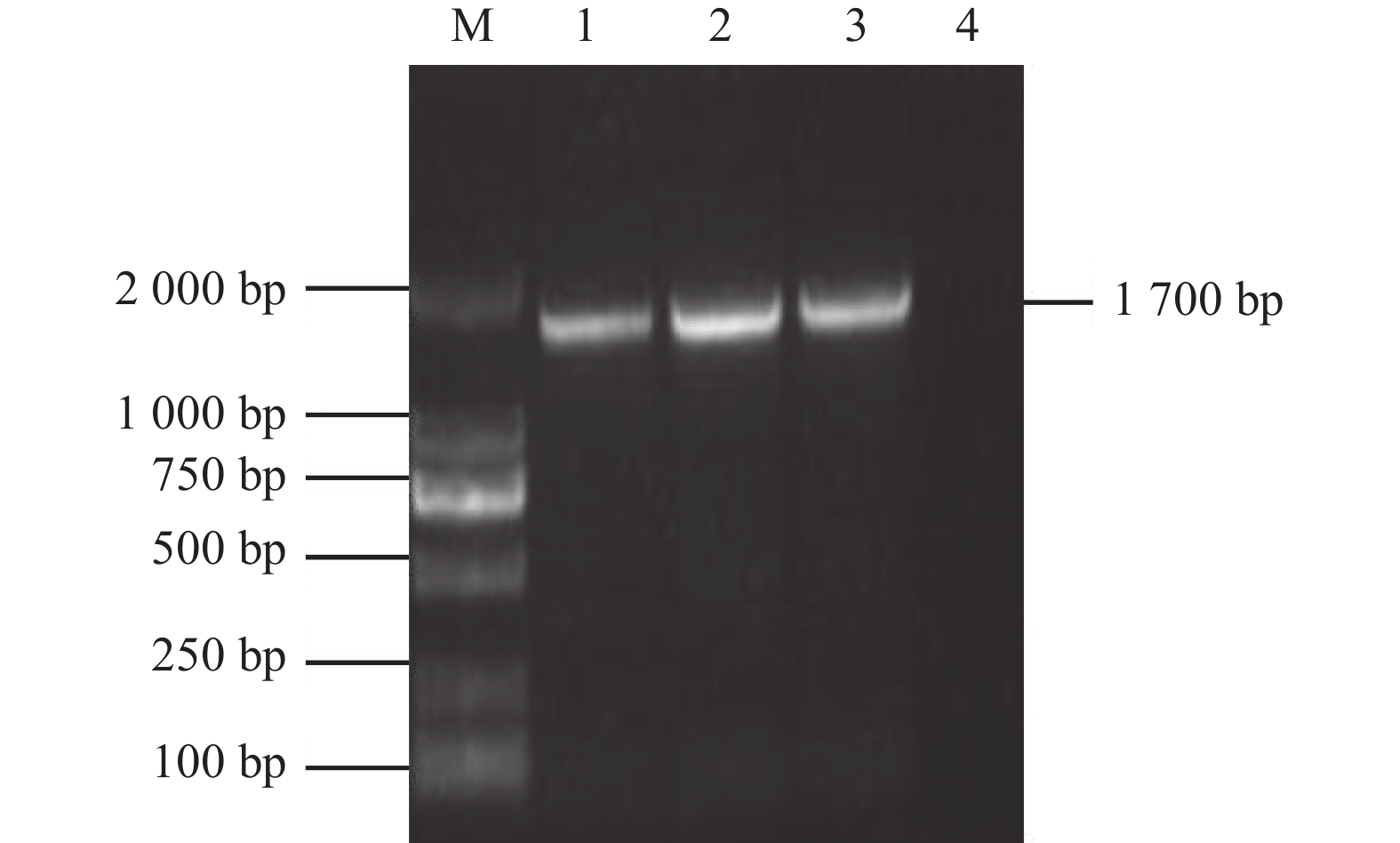
利用设计引物对2株IBV分离株的S1基因进行扩增,并设置阴、阳性对照。从图4中可见,在1 700 bp左右出现与预期目的条带大小相符的片段。对经PCR鉴定为阳性的质粒送往测序公司进行测序,序列拼接显示FJ-NP01株和FJ-FZ01株S1基因长度分别为1629 nt和1620 nt,分别编码543 aa和540 aa。FJ-NP01株和FJ-FZ01株S1基因序列提交至GenBank,获得的登录号分别为ON548486和ON548487。
2.3 IBV分离株S1基因遗传进化、同源性及裂解位点分析
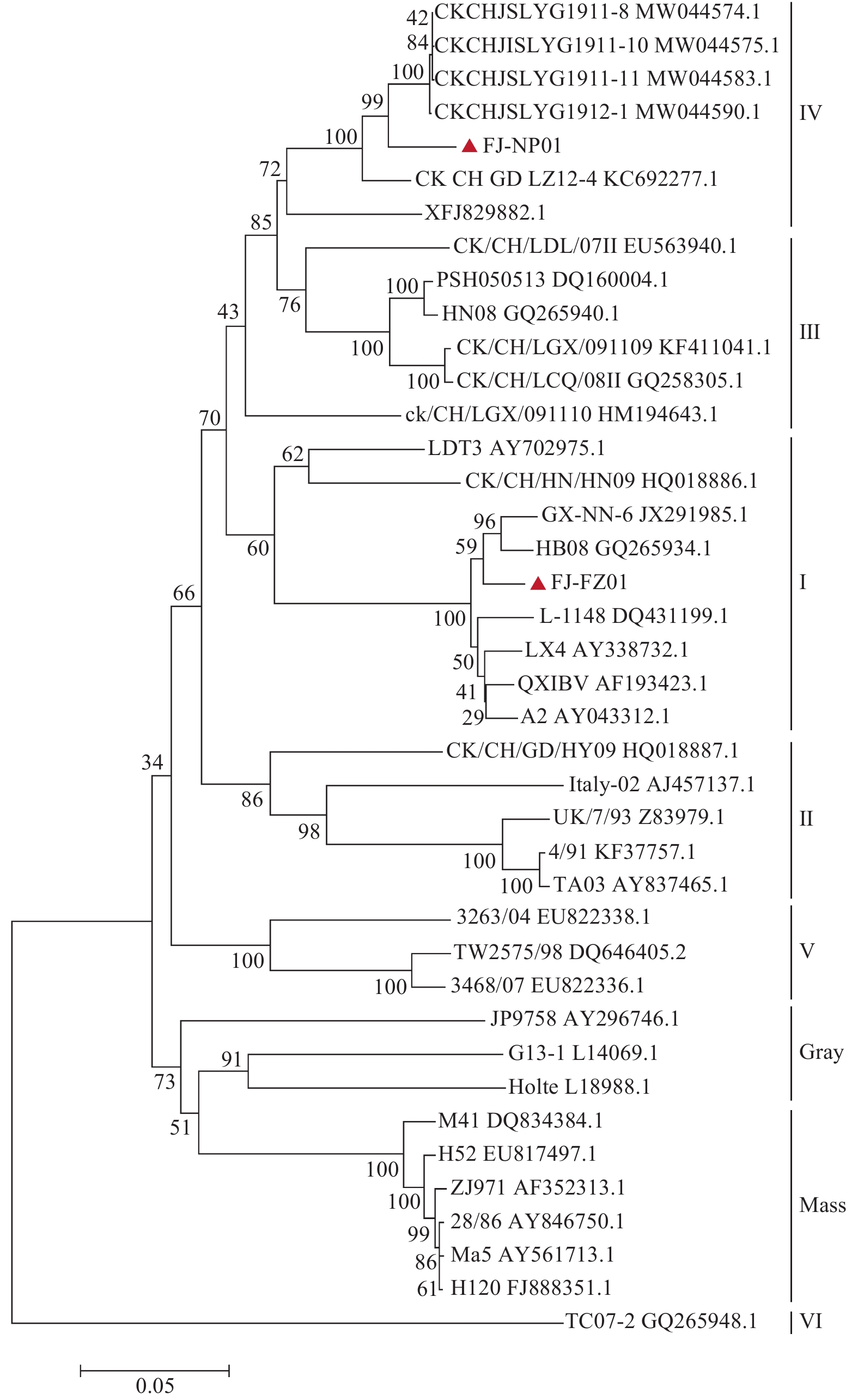
将分离株序列与GeneBank中下载的37株IBV S1基因参考序列,利用MEGA7软件绘制S1基因的系统进化树。结果显示:FJ-NP01株和FJ-FZ01株与所有参考毒株共同形成8个不同的进化分支;其中FJ-FZ01株与 QXIBV为代表的基因型I 在同一进化分支中;分离株FJ-NP01在基因型Ⅳ进化分支中;2株分离株与国内常用Mass型疫苗株进化距离均较远(图5)。核苷酸序列和推导的氨基酸序列同源性比对分析结果显示,2株分离株间的核苷酸和氨基酸同源性较低,分别为83.2%和79.6%; FJ-FZ01株与基因型I分支的所有参考毒株间核苷酸和氨基酸同源性分别为91.9%~98.1%和 94.5%~95.6%; FJ-NP01株与基因型Ⅳ分支的所有参考株核苷酸和氨基酸同源性分别为94.3%~95.7%和92.5%~94.7%;2株分离株与我国使用的Mass型常规疫苗核苷酸和氨基酸序列同源性仅为75.7%~76.3%和77.1%~83.5%。推导的氨基酸序列显示,FJ-FZ01株 S1基因裂解位点为HRRRR,与基因型I分支所有参考毒株裂解位点一致;FJ-NP01株 S1基因裂解位点为HRRKR,与已报道的基因型Ⅳ的IBV分离毒株的裂解位点不同,与基因型Ⅵ参考毒株TC07-2的裂解位点一致。
2.4 IBV分离株S1基因重组分析
利用SimPlot 3.5.1软件对2株分离株的S1基因序列进行重组分析,发现FJ-NP01株用SimPlot和BootScan方法分析均可推测亲本毒株CK CH GD LZ12-4和L-1148出现交叉,预示可能存在基因重组。利用RDP 4.101软件对重组事件进行验证,结果显示FJ-NP01株是由基因型Ⅳ毒株CK CH GD LZ12-4与基因型I 毒株L-1148在S1基因处发生重组而产生的新毒株,其核苷酸序列1438~1506 nt与推测的亲本毒株CK CH GD LZ12-4同源性达97%,其他S1基因核苷酸序列与推测的亲本毒株L-1148同源性达95.9%,RDP 4.101软件分析计算的P值为6.974×10−8(表2)。
表 2 RDP 4. 101软件分析 IBV 分离株的 S1 基因遗传重组结果Table 2. Recombinant results of S1 of IBV isolate analyzed by RDP 4. 101 software重组
Recombinant破裂点
Break points主要亲本
Major parent次要亲本
Minor parentP值
P value毒株
Strain基因型
Genotype头端
Begin/nt末端
End/nt命名
Name基因型
Genotype同源性
Homology/%命名
Name基因型
Genotype同源性
Homology/%FJ-NP01 Ⅳ 1438 1506 CK CH GD LZ12-4 Ⅳ 97% L-1148 I 95.9 6.974×10−8 3. 讨论
自1931年美国学者Schalk和Hawn首次报道IB以来,该病至今仍是影响世界家禽养殖业发展的重要传染性疾病之一[14]。究其原因乃是IBV出现了越来越多的基因型变异株,以及弱毒苗的广泛使用在某种程度上加快了病毒本身的变异,导致该病的防控难度日益加大,不可否认的是疫苗在控制IB的发生中发挥着重要作用,然而随着变异株的不断出现,研制出安全、高效、广谱的疫苗则是今后科研工作者的重要研究方向。
本研究从福建地区疑似发生IB的鸡场中分离到了2株病毒,通过电镜观察和RT-PCR方法进行了鉴定,确认分离到的病毒均为IBV,分别命名为FJ-NP01和FJ-FZ01;进一步分析发现FJ-NP01株属于基因型Ⅳ,FJ-FZ01株属于基因型I。
S1基因是当前研究IBV遗传变异与进化分析的靶标基因,通过分析S1基因序列有助于监测IBV的流行态势[16]。本研究通过对FJ-FZ01株和FJ-NP01株 S1基因进行克隆测序分析;系统进化树分析表明FJ-FZ01株属于基因型I,与位于同一分支的参考毒株相比,核苷酸序列及其推导的氨基酸序列同源性极高,分别在91.9%~98.1%和 94.5%~95.6%,且具有典型HRRRR裂解位点特征。基因型I毒株是我国IBV主要流行毒株,据统计50%~60%的IB病例由基因型I引起。李彬等[16]对2019–2021年我国29个省级行政区IBV分型统计结果显示,基因型I仍然是主要流行的毒株,且有不断扩大的趋势。Feng等[5]报道对中国2011–2012年华南地区分离的62株IBV有32株属于基因型I。本研究分离的 FJ-FZ01株亦属于基因型I,与国内主要流行毒株一致。然而,基因型I毒株与现有Mass型疫苗株的亲缘关系较远,导致Mass型疫苗不能对基因型I毒株提供完全保护。基因重组是导致众多IBV变异毒株出现的原因之一,重组可发生在疫苗株之间、疫苗毒株与野毒株之间及野毒株之间[3]。陈彤等[19]对合肥分离株 CK/CH/GX/LC17-1的 S1 基因重组分析发现,该毒株是由疫苗株Ark型ArkDPI毒株与Mass型Ma5毒株S1基因发生了重组形成的新毒株。吴倩倩等[20]对河南IBV分离株CK/CH/HN/NY1206/2017、CK/CH/HN/XY911/2017 进行重组分析,发现2株分离毒株均是由4/91(CHⅡ)基因型毒株 LZ07 和 JP/Saitama/2006 重组产生的新毒株。本研究通过SimPlot和RDP软件对FJ-NP01株的S1基因序列进行遗传重组分析,发现FJ-NP01株是由基因型Ⅳ毒株 CK CH GD LZ12-4与基因型I毒株L-1148在S1基因处发生重组而产生的新毒株,其核苷酸序列1438~1506 nt,与推测的亲本毒株CK CH GD LZ12-4同源性达97.0%,其他S1基因核苷酸序列与推测的亲本毒株L-1148同源性达95.9%,这类重组变异株在福建地区尚无相关报道。另外,本研究发现重组变异株FJ-NP01 S1基因裂解位点为HRRKR,与已报道的基因型Ⅳ分离毒株的裂解位点不同,与基因型Ⅵ参考毒株TC07-2的裂解位点一致。因此,后续需进一步进行验证FJ-NP01株是否因为基因重组和裂解位点的改变,导致其毒力、致病性和组织嗜性等发生改变。
综上所述,本研究分离鉴定了2株IBV,通过对S1基因克隆测序分析结果显示,FJ-FZ01株与国内流行毒株一样,FJ-NP01株发生了重组变异,表明福建地区IBV流行较为复杂,现有Mass型疫苗在福建省可能起不到良好的免疫保护作用。因此,需加强对福建省IBV的流行病学监测,为新疫苗的研发提供参考资源,也为福建省IB防控提供科学依据。
-
表 1 IBV参考毒株
Table 1 IBV reference strains
毒株 Virus 登录号 Locus 毒株 Virus 登录号 Locus Ma5
H120
LDT3
4/91
H52
28/86
M41
G13-1
Holte
UK/7/93
Italy-02
TW2575/98
3468/07
JP9758
TA03
GX-NN-6
TC07-2
PSH050513
QXIBVAY561713
FJ888351
AY702975
KF377577
EU817497
AY846750
DQ834384
L14069
L18988
Z83979
AJ457137
DQ646405
EU822336
AY296746
AY837465
JX291985
GQ265948
DQ160004
AF193423ZJ971
L-1148
A2
LX4
HB08
HN08
CK/CH/GD/HY09
CK/CH/HN/HN09
CKCHJSLYG1911-8
CKCHJSLYG1911-10
CKCHJSLYG1911-11
CK/CH/LGX/091109
CK/CH/LDL/07II
X
CK/CH/LCQ/08II
ck/CH/LGX/091110
CKCHJSLYG1912-1
CK CH GD LZ12-4AF352313
DQ431199
AY043312
AY338732
GQ265934
GQ265940
HQ018887
HQ018886
MW044574
MW044575
MW044583
KF411041
EU563940
FJ8298882
GQ258305
HM194643
MW044590
KC692277表 2 RDP 4. 101软件分析 IBV 分离株的 S1 基因遗传重组结果
Table 2 Recombinant results of S1 of IBV isolate analyzed by RDP 4. 101 software
重组
Recombinant破裂点
Break points主要亲本
Major parent次要亲本
Minor parentP值
P value毒株
Strain基因型
Genotype头端
Begin/nt末端
End/nt命名
Name基因型
Genotype同源性
Homology/%命名
Name基因型
Genotype同源性
Homology/%FJ-NP01 Ⅳ 1438 1506 CK CH GD LZ12-4 Ⅳ 97% L-1148 I 95.9 6.974×10−8 -
[1] REN M T, SHENG J, MA T, et al. Molecular and biological characteristics of the infectious bronchitis virus TC07-2/GVI-1 lineage isolated in China [J]. Infection, Genetics and Evolution, 2019, 75: 103942. DOI: 10.1016/j.meegid.2019.103942
[2] REN M T, ZHANG L L, HOU Y T, et al. Genetic, antigenic, and pathogenic characteristics of infectious bronchitis virus GI-7/TW-II in China [J]. Avian Diseases, 2020, 64(2): 183−196. DOI: 10.1637/0005-2086-64.2.183
[3] XU L W, HAN Z, JIANG L, et al. Genetic diversity of avian infectious bronchitis virus in China in recent years [J]. Infection, Genetics and Evolution, 2018, 66: 82−94. DOI: 10.1016/j.meegid.2018.09.018
[4] REN G C, LIU F, HUANG M R, et al. Pathogenicity of a QX-like avian infectious bronchitis virus isolated in China [J]. Poultry Science, 2020, 99(1): 111−118. DOI: 10.3382/ps/pez568
[5] FENG J L, HU Y X, MA Z J, et al. Virulent avian infectious bronchitis virus, People's republic of China [J]. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 2012, 18(12): 1994−2001. DOI: 10.3201/eid1812.120552
[6] BICKERTON E, MAIER H J, STEVENSON-LEGGETT P, et al. The S2 subunit of infectious bronchitis virus beaudette is a determinant of cellular tropism [J]. Journal of Virology, 2018, 92(19): e01044−e01018. DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01044-18
[7] ZHANG Y, XU Z C, CAO Y C. Host antiviral responses against avian infectious bronchitis virus (IBV): Focus on innate immunity [J]. Viruses, 2021, 13(9): 1698. DOI: 10.3390/v13091698
[8] QUINTEROS J A, IGNJATOVIC J, CHOUSALKAR K K, et al. Infectious bronchitis virus in Australia: A model of coronavirus evolution - a review [J]. Avian Pathology, 2021, 50(4): 295−310. DOI: 10.1080/03079457.2021.1939858
[9] MA T X, XU L, REN M, et al. Novel genotype of infectious bronchitis virus isolated in China [J]. Veterinary Microbiology, 2019, 230: 178−186. DOI: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2019.01.020
[10] MANSWR B, BALL C, FORRESTER A, et al. Immunopathogenesis of infectious bronchitis virus Q1 in specific pathogen free chicks [J]. Microbial Pathogenesis, 2020, 149: 104535. DOI: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104535
[11] HUANG M J, LIU Y, ZOU C, et al. A highly pathogenic recombinant infectious bronchitis virus with adaptability in cultured cells [J]. Virus Research, 2021, 292: 198229. DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198229
[12] VAN BORM S, STEENSELS M, MATHIJS E, et al. Metagenomic sequencing determines complete infectious bronchitis virus (avian Gammacoronavirus) vaccine strain genomes and associated viromes in chicken clinical samples [J]. Virus Genes, 2021, 57(6): 529−540. DOI: 10.1007/s11262-021-01872-7
[13] LACONI A, WEERTS EAWS, BLOODGOOD JCG, et al. Attenuated live infectious bronchitis virus QX vaccine disseminates slowly to target organs distant from the site of inoculation [J]. Vaccine, 2020, 38(6): 1486−1493. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.11.064
[14] MOHARAM I, SULTAN H, HASSAN K, et al. Emerging infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) in Egypt: Evidence for an evolutionary advantage of a new S1 variant with a unique gene 3ab constellation [J]. Infection, Genetics and Evolution, 2020, 85: 104433. DOI: 10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104433
[15] 雍璐, 吕迪, 范文胜, 等. 台湾型传染性支气管炎病毒重组株的分离鉴定及S1基因序列和血清型分析 [J]. 中国家禽, 2022, 44(4):29−35. DOI: 10.16372/j.issn.1004-6364.2022.04.005 YONG L, LYU D, FAN W S, et al. Isolation and identification of Taiwan genotype avian infectious bronchitis virus recombinant strain and analysis of its S1 gene sequence and serotype [J]. China Poultry, 2022, 44(4): 29−35.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.16372/j.issn.1004-6364.2022.04.005
[16] 李彬, 韩晓青, 刘红祥, 等. 2019—2021年我国29个省级行政区鸡传染性支气管炎流行病学调查 [J]. 中国动物检疫, 2022, 39(4):19−25. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-944X.2022.04.004 LI B, HAN X Q, LIU H X, et al. Epidemiological investigation on avian infectious bronchitis in 29 provincial administrative regions of China from 2019 to 2021 [J]. China Animal Health Inspection, 2022, 39(4): 19−25.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-944X.2022.04.004
[17] 何家辉, 封柯宇, 李鸿鑫, 等. 2株鸡传染性支气管炎病毒的分离鉴定与S1、M和N基因序列分析 [J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2021, 57(1):10−14. HE J H, FENG K Y, LI H X, et al. Isolation, identification and S1, M and N gene sequence analysis of two strains of avian infectious bronchitis virus [J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2021, 57(1): 10−14.(in Chinese)
[18] 闫芳, 岳文斌, 刘娟, 等. 鸡传染性支气管炎病毒地方流行株的分离与鉴定 [J]. 中国兽医学报, 2009, 29(7):845−848. DOI: 10.16303/j.cnki.1005-4545.2009.07.007 YAN F, YUE W B, LIU J, et al. Isolation and biological properties of avian infectious bronchitis virus isolated from Shanxi Province [J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2009, 29(7): 845−848.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.16303/j.cnki.1005-4545.2009.07.007
[19] 陈彤, 刘金, 封柯宇, 等. 2016—2017年广西鸡传染性支气管炎病毒S1基因进化分析 [J]. 中国家禽, 2019, 41(12):22−25. CHEN T, LIU J, FENG K Y, et al. Phylogenetic analysis of S1 gene of avian infectious bronchitis virus isolated from Guangxi during 2016 to 2017 [J]. China Poultry, 2019, 41(12): 22−25.(in Chinese)
[20] 吴倩倩, 许鑫, 陈钦玺, 等. 3株传染性支气管炎病毒蛋鸡源河南株的S1基因序列分析 [J]. 河南农业科学, 2019, 48(6):123−130. DOI: 10.15933/j.cnki.1004-3268.2019.06.019 WU Q Q, XU X, CHEN Q X, et al. Sequence analysis of S1 gene of three avian infectious bronchitis virus strains isolated from layer of Henan Province [J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 48(6): 123−130.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.15933/j.cnki.1004-3268.2019.06.019
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 姜业硕,曹孟飞,班秋艳,王文利,梁丽云. 茶叶抗氧化CNKI文献计量及研究热点分析. 茶叶. 2022(02): 69-74 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 练珊珊,陈佳,吕立堂. 15个茶树品种多糖、纤维素、木质素含量的分析. 广东茶业. 2021(01): 15-20 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王丽,官小倩,余能煌,林芷青. 不同焙火程度对武夷肉桂品质与抗氧化活性的影响. 茶叶通讯. 2020(02): 282-286 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 许陆达,黄苏萍,杨柳媛. 茶多糖的组成及其对糖代谢的作用机制探讨. 广东茶业. 2020(06): 25-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 宋振硕,杨军国,张磊,林清霞. 烘焙类茶食品的研究进展. 食品工业科技. 2019(01): 321-325 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 杨军国,宋振硕,陈键,王丽丽,林清霞,陈林. 粗茶多糖的膜-纤维素柱色谱分离过程的抗氧化活性研究. 茶叶学报. 2018(02): 71-76 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 杨军国. 功能型速溶茶及其加工工艺探讨. 福建茶叶. 2018(08): 6-8 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 袁勇,尹钟,谭月萍,周重旺. 茶多糖的提取分离及生物活性研究进展. 茶叶通讯. 2018(03): 8-12 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: