A SYBR Green I-based qRT-PCR Assay for Detecting Duck BMPs
-
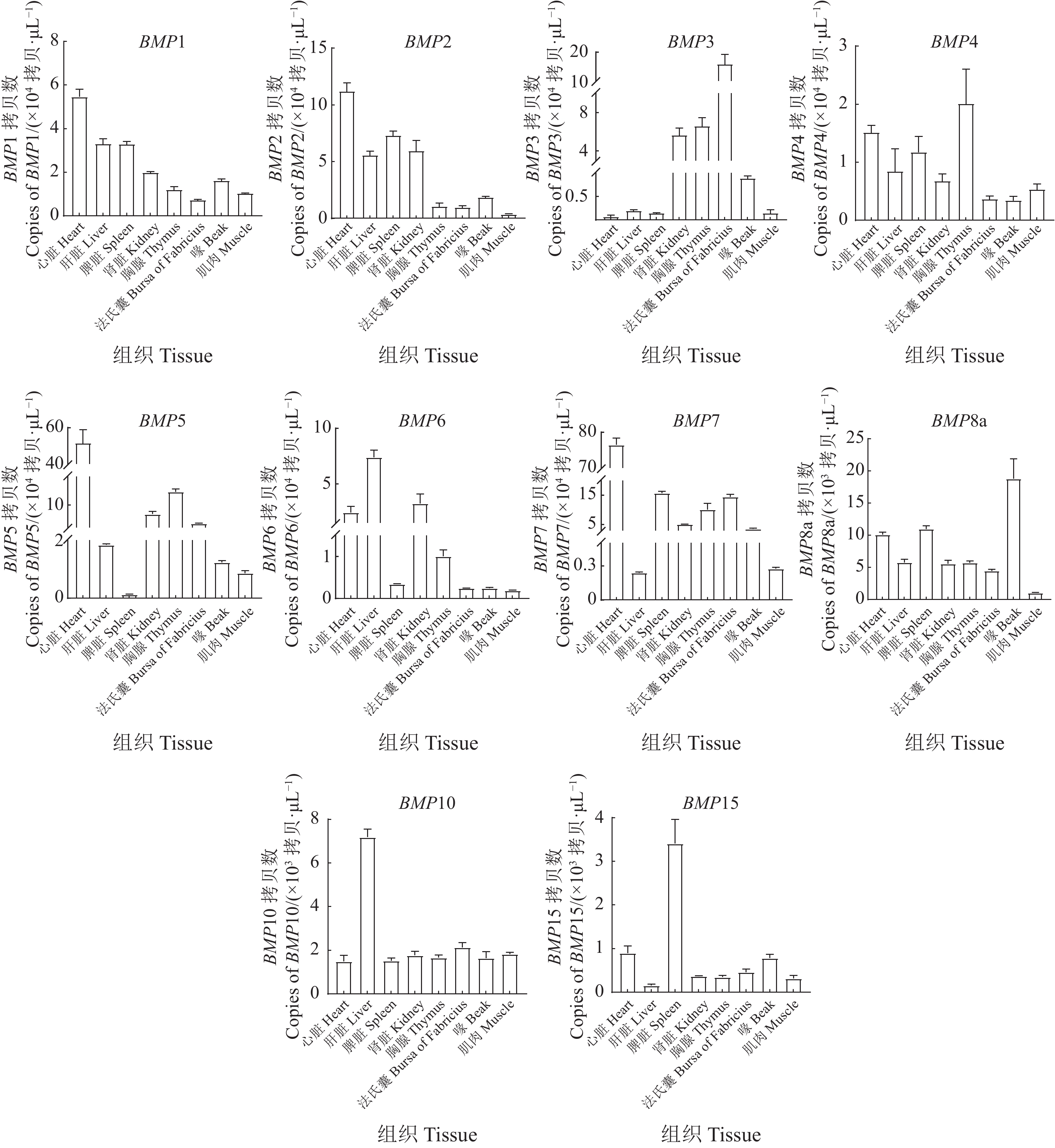
摘要:目的 旨在建立一种检测鸭骨形态发生蛋白(BMPs)mRNA转录水平的SYBR Green Ⅰ实时荧光定量RT-PCR检测方法。方法 根据GenBank中BMP1、BMP2、BMP3、BMP4、BMP5、BMP6、BMP7、BMP8a、BMP10和BMP15的核苷酸序列设计并合成特异性引物进行PCR扩增,产物回收后克隆至pMD-18-T载体,构建阳性重组质粒作为标准品,优化SYBR Green Ⅰ荧光定量PCR反应条件,建立其标准曲线,对建立的方法进行特异性、敏感性和重复性试验。结果 建立的BMP1、BMP2、BMP3、BMP4、BMP5、BMP6、BMP7、BMP8a、BMP10和BMP15基因实时荧光定量检测方法特异性强,无引物二聚体及非特异性产物,熔解曲线为单峰,相关系数R2均大于0.998,组间和组内变异系数均小于1%。应用该方法检测BMPs基因在半番鸭组织中的表达水平,结果显示,BMP1、BMP2、BMP5和BMP7基因在心脏中表达量较高,分别为5.5×104、1.1×105、5.1×105和7.7×105拷贝·μL−1;BMP6和BMP10基因在肝脏中表达量较高,分别为7.5×104和7.6×103拷贝·μL−1;而BMP3、BMP4、BMP8a和BMP15分别在法氏囊、胸腺、喙和脾脏中表达量最高,分别为1.5×105、2.1×104、1.8×103和3.3×103拷贝·μL−1。结论 本研究建立的实时荧光定量PCR方法特异性强、重复性好,为检测鸭BMPs表达水平提供了技术手段。
-
关键词:
- 鸭 /
- 骨形态发生蛋白(BMPs) /
- 荧光定量PCR /
- SYBR Green I
Abstract:Objective An assay for detecting mRNA transcription of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) in ducks using the SYBR Green Ⅰ-based qRT-PCR was developed.Methods Specific primers were designed and synthesized according to the nucleotide sequences of duck BMPs in GenBank. The PCR amplified products were cloned into pMD-18-T vector, and the recombinant plasmids DNA used to establish standard curves. Specificity, sensitivity, and repeatability of the methodology were examined.Result The newly developed qRT-PCR assay showed singe specific melting peaks of BMP1, BMP2, BMP3, BMP4, BMP5, BMP6, BMP7, BMP8a, BMP10, and BMP15 separately with correlation coefficients (R2) higher than 0.998. The coefficients of variation within and between groups were less than 1%. The mRNA expressions of the BMPs were detected in different tissues of hybrid Muscovy ducks. The expressions of BMP1, BMP2, BMP5, and BMP7 in the heart were significantly higher than those in other tissues at 5.5×104, 1.1×105, 5.1×105, and 7.7×105 copies·μL−1, respectively. BMP6 and BMP10 were highly expressed in the liver at 7.5×104 and 7.6×103 copies·μL−1, respectively, while BMP3 in Bursa of Fabricius, BMP4 in the thymus, BMP8a in the beak, and BMP15 in the spleen at 1.5×105, 2.1×104, 1.8×103, and 3.3×103 copies·μL−1, respectively.Conclusion The newly developed qRT-PCR assay for the determination of mRNA expression of BMPs in ducks was specific, sensitive, repeatable, and applicable.-
Keywords:
- Duck /
- bone morphogenetic proteins /
- qRT-PCR /
- SYBR Green I
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】木薯是世界三大薯类作物之一,有“地下粮仓” “淀粉之王”的美誉,是世界上8亿多人口赖以生存的粮食[1]。其用途广泛,在中国,木薯直接食用占比很小,主要用于淀粉及酒精加工[2]。广西是我国木薯主产区,其种植面积和产量约占全国的60%以上。近十年来由于农业结构化调整,广西木薯产业受到巨大冲击,种植面积逐年萎缩,但市场对木薯需求却十分旺盛。据统计,2017年我国进口木薯干片800万t,是我国年产量的5倍以上[3],可见中国对木薯干片需求之大,也间接反映了我国木薯原材料远远满足不了国内工业需求。因此选育高产高粉、适应性广、低氢氰酸的综合型木薯新品种,对保障我国木薯原材料供给、促进广西木薯产业可持续发展具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】多年来,通过育种工作者的不懈努力,一批批优质的木薯新品种[4-8]得以被应用推广,改善了我国木薯品种单一和退化的状况。当前广西主栽工业用高产品种主要有华南205、南植199、华南5号[9]和新选048[10],而华南8号[5]、桂热911[11]和桂热4号[12]则零星分布,鲜食型品种主要有华南9号[13]、桂热891[14]、桂热9号、面包木薯1号和面包木薯2号[15],间套作型品种有桂热911、华南205、南植199、华南124、华南9号、华南8号和华南12号[16],为推动广西木薯行业的快速发展提供了有力保障。但是这些品种基本上只具备高产、高粉、低氢氰酸、抗风等1~2个特点,华南101面包木薯和桂热891的产量、华南系列木薯品种的抗寒性、华南606的抗风能力等都有待提高。【本研究切入点】截至2016年底,广西审定的木薯品种大多数是从国外引进的品系或者杂交种子,经系列试验、鉴定筛选而育成,广西本土有性杂交获得的品种屈指可数,并且绝大部分品种只具备高产或者高粉等单一特点,缺乏土生土长的广适性、高产和高淀粉等综合性状优良木薯新品种。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究采用开花调控技术,选育出高产、高淀粉、低氢氰酸含量,适应性强的综合型木薯品种,以促进木薯产业增收增效,提高种植木薯的经济效益,保障我国木薯产业的可持续发展。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
参试品(株)系:(1)亲本:母本新选048(XX048),高产低粉,源自广西大学农学院,父本桂热891(GR891),高产高粉、株型矮小紧凑、早熟、低氢氰酸,源自广西壮族自治区亚热带作物研究所,F1代(编号为2014-68);(2)加工主栽品种华南205(SC205)和食用主栽品种华南9号(SC9)作双对照品种。
1.2 试验方法
2011年以新选048(♀)× 桂热891(♂)为亲本材料,采用开花调控技术获得杂交种子,2012年进行优良单株评选,2013年和2014年分别进行初级系比试验和中级系比试验, 2015–2017年进行高级系比试验,2017–2018年进行区域性试验,2018–2019年进行生产性试验。2019年12月11日进行现场测产,品种申请审定时定名为桂热11号(GR11),于2020年11月3日通过全国“热带作物品种”审定(热品审2020002)。
1.2.1 优良单株评选
2012年开展单株评选试验,观测株型、结薯性状和薯型等。
1.2.2 系比试验
2013年进行初级系比试验,每个株系5株,每10个株系种植一组对照(SC205);2014年进行中级系比试验,每个株系种植20株,采用双行各10株模式种植,每5个株系种植一组对照(SC205);2015–2017年进行高级系比试验,小区面积为5.0 m×5.0 m,株行距1.0 m×1.0 m,3次重复,随机区组设计,以SC205和SC9作双对照。3个系比试验均于生育期间观测株型、整齐度、植物学性状和结薯性状,于12月收获时测定鲜薯产量、淀粉含量(比重法)。
鲜薯产量测定:随机抽取10株木薯测定鲜薯重后折算成单位面积鲜薯产量;
淀粉含量(比重法)的测定:随机抽样约5000 g鲜薯,先称其在空气中的质量(m1),再称其在水中的质量(m2),然后按照下面公式计算鲜薯淀粉含量(SC),SC=210.8×m1/(m1−m2)−213.4[17]。
1.2.3 区域性试验
2017–2018年在广西南宁、武鸣、桂平及江西南昌、海南白沙等5个试验点进行区域性试验,小区面积5.0 m×5.0 m,株行距1.0 m×1.0 m,3次重复,随机区组设计,以SC205和SC9作双对照。试验于每年4月种植,按NY/T 1681—2009、NY/T 1685—2009的标准进行管理,当年12月测定鲜薯产量和淀粉含量(比重法)。
1.2.4 生产性试验
2018–2019年在广西南宁、广西武鸣、桂平及江西南昌、海南白沙等5个试验点进行生产性试验,广西区内各点的试验面积为0.67 hm2,区外各点的试验面积为0.33 hm2,株行距1.0 m ×1.0 m,以SC205和SC9作双对照。每年的3~4月种植,按NY/T 1681—2009、NY/T 1685—2009的标准进行管理,当年12月测定鲜薯产量和淀粉含量。在广西南宁点随机抽取鲜薯样品送至广西华测检测认证有限公司测定蛋白质、总糖、粗纤维、淀粉、维生素、胡萝卜素和氢氰酸含量以及干物质率,在广西桂平和江西南昌试验点随机抽取鲜薯样品,送至广西华测检测认证有限公司测定淀粉、氢氰酸含量以及干物质率。
1.2.5 新品种GR11指纹图谱鉴定
利用2对微卫星标记引物对GR11等8份材料进行指纹图谱鉴定,在7%聚丙烯酰胺凝胶上以100 W电泳35 min。
1.2.6 现场鉴定
2019年专家现场(南宁点)鉴评时随机连续抽取10株木薯,测定株高、主茎高度、主茎直径、单株鲜薯产量等性状指标。各点收获时均测定鲜薯产量,并随机抽点采集木薯鲜样,送至广西华测检测认证有限公司进行淀粉等相关品质的测定。
1.3 数据处理和分析
运用WPS office(11.1.0.11294)的WPS表格对试验数据进行整理统计,用SPSS 21.0对数据进行方差分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 杂交和优良单株评选
2011年获得的杂交种子于2012年开展单株评选,筛选出株型紧凑、茎秆直立,无分枝,结薯集中、块根水平分布的优良单株。
2.2 系比试验结果
2013年12月下旬,在初级系比试验收获时,选取茎秆直立、株型紧凑、整齐度好、结薯集中、块根水平伸长、薯块大小均匀的优良株系480个(约占总株系20%),其中GR11平均鲜薯产量3.87 kg·株−1,比对照SC205(2.50 kg·株−1)增产54.80%。
2014年12月中旬,在中级系比试验收获时,筛选出株型和块根性状稳定,鲜薯产量和淀粉含量均显著高于SC205的优良株系约100个,其中GR11鲜薯总产量106.00 kg,比对照SC205(68.59 kg)增产54.54%;淀粉含量为35.8%,比对照SC205(29.3%)提高了6.5个百分点。
通过连续3年的高级系比试验可知(表1),GR11与2个对照的鲜薯产量存在显著差异,平均鲜薯产量为38.64 t·hm−2,分别比SC205和SC9增产72.32%、73.47%,平均淀粉含量为28.1%,比SC205高4.0个百分点,比SC9高0.9个百分点。
表 1 2015–2017年GR11高级系比试验Table 1. Advanced performance trail results on GR11 in 2015-2017年份
Year品种
Variety鲜薯产量
Fresh root yield/(t·hm−2)比对照增产
Increasing rate/%淀粉含量
Starch content/%Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ 平均
AverageSC205
(CK)SC9
(CK)Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ 平均
Average2015 GR11 33.91 39.50 35.86 36.42±1.6 a 86.31 71.48 26.3 25.3 27.0 26.2±0.5 a SC205(CK) 20.80 18.60 19.25 19.55±0.7 b − − 20.7 20.5 19.0 20.1±0.5 b SC9(CK) 21.39 20.34 21.99 21.24±0.5 b − − 27.1 28.1 27.6 27.6±0.3 a 2016 GR11 36.40 35.42 48.12 39.98±4.1 a 92.12 76.20 29.0 28.3 29.8 29.0±0.4 a SC205(CK) 21.53 19.79 21.10 20.81±0.5 b − − 25.8 25.6 26.0 25.8±0.1 c SC9(CK) 21.80 23.05 23.23 22.69±0.4 b − − 27.0 26.8 27.5 27.1±0.2 b 2017 GR11 37.90 38.27 42.35 39.51±1.4 a 38.52 72.74 27.4 28.9 30.9 29.1±1.0 a SC205(CK) 24.42 29.87 31.26 28.52±2.1 b − − 26.5 25.9 26.5 26.3±0.2 b SC9(CK) 24.82 23.46 20.34 22.87±1.3 b − − 26.7 27.2 26.4 26.8±0.2 b 注:(1)表中不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。(2)“-”表示此项无。
Note: (1)Different lowercase letters in the table indicate significant differences at 0.05 levels in Duncan test.(2)"-"indicates that this item is absent.2.3 区域性试验结果
为了进一步验证其区域适应性及丰产性能的稳定性,2017–2018年分别在广西南宁、武鸣、桂平,江西南昌和海南白沙等5个试验点进行区域性试验,以当家品种SC205和食用品种SC9作双对照,结果见表2。GR11平均鲜薯产量为41.22 t·hm−2,显著高于对照SC205,增产幅度9.37%~70.95%,平均增幅19.05%;GR11产量极显著高于对照SC9,增产幅度40.66%~85.11%,平均增幅61.15%。GR11在不同地区及年度间,均比对照SC205和SC9高产,由于不同地区地理条件及管理水平不同,SC205和SC9在广西南宁相比其他4个试验点鲜薯产量偏低,而GR11则不受影响,由此可见,GR11相比对照具有更广泛的适应性和更高的丰产性。GR11平均淀粉含量为29.2%,分别比对照SC205和SC9高2.6、1.0个百分点。可见无论是鲜薯产量还是淀粉含量,GR11均明显高于加工主栽品种SC205和食用主栽品种SC9,具有鲜薯产量高、淀粉含量高、稳定性好、适宜种植区域广等特点。
表 2 2017–2018年GR11区域性试验Table 2. Regional trail results on GR11 in 2017–2018年份
Year试验地点
Site鲜薯产量
Fresh root yield/(t·hm−2)比对照增产
Increasing rate/%淀粉含量
Starch content/%GR11 SC205(CK) SC9(CK) SC205(CK) SC9(CK) GR11 SC205(CK) SC9(CK) 2017 南宁 Nanning 39.36 19.68 22.87 100.00 72.10 29.1 26.2 26.8 2018 南宁 Nanning 40.47 28.52 23.36 41.90 73.24 29.4 26.3 27.7 平均 Average 39.92 24.10 23.12 70.95 72.67 29.3 26.3 27.3 2017 武鸣 Wuming 42.46 39.59 29.20 7.25 45.41 27.9 25.3 27.6 2018 武鸣 Wuming 41.51 37.23 26.38 11.50 57.35 29.2 26.5 28.6 平均 Average 41.99 38.41 27.79 9.37 51.38 28.6 25.9 28.1 2017 桂平 Guiping 41.30 34.43 23.34 19.95 76.95 30.0 27.2 29.7 2018 桂平 Guiping 41.61 37.51 21.53 10.93 93.27 28.4 26.6 28.3 平均 Average 41.46 35.97 22.44 15.44 85.11 29.2 26.9 29.0 2017 南昌 Nanchang 43.54 39.47 24.73 10.31 76.06 29.9 27.8 29.2 2018 南昌 Nanchang 42.27 38.19 27.73 10.68 52.43 30.2 28.2 28.5 平均 Average 42.91 38.83 26.23 10.50 64.25 30.1 28.0 28.9 2017 白沙 Baisha 39.29 35.39 28.33 11.02 38.69 28.5 26.2 28.0 2018 白沙 Baisha 40.38 36.22 28.31 11.49 42.64 29.1 25.9 27.8 平均 Average 39.84 35.81 28.32 11.25 40.66 28.8 26.1 27.9 2.4 生产性试验结果
为了示范推广,2018–2019年分别在广西南宁、武鸣、海南白沙等5个试验点进行生产性试验及品质分析,广西区内各点的试验面积为0.67 hm2,区外各点的试验面积为 0.33 hm2,以当家品种SC205和食用品种SC9作双对照,结果见表3。除2019年南昌遭遇极端干旱天气,造成各参试品种的产量偏低,其中GR11低至27.60 t·hm−2,以及桂平当地习惯采用间套种花生的种植模式,造成木薯产量稍偏低,GR11鲜薯产量为38 t·hm−2左右外,其余的GR11鲜薯产量均在40.76 t·hm−2以上,最高的为白沙点,高达43.34 t·hm−2,表现出了高产稳产。GR11在不同年度、不同试验点,均比加工主栽品种SC205和食用主栽品种SC9高产,分别增产9.51%~57.26%和27.30%~89.51%,平均增产率分别为28.38%和52.03%。生产试验结果表明,GR11适应性广、高产稳产、丰产性好,适宜在种植区大面积推广种植。
表 3 2018–2019年GR11生产性试验Table 3. Production trail results on GR11 in 2018–2019年份
Year试验点
Site鲜薯产量
Fresh root yield/(t·hm−2)比对照增产
Increasing rate/%GR11 SC205(CK) SC9(CK) SC205(CK) SC9(CK) 2018 南宁 Nanning 40.76 28.28 22.02 44.13 85.10 2019 南宁 Nanning 42.24 31.17 31.95 35.51 32.21 平均 Average 41.50 29.73 26.99 39.82 58.66 2018 武鸣 Wuming 42.36 38.68 24.86 9.51 70.39 2019 武鸣 Wuming 41.78 32.04 32.82 30.40 27.30 平均 Average 42.07 35.36 28.84 19.96 48.85 2018 桂平 Guiping 36.39 32.52 22.34 11.90 62.89 2019 桂平 Guiping 39.38 32.07 29.81 22.79 32.10 平均 Average 37.89 32.30 26.08 17.35 47.50 2018 南昌 Nanchang 41.73 29.06 22.02 43.60 89.51 2019 南昌 Nanchang 27.60 17.55 17.37 57.26 58.89 平均 Average 34.67 23.31 19.70 50.43 74.20 2018 白沙 Baisha 41.19 35.21 27.95 16.98 47.37 2019 白沙 Baisha 43.34 32.48 29.84 33.44 45.24 平均 Average 42.27 33.85 28.90 25.21 46.31 GR11鲜薯品质抽检结果:蛋白质0.75 g·hg−1、氢氰酸22.3 mg·kg−1 、总糖1.5 g·hg−1 、粗纤维1%、淀粉33.0 g·hg−1 、干物质含量36.48%、维生素C 37.2 mg·hg−1 、胡萝卜素123 μg·hg−1 。
江西南昌点GR11鲜薯淀粉含量30.3 g·hg−1 ,比对照SC205(26.9 g·hg−1)提高了3.4个百分点;GR11干物质率39.6%,比对照SC205(34.6%)提高了5.0个百分点;氢氰酸20.5 mg·kg−1 。广西桂平点GR11鲜薯淀粉34.5 g·hg−1 ,比对照SC205提高了4.0个百分点;GR11干物质率41.8%,比对照SC205提高了4.3个百分点;氢氰酸23.9 mg·kg−1 (表4)。
表 4 2018–2019年GR11与对照SC205的淀粉和干物质率对比结果Table 4. Contents of starch and dry matters of GR11 and SC205 tested in 2018–2019年份
Year试验点
Site淀粉含量
Starch content/(g·hg−1 )干物质率
Dry matter content/%氢氰酸
HCN/(mg·kg−1 )GR11 SC205(CK) GR11 SC205(CK) GR11 SC205(CK) 2018 南昌 Nanchang 30.3 26.9 39.6 34.6 20.5 - 2019 桂平 Guiping 34.5 30.5 41.8 37.5 23.9 - 注:“-”表示未测定,下同。
Note: “-” indicates that this item is not measured, the same below.2.5 现场测产结果
2019年12月11日在广西南宁市兴宁区三塘镇广西壮族自治区亚热带作物研究所木薯研究基地现场测产,植后8个月平均单株鲜薯产量为4.222 kg,折合成每667 m2产鲜薯2.816 t,比对照(SC205)增产35.51%,比对照(SC9)增产32.21%,GR11与双对照的鲜薯产量差异均达显著水平。
2.6 GR11的产量潜力和生产性能评价
经过历年各级试验比较,表明GR11具有高产、稳产的产量潜力和生产性能及广泛的适应性。GR11与双对照SC205和SC9历年平均鲜薯产量对比情况见表5。
表 5 2015–2019年GR11鲜薯产量及淀粉含量Table 5. Tuber yield and starch content of GR11 tested in 2015-2019年份
Year鲜薯产量
Fresh root yield/(t·hm−2)比对照增产
Increasing rate/%淀粉含量
Starch content/%GR11 SC205(CK) SC9(CK) SC205(CK) SC9(CK) GR11 SC205(CK) SC9(CK) 2015 36.42 19.55 21.24 86.29 71.47 26.2 20.1 27.6 2016 39.98 20.81 22.69 92.12 76.20 29.0 25.8 27.1 2017 40.35 31.12 24.28 29.68 66.19 29.1 26.0 27.2 2018 40.77 34.14 24.65 19.42 65.40 29.8 26.8 - 2019 38.87 29.06 28.36 33.76 37.06 34.5 30.5 - 平均Average 39.28 26.94 24.24 45.83 62.01 29.7 25.8 27.3 2015–2019年,GR11每年单产均超过36 t·hm−2,最低36.42 t·hm−2,最高40.77 t·hm−2,说明该品种具有高产、稳产的特性。平均鲜薯产量39.28 t·hm−2,相比SC205和SC9,增产效果显著,比SC205平均增产12.34 t·hm−2,增幅45.83%,比SC9平均增产15.03 t·hm−2,增幅62.01%,近年来木薯市场鲜薯收购平均价格约600元·t−1[18],GR11分别比对照SC205和SC9增值7404 元·hm−2 、9018元·hm−2 ,经济效益增加明显。
2.7 GR11淀粉含量分析
从表5可以看到,GR11除了第1年外,其余4年淀粉含量≥29.0%,这表明了GR11具有高淀粉含量的特性,5年平均淀粉含量为29.7%,比对照SC205(25.8%)高3.9个百分点,2015–2017年GR11平均淀粉含量为28.1%,比SC9高0.8个百分点。
2.8 GR11的品质评价
多年各级品比试验结果表明,GR11品质优良,连续3次鲜薯氢氰酸含量抽检结果分别为22.3、20.5 和23.9 mg·kg−1 ,均低于50 mg·kg−1的国家安全食用标准,表明该品种具有可食用的特性。此外,GR11鲜薯蛋白质0.75 g·hg−1 、总糖1.5 g·hg−1、粗纤维1.0%、维生素C 37.2 mg·hg−1、胡萝卜素123 μg· hg−1。GR11食味粉而香,耐煮性好(煮糖水和打火锅不易成糊状)。
2.9 GR11指纹图谱鉴定
采用SSR6、SSR10两对微卫信标记对GR11等8份材料进行指纹图谱鉴定,可以获得4个等位基因,在这8份材料中GR11具有唯一的特征带SSR6-b/SSR10-ab(表6和图1),因此SSR6、SSR10可以作为本品种的标记指纹。
表 6 桂热11号分子指纹模式图谱Table 6. Molecular fingerprints of GR11编号
Number品种
Variety引物SSR6
Primer SSR6引物SSR10
Primer SSR10a b a b 1 SC9 ◆ ◆ − ◆ 2 SC205 − ◆ ◆ − 3 GR891 − ◆ ◆ − 4 NZ199 − ◆ ◆ − 5 XX048 ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ 6 GR11 − ◆ ◆ ◆ 7 GR10 − ◆ − ◆ 8 561 ◆ ◆ − ◆ 注:“◆”表示该位点有特征条带,“−”表示该位点无条带。
Note: “◆” indicates loci with characteristic bands; “−” loci without bands.2.10 抗逆性表现
GR11连续3年田间均表现出耐寒性、耐旱性强,中抗朱砂叶螨,苗期容易感染细菌性枯萎病,但也容易恢复,不影响鲜薯产量(表7)。
表 7 2017–2019年GR11抗逆性表现Table 7. Stress resistance of GR11 shown in 2017–2019抗逆性
Stress resistance2017 2018 2019 GR11 SC205 SC9 GR11 SC205 SC9 GR11 SC205 SC9 耐寒性 Cold tolerance S M M S M M S M M 耐旱性 Drought tolerance S M M S M M S M M 细菌性枯萎病抗性 Resistance to bacterial blight S R R S R R S R R 朱砂叶螨抗性 Resistance to tetranychus cinnabarinus MR S R MR S R MR S R 注: (1)M-耐寒性、耐旱性中等;(2)S-耐寒性、耐旱性强;(3)S-细菌性枯萎病、朱砂叶螨感病;(4)R-抗细菌性枯萎病、朱砂叶螨病;(5)MR-中抗细菌性枯萎病、朱砂叶螨。
Note: (1) M: moderate cold and drought tolerance. (2) S: strong cold and drought tolerance. (3) S: susceptible to bacterial blight and Tetranychus cinnabarinus infestation. (4) R: resistant to bacterial blight and T. cinnabarinus infestation. (5) MR: moderately resistant to bacterial blight and T. cinnabarinus infestation.3. 讨论与结论
广西是我国木薯主产区,当前推广栽培的木薯品种绝大部分都是从国外或者省外引进的,或者是引进杂交种子、优质种质资源经系列试验后选育而成的[19],但引进的绝大部分品种只具备高产或高粉中的1个优点,缺乏广西本土广适性、高产和高淀粉等综合性状优良的木薯新品种。本研究以新选048为母本,桂热891为父本,采用人工开花调控技术进行诱导并杂交获得种子经过系列试验,最后鉴定、筛选出高产高淀粉,氢氰酸含量低,适应性广,丰产稳产性好,具有耐旱耐寒和较抗螨、不易落叶等特点,适合在广西、海南和江西等木薯主产区推广种植的鲜食加工兼用型优良品种GR11,这是广西首个通过国审的有性杂交木薯新品种。
在生产性试验中,GR11平均鲜薯产量39.68 t·hm−2,比加工主栽品种SC205增产28.38%,淀粉含量和干物质率分别为32.4%、40.7%,比对照SC205分别提高了3.7百分点和4.7个百分点。木薯淀粉含量和干物质率是衡量淀粉和酒精加工生产经济效益的2个重要指标,两者含量越高,转化效益越大[7],GR11潜力可见一斑。SC9是目前主栽的食用品种,其食用方法有切块或切段蒸煮,或磨制成淀粉后,采用蒸、煎、炸等方式制作成美食[13],GR11氢氰酸含量非常低(鲜食平均22.2 mg·kg−1 ),食味粉而香,耐煮性好,尤其是打火锅时不易成糊状。该品种不易落叶,不分枝,株型紧凑,结薯集中,有望应用于机械化种植,这将有助于降低劳动成本,提高农业生产经济效益。随着木薯产业的不断发展,木薯的病虫害也越来越多,其中细菌性枯萎病和朱砂叶螨是两种主要的病虫害[20,21],GR11具有较强的抗螨能力,但苗期易感染细菌性枯萎病,注意加强防范。广西、广东和海南三省是木薯主要种植区,经过多年试验,GR11在江西南昌也表现出了极强的丰产稳产性,这为木薯北移奠定了基础,同时对推动木薯产业的发展具有重要意义。
研究结果表明,GR11具有丰产稳产,高淀粉,低氢氰酸,茎干直立、不分枝、株型紧凑,结薯集中、大小均匀等优点,此外还具备耐旱耐寒和较抗螨,不易落叶,适应性广的特点,适宜在广西、海南和江西等木薯主产区推广种植。
-
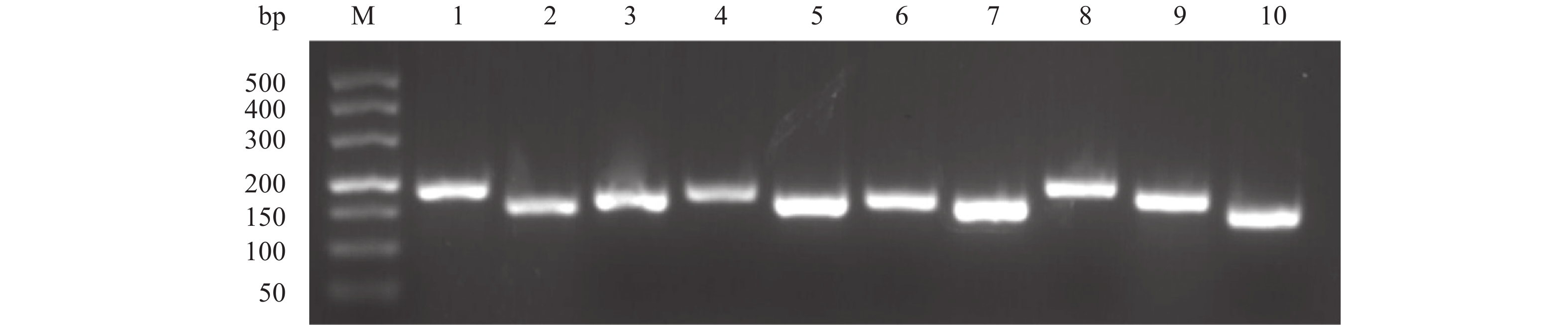
图 2 BMP基因的SYBR Green I荧光定量PCR扩增曲线
A:1~6分别为6.03×108~6.03×103 copies·μL−1,7为DEPC水;B:1~6分别为6.41×108~6.41×103 copies·μL−1,7为DEPC水;C:1~6分别为1.73×108~1.73×103 copies·μL−1,7为DEPC水;D:1~6分别为6.22×107~6.22×102 copies·μL−1,7为DEPC水;E:1~6分别为1.84×108~1.84×103 copies·μL−1,7为DEPC水;F:1~6分别为1.85×107~1.85×102 copies·μL−1,7为DEPC水;G:1~6分别为1.49×107~1.49×102 copies·μL−1,7为DEPC水;H:1~6分别为7.01×107~7.01×102 copies·μL−1,7为DEPC水;I:1~6分别为6.03×108~6.03×103 copies·μL−1,7为DEPC水;J:1~6分别为2.86×107~2.86×102 copies·μL−1,7为DEPC水。
Figure 2. Amplification curves of BMPs by SYBR Green I qRT-PCR
A: 1–6 represent 6.03×108–6.03×103 copies·μL−1, respectively, 7 represents DEPC water; B: 1–6 represent 6.41×108–6.41×103 copies·μL−1, respectively, 7 represents DEPC water; C: 1–6 represent 1.73×108–1.73×103 copies·μL−1, respectively, 7 represents DEPC water; D: 1–6 represent 6.22×107–6.22×102 copies·μL−1, respectively, 7 represents DEPC water; E: 1–6 represent 1.84×108–1.84×103 copies·μL−1, respectively, 7 represents DEPC water; F: 1–6 represent 1.85×107–1.85×102 copies·μL−1, respectively, 7 represents DEPC water; G: 1–6 represent 1.49×107–1.49×102 copies·μL−1, respectively, 7 represents DEPC water; H: 1–6 represent 7.01×107–7.01×102 copies·μL−1, respectively, 7 represents DEPC water; I: 1–6 represent 6.03×108–6.03×103 copies·μL−1, respectively, 7 represents DEPC water; J: 1–6 represent 2.86×107–2.86×102 copies·μL−1, respectively, 7 represents DEPC water.
表 1 BMP基因的扩增引物
Table 1 BMP amplification primers
引物名称
Primer name引物序列(5′-3′)
Primer sequence扩增长度
Amplification length/bp参考序列编号
GenBank No.BMP1-F CTTGAAGATGGAGCCGGAG 182 XM038166990 BMP1-R TGTCTCCTTTGCTCAGCCTC BMP2-F CCACGAAGAAGTTTTGGAAG
CTGTTGTTCTCAAAGGCTCC156 XM027453308 BMP2-R BMP3-F ATGAACTTCTGATCGGTGTC 170 XM038178529 BMP3-R GACCCTTGTCAGAGGATTAC BMP4-F CCACCATGAAGAGCACCTGG
TTTATCCGGTGGAAGCCCCT180 XM038179087 BMP4-R BMP5-F CCCAACAGGGATGCAGACTT
ACTTCGACCGTCCCCAGTTT165 XM038177391 BMP5-R BMP6-F CAAACAGATCCTCTGACCTG
TTTACACTGAAACCGTCCTG169 XM027451601 BMP6-R BMP7-F AAAGCATAGACGGGCAAAGC
TTTGGATCGATTCTGGCTCC167 XM005010474 BMP7-R BMP8a-F GCACCCTGCACATCAGCATC
AGCCCATCATCCGTCTCCAC202 XM038167176 BMP8a-R BMP10-F TCCTGGACTTGGAGAACCTG 181 XM038167140 BMP10-R GAATCCCAGCCAATCTCCTT BMP15-F ACGCCGTGGTGCAGAACTTGGT 157 XM027465364 BMP15-R CAGGACTCTGCGATCATGTTCT 表 2 实时荧光定量PCR敏感性检测
Table 2 Sensitivity of qRT-PCR assay
基因
Gene质粒浓度
Concentration of
plasmid standard /
(拷贝·μL−1)Ct值(¯x±SD)
Ct value (¯x±SD)变异系数
Coefficient of
variation/%BMP1 6.03×103 26.48±0.05 0.18 6.03×102 29.94±0.10 0.33 6.03×101 33.63±0.56 1.67 BMP2 6.41×103 28.93±0.03 0.11 6.41×102 32.36±0.23 0.71 6.41×101 33.97±0.62 1.83 BMP3 1.73×103 26.11±0.03 0.12 1.73×102 29.40±0.21 0.72 1.73×101 33.10±0.72 2.20 BMP4 6.22×103 29.07±0.10 0.34 6.22×102 32.09±0.10 0.34 6.22×101 33.94±0.55 1.64 BMP5 1.84×103 28.38±0.16 0.58 1.84×102 30.10±0.24 0.82 1.84×101 31.17±0.42 1.36 BMP6 1.85×103 28.45±0.02 0.08 1.85×102 31.92±0.09 0.27 1.85×101 36.35±0.46 1.28 BMP7 1.49×103 29.39±0.07 0.25 1.49×102 32.72±0.10 0.31 1.49×101 36.30±0.58 1.59 BMP8a 7.01×103 26.44±0.04 0.15 7.01×102 30.10±0.07 0.24 7.01×101 33.98±0.48 1.41 BMP10 1.34×104 24.53±0.07 0.31 1.34×102 27.43±0.18 0.68 1.34×101 30.44±0.53 1.74 BMP15 2.86×103 28.11±0.07 0.23 2.86×102 32.14±0.19 0.58 2.86×101 35.93±0.80 2.23 表 3 荧光定量PCR重复性试验结果
Table 3 Reproducibility of qRT-PCR assay
基因
Gene组内重复性试验Ct值
The Ct values of intra-assay组间重复性试验Ct值
The Ct values of inter-assay平均值±标准差
Means ± SD变异系数
CV/%平均值±标准差
Means ± SD变异系数
CV/%BMP1 20.19±0.02 0.12 20.04±0.08 0.42 BMP2 26.71±0.03 0.11 26.90±0.19 0.69 BMP3 28.88±0.08 0.28 28.79±0.12 0.41 BMP4 29.20±0.08 0.28 29.32±0.16 0.56 BMP5 31.06±0.06 0.20 31.37±0.23 0.72 BMP6 26.87±0.04 0.13 26.81±0.20 0.74 BMP7 23.40±0.03 0.12 23.52±0.11 0.47 BMP8a 32.14±0.07 0.22 32.11±0.19 0.60 BMP10 27.81±0.07 0.24 27.69±0.18 0.65 BMP15 25.13±0.01 0.06 25.17±0.08 0.32 -
[1] LOWERY J W, ROSEN V. Bone morphogenetic protein-based therapeutic approaches [J]. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 2018, 10(4): a022327. DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a022327
[2] YADIN D, KNAUS P, MUELLER T D. Structural insights into BMP receptors: Specificity, activation and inhibition [J]. Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews, 2016, 27: 13−34.
[3] 雷小灿, 李兰玉, 李志鹏, 等. BMP1基因在动物卵泡发生和胚胎发育中的表达规律及调控机制的研究进展 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2015, 31(2):65−70. LEI X C, LI L Y, LI Z P, et al. Advance in the expression pattern and regulatory mechanism of BMP1 on animals folliculogenesis and embryo development [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2015, 31(2): 65−70.(in Chinese)
[4] CHEN D, ZHAO M, MUNDY G R. Bone morphogenetic proteins [J]. Growth Factors (Chur, Switzerland), 2004, 22(4): 233−241. DOI: 10.1080/08977190412331279890
[5] OTSUKA F, MOORE R K, SHIMASAKI S. Biological function and cellular mechanism of bone morphogenetic protein-6 in the ovary [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2001, 276(35): 32889−32895. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M103212200
[6] ZHAO G Q, HOGAN B L. Evidence that mouse Bmp8a (Op2) and Bmp8b are duplicated genes that play a role in spermatogenesis and placental development [J]. Mechanisms of Development, 1996, 57(2): 159−168. DOI: 10.1016/0925-4773(96)00543-6
[7] HAN H X, LEI Q X, ZHOU Y, et al. Association between BMP15 gene polymorphism and reproduction traits and its tissues expression characteristics in chicken [J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(11): e0143298. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143298
[8] ZHANG H, BRADLEY A. Mice deficient for BMP2 are nonviable and have defects in amnion/chorion and cardiac development [J]. Development (Cambridge, England), 1996, 122(10): 2977−2986. DOI: 10.1242/dev.122.10.2977
[9] GUENTHER C A, WANG Z, LI E, et al. A distinct regulatory region of the Bmp5 locus activates gene expression following adult bone fracture or soft tissue injury [J]. Bone, 2015, 77: 31−41. DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2015.04.010
[10] SAINI S, DURAISAMY A J, BAYEN S, et al. Role of BMP7 in appetite regulation, adipogenesis, and energy expenditure [J]. Endocrine, 2015, 48(2): 405−409. DOI: 10.1007/s12020-014-0406-8
[11] BANOVAC I, GRGUREVIC L, RUMENOVIC V, et al. BMP3 affects cortical and trabecular long bone development in mice [J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(2): 785. DOI: 10.3390/ijms23020785
[12] YUAN Y M, MA N, ZHANG E B, et al. BMP10 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression via PTPRS–STAT3 axis [J]. Oncogene, 2019, 38(48): 7281−7293. DOI: 10.1038/s41388-019-0943-y
[13] YE L, KYNASTON H, JIANG W. Bone morphogenetic protein-10 suppresses the growth and aggressiveness of prostate cancer cells through a smad independent pathway [J]. The Journal of Urology, 2009, 181(6): 2749−2759. DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2009.01.098
[14] YE L, BOKOBZA S, LI J, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-10 (BMP-10) inhibits aggressiveness of breast cancer cells and correlates with poor prognosis in breast cancer [J]. Cancer Science, 2010, 101(10): 2137−2144. DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01648.x
[15] 刘强, 顾金金, 张龙锋. 骨形态发生蛋白在类风湿关节炎患者外周血单个核细胞中表达 [J]. 黑龙江医学, 2020, 44(9):1203−1207. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5775.2020.09.013 LIU Q, GU J J, ZHANG L F. Expression of bone morphogenetic proteins in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Heilongjiang Medical Journal, 2020, 44(9): 1203−1207.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5775.2020.09.013
[16] 谢湘涛. 骨形态发生蛋白-4、5、6、7在脑损伤并骨折大鼠中的表达及意义[D]. 南宁: 广西医科大学, 2016. XIE X T. The expression and significance of bone morphogenetic protein-4, 5, 6, 7 in rats with fracture combined traumatic brain injury[D]. Nanning: Guangxi Medical University, 2016. (in Chinese)
[17] 艾锦新. 黔北麻羊BMP2、BMP4基因甲基化与生长性状的遗传效应研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2020. AI J X. Genetic effects of BMP2 and BMP4 gene methylation and growth traits in Qianbei brown goat[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2020. (in Chinese)
[18] 毛非凡. 军曹鱼早期骨骼发育特征及骨形态发生蛋白基因家族鉴定分析[D]. 湛江: 广东海洋大学, 2021. MAO F F. Genome-wide identification and expressionprofiling of the bone morphogenetic proteins gene family, osteologicalontogeny in larval and juvenile Rachycentron canadum[D]. Zhanjiang: Guangdong Ocean University, 2021. (in Chinese)
[19] 路鹏. 新西兰白兔骨形态发生蛋白(BMPs)的克隆及时空差异性表达[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2013. LU P. Cloning and temp-spatial expression pattern of bone morphological protein(BMPs) in New Zealand rabbit[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2013. (in Chinese)
[20] SOMI S, BUFFING A A M, MOORMAN A F M, et al. Dynamic patterns of expression of BMP isoforms 2, 4, 5, 6, and 7 during chicken heart development [J]. The Anatomical Record Part A, Discoveries in Molecular, Cellular, and Evolutionary Biology, 2004, 279(1): 636−651.
[21] HASSEL S, SCHMITT S, HARTUNG A, et al. Initiation of Smad-dependent and Smad-independent signaling via distinct BMP-receptor complexes [J]. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery American Volume, 2003, 85-A(S3): 44−51.
[22] HUANG F, HU L, ZHANG Y M, et al. BMP4 moderates glycolysis and regulates activation and interferon-gamma production in CD4+ T cells [J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2021, 12: 702211. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.702211
[23] WANG S J, CHEN C, YU L, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 6-mediated crosstalk between endothelial cells and hepatocytes recapitulates the iron-sensing pathway in vitro [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2021, 297(6): 101378. DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101378
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 梁振华,陈会鲜,李恒锐,韦婉羚,黄珍玲,阮丽霞,何文,兰秀,杨海霞. 木薯新品种桂薯1505的选育及栽培技术. 热带作物学报. 2025(03): 629-637 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 罗燕春,赵鑫鑫,盘欢,廖琦,俞奔驰,劳赏业,范锡恩,刘翠娟,李荣云,曾新华,付海天. 9个不同使用类型木薯品系在合浦县的适应性研究. 中国农学通报. 2024(18): 31-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李恒锐,张秀芬,叶骏菲,张远飞,农雪钰,杨梅琼,陈会鲜,韦婉羚,蔡兆琴,卢美瑛,阮丽霞. 木薯新品种桂薯1289的选育与抗螨性研究. 热带作物学报. 2024(10): 2138-2148 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 周时艺,韦云东,陈蕊蕊,盘欢,李军,罗燕春,郑华. 不同食用木薯品种(系)商品薯可食率的调查. 农业研究与应用. 2023(02): 24-28 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 卢赛清,俞奔驰,周时艺,陈炯宇,宋恩亮,徐钏,雷开文,马崇熙,王帝,韦丽君. 高产高淀粉早熟木薯新品种桂热13号的选育. 热带作物学报. 2023(09): 1776-1785 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: